
The Influence of Traditional Games on the Perceptual Motor Skills
and Skill-related Physical Fitness
Sudardiyono
1
, Hari Yuliarto
1
, Yudanto
1
and Sujarwo
1
1
Faculty of Sports Science, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Traditional Games, Perceptual Motor Skills, Physical Fitness, Elementary Students.
Abstract: Perceptual motor skills and skill-related physical fitness are crucial to be developed by the elementary
students. The development can be achieved by freely doing the interesting physical activities. Traditional
games are sorts of enjoyable and exciting games which can be done by the elementary students. The objective
of this research is to find out the influence of traditional games on the perceptual motor skills and skill-related
physical fitness of the elementary students. It was pre-experimental research with one group pretest and
posttest design. The subjects of the research were 30 elementary students. In collecting the data, perceptual
motor test by Rachman (2004) was administered as the research instrument. Speed was measured by doing
40-meters run. Power was measured by performing standing board jump. Furthermore, agility was measured
by doing 4x10 shuttle run (Nurhasan, 2004). The data were analyzed by administering a t-test by comparing
mean scores in the pretest to that in the posttest. The research findings showed that the mean scores in the
posttest were higher than that of in the pretest: 1) Perceptual motor skills: posttest mean score 23,70 > pretest
mean score 18,90, p < 0,05, 2) Speed: posttest mean score 8,16 < pretest mean score 8,86, p < 0,05, 3) Agility:
posttest mean score 12,67 > pretest mean score 13,46, p < 0,05, and 4) Power: posttest mean score 1,44 >
pretest mean score 1,33, p < 0,05. In conclusion, there was influence of traditional games on perceptual motor
skills and skill-related physical fitness.
1 INTRODUCTION
Physical fitness and motor skills development are part
of the objectives of Physical Education, Health, and
Sports. Physical fitness is one of the physical aspects
of the total fitness which allows a person to
productively live the life and adapt to the physical
load properly. Previous research revealed that there
was significance correlation between physical fitness
and the involvement of physical activities. The more
the students actively involved in the physical
activities, the fitter, slimmer, and less healthy risk
would be (Thomas, Lee, Thomas, 1998:10). In
addition, some prior research about the physical
fitness showed that the physical fitness status of
Indonesians including the students was in the low
level. The followings are some previous research: 1)
the research by Depdiknas in Mutohir (2009) about
the level of physical fitness of elementary, junior and
senior high school students. For the elementary
students, it revealed the following percentage: 15%
(very poor), 48% (poor), 31% (fair), 6% (good), and
0% (very good); for junior high school students, there
were 8% (very poor), 46% (poor), 40% (fair), 6%
(good), and 0% (very good); for senior high school
students, there were 7% (very poor), 40% (poor),
46% (fair), 7% (good), and 0% (very good); and for
vocational high school students, there were 11% (very
poor), 45% (poor), 39% (fair), 5% (good), and 0%
(very good), and 2) the research conducted by
Mutohir and Maksum (2007) about the people
physical fitness level which found that there were
37,40% (very poor), 43,90% (poor), 13,55 % (fair);
and 5,15% (good and very good).
One of the causes of the students’ low physical
fitness-with its all risks- is the lack of the physical
activities. The Centers for Disease Control and
Prevention or CDC (2006) states that the children
who are physically passive tend to be the same when
they are adult.
As a result, it can increase the risks of obesity and
comes to the chronic-degenerative disease prevalence
such as hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease. In
relation to the physical fitness, it consists of physical
fitness components which are related to health:
cardiorespiratory fitness, muscular strength, muscular
440
Sudardiyono, ., Yuliarto, H., , Y. and , S.
The Influence of Traditional Games on the Perceptual Motor Skills and Skill-related Physical Fitness.
DOI: 10.5220/0009788304400443
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Spor t Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 440-443
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

endurance, flexibility, and body composition. On the
other hands, the physical fitness components which
are related to skills are speed, explosive power,
balance, agility, coordination, and reaction time.
The improvement of the students’ motor skills,
primarily in relation to the perceptual motor skills is
also believed to be one of the important aspects.
Perceptual motor skills reflected in the children’s
motor development help them explore the knowledge
from the environment which is then formulated to be
the concepts expressed by the motor ability. The
children who easily and quickly move the body tends
to have self-confidence and positive self-conception.
Cratty (1967) highlights that the children who cannot
manage their movement well have low self-
conception and often get difficulty to socially and
emotionally adapt (Laszlo & Bairstow, 1985).
Moreover, Edwards (2010) in Rachman (2018)
explains that first to third-grade students who get
difficulty in studying at school also get difficulty in
the perceptual motor development. As a result, the
difficulty in the perceptual motor skills has the basic
correlation to the school achievement. In line with
this, Thomas, Thomas and Lee (1998) show the
influences of perceptual motor skills on the cognitive
function encompassing: (1) the consequences and the
correlation between perceptual motor skills and
academic achievement, (2) perceptual motor skills as
the basic of the academic readiness and performance,
for example the good eye-hand coordination for the
good writing ability. In addition, Morales, et.al (2011)
also state that the performance of perceptual motor is
closely related to the academic achievement. They
highlight that the children who are good in the
perceptual motor skills are also good in their cognitive
aspects. Therefore, it is assumed that every response
yielded by the interaction with the environment
produces the response of the motor perception.
Although there are some responses which are more
complex, basically, perceptual motor skills are the
performances which involve the ability to interpret
the whole information (visual, kinesthetic, audio, and
tactile) which is transferred to the central nervous
system. In line with this, perceptual motor skills are
believed as the ability produced by the interaction
with the environment which involves the process of
observation and mobility. It is identified as a term
used to correlate between cognitive functions and
motor skills on the children. The concept of
perceptual motor skills deals with the process of
capturing information from the environment to
produce the motor behavior. Perceptual motor skills
can influence other skills in life such as cognitive
functions, academic skills, social and emotional
development, and self-concept.
Perceptual motor skills are constructed by the
movement components consisting of (1) body
awareness, (2) spatial awareness, (3) qualities of
movement, (4) directional awareness, (5) temporal
awareness, and (6) relationships. Based on the
previous research, developing the perceptual motor
for children was fundamental to supporting the
children’s academic skills (Nourbakhsh, 2006). To
develop the perceptual motor skills and physical
fitness, it can be done by doing the physical activities.
One of the physical activities, generally in Physical
Education, Health, and Sports and specifically in
elementary school is playing the traditional games.
The traditional games are the local and regional
games which have unique names and ways of playing
in each region. There are some examples of traditional
games such as Bentengan, Gobak Sodor, Balap
Karung, Lompat Tali, Kasti, and so forth.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The design of the research was pre-experimental
research. It used one group pretest and posttest
design. The subjects of the research were 30
elementary students. The traditional games played
were Hadang, Benteng, Lari Karung, Tujon, Nini
Thowok, and Gateng. The traditional games were
played three times a week for 8 weeks. Each meeting
lasted for 60 minutes. In collecting the data, the
perceptual motor test by Rachman (2004) was used as
the instrument. The speed was measured by doing 40-
meters run; power was measured by doing standing
board jump; and agility was measured by doing 4x10
shuttle run (Nurhasan, 2004). The data were analyzed
by administering a t-test by comparing mean scores
in the pretest and the posttest.
3 RESULT
Table 1 shows the descriptive statistic of the raw data
of the perceptual motor components and skill-related
physical fitness development in the pretest and
posttest.
Table 2 shows the value of sig. 0,000 > 0,05.
Therefore, it could be concluded that there was no
significance influence of traditional games on the
perceptual motor skills.
The Influence of Traditional Games on the Perceptual Motor Skills and Skill-related Physical Fitness
441
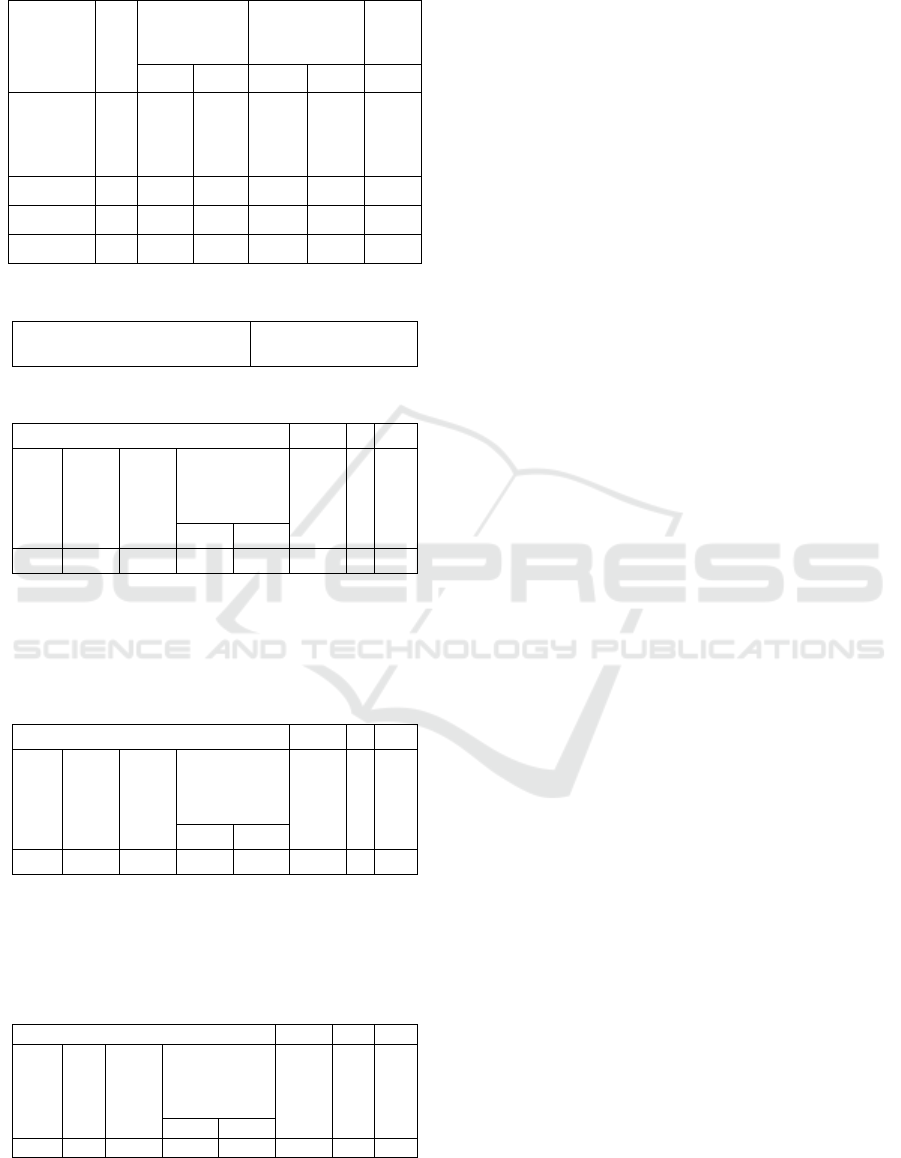
Table 1: Descriptive statistic of the perceptual motor
components and skill-related physical fitness development.
Compon
ents
n
Pretest
Posttest
Impro
veme
nt
M
SD
M
SD
Percept
ual
Motor
Skills
30
18,90
1,47
23,70
1,32
25,40
Speed
30
8,86
0,68
8,16
0,54
7,81
Agility
30
13,46
0,68
12,67
0,52
5,78
Power
30
1,33
0,15
1,44
0,12
8,14
Table 2. t-Test of perceptual motor components.
Z
Asymp. Sig (2-2 tailed)
-4.813
b
.000
Table 3: t-Test of speed.
Paired Differences
t
df
Sig.
Mean
SD
Std.
Error
Mean
95 %
Confidence
Interval of the
Difference
Lower
Upper
.6916
.2987
.0545
.5801
.8032
12.67
29
.000
Table 3 shows the sig. value 0,000 < 0,05. In
conclusion, there was significance influence of
traditional games on speed.
Table 4: T-Test of agility.
Paired Differences
t
df
Sig.
Mean
SD
Std.
Error
Mean
95 %
Confidence
Interval of the
Difference
Lower
Upper
.7900
.4047
.0739
.6388
.9411
10.669
29
.000
Table 4 shows the sig. value 0,000 < 0,05. In
conclusion, there was significance influence of
traditional games on agility.
Table 5: T-Test of power.
Paired Differences
t
df
Sig.
Mean
SD
Std.
Error
Mean
95 %
Confidence
Interval of the
Difference
Lower
Upper
17.460
1.436
.2622
16.9239
17.9967
66.571
29
.000
Table 5 shows the sig. value 0,000 < 0,05. As a
result, there was significance influence of traditional
games on power.
4 DISCUSSION
The traditional games actually have many advantages
for the children. Besides they need low cost, they can
promote the physical fitness. The traditional games
can help the children train their physic and mental
aspects. Misbach (2006) says that the traditional
games can stimulate various aspects of children
development as follows. (1) Motor aspects by training
the endurance power, flexibility, sensory motor, gross
motor and fine motor skills. (2) Cognitive aspects by
developing the imagination, creativity, problem
solving, strategy, anticipative skills, and contextual
awareness. (3) Emotional aspects by being the
emotional catharsis media. (4) Linguistic aspects in
the form of value concept awareness. (5) Social
aspects by conditioning the children to have the good
relationship, cooperation, maturity, and training them
to be socially skilled by role playing with other
people. (6) Spiritual aspects, traditional games can
bring the children to be aware of relationships with
something that is Great (transcendental). (7)
Ecological aspects by facilitating the children to
understand how to wisely utilize the natural elements
and moral values aspects by facilitating the children
to fully comprehend the inherited moral values.
In this research, the traditional games played by
the students such as Hadang, Benteng, Balap/Lari
Karung, Tujon, Nini Towok, and Gateng basically
have different movement characteristics as follows
(1) the primary characteristic of movements in
Hadang and Benteng is running. These games allow
the players to quickly move and change the directions
so they cannot be easily caught by the opponents.
Based on the movement characteristics, the games can
stimulate the students’ speed, agility, spatial and
directional awareness, (2) Balap Karung, Tujuon,
Nini Towok and Gateng have the main movement
characteristics such as running and jumping. In line
with this, the jumping movement can stimulate the
students’ power.
The students’ perceptual motor development
therefore can be increased by playing those traditional
games as one of the physical activities. According to
Rudolph Laban in Rachman (2004), one’s perceptual
motor skills are built from (1) body awareness, (2)
spatial awareness, (3) qualities of movement, and (4)
relationships. The body awareness is closely related
to how the body move. Spatial awareness deals with
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
442

where the body move. Meanwhile, the aspect of
qualities of movement is associated with how the
body move. In addition, the aspect of relationships is
linked to who moves and what are moved by the
body.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The results of the research show the traditional games
such as Hadang, Benteng, Balap/Lari Karung, Tujon,
Nini Towok, and Gateng have significance influence
on the students’ perceptual motor skills and skill-
related physical fitness. Based on this research,
hopefully the teachers employ the traditional games
to improve the students’ perceptual motor skills and
skill-related physical fitness.
REFERENCES
CDC., 2006. What does physical activity for kids?
Available on at www.cdc.Org
Laslow, J.I., Bairstow, P.J., 1985. Perceptual motor
behaviour: development assesment and therapy. Holt,
Rinehart, and Winston. London.
Misbach, I., 2006. Peran permainan tradisional yang
bermuatan edukatif dalam menyumbang pembentukan
karakter dan identitas bangsa. Laporan Penelitian.
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia. Bandung. Tidak
diterbitkan.
Morales, J., Gonzales, L. M., Guerra, C. V., Virgili, C., &
Unnithan, V., 2011. Physical activity, perceptual motor
performance, and academic learning in 9 to 16 years old
school children. International Journal of Sport
Psychology, 42: 401-415.
Mutohir, T.C., 2009. Program pembinaan dan
pengembangan olahraga pendidikan terpadu jangka
panjang. Makalah. Disampaikan dalam Semiloka
Bidang Iptek. Kemenegpora. Jakarta.
Mutohir, T.C. dan Maksum., 2007. Sport development
index: konsep, metodologi, dan aplikasi. Cetakan
Pertama: PT Indeks. Jakarta.
Nurhasan., 2004. Penilaian pembelajaran penjaskes.
Universitas Terbuka. Jakarta.
Nourbakhsh, P., 2006. Perceptual motor abilities and their
relationships with academic performance of fifith grade
pupils in comparison with oseretsky scale. Journal of
Kiensiology, 38 (1): 40-48.
Rachman, H.A., 2004. Keterampilan bermain sofball siswa
sekolah dasar. Disertasi. Jakarta: PPs UNJ.
Rachman, H.A. 2018. Intervensi perseptual motorik dalam
perkembangan gerak anak prasekolah di Daerah
Istimewa Yogyakarta. Laporan Penelitian Research
Group. FIK UNY. Yogyakarta.
Thomas, J.R., Lee, A. M., dan Thomas, J.R. 1998. Physical
education for children: concepts into practice. Human
Kinetics. Champaign, I.
The Influence of Traditional Games on the Perceptual Motor Skills and Skill-related Physical Fitness
443
