
Analysis of Oros Modeler Data Reporting Process to SAP HANA in
Activity based Costing for Indonesia Telecommunication Industry
Dennis Nigel Cunong
1
, Muhardi Saputra
1
and Warih Puspitasari
1
1
Information System, School of Industrial and System Engineering, Telkom University, Bandung 40257, Indonesia
Keywords:
Oros Modeler, SAP HANA, Activity Based Costing, SAP Activate, Enterprise Resource Planning
Abstract:
PT.XYZ is involved in providing a wide range of telecommunications services and telecommunications net-
works throughout Indonesia. Oros Modeler is an application that has been used by PT.XYZ for a long time.
There is no detailed product cost breakdown in Oros Modeler’s funding and reporting process, so the infor-
mation obtained from Oros Modeler is only the actual cost (total cost of production). As a result, the industry
regulation PER-02 / MBU / 2013 was created, which can be designed to support applications for business
process objectives, so PT.XYZ hopes to implement SAP HANA with the goal of reporting results that are
expected to contain only SAP components. Components are formed to model the final product through cost-
based activity modeling. The method used is the SAP Activate method. SAP HANA can be identified by its
constituent components by reporting each product that constitutes a cost object, there by identifying each cost
object product offered by PT.XYZ in more detail and more accurately.
1 INTRODUCTION
Oros Modeler is an application that is used to model
Activity Based-Costing (ABC). Oros Modeler can
map the cost of each division and can distribute it
to each subdivision within it. Oros Modeler can
store all information in one model by classifying
each for costs, departments and each existing process
(ABC Technologies, 2001).
Based on the Regulation of the Minister of State-
Owned Enterprises Number: PER-02 / MBU / 2013,
explains that in managing Information Technology,
companies can design detailed applications that are
tailored to the direction of the organization in the next
3-5 years.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is one of the
lastest technology technologies that many organiza-
tions have undertaken (Sadrzadehrafiei et al., 2013)
. ERP system is an enterprise package to integrates
all necessary business functions into a single system
with a shared database. This software package can be
customized to the specific needs of each organization
(Matende and Ogao, 2013). ERP management cov-
ers all the key areas of business, from accounting and
budgeting, human resource management, document
circulation to reporting (Ociepa-Kubicka, 2017). SAP
is a proven and widely used ERP application capable
of integrating multiple business modules, with each
module representing a specific business function (Jun-
narkar and Verma, 2017). Data analysis is the process
to check the data with the goal of answer a business
question to support decision making. Analysis can
reveal powerful can uncover why something is hap-
pening and what can do about it. Reporting uses data
to track the performance of business, while analysis
uses data to answer a strategic question for business.
Reporting and analysis rely on each other. Reporting
explain about what question to ask, and analysis at-
tempts to answer those questions. (Data Hero, 2019)
PT XYZ is the largest company in the field of
telecommunications in Indonesia. previously PT
XYZ had used the Oros modeler in allocating finan-
cial data and control, but the Oros modeler application
was out of date because the Oros modeler was offline
and not real-time and the reporting results only dis-
played the actual cost of various products made (total
of the cost of the product made) so it is not known how
many constituent components are in making a prod-
uct so information is not detailed and specific. use
SAP HANA especially using the activity-based cost-
ing module (CO-OM-ABC) so that each Cost Object
Product produced can be known what compiler com-
ponents are needed to produce the desired Cost Object
so that the results of reporting become more detailed
and more accurate in identifying each Cost Object in
PT XYZ. This research aims to compare the results
246
Cunong, D., Saputra, M. and Puspitasari, W.
Analysis of Oros Modeler Data Reporting Process to SAP HANA in Activity based Costing for Indonesia Telecommunication Industry.
DOI: 10.5220/0009908602460252
In Proceedings of the International Conferences on Information System and Technology (CONRIST 2019), pages 246-252
ISBN: 978-989-758-453-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

of reporting on the Oros model and the SAP HANA
which applications are suitable for the application of
large amounts of data and help the process of identi-
fying product cost objects become more specific.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Oros Modeler
Oros Modeler facilitates the creation of activity in-
formation to help manage, store and determine all re-
source expenditures in process, product and service
activities. Oros Modeler stores all information in a
database called a model. Each model has activity in-
formation for each specific activity (ABC Technolo-
gies, 2001). Oros Modeler can use fast and flexible
Activity BasedCosting (ABC) modeling. Information
in the modeis governed by a structure called mod-
ules. Modules organize each model’s information to
make it easy to understand. A model in Oros Modeler
is composed of three component modules consisting
(ABC Technologies, 2001) :
Figure 1: Component Oros Modeler. (ABC Technologies,
2001)
Figure 1 describes the flow component module in-
formation about resource (expenses), activities, and
cost objects (products, services, or customers).
2.1.1 Resource Module
The Resource Module contains expenses (costs) for
the organization or department such as salaries, raw
materials, and depreciation. These costs can be
grouped into one center. Each center can contain
many centers and other accounts (ABC Technologies,
2001).
2.1.2 Activity Module
The Activity Module contains several activities. Each
activity has a center and account data with varying
cost elements. Costs can be provided for activities
from resource accounts or other account activities.
Thus, the total costs assigned to the account plus the
cost element (ABC Technologies, 2001).
2.1.3 Cost Object Module
The Cost Object module contains cost objects such as
products, services, channels and customers. The cost
object has a center and an account for each cost of the
resource, activity, cost object or a combination of the
three (ABC Technologies, 2001).
2.2 Enterprise Resource Planning
(ERP)
ERP is entreprise-wide information system that inte-
grates and controls the business processes in the en-
tire organization. ERP system is an enterprise infor-
mation system designed to integrate and optimize the
business processes an transaction in company. ERP
is industry-driven concept and systems, and is univer-
sal accept by business and organizational industry as
a solution practice to integrated enterprise informa-
tion system. ERP system have become vital strate-
gic tools in today competitive business environment
(Addo-Tenkorang and Helo, 2011).
2.2.1 Benefits of ERP
The following are the benefits of ERP in company
(Monk and Wagner, 2012) :
1. ERP system can minimize data duplication, so
that ERP can produce operating cost savings. ERP
systems can help company produce goods and ser-
vices faster so that more sales can be generated
each month.
2. ERP system can provide data and information that
is real-time, so companies can improve communi-
cation to customers, which can improve relation-
ships with customers and increase sales
3. ERP system which in its implementation can suc-
cessfully save company, supplier, and customers
from loss
2.3 SAP HANA
SAP HANA (High Performance Analytical Appli-
ance) is the next generation SAP business package
(SAP, 2019). SAP HANA is a new product that built
on a platform in today memory, designed with the
principle of experience using SAP Fiori (UX). SAP
HANA provide simplifications in data models, user
experience, decision making, business process, and
models to help business run simply (SAP, 2019). SAP
HANA is a data platform in memory that is used for
on-site software and cloud. SAP HANA is the best
suited for conducting real-time analysis with more
data compared to applications on the market today.
Analysis of Oros Modeler Data Reporting Process to SAP HANA in Activity based Costing for Indonesia Telecommunication Industry
247
2.3.1 History of SAP HANA
SAP began in 2011 when SAP introduced Hana as
the next generation storage platform to dramatically
simplify customer inventions and even replicate the
business in real time. In January 2013, SAP intro-
duced SAP Business Suite, based on SAP HANA (a
suite on Hana), to help companies accelerate their
real-time business and streamline their SAP Business
Suite by consolidating transactions and analytics into
a single storage platform become. Note that in this
release, SAP is the only software vendor on the mar-
ket that enables SAP Business Suite customers to in-
tegrate transactions and analytics into a single stor-
age platform. The market response was so strong
that more than 2,000 customers were won in just two
years. It was the fastest growing product from SAP
at that time. Based on its success so far, SAP re-
leased the next generation Business Suite in February
2015: SAP Business Suite 4 Hana (SAP S / 4Hana),
a new product since SAP R / 3. The biggest change.
SAP S / 4Hana is the complete SAP Business Suite
based on the most advanced storage platform (SAP
HANA). SAP S / 4Hana offers comprehensive simpli-
fication (customer acceptance, data model, user expe-
rience, decision making, business processes and mod-
els). With innovations (Internet of Things, Big Data,
Enterprise Network and Mobile First) companies can
easily operate in the digital economy.
2.3.2 Module SAP HANA
Modules on SAP HANA are individual components
of SAP HANA implementation (Gaska, 2018) . Each
module offers functionality for different business pur-
poses such as general ledger, logistics, and material
management. Simplicity is one of the main objec-
tives of SAP in making SAP HANA modules. Over
the decades, SAP has changed a lot because it was
updated to take advantage of new computing capabil-
ities. The SAP HANA module utilizes the benefits of
the SAP HANA database so users can easily upgrade
and quickly take advantage of new features after they
are released by SAP. SAP HANA can also integrate
third party applications (Gaska, 2018).
The SAP HANA module is growing rapidly.
There are many modules under several categories.
One of the most popular modules in SAP HANA
is SAP Finance. In SAP HANA by integrating the
database, SAP Finance can combine financial data
with nonfinancial data .
space
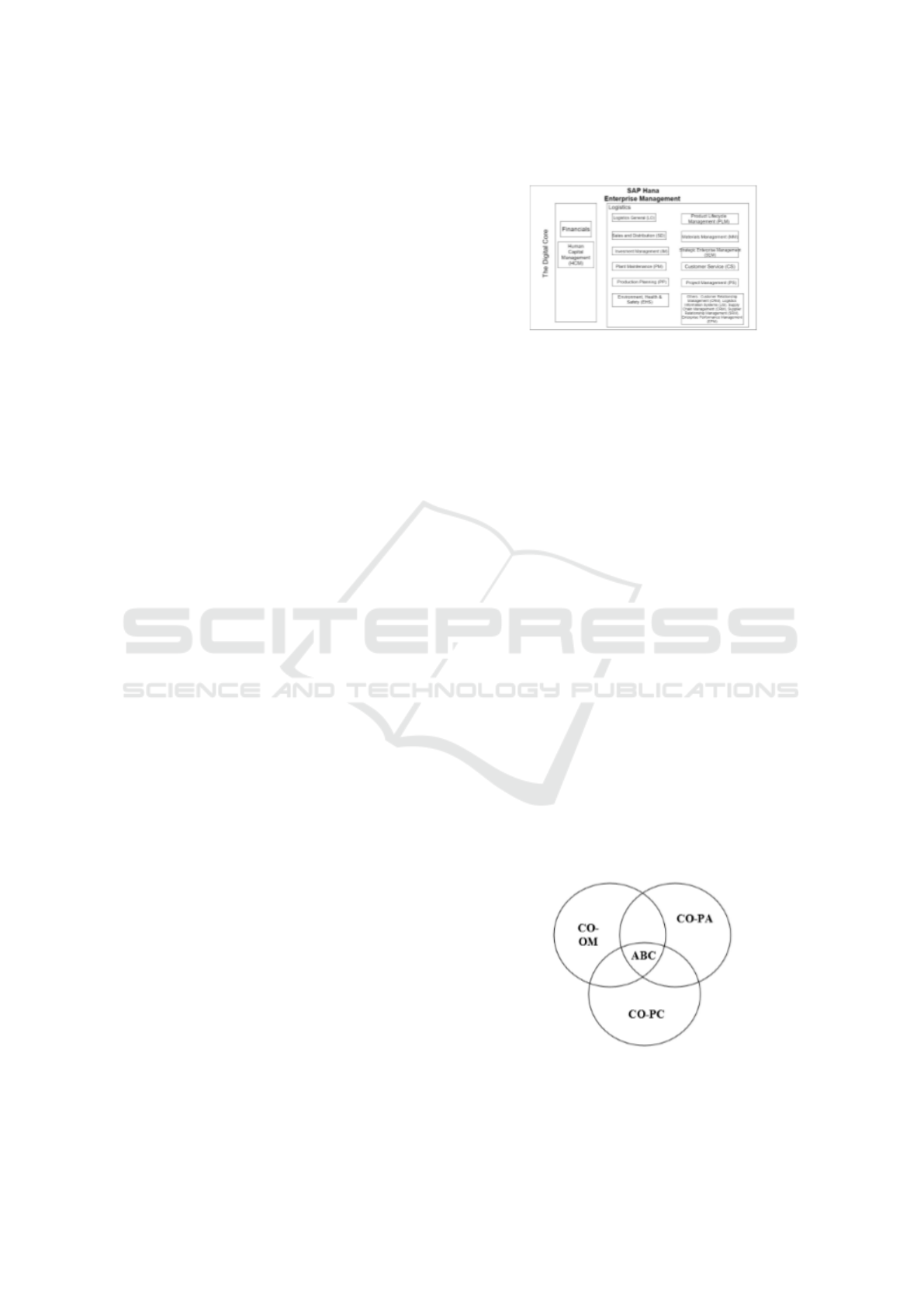
Figure 2: Modules in SAP HANA
Figure 2 Describe Additional modules in-
clude Plant Maintenance (PM), Product Life Cy-
cle Management (PLM), Human Capital Manage-
ment (HCM), Production Planning (PP), Project Sys-
tem (PS), Controlling (CO), Sales and Distribu-
tion (SD), Investment Management (IM), Strategic
Enterprise Management (SEM) Customer Relation-
ship Management (CRM) Logistics Information Sys-
tems (LIS), Supply Chain Management (SCM) Cus-
tomer Service (CS), Materials Management (MM),
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM), Enter-
prise Performance Management (EPM), Treasury
NetWeaver, Environment, Health and Safety (EHS)
(Gaska, 2018).
2.4 Activity based Costing
Activity-Based Costing is a method that assumes
that each activity will produce costs and cost objects
(products, services, customers) incurred will create
demand for activities (SAP, 2019). The ABC system
recognizes that a business must understand the fac-
tors that drive an activity, the costs incurred from an
activity, and how those activities are linked to a cost
object. First of all, ABC will place a cost on each
activity. After that, the cost of each activity is only
charged to products that do require that activity.
Figure 3: Component ABC (SAP, 2019)
Figure 3 describes a component of activity-
based costing CO-PA (Profitability Analysis), CO-PC
CONRIST 2019 - International Conferences on Information System and Technology
248

(Product Cost Controlling), CO-OM (Overhead Cost
Controlling)
2.4.1 CO-PA (Profitability Analysis)
Profitability analysis is one of the modules in ERP
that users can report sales data and income data us-
ing different characteristics (such as customers and
products) and numbers (such as the number of units,
prices, and costs). CO-PA is used for strategic report-
ing rather than as a financial reporting tool.
2.4.2 CO-PC (Product Cost Controlling)
Product cost planning is used to plan costs and set
prices. Determine the cost of goods produced and
sales costs for each unit of goods. The purpose of set-
ting costs is to estimate the standard costs, estimate
the modified standard costs and actual costs accord-
ing to the time of implementation. Standard costs are
used to determine the level of stock of goods. Plan
costs are recorded on the cost object and are scaled
compared to those incurred on actual / target costs.
2.4.3 CO-OM (Overhead Cost Controlling)
Overhead cost controlling is used to allocate, plan,
control, and monitor overhead costs. This is an im-
portant preparation for analyzing profitability and set-
ting the right product costs. Planning overhead costs
is used to control costs and evaluate internal activities.
The SAP system provides many methods of allocating
overhead. By using the method in SAP can allocate
overhead costs according to provenance. At the end
of the period, when all allocations have been made,
the cost of the plan (target) is compared with the ac-
tual costs so that it can make a sourcebased analysis
of the resulting target. Along with time-saving cost
allocation, integration of overhead control in the SAP
system can reduce actual data entry and reduce the
work involved in planning.
3 METHODOLOGY
The SAP Activate method is a new method created
by SAP that is designed for the SAP HANA sys-
tem (Singh, 2017). The SAP Activate methodology
supports projects that implement cloud-based, hybrid
and on-premise SAP solutions. SAP Activate used
on SAP HANA is a unique collaboration of SAP
Best Practice, Methodology, and SAP Guided Con-
figuration. So it allows companies that implement
SAP HANA to start quickly, intelligent building and
run simply while continuing to innovate in the cloud
(Singh, 2017). SAP Activate methodology have 6
phase for ERP implementation. Start from Discover,
Prepare, Explore, Realize, Deploy, and Run.
Figure 4: SAP Activate Methodology (Singh, 2017)
Figure 4 describes these phases of SAP Activate
Methodology are illustrated in the flow diagram and
detail explanation :
Figure 5: Flow Diagram SAP Activate.
Analysis of Oros Modeler Data Reporting Process to SAP HANA in Activity based Costing for Indonesia Telecommunication Industry
249

In this study, focus in implementing 4 phase in
SAP Activate Methodology from stage discover to
stage realize, because stage deploy and run stages are
still in the working stage for posting data into SAP
HANA so that on this occasion researcher only ex-
plained to the stage of stage realize.
Figure 6: SAP Activate Methodology Research Method
(Singh, 2017)
Figure 6 explain SAP Activate Methodology as
the research method until Realize stage
4 ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Discover
First time the researchers defined in PT.XYZ espe-
cially reporting in the Oros modeler and SAP HANA
then analyzed the data equations of the two appli-
cations. Literature studies are used to find general
knowledge related to research such as literature re-
view and methodology
Figure 7: Creating a report (ABC Technologies, 2001)
Figure 7 explains the first step is to make a report
in the Oros modeler, then generate a report to display
the report and display it on the screen and then select
the report module that we want to select, such as unit
cost report. we can also choose the period of time
and select data such as the module resources, activi-
ties and cost objects according to the report that we
want
space
Figure 8: Data flow Oros Modeler (ABC Technologies,
2001)
Figure 8 explains about data flow cost allocation
process in Oros Modeler, the allocation start from re-
source such as salary, depreciation, and flow to ac-
tivity. Activity define all process such as business
planning, policy and procedure development or eval-
uation, implementation and monitoring of business
proposal. Last flow to Cost Object, In Cost Object,
is the product-related cost or non-product related cost
of PT.XYZ such as network cost split charge, network
cost virtual private network (VPN) and Network Cost
Premium Call.
4.2 Prepare
Once the information has been entered into the
activity-based management model, the costs have
been calculated, and the data reviewed, the next step
in analyzing the data is generating reports. Benefits
of generating reports include:
1. Validate the model
2. Produce printouts that present an overall view of
your data
3. Analyze costs on the screen
4. Produce files for inclusion in other programs, such
as spreadsheets or word processors
5. Focus on a specific area of interest
6. Emphasize certain data to other data
Oros Modeler can do all this and much more by
allowing you to use report templates to determine the
type of information reported and how it is presented.
The report templates are:
CONRIST 2019 - International Conferences on Information System and Technology
250
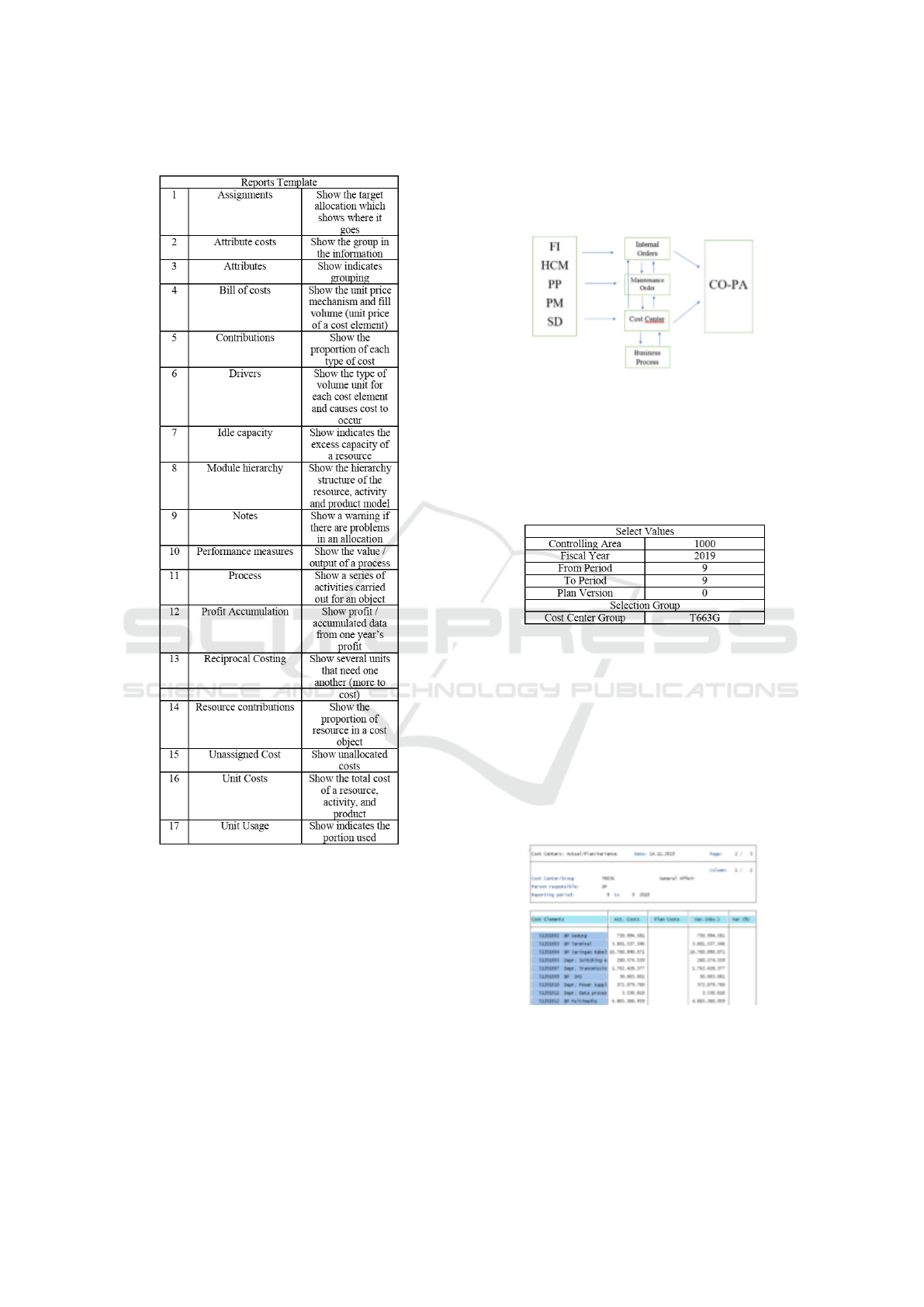
space
Figure 9: The Report Template.
Figure 10below explains the business process flow
from the FI, HCM, PP, PM, SD and other modules
towards internal orders, maintenance orders and cost
centers. business processes have own hierarchy. In-
ternal flow orders can be related to maintenance or-
ders, cost centers and related to others, the direction
of the arrow (cost drivers) coming out of the cost cen-
ter is called assessment and the direction of the arrow
entering the cost center is called settlement. then the
direction of the arrow from internal orders, mainte-
nance orders, and cost centers enter the CO-PA (prof-
itability analysis). CO-PA is the information used to
make a report. CO-PA is a middle-up reporting model
that must be simple, on information and flexible when
it has entered the COPA can not return to internal
orders, maintenance orders and cost centers. report
design combines value fields and characteristics. In
making a report in SAP HANA using report painter
Figure 10: Process Business in SAP HANA
4.3 Explore
In stage explore, based on the reporting on SAP
HANA and analysis of data that can be entered in the
results of reporting.
Figure 11: The Sample Measurement of Three Tourist Des-
tination.
Figure 11 explains about when filling in the table
above in the Oros modeler it will display the report in
SAP HANA the figure below the control area is the
organizational element, fiscal year states the year you
want to choose, then from period and to period ex-
plains the range of months, Plan versions all to depict
alternative plans in the system and Finally, we fill in
the cost center group which we want to display, for
example, T663G.
Figure 12: Reporting in SAP HANA (2019)
Figure 12 explains the sample report that is avail-
able in Sap at the T663G (General Affair) cost center
in the 9th 9th month of 2019, there are cost elements
along with their explanations, actual costs, plan costs,
variants.
Analysis of Oros Modeler Data Reporting Process to SAP HANA in Activity based Costing for Indonesia Telecommunication Industry
251

4.4 Realize
Figure 13: The Sample Measurement of Three Tourist Des-
tination.
Figure 13 describes fit and gap analysis compare
to the results of reporting on the Oros modeler and
SAP HANA. Using the Oros modeler the resulting
report cannot be integrated between other modules
so it requires sap HANA to integrate the reporting
results into one that we can customize according to
what report we want to display so that SAP HANA
can combine the desired report results into one result
and make it easier the reader in identifying the results
of the report.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The conclusion of this research in using the results
of reporting SAP HANA which has been centralized
and easy to find the data in a search for PT.XYZ.
Oros modeler has started to be abandoned now and
started to use SAP HANA to make the allocation pro-
cess and reporting results into one so that it is easy
to find the desired reporting data. SAP implemen-
tation in PT.XYZ using SAP Activate methodology
starts from Discover, Prepare, Explore, Realize, De-
ploy, and Run. In this research, the researcher ex-
plains from Discover, Prepare, and Explore. Activity-
based costing allocation method support cost alloca-
tion process to control and maintenance of the pro-
cess in SAP HANA. The researcher also give recom-
mendation to PT.XYZ to The result SAP HANA ad-
justs to the data needed by PT. XYZ to make the data
search and make it easier to see the components of
each product that are made so that it becomes more
effective and efficient. For future research sugges-
tions are building on a particular finding in research,
re-evaluating and expanding a theory (framework and
model).
compare the results of reporting sap R/ 3 and SAP
HANA which results are easy to understand simple
and clear information.
REFERENCES
ABC Technologies, I. (2001). Oros modeler tutorial.
Addo-Tenkorang, R. and Helo, P. (2011). Enterprise re-
source planning (erp): A review literature report. In
Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering
and Computer Science, volume 2, pages 19–21.
Gaska, C. (2018). Symmetry corp.
Junnarkar, A. R. and Verma, A. (2017). Study on system
application product (sap)–an important enterprise re-
sourse planning tool for achievement of organisational
vision, mission and operational performance.”.
Matende, S. and Ogao, P. (2013). Enterprise resource plan-
ning (erp) system implementation: a case for user par-
ticipation. Procedia Technology, 9:518–526.
Monk, E. and Wagner, B. (2012). Concepts in enterprise
resource planning. Cengage Learning.
Ociepa-Kubicka, A. (2017). Advantages of using enterprise
resource planning systems (erp) in the management
process. World Scientific News, 89:237–243.
Sadrzadehrafiei, S., Chofreh, A. G., Hosseini, N. K., and
Sulaiman, R. (2013). The benefits of enterprise
resource planning (erp) system implementation in
dry food packaging industry. Procedia Technology,
11:220–226.
SAP (2019). Sap.com.
Singh, V. (2017). Manage Your SAP Projects with SAP Acti-
vate: Implementing SAP S/4HANA. Packt Publishing
Ltd.
CONRIST 2019 - International Conferences on Information System and Technology
252
