
The Description of People with Disabilities in Beng
k
alis District
During 2017-2018 in Riau Province
Syarifah Ivonesti
1
, Rany Fitriany
2
, Dewi Lutfianawati
3
1
STAIN Bengkalis, Riau Province
2
University of Putra Indonesia (UPI) YPTK Padang
3
University of Malahayati Lampung
Keywords: Bengkalis, Disability, Riau Province.
Abstract: Objective: The number of people with disabilities in Riau province and Pekanbaru city increases every year.
Therefore, we need an effort to optimize the potentials of people with disabilities. Disabled people have the
same rights as other people. Method: A descriptive research originated from the data from the Social
Service Office of Bengkalis Regency, Riau Province in 2017 - 2018 found 128 people with disabilities; 69
of them are men and 59 others are women. The types of disability are Physical and Speech Disability, Deaf
or Hearing Impairment, Physical Disabilities such as stump arm(s) and leg(s), Speech Impairment, Physical
Disability due to Paralysis, Physical Disability, and Severe / Double Disability. Conclusion: The
government has several ways or programs to help developing these potentials of people with disabilities.
The supports provided for them are workshop or a garage, workshop equipment, two-wheeled workshop
equipment, daily shop, sewing machines and equipment, wheelchairs, hearing aid, prosthetic limbs,
prosthetic limbs and arms, and basic needs.
1 INTRODUCTION
The number of people with disabilities in Pekanbaru
City recorded in 2016 was 860 people. From the
data above, not all people with disabilities have the
chance to get education or employment. Based on
data from the Central Bureau of Statistics in
Pekanbaru, there are only 36.49% of people with
disabilities who get education and only 45.12% of
whom get jobs. From the number of people with
disabilities who receive education and employment,
it can be seen that there are around 54% of the
number of persons with disabilities in Pekanbaru
City who do not have education and employment
(Vawitrie, 2018). This also happened in Bengkalis,
one of the regencies in Riau province. Some of the
disabilities were speech impaired, deaf, physical
disabilities, multiple disabilities; physical disability
and speech impairment, physical disability with
stumped arm(s) and limb(s), physical disability due
to paralysis and severe disability.
The population of people with disabilities is
quite high. According to WHO, the number of
people with disabilities reaches 15% of the number
of the total population. If the number of the total
population in Indonesia reaches 250 million, then
the population of people with disabilities is around
36 million (Thohari S, dkk, 2018). The number of
people with disabilities is increasing statistically.
The United Nations shows that out of the estimated
500,000 people with disabilities, around 80% of
them live in developing countries. Less than 10%
have access to education, health services and
livelihood opportunities, more than 80% of people
with disabilities are unemployed, and in developing
countries, 75% - 90% people with disabilities live in
poverty. In Indonesia, the number of people with
disabilities is around 0.25% to 10% of the total
population (Setyaningsih, 2016).
According to WHO, a disability is the inability to
carry out certain activities as normal people which
are caused by impairment conditions related to age
and society where a person is located. According to
law number 8 of 2016, persons with disabilities are
those who experience long-term physical,
intellectual, mental or sensory limitations who
interact with the environment and experience
obstacles and difficulties to participate fully and
effectively with citizens of other countries based on
similar rights.
340
Ivonesti, S., Fitriany, R. and Lutfianawati, D.
The Description of People with Disabilities in Bengkalis District During 2017-2018 in Riau Province.
DOI: 10.5220/0009766403400344
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Psychology (ICPsy 2019), pages 340-344
ISBN: 978-989-758-448-0
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

People with disabilities have the same rights as
other people. The rights of persons with disabilities
based on the law no 4 of 1997 affirms that people
with disabilities are part of Indonesian society which
also have the same position, rights, obligations and
roles. They also have equal rights and opportunities
in all aspects of life and livelihood. In article 6, it is
explained that each person with disabilities has the
right to: (a) education in all units, paths, types and
levels of education; (b) decent work and livelihood
according to the type and degree of disability,
education, and ability; (c) the same treatment to play
a role in development and enjoy the results; (d)
accessibility in the framework of its independence;
(e) rehabilitation, social assistance, and maintenance
of social welfare levels; and (f) the same rights to
grow their talents, abilities and social life, especially
for children with disabilities in the family and
community environment.
In fulfilling disability rights, the Social Service
implements a program of assistance for disabilities
such as providing assistance in form of workshops,
two-wheeled workshop equipment, daily shops,
sewing machines and equipment, assistance in the
form of wheelchairs, hearing aid, prosthetic limbs,
fake limbs and basic food.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Definition of Disability
Kauffman (2011) disability is an inability to do
something, a diminished capacity to do something, a
diminished capacity to perform ini a specific way
(an impairment); a handicap, however, is a
disadvantage imposed on an individual. Thus, a
disability migh or might not be a handicap,
depending on the circumstances.
According to Law No. 8 of 2016 concerning
people with disabilities, people with disabilities are
every person who experiences physical, intellectual,
mental, and / or sensory limitations for a long time
that in interacting with the environment they can
experience obstacles and difficulties to participate
fully and effectively with other citizens based on
equality of rights.
Disability is a term that means a physical or
mental condition that limits one's movements, senses
or activities (Ashar, 2019). Physical or mental
condition related to body structure; Activity
limitations are difficulties faced by individuals in
carrying out a task or an action; while limiting
participation is a problem experienced by
individuals involved in life situations. Therefore,
disability is not just a health problem, but a complex
phenomenon that reflects the interaction between a
person and the community where he lives. Certain
interventions are needed to remove environmental
and social barriers (Ashar, 2019).
Thus, disability is a condition of people
who experience physical, intellectual, and sensory
limitations for a long time; those who interact with
the environment, those who experience obstacles
and difficulties to participate.
2.2 Types of Disabilities
2.2.1 Deaf (Hearing Impairment)
According to Musyarrafah & Djalal, (2011) Deaf is
a term used to describe the condition of a person
who loses his hearing or the inability of a person to
capture stimuli auditorily through his sense of
hearing (Evitasari, 2015). According to Hallahan,
Kauffman, and Pullen (2009), in terms of age,
deafness is divided into two; congenital deafness
(hearing disabilities that occur at birth, which can be
caused by genetic factors, disorders during fetal
development, and disorders during the birth process)
and adventitious deafness (the inability to hear due
to illness or traumatic events that occur in
individuals without a history of hearing loss at birth)
(Evitasari, 2015).
According to the Ministry of Education, a deaf
person is a person who has lost the ability to hear so
that it inhibits the process of language information
through hearing, whether using or not using hearing
aids to the extent that a person's hearing is sufficient
to enable the successful process of language
information through hearing (Riahta, 2015).
According to Moores (2001), hearing impaired
and deaf are two different conditions. Hearing
impaired is when someone has a hearing loss on a
small scale (at a level of 35 db to 69 dB), so that he
does not experience obstacles in understanding the
conversation of others and can be cured in a certain
period of time by using medical assistance, such as
the use of hearing aids. While, deaf (Morres, 2001)
is a condition when someone loses his hearing on a
large scale or can only receive fragmented sounds
with or without the use of aids, so that he
experiences obstacles in understanding the
explanations of others through his hearing (Riahta,
2015).
The Description of People with Disabilities in Bengkalis District During 2017-2018 in Riau Province
341

2.2.2 Speech Impairement
Wasista (2013) Speech impaired is a condition when
someone has a difficulty in communicating. This can
be caused by the lack of or non-functioning speech
tools, such as the oral cavity, tongue, palate and
vocal cords. In addition, lack of or malfunctioning of
the auditory organs, delay in language development,
damage to the nervous system and muscle structure,
as well as an inability to control motion can also
result in limitations in communication. Among those
individuals who experience communication
difficulties, there are those who cannot communicate
at all; they can make sounds but they do not say
words and some others can communicate but are
unclear (Suyadnya, 2018).
2.2.3 Diffability (People with Physical and
Health Disorders)
Physical disability is a form of abnormality or
disability in the muscular system, supply bones and
nerves caused by viral diseases, and accidents either
it occurs before, at , or after birth (Megasari, 2016;
Adelina, 2018). The level in physical disability can
be grouped into three; mild, moderate and severe.
Disorders or damages can occur before birth
(prenatal phase), at birth (perinatal phase), and after
the birth process (postnatal phase) (Megasari, 2016;
Adelina, 2018).
2.2.4 Multiple Disability
According to the association of severe handicaps
(TASH), multiple disability (Severe disabilities) is
an individual with disabilities of all ages, races,
creeds, national origins, genders and sexual
orientations who require ongoing support in more
than one major life activity in order to participate in
an integrated community and enjoy a quality of life
similar to that available to allitizens. Suppport may
be required for life activities such as mobility,
communication self-care, and learning as necessary
for community living employment and self
sufficiency (Snell & Brown, 2006 in Hallallan, etd,
2009). People who experience severe disability in all
areas usually have more than one disability. The
combination of mild disability can cause severe
education problems. Children with this disorder
usually have problems in terms of speech, language
use and / or limitations in perceptual cognitive and
abnormal behavior. Multiple disabilities include :
blind – deaf people, blind – physically disabled
people, blind – mentally disabled people who can be
trained, blind – mentally disabled people who can be
educated, deaf – physically disabled people, deaf -
mentally disabled people who can be trained, deaf -
mentally disabled people who can be educated,
physically disabled – mentally disabled people who
can be trained, etc (Mangunsong, 2011).
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This is a descriptive research. A descriptive research
originated from the data from the Social Service
Office of Bengkalis Regency, Riau Province in 2017
- 2018 found 128 people with disabilities; 69 of
them are men and 59 others are women. From
assessment with psychology and doctors
examination this data consist of the types of
disability are Physical and Speech Disability, Deaf
or Hearing Impairment, Physical Disabilities such as
stump arm(s) and leg(s), Speech Impairment,
Physical Disability due to Paralysis, Physical
Disability, and Severe / Double Disability.
4 RESULT
Based on the results of the data analysis, the
research findings can be described in detail in the
form of frequency distributions of gender, address.
The following is the description of therespondents
by sex:
Table 1: Characteristics of Samples Based on Gender.
No Gender Number Percentage
(%)
1 Male 69 53.9%
2 Female 59 46.1%
Total 128 100%
Based on the data in the table above, there are
128 people with disabilities in Bengkalis Regency,
with the number of male is higher than female. The
number of people with disabilities are; 69 male, or
53.9% of the total number and 59 female, or 46.1%
of the total number.
ICPsy 2019 - International Conference on Psychology
342
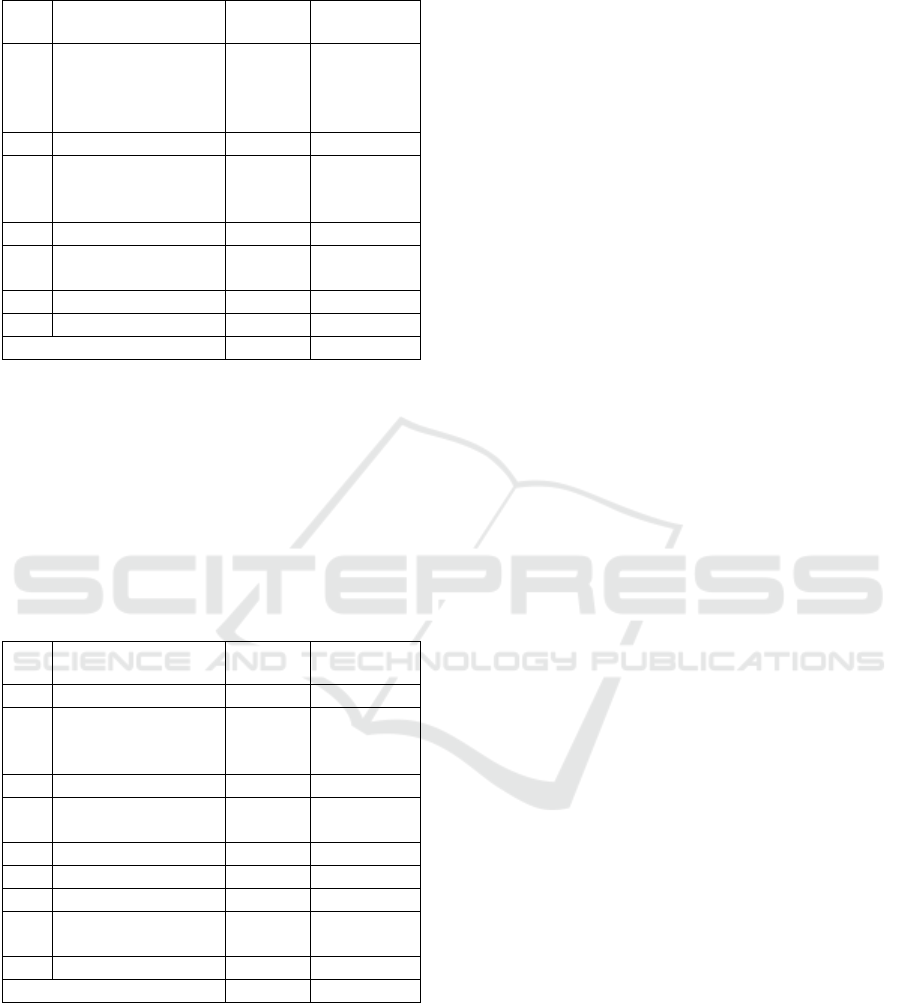
Table 2: Data of the Type of Disability and Percentage.
No Type of Disability Number Percentage
(
%
)
1 Physical and speech
impairment
(multiple
disabilities)
2 1.6%
2 Deaf 15 11.7%
3 Physical disability
such as arms or
limbs defects
5 3.9%
4 Speech impairment 4 3.1%
5 Physical disability
due to paralysis
41 32.0%
6 Physical disability 12 9.4%
7 Severe disability 49 38.3%
Total 128 100%
Based on data, the percentage of 128 people with
disabilities in Bengkalis Regency are 1,6% or 2
people with physical disabilities and speech
impairment, 15 deaf people, 3.9% or 5 people with
physical disability (legs or arms stump), 32% or 41
people with physical disability due to paralysis,
9,4% or 12 people with physical disabilities, 38,3%
or 49 people with severe or multiple disabilities.
Table 3: Data of the Type of Support.
No Type of Support Total Percentage
(
%
)
1 Workshops 2 1.6%
2 Two-wheeled
workshop
equipmen
t
1 0.8%
3 Dail
y
shops 5 3.9%
4 Sewing machines
and equipmen
t
4 3.1%
5 Wheel chairs 41 32.0%
6 Hearin
g
aids 15 11.7%
7 Prosthetic limbs 5 3.9%
8 Prosthetic arms
and limbs
6 4.7%
9 Basic necessity 49 38.3%
Total 128 100%
Based on the data above, the support provided to
2 people (1,6% of the total number of the people
with disabilities) with physical disabilities and
speech impairments received workshop support. 1
person who is deaf (0,8% of the total number of the
people with disabilities), received two-wheeled
workshop equipment. 5 people (3,9% of the total
number of the people with disabilities) with stumped
arms or limbs got daily shops. 4 people (3,1% of the
total number of the people with disabilities) with
speech impairment, received sewing machines and
equipment. 41 people (32% of the total number of
the people with disabilities) with physical disability
because of paralysis got wheelchairs. 15 people
(11,7% of the total number of the people with
disabilities) with hearing impairment received
hearing aids. 5 people (3,9% of the total number of
the people with disabilities) with physical
disabilities received prosthetic limbs. 6 people (4.7%
of the total number of the people with disabilities)
with physical disabilities received prosthetic limbs
and arms. 49 people (38.3% of the total number of
the people with disabilities) with severe or multiple
disabilities received some basic food.
5 CONCLUSION AND
RECOMMENDATION
5.1 Conclusion
1. Based on the data obtained, there was a role
of government in supporting people with
disabilities in the attempts to fulfill the
rights of people with disabilities.
2. There were 128 people with disabilities
found in Bengkalis Regency where the
number of male is more dominant than the
female. There were 69 or 53.9% male and
59 or 46.1% female.
3. The type of support had been adjusted to
the conditions experienced by each person
with disabilities.
4. Based on the data and the types of supports
provided to the people with disabilities,
people with physical disabilities and speech
impairment were given workshop support,
deaf people were given two-wheeled
workshop equipment, physically disabled
people such as stumped legs or hands were
given daily shops, speech impaired people
were given sewing machines and
equipment, people with physical disability
due to paralysis were given wheel chairs,
deaf people were given hearing aid, people
with physical disabilities were given
prosthetic limbs, people with physical
disabilities were given prosthetic limbs and
arms and people with severe or multiple
disabilities were given basic food.
The Description of People with Disabilities in Bengkalis District During 2017-2018 in Riau Province
343

5.2 Recommendation
1. For the Bengkalis Regency government to
maintain the existence of aid programs and
give psychological motivation to people
with disabilities to continue working.
2. To build a cooperation with local
institutions or companies to channel the
work produced by disability.
3. The type of support should be given based
on the talents and interests of people with
disabilities.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This authors gratefully acknowledgment the
contributions Social Service Office of Bengkalis
Regency, Eji Marlina and Syarifah Hidayah.
REFERENCES
Adelina, F, dkk (2016). Bagaimana agar penyandang tuna
daksa mampu menjadi pribadi yang bahagia?. Jurnal
Sains Psikologi, 7(2), 119-125.
Ashar, D, dkk (2019). Panduan Penanganan Perkara
Penyandang Disabilitas Berhadapan dengan Hukum.
Di terbitkan oleh Masyarakat Pemantau Peradilan
Indonesia Fakultas Hukum Universitas Indonesia
(MaPP FHUI) bekerjasama dengan Australia
Indonesia, Partnership for Justice 2 (AIPJ 2).
Evitasari, I. A, G, S. dkk (2015). Proses Penerimaan Diri
Remaja Remaja Tunarungu Berprestasi. Jurnal
Psikologi Udayana, Vol. 2, Hlm 138-150.
Kaufman J. M & Daniel P. H (2011). Handbook of Special
Education, University of Virginia Routledge New
York and London.
Mangunsong, F. (2011). Psikologi dan pendidikan anak
berkebutuhan khusus (ed. 2). Lembaga pengembangan
sarana pengukuran dan pendidikan psikologi (LPSP3),
kampus baru UI, Depok.
Riahta, R, dkk (2015), Program Studi Psikologi Universias
Brawijaya regulasi emosi mahasiswa penyandang
tunarungu dalam relasi dengan kawan sebaya, Jurnal
Indonesia journal of disability studies (IJDS), 2(1),
43-51.
Suyadnya, I. W.P, dkk (2018). Alat bantu komunikasi
terintegrasi bagi penyandang tuna wicara berbasis
sensor gerak dan openwrt, E-Journal SPEKTRUM,
5(2), 176-182.
Setyaningsih, R. (2016). Pengembangan kemandirian bagi
kaum difabel (studi kasus pada peran Paguyuban
sehati dalam upaya pengembangan kemandirian bagi
kaum difabel di Kabupaten Sukoharjo), Jurnal
Sosiologi DILEMA, 31(1), 42-52.
Undang-Undang Negara Republik Indonesia Nomor 4
Tahun 1997 tentang Penyandang Cacat. Direktorat
Jenderal Pelayanan dan Rehabilitasi Sosial RI, 2006.
[Di unduh 14 Mei 2019].
Undang-Undang Republik Indonesia No 8 tahun 2016
tentang penyandang disabilitas [Di unduh 14 Mei
2019].
Vawitrie., Y (2018). Implementasi rehabilitasi sosial bagi
penyandang disabilitas di kota Pekanbaru, Jurnal
JOM FISIP, 2(5), 1-3.
ICPsy 2019 - International Conference on Psychology
344
