
Blockchain Technology for University Diploma Certificate
Meyliana
1
, Yakob Utama Chandra
1
, Cadelina Cassandra
1
, Henry Antonius Eka Widjaja
1
, Surjandy
1
,
Erick Fernando
1
, Jonas Aditya Sunandar
2
and Harjanto Prabowo
3
1
Information Systems Department, School of Infomration Systems, Bina Nusantara University, Jakarta, Indonesia
2
School of Computer Science, Bina Nusantara University, Jakarta, Indonesia
3
Computer Science Department, BINUS Graduate Program – Doctor of Computer Science, Bina Nusantara University,
Keywords:
Blockchain, University Certificate Diploma, Simulation Test, Blockchain for Publishing Certificate, Multi-
Chain
Abstract:
University Diploma certification is the valuable document published one time by university for student who
graduated and never generated twice. The worthy of university Diploma Certification document brings a lot
of changes for owner; therefore, many people try to falsify the university diploma certification. Several falsify
university diploma certification founded by ministry of higher education in Indonesia for the last several years,
and recently, this study tries to explore the new Blockchain technology as facilitator to solve the problem and
due to the characteristic of Blockchain that immutable, peer-to-peer, distributed possible to apply. Several
early studies found and reported theoretically, Blockchain technology is possible to solve the falsify university
diploma certificate issues. Therefore, this business process simulation testing tries to explore the possibility
of using Blockchain Technology for university certificate, McRhys model used as framework for publishing
the university certificate diploma and the result of this study may increase the likelihood of implementation of
Blockchain Technology to produce the university certification diploma that immutable and reduce the forgery
of university certificate diploma.
1 INTRODUCTION
University certification diploma (UCD) that produce
once by university is a valuable document for the uni-
versity student for his/her future career and might pos-
sible to use for identity as well. The UCD might not
likely to produce twice. Somehow, several people try
to fabricate the UCD. In the last several year higher
ministry of education in Indonesia was found and
some technic to fabricate UCD found (Adiya, 2017)
(Agriesta, 2017) and the similar case was found in
2015 as well (Linggasari, 2015).
Contemporary, the ministry of higher education
in Indonesia is trying to prevent the fabricate UCD
in the future. Blockchain technology founded by
Satoshi Nakamoto (unknow as a group name or a per-
son name) in 2008 (Nakamoto et al., 2008) that have
characteristic immutable, unchangeable, distributed,
peer-to-peer, consensus might be facilitated to solve
the issues.
Early research reported that new Blockchain
technology might be apply in several indus-
try such as enterprise system (Swan, 2015),
Health/medicine(Vruddhula, 2018)(Sylim et al.,
2018) , Governance (Paech, 2017), Supply Chain
Management (Kayikci, 2018) (Fernando et al., 2018)
(Meyliana et al., ) and education as well(Palma
et al., 2019) (Grech and Camilleri, 2017) (Devecchi
et al., 2017) in education sector thermionically
reported Blockchain Technology very possible to
facilitate the issue of falsify university certificate
diploma. This ongoing experimental study will focus
on the usage of Blockchain for publishing UCD,
the private and permissioned Blockchain called
Multichain(Greenspan, 2015) used in this simulation
test study, McRhys as a framework used in this study,
especially part of publish process of university cer-
tificate diploma (Meyliana et al., ), this is research is
a continuation of previous research who successfully
create the McRhys framework, in this research will
try to simulation of implement to one of Blockchain
system and applications which is Multichain, the
system and applications will use “asis” condition no
modification has been made. The research tries to
Meyliana, ., Chandra, Y., Cassandra, C., Widjaja, H., Surjandy, ., Fernando, E., Sunandar, J. and Prabowo, H.
Blockchain Technology for University Diploma Certificate.
DOI: 10.5220/0009907801930198
In Proceedings of the International Conferences on Information System and Technology (CONRIST 2019), pages 193-198
ISBN: 978-989-758-453-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
193
explore the possibility of using “asis” Blockchain for
university certificate diploma.
Focus group discussion have been made with sev-
eral parties that capable in UCD production such
as Rectorate unit manager, academic supporting unit
manager, student registration and scheduling unit
manager, academic operation manager, Student Ad-
visory Unit manager. Thus, the study will show the
result of using Blockchain technology to enhance the
existing system to produce UCD become robust.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW AND
METHODOLOGY
In this section will explain about Blockchain, Pri-
vate and Permissioned Blockchain, Research Design,
Business Process Simulation Testing, and Distributed
monitoring and one-time process publish diploma cer-
tificate method.
2.1 Blockchain
Blockchain is a new technology found in 2008
by a person or a group that commonly known as
Satoshi Nakamoto and since 2014 Blockchain with
the smart contract feature makes Blockchain possi-
ble to implement or use for enterprise system (Swan,
2015), such as for Supply Chain Management logis-
tic(Sadouskaya, 2017) (Marr, 2018) (Meyliana et al.,
) , health industry (Kumar and Tripathi, 2019) (Tseng
et al., 2018) and Education sector (Palma et al., 2019)
(Turkanovi
´
c et al., 2018).
2.2 Private and Permissioned
Blockchain
Many types of Blockchain contemporary, permis-
sion less Blockchain it means no permission rules on
the Blockchain system, for example, is Bitcoin apps
where everyone can see the transaction, and everyone
can write or perform the operation. The other types of
Blockchain is permission Blockchain, where there is
permission or rule that can be set on the Blockchain.
For example, MultiChain (Greenspan, 2015) it means
everyone can write or make the transaction, but only
particular person that have permission.
2.3 Research Design
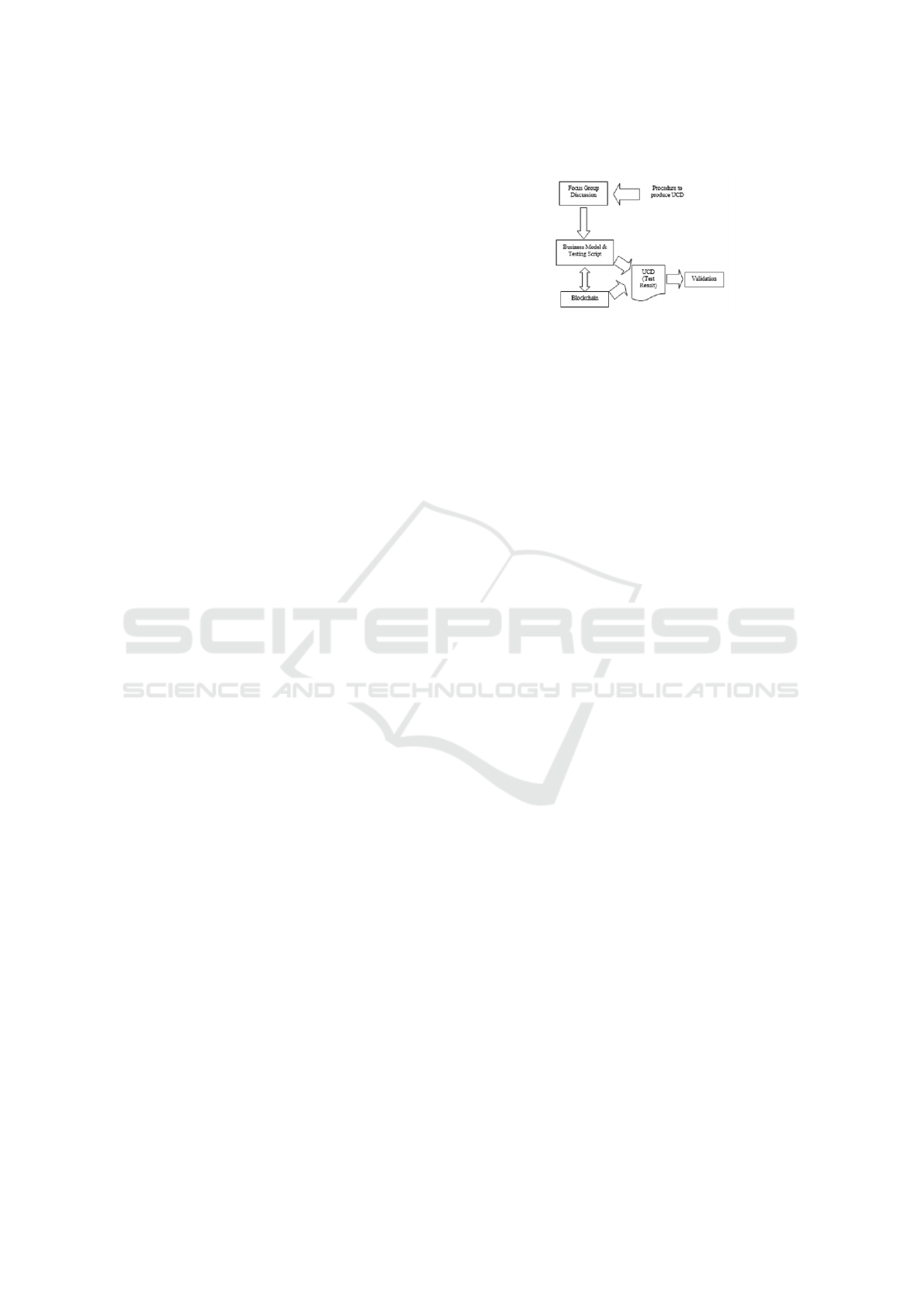
The stage of research in this study start with focus
group discussion to discuss about procedure to pro-
duce UCD, the detail can be seen at figure 1.
space
Figure 1: Research Design & Simulation Step
2.4 Business Process Simulation Testing
Business Process Simulation Testing (BPST) is a
part of Business Process Reengineering. BPST is a
method used in this research. BPST is one of the
green testing methodologies that use minimum re-
sources; the result of the test considers reliable and
similar to real. Steps for BPST start with an expla-
nation of the system used, business model, and sce-
nario of testing, testing result and validation (Rosen-
thal et al., 2018).
2.5 Distributed Monitoring and
Onetime Process Publish Diploma
Certificate Method
This study used Blockchain Technology to issue uni-
versity certificate. However, to minimize the forgery
of diploma certificate, this study used the Distributed
Monitoring method and one time publish certificate
diploma.
Blockchain with distributed ledger system will
share the absent student activity, student course score,
thesis final exam result to all related parties (student
center, judicium unit, academic service) to be moni-
tored before the diploma certificate publish, if the stu-
dent meet all conditions and agreed by all parties then
the student data and information will be transferred
to judicium unit and the diploma certificate will only
publish 1 time in life from judicium unit to univer-
sity student. The process exhibit in Figure 2, where
all parties link in Blockchain and its model is part of
McRhys Framework (Meyliana et al., ). By using the
method, the falsify of diploma university can be min-
imized and not controlled by a single department that
may cause the fraudulence.
Figure 2 shows the McRhys business process to
produce university certificate diploma, from student
activities such as course registration, student lecturing
activities and so on will be recorded in Blockchain,
the other activities that will be recorded in Blockchain
such as Lecturer activities such as lecturing, giving
CONRIST 2019 - International Conferences on Information System and Technology
194

score of exam, and all the activities will be validated
by respective department, for example, scoring exam
from lecturer to student will be verified by academic
operation, study activity will be confirmed by aca-
demic service, thesis defense will be approved by
Faculty office, Academic service. However, after stu-
dent can fulfil all requirement than the graduation will
be prepared, faculty office together with rectorate of-
fice, student advisory center, and student activity unit
will arrange the necessary document required until
university certificate diploma publish.
Figure 2: Blockchain Process to Publish Certificate
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The environment of Blockchain laboratory will be
described in this part from operating system usage,
database, Blockchain setup environment. The proce-
dure of this experiment is exploring the possibility of
the design to fill the UCD information to Blockchain
Database or field. In this stage, there is no com-
munication or networking aspect has been discussed;
web applications or mobile application will not be ad-
dressed or reported.
3.1 System Information of Operating
Systems
An operating system is one of the essential parts. The
Blockchain lab uses Ubuntu as an operating system
and can be seen in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Operating System
3.2 System Information of Database
Beside operating system, another important aspect is
a database, in this case, the Blockchain Lab using or-
dinally database, which is an SQLite database.
3.3 Application Structure of a Node
Figure 4: Blockchain Node
The hierarchy of MultiChain is a node as a one
Private Blockchain and is a node; there are many ad-
dresses can be created, and each address might pos-
sible to have an asset. In this Blockchain Lab, only
single node applied in the server or single node. The
picture captured from MultiChain dashboard menu,
see in Figure 4.
Many addresses are possible to create in a node
and address commonly known as pseudo-name that
created by using hashing 256 technique, and in a sin-
gle node, it possible to create many addresses.
In Figure 5 can be seen address and MultiChain
allowed the set label to make it easy to identify the
address, besides the Label, it can be seen the permis-
sion set for each address The last is an asset; asset can
be transferred by assigned the ownership to address in
this case address represent the university student see
figure 6.
Figure 5: Blockchain Addressees in Node
Blockchain Technology for University Diploma Certificate
195
space
Figure 6: Blockchain Asset
3.4 Implementing Blockchain
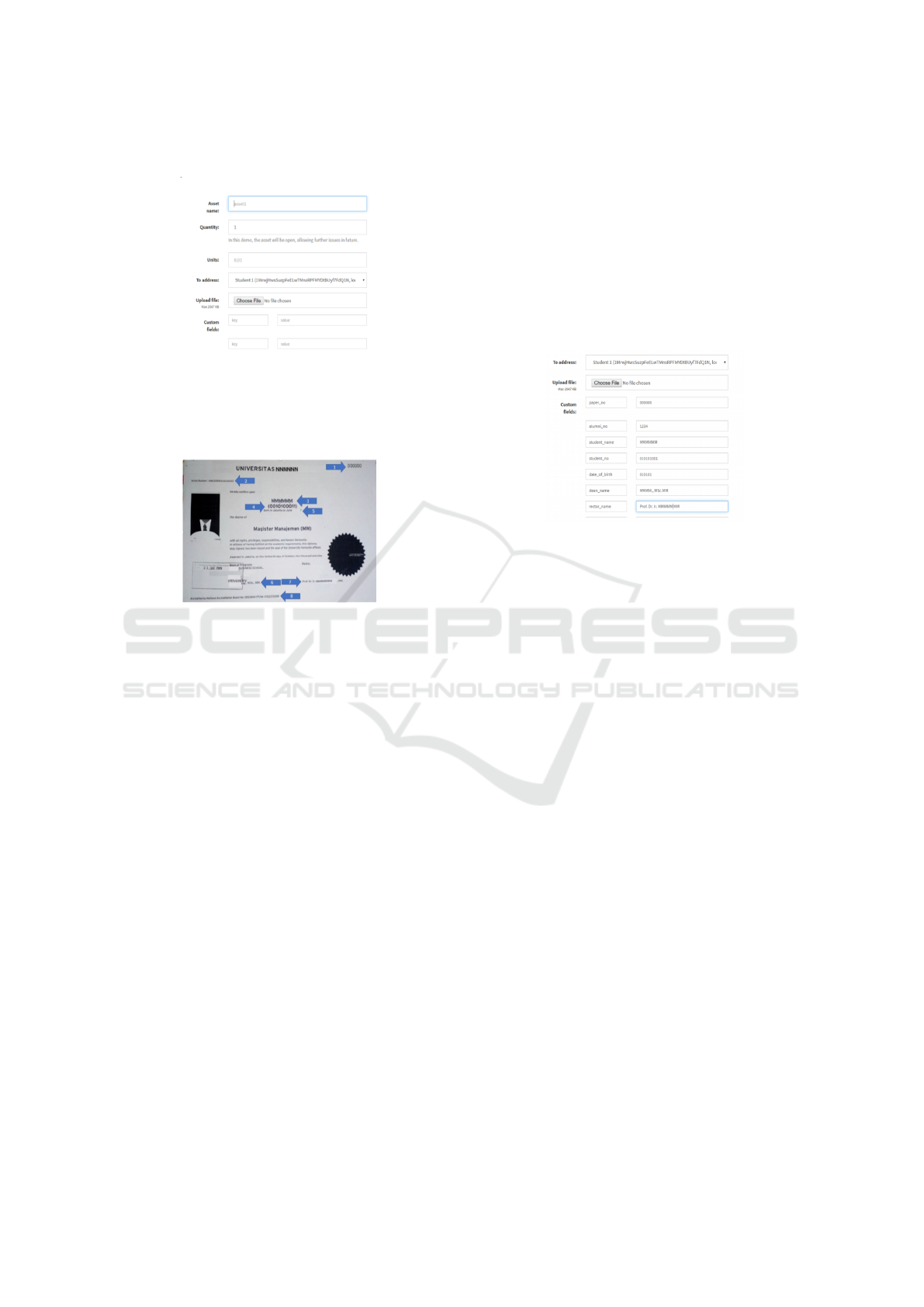
Figure 7: University Certificate Diploma
In this part will show how Blockchain can be ap-
plied to produce UCD. From figure 6 is an example of
UCD and there are eight essential fields found,
• Point 1 is paper number, is a unique number that
represents sequence paper number.
• Point 2 is alumni number, is a unique number that
represents of alumni number after graduated from
the university.
• Point 3 is the student name, is a student name who
graduated from the university.
• Point 4 is student number, is a unique number that
represents of student number, used while studying
in the university.
• Point 5 is a student date of birth, is a dateof-birth
of the student.
• Point 6 is authorized signature, is a name of the
authorized person that will give a signature on the
university certificate diploma, for example, is a
dean.
• Point 7 is rector signature, is an authorized person
that will sign the university certificate diploma.
• Point 8 is ministry higher education certificate
number, is a unique number come from the min-
istry of higher education,
Exhibit in Figure 7, it can be implemented with
Blockchain in asset area, can be seen in Figure 6,
where the field of the asset can be inputted with the in-
formation from UCD. By following this technique, all
the information written on the Blockchain will be pro-
tected (hash), unchanged, and immutable. Figure 8
can be seen the asset field filled with the value of UCD
such as paper number, alumni number, student num-
ber, date of birth, authorized signature person name
(dean and rector), and the last is registry number from
the ministry of higher education.
Figure 8: Blockchain UCD
3.5 Discussion
The benefit of the characteristic of Blockchain to pro-
duce UCD
• Immutable, by using blockchain technology the
university certificate diploma will be existing for-
ever started the date of the certificate published
• Unchanged, the data on the university certificate
diploma will never be changed forever, and cannot
be falsified
• Distributed, the one who has the ability to see the
university certificate diploma will be able to see
the UCD.
• Secure, by using Blockchain, the information is
protected (hashing), and the Merkle Tree method
applied using multiple hashing technique. There-
fore, all transactions written on Blockchain will
be secured. The value of each field, such as paper
number, alumni number, student name (see figure
7), will be protected and cannot be changed and
immutable or exist forever. No duplication UCD
can happen.
Implementation of Blockchain in producing UCD
makes the consistency of information, and the relia-
bility of UCD can be ensured, protect the brand image
of the university.
On the other hand, the limitation of the implemen-
tation of Blockchain for UCD has been detected as
well, even though the project is running recently. The
challenge found such as
CONRIST 2019 - International Conferences on Information System and Technology
196

• Duplication of data, where the data exist in the
contemporary system and at Blockchain.
• Double posting, the data should post twice to or-
dinary database and Blockchain database.
3.6 Simulation Testing Result
Validation
Validation is one of the critical parts of the simulation
test to ensure the result meets with the requirement.
The validation of testing result has been done by a
university-related party such as vice-rector, rector of-
fice that directly involved in this part.
3.7 Simulation Testing Exclusion or
Challenge
The simulation testing will not cover system scala-
bility; no customization has been made (use “asis”
system). The several challenges found during the
simulation test such as the recent business process
need to adjust, cause the business process might not
be possible to operate as Blockchain system char-
acteristic such as no update or changes of data is
allowed (except creating another transaction), inte-
gration between Blockchain system application and
contemporary system used require plan, for exam-
ple, the primary key and Blockchain address need to
match. However, during the double-entry simulation,
the strategy is applied or manual entry due to time
constraint. Therefore, business process reengineering
will be involved in the university operation in case
Blockchain will be used in the future.
The lack of knowledge about Blockchain Technol-
ogy as one of the challenges found during the simu-
lation test, the many times explanation of Blockchain
Technology had been done during the discussion, the
recent system and application development method
cannot apply directly into the Blockchain system and
application, and database concept, such as distributed
Blockchain characteristic it should be implemented
carefully because of data secrecy referred for uni-
versity certificate diploma (no duplication of certi-
fication number, student number, alumni number).
Blockchain system application challenge, the stan-
dard Blockchain system application used in the simu-
lation testing, not the enterprise Blockchain, the lower
security mode used. Therefore, there will be a gap in
the security process transaction (hashing calculation
process) in the future.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This study of Blockchain for UCD is in the right
stage. The next phase will be discussed for uni-
versity student transcripts connecting to Blockchain
with other industry that produces certification such as
IBM, Microsoft, Oracle, etc. Besides that, the most
important part is the connection to the Ministry of
Higher Education as the center of certification regis-
tration in Indonesia. In this research, McRhys uni-
versity model or framework is applied especially for
university certificate diploma process. It can be used
and adapted with Blockchain Technology, especially
with Multichain Blockchain system and application.
The simulation test represents the objective of the re-
search yet not comprehensive in some aspects.
The distributed monitoring and one-time diploma
certificate issuance are focused on Blockchain Tech-
nology. It functionates to minimize the falsification
and fraudulence of university diploma certificate. At
the same level, the department can mitigate the issue.
Because of the inevitable changes of information in
university, diploma certificate will be recorded in the
Blockchain system and application; Any attempts to
modify the field of the database will be protected by
Blockchain mechanism. It implements hashing 256
and Merkle tree method that operated multiple hash-
ing on each level of data in the database.
The scalability and time constrain of Blockchain
Technology system need to be tested due to the vast
publish of certificate diploma. The scalability might
be changed in the future due to the Blockchain is in
developing phases for an enterprise system to accel-
erate the process. The problem related to a fake cer-
tificate is possible to solve by Blockchain technology.
The future research is required to improve the scala-
bility of the system, infrastructure design, integration
process between the new system, and Blockchain sys-
tem application at the end.
Future study required to continue this research
by putting some dummy data (for example, 25% to
50% of total in real graduated certificate diploma) that
should publish in the same date and calculate the pro-
cessing time consume by Blockchain.
Blockchain Technology for University Diploma Certificate
197

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study is supported by the Directorate Gen-
eral of Strengthening for Research and Develop-
ment, Ministry of Research, Technology, and Higher
Education, Republic of Indonesia as a part of
Penelitian Terapan Unggulan Perguruan Tinggi Re-
search Grant to Binus University entitled “Implemen-
tasi Blockchain Platform Untuk Menciptakan “Good
Governance” pada Perguruan Tinggi” or “The Im-
plementation of Blockchain Platform to Create“Good
Governance” in Higher Education” with contract
number: 12/AKM/PNT/2019 and contract date: 27
March 2019.
REFERENCES
Adiya, N. (2017). Kasus ijazah palsu, ketua lembaga pen-
didikan di samarinda ditangkap.
Agriesta, D. (2017). Menristek dikti minta seluruh pembuat
ijazah palsu ditangkap.
Devecchi, C., Turner, S., Armellini, A., Brooks, I., Mel-
lish, B., Petford, N., Taeed, O., and Hadawi Cbe,
A. (2017). Ser05 blockchain educational passport
blockchain educational passport: Decentralised learn-
ing ledger (dll).
Fernando, E., Spits, H. L. H., Kosala, R., Abdurachman,
E., and Supangkat, S. H. (2018). Key factor adoption
blockchain technology in smart supply management:
Literature review. In 2018 International Seminar on
Research of Information Technology and Intelligent
Systems, pages 99–102.
Grech, A. and Camilleri, A. F. (2017). Blockchain in edu-
cation.
Greenspan, G. (2015). Multichain private blockchain-
white paper. URl: http://www. multichain.
com/download/MultiChain-White-Paper. pdf.
Kayikci, Y. (2018). Sustainability impact of digitization in
logistics. Procedia Manufacturing, 21:782–789.
Kumar, R. and Tripathi, R. (2019). Traceability of coun-
terfeit medicine supply chain through blockchain. In
2019 11th International Conference on Communica-
tion Systems & Networks (COMSNETS), pages 568–
570. IEEE.
Linggasari, Y. (2015). Menteri nasir: 187 pemilik ijazah
palsu punya jabatan penting.
Marr, B. (2018). How blockchain will transform the sup-
ply chain and logistics industry. Retrieved February,
22:2018.
Meyliana, Y. U. C., Cassandra, C., Surjandy, H. A. E., Wid-
jaja, E. F., Prabowo, H., and Joseph, C. Defying
the certification diploma forgery with blockchain plat-
form: A proposed model.
Nakamoto, S. et al. (2008). A peer-to-peer electronic cash
system. Bitcoin.–URL: https://bitcoin. org/bitcoin.
pdf.
Paech, P. (2017). The governance of blockchain finan-
cial networks. The Modern Law Review, 80(6):1073–
1110.
Palma, L. M., Vigil, M. A., Pereira, F. L., and Martina, J. E.
(2019). Blockchain and smart contracts for higher
education registry in brazil. International Journal of
Network Management, 29(3):e2061.
Rosenthal, K., Ternes, B., and Strecker, S. (2018). Business
process simulation: A systematic literature review.
Sadouskaya, K. (2017). Adoption of blockchain technolo-
gyin supply chain and logistics.
Swan, M. (2015). Blockchain: Blueprint for a new econ-
omy. ” O’Reilly Media, Inc.”.
Sylim, P., Liu, F., Marcelo, A., and Fontelo, P. (2018).
Blockchain technology for detecting falsified and sub-
standard drugs in distribution: pharmaceutical sup-
ply chain intervention. JMIR research protocols,
7(9):e10163.
Tseng, J.-H., Liao, Y.-C., Chong, B., and Liao, S.-w.
(2018). Governance on the drug supply chain via
gcoin blockchain. International journal of environ-
mental research and public health, 15(6):1055.
Turkanovi
´
c, M., H
¨
olbl, M., Ko
ˇ
si
ˇ
c, K., Heri
ˇ
cko, M.,
and Kami
ˇ
sali
´
c, A. (2018). Eductx: A blockchain-
based higher education credit platform. IEEE access,
6:5112–5127.
Vruddhula, S. (2018). Application of on-dose identifica-
tion and blockchain to prevent drug counterfeiting.
Pathogens and global health, 112(4):161–161.
CONRIST 2019 - International Conferences on Information System and Technology
198
