
Selection between AHP and TOPSIS for Academic Information Systems
Decision Making Model
Jeffry Andhika Putra
1
, Tsabit Rakhman
2
and Muhammad Kunta Biddinika
3
1
Department of Informatics Engineering, Universitas Janabadra, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
2
Department of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
3
Department of Civil Engineering, Universitas Janabadra, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords:
Academic Information System, Open Source, MADM, AHP, TOPSIS.
Abstract:
One way to develop a system of academic information using applications Free Open Source (FOS) that are
circulating. Academic information system developers need to determine the appropriate FOS used to develop
academic information system based on the criteria required and reliability of FOS. One way to help decision-
making can be used MADM models using AHP and TOPSIS. In this study, applying a comparative analysis
of the two methods, the method of AHP and TOPSIS with analytical testing calculations used to compare
the three-applications FOS Academic Information System, Campus Academic Information System (Siakad),
Academic Information Systems Integrated (Sikadu), as well as SISFOKOL to develop academic information
systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
Technological developments have an impact on uni-
versity academic services. At first, the academic ser-
vice is only done by hand using paper media and sta-
tionery (display devices), with the growing scale of
academic service which means user can no longer
do, many universities use Microsoft Office applica-
tions to perform academic services but each univer-
sity institution has its own characteristics so that the
necessary academic service system is unique aca-
demic information in accordance with the needs of
each university. To develop an academic informa-
tion system application do not require large funds
to the presence of Free Open Source (FOS). FOS
helping universities realize the management of infor-
mation technology-based academic services without
thinking about software procurement funds (Rousidis
and Christodoulou, 2019), FOS can be developed and
modified freely adapted to the needs.
It is necessary to pay more attention to deter-
mining FOS according to the needs of each univer-
sity and its reliability because each FOS has advan-
tages and disadvantages. In determining the most ap-
propriate FOS needs and can reliably use the tech-
nique of decision-making methods Multiple Attribute
Decision Making (MADM), including Simple Addi-
tive Weighting (SAW), Weight Product (WP), TOP-
SIS, and AHP methods (Kazimieras Zavadskas et al.,
2019), This study using AHP and TOPSIS later than
the methods are superior and relevant to the research
problems.
AHP is a multi-criterion that can perform
decision-making process with many criteria (Terzi,
2019). AHP superiority compared to other MADM
models are able to analyze simultaneously as well as
integrated between quantitative and qualitative crite-
ria (Distel, 2018). AHP can help facilitate decision-
making by many criteria. Research using AHP pre-
viously been done in the manufacture and analysis of
the rector election system by using AHP (Fitriastuti
et al., 2019), Other studies of AHP has done research
on the selection of open source digital library applica-
tions using AHP with three open source alternatives.
In addition to the AHP, TOPSIS can also perform
multi-criteria decision-making (Distel, 2018) to pro-
vide a solution by comparing each alternative with
the best and worst alternative (Fitriastuti et al., 2019).
TOPSIS widely used on the grounds concept is sim-
ple, easy to understand computation, efficient, and
have the ability to measure the relative performance
of alternatives in the decision of a simple mathemati-
cal form (Distel, 2018). Research by TOPSIS method
was made for selecting suppliers in the pharmaceuti-
cal distribution industry method approach (Putra and
Sylvandinata, 2019).
86
Putra, J., Rakhman, T. and Biddinika, M.
Selection between AHP and TOPSIS for Academic Information Systems Decision Making Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0009878700860089
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Applied Science, Engineering and Social Sciences (ICASESS 2019), pages 86-89
ISBN: 978-989-758-452-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

The problem is how to find a better model of AHP
or TOPSIS in decision making of academic informa-
tion systems at Department of Informatics Engineer-
ing Universitas Janabadra. So, the goal is to produce
the right solution in selecting the appropriate FOS and
more relevant to know the method used in this case
between the AHP and TOPSIS methods.
2 MANUSCRIPT PREPARATION
Following a decision support system theory MADM
models used in this study:
2.1 Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP)
Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) is a functional
hierarchy to the main input of human perception.
Method was developed to search for a rank (priority)
of the various alternatives in solving a problem (Es-
colar et al., 2019). AHP in resolving problems with
some design principles, which must be understood,
such as (Maxwell, 2019); (1) Creating a hierarchy, (2)
Assessment criteria and alternatives, (3) Synthesis of
Priority (Setting priorities), and (4) Logical consis-
tency.
2.2 AHP Steps
There are several steps in the completion of the AHP
method, as follows (G
¨
urb
¨
uz, 2019):
1. Defining the problem and determine the desired
solution, then hierarchical structuring.
2. Prioritization; (a) the contribution size of each ele-
ment to achieve the goal, (b) compiled by the rela-
tive level of interest of each element, (c) summing
columns, (d) creating a new matrix by means of
each element divided by the number of columns,
(e) summing lines, (f) creating a new matrix with
elements result the number of rows divided by the
total sum. The results of the final division called
Eigen Vector.
3. Logical consistency Consistency means two
things: first that thought or similar objects are
grouped according to homogeneity and relevance.
The second meaning is that the consistency of the
intensity of the relationships between ideas or ob-
jects based on a certain criterion to justify each
other logically; (a) create new matrix by multi-
plying the initial matrix with Eigen Vector, (b)
add up in rows, (c) for the sum with Eigen Vec-
tor, the division called Eigen Value, (d) Count the
ways by; (i) add up by Eigen Value, (ii) the sum
is divided by the order, then the result is called a
lambda max or t, (iii) calculate CI (Consistency
Index), (iv) calculate CR (Consistency Ratio)
4. Rin is the Random Index. Random Index (RIN),
also called Random Consistency (RC) (G
¨
urb
¨
uz,
2019) during the CR value does not exceed 10%,
or 0.10, the value given paired comparisons are
considered consistent.
5. Priority calculate Alternatives There are two types
of data on the alternative, namely the qualitative
as well as quantitative data types. The calculat-
ing a priority of these two data types are different,
the qualitative data is by comparing each alterna-
tive. Comparisons were by pairwise comparison
matrix similar to determining the priority crite-
ria in step number two above. Quantitative data
on the priority type depends on the type of crite-
ria (sub-criteria), namely, the cost (cost) and gain
(benefit) ((Distel, 2018).
2.3 Stage Data Collection
Collecting data is through observation and literature
study. The observations were to collect data and infor-
mation, as well as exploring and comparing the sys-
tem, interviews were conducted with the management
of the department, a literature study is to understand
the application well as understand the concept of the
application of AHP and TOPSIS via the internet, pa-
pers, journals, and books that are relevant.
2.4 Preliminary Analysis Phase
Initial analyzes do an analysis of the criteria and
the application of methods in selecting the FOS for
the development of academic information systems
(Uskov et al., 2017) . There are two application meth-
ods in this case is the method of AHP and TOPSIS.
Then they will be compared to find more relevant
method used to select the appropriate FOS.
2.5 Testing Phase
The testing phase is done by analyzing the compara-
tive analysis with conformity to calculate the degree
of conformity (Tki) on each method using the for-
mula: -
T k
i
=
Xi
DataFADM(100%)
(1)
Where Tki = Suitability, Xi = average scores of
data methods. Looking Xi using the formula:
Selection between AHP and TOPSIS for Academic Information Systems Decision Making Model
87
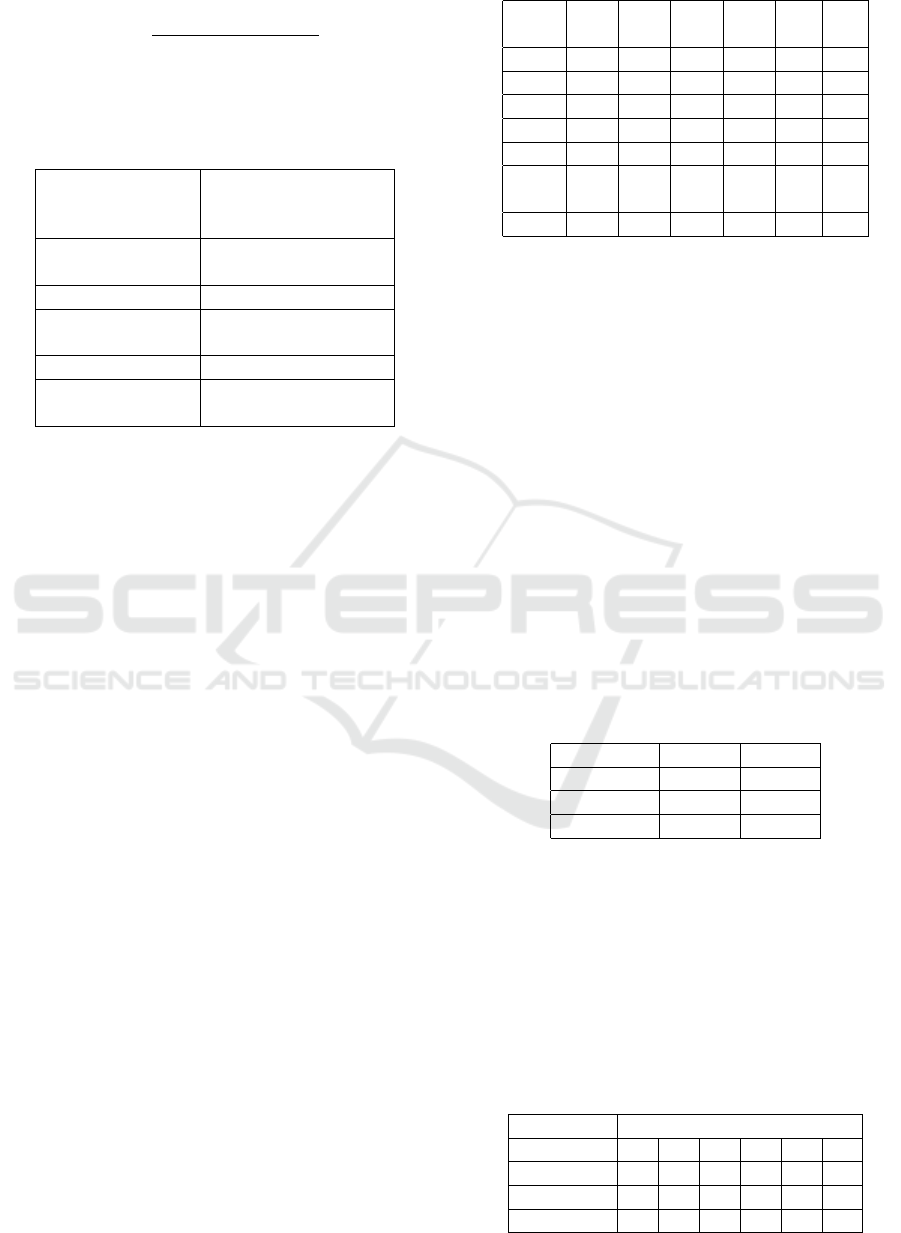
X
i
=
ΣDataAHPorTOPSI
n
(2)
Concordance rate is measured by the percentage
level at Table 1.
Table 1: Table Percentage level of concordance
The percentage
rate of confor-
mity
Category
31% - 45% Unsatisfactory / no
good
46% - 60% Unsatisfactory / poor
61% - 75% Quite satisfactory /
good enough
76% - 85% Satisfactory / good
86% -100% Very satisfactory /
good
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The initial phase of the analysis is to describe the al-
ternative open source applications are required selec-
tion criteria to give weight to the criteria in order of
importance and needs. As an alternative application is
given as follows; (1) Campus Academic Information
System (Siakad), (2) Integrated Academic Informa-
tion System (Sikadu), (3) SISFOKOL.
Six criteria were used here; features, technology,
source code program, flexibility and support the de-
veloper. Each criterion is determined whether the na-
ture of cost/benefits, costs mean less value the good,
while the profits instead. On the criteria here, all
categorized advantage. Furthermore, each criterion
is weighted based on the results of the third explo-
ration application, interview-related needs, and inter-
view some expert programmers, further testing using
AHP and TOPSIS.
3.1 Calculation Method of AHP
In the hierarchy there are six main criteria of Ease
(Kem), Features (Fit), Source Code (Sourc), Flexibil-
ity (Fleks), as well as support the Developer and the
Community (Duk).
Step 1. Develop a pairwise comparison matrix us-
ing the concept of Saaty intensity scale, as shown in
Table 2.
Table 2: Pairwise Comparison Matrix
Crit
eria
Kem Fit Tek sou
rc
refl
ex
kerc
hief
Kem 1 3 3 1 4 3
Fit 0.33 1 1 0.33 3 1
Tek 0.33 1 1 0.33 3 1
sourc 1 3 3 1 4 3
reflex 0.25 0.33 0.33 0.25 1 0.33
kerch
ief
0.33 1 1 0.33 3 1
total 3.24 9.33 9.33 3.24 18 9.33
Step 2. Normalization of each column (A’) and
calculating the average of each row (W).
a) Normalization of each column (A’), each entry
matrix divided by the total number of columns.
b) Calculating the average of each row (W). The av-
erage of each row of the matrix entries and the
results are expressed as a priority vector.
Step 3. Calculate the consistency index (CI):
count (A) (W
t
)
CR = 0.0162 / 1.24 = 0.0131
CR < 0.1, so consistent.
CR = 0.0162 / 1.24 = 0.0131 CR < 0.1, so consis-
tent.
Step 5. Ranking of the calculation based on the
weight of each criterion, do multiplication weighting
each criterion to the weights of the level of interest
among the criteria. The results can be seen in Table 3.
Table 3: Ranking of results tables
Result Rank
SISFOKOL .2495 3
Sikadu .3262 2
Siakad .3514 1
3.2 Calculation Method of TOPSIS
Step 1. Determine the importance scale of each cri-
terion (C1), features (C2), technology (C3), program
source code (C4), flexibility (C5), developer and com-
munity support (C6), rated on a scale up to five and
decision makers give preference to weight on the
same scale. The results can be seen in Table 4.
Table 4: Scale the importance of each criterion
Alternative Criteria
1 2 3 4 5 6
Siakad
Sikadu
SISFOKOL
ICASESS 2019 - International Conference on Applied Science, Engineering and Social Science
88

Step 2. Normalize matrix (R) decision.
Step 3. Calculation of weighted normalized ma-
trix (Y), that is by multiplying the normalized matrix
(R), by weighting preference (W)
Step 4. Determine the positive ideal solution (A+)
and the ideal negative solution (A-)
Step 5. Determine the distance between the
weighted values of each alternative to the ideal pos-
itive solution (Si+) and the ideal negative (Si-) solu-
tion.
Step 6. Calculate the proximity of each alternative
to the ideal solution Analysis of AHP calculations and
TOPSIS.
Criteria ranking is determined based on rules that
have the highest weight value are in the first priority
to be chosen and occupy the first rank. Sequential
ranking starts from the criteria having the largest to
the smallest weight value. The results of ranking with
the AHP and TOPSIS methods can be seen in the fol-
lowing Table 5:
Table 5: AHP and TOPSIS ranking
Alternative Weight value AHP
rank-
ing
TOPSIS
rank-
ing
AHP TOPSIS
Siakad 0,3514 0,7228 1 1
Sikadu 0,3262 0,3741 2 4
SISFOKOL 0,2495 0,5728 3 2
Based on the table above, an analysis is con-
ducted to find out the relevant methods for the prob-
lem by calculating the level of suitability (Tki) of each
method. To find out the results of the level of con-
formity (Tki), the first step is to find out the average
value in each method. calculated using the following
formula:
Xi
AHP
=
1, 1005
4
= 0, 275125
Xi
TOPSIS
=
2, 217
4
= 0, 53175 (3)
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of a comparison analysis between
the level of conformity (Tki) of AHP method and
TOPSIS, both methods are in a very satisfying range
in assisting decision making in the MADM model but
for cases that use qualitative data and multicriteria
AHP method is more suitable to use than TOPSIS.
The ranking results using the AHP and TOPSIS meth-
ods are the same in rank 1 category, but different in the
next ranking. Siakad can be taken as FOS to develop
academic information systems. The AHP method has
a higher level of suitability than the TOPSIS method,
so the use of the AHP method is more relevant to the
problem and can be used as one of the decisionmaking
models for the MADM application that best meets the
criteria. This research still has deficiencies in terms
of determining the weight of criteria and determining
the level of importance because it is still based on the
perceptions of decision makers obtained from inter-
views and some experts in their fields are not based
on processing the results of the questionnaire.
REFERENCES
Distel, B. (2018). Bringing light into the shadows: A qual-
itative interview study on citizens’ non-adoption of
e-government. Electronic Journal of e-Government,
16(2).
Escolar, S., Villanueva, F. J., Santofimia, M. J., Villa, D.,
del Toro, X., and L
´
opez, J. C. (2019). A multiple-
attribute decision making-based approach for smart
city rankings design. Technological Forecasting and
Social Change, 142:42–55.
Fitriastuti, F., Setiyorini, A., and Putra, J. A. (2019).
Meausuring the quality computer based test services
using servqual method (case study admission system
university of janabadra). In Journal of Physics: Con-
ference Series , volume 1175, page 012074. IOP Pub-
lishing.
G
¨
urb
¨
uz, T. (2019). Strategy formulation using a hybrid
mcdm approach for strategic position and action eval-
uation (space) matrix method. Journal of Aeronautics
and Space Technologies, 12(1):1–17.
Kazimieras Zavadskas, E., Antucheviciene, J., and Chat-
terjee, P. (2019). Multiple-criteria decision-making
(mcdm) techniques for business processes information
management.
Maxwell, J. A. (2019). Distinguishing between quantita-
tive and qualitative research: A response to morgan.
Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 13(2):132–137.
Putra, J. A. and Sylvandinata, A. (2019). The influence of
e-learning design with ease of use as a factor of in-
creasing student achievement: A literature review. In
Journal of Physics: Conference Series, volume 1175,
page 012070. IOP Publishing.
Rousidis, D. and Christodoulou, G. (2019). A guide for
the optimum selection of a free open source integrated
library system. Qualitative and Quantitative Methods
in Libraries, 7(1):39–49.
Terzi, E. (2019). Analytic hierarchy process (ahp) to solve
complex decision problems. Southeast Europe Jour-
nal of Soft Computing, 8(1).
Uskov, V. L., Bakken, J. P., Howlett, R. J., and Jain, L. C.
(2017). Innovations in smart universities. In Inter-
national Conference on Smart Education and Smart
E-Learning, pages 1–7. Springer.
Selection between AHP and TOPSIS for Academic Information Systems Decision Making Model
89
