
Assessing the Economic Value of Cultural Heritage Site: A Case of the
Kekayon Puppet Museum in Yogyakarta
Endah Saptutyningsih
1
and Pandhu Nugroho Yoga Pamungkas
1
1
Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords:
willingness to pay; contingent valuation method; cultural tourism; heritage tourism; museum
Abstract:
Some museums in Indonesia uphold the same mission, namely in the efforts to preserve culture in Indonesia.
As part of a cultural preservation, the Kekayon Puppet Museum Yogyakarta educate visitors about Javanese
culture through puppet. This study estimates the economic value of a cultural heritage site by investigating
visitors’ willingness to pay (WTP) for preserving the cultural heritage by visiting the museum. Using a lo-
gistic regression, we tested the determinants of visitors’ WTP. The results indicate that the visitors contribute
less by entrance fee payment. The average WTP value were IDR12,000 (USD 0.83). There are 81.39 percent
of respondents willing to contribute. This indicates that most of the visitors had a low contribution for the
Museum. This study contributes to the museum administrators, especially cultural heritage museums by iden-
tifying the value of visitor’s WTP and the determinants of WTP for visiting the museum, so they can promote
the importance of cultural heritage tourism and improve the facilities of the museum.
1 INTRODUCTION
The existence of a museum is needed for the com-
munities. The museums has been the main repository
of storing objects and cultural and educational relics
of a country. The economics research field is quite
useful, for example in estimating the value of visitors
at their place of visit by using contingent valuation
(Johnson and Thomas, 1998). The logistic regression
could be employed to explore whether early exposure
to the arts of influence participation as adults. The
initial exposure resulted in later participation and that
the effects of exposure seemed to be strongest in the
years before and after adolescence (Gray, 1998).
This study aimed at identifying the factors had
impact on willingness to pay of visitors to visit mu-
seum. In this study, we used Kekayon Puppet Mu-
seum (Museum Wayang Kekayon) Yogyakarta as the
object. The tourism potential in Yogyakarta does not
only rely on the potential of nature and culture that
is very amazing, but also presents the potential of
historical tourism and cultural reserves that are very
interesting to visit. One tourist attraction that has a
high historical value is the museum. The Museum
is a permanent non-profit institution in providing ser-
vices to the community and development, open to the
public who receive, maintain, research, deliver and
exhibit for the purpose of learning, education and sat-
isfaction, facts about humans and their environment
(ICOM, 2007). Some museums in Indonesia uphold
the same mission, namely in the efforts to preserve
culture in Indonesia. The Kekayon Puppet Museum
Yogyakarta is also part of a cultural preservation mis-
sion through education of tourists about Javanese cul-
ture through puppet (wayang). As a cultural heritage,
the museum have characteristics of public goods, and
therefore non-market valuation techniques can be em-
ployed for assessment. The most important valuation
method is contingent valuation (CV) method (Ready,
2002).
Most of the CV methods have applied to assess
goods and environmental benefits, and only a few
studies have applied to non-profit cultural organiza-
tions. Most of these studies have directed at gener-
ally supported cultural activities. Some CV studies
related to culture (Throsby et al., 1983) (Morrison and
Westi, 1986) (Martin, 1994) (Hansen, 1997). Still few
CV studies have conducted on the value of culture (or
non-profit cultural organizations). For filling this gap,
this study would estimate the economic value of cul-
tural heritage site, namely The Kekayon Puppet Mu-
seum Yogyakarta using CV method. By logistic re-
gression, this study examined the impact of sociode-
mographic, travel cost, distance, facilities, etc. had
impact on WTP visitors to visit the museum.
230
Saptutyningsih, E. and Pamungkas, P.
Assessing the Economic Value of Cultural Heritage Site: A Case of the Kekayon Puppet Museum in Yogyakarta.
DOI: 10.5220/0009867702300234
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Creative Economics, Tourism and Information Management (ICCETIM 2019) - Creativity and Innovation Developments for Global
Competitiveness and Sustainability, pages 230-234
ISBN: 978-989-758-451-0
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 THE KEKAYON PUPPET
MUSEUM YOGYAKARTA
The Kekayon Puppet Museum is a private museum
that managed by the Kekayon Social Foundation and
it was established since July 23, 1991. The museum
is also an official member part of the Museum of the
Musyawarah Museum or Barahmus. It began fully
operated on June 17, 1992. As one of the museums in
Indonesia that participated in storing and exhibiting
puppets, the Kekayon Puppet Museum not become
the main destination of tourists, both domestic and
foreign tourists yet.
Based on data from tourist visits to the Kekayon
Puppet Museum in recent years, there have been fluc-
tuations in the number of tourist visits to the Kekayon
Puppet Museum in the last 3 years through data from
the Yogyakarta Special Region Tourism Office. The
Kekayon Puppet Museum. The Kekayon Puppet Mu-
seum is not included in the top 10 list of 31 museums
yet. In 2017, the De Mata Art Museum had the high-
est total visitors of 613,812 tourists and Affandi Mu-
seum had the lowest total visitors, which was 19,148.
Tourists visiting the Special Region of Yogyakarta
still choose to visit other museums rather than visiting
the Kekayon Puppet Museum. Of course, with vari-
ous kinds of promotional efforts or improvements to
facilities such as making more attractive puppet dis-
plays and other vehicles that are able to attract visi-
tors to come in the next few years it is expected that
the total number of tourist visits at the Kekayon Pup-
pet Museum increases.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Study Site
This study conducted in the Kekayon Puppet Mu-
seum. The Kekayon Puppet Museum Yogyakarta is
also part of a cultural preservation mission through
education of tourists about Javanese culture through
puppet (wayang). The museum has more than 5,000
several awards related to the quality of the facili-
ties provided, namely two national awards from the
Roaming Community as a Nomination Museum for
Local Culture Wisdom in 2016 and Nomination of
Friendly Museum in 2017.
3.2 Sampling Procedure
The sampling method in this study used convenience
sampling technique. With convenience sampling
techniques researchers can save in terms of time and
costs and sampling respondents easily measured then
usually very helpful and want to be invited to coop-
erate. The use of this sampling method is very ap-
propriate for this type of research with groups that
focused and explorative research to find ideas or ini-
tial testing of a hypothesis. We surveyed the visitors
who are willing to provide information needed by re-
searchers through questionnaires distributed, and in-
terviews conducted to obtain information directly or
indirectly. The required sample size for the surveys
was determined by the Slovin formula. We examined
a total of 172 respondents who visit The Kekayon
Puppet Museum.
3.3 Survey Design and Administration
We surveyed visitors in the study site to investigate
their support for improving The Kekayon Puppet Mu-
seum. Their support were measured they willing or
not to provide financial support for improving the
Kekayon Puppet Museum by the entrance fee pay-
ment. These identified the visitors who care or not
about the cultural heritage site. In order to identify the
amount of entrance fee for the museum, we conducted
a focus group discussion with 20 visitors knowledge-
able about the topic. In the discussion, we utilized
the contingent valuation method that constructed a
hypothetical market to measure participants’ willing-
ness to pay for a certain change in sites (Mazzanti,
2003)(Sanz et al., 2003)(Bedate et al., 2004). Based
on bids above IDR 5,000 (USD 0.36), results of a
single bound study showed that the informed visitors
were willing to pay of IDR 12,000 (USD 0.83) at av-
erage for visiting the museum. This value indicate
the economic value of the museum from the point of
view of informed visitors. It could distinguish visitors
with sufficient financial support for the museum from
those without. Based on this estimation, we designed
a question to find out whether participants would will-
ing or not willing to pay IDR 12,000 (USD 0.83) for
the entrance fee.
3.4 Data Analysis
The researcher applied a single dichotomous choice
method tied to two possible respondent answers
namely ”yes” or ”no”. The dichotomous choice
method best uses the Contingent Valuation Method
(CVM) approach because this method is closest to
market behavior when consumers will choose to buy
something or not at a certain price (Bateman et al.,
2002). Contingent Valuation is still widely used to as-
sess a tourist spot because the technique describes an
Assessing the Economic Value of Cultural Heritage Site: A Case of the Kekayon Puppet Museum in Yogyakarta
231
individual by generating value directly from an indi-
vidual through a survey (Mazzanti, 2003)(Sanz et al.,
2003)(Bedate et al., 2004).
We employed a logistic regression (Wang and El-
hag, 2007) to identity the impacts of the determi-
nants on visitors’ WTP for visiting The Kekayon Pup-
pet Museum. The dependent variable of the model
was the visitor’s WTP for for visiting The Kekayon
Puppet Museum, where 1 indicated their agreements
(they willing to pay as IDR 12,000) and 0 showed
their disagreements (they are not willing to pay as
IDR 12,000). The independent variables of the model
included the sociodemographic characteristics, visit
characteristics, and site characteristics (Figure 1).
The logistic regression of this study is
log(
p
1 − p
) = β + Σ
n
( j = 1)
βX
ji
Σ
m
(k = 1)
Y
k
Dki + e
(1)
log
(
p
(1 − p)) = β +β
1
INC +β
2
SEX + β
3
EDUC+
β
4
AGE + β
5
MARRIAGE + β
6
FREQ + β
7
TC+
β
8
FACILIT IES + β
9
DISTANCE+
β
10
SUBST ITUT ION + e (2)
where p is willingness to pay for the Kekayon
Puppet Museum (p = 1, if the respondent is willing to
pay; 1-p, if the respondent is not willing to pay); 1-p
is not willing to pay for visiting the Kekayon Puppet
Museum p / (p-1) = Odds Ratio (Risk); Xj is vector
of independent variable; Dk is vector of dummy vari-
able. αβi dan Yk=e is parameters that are assumed to
be random tool logistic functions.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The study results indicated that 81.4% of the respon-
dents (n=140) willing to pay for visiting The Kekayon
Puppet Museum, while the 18.6% (n=32) did not will-
ing.
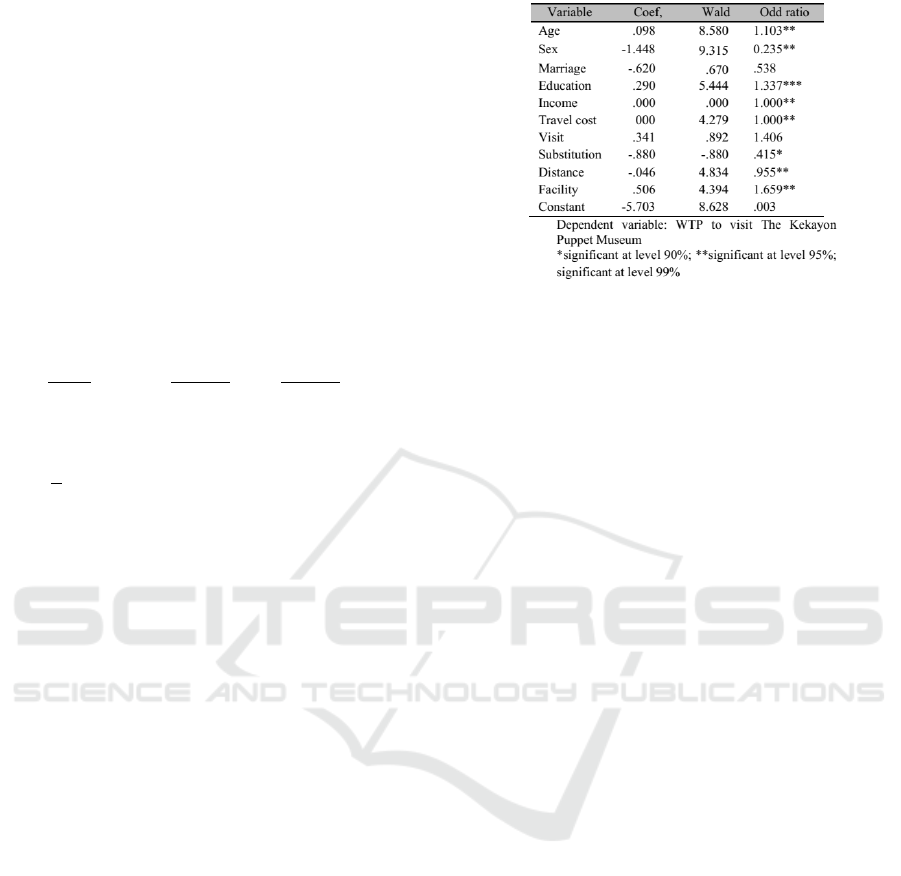
Age has a positive significant effect on willing-
ness to pay for visiting the museum. Most of the re-
spondents were young and active as students where
there was a special purpose in visiting the museum.
Respondents who have more than 30 years of age
have a greater willingness to pay because they al-
ready have a steady income. This research is in line
with the hypothesis of other research (Murzyn-Kupisz
and Działek, 2013). This in line with some previ-
ous studies (Nandagiri et al., 2015) (Tao et al., 2012)
(Van Sandt and Thilmany, 2016) (Chansina and Seen-
prachawong, 2017) (Adamu et al., 2015).
Figure 1: Regression Result.
Sex has a significant effect on willingness to pay
to visit the museum. The results of this study are in
line with the results of other researches (Nandagiri
et al., 2015)(Van Sandt and Thilmany, 2016)(Fonseca
et al., 2010). The coefficient value of the sex variable
is negative, which means that women have more WTP
than men to visit The Kekayon Puppet Museum.
The results of this study are supported by other re-
search (Priambodo and Suhartini, 2016) Marital sta-
tus has no significant effect on the value of willing-
ness to pay for The Kekayon Puppet Museum. The
value of the variable coefficient of marital status is
negative.
The results of the binary logistic regression test
show that there is a positive and significant rela-
tionship between education with the willingness to
pay. It means that the higher level of education, the
higher the willingness to pay for visiting the museum.
In other words, knowledge from someone will in-
crease regarding awareness to maintain cultural her-
itage such as puppets and maintain the facilities from
the museum so that the possibility of the risk of pup-
pet damage will be smaller. A similar study who
investigated the Malaysian Museum regarding will-
ingness to pay for improving the quality of the mu-
seum facilities’ improvement (Fadhil et al., 2017),
The study also mentions that if the longer years of
schooling, the higher willingness to pay for the im-
provement. Some previous studies found the effect of
education on WTP (Nandagiri et al., 2015) (Adamu
et al., 2015) (Fonseca et al., 2010) (Fadhil et al.,
2017) (Calleja et al., 2017). Income has a positive
and significant influence on willingness to pay. This
indicates that the higher the income level of the re-
spondents, the higher the willingness to pay for ad-
mission to museums. The results of previous stud-
ies are also in line with this hypothesis carried out
by other studies (Nandagiri et al., 2015) (Tao et al.,
2012) (Van Sandt and Thilmany, 2016) (Chansina and
ICCETIM 2019 - International Conference on Creative Economics, Tourism Information Management
232

Seenprachawong, 2017) (Adamu et al., 2015)(Fon-
seca et al., 2010). Travel costs have a significant pos-
itive effect on WTP to visit The Kekayon Puppet Mu-
seum. This indicates that when there was an increase
in travel costs, the willingness to pay from respon-
dents for the Kekayon Yogyakarta Puppet Museum
also increased. Some studies have found the effect of
travel cost on WTP of tourist attractions (Van Sandt
and Thilmany, 2016) (Lamsal et al., 2016).
From the binary logistic regression results show
that the visit frequency variable has no effect on
willingness to pay, The respondents who visited the
Kekayon Yogyakarta Puppet Museum were the first
time for the majority. In other words, many re-
spondents just found out information about the the
Kekayon Puppet Museum with the main purpose of
coming to study. The majority of respondents are
young with status still students who do not have
a fixed income or still rely on giving money from
parents. In other words, respondents visiting the
Kekayon Puppet Museum aimed at study and some
of them were for recreational purposes only.
The results of this study are in line with the re-
search conducted by other study (Rozikin, 2016). The
substitution has a significant influence on the value
of willingness to pay to visit the museum. The co-
efficient value of the substitution variable is negative
which indicates that if the respondent visits another
tourist spot, the willingness to pay visitors for repairs
to the facility will be lower. This negative relation-
ship between the substitution variable and the WTP
variable is due to the increasing number of respon-
dents visiting other tourist attractions will reduce the
allocation of visitors to the improvement of museum
facilities. This phenomenon occurs because visitors
have made travel plans and the Kekayon Puppet Mu-
seum is one of the tourist destinations but is not the
main goal of the respondents.
Distance has a significant influence on repairing
facilities at the Kekayon Puppet Museum. This is in
line with other research (Lamsal et al., 2016). The
distance coefficient has a negative sign, indicating that
if the visitor’s residence is further away to the mu-
seum, the willingness to pay visitors for visiting the
museum will be lower. The negative relationship be-
tween the distance variables with WTP variables in
this study is because the farther the distance that must
be taken will reduce the price of admission to the mu-
seum.
The results of this study are similar to the research
conducted other study (Murzyn-Kupisz and Działek,
2013). The facility variable has a significant influ-
ence on the willingness to pay to visit the museum
that will be used for repairing the facilities of the
Kekayon Puppet Museum. The facility variable co-
efficient value is positive which indicate that if the
facilities provided by museum managers are getting
better, it will encourage the willingness to pay visi-
tors for visiting the museum will be higher. So that it
can be concluded that the facility variable has a posi-
tive and significant influence on the increase in WTP.
5 CONCLUSION
The study examines the effect of some determinants
of WTP to visit the cultural heritage site. We sur-
veyed the visitors of the Kekayon Puppet Museum,
Yogyakarta which was one of the cultural heritage site
part of a cultural preservation mission through educa-
tion of tourists about Javanese culture through puppet
(wayang).
The results indicated that 81.4% of the respon-
dents (n=140) willing to pay for visiting the museum,
while the 18.6% (n=32) did not willing. Among
the sociodemographic characteristics, age, sex, edu-
cation and income have effect on WTP to visit the
museum. The travel cost and the facility of the mu-
seum had positive and significant influence to WTP,
respectively. There were the negative effect of substi-
tution of another sites and distance from residence to
the museum to the WTP for visiting the museum.
The low WTP of visitors indicate a low interest
in visitors to cultural heritage tourism especially at
Kekayon Puppet Museum, Yogyakarta. These needs
to be concerned by the museum administrator to pro-
mote the importance of cultural heritage tourism.
They should improve the facilities and attractive spot
visits for visitors who have an interest in cultural
tourism. As one of the cultural heritage site in Yo-
gyakarta, the manager of the Kekayon Puppet Mu-
seum should be increase the facilities for higher ed-
ucation of visitor and an interesting attraction related
to the Javanese cultural.
The future research still needed to confirm the de-
terminants of WTP to visit the museum, as cultural
heritage site in other provinces of Indonesia, as well
as other countries as these effects might change under
different social and cultural conditions. This expected
to increase cultural tourism in Indonesia, which is
known as a country with various ethnic groups that
are rich in culture.
Assessing the Economic Value of Cultural Heritage Site: A Case of the Kekayon Puppet Museum in Yogyakarta
233

REFERENCES
Adamu, A., Yacob, M. R., Radam, A., and Hashim, R.
(2015). Factors determining visitors’ willingness to
pay for conservation in yankari game reserve, bauchi,
nigeria. International Journal of Economics & Man-
agement, 9.
Bateman, I. J., Carson, R. T., Day, B., Hanemann, M., Han-
ley, N., Hett, T., Jones-Lee, M., Loomes, G., Mourato,
S., Pearce, D. W., et al. (2002). Economic valuation
with stated preference techniques: a manual. Eco-
nomic valuation with stated preference techniques: a
manual.
Bedate, A., Herrero, L. C., and Sanz, J.
´
A. (2004). Eco-
nomic valuation of the cultural heritage: application
to four case studies in spain. Journal of cultural her-
itage, 5(1):101–111.
Calleja, A., D
´
ıaz-Balteiro, L., Iglesias-Merchan, C., and
Soli
˜
no, M. (2017). Acoustic and economic valuation
of soundscape: An application to the ‘retiro’urban for-
est park. Urban forestry & urban greening, 27:272–
278.
Chansina, K. and Seenprachawong, U. (2017). Willingness
to pay for historic structures preservation: An empiri-
cal study of vat phou at champasak province, lao pdr.
, 11(1):8–8.
Fadhil, S. F. M., Radam, A., Ya’cob, M. R., and Samdin,
Z. (2017). Willingness to pay on visit to museum:
A concept paper of choice modelling application for
national museum of malaysia. Journal of Islamic,
2(5):47–64.
Fonseca, S., Rebelo, J., et al. (2010). Economic valuation
of cultural heritage: Application to a museum located
in the alto douro wine region-world heritage site.
Gray, C. M. (1998). Hope for the future? early exposure
to the arts and adult visits to art museums. Journal of
Cultural Economics, 22(2-3):87–98.
Hansen, T. B. (1997). The willingness-to-pay for the royal
theatre in copenhagen as a public good. Journal of
cultural economics, 21(1):1–28.
Johnson, P. and Thomas, B. (1998). The economics of mu-
seums: a research perspective. Journal of cultural
economics, 22(2-3):75–85.
Lamsal, P., Atreya, K., Pant, K. P., and Kumar, L. (2016).
Tourism and wetland conservation: application of
travel cost and willingness to pay an entry fee at
ghodaghodi lake complex, nepal. In Natural Re-
sources Forum, volume 40, pages 51–61. Wiley On-
line Library.
Martin, S. (1994). Industrial economics economic analysis.
Mazzanti, M. (2003). Discrete choice models and valuation
experiments. Journal of economic studies.
Morrison, W. G. and Westi, E. G. (1986). Subsidies for the
performing arts: Evidence on voter preference. Jour-
nal of Behavioral Economics, 15(3):57–72.
Murzyn-Kupisz, M. and Działek, J. (2013). Cultural her-
itage in building and enhancing social capital. Jour-
nal of Cultural Heritage Management and Sustainable
Development.
Nandagiri, L. et al. (2015). Evaluation of economic value of
pilikula lake using travel cost and contingent valuation
methods. Aquatic Procedia, 4:1315–1321.
Priambodo, O. and Suhartini, S. (2016). Valuasi ekonomi
kusuma agrowisata kota batu, jawa timur. HABITAT,
27(3):122–132.
Ready, R. C. (2002). ’methods for valuing cultural her-
itage’in stale navrud and richard c. ready (eds.). valu-
ing cultural heritage: Applying environmental valua-
tion techniques to historic buildings, monuments and
artifacts. edward elgar, cheltenham.
Sanz, J.
´
A., Herrero, L. C., and Bedate, A. M. (2003).
Contingent valuation and semiparametric methods: A
case study of the national museum of sculpture in val-
ladolid, spain. Journal of cultural economics, 27(3-
4):241–257.
Tao, Z., Yan, H., and Zhan, J. (2012). Economic valuation
of forest ecosystem services in heshui watershed using
contingent valuation method. Procedia Environmental
Sciences, 13:2445–2450.
Throsby, C. D., Withers, G. A., et al. (1983). Measuring
the demand for the arts as a public good: theory and
empirical results. Economics of cultural decisions.,
pages 177–191.
Van Sandt, A. and Thilmany, D. (2016). Exploring the
economics of agritourists: Customizing travel cost
methods to evaluate differences across the western us.
Technical report.
Wang, Y.-M. and Elhag, T. M. (2007). A comparison of
neural network, evidential reasoning and multiple re-
gression analysis in modelling bridge risks. Expert
Systems with Applications, 32(2):336–348.
ICCETIM 2019 - International Conference on Creative Economics, Tourism Information Management
234
