
Characteristics of Breast Cancer Patients
in YKPI Singgah Home in 2019
Lia Suci Kriswanti
1
and Ira Marti Ayu
2
1
Public Health Student Faculty of Health Sciences, Esa Unggul University, Jakarta, Indonesia
2
Faculty of Health Sciences, Esa Unggul University, Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Breast Cancer, Age Diagnosed, Stadium, Number of Children, Menarche, Menopause, Age of Childbirth,
Breastfeeding, Contraception.
Abstract: Based on YKPI data, there is an increase in the number of breast cancer patients from 2017 to 2018, from
124 patients to 194 patients. The purpose of this study was to determine the characteristics of breast cancer
patients at the YKPI Shelter House in 2019. This study used a case series design, with a sample of 32
people. The sampling technique used purposive sampling with univariate data analysis. This research was
conducted in April-June 2019. The results of univariate, namely the highest proportion of the age diagnosed
for the first time at risk (<50 years) was 84.4%, stage 2 was 43.8%, had children as much as 78.1%, age first
time giving birth is not at risk (<30 years) by 84%, breastfeeding is 65.6%, menarche age> 12 years is
53.1%, not yet menopause is 81.3%, has no family history of 68.8%, and the age at first giving birth is not at
risk (<30 years) using hormonal contraception by 50%. It is expected that YKPI will intensively socialize to
all parts of Indonesia and it is expected that all Indonesian women care about their health, especially breast
health by taking into account the risk factors that exist.
1 PRELIMINARY
Globally, regionally, and nationally in 2030, it is
projected that an epidemiological transition will
occur from communicable diseases to non-
communicable diseases (PTM). Non-communicable
diseases (PTM) are chronic diseases that are not
transmitted from person to person, such as heart
disease, stroke, cancer, diabetes, and Chronic
Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) which
causes almost 70% of deaths in the world (Ministry
of Health Republic of Indonesia, 2017). Indonesia
has experienced an epidemiological transition and
also faces a double burden. This is indicated by the
presence of communicable and non-communicable
diseases simultaneously in the community. The
epidemiological transition is characterized by a shift
in patterns of disease and patterns of the cause of
death in the community, namely a decrease in the
incidence of certain infectious diseases and an
increase in the incidence of various types of non-
communicable diseases (Noor, 2008).
Non-communicable diseases (PTM) have an
impact on the economy and productivity of patients
and their family members. This is because PTM
treatment requires a long time and a large cost
(Kemenkes RI, 2013). The direct impact on the
economy is the cost of treatment, while the indirect
impact is the loss of work time, school time, and
other costs incurred besides treatment such as
transportation and accommodation during patient
care. In addition, social losses due to PTM, among
others, cause panic in the family, disability, and
death (Simbolon, et al., 2015).
One non-communicable disease (PTM) is cancer.
Cancer is a disease caused by a single cell that
grows abnormally and is out of control so that it
becomes a malignant tumor that can destroy and
damage healthy cells or tissues (Simbolon et al.,
2015). In 2012, the number of cancer cases was
14,067,894 with 8,201,575 deaths worldwide
(WHO, 2012). Whereas, in 2018, the number of
cancer cases was 18.1 million with 9.6 million
deaths worldwide (WHO, 2018). From these data, it
can be concluded that there has been a significant
increase in the number of cancers and the number of
deaths worldwide. Data in Indonesia is estimated
that there are 100 new sufferers per 100,000
population each year. This means that of the
237,000,000 population, there are around 237,000
380
Kriswanti, L. and Ayu, I.
Characteristics of Breast Cancer Patients in YKPI Singgah Home in 2019.
DOI: 10.5220/0009782803800391
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Health (ICOH 2019), pages 380-391
ISBN: 978-989-758-454-1
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

new cancer sufferers each year. Breast cancer is a
malignant tumor that grows in breast tissue, can
grow in mammary glands, milk ducts, fat tissue or
connective tissue in the breast (Simbolon et al.,
2015). Risk factors for breast cancer in women
include reproductive factors (early menarche age,
first pregnancy in old age, low parity, lactation
period), endocrine factors (hormonal contraception)
and genetic factors (family members with breast
cancer) (Rasjidi, 2010).
In the UK, the most common type of cancer in
women in 2012 is breast cancer (Eccles, 2013). The
magnitude of the problem regarding breast cancer
can be seen from the number of cases of breast
cancer found in H. Adam Malik General Hospital
Medan also experienced an increase of 325 cases in
2013 and 444 cases in 2014 (Maysarah, 2016).
The results of this study are in line with Saragih's
research (2011) which states that the highest
proportion of the age of breast cancer sufferers is the
age of 35-50 years as many as 104 people (53.1%),
Fitoni research (2012) which states that the highest
proportion of breast cancer sufferers is having
children as many as 46 people (65.7%), and Sitopu
research (2012) which states that the proportion of
the age at first giving birth to breast cancer sufferers
is highest (≤30 years) as many as 65 people (92.9%),
breastfeeding behavior totaling 50 people (90.9%),
menarche age> 12 years amounted to 70 people
(94.6%), and postmenopausal sufferers which
amounted to 39 people (66.1%). In addition, the
results of this study are in line with the research of
Rondonuwu (2016) which states that the highest
proportion of breast cancer sufferers are those who
do not have a family history (mother or sister)
totaling 145 people (96%) and the Sitopu study
(2012) the highest proportion using Hormonal
contraception numbered 31 people (77.5%).
Breast cancer causes some harm to the patient
and the person accompanying the patient. This is
because they have to lose their jobs and have an
impact on financial problems, such as the cost of
round-trip accommodation for treatment that must
be borne by patients and their families. Treatment of
breast cancer requires a long time, while there are
still many areas that do not have access to adequate
medical equipment. Therefore, to get the best
treatment, many breast cancer patients who come
from the area to Dharmais Hospital in Jakarta. When
patients choose treatment in Jakarta, they will have
constraints related to residence. They must find
lodging and incur additional costs. This is the
background of YKPI's founding. YKPI is a halfway
house foundation, a boarding house for female
patients who have difficulty in obtaining lodging
amid medical obligations at Dharmais Hospital. The
address of the YKPI guest house on Jl. Anggrek
Nelimurni II No.C / 33, Kemanggisan, Palmerah,
West Jakarta.
In addition to lodging, the shelter also provides
several facilities, namely nutritious food every day.
The existence of a halfway house is able to provide
transportation costs relief for cancer patients due to
the presence of facilities in the form of
mammography cars to pick up and take patients to
Dharmais Hospital. The close location also makes it
easier for patients to be taken to Dharmais Hospital
when conditions are weak and need treatment. The
benefits of living in a halfway house are even more
than that, a halfway house also helping patients
psychologically. Living with fellow breast cancer
patients allows them to share and strengthen each
other, such as sharing experiences of dealing with
symptoms of illness, pain, and other emotional
support. This can increase motivation in undergoing
treatment between patients. To be able to use this
facility, the conditions are easy, namely female
breast cancer patients, originating from Jabodetabek,
and preferably with BPJS class 3.
For the prevention and control of breast cancer in
Indonesia, YKPI continues to support government
programs through early detection of breast cancer
using the Breast Self-Examination (BSE) and
Clinical Breast Examination (SADANIS) methods
by conducting socialization-socialization both
internally and externally. Internal is a socialization
activity in a halfway house for breast cancer patient
companions, while external is a socialization activity
in several cities in Indonesia through seminars
attended by breast cancer patients and no breast
cancer patients.
The shelter is not just a place to stay. There,
cancer patients will be given activities to develop
skills. With this positive activity, patients can fill
their spare time between treatments, such as cooking
together, eating together, making joint crafts such as
making necklaces, bracelets, and other crafts to later
be sold as a source of economic income for breast
cancer patients.
In 2017 the number of patients staying at YKPI
totaled 124 patients. In 2018 the number of patients
staying at YKPI totaled 194 patients. From these
data, it can be concluded that there has been an
increase in the number of breast cancers from 2017
to 2018 at YKPI. In addition, based on a preliminary
survey conducted at the YKPI Shelter Home the
number of breast cancer sufferer’s data from April to
June 2019 was 32 people. Based on this, researchers
Characteristics of Breast Cancer Patients in YKPI Singgah Home in 2019
381

are interested in knowing the characteristics of
breast cancer sufferers at YKPI in 2019.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
This study used respondents of all patients who were
in YKPI Halfway House in 2019, amounting to 32
patients. This study uses quantitative research with a
case series design. This study uses data on patient
registration forms at the YKPI Shelter, PA sheets
from doctors, and questionnaires, and the analysis
used in this study is univariate analysis.
3 RESEARCH RESULT
3.1 Univariate Analysis
3.1.1 Description of Age of Breast Cancer
Patients at YKPI Shelter in 2019
Based on the results of research on the age variable
breast cancer patients are divided into 2 categories,
namely at risk and not at risk. If the age of the first
diagnosis of breast cancer ≥ 50 years is categorized
at risk and if the age of breast cancer patients <50
years is categorized as not at risk. The following is
an age table for breast cancer sufferers at YKPI
Shelter in 2019:
Table 1: Age Distribution of Breast Cancer Patients at
YKPI Shelter in 2019.
No
Age Distribution of Breast
Cancer
(n) (%)
1 Risk
5 15,6
2 Not Risk 27 84,4
Total
32 100
Based on table 1 it is known that from 32
respondents, the highest proportion of age of breast
cancer patients is the age of those who are not at risk
(<50 years) amounted to 27 people (84.4%) and the
lowest proportion of age is the age of people at risk
(≥ 50 years) amounted to 5 people (15.6%).
3.1.2 Overview of Stage of Breast Cancer
Patients at YKPI Shelter in 2019
Based on the results of research on the stage
variables of breast cancer patients divided into 4
categories, namely stage 1, stage 2, stage 3, and
stage 4. The following is a table of stages of breast
cancer patients at YKPI Shelter in 2019:
Table 2: Age Distribution of Breast Cancer Patients at
YKPI Shelter in 2019.
No
Stadium of Breast Cancer
Patients
(n) (%)
1 Stadium 1
7 21,9
2 Stadium 2
14 43,8
3 Stadium 3
8 25,0
4 Stadium 4 3 9,4
Total
32 100
Based on table 2 it is known that from 32
respondents, the highest proportion of staging of
breast cancer patients is stage 2 with 14 people
(43.8%) and the lowest proportion is stage 4 with 3
people (9.4%).
3.1.3 Description of the Number of Children
with Breast Cancer at YKPI Shelter in
2019
Based on the results of research on the variable
number of children with breast cancer divided into 2
categories, namely having children and not having
children. The following is a table of the number of
children with breast cancer at YKPI Shelter in 2019.
Table 3: Distribution of the Number of Children in Breast
Cancer Patients at YKPI Shelter in 2019.
No
The Number of Children in
Breast Cancer Patients
(n) (%)
1 Do not have children
7 21,9
2 Have children 25 78,1
Total
32 100
Based on table 3 it is known that of the 32
respondents, the highest proportion of breast cancer
sufferers is having 25 children (78.1%) and the
lowest proportion is not having children amounting
to 7 people (21.9%).
3.1.4 Overview of Age for First Time
Childbirth of Breast Cancer Patients
at YKPI Shelter in 2019
Based on the results of research on the age variable
for the first-time giving birth to breast cancer
sufferers is divided into 2 categories namely at risk
and not at risk. If the age of first birth ≥30 is
categorized at risk and if the age of first birth <30 is
categorized as not at risk. The data analyzed were
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
382
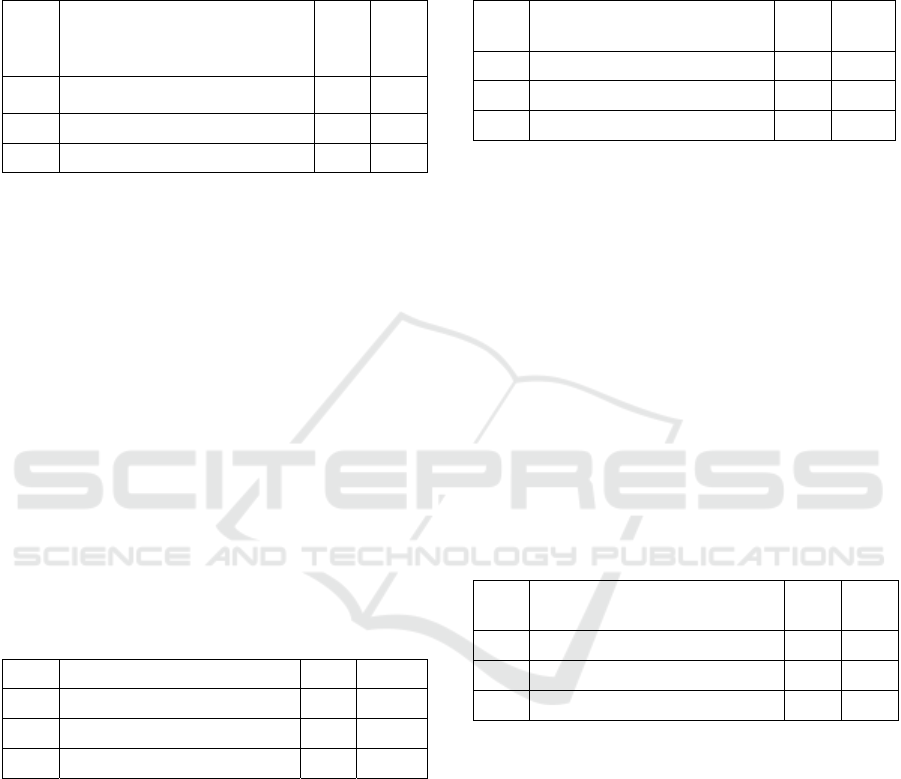
only 25 women who had given birth. The following
is the age table for giving birth to a breast cancer
sufferer at YKPI Shelter.
Table 4: Age Distribution First Time Giving Birth to a
Breast Cancer Patient at YKPI Shelter in 2019.
No
Age Distribution First Time
Giving Birth to a Breast Cancer
Patient
(n) (%)
1 Risk
4 16
2 No risk 21 84
Total 25 100
Based on table 4 it is known that of the 25
respondents, the highest proportion of age at first
giving birth to breast cancer patients is not at risk
(<30 years) totaling 21 people (84%) and the lowest
proportion is at risk (≥30 years) totaling 4 people
(16%).
3.1.5 Overview of Breastfeeding for Breast
Cancer Patients at YKPI Shelter in
2019
Based on the results of research on breastfeeding
behavior variables breast cancer patients are divided
into 2 categories, namely breastfeeding and never
breastfeeding. The following is a table of
breastfeeding behavior of breast cancer sufferers at
YKPI Shelter in 2019:
Table 5: Distribution of breastfeeding for Breast Cancer
Patients at YKPI Shelter in 2019.
No breastfeeding (n) (%)
1 breastfeeding 21 65,6
2 Never breastfeeding 11 34,4
Total 32 100
Based on table 5 it is known that from 32
respondents, the highest proportion of breast cancer
sufferers was breastfeeding by 21 people (65.6%)
and the lowest proportion was not breastfeeding by
11 people (34.4%).
3.1.6 Description of the Age of Menarche in
Breast Cancer Patients at YKPI
Shelter in 2019
Based on the results of research on the variable age
of menarche breast cancer patients are divided into 2
categories, namely menarche age ≤ 12 years and
menarche age> 12 years. The following is an age
table for menarche breast cancer sufferers at YKPI
Shelter in 2019:
Table 6: Age Distribution of Breast Cancer Menarche at
YKPI Shelter in 2019.
No
Age Distribution of Breast
Cancer Menarche
(n) (%)
1 ≤ 12 years old 5 46,9
2 >12 years old 17 53,1
Total 32 100
Based on table 6 it is known that from 32
respondents, the highest proportion of menarche age
of breast cancer patients is menarche age> 12 years
totaling 17 people (53.1%) and the lowest proportion
is age <12 years totaling 15 people (46.9%).
3.1.7 Overview of Menopause in Breast
Cancer Patients at YKPI Shelter in
2019
Based on the results of research on menopause
variables of breast cancer patients are divided into 2
categories namely not yet menopause and
menopause. The following is a menopause table for
breast cancer sufferers at YKPI Shelter in 2019:
Table 7: Distribution of Menopause in Breast Cancer
Patients at YKPI Shelter in 2019.
No
Menopause in Breast Cancer
Patients
(n) (%)
1 Not yet Menopause 26 81,3
2 Already Menopause 6 18,8
Total 32 100
Based on table 7 it is known that of the 32
respondents, the highest proportion of breast cancer
sufferers was 26 postmenopausal sufferers (81.3%)
and the lowest proportion had reached 6 menopauses
(18.8%).
3.1.8 Overview of Family History of Breast
Cancer Patients at YKPI Shelter in
2019
Based on the results of research on the variable
family history of breast cancer patients divided into
2 categories, namely family history, and no family
history. The following is a family history table for
breast cancer sufferers at YKPI Shelter in 2019:
Characteristics of Breast Cancer Patients in YKPI Singgah Home in 2019
383
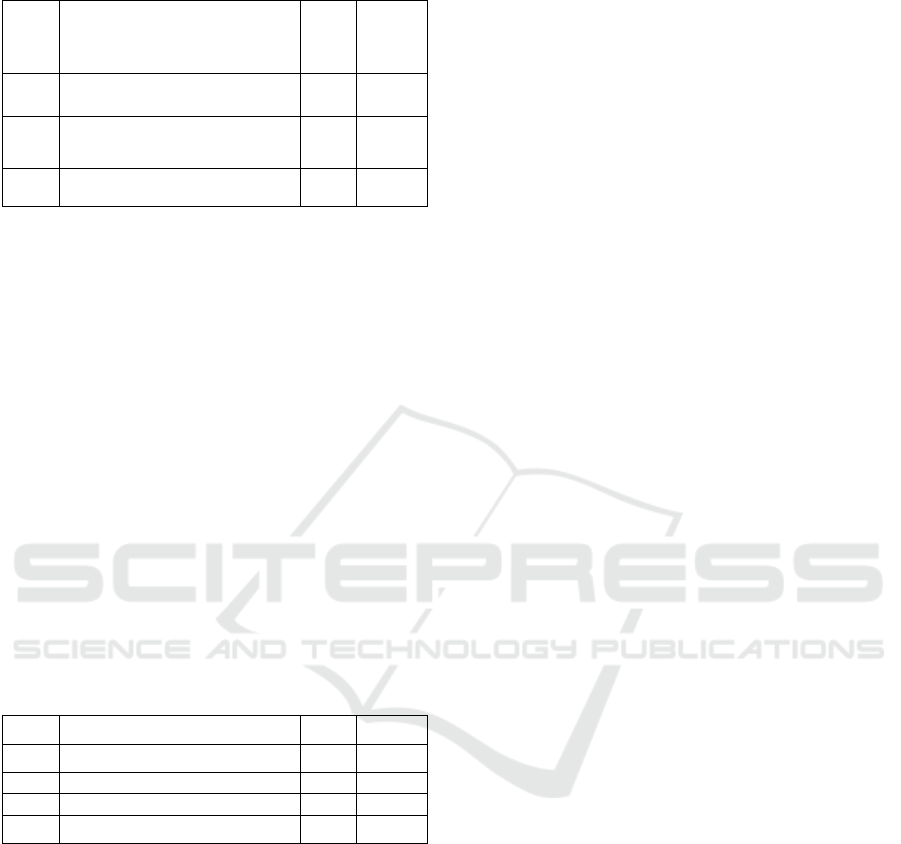
Table 8: Distribution of Family History of Breast Cancer
Patients at YKPI Shelter in 2019.
No
Distribution of Family
History of Breast Cancer
Patients
(n) (%)
1 Yes
10 31,3
2 No
22 68,8
Total 32 100
Based on table 8 it is known that of the 32
respondents, the highest proportion of patients with
breast cancer were those who did not have a family
history of 22 people (68.8%) and the lowest
proportion were patients who had a family history of
10 people (31.3%).
3.1.9 Overview of Hormonal Contraception
of Breast Cancer Patients at YKPI
Shelter in 2019
Based on the results of research on the variable use
of hormonal contraception of breast cancer patients
divided into 3 categories, namely using hormonal
contraception, not using hormonal contraception,
and never using hormonal contraception. The
following is a table of hormonal contraceptive use
for breast cancer sufferers at YKPI Shelter in 2019:
Table 9: Distribution of Hormonal Contraception of Breast
Cancer Patients at YKPI Shelter in 2019.
No Hormonal Contraception (n) (%)
1 Yes
14 43,8
2 No 11 34,4
3 Never 7 21,9
Total
32 100
Based on table 9 it is known that the highest
proportion of breast cancer patients using hormonal
contraception is 14 people (43.8%) and the lowest
proportion has never used 7 people (21.9%).
4 DISCUSSION
4.1 Description of Age of Breast
Cancer Patients at YKPI Shelter in
2019
Based on the results of research on 32 breast cancer
patients, it is known that the highest proportion of
the age of breast cancer patients is the age of
patients who are not at risk (<50 years) as many as
27 people (84.4%). The results of this study are in
line with Saragih's research (2011) which states that
the highest proportion of the age of breast cancer
sufferers is the age of 35-50 years as many as 104
people (53.1%) and the Sitopu study (2012) which
states that the highest proportion of the age of breast
cancer patients occurred at the age of fewer than 50
years as many as 101 people (70.6%).
The risk of breast cancer increases with age. The
longer a person's life span, the possibility of genetic
damage (mutations) also increases. On the other
hand, the ability to repair the body (healing) is
decreasing (Handayani, et al 2012). However, at this
time, the age of the first time being diagnosed with
breast cancer in women has experienced a shift. Age
was first diagnosed with breast cancer in the past
had an average age above 50 years, now the age of
the first time diagnosed with breast cancer is in the
range of 35-50 years. That are many breast cancer
sufferers who are in a productive age (Savitri, 2015).
Based on the results of the study, the highest
proportion of people who were first diagnosed with
breast cancer is the age that is not at risk, that is,
under 50 years of age. Based on the results of the
interview, it was found that the cause of age at first
time was diagnosed with breast cancer at no risk at
age under 50 years due to respondents' lack of
exercise. However, after being at YKPI respondents
had started exercising. This is because the
respondents took part in the gymnastics conducted
on Friday. Therefore, it is better for the community,
especially women who have a risk-free age of under
50 years, should start to get used to a healthy life.
Regular exercise can minimize the risk of breast
cancer. This is because it is in accordance with the
theory of Subaja (2014) which states that regular
exercise habits make the body rich in oxygen so that
it can fight breast cancer cells in the body,
considering that breast cancer cells do not like a host
or a body that is rich in oxygen.
4.2 Depiction of the Stage of Breast
Cancer Patients at YKPI Shelter in
2019
Based on the results of research on 32 breast cancer
patients, it is known that the highest proportion of
stage breast cancer patients is stage 2 as many as 14
people (43.8%). The results of this study are in line
with research (Purba, 2009) which states that the
highest proportion of staging of breast cancer
patients is stage 2 (36.7%).
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
384

Breast cancer patients who are still in stages 1 and 2
have a smaller chance of breast removal and a higher
life expectancy. However, if patients with breast
cancer are already in stages 3 and 4, the more
difficult the treatment. In addition, at stages 3 and 4
the cost of treatment required is also greater and the
life expectancy of breast cancer patients getting
smaller (Savitri, 2015).
Breast self-examination or BSE is an activity that
can be done to detect breast cancer early. This is to
increase awareness of how important alertness is to
an abnormal lump in the breast. Breast self-
examination or BSE is done regularly every month,
precisely after menstruation is complete. If unusual
things are found in the breast such as a lump, then
immediately do SADANIS namely a clinical breast
examination to a competent doctor to get further
action (Marimbi, 2011).
Based on the results of the study, the highest
proportion of breast cancer stage is stage 2. Based
on the results of interviews, it was found that the
highest breast cancer stage is stage 2 because the
respondents managed to recognize abnormalities that
occur in their breasts early on. The respondents
screened the breast self-examination method or BSE.
In this examination, the respondents found the
condition of their breast abnormalities, such as a
lump on breasts, nipples that secrete fluid, and
swelling of the breasts. When the respondent feels
these symptoms, the respondent immediately
conducts SADANIS namely a clinical breast
examination at a health facility to get further action.
This is in accordance with the YKPI program,
which is to prevent and control breast cancer in
Indonesia through breast self-examination or breast
self-examination and clinical breast examination or
SADANIS by conducting socialization-socialization
both internally and externally. Internal socialization
is a socialization activity in a halfway house for
breast cancer patient companions, while external
socialization is a socialization activity in several
regions in Indonesia through seminars attended by
breast cancer patients and no breast cancer patients.
However, the socialization has limitations,
namely that not all regions in Indonesia have been
reached by YKPI, so there is still a delay in
diagnosis due to the lack of information obtained by
the public. Therefore, suggestions for YKPI to
further expand the reach of outreach to all regions in
Indonesia. In addition, YKPI can work together
across sectors, namely puskesmas to conduct
socialization to the public. Therefore, when they
begin to feel symptoms of breast cancer in their
bodies, they can immediately conduct a clinical
breast examination at a health facility to receive
further action. The sooner breast cancer is
discovered in a woman, the earlier the stadium will
be experienced. This will certainly have an impact
on the higher life expectancy.
4.3 Description of the Number of
Children with Breast Cancer at
YKPI Shelter in 2019
Based on the results of research on 32 breast cancer
patients, it is known that the highest proportion of
children with breast cancer is having 25 children
(78.1%). The results of this study are in line with the
study of Fitoni (2012) which states that the highest
proportion of breast cancer sufferers is having 46
children (65.7%).
Women who already have children have a lower
risk of breast cancer compared to women who do not
have children. This is because women who
experience pregnancy, the hormone estrogen in the
body will decrease. However, in women who do not
experience pregnancy, the hormone estrogen in the
body will increase and stimulate the growth of breast
cancer cells (Lincoln & Wilensky, 2008). In women
who already have children, various hormones will
appear in the body and act as a buffer (balancer) in
the body. So, when the estrogen hormone in the
body is not balanced, it is likely to trigger the
formation of cancer in the breast (Manuaba, 2008).
In women who experience pregnancy, will have a
pregnancy hormone called the hormone
progesterone. The hormone progesterone is
produced in very large quantities and serves to
protect and feed the fetus. If progesterone levels are
high, then estrogen levels in the body will decrease.
Vice versa, if the level of the hormone progesterone
falls, then the level of the hormone estrogen in the
body will increase. This increased estrogen hormone
can stimulate the growth of breast cancer cells
(Putra, 2015). During pregnancy, a substance called
HCG appears. The substance HCG (Human Chronic
Gonadotropin) is a substance that sends genetic
signals to cell tissues to provide protection or
protection against cancer cells. This HCG substance
will stimulate the formation of the hormone
progesterone by the corpus luteum. In this condition,
the dominant hormone that occurs in women is the
hormone progesterone, while the hormone estrogen
tends to decrease. This condition causes women to
be protected from breast cancer (Lee, 2008)
However, based on the results of the study, the
highest proportion of breast cancer sufferers is
having children. Based on the results of the
Characteristics of Breast Cancer Patients in YKPI Singgah Home in 2019
385

interview, this is because there are respondents who
are busy taking care of their children and some are
busy working, so because of this busyness causes
them to consume less fibrous food, even though
substances in fibrous food are able to carry excess
estrogen hormone to get out of the body. This is
consistent with Lee's theory (2008) which states that
the risk of breast cancer in women can be minimized
by consuming foods that contain fiber. Foods that
contain fiber, including whole grains, fruits,
vegetables, and nuts. The fiber contained in food
will carry excess estrogen to get out of the body, so
as to minimize the occurrence of breast cancer.
Therefore, it is better for the community,
especially women who already have children to
actively familiarize a healthy lifestyle, even though
they are busy taking care of children and work. One
of them, by diligently consuming foods that contain
fiber such as grains, vegetables, and fruit because
this habit is able to protect the body from breast
cancer.
4.4 Age Portrait for the First Time
Childbirth of Breast Cancer
Patients at YKPI Shelter in 2019
Based on the results of research on 25 breast cancer
patients, it is known that the highest proportion of
age at first birth is not at risk (≤30 years) totaling 21
people (84%). The results of this study are in line
with the study of Fitoni (2012) which states that the
proportion of age at first giving birth to breast cancer
sufferers is highest (≤30 years) totaling 29 people
(63.04%). The results of this study are also in line
with the research of Sitopu (2012) which states that
the proportion of age for the first time giving birth to
the highest breast cancer sufferers was highest (≤30
years) as many as 65 people (92.9%).
According to Rosma's theory (2008) that each
menstrual cycle of FSH (follicle stimulating
hormone) released by the anterior pituitary lobe
raises some primary follicles which can develop into
de graff follicles which will produce the hormone
estrogen. Women who become pregnant at an older
age will experience more menstrual cycles before
becoming pregnant. This heavy menstrual cycle
causes the body to be exposed to more estrogen.
This much estrogen hormone will stimulate the
growth of breast cancer cells.
However, based on the results of the study, the
highest proportion of the age of first childbirth is at
risk, which is under 30 years. Based on the results of
the interview, this is because the faster the
respondents get married and have children, the more
respondents use contraception. In this study, based
on the data it appears that female respondents who
gave birth to children were not at risk, namely at the
age of more than 30 years, many used hormonal
contraception as many as 11 people. Based on
interviews, the younger women use hormonal
contraception, the higher the risk of developing
breast cancer. This is because the content of
progestin or progesterone synthesis contained in
pills or injections causes breast cancer. This is
consistent with the theory of Lee (2008) which states
that when women decide to get married and have
children under the age of 30, then these women will
tend to use contraception.
Therefore, it is better for women, especially
women who have the age of first birth without risk,
which is under 30 years to replace their
contraceptives from hormonal contraceptives,
namely pills, injections, or implants into non-
hormonal contraception (IUD). This is in accordance
with Nugroho (2011) who states that IUD
contraception is very suitable because it does not
stimulate the presence of the hormone estrogen.
4.5 Description of Breast Cancer
Behavior for Breast Cancer
Patients at YKPI Shelter in 2019
Based on the results of research on 32 patients with
breast cancer, it is known that the highest proportion
of breast cancer patients' behavior is the behavior of
ever breastfeeding as many as 21 people (65.6%).
The results of this study are in line with research
conducted by Sitopu (2012), the highest proportion
is breastfeeding behavior of 50 people (90.9%).
Women who have breastfed have a smaller risk
factor for breast cancer than women who have never
breastfed. In women who breastfeed stimulation
occurs on the nipples of her breasts, causing an
increase in the hormone prolactin. With the increase
of the hormone prolactin, there will be a decrease in
estrogen levels in the body and minimize the
occurrence of breast cancer (Pollard, 2012).
However, based on the results of the study, the
highest proportion of breastfeeding behavior is ever
breastfeeding. Based on the interview results,
respondents breastfeed their babies for at least 6
months. Based on Pollard's theory (2012) states that
when breastfeeding for 6 months can be a natural
contraceptive known as the LAM (Lactational
Amenorrhea Method). LAM as a natural
contraceptive can control and reduce the hormone
estrogen so that it can reduce the risk of developing
breast cancer. However, LAM can be a natural
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
386

contraceptive if the mother gives exclusive
breastfeeding, which is giving breast milk every 4
hours during the day and every 6 hours at night.
However, in working mothers who are separated
from their babies, LAM cannot function as a natural
contraceptive. For working mothers, it is better to
use contraception, the IUD.
Therefore, it is better for women, especially
women who are breastfeeding their children to
replace their contraception from hormonal
contraception, which is pills, injections, or implants,
into non-hormonal contraceptives, namely IUDs.
This is in accordance with Nugroho (2011) who
states that IUD contraception is very suitable
because it does not stimulate the presence of the
hormone estrogen.
4.6 Picture of Age of Menarche in
Breast Cancer Patients at YKPI
Shelter in 2019
Based on the results of research on 32 breast cancer
patients, it is known that the highest proportion of
menarche age of breast cancer patients is> 12 years
old totaling 17 people (53.1%). The results of this
study are also in line with the Sitopu study (2012),
the highest proportion is> 12 years old, amounting to
70 people (94.6%).
The FSH hormone secreted by the pituitary gland
stimulates the maturation of follicles in the ovary so
that the ovary secretes the hormone estrogen. The
hormone estrogen is produced for the first time
when a woman is ready to enter puberty. Menarche
is a general term when a woman experiences first
time bleeding from the uterus or often referred to as
first menstruation. Menarche age that is too early in
women, which is less than 12 years causes exposure
to the hormone estrogen in the body becomes faster.
This estrogen hormone can trigger breast cancer cell
growth (Mulyani and Rinawati, 2013).
The earlier women experience their first
menstruation (menarche), which is before the age of
12 years, the greater the risk of suffering from breast
cancer, which is 2-4 times greater than women who
experience first menstruation (menarche) after the
age of 12 years. Early puberty is one of the risks of
breast cancer. The faster a woman reaches puberty,
the longer her breast tissue can be affected by the
estrogen-causing elements of cancer (Lee, 2008).
Based on the results of the study, the highest
proportion of menarche age is> 12 years old. Based
on interviews, it was found that the cause of
menarche age was> 12 years of age due to the
unhealthy lifestyle of respondents. Respondents
often consume junk food or fast food and fried
foods. The reason respondents have the habit of
consuming junk food or fried food is that this food is
easy to get, is practical and fast, so it does not spend
too much of their time. This is in accordance with
the theory of Savitri (2015) which states that an
unhealthy lifestyle is a wrong diet, such as excessive
consumption of junk food. As a result of consuming
excessive junk food is an increase in body fat. If the
fat in the body increases, then the level of estrogen
in the body will increase. With this increase in
estrogen levels, it can trigger breast cancer cells to
actively develop.
In addition, respondents also consume fewer
vegetables and fruits, whereas in vegetables and
fruits there are substances that can protect the body
from breast cancer. This is consistent with the theory
of Mulyani & Rinawati (2013) which states that the
risk of breast cancer can be overcome by diligently
consuming vegetables and fruits every day at least 5
servings. This is because in vegetables and fruits
there are beneficial substances such as vitamins,
minerals, fiber, phytochemicals and other
compounds that can protect the body from attacks of
breast cancer. Increasing the hormone estrogen in
women can be minimized by consuming lots of
fruits and vegetables. This is because these foods
contain lots of fiber and vitamin C which are
anticarcinogenic and radioprotective as well as
antioxidants that can counteract free radicals so they
can fight breast cancer (Rasjidi, 2010).
After the respondents were at the YKPI shelter,
respondents began to change their lifestyle. This is
because YKPI has a regulation that regulates all
matters related to food consumed by breast cancer
sufferers. The regulated food included fruit and
vegetables for respondents to eat at the halfway
house.
For the community, especially women who have
a menarche age> 12 years should start getting used
to a healthy life, such as getting a proper diet by
reducing junk food consumption and increasing
consumption of vegetables and fruits every day at
least 5 servings because this habit is able to protect
the body from attacks breast cancer.
4.7 Menopause depiction of Breast
Cancer Patients at YKPI Shelter in
2019
Based on the results of research on 32 breast cancer
sufferers, it is known that the highest proportion of
breast cancer sufferers are 26 postmenopausal
sufferers (81.3%). The results of this study are in
Characteristics of Breast Cancer Patients in YKPI Singgah Home in 2019
387

accordance with Sitopu's (2012) research, the highest
proportion was 39 postmenopausal sufferers (66.1%).
In women who have not experienced menopause,
will experience more menstrual cycles compared to
women who have experienced menopause. This
heavy menstrual cycle causes the body to be
exposed to more estrogen. This much estrogen
hormone will stimulate the growth of breast cancer
cells (Utami, 2012). When women have not yet
experienced menopause, the ovaries together with
fat tissue produce the hormone estrogen. However,
when women experience menopause, the estrogen
hormone will decrease dramatically. As a result of
the decline in the hormone estrogen can minimize
the growth of breast cancer cells (Savitri, 2015).
Based on the results of the interview, the highest
proportion of breast cancer sufferers is the patient
who has not yet menopause. This is because
respondents have unhealthy lifestyles, which consume
fewer vegetables and fruits. We recommend that
women, especially women who have not been
exposed to cancer to be diligent in consuming foods
such as vegetables and fruit because this habit is able
to protect the body from breast cancer.
However, based on the results of the study, the
highest proportion of menarche age is> 12 years old.
Based on interview results, respondents who have
menarche age> 12 years have an unhealthy lifestyle.
Respondents consume a lot of foods that contain high
fat such as butter, margarine, and coconut milk. In
addition, respondents also consume less soy. This is
consistent with Putra's (2015) theory which states that
too much fat can trigger an increase in the hormone
estrogen. Increased estrogen hormone, capable of
causing breast cancer, In addition, decreased levels of
the hormone estrogen can be done by consuming
foods derived from soybeans. This is because soy
contains a lot of protein that can prevent breast tissue
from producing high estrogen (Utami, 2012).
Therefore, it is better for women, especially
women with menarche age of breast cancer patients>
12 years in order to reduce foods with high-fat
content such as butter, margarine, and be diligent in
consuming foods derived from proteins such as soy.
This is because these habits can reduce levels of the
hormone estrogen so as to minimize the occurrence
of breast cancer.
4.8 Description of Family History
(Mother or Sister) in Breast Cancer
Patients at YKPI Shelter in 2019
Based on the results of research on 32 patients with
breast cancer, it is known that the highest proportion
of breast cancer patients are those who have no
family history (mother or sister) totaling 22 people
(68.8%). The results of this study are in line with
Rondonuwu's research (2016) which states that the
highest proportion of breast cancer sufferers are
those who have no family history (mother or sister)
totaling 145 people (96%), Purba research (2004)
the highest proportion in patients who do not have a
family history (mother or sister) totaling 92 people
(84.4%), Siallagan research (2012) the highest
proportion are sufferers who do not have a family
history (mother or sister) totaling 90 people (52.3%)
and research Ayudia (2017) the highest proportion is
sufferers who have no family history (mother or
sister) of 90 people (52.3%)
Women who have a family history of breast
cancer have more than doubled the risk of
developing breast cancer compared to women who
have no family history. This is because breast cancer
increases with inherited genetic factors (Sholihin,
2017). Women who have a family history of having
had breast cancer are more at risk of developing
breast cancer due to mutations or defective copies of
genes that are hereditary and are genetically
inherited (Maysaroh, 2013). The risk of breast
cancer will be higher in women who have blood ties
with families who have had cancer. The family can
come from mothers, sisters or daughters (first-degree
families) who suffer from breast cancer will double
the risk of developing breast cancer (Mulyani &
Rinawati, 2013).
However, based on the results of the study, the
highest proportion of breast cancer sufferers are
sufferers who have no family history (mother or
sister). From the data, it was also found that
respondents who did not have a history of breast
cancer also used hormonal contraception as many as
9 people (40.9%). Therefore, women, especially
those who do not have a family history to switch
from using hormonal contraception to non-hormonal
contraception, the IUD. This is consistent with Lee's
theory (2008) which states that the IUD is very
suitable for use because the IUD does not stimulate
an increase in the hormone estrogen.
4.9 Description of Hormonal
Contraception of Breast Cancer
Patients at YKPI Shelter in 2019
Based on the results of research on 32 breast cancer
sufferers, it is known that the highest proportion of
breast cancer sufferers using hormonal contraception
is 14 (43.8%). The results of this study are in line
with the research of Sitopu (2012), the highest
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
388

proportion using hormonal contraception is 31
people (77.5%).
Contraception is one of the efforts that can be
chosen in order to prevent conception and
pregnancy. Contraception is divided into 2, namely
hormonal and non-hormonal. Hormonal
contraception consists of pills, injections, and
implants. Meanwhile, non-hormonal contraception
consists of an IUD or tubectomy. The younger
women use oral contraceptives (pills or injections),
the higher the risk of developing breast cancer. This
is because the content of progestins contained in
pills or injections can cause breast cancer (Lee,
2008).
Prolonged use of birth control pills can increase a
woman's risk of breast cancer because cells that are
sensitive to hormonal stimulation may experience
changes in benign degeneration or become
malignant and this risk will decrease automatically
when the use of birth control pills stops (Mulyani &
Rinawati, 2013). The use of oral contraceptives is a
risk factor that can trigger and increase the risk of
breast cancer but is only limited to a certain period
of time. Women who use oral contraceptives in the
form of pills for a period of more than 5 years have a
greater risk of developing breast cancer. However,
when women stop using it, the risk of developing
breast cancer will also decrease (Savitri, 2015). Of
all types of contraception, the use of contraceptives
in the form of an IUD is very suitable for use
because the IUD does not stimulate an increase in
the hormone estrogen (Nugroho, 2011).
Based on the results of the study, the highest
proportion using hormonal contraception were 21
people (46.9%). The use of hormonal contraception,
with details of the pill 12 people with an average
length of 6 years, injecting 6 people with an average
length of 3 years and implants 3 people with an
average length of implants 5 years. Based on the
interview results it was found that the reason
respondents chose hormonal contraception is that the
price is relatively cheap and easy to obtain.
Aside from this, respondents also have long used
hormonal contraception with an average use of five
years. Even though the longer a person uses
hormonal contraception, the greater the risk of breast
cancer. Therefore, it is better for women, especially
those who use hormonal contraception to replace the
contraceptive from hormonal contraception that they
use to become a non-hormonal contraceptive IUD if
they still want to have more children, or tubectomy
if they do not want to have more children. This is in
accordance with the theory because the IUD
contraceptive method does not stimulate the
emergence of the hormone estrogen so that it can
minimize the occurrence of breast cancer suitable for
use because the IUD does not stimulate an increase
in the hormone estrogen (Nugroho, 2011).
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of research and discussion in
the previous chapter it can be concluded:
1. The highest proportion of breast cancer
sufferers at the YKPI stop in 2019 is not at risk
(<50 years) of 27 people (84.4%).
2. The highest proportion of staging of breast
cancer sufferers in YKPI shelters in 2019 is
stage 2 of 14 people (43.8%).
3. The highest proportion of children with breast
cancer in YKPI shelters in 2019 is having 25
children (78.1%).
4. The highest proportion of the age of first
giving birth to breast cancer patients at YKPI
shelter in 2019 is the age of the first time
giving birth without risk (<30 years) by 21
people (84%).
5. The highest proportion of breastfeeding
children with breast cancer in YKPI shelters in
2019 is breastfeeding for 21 people (65.6%).
6. The highest proportion of menarche (first
menstruation) of breast cancer sufferers at
YKPI stop in 2019 is the age of menarche> 12
years by 17 people (53.1%).
7. The figure for the proportion of menopause
(menstruation stops) the highest breast cancer
sufferers in YKPI shelters in 2019 is not yet
experiencing menopause by 26 people
(81.3%).
8. The highest proportion of the family history of
breast cancer sufferers in YKPI shelters in
2019 is not having a family history of 22
people (68.8%).
9. The proportion of contraceptive use of breast
cancer sufferers in YKPI shelters in 2019 is
hormonal contraception of 14 people (43.8%).
6 SUGGESTION
For the community, especially women who have a
risk of breast cancer
1. We recommend that people, especially women
who have a risk-free age that is under 50 years
of age, begin to get used to a healthy life by
Characteristics of Breast Cancer Patients in YKPI Singgah Home in 2019
389

getting used to regular exercise. This is
because regular exercise makes the body rich
in oxygen so that it can fight breast cancer
cells in the body.
2. We recommend that people, especially women
to be diligent in doing breast self-examination
or breast self-examination every month,
precisely 5-7 days after menstruation.
Furthermore, if there are symptoms of breast
cancer immediately do SADANIS which is a
clinical breast examination in the health
service.
3. We recommend that the community, especially
women who already have children to actively
familiarize a healthy lifestyle, even though
busy taking care of children and work. One of
them, by diligently consuming foods that
contain fiber such as grains, vegetables, and
fruit because this habit is able to protect the
body from breast cancer.
4. It is better for women, especially women who
are at the age of first birth to have a risk-free
age below 30 years to replace their
contraceptives from hormonal contraception,
which are pills, injections, or implants into
non-hormonal contraception (IUD). This is
because hormonal contraception contains
estrogen. The hormone estrogen in the body is
what can trigger breast cancer.
5. It is better for women, especially women who
breastfeed their children to replace their
contraceptives from hormonal contraceptives,
namely pills, injections, or implants, to
become non-hormonal contraceptives, namely
IUDs. This is because IUD contraception is
very suitable for nursing mothers because it
does not stimulate the hormone estrogen.
6. It is better for the community, especially
women who have menarche age> 12 years
should start to get used to a healthy life, such
as getting a proper diet by reducing junk food
consumption and increasing consumption of
vegetables and fruits every day at least 5
servings because this habit is able to protect
the body from breast cancer attack.
7. We recommend that women, especially
women who are not yet menopausal in order to
reduce foods with high-fat content such as
butter, margarine, and diligently consume
foods derived from soybeans. This is because
these habits can reduce levels of the hormone
estrogen so as to minimize the occurrence of
breast cancer.
8. It is better for women, especially women who
do not have the risk of breast cancer to replace
their contraception from hormonal
contraception, which is pills, injections, or
implants, into non-hormonal contraceptives,
namely IUDs. This is because IUD
contraception is very suitable for nursing
mothers because it does not stimulate the
hormone estrogen.
9. We recommend that women, especially those
who use hormonal contraception to replace
contraception from hormonal contraception
they use become non-hormonal contraceptives,
namely an IUD if they still want to have more
children, or tubectomy if they do not want to
have more children.
REFERENCES
Ardiana. (2013). Analysis of Reproductive Risk Factors
Related to the Occurrence of Breast Cancer in Women
2013. Faculty of Medicine, University of Padjadjaran.
Ayudia, F. (2017). Factors Causing the Occurrence of Ca
Mamae in Fertile Age Women in RSUP DR.
M.Djamil Padang 2017. Alifah Academy of
Midwifery.
Fitoni, H. (2012). Risk Factors for Breast Cancer at DR.
Soedarso Hospital Pontianak 2012. Faculty of
Medicine, Tanjungpura University.
Handayani, L., Suharmiati, & Ayuningtyas, A. (2012).
Cervical Cancer and Breast Cancer. Jakarta: Agro
Media Reader.
Lee. (2008). Breast cancer. Jakarta: Daras Books.
Lincoln, J., & Wilensky. (2008). Breast cancer. Jakarta:
Workshop Achievement.
Marimbi. (2011). Breast milk and breast tumors.
Yogyakarta: Nuha Medika.
Maysaroh, H. (2013). Cancer in Women. Klaten: Trimedia
Reader.
Mulyani, N. S., & Rinawati, M. (2013). Breast Cancer and
STDs in Pregnancy. Yogyakarta: Nuha Medika.
Nugroho, T. (2011). Breast milk and breast tumors.
Yogyakarta: Nuha Medika.
Purba, N. M. (2009). Characteristics of Breast Cancer
Patients hospitalized at ST. Elisabeth Medan in 2000-
2002. University of Northern Sumatra. Putra, S. R.
(2015). Complete Book of Breast Cancer. Yogyakarta:
Like.
Rasjidi, I. (2010). Epidemiology of Cancer in Women.
Jakarta: PT Elex Media Komputindo.
Rondonuwu, I. A. (2016). Profile of breast cancer in Prof.
RSUP Dr. R. D. Kandou Manado in 2013 - 2014.
Faculty of Medicine, Sam Ratulangi University,
Manado.
Saragih, L. B. (2011). Characteristics of Breast Cancer
Patients Cared for in the Longing Room B-2 General
Hospital, Haji Adam Malik Medan Hospital in 2007-
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
390

2008. Faculty of Medicine, University of North
Sumatra.
Savitri, A. (2015). Breast, Cervical & Uterine Cancer.
Yogyakarta: New Library Press.
Sholihin, R. (2017). Overcoming Cancer Silent Killers.
Jakarta: Roman Reader.
Siallagan, S. (2012). Characteristics of Inpatient Breast
Cancer Patients at the General Hospital Dr. Pirngadi
Medan in 1999-2003. Faculty of Medicine, University
of North Sumatra.
Sitopu, S. D. (2012). Characteristics of Inpatient Breast
Cancer Patients in Gynecological Obstacles in RSUP.
H. Adam Malik Medan, 1998 - 2002. Faculty of
Medicine, University of North Sumatra.
Subaja, H. P. (2014). Malignant Cancer Female Killer.
Yogyakarta: FlashBooks.
Utami, S. (2012). Breast cancer. Jakarta: Like Books.
Characteristics of Breast Cancer Patients in YKPI Singgah Home in 2019
391
