
Male and Female Speech Style in Retelling Story: Are They
Different?
Mujahidah, Nanning, Sri Mulianah, Magdahalena, Kalsum, Irna Maming
Tarbiyah Faculty, IAIN Parepare
Keywords: Male, Female, Retelling Story, Casual Style.
Abstract: This aims of this study namely to know the Comparison Between Male and Female Speech Style on
Retelling Story at English Department of IAIN Parepare. The population of this research was the students of
English Department, while the sample was the fifth semester students, consist of 20 students, 10 male
students and 10 female students was taken by using purposive sampling. The instrument of this research was
used in this research was speaking test, and model of the test namely retelling story. The procedures of
collecting data namely, ask the student to retell the story that have been given the tittle by the researcher and
then students retell the story while recoding by the researcher. The technique of data analysis that used in
this research were reduction, display, and draw conclusion. The result of data analysis showed that, male
and female had the same style in retelling story. They used formal style, casual style, and intimate style. In
the other hand, speech style that was mostly used by the male was consultative style. While female was
mostly used casual style, in this case female more dominantly used casual style because they want the
hearer enjoy the story and relax when they were retold. In the other hand there was the difference between
male and female were in using vocabulary, pronunciation, grammar and intonation in retelling the story and
its recommended for next researcher.
1
INTRODUCTION
Gender is an important division in all societies. It is
of enormous significance to human beings. Being
born male or female has far-reaching consequences
for an individual. It affects how we act in the world,
how the world treats us (Talbot, 1998, p.3).
According to Trudge (cited in Talbot, 1998, p.27),
female use the prestige variants more often than
male.
This is because they are less secure socially
and
more likely to be judged on appearances then
male.
Male, on other hand, are judged by what they
do, so
that they are not under pressure to use the
prestige
variants. Moreover, the non-Standard forms
found in
vernacular, used predominantly by the
working
class, have masculine connotations which
motivate
male to use them, but not female. In this
field, it
quite clear that male and female are
different.
Studying gender is important to do, and one of
the most interesting aspects to study is the
differences between male and female. Male and
female differ psychologically in the way they act,
from the style in which they communicate to the
way in which they attempt to influence others.
Gender differences in communication also have
implications for gender differences across leadership
styles of male and female. Female stand in close
proximity to each other, maintain eye contact, and
gesture more frequently. Male hold their distance,
rarely establish eye contact, and gesture less
dramatically. Male and female express their gender
communication differences in content, style, and
structure.
In some traditional, tribal societies, male and
female have a whole range of different vocabularies.
The men have great expressions peculiar to them,
which the women understand but never pronounce
themselves. On the other hand, the women have
words and phrases which the men never use, or they
would be laughed to scorn. Thus, it happens that in
their conversations it often seems as if the women
had another language than the men. The idea that
male and female use language differently has long
history within „folk linguistics‟, a term used by some
researchers to refer to sets of popular belief about
language. People believe that male and female have
different speech style.
The differences of male and female language
have
Mujahidah, ., Nanning, ., Mulianah, S., Magdahalena, ., Kalsum, . and Maming, I.
Male and Female Speech Style in Retelling Story: Are They Different?.
DOI: 10.5220/0009836800650076
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on English Language Teaching, Linguistics and Literature (ELITE 2019) - Promoting Global Diversity, Partnership and Prosperity through
English Development, pages 65-76
ISBN: 978-989-758-459-6
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
65

been the concern of many researchers until this
decade. Xia, (2013), for example, analyzes the
differences in the aspects of pronunciation,
intonation, vocabulary, syntax, manners, attitudes,
and non-verbal differences. According to Xia (2003,
p.1), the studies on a variety of languages in the
world show that women‟s pronunciation is better
than men‟s. In addition, Xia (p. 2) argues that
women tend to speak in a high-pitch voice for the
physiological and psychological factors. Women‟s
high voice indicates „timidity” and “emotional
instability”, two characteristics associate to women.
In the aspect of vocabulary, men and women use
different vocabulary because some vocabularies
considered as to be used only by men or some others
only by women. Moreover, Xia (p. 2) claims that
men and women use different grammar. For
example, when women talk, they take what others
think as consideration, For example, it is commonly
to hear women say “well…, you know …, maybe I’m
wrong, but…”. Moreover, women use more
interrogative sentences than men. Likewise, men use
more imperative sentence, and women use more
polite pattern by using model verbs can, could, and
may (p.3). Women are also found to be more careful
about grammar.However; Xia (p.5) claims that the
men and women‟s language differences are due to a
stereotype that could be changed, and since language
is closely related to society, the development of
productive forces and civilization caused the
differences are not clearly seen any more now.
Based on the introduction above, the researcher
is interested in doing a research on the difference of
speech styles of male and female students in
retelling English story. It is likely assumed that the
ignorance of teacher on the speech style difference
of his/her students would be a barrier for their
learning success. On the other hand, by knowing
speech style of each gender, teacher will easily
decide the way to communicate to the students.
Likewise teacher can get the benefits of students‟
high interest to materials.
This article will answer the following research
questions: How are male students‟ speech style in
retelling English story at students of English
Department IAIN Parepare? How are female
students‟ speech styles in retelling English story at
students of English Department IAIN Parepare? Is
there any significant difference between male and
female speech style in retelling English story?
2
LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Speech Style
Style refers to the selection of linguistic forms to
convey social or artistic effect. Style also acts as a
set of instructions. Style is a pivotal construction in
the study of sociolinguistic variation. It is the locus
of the individual‟s internalization of broader social
distributions of variation. Besides that, according to
Holmes style is the kind of language variety in
which
the speaker selects certain linguistic forms
rather
than others that contain the same information.
One of
the kinds of language variety based on use is
style.
The messages it conveys are not normally
conveyed
in words. Indeed, the idiom “didn‟t get the
message”
may refer to listener‟s not picking up a
speaker‟s
stylistic cues, even though he or she
understood just
fine the actual words used. We
manipulate others
with style, even as we are
manipulated ourselves,
usually unconsciously.
Style forms a communication system in its own
right, on that determines how a social interaction
will proceed, or if it will proceed at all. If it is to
continue, style tells how, weather formally or
informally. Style may also tell listeners how to take
what is being said: seriously, ironically, humorously,
dubiously, or in some other way. Often when style
of an utterance contradicts the meaning of the words
and grammar, the style is believed. Since style tell us
how to interpret a message, this is not surprising. For
example, if “john is nice” is said sarcastically, the
style instructs, „take these words to mean the
opposite of what they actually say‟. Thus, “john is
nice” can mean „John is not nice‟. Similarly, a timid
“I‟m not afraid “still conveys „I‟m afraid. And,
highly formal “I do hope we shall be friends, Miss
Tippet” is not likely to yield close confidences. Style
forms a mini-communication system that works
along with language itself, yet is it apart from it
(Elaine Chaika, 1982, p.29).
2.2 Types of Speech Style
Martin Joos in Chaer and Agustin (2010, p.70)
differentiate five types of speech styles based on the
degree of formality in language use. They are
described as follows:
2.2.1 Frozen Style
Frozen style or oratorical style is considered as
the
most formal style and elegant variety. It is
usually
used in the situation which is celebrated with
respect
ELITE 2019 - English Linguistics, Literature, and Education Conference
66

or formal ceremonies, constitutions, and
state
documents. The characteristics of frozen style
are
the use of maintained and unchanged sentence
structures, long and careful sentence constructions,
over intonation, and almost no responses between
the speaker and hearer. Frozen style usually tends to
be monolog, is usually used in long sentence with
good grammatical and vocabulary.
2.2.2 Formal Style
Formal or deliberative style is the type of
language
style that is used in situation in which the
speakers
are very careful about pronunciation,
choice of words,
and sentence structure. It is
commonly used in
important or serious situations,
such as in scholar
and technical reports, classrooms,
formal speeches,
and sermons. The characteristics of
formal style are
having a single topic, using a
sentence structure that
shows less intimacy between
the speaker and listener,
and using standard forms.
Consultative style
Consultative style or business style is
generally
used in a semi-formal communication
situation. It
is used in transaction, information
exchange, and
operational process. Consultative
style is used in
conversations such as seller-buyer
conversation,
doctor-patient conversation, and small
group
discussion.
The typical occurrence of consultative
speech is
between two people. Therefore, it is
usually two-
way participation. While one is
speaking, at
intervals, the others give short
responses, mostly
drawn from a small inventory of
standard signals.
Back channel behavior, such as:
“Yes”, “No”,
“Uhhuh”, “Mmm”, “Huh”, “That‟s right”, “I think
so”, “Oh! I see”, Yeah”, Yes, I
know” or “well...” are
common.
2.2.3 Casual Style
Casual style is a style used in an informal
and a
relaxed situation. Casual style is mostly used
between friends or between family members. The
characteristics of casual style are the use of
nickname
when addressing one another, the use of
rapid
pronunciation, the use of slang, and the use of
non-
standard forms and words.
Casual style is the style we used to integrate
an
audience into social group. “Anybody home?”,
“Car
broke down”, “Got a match?”, “Need help?”
Such
expressions are highly diagnostic feature of the
casual
style; they will generally be interpreted as
signaling informality. However, most speakers are
not aware either of the phenomenon or its
significances. That is, they do not know what is
about
an utterance that gives them the impression of
formality. The examples for this style are:
“Don‟t get up!”
“I believe that I can find one” (formal grammar)
“Believe I can find one” (casual grammar)
2.2.4 Intimate Style
Intimate style is the most casual style, and it
is
commonly used between family members, couples
or
lovers, and intimate friends. The characteristics of
this
style are the use of private codes, words
signaling
intimate relation, rapid and slurred
pronunciation,
and non-verbal communication. For
example: Mbul,
kemana aja kamu?(„Mbul, where
have you been?‟).
The speaker addresses the hearer
by using the word
“Mbul”, which shows intimate
relationship between
the participants. Also, the
speaker uses the non-
standard word “aja” instead of
the standard one
“saja”.
The word that generally signal intimacy
such as,
“dear”, “darling”, and even “honey”, or
“hone” might
be used in this situation.
2.3 Male and Female Speech Style
Men and women use language differently.
Differences in the choice of vocabulary,
grammatical
patterns, and prosodic means are
distinct enough to
speak of male and female speech
styles. The
existence of the two speech styles is the
linguistic
reflection of social relations: until recently
male have
exercised more power in society and the
tendency is
still rather strong. Male‟s verbal
behavior is more
aggressive as it is supposed to
demonstrate a position
of dominance. Female were
assigned a submissive
role both in the workplace
and at home, which
accounts for more co-operative
and less aggressive
female speech strategies.
Male speech strategies have the following
features:
a.
initiating and receiving more verbal and non-
verbal interaction than women;
b.
introducing more topics while talking with other
people;
c.
interrupting and disputing more frequently;
d.
giving monosyllabic responses;
e.
ignoring another person‟s remarks;
f.
making one‟s point directly, explicitly, and
rationally;
g.
being dogmatic;
h.
being reserved.
Male and Female Speech Style in Retelling Story: Are They Different?
67

Female, on the other hand, has the following
speech
strategies:
a.
supporting and maintaining conversation rather
than initiating it by asking more questions, by
encouraging the speaker to proceed, by
responding more to other people‟s remarks;
b.
being more positive than males;
c.
being verbose;
d.
being emotive rather than objective;
e.
being less dogmatic than males.
Systematic differences of male and female are
also found in the prosodic features of pitch and
intonation. Thus, researchers have proposed that
there are intonation patterns that are unique to
women (and that connote insecurity), or are
differently preferred by men and women; for
example, women are more likely to use both the
surprise pattern of „Oh that‟s awful‟ and the polite
cheerful pattern of „ Are you coming?‟ similarly,
there are differences in pitch for groups of men, of
women, and of children that are much sharper that
variation in vocal-tract sixe could reasonably
explain, suggesting that the differences between
male and female formant values, thought related to
vocal-tract size, is probably a linguistic conversation
(Anderson, 1990, p. 27).While speaking, men rely
more on the lexical and grammatical systems;
alongside these two, women make effective use of
the prosodic system − their pitch range is usually
wider than men‟s, stress patterns are more distinct.
As to vocabulary and syntactic structures, men tend
to use slang, obscene words, terms, simple,
sometimes incorrect sentences. Women are likely to
use effect and emotively charged words,
exclamations, intensifiers (so, such, etc.), diminutive
forms and terms of endearment, deferential forms,
socially prestigious lexical and syntactic forms,
forms of politeness, tag questions, coordinate and
subordinate syntactic structures. These are but the
most general features of male and female styles of
speech. The lists are far from being complete; there
are, of course, many exceptions, and individual,
social, and stylistic variations. In addition, in
communication, the system of male/female speech
styles overlaps with that of powerful/powerless
speech. Forms of powerless speech are tag
questions, hedges, apologies, phrases that disclaim
responsibility (for example, I‟m not sure),
exclamations, forms of politeness, broken sentences,
illogical sequences.
Retelling Story. Retelling is an activity to help
students
focus on their understanding of what they
read and
challenge them to communicate what they
have
learned to others. Retelling can came in the
form of
an oral presentation or a written assignment
and
involves attention to the main narrative
components
to including character, setting,
problems, evens,
solution, and theme. Retelling,
which is considered a
post reading or post listening
recall in which readers
or listeners tell that what they
remember either
orally or in writing or illustration is
perhaps one of the simplest and most powerful ways
to enhance
children‟s comprehension and their desire
to read.
Story telling requires the reader or listener to
integrate and reconstruct the parts of a story. They
reveal not only what readers or listener remember,
but also what they understand. Retelling builds story
comprehension. Retelling requires children to think
more conceptually- to look at the bigger picture rather
than answering specific questions about the
text
(Sgorous, Gold, & Gibson, 2003).
Retelling story is an oral activity where
language
and gestures are used in a colorful way to
create
scenes in a sequence. In addition, retelling is
grounded in an understanding of the crucial role that
oral language plays in both the formation and
sharing of meaning.
Furthermore, according to Miller and
Pennycuff
(2006) retelling story in the classroom is
one way to
improve oral language. In line with this,
Pellowski
(1990) states that retelling the story is one
of the arts
or crafts of narration of stories in verse
and prose.
He also states that retelling story is an
effective
instructional strategy for enhancing the
comprehension of proficient and less proficient
students. It means that, retelling story is a
component of authentic assessment that can be
introduced when the students demonstrate
proficiency in identifying key story element.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
The research used qualitative method in
order to
give description about the differences
between male
and female speech style in retelling
English
story.This research was conducted at IAIN
Parepare.
The subject of the research was the fifth
students of
English Education Department of IAIN
Parepare,
consisted of 10 male and 10 female. To
get the
research data, the researchers used
documentation.
In this research the students‟ voice
was recorded.
The researchers used data reduction, data
display, and verification in analyzing the research
data. Data from audio recording was transcribed into
ELITE 2019 - English Linguistics, Literature, and Education Conference
68
written transcript. Then, the transcript was analyzed
and identified to determine the utterances which
consisted of speech styles phenomenon and the
utterances which did not. The utterances which did
not contain speech styles were omitted, so that the
utterances which contained speech style were kept.
After doing data reduction, the researchers
drawn the data into data display. The data display
shows the research focus that is the types of
students‟ speech styles in retelling story.
In verification stage, the researchers drew
conclusions based on the data display. The
researcher concludedthe types of speech styles used
by the male and female students based on Joos‟
theory.
4 FINDINGS
4.1 Male Speech Styles
Speech styles used by female when they were
retelling story were shown in the following table.
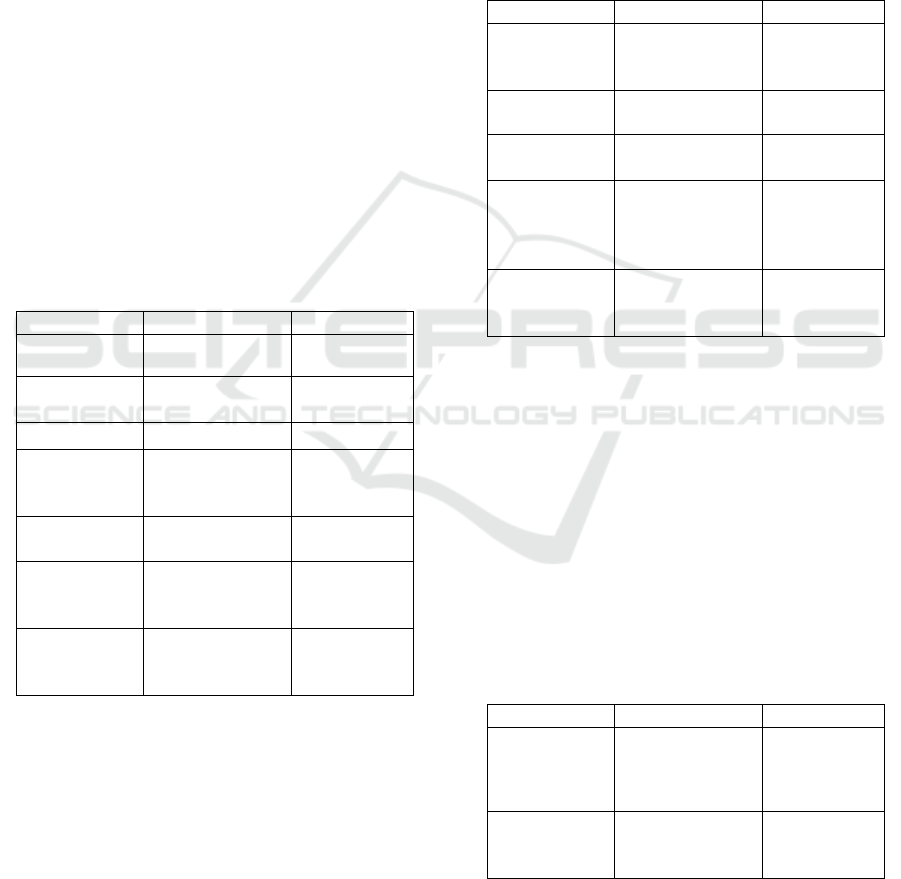
Table 1: Display data of respondent 1.
Utterance
Speech style
Respondent 1
“You should stay
in the home.”
Consultative
“mmmm, I want
join the party
Consultative
”yes, I want”.
Consultative
“I don‟t have
dress and I feel
sad about this”.
Casual
“Don‟t worry, I
want to help you”.
Casual
“This magic of the
dress is wanna
have done”.
Casual
“And then the
prince pick up the
glass slipper”.
Casual
The table 1 shows that respondent 1 used two
types of speech styles, namely consultative and
casual styles. The utterance of respondent 1, “You
should stay in the home”, was classified as
consultative style, because one of the characteristic
of consultative style is giving command, request,
and suggestion. In this story, Cinderella‟s step
mother asked her to stay at home. The next two
utterances: “Mmm, I want join the party” and “yes,
I want” were also classified as consultative style.
The utterances used back channel, and Joos states (in
Chaer, 1998) that consultative style is characterized
by the use of back channel. The other speech style
used was casual style as in the utterances: “Don’t
worry, I want to help you” and “This magic of the
dress is wanna have done”. Those two utterances
were categorized as casual style because the
respondent slurred the pronunciation. Likewise the
utterance “And then the prince pick up the glass
slipper” was categorized into casual style because
the respondent used slang.
Table 2: Data display of respondent 2.
Utterance
Style
Respondent 2
Cinderella, you
should fix home
all night
Consultative
you have to back
before midnight
Consultative
Cinderella can‟t
go
Casual
Cinderella
didn‟thave beauty
dress to go to the
big party,
Casual
Cinderella really
wants to go there,
but she can‟t.
Casual
The table 3, indicates that respondent 2 used
two types of speech styles, namely consultative and
casual style. “Cinderella, you should fix home all
night” and “so you have to back before midnight”
was classified as consultative style because of the
use of command. In the story, Cinderella‟s
stepmother asked her to fix home, and then the fairy
asked Cinderella to arrive home before midnight.
The following utterances:“Cinderella can’t go”,
Cinderella didn’t have beauty dress to go to the big
party”, Cinderella really want to go there, but she
can’t”, were classified as casual style because the
respondent used slurred pronunciation.
Table 3: data display of respondent 3.
Utterance
Style
Respondent 3
She told
Cinderella to came
home, before
midnight
Consultative
He didn‟t have
time to put it back
on.
Casual
Based on table 3, the respondent 3 used two
speech styles when he was retelling story, those
speech styles were consultative and casual style. It
Male and Female Speech Style in Retelling Story: Are They Different?
69
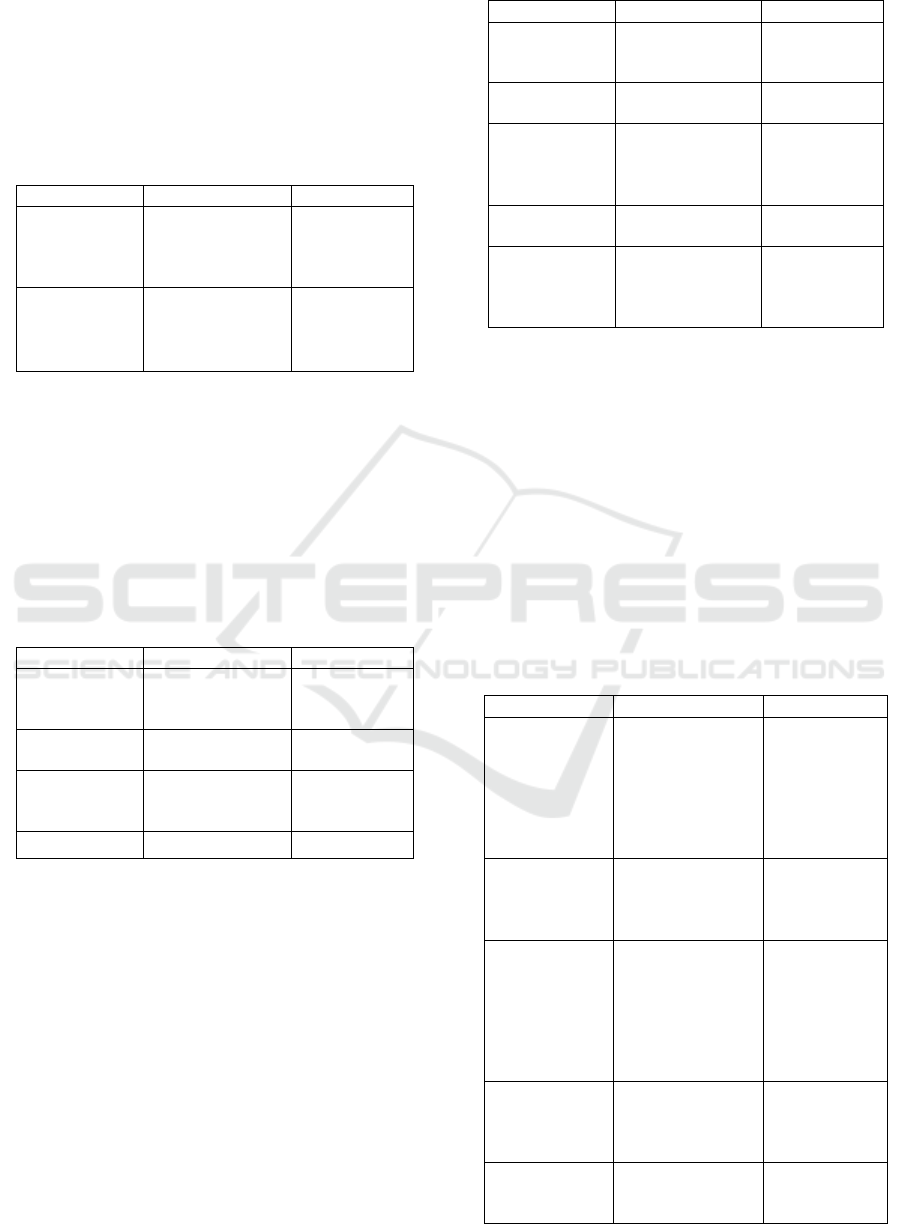
can be seen in utterance of respondent 3, “She told
Cinderella to came home, before midnight” was
categorized as consultative style because the use of
suggestion. In other utterance of respondent 3 “he
didn’t have time to put it back on” was classified as
casual style because the respondent slurred
pronunciation “didn‟t”.
Table 4: data display respondent 4.
Utterance
Style
Respondent 4
Long long time
ago there was a
girl name
Cinderella
Casual
Suddenly came
someone help
Cinderella to out
of from this place
Casual
Table 4 indicates that respondent 4 used one
type of speech style, namely casual style. The
firstutterance“long-long time ago there was a girl
name Cinderella” was categorized as casual style
because the respondent used non-standard form
“long-long”, while the second utterance:”suddenly
came someone help Cinderella to out of from this
place”, was classified as casual style because the
respondent used ungrammatical sentence.
Table 5: data display of respondent 5.
Utterance
Style
Respondent 5
You must reach
back home by
them
Consultative
The step mother
didn‟t
like her
Casual
Even her step
sister
didn‟t
recognize her
Casual
“never my dear
Intimate
The utterance” You must reach back home by
them” in table 5. above was classified as
consultative style because the use of command. The
other utterances, “The stepmother didn’t like her”
and “even her stepmother didn’t recognize her”
were casual style because the respondent slurred
pronunciation in the word “didn‟t”. Likewise, the
utterance “Never my dear” was classified as intimate
style because the respondent used private code.
Table 6: data display of respondent 6
Utterance
Style
Respondent 6
Cinderella didn‟t
have much time to
sew dresses
Casual
Don‟t be worry
my little girl
Casual
Step mother don‟t
allow Cinderella
to try the slipper
glasses
Casual
They life happy
ending forever.
Casual
Don‟t be worry
my little girl, you
will be came to big
party
Intimate
The utterances of respondent 6 in the table 6
namely “Cinderella didn’t have much time to sew
dresses”, “Don’t be worry my little girl”, “Step
mother don’t allow Cinderella to try the slipper
glasses” were classified as casual style because the
respondent slurred pronunciation in the word
“didn‟t,
don‟t”. The other utterance, ““They life
happy
ending forever”, was also classified as casual
style
because it is ungrammatical sentence.
Furthermore,
the utterance “Don’t be worry my little
girl, you will
be came to big party”, was classified
as intimate
style because the use of private code,
“my little
girl”.
Table 7: data display of respondent 7.
Utterance
Style
Respondent 7
Of course, you
didn‟t have any
dress but I will
facilitated you to
has the dress and I
will guide u to go
to the party‟
Consultative
‟Wow thank you
thank you so much
but how could I go
to the party
Consultative
‟Oh Cinderella,
you
have to go home at
the middle of the
night because this
magic just work
only until
midnight‟‟
Consultative
The step mother
didn‟t allow the
Cinderella to go to
the party,
Casual
Don‟t cry I can
send I to the ball
now I can send you
Casual
ELITE 2019 - English Linguistics, Literature, and Education Conference
70
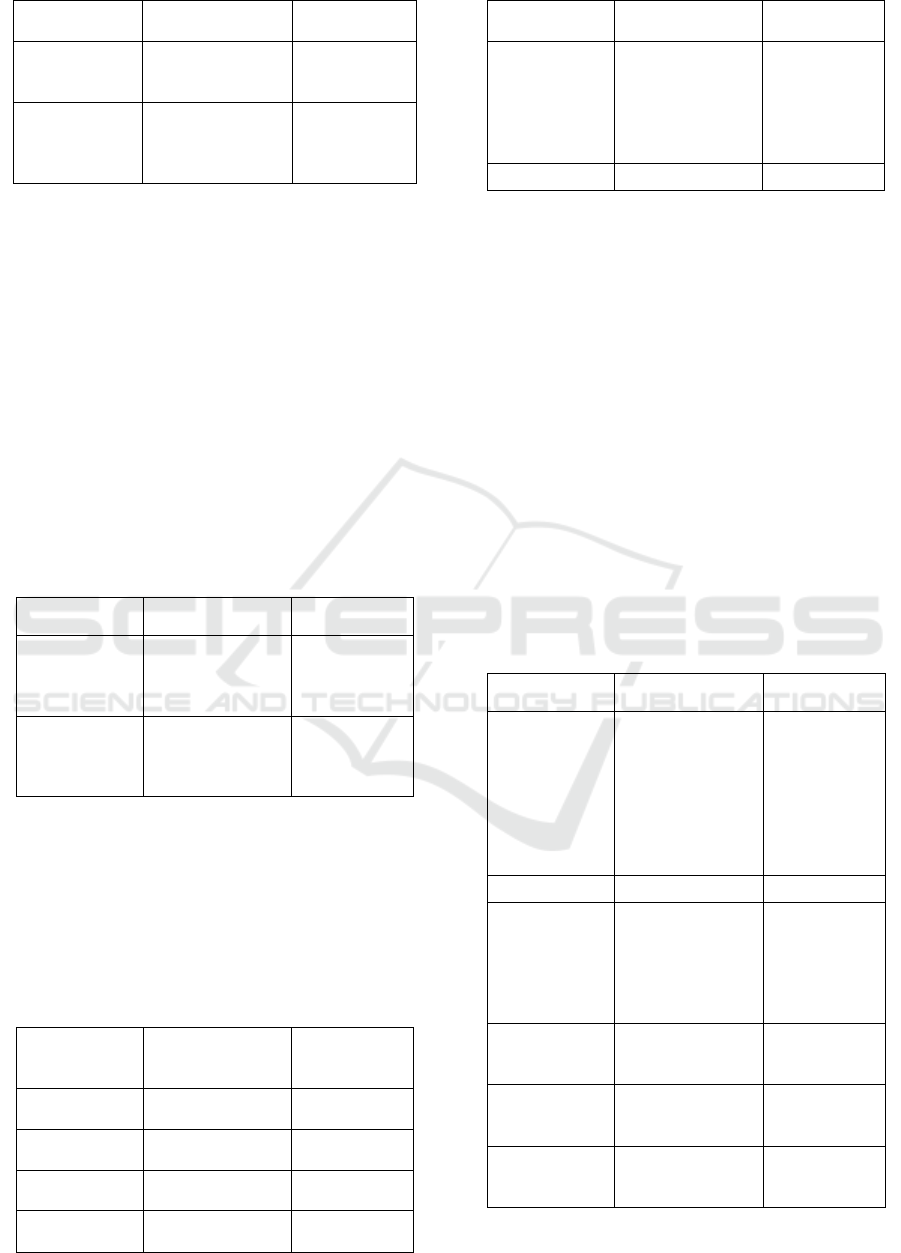
I can guide you to
the party now
I don‟t have a
dress to wear and
the party‟‟
Casual
You didn‟t have
any dress but I will
facilitated you to
has the dress
Casual
The utterances of respondent 7 in the table 7,
namely “Of course, you didn’t have any dress but I
will facilitated you to has the dress and I will guide
u to go to the party”, “Wow thank you thank you so
much but how could I go to the party”, “Oh
Cinderella, you have to go home at the middle of the
night”, were classified as consultative style because
the use of back channel. The utterances “The step
mother didn’t allow the Cinderella to go to the
party”, “Don’t cry I can send I to the ball now I can
send you I can guide you to the party now”, “I don’t
have a dress to wear and the party’’, and “You
didn’t have any dress but I will facilitated you to has
the dress”, were classified as casual because the
respondent used slurred pronunciation.
Table 8: data display respondent 8.
Utterance
Style
Respondent 8
Fairy godmother
also tell Cinderella
to go home before
midnight
Consultative
She just run and
her glass slipper
take off from her
feet
Casual
The utterance of respondent 8 (table 8):”Tell
Cinderella to go home before midnight” was
identified as consultative style because the used of
suggestion. In addition, the utterance” She just run
and her glass slipper take off from her feet“was also
classified as casual style because of the use of
ungrammatical sentence.
Table 9: Data display of respondent 9.
Her mother didn‟t
allow Cinderella to
join in the event
Casual
I don‟t have a
dress
Casual
Don‟t be worry
about it
Casual
I don‟t have
transportation yet
Casual
Don‟t be worry I
will find out
Casual
Don‟t pass the
midnight
Casual
Stepsister didn‟t
recognize that a
beautiful girl
whose stand in
front them is
Cinderella
Casual
“Never my dear?”
Intimate
As seen in the table 9, the researcher found
three
types of speech styles used by respondent 9.
The
first is consultative style, as in utterances, “I
don’t
have a dress and transportation to go there”,
and
“You could go there”. The characteristic of
consultative style found in these utterances is the use
of dialogue. The second is casual style, as in
utterances, “Didn’t appreciate her, “Her mother
didn’t allow Cinderella to join in the event”, “I
don’t
have a dress”, “Don’t be worry about it”, “I
don’t
have transportation yet”, “Don’t be worry I
will
find out”, “Don’t pass the midnight”, and
“Stepsister didn’t recognize that a beautiful girl
whose stand in front them is Cinderella”. The
respondent used slurred pronunciation in all of those
utterances. The third is intimate style; it can be seen
in utterance “Never my dear”. In this utterances,
because the respondent used private code.
Table 10: Data display of respondent 10.
Utterance
Style
Respondent 10
Of course, would
not be worry and
wave the wand to
transform
Cinderella‟s old
clothes into the
new dress which
very beautiful
Consultative
Wow thank you
Consultative
You have to go
home the middle
of the night,
because this magic
will work only
until midnight
Consultative
They didn‟t not
allow her to go to
the party
Casual
She didn‟t not
come back to pick
it up
Casual
He even didn‟t
know her name
prince
Casual
Male and Female Speech Style in Retelling Story: Are They Different?
71
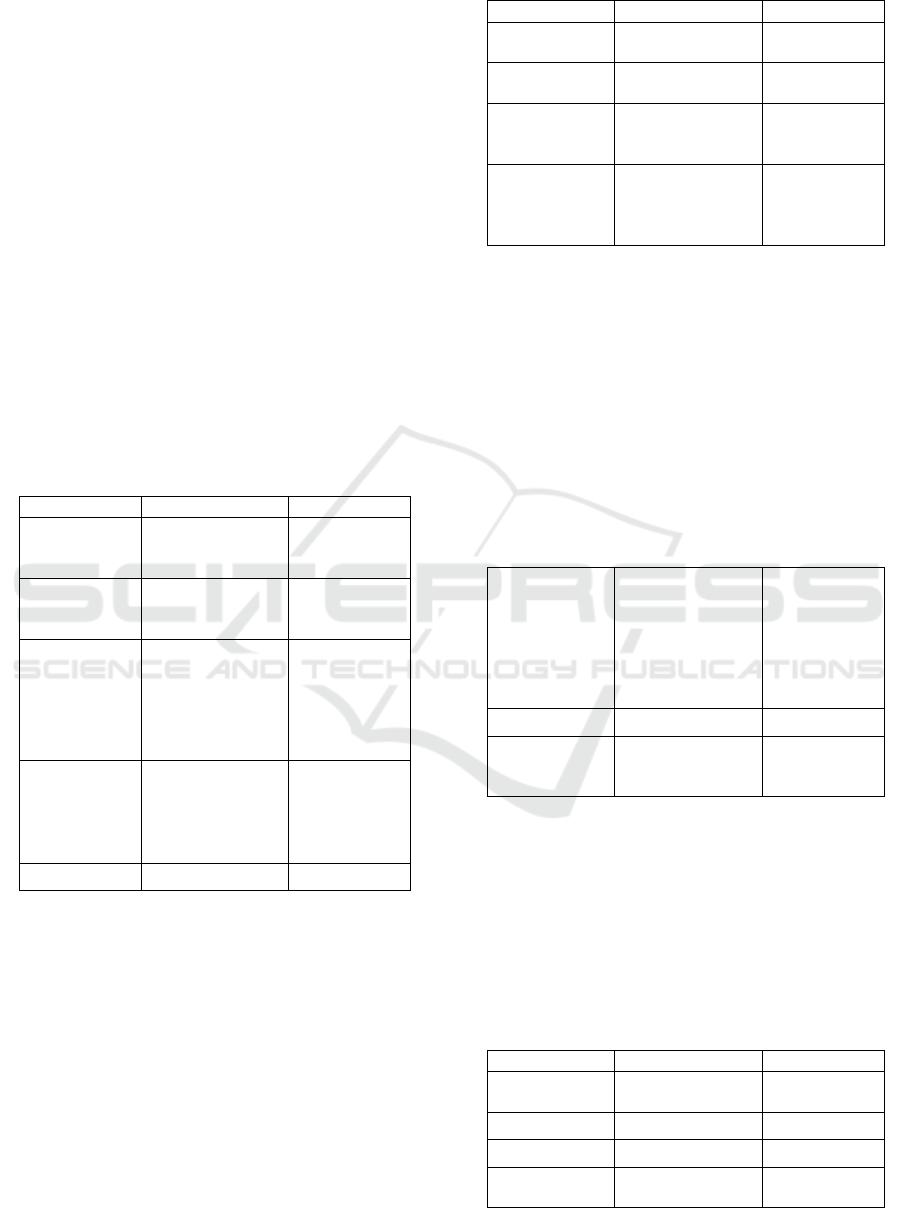
In the table 10, the researcher found two
types
of speech styles used by the respondent. The
first is
consultative style. That style can be seen in
utterances “Of course, would not be worry and wave
the wand to transform Cinderella’s old clothes into
the new dress which very beautiful, “Wow thank
you”, and “You have to go home the middle of the
night, because this magic will work only until
midnight”. Those utterances consist of back channel
(of course, wow) and suggestion. Therefore those
utterances were categorized as consultative style.
The
second is casual style. That style can be seen in
utterances: “They didn’t not allow her to go to the
party”, “She didn’t not come back to pick it up”,
and “He even didn’t know her name prince”. When
the respondent 10 produced those utterances, he
slurred the pronunciation of some words.
Data Display and Analysis Female Speech Style.
Data display and the analysis female
speech styles
are presented in following table:
Table 11: Data display of respondent 1.
Utterance
Style
Respondent 1
Cinderella was not
allowed to going
to the ball.
Formal
So she must leave
the hall before
then,
Consultative
Yapp the
stepmother in last
minute attempt to
prevent her step
daughter better
things
Consultative
Yapp the arrogant
women hadn‟t
beat on Cinderella
for this the other
glass slipper,
Consultative
She does so
Casual
Based on the table 11, the utterance of
respondent 1 “Cinderella was not allowed to going
to the ball” was categorized as formal style because
the use of complete and grammatical sentence. The
utterances of respondent 1 namely “So she must
leave the hall before then, and “Yapp the
stepmother in last minute attempt to prevent her step
daughter better things” and “Yapp, the arrogant
women hadn’t beat on Cinderella for this the other
glass slipper” were categorizes as consultative style
because the respondent used command. In addition,
she also used back channel in the word “Yapp”. The
utterance,” She does so” was identifieds as casual
style because of the use of omission.
Table 12: Data display of respondent 2.
Utterance
Style
Respondent 2
How could I go to
the party
Formal
Cinderella entered
the palace
Formal
Cinderella must go
home at twelve
night.
Consultative
She can‟t join with
her stepsister to
going to the ball at
the night…
Casual
As seen in the table 12, the utterances of
the
respondent, namely “How could I go to the
party?”
and “Cinderella entered the palace” were
categorized as formal style because the respondent
used standard form. Furthermore, in the utterance
“Cinderella must go home at twelve night”, the
respondent used consultative style because he used
command. In addition, in the utterance” She can’t
join with her stepsister to going to the ball at the
night”, the respondent used casual style by
producing slurred pronunciation.
Table 13: Data display of respondent 3.
Respondent 3
Cinderella, step
mother and
stepsister want to
go there, but they
didn‟t allow
Cinderella go with
them
Casual
Cinderella go there
Casual
Finally prince and
Cinderella with
happy together.
Casual
Based on table 13 the utterances of respondent 3
was classified into casual style as the use of slurred
pronunciation in the word “didn‟t”, and the use of
ungrammatical structure, as in utterances
“Cinderella, step mother and stepsister want to go
there, but they didn’t allow Cinderella go with
them”, Cinderella go there”, and “Finally prince
and Cinderella with happy together”.
Table 14: Data display of respondent 4.
Utterance
Style
Respondent 4
Cinderella come
down
Casual
They turn up dress
Casual
Don‟t cry my child
Casual
I don‟t have a
dress to wear
Casual
ELITE 2019 - English Linguistics, Literature, and Education Conference
72
Her step sisters
didn‟t know who
she was
Casual
He pick it up her
shoe
Casual
But didn‟t match
Casual
Don‟t cry my
child, you shall go
to the ball”
Intimate
Based on the table 14, the researcher found two
types of speech styles used by the respondent. The
first is casual style, it can be seen in utterances
“Cinderella come down”, “They turn up dress”,
“Don’t cry my child”, “I don’t have a dress to
wear”, “Her step sisters didn’t know who she was”,
“He pick it up her shoe” and “But didn’t match”.
When respondent 4 produced those utterances, she
slurred the pronunciation of some words. The
second is intimate style, as the respondent used
privacy code, it can be seen in utterance, “Don’t cry
my child, you shall go to the ball”.
Table 15: Data display of respondent 5.
Respondent 5
Of course, two
stepsisters of
Cinderella and her
stepmother so
excited to came in
the party
Consultative
Of course, two step
sister‟s
Cinderella
try to make match
the size of slipper
with her fit
Consultative
They didn‟t realize
Casual
He didn‟t know
who is she
They are living
together and happy
together.
Casual
Utterance
Style
As seen in the table 15, the respondent used two
types of speech styles when she was retelling story.
The first is consultative style, it can be seen in
utterance “Of course, two stepsisters of Cinderella
and her stepmother so excited to came in the party”
and “Of course, two step sister’s Cinderella try to
make match the size of slipper with her fit”. As those
utterances consist of back channel, they were
classified as consultative style. The second is casual
style, it can be seen in utterance, “They didn’t
realize”, He didn’t know who is she”, and “They
living together and happy together”. In these two
utterances, the respondents used slurred
pronunciation in the word “didn‟t” and
ungrammatical sentence.
Table 16: Data display of respondent 6.
Utterance
Style
Respondent 6
She should come
back to her home
until twelve clock
or all of the
miracle will be
disappear
Consultative
Her mother sick
and finally pass
away
Casual
Cinderella so sad
and cry
Casual
The utterance of respondent 6 (table 16) “She
should come back to her home until twelve clock or
all of the miracle will be disappear” was classified
into consultative style because the use of command
sentence. The others utterance “Her mother sick and
finally pass away” and “Cinderella so sad and cry”
were classified into casual style because the use of
ungrammatical sentence.
Table 17 data display respondent of 7
Utterance
Style
Respondent 7
Fairy godmother
ask her to go home
at middle of the
night
Consultative
Who didn‟t threat
her well.
Casual
But they didn‟t
allow Cinderella
to go and leave
her alone at home.
Casual
Don‟t cry
Casual
The utterance of respondent 7 (table 17)“Fairy
godmother ask her to go home at middle of the
night” was classified into consultative style because
the use of suggestion sentence. The others utterances
“Who didn’t threat” her well”,” but they didn’t
allow Cinderella to go and leave her alone at
home”, and “Don’t cry” were classified into casual
style because when respondent 7 produced those
utterance she slurred pronunciation of words “don‟t
and didn‟t”
Table 18: Data display respondent of 8.
Utterance
Style
Respondent 8
“wow thank you
Consultative
“Cinderella, you
have to go home at
the middle of the
night, because her
magic will works
only until midnight
Consultative
Male and Female Speech Style in Retelling Story: Are They Different?
73
Cinderella‟s
stepmother don‟t
wont if Cinderella
join to the party
Casual
Don‟t worry and
don‟t cry
Casual
She didn‟t come
Casual
Pick it up
Casual
The clock exact in
twelve
Casual
Their fit don‟t
match
Casual
The utterance of respondent 8 (Table 18) “Wow
thank you”, and “Cinderella, you have to go home
at the middle of the night, because her magic will
works only until midnight”. Were classified into
consultative style because the respondent use one of
characteristic of consultative style is use black
channel and giving command. The others utterances
“Cinderella’s stepmother don’t wont if Cinderella
join to the party”, “She didn’t come”,” Their fit
don’t match” were classified into casual style
because she slurred pronunciation, the use slang, and
the use non-standard form. The use of slang it can be
seen, when she said: “Pick it up”. The use of non-
standard form, it can be seen: “The clock exact in
twelve”.
Table 19: Data display respondent of 9.
Utterance
Style
Respondent 9
You must reach
back home by
then!
Consultative
Stepmother didn‟t
like her
Casual
Cinderella looked
up
Casual
Her step sister
didn‟t
recognize
her
Casual
They couldn‟t
make it
Casual
Never my dear
Intimate
The utterance of respondent (Table 19)
“Stepmother didn’t like her”, “Her step sister didn’t
recognize her”, “They couldn’t make it” and
“Cinderella looked up” were classified as casual
style because when the respondent produces that
sentence she slurred pronunciation of some words.
The utterance “You must reach back home by
then!” Was classified as consultative style, because
the fairy giving commands to Cinderella for arrive at
home. The utterance “never my dear” was classified
into intimate style because the respondent used
private code “my dear” that indicated intimate style.
Table 20: Data display respondent of 10.
Utterance
Style
Respondent 10
Cinderella should
be at home in the
middle of night
Consultative
Don‟t Cry
Cinderella
Casual
If you don‟t
Casual
have dress to go to
the party
When Cinderella
arrive there
Casual
Beautiful glass
slipper came off
Casual
If you don‟t have
dress to go to the
party.
Casual
They
didn‟t
match
Casual
The utterance of respondent 10 (20) “Cinderella
should be at home in the middle of night”, was
classified as consultative style because the fairy
giving command to Cinderella for arrive at home.
The utterance of “Don’t Cry Cinderella”, “If you
don’t have dress to go to the party”, “If you don’t
have dress to go to the party”, “They didn’t match”.
And also “”, and “Beautiful glass slipper came off”
were categorized as casual style because the used of
slurred pronunciation when retell the story.
The table below shows the frequency of male
and female speech style:
Table 21: Frequency of Male speech style.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Total
Frozen
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
0
Formal
-
-
-
-
-
-
1
-
-
-
1
Consulta
tive
3
2
1
1
3
1
3
3
17
Casual
4
3
1
2
2
4
5
1
8
3
33
Intimate
-
-
-
-
1
1
-
-
1
-
3
Table 22: Frequency of female speech style.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Total
Frozen
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
0
Formal
1
2
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
3
Consul
tative
2
1
2
1
1
2
1
1
11
Casual
1
1
4
7
3
2
3
6
4
6
37
intimate
-
-
-
1
-
-
-
-
1
-
2
ELITE 2019 - English Linguistics, Literature, and Education Conference
74

5 DISCUSSION
Both male and female were used formal,
consultative, casual and intimate styles when they
were retelling story. Formal style used once by male
while it is used four times by female. It indicates that
female tends to use formal style than male. This data
proves Orton‟s statement in Talbot (1998: 21) that
male speak vernacular more frequently than female.
In consultative style, male more dominantly
used
consultative style than female. Male used this
style
17 times and female used this style 11 times
when
they were retelling story.
Like consultative style, casual style was used
by
both male and female when they were retelling
story. Male used this style 17 times and female used
11 times. It shows that female more dominantly
used
casual style than male. Both male and female
used
this style because they felt enjoy and relax if
they
were retelling by using this style. Beside the
listeners also would enjoy and felt unpressured. It
made casual style was the most frequent style used
by male and female when they were retelling story.
The last speech style that was used by male and
female is intimate style. Both male and female used
this style in the same frequency (3 times). It
indicates that not only formal, casual and
consultative
styles, intimate style also could be used
in retelling
story.
Of the five kinds of speech styles that have
been mentioned by Joos in Haer & Agustina (2010:
70), only four speech styles found in this research.
It indicates that no one used frozen style in retelling
story. The data also shows that casual style is the
most frequent speech style used by both male and
female when they were retelling, and formal style
was the least one.
In addition, the researcher also found that male
and female were different in some aspects. Male
mostly used non-standard words than female when
they were retelling story. This is in line with
Lakoff‟s statement in Talbot (1998: 40) that female
are not to supposed to talk rough. Likewise, female
tends to use standard form than male (Coates, 1993:
70)This statement is also supported by Trudgill
(1990) that male use non-standard word because
this is their vernacular, male also talk rougher than
female. Male and female were also different in their
grammar. The data shows that female is more aware
to grammar than male.
The researcher found that pronunciation of
female
is better than male. This data is supported by Shuy in
Xiungfang Xia, who conducted a study in
this field,
and he found that 62.2% of men
pronounced “-ing”
in wrong way, but only 28.9% of
women did not
pronounce correctly. It can be seen
when male
produced some words, they often used
wrong
pronunciation, for example when they
produced the
word “palace” (istana) they
pronounced the word
as “place” (tempat), and also
when they produced
the word “godmother” (peri)
they pronounced that
word as “good mother” (ibu
yang baik), appeared
(muncul) as “a fear”
(ketakutan), and “found”
(menemukan) they fond”
(sangat cinta).
This finding is supported by Jespersen in Coates
(1993), that women had a more advance
pronunciation than men. Beside the differences in
words choice and pronunciation, female also talk
much than male. It can be seen from the speaking
duration of male and female. Female were longer
than male. This is also supported by Jespersen (in
Coates, 1993) who says that female talk much.
Male and female are also different in intonation.
The researcher found that female more comprehend
the story when they were retelling while male just
retold the story without aware of their intonation.
Lakoff in Xiungfang (2013) says that women usually
answer a question with rising intonation pattern
rather than falling intonation. Bydoing this, they can
show their gentleness; however, sometimes this
intonation shows a lack of confidence. As a
contrary,
men like to use falling intonation to show
that they
are quite sure of what they are saying.
Falling
intonation also shows men‟s self-confidence
and
power. Sumarsono in Zul Amri (2009:102)
states
that male and female were different in many
aspects
such as gesture, expression, voice and
intonation,
phoneme and speech style.
The researcher also found that when male were
retelling story, they could improve story even they
did not follow the line of the story. They made other
line story but the main point of the story still kept by
them. They were also enjoy when they were retelling
the story although some of them were lack of
pronunciation, used non-standard word, and
grammar. They also retold the story faster than
female.
On the contrary, female retold story slower than
male. Most of the female were good in
pronunciation
and grammar although they could not
improve the
story. They just retold the story based
on the story
line that had been given to them. Unlike
male, female
were aware of grammar, pronunciation,
and words
choice. Likewise, their intonation was also better.
Therefore, the researcher concludes that
female is
better than male in retelling story.
Male and Female Speech Style in Retelling Story: Are They Different?
75

6
CONCLUSION
The conclusion of this research is listed in
the
following:
1.
There were four speech styles that were used by
male when they were retelling story. Those
speech
styles were formal, consultative, casual
and intimate
style. Among the four styles, male
dominantly used
consultative to retell story
because they wanted
response from the listeners.
Also, by using
consultative style they wanted to
get clarification
from the listeners.
2.
There were four speech styles that were used by
female when they were retelling story. Those
styles
were formal, consultative, casual and
intimate style.
Female dominantly used casual
style in retelling
story because they wanted the
listeners enjoy the
story and feel relax when they
listened to the story.
3.
Both male and female used the same speech
styles. Those were formal, consultative, casual
and
intimate style. The difference was on the
frequency
of the use of the styles. Male was
dominant in using
consultative style while
female was dominant in
using casual style. Male
and female were also
different in some aspects
such as vocabulary,
grammar, pronunciation, and
intonation.
REFERENCES
Andersen Elaine Slosberg. 1990. Speaking With Style.
Londo and New York: Routledge.
Arikunto Suharsimi. 2008. Dasar-Dasar Evaluasi
Pendidikan. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
Chaer Abdullah & Leoni Agustina.2010. Sosiolinguistik.
Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
Chaika Elaine. 1982. Language the Social Mirror. London:
Newbury House Publisher, Inc.
Chambers, J K. Sociolinguistics Theory. Oxford UK &
Cambridge USA: Blackwell.
Coates, Jennifer. 1986. Women, Men and Language. Cet.2;
Longman: New York.
Coulmas Florian. 1997. The Handbook of Sociolinguistics.
USA: Blackwell.
Holmes, Janet. (1992). An introduction to sociolinguistics.
England: Longman Group UK Ltd.
Massachusestts Rowle. 1982 language and the social
mirror. London: Ewbury house publishers, inc.
McKay Sandra Lee., and Hornberger Nancy H. 1996.
Sociolingistic and Language Teaching. Cambridge:
University Press.
Mesthrie Rajend, Swann Joan, etc. 2000. Introduction
Sociolinguistics. Edinburgh: University Press.
Morrow M.L. 1989. Using Story Telling to Develop
Comprehension. New York: International Reading
association, 1989
R.A Hudson. 1987. Sociolinguistics. New York: Cambridge
University Press.
Ronsumbre & Kuntjara. Speech Style Used by Young
Female and Male teachers in teaching English to Their
English to Their Older Students, Unpublished: a scrib
Study Program of English Department Faculty of
Letters, Petra Chiristian University Surabaya, Eats
Java.
Sgourous Charissa. Judith Gold and Akini Gibson. The
Power of Story Reteling.
Siregar, Sofyan. 2014. Statistik Parametrik untuk
Penelitian Kuantitaf dilengkapi dengan perhitungan
Manual dan Aplikasi SPPs Versi 17. Cet 2; Jakarta:
Bumi Aksara.
Spearch Richard A. 2007. American Slang Dictionary.
Previously publisher: Mc Graw-Hill‟s dictionary of
American Slang and Colloquial Expression
Sugiyono. 2015. Metode Penelitian Pendidikan. Bandung:
Alfabeta.
Talbot Mary M. 1908. Language and Gender. Cambridge:
Polity Press.
Trianto. 2011. Pengantar Pendidikan bagi Pengembangan
Profesi Pendidikan & dan Tenaga Kependidikan. Cet
2; Jakarta: Kencana Prenada Media Group.
Wardhaugh Ronald. 2006. An Introduction to
Sociolinguistics. USA: Blacwell.
Xiungfang Xia.2013. Gender Differences in Using
Language. Academy Publisher Manufactured in
Finland.
Zul Amri. 2009. “Perbedaan Bahasa Siswa Laki-Laki dan
Siswa Perempuan: Sebuah Study Kasus Di Kelas V
SDN 09 Air Tawar Barat Padang Sumatra Barat”
unpublished scrib: FBSSUniversity.
ELITE 2019 - English Linguistics, Literature, and Education Conference
76
