
LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis) Score
as a Predictor of Necrosis and Perforation in Cases of Pediatric
Appendicitis in Haji Adam Malik Hospital Medan
Rizki Irwansyah Sembiring
1*
, Fikri Erjan
1
and Zulfikar Lubis
2
1
Department of Surgery, Haji Adam Malik Hospital,Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
2
Department of Clinical Pathology, Haji Adam Malik Hospital, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Appendicitis, Children, Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis (LRINEC) Score, Prognostic
Abstract: Pediatric Appendicitis Score has been used as a tool in assessing the risk of necrotizing fasciitis in cases of
soft tissue infection. This study aims to determine the LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing
Fasciitis) Score as a predictor of necrosis and perforation in cases of pediatric appendicitis in Haji Adam
Malik Hospital Medan. The study was prospective with patient data collection from January 2014 to
December 2014. Patient data were collected including age, LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for
Necrotizing Fasciitis) Score, and postoperative histopathology. For 12 months, 30 patients with acute
appendicitis who met the inclusion criteria obtained a strong correlation of Laboratory Risk Indicator for
Necrotizing Fasciitis (LRINEC) Score with operating findings, Pearson correlation coefficient (r) of .551
and p-value 0.002 (0.002 <0.05, significance 0.05). With the LRINEC score cutoff ≥ 9, it has a positive
predictive value of 78.5% (95% CI) and a negative predictive value of 62.5% (95% CI). The sensitivity
itself is 64.7% and the specificity is 76.9%. This can be utilized in the management of preoperative and
postoperative appendicitis patients in children.
1 INTRODUCTION
Appendicitis is cases of pediatric surgical
emergencies that are often encountered. The most
common complications are necrosis and perforation
which is one of the emergency abdomens that
requires immediate surgery (Ballester, 2009, Victor,
2012, Maki, 2012, Adelia, 2012, Huckins, 2013).
The incidence of acute appendicitis in children in
the world ranges from 1 - 8% of all pediatric patients
who come to the Emergency Department (Jangra,
2013). In 2009, 60 cases of acute appendicitis were
registered in the Haji Adam Malik Hospital, Medan
(Ivan, 2009).
There is no good scoring system to assess the
risk of necrosis and perforation in cases of pediatric
appendicitis. Previous research has been conducted
on the use of LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator
for Necrotizing Fasciitis) score as a diagnostic tool
to determine the risk of necrotizing fasciitis in cases
of soft tissue infection. By the same principle of
pathophysiology, the author is interested in
researching LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for
Necrotizing Fasciitis) score as a predictor of necrosis
and perforation of appendicitis cases of children at
Haji Adam Malik Hospital, Medan.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study is an analytical study with a retrospective
design using a correlation test. The significant
number used is p <0.05. We retrospectively
reviewed all pediatric patients with a diagnosis of
appendicitis who underwent surgery at Haji Adam
Malik Hospital, Medan from January 1, 2014, to
December 31, 2014. Sampling in this study was
carried out in total sampling, where 30 samples were
obtained.
Statistical analyses were performed using the
SPSS statistical software (version 11.0, SPSS,
Chicago, IL). Sixth variables were analyzed. The
first biochemical and hematologic tests were done
on admission were analyzed. Variables analyzed
were age, gender, total white cell count, hemoglobin,
102
Sembiring, R., Erjan, F. and Lubis, Z.
LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis) Score as a Predictor of Necrosis and Perforation in Cases of Pediatric Appendicitis in Haji Adam Malik Hospital Medan.
DOI: 10.5220/0009861301020105
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease (ICTROMI 2019), pages 102-105
ISBN: 978-989-758-469-5
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
serum sodium, glucose, creatinine (Cr), and C-
reactive protein (CRP).
The LRINEC score of each patient was
calculated by totaling the scores of each independent
variable. The predictive accuracy of the LRINEC
score was expressed as the area under the
receiver operating characteristic curve. The curve
represents the relationship between corresponding
values of sensitivity and specificity with all possible
values of probabilities as a cutoff point to predict for
the presence of necrosis and perforation.
3 RESULTS
Thirty pediatric patients with appendicitis were
analyzed, complicate appendicitis in 17 patients
(56.67%) and simple appendicitis in 13 patients
(43.44%). There were 16 males (53.3%) and 14
females (46.7%) with a mean age of 11 years.
LRINEC Score data are normally distributed.
The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test normality test
obtained the Asymp value. Sig. (2-tailed) of 0.519
(greater than 0.05). Of the 30 samples obtained an
average LRINEC score of 7.27 patients with the
highest total score was 7. The standard deviation for
the LRINEC Score is 3.65.
The moderate risk group (LRINEC score 6-7)
found 5 samples (63.5%) with complicated
appendicitis and 3 samples with simple appendicitis.
Whereas in the high-risk group (LRINEC score> 7)
there were 11 samples (73.3%) with complicated
appendicitis and 4 samples with simple appendicitis.
The higher value of the LRINEC score, the more
proportion of surgical findings is complicated. From
the chi-square statistical analysis of the LRINEC
risk group with the findings of the Asimp value. Sig
for 0.031 (0.031 <0.05). It was concluded that there
was a significant relationship between LRINEC
score and operating findings.
Correlation of Laboratory Risk Indicator for
Necrotizing Fasciitis (LRINEC) Score with
operating findings
Using Pearson correlation, Pearson correlation
coefficient (r) was equal to .551 or strong, with p-
value 0.002 (0.002 <0.05, significance 0.05). So that
the higher the Laboratory Risk Indicator for
Necrotizing Fasciitis (LRINEC) Score, the more
operational findings lead to complications.
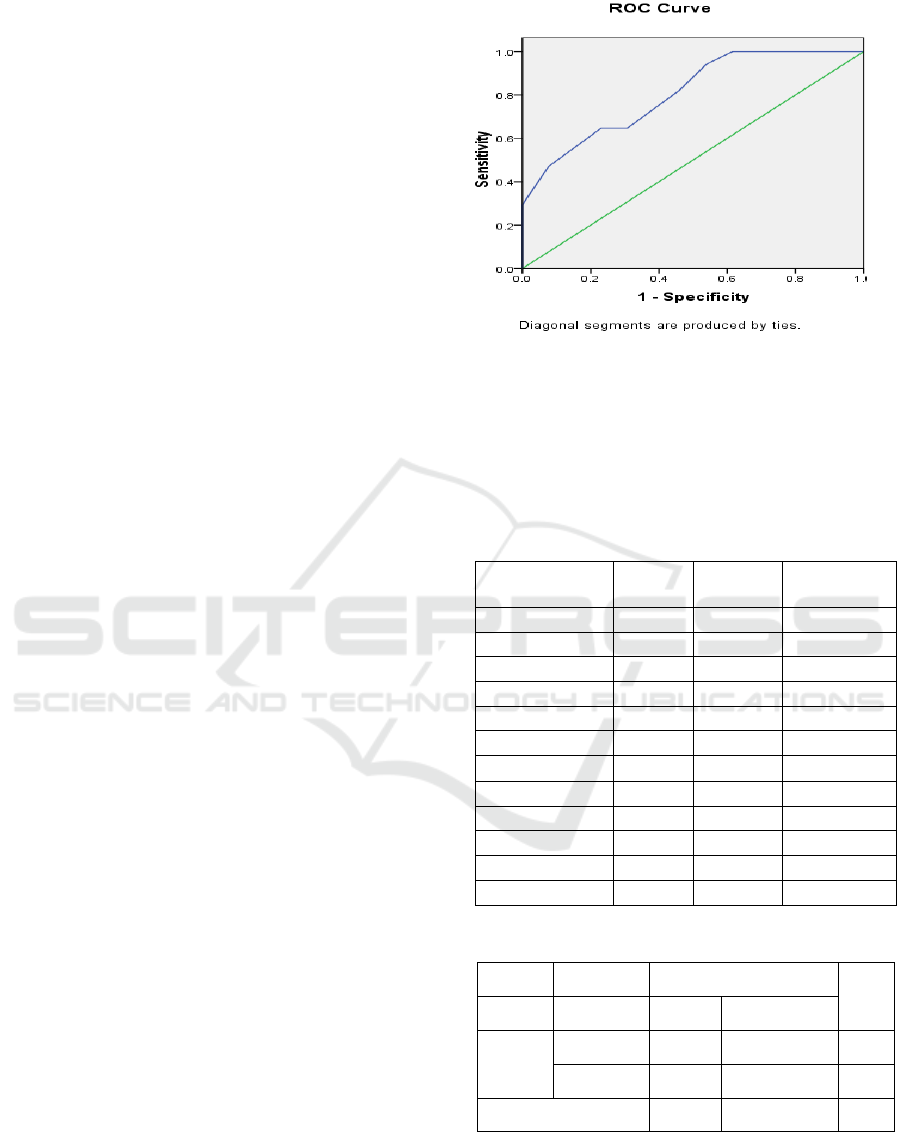
Figure 1: Receiver operating characteristic curve
The area under the curve for LRINEC score as a
predictor of cases of pediatric appendicitis in this
study was 0.805 (95% Confident interval, 0.651-
0.960). The perfect predictor has an Az value of 1. A
score of ≥ 9 is the cut off point in this study.
Table 1: Sensitivity and specificity of LRINEC
Positive if Greater
Than or Equal To
a
Sensitivity
1 -
Specificity
Sensitivity +
Specificity
.00 1.000 1.000 1.000
1.50 1.000 .692 1.308
2.50 1.000 .615 1.385
4.50 .941 .538 1.403
6.50 .824 .462 1.362
7.50 .647 .308 1.339
8.50 .647 .231 1.416
9.50 .471 .077 1.394
10.50 .294 .000 1.294
11.50 .176 .000 1.176
12.50 .118 .000 1.118
14.00 .000 .000 1.000
Table 2: Prediction value of LRINEC score
Histopathology
Total
Simple Complicate
LRINEC
Score<9 10 6 16
Score≥9 3 11 14
Total 13 17 30
With LRINEC cutoff score of ≥ 9 has a positive
predictive value of 78.5% (CI 95%) and negative
predictive value 62.5% (CI95%). The sensitivity is
64.7% and the specificity is 76.9%.
LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis) Score as a Predictor of Necrosis and Perforation in Cases of Pediatric
Appendicitis in Haji Adam Malik Hospital Medan
103

4 DISCUSSION
From the results of this study, the majority of the
samples were male as many as 16 patients (53.3%)
and the remaining women were 14 patients (46.7%).
From epidemiological data, there were no
differences in the incidence of appendicitis between
men and women in children (Schwartz, 2009).
Most cases in this study were complicated
appendicitis, 17 patients (56.67%). Patients with
simple appendicitis were 13 patients (43.33%). This
is supported by previous research conducted in the
Netherlands (Rotterdam Hospital) by V.C
Cappendijk et al. Of the 129 acute appendicitis
samples in children found 71% with perforated
appendicitis.
Necrotizing Fasciitis is associated with severe
sepsis. SIRS and sepsis cause changes in
biochemical and hematological variables. LRINEC
score is very important in measuring this change and
predicts the probability of necrotizing fasciitis based
on the severity of sepsis.
Research by Maurer et al. (2014) showed that
hyponatremia, fever, and tachycardia had moderate
to high specifications for colonic perforation.
LRINEC score can be used for early detection of
cases of necrotizing fasciitis in patients with severe
soft tissue infections. LRINEC score of more than 5
has a positive predictive value of 92.0% (95% CI),
while a score of more than 7 has a positive
predictive value of 93.4%.
The higher the value of the LRINEC score, the
more the proportion of surgical findings is obtained.
In the moderate risk group (LRINEC Score 6-7),
there were 5 patients (62.5%) of surgical
complications of appendicitis. Whereas in the high-
risk group (LRINEC Score 8-13) there were 11
patients (73.3%) with complicated appendicitis.
Previous research by Wong (2004) in the case of
LRINEC score necrotizing fasciitis was able to
classify patients into 3 risk categories low (LRINEC
score <6) with a risk of soft tissue necrosis <50%,
moderate (LRINEC score 6-7) with the risk of
necrosis soft tissue 50-75%, and high (LRINEC
score> 7) with the risk of soft tissue necrosis> 75%.
From the results of Laboratory Risk Indicator for
Necrotizing Fasciitis (LRINEC) correlation
statistical analysis with the findings of operations,
the Pearson correlation coefficient (r) is equal to
.551 or strong. Based on existing criteria, the
relationship between the Laboratory Risk Indicator
variables for Necrotizing Fasciitis (LRINEC) scores
with surgical findings is significant because of the
significance is 0.02. (the significance is < 0.05). The
area under the curve for LRINEC score as a
predictor of cases of pediatric appendicitis in this
study was 0.805 (95% Confident interval, 0.651-
0.960). The cut-off LRINEC score 9 has a positive
predictive value of 78.5% (95% CI) and a negative
predictive value of 62.5% (CI95%). The sensitivity
is 64.7% and the specificity is 76.9%.
Based on research by Chin-Ho Wong and Kok-
Chai Tan in 2014 at Changi General Hospital
Singapore, LRINEC score of more than 5 had a
positive predictive value of 92.0% (95% CI), while a
score of more than 7 had a positive predictive value
of 93.4 %.
Liao et al from Tzu Chi University in 2012
validated LRINEC scores in cases of necrotizing
fasciitis at Tzu Chi General Hospital, Chiayi
Taiwan. From a sample of 3155 patients, it was
concluded that a score of> 5 LRINEC scores had a
sensitivity of 59.2% and a specificity of 83.3%, a
positive predictive ratio of 37.9% and a negative
predictive ratio of 92.5%.
The study by Kaser et al. (2013) concluded that
temperature, heart rate, serum sodium levels, CRP
and leukocytes correlated significantly with
perforated colonic diverticulitis and perforated
appendicitis. Where there was an increase in
temperature (P = 0.029, OR = 1.508), heart rate,
decreased serum sodium level (P = 0.047, OR =
0.912), increase in CRP (P <0.001, OR = 1,006).
Mosele et al (2010) retrospectively assessed
laboratory results in 46 patients with colonic
ischemia proven by biopsy. Higher leukocyte means
scores (P <0.0001), creatinine (P = 0.003), urea
(P=0.008), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH P
<0.0001) between groups with colon ischemia
compared to the control group.
Montoro et al (2011) prospectively studied 364
patients with definite and probable colonic ischemia.
Leukocytes> 15x109 / l, hemoglobin <12g / dL, and
albumin <2.8g / l were more frequent in patients
with severe ischemic colon.
Anon et al (2006) assessed 85 patients
retrospectively and found that patients with severe
colonic ischemia had a frequency of anemia (Hgb
<12g / dL, 37.5% vs 10.1%; P = 0.012) and
hyponatremia (serum sodium <136mEql / L , 46.6%
vs. 14.9%; P = 0.012) which is high.
Research by Cevikel (2004) concluded that there
was a correlation between CRP levels and bacterial
translocation in obstruction cases. Where an increase
in CRP is parallel with an increase in the number of
colonies forming units (CFU) from lymph node
mesenteric (MLN) and liver cultures (P <0.001)
ICTROMI 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease
104

5 CONCLUSION
LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing
Fasciitis) score can be applied as a predictor of
necrosis and perforation in cases of pediatric
appendicitis in H. Adam Malik General Hospital
Medan with a cutoff of 9.
LRINEC Score can be included in the clinical
pathway in the policy of preoperative management
of appendix cases in children both BPJS programs
and other insurance programs and as a standard of
service in RSUP. H. Adam Malik Medan.
For further research on antibiotic variables that
have been given as well as secondary infections that
can be included as one of the variables in assessing
LRINEC score as predictors of cases of appendicitis.
REFERENCES
Anon et al. Factors predicting poor prognosis in ischemic
colitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Aug 14; 12(30):
4875–4878.
Cevikel. C-reactive protein may be a marker of bacterial
translocation in experimental intestinal obstruction.
ANZ J Surg. 2004 Oct;74(10):900-4.
Chin-Ho Wong and Kok-Chai Tan. The LRINEC
(Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis)
score A tool for distinguishing necrotizing fasciitis
from other soft tissue infections. Crit Care Med 2004
Vol. 32, No. 7
Liao et al. Validation of the laboratory risk indicator for
necrotizing fasciitis (LRINEC) score for early
diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Tzu Chi Medical
Journal. 2012. 24(2):73–76.
Montoro et al. Clinical patterns and outcomes of
ischaemic colitis: results of the Working Group for the
Study of Ischaemic Colitis in Spain. Scand J
Gastroenterol. 2011. 46(2):236-46.
Moseley M, Cardin F, Inelmen EM et al. Ischemic colitis
in the elderly: predictors of the disease and prognostic
factors to a negative outcome. Scand J Gastroenterol
2010;45:428–433.
Murer et al. Hyponatremia Is a Specific Marker of
Perforation in Sigmoid Diverticulitis or Appendicitis
in Patients Older Than 50 Years. Gastroenterology
Research and Practice. 2013, 462891.
Wong CH, Chang HC, Pasupathy S, et al: Necrotizing
fasciitis: Clinical presentation, microbiology, and
determinants of mortality.
LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis) Score as a Predictor of Necrosis and Perforation in Cases of Pediatric
Appendicitis in Haji Adam Malik Hospital Medan
105
