
Tourist Perceptions of the Quality of Traditional Culinary Products
in Priority Tourism Destinations in Borobudur Central Java
Ayu Nurwitasari, Nuraeni Handayaningrum, Endang Komesti Sinaga, Cucu Kurniati, Nur Komariah
Prodi D3 Tata Boga, Prodi D4 Manajemen Pengaturan Perjalanan Sekolah Tinggi Pariwisata Bandung, Jl. Dr. Setiabudhi
186, Bandung, Indonesia
Keywords: Tourism Perception, Quality of Culinary Products, Culinary Tourism
Abstract: One of the tourism products that is being actively developed in the Borobudur Region is Culinary Products.
Deputy of Nusantara Tourism Development said that the Borobudur region's culinary products raised many
elements of the local cultural flavor of the local community. Unfortunately there are no studies that study
how the quality of food offered at the Central Java Borobudur Priority Tourism Destination. With
information about the quality of culinary products offered at Borobudur priority destinations, it is hoped that
the government can improve the competitiveness of Borobudur priority areas on the national and
international tourism arena. This study aims to determine the Perception of Tourists About the Quality of
Traditional Culinary Products in the Priority Tourism Destinations of Borobudur, Central Java. The research
method used in this study uses the Importance-Performance Analysis method. The sample in this study were
tourists visiting the Borobudur culinary tour of 100 people. From the results of this study it can be seen that
based on the perceptions of tourists on the performance of the quality of traditional culinary products in the
Central Java Tourism Destination Borobudur Priority measured by descriptive analysis as a whole is in the
Good category that is equal to 75.62%. In addition, based on research using Important Performance
Analysis (IPA) in the Cartesian diagram there are one main priority attribute in quadrant A, four attributes
with low priority in quadrant C and one redundant attribute in quadrant D which must be improved to
improve tourist perceptions of product quality culinary namely as follows: a. Quadrant A (Top Priority),
which is a culinary product that is presented has an appropriate nutritional content, quadrant C (Low
Priority) 1) Presentation of the culinary product that is served, 2) The level of maturity of the food served, 3)
The texture of the culinary product served, 4) Appearance color of culinary products. c. Quadrant D
(Excessive) 1) The taste of the food served.
1 INTRODUCTION
Culinary products are one of the values that develop
in an area that shows the identity of the human
groups that live in it. Some anthropologists believe
that cooking has been around 250 thousand years
ago when the stove was first discovered. Since then,
cooking techniques have continued to develop and
each region in the world has its own cooking
techniques and food variations. This makes food as a
thing that has a function as a cultural product.
(National culinary development plan 2015-2019).
In addition to high taste and innovation in a
culinary product, tourists now also expect quality
culinary products. The popularity of Indonesian
traditional cuisine had declined but again rose in the
early 2000s when the position of food and drinks
which is a basic human need began to shift for most
of Indonesian society. Hadisantosa (1993) in Sabana
(2007: 2) defines traditional food as daily culinary
consumed by ethnic groups and specific regions,
processed based on recipes that are hereditary. Local
culinary products are considered better than other
culinary that is not authentic and is considered
unable to describe the cultural richness of a
destination. That is because local culinary products
are considered able to meet the needs of tourists who
want to know the uniqueness of a destination
through food that is commodified and meets culinary
production standards. (Blakey, 2006: 3).
The Ministry of Tourism (Kemenpar) has
designated the Borobudur Region as Indonesia's
leading tourist destination. This was conveyed by
the Deputy for Tourism and Tourism Investment
Destination and Development Sector at the National
Coordinating Meeting of the Ministry of Tourism
100
Nurwitasari, A., Handayaningrum, N., Sinaga, E., Kurniati, C. and Komariah, N.
Tourist Perceptions of the Quality of Traditional Culinary Products in Priority Tourism Destinations in Borobudur Central Java.
DOI: 10.5220/0009802801000105
In Proceedings of the 1st NHI Tourism Forum (NTF 2019) - Enhancing Innovation in Gastronomic for Millennials, pages 100-105
ISBN: 978-989-758-495-4
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
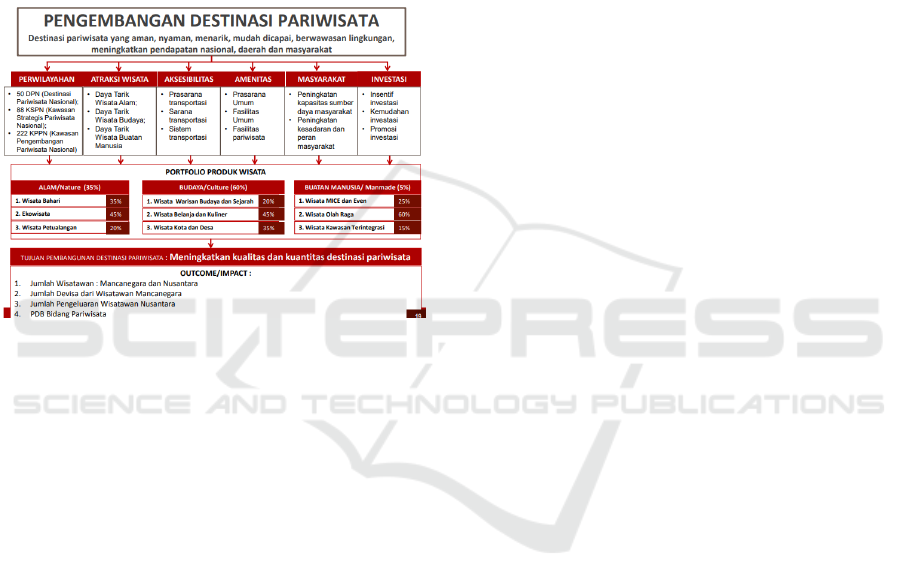
"sel acceleration of Tourism Development in the
Context of Achieving the Target of 12 Million
Tourists and 260 Million 2016 Tourists". The main
development of the Borobudur Tourism Industry
refers to the development of tourism, increasing the
competitiveness of tourism business products,
increasing tourism business partnerships, developing
environmental responsibility and increasing tourism
investment. The target is to make Borobudur Region
Tourism make Indonesia a world tourism
destination, contribution to GDP (WTTC), foreign
exchange, work opportunity contribution to the
community.
Figure 1: Tourism Destination Development (Source:
Ministry of Tourism, 2016).
Based on Figure 1 above it can be seen that one
of the tourism products that is being actively
developed in the Borobudur Region one of which is
Culinary Products. Deputy of Nusantara Tourism
Development said that the Borobudur region's
culinary products raised many elements of the local
cultural flavor of the local community. This is in line
with what is stated in Law Number 10 of 2009
concerning Tourism which states that the
Implementation of Tourism is intended to increase
national income in order to improve the welfare and
prosperity of the people, expand and equalize
business and employment opportunities, encourage
regional development, introduce and utilize tourist
objects and attractions in Indonesia and foster a
sense of love for the motherland and strengthen
friendship between nations. Unfortunately there are
no studies that study how the quality of food offered
at the Central Java Borobudur Priority Tourism
Destination. With the information on the quality of
culinary products offered at Borobudur priority
destinations, it is hoped that the government can
improve the competitiveness of Borobudur priority
areas on the national and international tourism
scene.
Based on this background, it is necessary to
know how the Tourist Perception of the Quality of
Traditional Culinary Products in the Priority
Tourism Destinations of Borobudur, Central Java.
By knowing the tourists' perceptions of the culinary
products of the Borobudur Region, the Government
and stakeholders can develop strategies so that the
culinary products of the Borobudur Region can
become one of the leading tourism products, and can
increase the attractiveness of the Borobudur Region
as a tourist destination.
1.1 Research Formulations
1. What about traditional culinary tourism
products in the Borobudur Region in Central
Java?
2. How is the quality of traditional culinary
products in Borobudur, Central Java?
1.2 Research Purposes
1. To find out the quality of traditional culinary
products in Borobudur, Central Java
2. To find out tourists' perceptions of the quality of
traditional culinary products in the Central Java
Borobudur Region
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Food Quality
Pauli (1979: 11) states the quality or quality of food
is influenced by:
1) Presentation, which is an attractive appearance
of food will arouse appetite so that there will be
a desire to enjoy it. For example the right
arrangement and color combination and the
appropriate presentation.
2) Taste and flavor, namely the aroma of food that
is delicious raises the desire to taste the food.
The taste and aroma of the food served must be
in accordance with the main ingredients,
seasonings and sauces used in processing.
3) Good food texture is according to the type of
food. Proper cooking methods and food
ingredients can affect texture.
4) The temperature of serving food must be in
accordance with the temperature of the type of
food such as hot food served hot or cold food
served cold.
Tourist Perceptions of the Quality of Traditional Culinary Products in Priority Tourism Destinations in Borobudur Central Java
101

5) Color of Food is an interesting color of food
that is fresh and natural will cause appetite
compared to burnt or pale colored food. And the
Character of Food is to distinguish one type of
food from another, so each food has its own
character or characteristics, such as the taste,
aroma of the food, decoration, sauce, and
texture of the food.
6) technological, microbiological and organoleptic
properties.
According to West, Wood and Harger, Gaman
and Sherrington and Jones in Margaretha and Edwin
(2012, 1) in general, the factors that influence food
quality are as follows:
a. Color
The colors of the ingredients must be combined
in such a way that they don't look pale or the
colors don't match. Color combinations are very
helpful in consumer appetite.
b. Appearance
Food must be well seen while on a plate, which
is an important factor. The freshness and
cleanliness of the food served is an important
example that will affect the appearance of the
food whether or not to be enjoyed.
c. Portion
In each serving of food the standard portion has
been determined which is called the standard
portion size.
d. Temperature
Consumers like variations in temperature
obtained from one food to another. Temperature
can also affect the taste, for example the sweet
taste in a food will be more felt when the food is
still warm, while the salty taste in the soup will
be less pronounced when the soup is still hot.
e. Texture
There are many food textures including smooth
or not, liquid or solid, hard or soft, dry or moist.
The level of thin and smooth and shape of food
can be felt through the pressure and movement
of receptors in the mouth.
f. Flavor
The flavor is a reaction from food that will
affect consumers before consumers enjoy food,
consumers can smell the food.
g. Level of maturity
The level of food maturity will affect the texture
of the food. For example carrots that are boiled
enough will be soft than carrots that are boiled
faster. For certain foods such as steak, each
person has their own taste about the level of
steak maturity.
h. Taste
The taste point of the tongue is the ability to
detect the basis of sweet, sour, salty, bitter. In
certain foods, these four flavors are combined to
make one unique and interesting taste to be
enjoyed.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This research is a quantitative research.
Questionnaires were distributed to tourists visiting
Borobudur priority destination areas. Secondary data
includes information obtained from the government,
tourist attractions management, and literature
review. Data were analyzed using the Importance-
Performance Analysis method. The use of the
Importance-Performance Analysis method is to
measure the level of satisfaction of culinary products
included in the quadrants on the Importance
Performance Matrix map. In this method the
measurement of tourist perceptions of culinary
products in the Borobudur priority destination is
measured.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Validity and Reliability Test
The results of validity testing with SPSS 25 show
that each question is valid, because it meets the
requirements of r count> r table (0.1966) so that all
statement items can be used in research. And also
considered reliable because the value of Cronbach’s
Alpha> 0.6 is 0.791 and 0.655.
4.2 Descriptive Analysis
Figure 2: Continuous Line of Reality
NTF 2019 - The NHI Tourism Forum
102
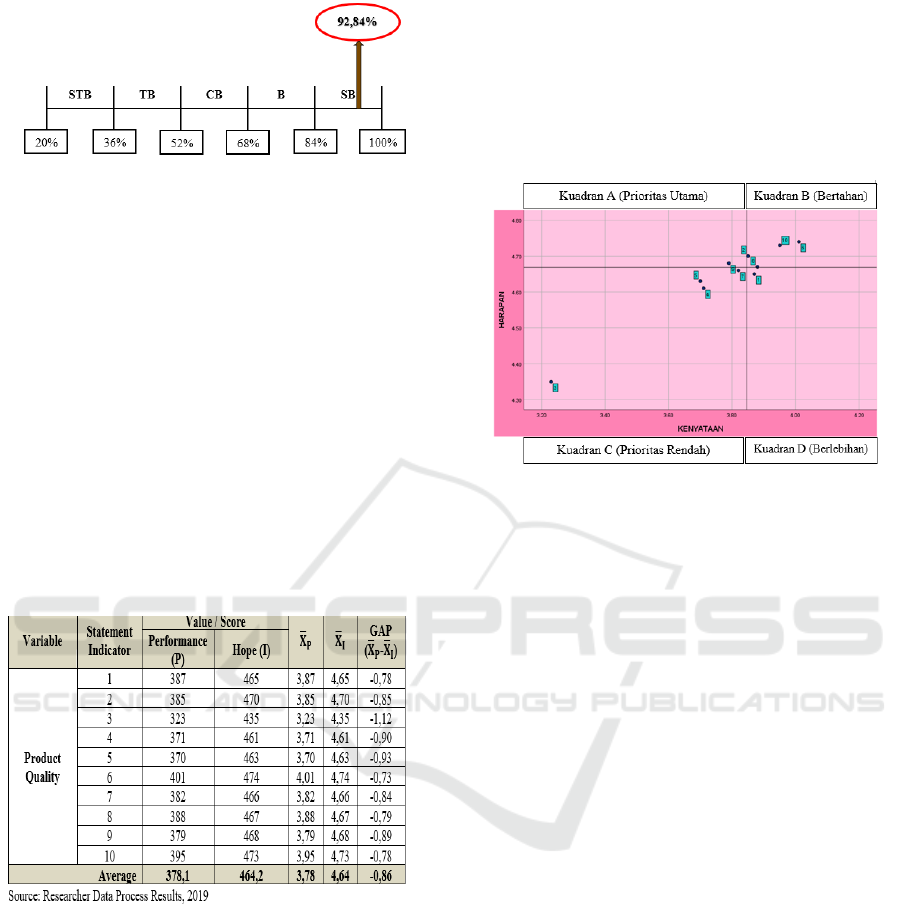
Figure 3: Expectation Line of Hope
Obtained the results of the calculation of the
performance attributes of Traditional Culinary
Product Quality in Borobudur Priority Tourism
Destinations in Central Java by 75.62% and from the
continuum line it can be seen the results of the
calculation of Product Quality performance are
stated "Good". As well as the results obtained by
calculating the expectation attribute of the Quality of
Traditional Culinary Products in the Central Java
Borobudur Priority Tourism Destination by 92.84%
and from the continuum line the results of the
expected calculation of Product Quality are stated to
be "Very Good".
4.3 Gap Analysis (GAP)
Table 1: Gap Calculation Results (GAP)
Based on the table above, it can be seen that all
statements are negative, which means that all
statements have gaps. This shows that the perception
of performance on Product Quality is currently
below the expectation of Quality of Traditional
Culinary Products in Borobudur Priority Tourism
Destinations Central Java.
4.4 Importance-Performance Analysis
(IPA)
To be able to see the position of the analyzed data it
can be seen in the Cartesian diagram. The existence
of the cartesian diagram will facilitate management
in an effort to improve product quality attributes that
are considered important by tourists in the following
diagram. Importance Performance Analysis Diagram
to find out the priority attributes in developing the
quality of traditional culinary products in the Central
Java Borobudur Priority Tourism Destination,
namely:
Figure 4: IPA Diagram
From the Cartesian diagram above it can be
seen the location of the attributes of Product Quality
attributes that influence tourist perceptions of the
quality of traditional culinary products in the Priority
Tourism Destinations of Borobudur, Central Java.
The interpretation of the Cartesian diagram can be
explained as follows:
Quadrant A shows the factors or attributes that
are considered to influence the perception of
tourists. Including service elements that are
considered very important. However, management
has not done it in accordance with the wishes of
tourists so that it is disappointing or it can be said
that consumers are not satisfied. There is one
attribute that is included in this quadrant, namely:
Item 9 (The culinary products served have the
appropriate nutritional content), according to tourists
the nutritional content of a culinary product is very
important but in reality the value of the nutritional
content of the culinary product is not given enough
attention by its managers.
Quadrant B shows the basic service elements
that have been successfully carried out by the
company. For this reason it must be maintained.
There are four attributes that are included in this
quadrant as follows:
1. Item 2 (The aroma of culinary products served),
the aroma of culinary products already feels
delicious so that it arouses the appetite of
tourists.
Tourist Perceptions of the Quality of Traditional Culinary Products in Priority Tourism Destinations in Borobudur Central Java
103

2. Item 6 (Temperature of culinary products
served), when presenting culinary products the
management has paid attention to the
temperature of the food temperature so it is
comfortable for consumption by tourists.
3. Item 8 (Culinary products are presented
reflecting local wisdom / local culture), tourists
have felt the food and culinary peculiarities of
the area or place they visited and visited.
4. Item 10 (Culinary products that are served are
safe for consumption), the manager has
produced quality food products, safe for
consumption and in accordance with tourist
demands.
Quadrant C shows several factors that are less
important influence for tourists. Its implementation
by ordinary companies and is considered less
important and less satisfying. There are four
attributes included in this quadrant, namely:
1. Item 3 (Presentation of culinary products
presented), the layout (plating) of culinary
product dishes has not fulfilled the wishes of
tourists because tourists not only pay attention
to the taste of the food but also enjoy the food
through its appearance.
2. Item 4 (Maturity level of food served),
according to tourists is still not right. The level
of maturity will certainly affect the taste of
food, and the level of maturity must also be
adjusted to the type of food ingredients.
3. Item 5 (Texture of culinary products presented),
according to tourists' perceptions is not as
expected, so compositions such as textures need
to be considered properly.
4. Item 7 (Appearance of color from culinary
products), tourists consider the color play of
food to be considered lacking because
contrasting, bright and bright colors can give a
fresh and tempting impression.
Quadrant D shows several factors that are
considered not too important and or not too
expected, so the management needs to allocate the
resources associated with these factors to other
factors that have higher priority management. There
is one attribute that is included in this quadrant is as
follows: Item 1 (The taste of the food served),
according to tourists the taste of food is too
excessive for example when giving spices, saltiness,
and other flavorings.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The level of perception of tourists is measured in
expectations and performance aimed at Traditional
Culinary Products in Borobudur Priority Tourism
Destinations in Central Java, with an average
expectation of 4.64 while the perceived performance
of tourists with an average score of 3.78. Then it can
be concluded that the perception of tourists about the
quality of culinary products is still not good because
the average value of expectations is greater than the
average value of performance.
Based on research using Important Performance
Analysis (IPA) in the Cartesian diagram there are
one main priority attribute in quadrant A, four
attributes with low priority in quadrant C and one
redundant attribute in quadrant D that must be
improved to improve tourist perceptions of the
quality of culinary products. At the gap level (GAP)
between performance and expectations, each
statement indicator item has a gap level (GAP),
because all the scores are negative. This shows that
the actual level of performance is still below the
expectations of tourists. This shows that tourist
perceptions of product quality are still not good, so
the company must be able to improve all the
attributes of each indicator of the statement.
REFERENCES
Ali Hasan, (2009), Edisi Baru Marketing, Yogyakarta:
Media Pressindo.
Assauri, Sofyan, (2002), Manajemen Pemasaran (dalam
konsep dan strategi),
Jakarta: Rajawali Grafindo.
Ascherio A, Rimm EB, Hernan MA, Giovannucci E,
Kawachi I, Stampher MJ, et al. Relation of
consumption of vitamin E, vitamin C, and caotenoids
to risk for stroke among men in the United States, Ann
Intern Med. 1999; 130: 963-970.
Blakey, E. dan S. Spence. Developing Metacognition in
ERIC Digest. http://www.erc.ed.goy/contentdelivery/
Buchari Alma, (2007), Manajemen Pemasaran dan
Pemasaran Jasa, Edisi. Revisi, Bandung: Alfabeta.
Dharmmesta, Basu Swastha dan Irawan. Manajemen
Pemasaran Modern, Edisi Kedua,. Yogyakarta 2001
Dharmmesta, Basu Swastha T. Hani Handoko, (2000),
Manajemen Pemasaran “ Analisa perilaku konsumen
“. Edisi pertama cetakan ketiga. BPFE Yogyakarta;
Yogyakarta.
Buchari Alma, (2007), Manajemen Pemasaran dan
Pemasaran Jasa, CV. Alfabeta: Bandung.
Ernayanti, dkk., (2003), Ensiklopedi Makanan Tradisional
di Pulau Jawa dan Pulau Madura. Deputi Bidang
Pelestarian dan Pengembangan Kebudayaan.
NTF 2019 - The NHI Tourism Forum
104

Eugen, Pauli, (1979), Classical Cooking The Modern Way.
New York.
Fiani, Margaretha S. & Edwin Japarianto, (2012), Analisa
Pengaruh Food Quality & Brand Image terhadap
Keputusan Pembelian Roti Kecik Toko Roti Ganep’s
di Kota Solo. Jurnal Manajemen Pemasaran.
Gardjito, M (Editor), (2006), Labu Kuning Sumber
Karbonhidrat Kaya Vitamin A, Yogyakarta: Tridatu
Visi Komunikasi.
Imam Maulana & Arus Reka Prasetia. (2016) Strategi
Kreatif Usaha Kuliner Indonesia Untuk Memperluas
Ke Kawasan Asia Tenggara Dalam Era Masyarakat
Ekonomi ASEAN (MEA)
John M. Echols dan Hasan Shadili, (1993), Kamus Inggris
Indonesia, Jakarta:
Gramedia. Ganti jurnal
Koentjaraningrat, (1996), Kebudayaan Mentalis dan
Pembangunan, Jakarta: Gramedia Pustaka Utama.
Kotler, Philip. (2000), Manajemen Pemasaran, Jakarta ;
PT.Prenhallindo.
Kotler, Philip & Armstrong, Gary, (2006), Prinsip-
prinsip Pemasaran, Edisi Keduabelas, Erlangga:
Jakarta.
Kotler, Philip, (2008), Manajemen Pemasaran Edisi 12
Jilid 2, Jakarta: Indeks.
Kotler, Philip and Gary Armstrong, (2008), Prinsip-
prinsip Pemasaran, Edisi 12, Jilid 1. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Kotler, Philip and Gary Armstrong, (2012) Prinsip-
prinsip Pemasaran, Edisi13, Jilid 1. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Kotler, Philip and Amstrong, Gary, (2009), Principles of
Marketing 13
th
edition, New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Pendit, S. Nyoman, (1994), Ilmu Pariwisata. Jakarta:
Pradnya Paramita.
Pride & Ferrel , (1995) Pemasaran : Teori dan Praktek
Sehari-hari, Jakarta : Binapura Aksara.
Rangkuti, Freddy, (2002), Measuring Customer
Satisfaction, Jakarta : PT. Gramedia Pustaka Utama.
Sabana, Choliq, (2007), Analisis Pengembangan Kota
Pekalongan Sebagai Salah Satu Kawasan Andalan di
Jawa Tengah, Tesis S2 tidak dipublikasikan,
Semarang: Universitas Diponegoro.
Stanton, Robert, ( 2007), Teori Fiksi, Yogyakarta:
Pustaka Pelajar.
Schiffman dan Kanuk, (2007), Perilaku Konsumen.Edisi
Kedua. Jakarta: PT. Indeks Gramedia
Tjiptono, Fandy dkk, (2006), Pemasaran Strategik,
Yogyakarta; Andi.
Tjiptono, Fandy , (2005), Pemasaran Jasa, Edisi pertama,
Yogyakarta; Bayumedia Publishing.
Walgito, B, (2002), Pengantar Psikologi Umum, Ed. 3.
Yogyakarta: Adi.
WA, Marsum, (1991), Restoran dan segala
permasalahannya, Yogyakarta: Andi
Offset.
Zeithaml, V. A., Bitner, M. J., & Gremler, D. D, (2006),
Services Marketing Integrating Customer Focus
across the Firm. Boston: MA McGraw-Hill.
Paradiso, Tourism & Transportation News. (2017, 16
April), Kemenpar Dukung Penuh Promosi Kuliner
dan Budaya di Tanjung Lesung. Diperoleh 25
Februari 2018, dari http://paradiso.co.id/kemenpar-
dukung-penuh-promosi-kuliner-dan-budaya-di-
tanjung-lesung.html
Pembangunan Destinasi Pariwisata Prioritas 2016 - 2019
UU No. 10 Tahun 2009
WTO
Tourist Perceptions of the Quality of Traditional Culinary Products in Priority Tourism Destinations in Borobudur Central Java
105
