
A Beginner Badminton Coach Training and Education Program: A
Workshop of Multi-goal Strategies
Yusuf Hidayat
1
, Yunyun Yudiana
1
, Tite Juliantine
1
1
Department of Sports Education, Faculty of Sports and Health Education, Universitas Pendidikan, Bandung, Indonesia
Keywords: Multi-Goal Strategies, Badminton, Beginner Coaches.
Abstract: The main purpose of the training and education program implemented in this study was to develop knowledge
and skills of beginner badminton coaches in applying multi-goal strategies (MGS) as an integral part of
psychological skill training (PST) in order to implement it in an integrated manner in badminton training
process. 20 beginner badminton coaches coming from ten different cities in West Java province, Indonesia,
were selected to participate in the workshop conducted for four days. It is expected that the output of the
program is a hypothetical model of an applicative conceptual framework of the use of MGS in badminton
coaching for young beginner student-athlete badminton players.
1 RELEVANCE
Apart from mental imagery, self-talk, and relaxation,
another crucial component of psychological strategy in
improving performance is goal setting, or GS (Thelwell
and Greenless, 2003). GS is a technique to determine
the orientation of training goal that mobilizes
individual behavior in achieving the goal (Hidayat,
2011). In the action theory, GS has a function as an
analysis strategy in the mental control level that is
responsible for initiating other psychological
strategies, such as self-talk and mental imagery
(Schack and Hackfort, 2007), and also for regulating
all student-athlete activities in all structure of movement
construction process (Hidayat, 2016).
According to the orientation dimension
(Zimmerman and Kitsantas, 1997; Gould, 2001; Cox,
2015), GS is classified into product goal (orientated on
the final result or focus on the task perfection), process
goal (focused on the skill mastery and skill
development), performance goal (directed on the
achievement of movement skill as a whole), dynamic or
shifting goal (oriented on the combination of process
and product goal), and multi-goal strategies (MGS).
Several studies found that MGS plays a higher role
compared to other GS, in terms of improving learning,
sport performance, or psychological skill development
(Kingston and Hardy, 1997; Steinberg and Maurer,
1999; Filby, Maynard, and Graydon, 1999; Hidayat,
2012). The urgency of MGS is getting higher and it is
strengthen by the function and the role of a coach as
a profile model and manager in the training process
(Hidayat, 2019). The coach is demanded to master
MGS, so that the quality of process and training result
can be improved. Being affirmed by (Freitas, Dias, and
Fonseca 2012), the implementation of MGS, as an
integral part of the PST, should consider the
characteristics of sport and athletes’ skill levels.
In accordance with the main arguments above, it is
necessary to do concrete actions to develop MGS
implementation program as a goal achievement
strategy in the integrated process of physical, technical,
and tactical skill training. Before designing the
implementation of MGS program, every coach should
acquire sufficient knowledge and skill about MGS and
strategies to implement it in the training process.
Therefore, it is important and strategic to conduct a
workshop on multi-goal strategies called A Beginner
Badminton Coaches Training and Education
Program: A Workshop of Multi-goal strategies
(BBCTEP of MGS) in relation with the mastery of
badminton basic skill (BBS).
2 METHODS
2.1 Participants
20 beginner badminton coaches aged 20-29 year old
participated in BBCTEP of MGS (M
years
= 24.5;
SD=1.18). All participants came from 10 badminton
Hidayat, Y., Yudiana, Y. and Juliantine, T.
A Beginner Badminton Coach Training and Education Program: A Workshop of Multi-goal Strategies.
DOI: 10.5220/0009784802810286
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Spor ts
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 281-286
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
281

schools or clubs in West Java. Beside coaches,
BBCTEP of MGS also involved 40 beginner student-
athletes aged 10-12 year old (M
years
=11.5; SD = .65),
consisting of 20 male student-athletes (M
years
=11.6;
SD = 1.30), and 20 female student- athletes (M
years
= 11.12; SD = 0.56), coming from two badminton
schools or clubs in Bandung. All student-athlete
participants were chosen through disproportional
stratified sampling technique (Johnson &
Cristensen, 2012) and divided into four groups.
2.2 Measurement
2.2.1 Workshop
The result of the workshop was measured by cognitive
test and affection scale assessment. Cognitive test was
used to measure the level of coaches’ mastery of the
workshop materials on the cognitive behavioral
component (Anderson and Krathwohl 2001;
Näsström, 2009). The test compiled 30 multiple
choice items and the result of split half reliability
estimation analysis arrived in Spearman-Brown
Prophecy reliability coefficient index =. 86.
The participants’ affective self-interest response to
the workshop was measured by two questions
(Hidayat, 2016) “what do you feel when you involved
in the workshop activities (pleasant, average, less
pleasant, unpleasant)”, and “what do you think of this
workshop activity (interesting, average, less interesting,
uninteresting).
2.2.2 Coaching Practical Training (CPT)
The observation of CPT was used to determine the
level of skill of the BBCTEP of MGS participants in
implementing MGS concept in the process of BBS
training (Hidayat, 2016). The measurement indicator
was based on the indicator of motor skill learning
process stages, including opening activities, main
training activities, and closing activities (Suherman,
2009; Hidayat, 2016; Hidayat & Sukadiyanto, 2016),
and elaborated into 9 (nine) out of 14 categories of
coaching behaviour in the Arizona State University
Observation Instrument or ASUOI (Lacy & Darst,
1984; Claxton, 1988; Isabel, Sobrinho, Antonio,
Felismina, & Michel, 2008), consisting of
preinstruction, concurrent instruction, post instruction,
questioning, manual manipulation, positive modelling,
hustle, praise, and management category. The result of
Lawshe’s content validity ratio (CVR) showed content
validity coefficient index (CVCI) between .60 -1.00.
CVCI in total = .89 (93.7%), .81 (89.8%) for opening
activities, .87 (92.1%) for main training activities,
and .96 (97%) for closing activities. According to one
way ANOVA (interclass correlation coefficient / ICC)
analysis technique, it was found that the total
reliability coefficient index among observers =.90, .94
for opening activities, .84 for main training activity,
and .95 for closing activities.
2.3 Procedure
BBCTEP of MGS consisted of workshop and CPT.
Workshop was conducted in classroom learning
through discussion, simulation, and role play.
Meanwhile, CPT was a training activity in the field in
the form of coaching practices (Vealey & Greenleaf,
2001; Weinberg & Gould, 2015; Hidayat, 2016). The
procedure of BBCTEP of MGS was conducted as
follows.
(1) Every participant followed workshop activities for
two days to study the way of designing and
developing MGS and its integration in the BBS
daily training program. The materials of the study
included: (a) BBS workshop analysis and the basic
concepts of MGS implementation on beginner
children student-athlete (day one), and (b)
workshop of approaches and MGS and CPT
learning structure (day two). The workshop process
was conducted in four stages (Boyett & Boyett,
1985), involving experience forming (participants
involved in group activities), reflection (the process
of reflecting their involvement in group activities),
conceptual forming (giving meaning on their
involvement in group activities), and conceptual test
(dialogical and multi-logical process between
participants and facilitators about the concept that
had been built that created a concept that might be
different with the existing conceptual design.
(2) Every participant did cognitive test before workshop
was begun (pre-test), at the end of the workshop
(post-test 1), and after CPT (post-test 2).
(3) CPT is a coaching practice to play a role as a
coach in the process of training (Hidayat 2016)
with the goal to implement MGS concept in the
process of BBS training. In this CPT activity, the
participants were divided into four groups based on
their GS type, including product goal group (G-1),
process goal group (G-2), the combination of product
and process goal group (G-3), and MGS group (G-
4). Each group consisted of 6 (six) persons (three
couples of coach) and all CPT groups received GS
and BBS intervention.
(4) CPT was conducted for two days, first day for
training under the coordination of facilitator, and 1
(one) last day for CPT of each group. The duration
of each CPT is 130 minutes. There were 3 (three)
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
282

coach couples in each group, and every coach couple
played a role as the coach and the other became
observers. The first coach couple of each group
performed at the first meeting, observed by 2 (two)
couples of other coaches from the same group. The
next turn was conducted successively until every
coach couple got 2 (two) opportunities to involve
in CPT.
The CVCI of CPT used Lawshe’s CVR
between .60-1.00, .90 (94.9%) for total CVCI, .83
(91.4%) for opening activity, .89 (94.3%) for main
training activity, and .98 (99%) for closing activity.
Meanwhile, from ANOVA analysis technique (ICC)
was found that the total reliability coefficient index
was 0.92, 0.97 for opening activity dimension, .86 for
main training activity dimension, and .98 for closing
activity dimension.
3 RESULTS
The success of BBCTEP of MGS is determined by the
indicator of the result and product. Cognitive ability and
self-interest are the representation of result indicator,
while product indicator is marked by MGS
applicative conceptual framework documents,
including cue words as the product of fractionation-
analytic BBS. Both of indicators were the result of
four stages of workshop process.
(1) In the experience formation stage, every
participant in each group studied the applicative
MGS concepts in BBS training;
(2) In the reflection stage, every participant did
reflection on all materials they learnt and wrote
them down in relation to the type of GS, combined
with another type of GS function, and how to
apply it in the learning process;
(3) In the conceptual formation, the result of
reflection of every member of group was
discussed in their group to get deeper study with
the reflection result of other groups so that the
MGS application concepts in the BBS learning
process was created;
(4) In the test of concept, every group presented their
application concepts they created to obtain
suggestions from facilitator and other groups so
that the hypothetical applicative concept of MGS
in BBS training process is created.
The result of analysis for cognitive test showed that
there were changes in the mastery level of BBCTEP of
MGS in every test. Participants’ mastery on the post
test 2 (86.40%) > post test 1 (72.50%) and pre test
(58.00%), and participants’ mastery on the post test 1
> pre test. The result of cognitive ability above was
strengthened by participants’ response level on the
process of the workshop. The response from 92%
participants was happy with the process of workshop
and 82% participants perceived that the workshop was
interesting. Meanwhile, the result of analysis of CPT
observation was found that mastery on implementing
coaching skill achievement is 79, 20% in total, 84% for
opening activity, 72,60% for main training activity,
and 100% for closing activity.
The manifestation of workshop product indicator,
in form of the concept of GS applicative strategy in
relation to BBS learning, whether it is for process GS
type, product GS type, dynamic GS type, or MGS
type, is as follows:
a. Deciding the framework of applicative concepts,
including the following steps.
(1) Formulating movement description of each
target skill/motor skill that will be learnt;
(2) Describing the skill into the stages of
movement implementation (preparation stage,
implementation stage, and final movement
stage);
(3) Determining behavior target of each stage of
movement practice, and deciding movement
descriptions of each target behavior;
(4) Arranging goal formulation for each target
skill and sub-goal for each target behavior;
(5) Determining training condition that will be
suitable with the goal and the sub goal;
(6) Deciding the sub-goals of specific
performance based on the goal formula of
each target behavior;
(7) Creating monitoring format for goal
achievement in form of training activity goal
worksheet and goal attainment log (Rushal,
2009)
b. Socializing MGS applicative concepts framework to
the student-athlete in form of education activity in
classroom as an initial activity before manipulation
program was conducted based on the structure of
MGS program;
c. Deciding the level of success of goal attainment
(personal and group) that is suitable with the
developed worksheet;
d. Conducting manipulation check.
Another workshop product is cue words as the
result of fractionation-analytic. The cue words for
process goal, consisting of 13 cue keys (stage 1) and
7 cue keys (stage 2) for high service-BS, 13 cue keys
(stage 1) and 11 cue keys (stage 2) for clear lob BS,
while for drop shot-BS was created 13 cue keys (stage
1) and 10 cue keys (stage 2). In addition, for dynamic
goal, 16 cue keys were created in stage 1 and 10 cue
keys in stage 2 for high service-BS, 16 cue keys (stage
A Beginner Badminton Coach Training and Education Program: A Workshop of Multi-goal Strategies
283

1) and13 cue keys (stage 2) for clear lob BS, and 16
cue keys (stage 1) and 13 cue keys (stage 2) for drop
shot-BS.
4 DISCUSSIONS
The main goal of BBCTEP of MGS is to improve the
beginner badminton coaches’ knowledge, attitude, and
skill in West Java related to the use of MGS integrated
in the whole training process. To achieve the goal, the
coaches involved in the workshop to study and to
decide the materials and the way of implementing
MGS in the process of BBS training for beginner
badminton students-athlete aged 10-12 year old in two
days. The result of cognitive test showed that BBCTEP
of MGS was effective to improve the participants
knowledge related to concepts and implementation
strategy of MGS in the process of BBS training. In the
effective aspect, the participants of the workshop
perceived that the activities were interesting and
pleasant.
The result of the two aspects showed that there was
relevance between materials and the process of
workshop with the demands and the
need of the
coaches in the field. From material aspect, the coaches
needed to study about method and psychological skill
training, especially MGS, which is still neglected until
today. The substance of the materials was strengthened
by the dynamic and interactive workshop providing
dialogical and multi logical process among the
participants, and between the facilitators. In the other
words, the process of workshop had facilitated the
interactive dialogue that initiates the participants’
interest and joyfulness since it was designed in a
dynamic, warm and full of togetherness process, that
the abstract material could be more concrete and
meaningful.
The result of the two aspects, strengthen by the
result of CPT observation, the level of implementation
achievement in every stage of the learning structure of
BBCTEP of MGS was above 80%. According to the
result, it can be concluded that the result of CPT
observation synergize with the result of cognitive and
affective aspects. It also completes and strengthens the
achievement result in total. In addition, cognitive and
affective aspects have been proven as conceptual-
practical provision to achieve the success in
implementing MGS in the process of BBS training. In
general, the results of the three aspects can be
conceptual-practical provision to be implemented in
the real training process and strengthen the belief on
the three aspects as the triadic reciprocity that complete
and strengthen each other.
The cue words as the workshop product, from
theoretical perspective, all the cue words were attained
based on the BBS fractionation-analytics in the form
of skill analysis (high service-BS, clear lob-BS, and
drop shot-BS). Pinheiro & Simon (1992) called it, “the
diagnostic process of movement skills” that is described
into implementation stags, target behaviour, and cue or
key words. It is suitable with the characteristics of MGS
that focus the athlete’s attention on the key elements of
motor skill. Each motor skill was analysed into stages
of movement implementation, including preparation
stage, implementation stage, and final stage (Pinheiro,
2000) and was set as sub-goal. Every stage was built by
several target behaviors (Schmidt & Wrisberg, 2000)
or critical features (Knudson & Morrison, 1996,
2002) and were set as indicators, and from every target
behavior, the cue words that have function as coaching /
teaching point were set and will be used by physical
education teachers or coach to mark the important
aspects from each part of movement conducted when
giving instruction or finding out mistakes in movement
that might be done by the student-athlete, and to be
used by the athlete as the self-talk cue. Figure 1
presents the BBS applicative concept construction
framework based on GS that signed the process of BBS
fractionation analytics construction until the cues or
key words are established.
Every key word has a function to mark the
movement task that has to be practiced by the student-
athlete. Therefore, every cue key signed the
description of the movement task that has to be
understood before practicing the movement. For that
reason, before conducting fractionation-analytics
process, the description of target skill and behaviour
that will be analysed are formulated and developed.
For example, “high-straight” is one of the keywords
from target behaviour in clear lob-BS that has a function
as the description signing the movement task that the
shuttlecock and the racket in the clear lob-BS should
be in the “up straight” and happen in the “highest” point.
Another example, “see the shuttlecock” as the cue key
of the movement target behaviour on the direction to
the shuttlecock in the clear lob and drop shot-BS that
has a function to sign the movement task description
that when they move to the direction of the
shuttlecock. The look should be at the direction where
the shuttlecock comes. The similar meaning is also
used for other cue keys.
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
284
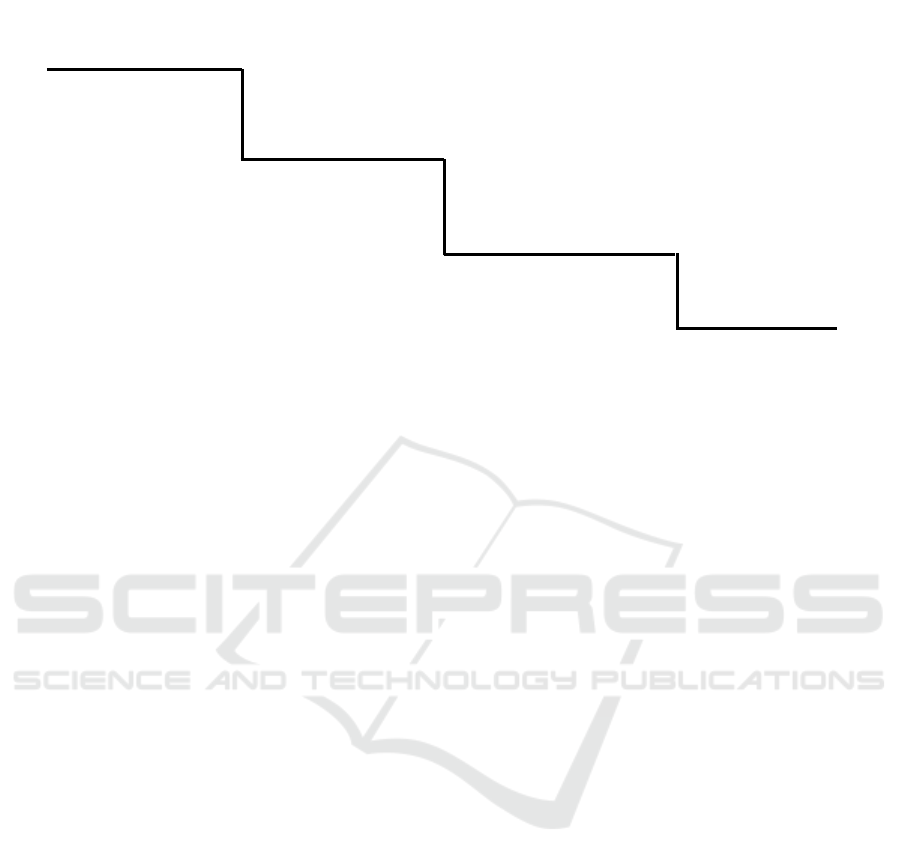
Figure 1: The Applicative concept framework of BBS fractionation-analytics construction process based on GS (Hidayat, 2016)
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the cognition and affection responses, it
concluded that the coaches perceived that their
involvement in BBCTEP of MGS is beneficial. The
effective resulted on cognitive aspect, strengthened by
affective response and skills in implementing MGS in
the process of training. As a model or hypothetical
product, MGS program is a mental training strategy or
psychological skills that can be used for beginner
student-athlete aged 10-12 year old. The application
stages can be done as follows: (1) developing
framework of applicative concept and integrating it into
the whole structure of training process plan, (2)
communicating MGS program to the student-athlete that
is suitable with the developed applicative framework,
(3) determining the level of success in achieving the
goals (personal and group), and (4) conducting
manipulation check related to the level of understanding
on the MGS and the difficulty level of the achievement.
REFERENCES
Lacy, A.C., & Darst, P.W. 1984. Evolution of a systematic
observation system: The ASU coaching observation
instrument. JTPE. 60-66
Claxton, A. 1988. Systematic observation of more and less
successful high school tennis coaches. Journal of
Teaching in Physical Education. 7, 302-310.
Pinheiro, V.E.D., & Simon, H.A. 1992. An operational
model of motor skill diagnosis. Journal of Teaching in
Physical Education, 11, 288-302.
Knudson, D.V., & Morrison, C.S. 1996. An integrated
qualitative analysis of overarm throwing. The Journal
of Physical Ecucation, Recreation and Dance, 7 (6), 31-
36.
Kingston, K.M., & Hardy, L. 1997. Effects of different
types of goals on processes that support performance.
The Sport Psychologist, 11, 277–293.
Zimmerman, B.J., & Kitsantas, A. 1997. Developmental
phases in self-reglation: Shifting from process to outcome
goals. Journal of Educational Psychology, 89(1), 29-
36.
Filby, W.C.D., Maynard, I.W., & Graydon, J.K. 1999. The
effect of multiple-goal strategies on performance.
Journal of Applied Sport Psychology. 11, 230-246.
Steinberg, G.M., & Maurer, M. 1999. Multiple goal
strategy: Theoretical implication and practical
approaches for motor skill instruction. Journal of
Physical Education, Recreation, & Dance. 70(2), 61-
65.
Boyett, J., and Boyett, J. 2000. The guru guide: The best
idea of the top management thinkers. John Wiley and
Sons, Inc., New York, USA
Pinheiro, V.E.D. 2000. Qualitative analysis: Putting it all
together. Qualitative analysis for the elementary grades.
Journal of Physical Education, Recreation & Dance,
71(1), 18-25.
Schmidt, R.A., & Wrisberg, C.A. 2000. Motor learning and
performance. New Jersey: Human Kinetics.
Anderson, L.W., & Krathwohl, D.R. 2001. A taxonomy for
learning, teaching, and assessing: A revision of Bloom’s
taxonomy of educational objectives. New York: Addison
Wesley Longman.
Gould, D. 2001. Goal setting for peak performance. In
Williams, J.M. Applied sport psychology. Personal
growth to peak performance. (pp.158-169) London:
Mayfield Publishing Company.
Vealey, R.S., & Greenleaf, C.A. 2001. Seeing and believing:
Undertanding and using imagery in sport. In Williams,
J.M. Applied sport psycho-logy. Personal Growth to
Target skill (goal)
(high service-BS, clear lob-BS, dropshot-BS)
Dimension (sub-goal)
(The implementation process)
Cue Words
Target behavior / Indicator / Critical
feature / Key elements
A Beginner Badminton Coach Training and Education Program: A Workshop of Multi-goal Strategies
285

Peak Performance. (pp.247-275). London: Mayfield
Publishing Company
Knudson, D.V., & Morrison, C.S. 2002. Qualitative analysis
of human movement. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.
Thelwell, R.C. & Greenlees, I.A. 2003. Developing competitive
endurance performance using mental skills training. Sport
Psychologist., 17: 318-337.
Schack, T., & Hackfort, D. 2007. Action theory approach
to applied sport psychology. In Tenenbaum, G., &
Eklund, R.C. (ed.). Hand book of sport psychology.
New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Isabel, M., Antonio, S., Antonio, R., Felismina, P., &
Michel, M. 2008. A systematic observation of youth
amateur volleyball coaches behaviours. International
Journal of Applied Sport Science. 20(2), 37-58.
Näsström, G. 2009. Interpretation of standards with
Bloom’s revised taxonomy: a comparison of teachers
and assessment experts. International Journal of Research
& Method in Education, 32 (1), 39-51. DOI:
10.1080/1743727090274-9262.
Rushal, B.S. 2009. Mental training for sport: A manual for
athletes, coaches, & sport psychologist. (4
th
. Eds).
California: Sports Science Associates
Suherman, A. 2009. Revitalisasi pengajaran dalam pendidikan
jasmani. Bandung: CV. Bintang Warli Artika
Hidayat, Y. 2011. The effect of goal setting and mental
imagery intervention on badminton learning
achievement motor skill at 10-12 years old: The context
of Indonesia. EDUCARE. International Journal for
Educational Studies. 3 (2), 129-144
Johnshon, B., & Christensen, L. 2012. Educational research
(4
th
. ed.) London: SAGE
Hidayat, Y. 2016. Pengaruh intervensi psiko- logis strategi
multi-teknik (IPSM) terhadap hasil
belajar keterampilan dasar bermain bulutangkis, motivasi
olahraga, & kepercayaan diri. (Disertasi: Tidak
dipublikasikan). Psikologi Universitas Gadjah Mada,
Yogyakarta.
Freitas, S.D., Dias, C., & Fonseca, A. 2012. What do
coaches think about psycho-logical skills training in
soccer? A study with coaches of elite portuguese teams.
International Journal of Sport Science. 3(3), 81-91.
Hidayat, Y. 2012. Pengaruh goal setting dan self-
monitoring dalam penguasaan keterampilan gerak &
motivasi intrinsik siswa SD. Cakrawala Pendidikan Jurnal
Ilmiah Pendidikan. XXXI(3), 495-511
Cox, R.H. 2015. Sport psychology: Concept and
application. Iowa: Wm.C. Brown Publishers.
Weinberg, R. S. & Gould, D. 2015. Foundation of sport and
exercise psychology. (4
rd
). Auckland: Human Kinetics.
Hidayat, Y. & Sukadiyanto 2016. The analysis of mental
imagery functions in badminton for novice athletes.
IJCTA, 9(35), 191-205.
Hidayat, Y. 2019. Workshop of self-talk inter-vention for
beginner of badminton coaches. Asian Journal of Scientif
Research, 12(2), 263-270. DOI: 10.3923/
ajsr.2019.263.270
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
286
