
Implementation of VARK Learning Styles in the MOOC User Interface
Design
Nungky Amalia Imran
1
, Paulus Insap Santosa
1
and Sri Suning Kusumadewi
1
1
Department of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords:
MOOC, VARK, Learning Style, User Interface.
Abstract:
The development of technology has a lot of influence on the current educational process. One of the effects of
technology is the development of Massive Open Online Course (MOOC) learning media which is still part of e-
learning. Massive and open MOOC has its own challenges in terms of scalability. Therefore, many researchers
are now starting to develop interface designs that are in accordance with the characteristics of the students.
This study aims to identify the learning styles of students in the MOOC course. The identification of student
learning styles is done by filling out questionnaires that focus on the VARK method (Visual, Aural, Read,
Kinetic). The results of the questionnaire analysis will be used as the basis by the researchers in designing the
MOOC user interface that applies the VARK learning style.
1 INTRODUCTION
E-learning has influenced the development of other
online-based learning platforms, such as the MOOC
(massive open online course). Several universities
and international non-profit institutions have devel-
oped MOOC which is quite popular, such as edX,
Coursera, Udacity, and others. Indonesia has a
MOOCs site that was developed seriously and can
be used free of charge, one of which is MOOC In-
donesiaX which was launched to coincide on the 70th
Independence Day of the Republic of Indonesia. In-
donesiaX cooperating with the Universitas Indonesia,
Institut Teknologi Bandung, PT Net Mediatama Tele-
visi and several other well-known Institutions (Rach-
matunisa, 2015).
There are several parameters needed to measure
the quality of MOOC (KampusUNJ, 2016) includ-
ing how the MOOC site presents content, how much
learning material is offered. In addition, supporting
institutions and institutions are no less important in
the sustainability of a MOOC. Because institutions
with good credibility will contribute and trust users.
Then the total visitors and popularity of social media
became several benchmarks for a MOOC. In another
study that measured the Successful (Yousef et al.,
2014) and Effectiveness (Gamage et al., 2015) of the
MOOC, from the two studies, there were similarities
in how a learning site would run successfully and ef-
fectively if the media could present exercises that rep-
resented all existing material and provide testing that
measurable for users. The appearance of a MOOC
site also has a large effect on effectiveness, because
the user interface that is easy to remember and attracts
visuals in the eyes will make users easier to under-
stand and can follow learning well. Recognizing the
importance of good MOOC content, many developers
seriously pay attention to the look and content of the
sites built. This can be seen from many sites that em-
phasize content, such as practice questions on each
material presented, the use of videos is also used in
the delivery of lecture material and the use of slides
containing text material lectures..
Previous research has carried out innovations in
developing content at the MOOC, including the incor-
poration of AIED (artificial intelligence in education)
(Kay et al., 2013) ITS (intelligence tutoring system)
(Baneres and Sa
´
ız, 2016), integration at SG (Serious
Games) (Freire et al., 2014), and a scheme for dis-
plays high-resolution video called DASH (Dynamic
adaptive streaming over HTTP) (Wang et al., 2015).
However, despite the many innovations made in the
development of MOOC, the combination of learning
styles and user interface design has not been widely
developed by researchers.
In this study, the author tries to look at the
characteristics of learning styles in students at the
Akademi Komunitas Industri Tekstil dan Produk Tek-
stil Surakarta (AK-Tekstil Solo). AK-Tekstil Solo is
under the auspices of the Ministry of Industry and is
220
Imran, N., Santosa, P. and Kusumawardani, S.
Implementation of VARK Learning Styles in the MOOC User Interface Design.
DOI: 10.5220/0009867502200223
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Creative Economics, Tourism and Information Management (ICCETIM 2019) - Creativity and Innovation Developments for Global
Competitiveness and Sustainability, pages 220-223
ISBN: 978-989-758-451-0
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

the first Community Academy in Indonesia that has
implemented dual systems in the learning process.
Dual system is an education system that applies the-
ory and practice directly to industry, in this context
the textile industry. As the pioneer of the Commu-
nity Academy, the AK-Tekstil Solo can be a model for
other vocational schools. The study was conducted by
identifying learning styles from student samples, then
the results of the data analysis will be used as a refer-
ence to create a user interface design. By combining
learning styles and MOOC the authors hope that par-
ticipants can experience a different user experience in
online-based learning.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Massive Open Online Course
(MOOC)
MOOC based on its acronym (Kay et al., 2013) has
three meanings for each element. Open, means that
it can be accessed by everyone or all circles. Besides
that, being open can also mean that users can access
the MOOC site for free anytime and anywhere. On-
line elements mean that people can access this site
with an internet network. Then in the course ele-
ments, this learning method has become a benchmark
for innovation in the education process. Because a
class offered usually presents the whole course ma-
terial or one course material with integrated learn-
ing material and formative assessment. These classes
are managed by instructors from the world’s top in-
stitutions. At present, there are several MOOCs that
are quite popular and are widely used throughout the
world, some of which are Coursera, edX, and Udacity.
2.2 Learning Style
The learning process is the most crucial stage for ev-
ery individual who is conducting lectures. Each indi-
vidual has an obligation to study the material in the
class that they follow, but now the learning process
that provides the most effective outcomes still does
not have a standard. Therefore, many researchers ap-
ply theory to learning styles in the educational pro-
cess.
2.3 VARK Learning Style
One model of learning styles that have been used in
learning media today is VARK (Visual Aural Read
Kinetic). VARK represents several aspects of the con-
cept of learning, where each of these aspects can be
selected by the training participants according to their
needs. VARK (D
´
ıaz et al., 2018) which is an acronym
of several words, the first is visual, which is how a
material can be delivered with visual images such as
tables, diagrams, symbols, and images. Second, is au-
ral, which is how learning material is delivered with
the help of audio, sound, pronunciation, conversation,
discussion and so on. Simply put, from the applica-
tion of the aural principle, there are features provided
for fellow users to communicate on a media, such as
chat and discussion forum features. Third, read/write
is a model that we can find in teaching and learning
activities in general, namely where the instructor and
class participants can read the material provided and
write both reports, essay questions, and other exer-
cises. Then the last one is kinetic, which is how the
material delivered can make participants feel as if it is
real so that it has the effect of a different experience
in learning. A simple example of kinetic is the use of
demonstrations, simulations, videos and films.
Figure 1: VARK Learning Style (Mitchell et al., 2015)
3 OBJECTIVE OF THIS STUDY
a. Propose the concept of designing the interface of
the MOOC and testing the participants
b. Develop an appearance by combining user learning
styles.
4 METHODOLOGY
This research is conduct to look at the number of
learning styles that are widely used in AK-Tekstil
Solo. The research method used was by filling out
questionnaires based on VARK’s learning style. The
research method used was by filling out question-
naires based on VARK’s learning style. The ques-
tionnaires are adapt from the vark-learn.com website
by translating into Indonesian. Assessment on the
Implementation of VARK Learning Styles in the MOOC User Interface Design
221
questionnaire used a 1-5 Likert scale with point 1 to
strongly disagree until point 5 to strongly agree.
The subjects of the study were all active AK-
Tekstil Solo students, both who were undergoing level
1 and level 2 and were willing to take part in the
study. The questionnaire was filled out by 50 students
with study programs on weaving engineering and gar-
ment engineering. Then to determine the final value
and trend of student learning styles, the summation of
each of the questions given is done. Questions are di-
vided into four parts which are distinguished based on
Visual, Aural, Read / Write, and Kinesthetic learning
styles.
5 RESULT
Respondent data is an important element in a study
that uses questionnaires. The following table is com-
plete data from respondents in this study.
Table 1: Respondents
Characteristic Amount Percentage
SEX
MALE 15 30%
FEMALE 35 70%
DEPARTMENT
TEKNIK PEMBU-
ATAN GARMEN
35 70%
TEKNIK PEM-
BUATAN KAIN
TENUN
15 20%
AGE 18-28
YEARS
OLD
Based on the data in the table, the respondents
who filled out this questionnaire were 50 people con-
sisting of 35 women and 15 men. Students who par-
ticipate in this research come from study programs
Teknik Pembuatan Kain Tenun and Teknik Pembu-
atan Garmen. The age range of respondents is 18 to
28 years.
Figure 2: Total Score
Based on the total score of the chart it can be seen
that kinetic is the learning style that is most chosen
by students, aural is second learning style that is most
chosen with total score 629, the third learning style
that is most chosen are read and the less that is chosen
by students is visual.
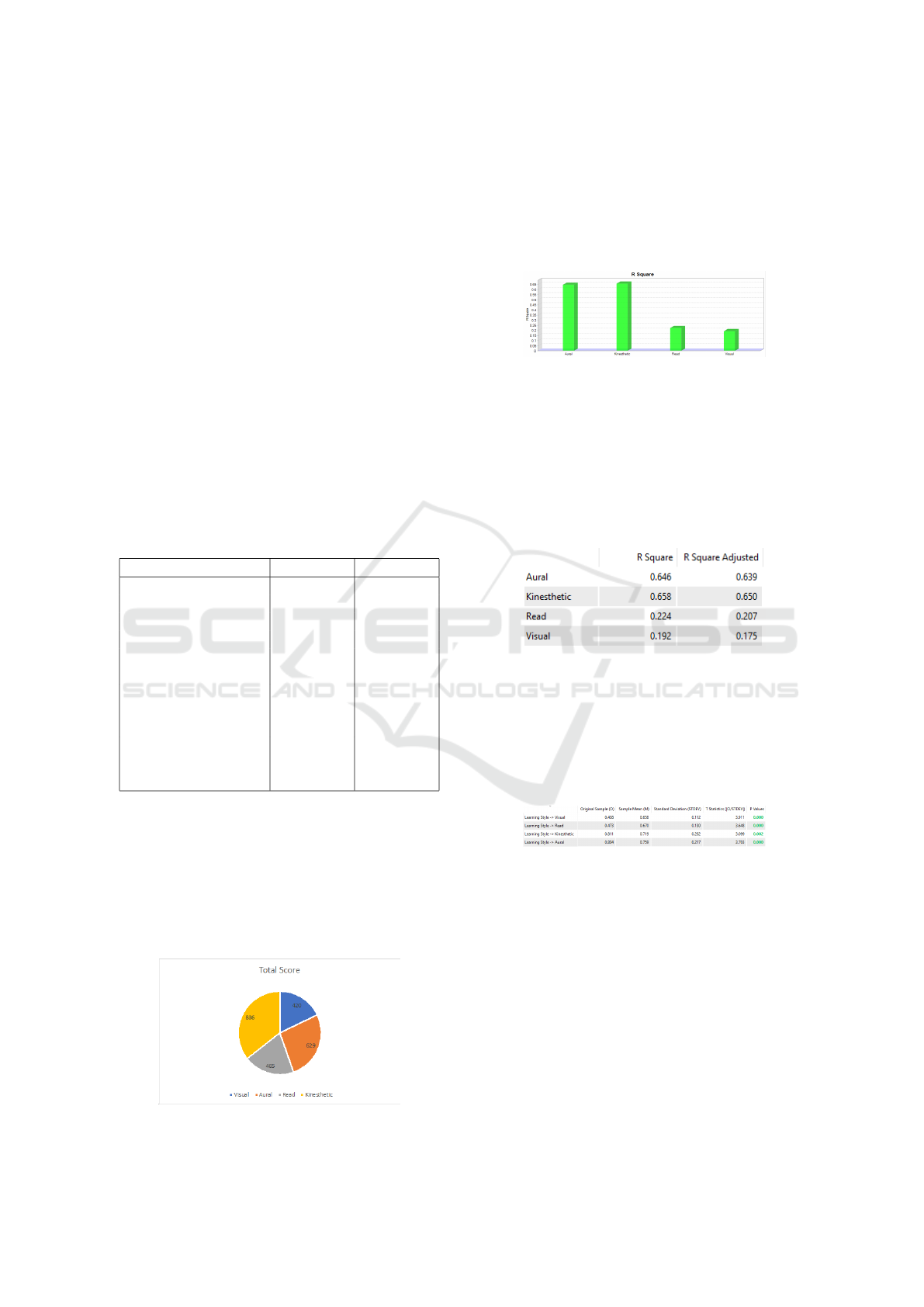
Figure 3: R Square Chart
Based on the testing of the structural model which
can be seen in Figure 3, it is not much different from
the total score described in the form of a pie chart.
The learning style that is most often done or sought
after by students is the Kinesthetic learning style, fol-
lowed by aural, read and final learning styles are vi-
sual. Further explanation of the analysis carried out
can be seen in Figure 4.
Figure 4: R Square Details
In testing the inner model can be seen the differ-
ence in the values that have been analyzed. Kinestetic
and aural are still the best grades that are most sought
after by students. While learning styles such as read-
ing and displaying images are less in accordance with
student learning style preferences.
Figure 5: Hyphothesis
In the hypothesis test the existing value can be ac-
cepted if it has the following conditions:
1. Jika nilai dari T Statistic > 1, 96
2. Jika nilai dari P Values < 0, 05
Based on the data in the picture, the analysis can
be concluded as follows:
1. Visual
3,911 > 1,96 is accepted
2. Read
3,648 > 1,96 is accepted
3. Kinesthetic
3,099 > 1,96 is accepted
ICCETIM 2019 - International Conference on Creative Economics, Tourism Information Management
222

4. Aural
3,703 > 1,96 is accepted
Then for the value values all the learning style cri-
teria have a value that is smaller than the 0.05 thresh-
old so that this hypothesis can be accepted.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the analysis that has been
done, it can be concluded that the learning styles that
are most in demand by AK-Tekstil Solo students are
Kinesthetic followed by Aural learning styles. How-
ever, for the Visual learning style and Read not so
much liked by students. Therefore, the user interface
design that will be designed will focus on a learning
style that the majority is chosen by students. In fur-
ther research, MOOC will be conducted by combin-
ing Aural learning styles. Because this learning style
is a teaching method that most closely resembles the
process with conventional classes.
Consideration of researchers not to focus on the
design with kinesthetic learning styles because the
learning criteria with this method require several other
tools so that the student learning experience can be
felt. Whereas aural focuses on sound and student
communication with classmates and lecturers who
teach. The learning style chosen by AK-Tekstil Solo
students is closely related to the learning system that
has been carried out. Because, vocational schools are
schools that focus more on practical subjects. There-
fore, the majority of students choose a learning style
that involves a lot of physical activity and discussions
with colleagues. In further research, researchers hope
to design the MOOC user interface in the textile field
by involving all existing learning styles. So that later
each student can choose material directly in accor-
dance with their learning style preferences. Then, the
final results of the classes that have been followed can
be carried out further research regarding the relevance
of student achievement to the learning material car-
ried out.
REFERENCES
Baneres, D. and Sa
´
ız, J. (2016). Intelligent tutoring system
for learning digital systems on mooc environments.
In 2016 10th International Conference on Complex,
Intelligent, and Software Intensive Systems (CISIS),
pages 95–102. IEEE.
D
´
ıaz, F. S., Rubilar, T. P., Figueroa, C. C., and Silva, R. M.
(2018). An adaptive e-learning platform with vark
learning styles to support the learning of object ori-
entation. In 2018 IEEE World Engineering Education
Conference (EDUNINE), pages 1–6. IEEE.
Freire, M., del Blanco,
´
A., and Fern
´
andez-Manj
´
on, B.
(2014). Serious games as edx mooc activities. In
2014 ieee global engineering education conference
(educon), pages 867–871. IEEE.
Gamage, D., Perera, I., and Fernando, S. (2015). A frame-
work to analyze effectiveness of elearning in mooc:
Learners perspective. In 2015 8th International Con-
ference on Ubi-Media Computing (UMEDIA), pages
236–241. IEEE.
KampusUNJ (2016). nikah situs kuliah online (mooc) ter-
baik indonesia?
Kay, J., Reimann, P., Diebold, E., and Kummerfeld, B.
(2013). Moocs: So many learners, so much poten-
tial... IEEE Intelligent systems, 28(3):70–77.
Mitchell, E. K., James, S., and D’Amore, A. (2015). How
learning styles and preferences of first-year nursing
and midwifery students change. Australian journal
of Education, 59(2):158–168.
Rachmatunisa (2015). Indonesiax, massive open online
course ’persembahan untuk negeri’.
Wang, Y., Wu, W., and Lou, Y. (2015). Mooc-dash: A dash
system for delivering high-quality moocs videos. In
2015 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia
(ISM), pages 113–119. IEEE.
Yousef, A. M. F., Chatti, M. A., Schroeder, U., and Wos-
nitza, M. (2014). What drives a successful mooc?
an empirical examination of criteria to assure de-
sign quality of moocs. In 2014 IEEE 14th Interna-
tional Conference on Advanced Learning Technolo-
gies, pages 44–48. IEEE.
Implementation of VARK Learning Styles in the MOOC User Interface Design
223
