
The Effect of Training Methods and Coordination on Football Skill
of 14 – 15 Year Old SSB Baturetno’s Players
Ricki Agusman
1
, Suharjana
1
1
Science Studies Program ,School of Postgraduates, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Block practice, series practice, coordination, basic football skill
Abstract: The objectives of the study are to find out (1) the difference of the effects between block practice method
and series practice method on football skill; (2) the difference between high coordination and low
coordination in football skill; and, (3) the relationship between methods (block practice and series practice)
and coordination (high and low) in football skill. The method used in this study is 2 x 2 experimental
design. The samples of the research are 20 players, taken randomly from the population. The coordination
instrument is Soccer Wall Volley Test, a soccer skill proficiency test developed by David Lee. The result of
ANAVA data analysis is 0,05. The results of the study are (1) there is a significant difference between the
effects of block practice method and series practice method on football skill. Block practice method gives a
better result than series practice method; (2) there is a significant difference between the effect of high
coordination and low coordination in football skill. High coordination gives better result than low
coordination; (3) there is a significant relationship between method (block practice and series practice) and
coordination (high and low) in football skill.
1 INTRODUCTION
It is important for football player to master the basic
skill of football. Mastering the basic skill is a vital
requirement for each player so that they can give
their best performance. Soccer skills such as
shooting, passing and ball control are very important
in the development of soccer players so that they can
handle any kind of situation in the real game
(Hujigen, Gemser, Post & Visscher, p.2010).
Meanwhile, a player who has poor skill is
probably caused by both internal and external
factors. Internal factors are any factors that come
from within the player itself, or other kind of skills
that differentiate one player from the other. One of
internal factors is coordination skill. Tessitore,
Perroni, Cortis, Meeusen, Lupo & Capranica (2011)
state that during a soccer match, players perform
several dynamic movements (i.e., kicks, sprints,
tackling, jumps), which require high strength and
power of leg muscles, proper timing, and transfer of
energy between segments. Much research has
stressed the importance of fine multijoint control to
improve soccer performance, suggesting that neural
coordination should be trained to improve the
player’s abilities.
The level of an athlete’s eye-feet coordination
skill can affect the output of the training. Therefore,
it takes serious and continual training to improve an
athlete’s basic football skill and technique. This is in
line with what Tiu, Salipot, Maquiraya, Burkley,
Castaneda & Gomez (2012, p.412) state, that eye-
feet coordination is the most important thing in
football. Ding & Feng (2014) add to this statement
that agility and coordination is also important.
Agility and coordination are combination of
strength, endurance, speed, and flexibility and they
have direct impact on players’ skill and performance
on the field.
Based on the early observation and interview
with SSB Baturetno Bantul’s coach, all the players
were very discipline on carrying their tasks
according to their positions and able to cooperate
well. However, on the other hand, their controll
skills were still poor, their passing technique were
slow and not precise. The success rate of their
passing is only 40% out of the total passing that
were done during observation. Their shooting skills
were also poor with low acuracy, and their ball
control and dribbling were not flexible and smooth.
The data from the last game shows that out of 12
shoot attempts, only 4 of them were accurate and
Agusman, R. and , S.
The Effect of Training Methods and Coordination on Football Skill of 14 – 15 Year Old SSB Baturetno’s Players.
DOI: 10.5220/0009789905210525
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 521-525
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
521

only 2 of them made points. If we see it from
psychological perspective, we could see that the
players’ mentalities were not ready for the game as
shown throughout the game. There are other factors
that affect 14-15 year old SSB Baturetno players’
performance; the training methods applied by the
coach were not varied and less attractive to SSB
Baturetno players, resulting in the lack of skill
acquired by the players. We have learned that
practice method and coordination are vital in
football, so the coach is expected to conduct fun and
joyful training for the players which facilitate them
to progress. In this case, researcher is interested to
find out if there is any effect of practice method and
coordination on football skill of SSB Baturetno
players aged 14-15.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
2.1 Type of Research
This research uses 2x2 experimental design as the
research design. According to Arikunto (2010: 207),
experimental research is a research that is meant to
find out if there is an effect of something that is done
to a research subject. The research design can be
seen in Table 1:
Table 1. Factorial Research Design
Training method
(A)
Coordination (B)
Block
Practice
(A1)
Series
Practice
(A2)
Hi
g
h
(
B1
)
A1. B1 A2. B1
Low (B2) A1. B2 A2. B2
Annotation:
A1B1 : Athletes trained with block practice
method and high coordination.
A2B1 : Athletes trained with series practic
method and high coordination.
A1B2 : Athletes trained with block practice
method and low coordination.
A2B2 : Athletes trained with series practice
method and low coordination.
2.2 Population and Samples of the
Reaserch
The population of this research is 38 SSB
Baturetno’s players. Their coordination skills were
tested using Soccer Wall Volley Test. This test is to
find out the players’ level of eye-feet coordination
skill. Then, based on their rank, the players were
divided into two groups: upper group and lower
group.
Based on the division, the researcher decided that
there are 27% of the population who are in the upper
group and 27% of the population were in the lower
group (Miller, 2008, p.68), which means that there
are 10 players with high eye-feet coordination and
10 players with low coordination. Then, these data
were separated into two groups through ordinal
pairing and the result is that there are 5 players from
each group who had high eye-feet coordination skill.
They were given block practice method and series
practice method, and the same things were done to
players who had low eye-feet coordination skill.
Furthermore, each group was given a pretest using
football skill test instrument before given the
treatments.
2.3 Data Instrument and Data
Collection Technique
The instrument used to assess the eye-feet
coordinaton skill in this reasearch is Soccer Wall
Volley Test. This test is a standard test with high
reliability (ICC = 0,97) in the context of assessing a
football player’s skill and acuracy of kicking a ball
(Daneshjoo, Mokhtar, Rahnama & Yusof, 2013,
p.492). The instrument used to assess the football
skill is the “David Lee” improvement test. This test
has 0.484 of validity and 0,942 of reliabillity
(Irianto, 2010, p.152 – 156).
2.4 Data Analysis Technique
To test the hypothesis, the researcher used ANAVA
two-way, and if a relationship is found, then a
further test would be done with Tukey. The results
are analyzed using SPSS version 20.0 for Windows
with 5% or 0,05 of significance rate.
3 RESULTS
The results of the hypothesis testing will be
presented by following these order: (a) the
difference on the effect between block practice
method and series practice method on training to
improve the basic football skill; (b) the difference
between the effect of high eye-feet coordination skill
and low eye-feet coordination skill to the basic
football skill; and (c) the relationship between
practice method (block practice and series practice)
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
522
and coordination level to the improvement of basic
football skill.
The description of the pretest and posttest of the
players’ basic skill is provided in Table 2 below:
Table 2: Statistical Descriptive of the Pretest and Posttest
of the Basic Football Skill
Group Statistic Pretest Posttest
(A1B1)
Total 212.96 203.96
Avera
g
e 42.5920 40.7920
SD .82950 .57050
(A1B2)
Total 217.05 214.25
Average 43.4100 42.8500
SD .22170 .40762
(A2B1)
Total 213.62 213.35
Avera
g
e 42.7240 42.6700
SD .84515 .38891
(A2B2)
Total 217.17 212.91
Average 43.4340 42.5820
SD .18636 .46219
3.1 Precondition Test’s Results
3.1.1 Normality Test
The normality test uses Kolmogorov Smirnov’s
method. The data normality test given to each group
is analyzed using SPSS version 20.0 for Windows
with 5% or 0,05 of significance rate. The summary
of the data is provided in Table 3 below:
Table 3. Normality Test
Data
P
Description
Pretest
A1B1 0,977
N
ormal
A2B1 0,902
N
ormal
A1B2 0,934
N
ormal
A2B2 0,703
N
ormal
Posttest
A1B1 0,740
N
ormal
A2B1 0,913
N
ormal
A1B2 0,740
N
ormal
A2B2 0,957
N
ormal
Based on the statistical analysis of the normality
test that was done using Z Kolmogorov Smirnov’s
method, the significance rate of all of the pretest and
posttest data shows p > 0,05, which means that the
data distribution is normal.
3.1.2 Homogeneity Test
The homogeneity test used in this research is the
Levene Test. The results of the homogeneity test is
provided in Table 4 below:
Table 4. Homogeneity Test
Group Sig Description
Pretest-
Posttes
t
0,291 homogeneous
3.1.3 Hypothesis Testing Results
The research’s hypothesis testing was done based on
data analysis’ research and two-way ANAVA
analitical interpretation. The result of the hypothesis
test is provided in Table 5 below:
Table 5. ANAVA Test
Source Type III
Sum of
Squares
F Sig.
Practice Metho
d
3.240 15.132 .001
Coordination 4.851 22.656 .000
Practice Method *
Coordination
5.757 26.885 .000
Based on the ANAVA test’s result above, it can
be seen that the p significance is 0,001. Because of p
significance is 0,001 < 0,05, this means that Ho is
rejected. This also means that there is a signifianct
difference on the effect of block practice method and
series practice method on the improvement of the
players’ basic football skill. Based on the analysis
result, the researcher found that block practice
method gives better result than serial practice
method, with 0,805 second in difference. This means
that the hypothesis statement “there is a significant
difference on the effect between training with block
practice method and training with series practice
method to the improvement of the players’ basic
football skill” is proven right.
Moreover, based on the ANAVA test’s result
above, it can be seen that the p significance is 0,000.
Because of p significance 0,000 < 0,05, this means
that Ho is rejected. This also means that there is a
significant difference on the effect of high
coordination skill and low coordination skill in the
improvement of the players’ football skill. Based on
the analysist result, the researcher found that players
with high coordination skill gett higher score than
players with low coordination skill, with 0,985
second of posttest’s average difference. This means
that the hypothesis statement “there is a significant
difference on the effect between high eye-feet
coordination skill and low eye-feet coordination skill
to the improvement of basic football skill” is proven
right.
The Effect of Training Methods and Coordination on Football Skill of 14 – 15 Year Old SSB Baturetno’s Players
523
Furthermore, based on the ANAVA test’s result
above, it can be seen that the p significance is 0,000.
Because of the p significance 0,000 < 0,05, this
means that Ho is rejected. This means that the
hypothesis statement “there is a significant
relationship between practice methods (block
practice and series practice) and eye-feet
coordination skill (high and low) with the
improvement of basic football skill” is proven right.
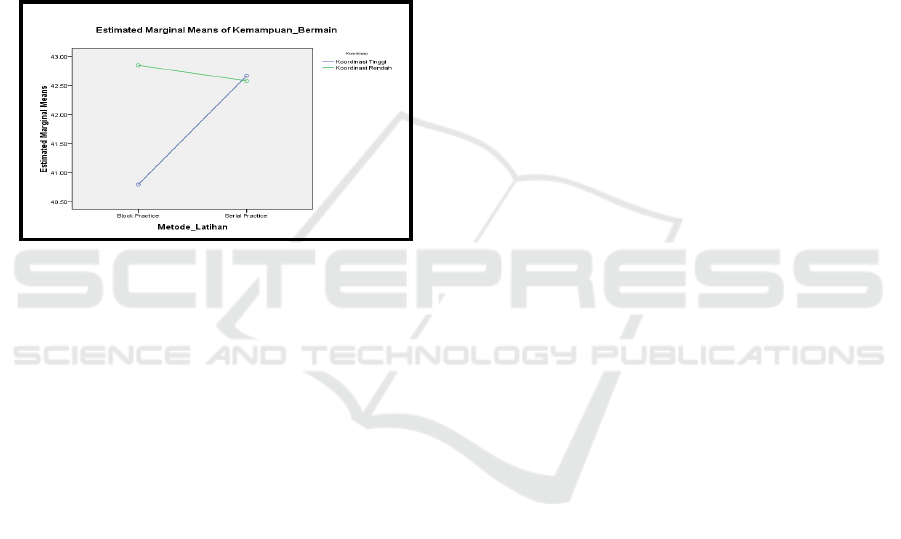
The diagram that shows the relationship between
practice method (block practice and series practice)
and eye-feet coordination skill (high and low) with
the improvement of basic football skill can be seen
in Figure 1 below:
Figure 1. The Result of the Relationship between Method
(Block Practice and Series Practice) and Eye-Feet
Coordination (High and Low)
Thus, based on the Tukey test’s result, the
asterisk mark (*) shows that the pairs that have
relationship or the pairs that show significant
difference are: (1) A1B1-A2B1, (2) A1B1-A1B2,
and (3) A1B1-A2B2, while the other pairs that do
not share difference on the effect are: (1) A2B1-
A1B2, (2) A2B1-A2B2, and (3) A1B2-A2B2.
3.2 DISCUSSION
3.2.1 The Effect of Block Practice Method
and Series Practice Method on Basic
Football Skill.
Based on the hypothesis testing, it is found that
block practice and series practice method have a
significantly different effect on the improvement of
basic football skill. Block practice method resulted
in a better improvement than series practice method.
This is caused by the fact that block practice method
has lower contextual level, so that athlete can adapt
to the given training. Meanwhile, in the series
practice method, the arrangement of the skill
practice contains more than one skill aspect with
practice arrangement order that is always the same
or consecutive in every practice session.
3.2.2 The Effect of Eye-Feet Coordination
Skill (High and Low) on Basic Football
Skill.
The analysis shows that players with higher eye-feet
coordination level show better basic skill than
players with lower eye-feet coordination level. As
we all know, football is a branch of sports that is
relatively more difficult than other. For example,
football players in the wing position are expected to
be able to do crossing (cross passing) while running
fast or sprinting. Football players who have a really
good coordination can do this technique easily,
while those who have poor coordination will find it
difficult. The main purpose of coordination is to
create a harmonious, rithmic, and complex
movement pattern. Thus, coordination practice is
very important to improve those skills.
Eye-feet coordination is an integration between
eye that holds the main function, which is to spot the
ball and to study the game’s situation when the
player is kicking the ball, and feet that holds the
function of moving or kicking the ball from the
previous spot. This is why a good eye-feet
coordination can result in a good game. We can
judge a player’s level of coordination skill by the
smoothness, acuracy, speed, and efficiency of his or
her movement. An athlete who has a good
coordination will not only perform certain skill
perfectly, but also will master new skill faster and
easier. Having good coordination allows a player to
move quickly from one movement pattern to the
other, so that his or her movement will be more
effective.
3.2.3 The Relationship between Practice
Method (Block Practice and Series
Practice) and Eye-Feet Coordination
Skill (High and Low).
As stated above, there is a significant relationship
between practice method (block practice and series
practice) and eye-feet coordination skill (high and
low) to improve basic football skill. The research
shows that the group of players trained with block
practice method and have higher coordination skill
performed better than those who have lower
coordination skill. This is because block practice
method demands the players to do a series of harder
movement than serial practice method does.
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
524

Meanwhile, group of players who have lower
coordination skill are better be trained with series
practice method. This is because the application of
block practice method and series practice method are
different, and the athletes’ level of coordination
skills are also different. Thus, their responses to the
materials given with different practice methods will
show the relationship between block practice
method and series practice method with high level of
coordination skill and low level of coordination skill
on the improvement of football skill.
4 CONCLUSION
Based on the research result and data analysis above,
the researcher draws several conclusions. (1) There
is a significant difference between the effect of
block practice method and series practice method on
the improvement of basic football skill. Block
practice method gives better result than series
practice method does. (2) There is a significant
difference between the effect of high level of eye-
feet coordination skill and low level of eye-feet
coordination skill on the improvement of basic
football skill. Athletes who have higher level of eye-
feet coordination skill showed better performance
than those who have lower level of eye-feet
coordination skill. (3) There is a significant
relationship between practice method (block practice
and series practice) and the level of eye-feet
coordination skill (high and low) for the
improvement of basic football skill.
REFERENCES
Arikunto, S., 2010. Prosedur penelitian; suatu pendekatan
praktik. (Edisi revisi) Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Daneshjoo, A., Mokhtar, A.H., Rahnama, N., Yusof, A.,
2013. Effects of the 11+ and harmoknee warm-up
programs on physical perform- ance measures in
professional soccer players. Journal of Sports Science
and Medicine, 12, 489-496.
Ding, D., Feng, J., 2014. Analysis of agility and
coordination training programs ef ects on football
skills based. An Indian Journal, Volume 10 Issue 21..
Huijgen, Gemser, Post, Visscher., 2010. Development of
dribbling in talented youth soccer players aged 12–19
years: A longitudinal study. Journal of Sports
Sciences, Vol. 28(7): pp.689–698.
Irianto, S., 2010. Pengembangan tes kecakapan david lee
untuk sekolah sepakbola (SSB) kelompok umur 14-15
tahun. Tesis magister, tidak diterbitkan, Universitas
Negeri Yogyakarta, Yogyakarta.
Miller, P.W., 2008. Measurement and teaching. Illinois:
Patrick W. Miller and Associates.
Tessitore, A., Perroni, F., Cortis, C., Meeusen, R., Lupo,
C., Capranica, L., 2011. Coordination of soccer
players during preseason training. Journal of Strength
and Conditioning Research, Vol 25(11), pp. 3059–
3069.
Tiu, W., Salipot, C.L., Maquiraya, C.A., Burkley, D.M.,
Castaneda, M., Gomez, M.G., 2012. Effects of a
modified football program in improving foot-eye
coordination among students with intellectual
disability. Educational Research. Vol. 3(4) pp. 412-
423.
The Effect of Training Methods and Coordination on Football Skill of 14 – 15 Year Old SSB Baturetno’s Players
525
