
The Influence of Quality of Sleep and Physical Activity on
Ph
y
sical Fitness
Erwin Setyo Kriswanto
1
, Indah Prasetyowati
1
, Jaka Sunardi
1
, Fredericus Suharjana
1
1
Physical, Health, and Recreation Education Department, Yogyakarta State University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Quality of sleep, Physical activity, Physical fitness
Abstract: This research intends to investigate the effect of sleep quality and physical activity on cardiorespiratory
fitness of students of Faculty of Sports Science (FIK) UNY. The research method used was survey which
used questionnaire and measurement tests. The measurements involved several instruments: Pittsburgh Sleep
Quality Index (PSQI) was used to measure sleep quality; Global Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPAQ)
was used to measure physical activity; multi stage fitness test was used to measure cardiorespiratory fitness.
The research population was FIK students. Data analysis technique employed regression test. The research
result indicates that both sleep quality and physical activity have a significant effect on physical fitness.
1 INTRODUCTION
Recently, the development of technology and
economic globally are facing very rapid changes
marked by emergence of industrial revolution 4.0.
The industrial revolution 4.0 begins in this century.
These technological and economic development have
both huge positive and negative impacts on humans.
Positively, of course, humans can easily access
broader insights, get more modern knowledge from
scientific studies, and be helped in daily activities.
Technology and health have huge influence. The field
of technology develops rapidly and it seems that
humans can be ‘harmed’ by the ease of using
technology; convenience offered by it causes people
to be lazy to move so that they tend to be more
sedentary.
The above phenomena also affect children. The
rapid development of technology makes elementary
school students tend to be lazy to move. World Health
Organization (WHO) states that non-communicable
diseases become global problems in the world. Lack
of physical activity is one of the causes of non-
communicable diseases, including diabetes mellitus,
heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and cancer.
These diseases today are the highest factors causing
death and unfortunately, the occurrences are always
increasing.
Riskerdas’s research shows that non-
communicable diseases and their prevalence tend to
decrease (asthma), but for other non-communicable
diseases, they tend to increase. Cancer in Special
Region of Yogyakarta (DIY province) ranks first with
4.9%, stroke (14.7%). DIY is ranked second for
kidney failure (38.7%) after Jakarta, while for
diabetes mellitus, DIY is ranked second (Indonesia
Ministry of Health, 2018). Non-communicable
diseases are seen from proportion of overweight and
obesity in adolescents, with age ≥ 18 in 2007 up to
2018 experiencing an increase. The increase of
overweight in 2007 is 8.7%, 11.5% in 2013, and
13.6% in 2018. While for obesity, in 2007 amounted
to 10.5%, in 2013 amounted to 14.8%, in 2018 took
21.8% (Ministry of Health, 2018).
93.6% of Indonesian people consume less
vegetables and fruits. 48.3% of Indonesian people
over 10 years old lack physical activity (based on
Health Research and Development Agency, Ministry
of Health, 2013). The percentage of women who lack
physical activity is 54.4%, higher than men who have
the percentage of 41.4%. In addition, these results
also strengthen that urban areas have greater
percentage (57.6%) compared to rural areas (43.3%).
Data from Basic Health Research 2013 (Riskesdas,
2013) show that in Indonesia, the proportion of
population aged ≥ 10 years classified as having less
physical activity is 26.1%. Furthermore, there were
22 provinces which exceeded that number. The five
highest are DKI Jakarta (44.2%), Papua (38.9%),
West Papua (37.8%), Southeast Sulawesi, and Aceh
(37.2%). For Special Region of Yogyakarta, the
Kriswanto, E., Prasetyowati, I., Sunardi, J. and Suharjana, F.
The Influence of Quality of Sleep and Physical Activity on Physical Fitness.
DOI: 10.5220/0009788804650470
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 465-470
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
465

proportion of population who have less physical
activity is 20.8%.
The research results are supported by the
condition of children who do more sitting activities
than other activities. The term ‘sitting is the new
smoking’ refers to sitting for a long time which can
cause someone to get metabolic syndrome like
smoking. Even when adults meet physical activity
guidelines, sitting for long period of time can disrupt
metabolic health. Sitting too long in car can increase
the risk of death (Owen, Healy, Matthews, and
Dunstan, 2010). Children have high prevalence rates
of overweight and obesity (Cardon, De Craemer, De
Bourdeaudhuij, and Verloigne, 2014). One of
possible causes is lack of physical activity. This is
also reinforced by WHO which states that physical
activity is fundamental in achieving energy balance
and weight control. Physical activity reduces the risk
of heart disease by 30%, diabetes by 27%, and breast
and colon cancers by 21% 25% (WHO, 2017).
Lack of physical activity is a main cause of death.
The development of technology also causes children
and adolescents to spend more time on smartphones
until late night, causing poor rest patterns (reduced
sleep quality). Low sleep quality and physical activity
can influence someone’s physical fitness levels.
Physical fitness is one indicator to assess whether
someone is fit or not. A person who has good fitness
is someone who can perform daily activities well and
without suffering excessive fatigue. Thus, from the
above problems, the quality of sleep and physical
activity are shown to be important in everyday life
and they influence cardiorespiratory fitness. Based on
that, this research intends to determine the effect of
sleeping quality and physical activity on
cardiorespiratory fitness of Faculty of Sport Sciences
of Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta (FIK UNY)
students.
2 THEORETICAL REVIEW
2.1 Quality of Life
Individuals are required to fulfill basic human needs
in order to maintain their life. One of the basic needs
that human need is sleeping. Sleep is basically needed
by everyone. Sleep is an unconscious state when
individual is awakened by giving stimuli (Guyton and
Hall, 2007). Sleep is a condition when the recovery
process for body and brain occurs and is very
important for achieving optimal health (Maas, 2011).
Everyone needs to have adequate sleep so the body
can function normally. Sleep is one of the important
factors for basic human physiological needs. Sleep
needs are included in physiological needs or primary
needs which are basic requirements for human
survival and this depends on the quality of sleep.
Sleep quality will affect someone’s psychological and
physical health; low sleep quality makes daily life
more stressful or causes someone to become less
productive.
Sleep needs of each individual varies, depending
on their age. Each individual must fulfill his/ her sleep
needs so that he/ she can do activities well. Sleep
quality is where a person can easily start sleeping and
maintain his or her sleep. A person's sleep quality can
be described by the length of sleep and complaints
that are felt during sleep or after waking up. Adequate
sleep needs are determined by sleep quality and sleep
hours factor. Furthermore, some of factors that affect
sleep quality are physiological, psychological,
environmental, and lifestyle factors. Physiological
factor has impacts, such as decrease in daily
activities, fatigue, weakness, decreased endurance
and instability of vital signs (Potter and Perry, 2010).
Whether someone is able to sleep or not is
influenced by several factors (Chen, et. Al., 2016) as
follows: (1)
Health Status
,
Someone who has healthy
body is able to sleep well, while those who is not
healthy, being able to sleep well will be challenging;
(2) Environment
,
The environment can have
influence on someone’ sleep. Clean environment,
cold temperatures, calm atmosphere, and adequate
lighting will facilitate a person to sleep well, and vice
versa, dirty environment, hot temperatures, crowded
atmosphere, and very bright lighting lead to worse
quality of sleep; (3) Psychological Stress
,
Anxiety
and depression will cause sleep frequency disorder.
This is because anxious conditions increase blood
norepinephrine through sympathetic nervous system.
This substance will reduce NREM and REM Stage
IV:
(1)
Diet
,
Foods that contain lots of L-tryptophan
such as cheese, milk, meat, and tuna can cause
someone to sleep easily. Conversely, drinks
containing caffeine or alcohol will cause sleep
disorder; (2) Lifestyle
,
Fatigue felt by someone can
also affect quality of his/ her sleep. Suffering from
middle level fatigue, people still can sleep well,
whereas excessive fatigue will cause shorter period of
REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep; (3) Medicine
,
Consuming medicine affects someone’s sleep. Drugs
may increase the arcing of noradrenergic neurons
which stimulates real sleep decrease in REM sleep
(neuron REM-off) and increases wakefulness.
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
466

2.2 Physical Activity
Physical
and health activities have very close
correlation and are the basis when a child or adult can
enjoy daily physical activity (Weiyun Chen, et al.,
2016). High level of physical activity will have
influence at the end of life when it is associated with
the risk of several chronic diseases and all causes of
death (Nelson, et al., 2007). A person who has passive
lifestyle or is not physically active is prone to diabetes
and other diseases that can cause death (Tao Chen, et
al, 2015). The results of Taras’s study (2005) reveal
that physical activity will improve learning
achievement. Physical activity is related to improving
overall health and can improve socialization and
mental health skills.
2.3 Physical Fitness
Cardiovascular endurance is the ability
of a person to
do physical activities in relatively long time with sub-
maximal weight (Nurhasan, 2005). Cardiovascular
endurance is the ability of lungs, heart, and blood
vessels to convey oxygen and nutrients to cells to
meet the needs of physical activity that lasts for a long
time (Hairy, 2007). Cardiovascular fitness is very
important to support muscle work by taking oxygen
and channeling it to all active muscle tissues, so that
it can be used for metabolic processes. Therefore,
cardiovascular fitness is considered the most basic
component of physical fitness and the most important
component that must be improved so that physical
fitness is always in a good condition (Hairy, 2007).
Cardiorespiratory endurance is the ability of the heart
and lungs to take oxygen and deliver the amount of
oxygen adequately to working muscles used in
performing activities that involve large amount of
muscles (for example: running, swimming and
cycling) for a long time. Based on the opinions above,
it can be concluded that what is meant by
cardiovascular endurance is the ability of the heart
and lung muscles to supply oxygen optimally
throughout body in relatively long time. This means
that functional cardiovascular can improve quality of
life.
Department of National Education (Depdiknas,
2000) states that factors which affect heart and lungs
endurance are as follows: (1)
heredity (Genetic),
From research conducted, it is concluded that 93.4%
ability of VO
2
Max is determined by genetic factors
which can only be changed by training/ exercise.
Genetic factors that play role can distinguish capacity
of heart, lungs, red blood cells, and hemoglobin;
(2)
Age
,
from children up to about 20 years old age, the
endurance of heart (cardiovascular) increases. It then
reaches its maximum limit on the age of 20-30 years.
The endurance is then inversely proportional to the
age, meaning that people who are 70 years old have
resistance of 50% of those who are aged 17 years old.
This is caused by the decrease in the organ transport
and the use of O
2
as the results of increasing age.
However, this decline can be reduced if people do
aerobic exercise; (3) Sex
,
until the age of puberty,
there is no difference in pulmonary heart endurance
(cardiovascular) between men and women. After that
age, the women endurance is 15-25% lower than men.
This difference is caused by difference in maximal
muscular power related to body surface, body
composition, muscle strength, hemoglobin amount,
lungs capacity, and so on; and (4) Physical activity
,
rest in bed for 3 weeks will reduce heart's endurance
(cardiovascular). Doing aerobic exercise for 8 weeks
after rest shows an increase in endurance of the lungs
and heart. The type of physical activity will affect the
capacity of higher cardiovascular endurance
compared to those who do gymnastic and fencing. In
obese patients, directed physical activity also
increases physical fitness in addition to weight loss.
Various types of tests to measure endurance of
heart and lungs or cardiovascular endurance as
follows (Suharto, et al., 2000):
(1) 4,800-meter Brisk
Test,
the 4800-meter brisk test aims to measure ability
and willingness of someone's physical work. This
method measures travel time needed to complete
4,800-meter brisk walk (fast walking). On the 4,800-
meter brisk test, several officers are required, namely
the officer who gives the sign to start; some
timekeepers; several field supervisors; security
officers; health workers; liaison officer; general
assistant. For timekeepers, the number is adjusted to
the needs. Facilities and infrastructure needed include
4,800-meter flat line / track; stopwatch or other time
meter that can show time, either hours, minutes, or
seconds; start flag; chest number, form and
stationery; and other supporting infrastructures. In
this test, there are several requirements that must be
met by participants and its organizer. For the
participants, their ages must be over than 13 years old,
having healthy condition, prepared for the test, and
wearing sport clothes. The test should be done in the
morning, no more than 11.00 a.m. In term of the rules,
the participants should walk as fast as possible, but
they are not allowed to run; during the test,
participants are not allowed to stop or take a rest; (2)
2,400-meter run test
, the aim of 2,400-meter run test
is to measure ability and readiness of someone's
physical works. This method measures travel time
The Influence of Quality of Sleep and Physical Activity on Physical Fitness
467

required to complete 2,400-meter run. Almost the
same as brisk test, it requires several officers, namely
the officer who gives the sign to start; some
timekeepers; several field supervisors; security
officers; health workers; liaison officer; general
assistants. For timekeepers, the number is adjusted to
the needs. The facilities and infrastructure needed
include 2,400-meter flat track / lane; stopwatch or
other time meter that can show time, either hours,
minutes, or seconds; start flag; chest number, form
and stationery; other supporting infrastructures. In
this test, there are several requirements that must be
owned by participants and its organizers. For the
participants, their ages must be over than 13 years old,
having healthy condition, prepared the test, and
wearing sport clothes. The test should be done in the
morning, no more than 11.00 a.m. In term of the rules,
the participants should walk as fast as possible, but
they are not allowed to run; during the test,
participants are not allowed to stop or take a rest; (3)
Harvard Step-ups Test
, this test is the oldest
measurement (made by Brouha in 1943) which is
used to determine aerobic ability, or sometimes called
as heart-lungs ability, cardiovascular endurance,
aerobic power, cardiovascular endurance, cardio
respiration endurance, and aerobic fitness (they all
have the same meaning). The purpose of this test is to
measure the ability or readiness of one's physical
works. Equipment needed include: 19-inch Harvard
bench for male and 17 inches for female; stop watch
to record the time; metronome to adjust up and down
rhythm; stethoscope to count the pulse (or fingers if
there is no stethoscope); form/ table and stationery;
and (4) MFT (Multistage Fitness Test)
, Junusul Hairy
(2007) states that the most appropriate way to find out
components of endurance is through tests. One of the
field tests used to find out VO
2
Max level is by
multistage test. Multistage Fitness Test (MFT) is a
type of endurance test that aims to determine VO
2
Max. In Indonesia, people usually call it Tung Test
(Bleep Test). Unit of this test is cc/ Kgbb/ minute.
This research employed the MFT (Multistage
Fitness Test) as cardiovascular endurance test.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
3.1 Research Design
The research employed survey method in the form of
correlational research type that aimed to find out the
correlation between sleep quality, physical activity
and physical fitness.
3.2 Research Subject
The population of the research was the students of
Faculty of Sport Sciences. Sampling technique used
was random sampling. Number of samples was 194
students.
3.3 Instrument and Data Analysis
Technique
The sleep quality instrument employed in this study
is Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), physical
activity and Global Physical Activity Questionnaire
(GPAQ), while the instrument for cardiorespiratory
fitness employed multistage fitness test. The data
were analyzed by using multiple regression analysis.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Prerequisite Test
The prerequisite test results which employed
normality test shows that the data were normally
distributed with α = 0.584> 0.05. Another
prerequisite test employing heteroscedasticity test
shows that there is inequality of variance from the
residual for all observations in regression model. If
Sig <α, it means that there is heteroscedasticity, while
if Sig>α, this means that there is no
heteroscedasticity. The analysis shows that sleep
quality sig=0.620>0.05 which implies that
heteroscedasticity did not occur. The result of
physical activity test shows that sig = 0.495> 0.05,
meaning that there is no heteroscedasticity.
Furthermore, residual assumption was normally
distributed; multicollinearity did not occur;
heteroscedasticity did not occur; the regression
equation was feasible
.
4.2 Hypothesis Test
Regression tests shows that the correlation coefficient
between sleep quality and physical fitness = -0.083
and sig = 0.011 with Sig <α (0.011 < 0.05). It means
that sleep quality has a significant effect on physical
fitness. Negative correlation coefficient (-0.083)
means that the higher the sleep quality score is, the
lower the physical fitness score is (VO2 Max),
whereas the lower the sleep quality score is, the
higher the physical fitness score (VO2 Max) is.
Based on the study, correlation coefficient
between physical activity and physical fitness is =
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
468
0.290 and sig = 0.000 with Sig <α (0,000 <0,05). It
means that physical activity has a significant effect on
physical fitness. The positive correlation coefficient
(0.290) means that the higher the physical activity
score (MET) is, the higher the physical fitness score
(VO2 Max) is, and the lower the physical activity
score (MET) is, the lower the physical fitness score
(VO2 Max) is.
Linearity test for physical fitness and sleep quality
shows Sig> α (0.953>0.05), indicating that physical
fitness data and sleep quality data are in a linear
relationship. Moreover, linearity test for physical
fitness and physical activity shows Sig> α (0.053>
0.05), implying that physical fitness data and physical
activity data is also in a linear relationship.
The correlation coefficient of sleep quality and
physical activity simultaneously with physical fitness
= 0.327 and F count = 11,457 with sig = 0,000. Sig
<α (0,000 <0,05), indicating that the quality of sleep
and physical activity have a significant effect on
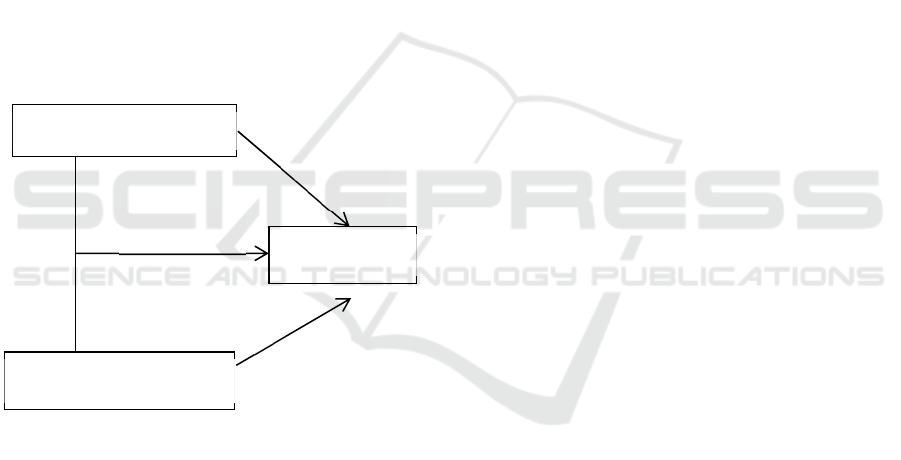
physical fitness. The brief explanation of it can be
seen in the figure below.
Figure 1: The effect of sleep quality and physical activity
on physical fitness
4.3 Discussion
In essence, there is a correlation between physical
activity and sleep quality. Regular physical activity
results in faster and better sleep (Nelson, 2007).
Physical activity and light exercise are healthy
activity which cause someone to fall asleep. Exercise
and fatigue can affect quality and quantity of sleep
because fatigue suffered from high activity can
require someone to have more sleep so as to maintain
energy balance that has been released. People who
have done activities and suffer fatigue will be able to
fall asleep faster because the slow-wave sleep phase
(NREM) is shortened (Hidayat, 2007).
Sleep relieves works of vital organs during daily
activities. Cells damaged during works are repaired
and when someone awakens, his or her body regains
energy to do next activities. Someone who has good
sleep quality will also have good performance on his/
her physical activities. Once the energy has been
fulfilled, people can do exercise and their fitness stays
well. On the other hand, if someone has poor sleep
quality, he or she will experience barriers in
performing physical activities. Loss of sleep can
cause difficulty in concentrating, changes in bodily,
mental and emotional functions (Hardinge and
Shryock, 2001). This can lead to obstruction of
physical activity which should be done properly.
Even if a person can do exercises with poor sleep
quality, his/ her appearance will be different from
those who have good sleep quality. Lack of sleep
results in decrease in someone’s physical and mental
health, such as excessive fatigue, pain, anxiety,
depression, and decreased quality of life (Anderson,
2003). Someone who is in the long run experiences of
sleep disorder can possibly damage his/ her body or
increase the risk of heart attack (Barnard, 2002).
Sleep quality and physical activity can affect
someone's physical fitness. Physical fitness is one
indicator to assess whether someone is fit or not.
Someone is considered to have good fitness if he or
she can do daily activities well and does not suffer
excessive fatigue. Cardiovascular fitness is very
important to support muscle’s work by taking oxygen
and channeling it to all active muscle tissues, so that
it can be used for metabolic processes. Therefore,
cardiovascular fitness is considered the most
fundamental component of physical fitness and the
most important component that must be improved so
that physical fitness is always in a good condition
(Hairy, 2007).
The purpose of performing physical activities is to
improve health status, maintain fitness, and prevent
disease. One’s bustle causes lack of physical activity
which can trigger diseases such as heart disease, high
blood pressure, and stroke (Griwijoyo, 2013). On the
other hand, busy activities cause someone to suffer
fatigue which affects his or her sleep quality. The
higher the level of fatigue suffered by someone, the
better the quality of sleep he or she has (Safriyanda,
2015). Results of a study conducted by Safaringga
(2018) regarding the correlation between physical
fitness and sleep quality of the last semester students
of physical education program show that physical
fitness can adequately affect one's sleep quality and
vice versa, if the physical fitness level is not good,
one's sleep quality will decrease. Furthermore, based
on the results of the study, the level of physical fitness
Sleep Quality
Physical Fitness
Physical Activity
r = -0,183
r = 0,290
R = 0,327
The Influence of Quality of Sleep and Physical Activity on Physical Fitness
469

of the majority of the students (24 students) is in unfit
category (63.2% of the population), while 12 students
(31.6%) are below the average level and the
remaining (2 students or 5.2% of the population) are
not very fit. The factors which influence the result are
the lack of exercise and quality of sleep. From the
research results, the number of students who had
average quality of sleep and severe problems is 28
(73.7%). They had poor sleep quality which means
that they experienced severe problems. While the
remaining 10 students (26.3%) faced medium
problems. Students’ poor sleep quality is influenced
by physical activity factors; students who are in their
last semester rarely do physical activities or sports.
Sleep quality and physical activity have influence
on someone's physical fitness. Maintaining the
quality of sleep means maintaining physical fitness.
Furthermore, by supportinfg the quality of sleep with
sports or physical activities, someone’s physical
fitness will get better.
5 CONCLUSION
Sleep quality and physical activity have a significant
effect on physical fitness.
REFERENCES
Anderson K.O, et al., 2003. Fatigue and sleep disturbance
in patients with cancer, patients with clinical
depression, and community-dwelling adults. J Pain
Symptom Manage 25:307–18.
Barnard, C., 2002. Kiat jantung sehat. (Terjemahan Sofia
Mansoor). Penerbit Kaifa. Bandung.
Depdiknas, 2000. Pedoman modul pelatihan kesehatan
bagi pelatih olahragawan pelajar. Depdiknas. Jakarta
Cardon G, De Craemer M, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Verloigne
M., 2014. More physical activity and less sitting in
children: Why And How?. Science & Sports. 29:S3–5
Griwijoyo, S., 2013. Ilmu kesehatan olahraga. PT Remaja
Rosdakarya: Bandung.
Guyton & Hall, 2007. Buku ajar fisiologi kedokteran. EGC.
Jakarta
Hardinge, M.G., Shryock, H., 2001. Kiat keluarga sehat
mencapai hidup prima dan bugar. (Terjemahan Ruben
Supit). Indonesia Publishing House. Bandung
Hairy, J., 2007. Dasar-dasar kesehatan olahraga.
Universitas Terbuka Departemen Pendidikan Nasional.
Jakarta.
Kemenkes RI, 2013. Strategi nasional penerapan pola
konsumsi makanan dan aktifitas fisik untuk mencegah
penyakit tidak menular. Jenderal Bina Gizi dan
Kesehatan Ibu dan ANAK. Kemenkes RI. Jakarta.
Kemenkes RI, 2018. Hasil utama riskesda 2018.
Kementerian Kesehatan Badan Penelitian dan
Pengembangan Kesehatan. Jakarta.
Maas, L. M., 2011. Asuhan keperawatan geriatrik:
diagnosis nanda.
Nelson, M.E., Rejeski, W.J., Blair, S.N., Duncan, P.W.,
Judge, J.O., King, A.C., Macera, C.A., Castaneda S. C.,
2007. Physical activity and public health in older adults:
Recommendation from the american college of sports
medicine and the american heart association.
Circulation 116, 1094-1105.
Nurhasan, 2005. Aktifitas kebugaran. Jakarta: Departemen
Pendidikan Nasional, Direktorat Jenderal Pendidikan
Dasar Dan Menengah.
Owen, N., Healy, G. N., Matthews, C. E., & Dunstan, D.
W., 2010. Too much sitting: the population-health
science of sedentary behavior. Exercise and sport
sciences reviews, 38(3), 105.
Potter, P. A., Perry, A. G., 2010. Fundamental
keperawatan. SalembaMedika. Jakarta. 7
th
edition.
Safaringga, E., 2018. Hubungan antara kebugaran jasmani
dengan kualitas tidur. Jurnal SPORTIF: Jurnal
Penelitian Pembelajaran, 4 (2).
Sarfriyanda, J., Karim, D., Dewi, A. P., 2015. Hubungan
antara kualitas tidur dan kuantitas tidur dengan prestasi
belajar mahasiswa. Jurnal Online Mahasiswa (JOM)
Bidang Ilmu Keperawatan, 2(2), 1178–1185. Retrieved
from
https://jom.unri.ac.id/index.php/JOMPSIK/article/vie
w/8282
Suharto., Dkk., 2000. Ketahuilah tingkat kesegaran
jasmani anda. Pusat Pengembangan Kualitas Jasmani.
Jakarta.
Tao Chen, et al., 2015. Tri-Axial accelerometer-determined
daily physical activity and sedentary behavior of
suburban community-dwelling older japanese adults.
Journal of Sports Science and Medicine, 14, 507-514
Taras, H., 2005. Physical activity and student performance
at school. J.Sch Health.
Weiyun Chen, et al., 2016. Association of quality physical
education teaching with students’ physical fitness.
Journal of Sports Science and Medicine, 15, 335-343
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
470
