
Internet of Things in Overall Equipment Effectiveness Production
System Applications
Dina Fitria Murad
1
, Bambang Dwi Wijanarko
2
, Denny
1
and Alfath Syahrian
1
1
Information Systems Department, BINUS Online Learning, Bina Nusantara University, Jakarta, Indonesia
2
Computer Science Department, BINUS Online Learning, Bina Nusantara University, Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords:
The internet of thing, industry 4.0, Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), manufacturing, machine services.
Abstract:
Utilization of Internet of Thing (IoT) can increase efficiency, and real-time optimization. IoT integration in
industrial machines helps the process of monitoring the production processing, thus avoiding single point of
failure and easier for resource expansion, so that the machines will be optimal in their use because it can be
known at the right time for maintenance. The purpose of this study is to optimize the use of machines in
production, especially the process of monitoring production machinery. Using the IoT and Overall Equipment
Effectiveness (OEE) approach to the machine, the data is calculated to facilitate the analysis process. The
application of the Internet of Things in the field of manufacturing production especially in this company has
proven to be effective in making industrial machine services become smarter, more transparent and efficient.
1 INTRODUCTION
PT. Ultra Sakti is a pharmaceutical company that pro-
duces OTC (Over The Counter) medicines, which are
drugs that can be sold freely on the market. In car-
rying out these drug production activities, PT. Ultra
Sakti always makes efforts to produce quality prod-
ucts by differentiating through quality strategy and
value strategy. Quality strategy is to provide prod-
ucts with better quality than competitor products to
build satisfaction and loyalty from customers. Strat-
egy value is carried out by submitting more amounts
to customers, both through more functional and bet-
ter services, while always maintaining an affordable
price for the products sold.
PT. Ultra Sakti is present in the pharmaceutical in-
dustry with the awareness that this industry must be
faced with innovation and the creation of high qual-
ity and competitive products. To strengthen the com-
pany’s presence, PT. Ultra Sakti is positioning itself to
be a pharmaceutical company that implements stan-
dard and modern production standards. Accompanied
by firm commitments and innovations that are carried
out sustainably, the company’s contribution to indus-
try acquisition is expected to increase. To create a
quality product, one of the systems development that
is carried out is to use internet technology that is im-
plemented on a production machine, its application is
carried out in the form of machine and data integra-
tion that can be used for the OEE (Overall Equipment
Effectiveness) process (see figure 1).
Figure 1: Production Process Flowchart.
To support the implementation and implementa-
tion of Industry 4.0 in PT. Ultra Sakti, the process of
developing technology and information that can help
the means of production activities, must be done auto-
matically and has been integrated with the core ERP
system, where data and information processing can be
done and generated quickly, easily and precisely. One
of the things that can be done to support this process is
to optimize the use of machines in production. To find
out and monitor the effectiveness of the use of these
machines, it can be done by calculating OEE on these
machines, so that the device can be known easily.
The application of IoT to manufacturing and sup-
ply chain management has become popular in vari-
ous industries like smart cities (Tanwar et al., 2018),
transportation (Murad et al., 2018), bigdata (Hashem
et al., 2016). Connected equipment, tracking peo-
ple and goods or devices, sampling cycle manage-
ment, and production cycle monitoring are one of
the IoT applications in the industry, data acquisition
Murad, D., Wijanarko, B., Denny, . and Syahrian, A.
Internet of Things in Overall Equipment Effectiveness Production System Applications.
DOI: 10.5220/0009909503050310
In Proceedings of the International Conferences on Information System and Technology (CONRIST 2019), pages 305-310
ISBN: 978-989-758-453-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
305
at the level of PLC (Programmable Logic Control)
and supervisor systems, then the data is processed
in Computing to connect to MES (Management Ex-
clusion System) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Plan-
ning) system. Meanwhile, a system that is interre-
lated to connect the central system owned by the com-
pany (ERP) with production tools can help the process
of monitoring the performance of existing production
machines and can assist in analyzing and calculating
OEE.
This research utilizes the Internet of Things (IoT).
IoT is a concept where particular objects have the
ability to transfer data over a network without requir-
ing interaction from human to human or from human
to computer devices. IoT emphasizes the integration
of process and management with the system by pro-
viding all data on-board (Nasir et al., 2018b) (Nasir
et al., 2018a). Utilization of IoT has also been carried
out by (Gunasekaran and Periakaruppan, 2017) where
IoT is implemented to create a smart home by using
Arduino as an I / O signal receiver from the installed
device, the working principle of the invention is the
same, Arduino is programmed to carry out commands
from the received signal, then the system will work as
instructed. With recent developments and the IoT ap-
plication, it has been possible to resolve this problem.
It is hoped that the system created can help the par-
ties involved, including production staff, operators &
heads of production and management, to monitor pro-
duction activities and know the results of OEE calcu-
lations in real-time so that they can quickly assist in
making decisions.
The purpose of this research is to build integrated
system automation between machines, technology,
and information using IoT. Based on that, the research
questions in this study are how the use of IoT can help
OEE systems become availability, performance, qual-
ity, and achievement in the use of machines.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Hardware
Hardware or hardware is all the physical parts of a
computer and is distinguished from the data that is
in it or that operates in it and is separated from the
software (software) that provides instructions for the
hardware in completing its work.
In this study, the authors use the following hard-
ware:
1. Computer
The computer is used as a web server; the oper-
ating system used is Windows 10. The machine
is in charge of storing scripts, images, and web-
site page content. Web Servers must be accessible
from all areas that have an internet connection.
2. M2M Controller
M2M Controller is hardware with Modbus / TCP
as a tool used to communicate between the signal
signaling device and other controller units such
as PLC or SCADA. The M2M controller can also
function as an input/output unit for long distances
in a client server-based communication control
system.
Figure 2: CONPROSYS M2M Controller
3. Arduino Uno R3
Arduino is an open-source single-board micro-
controller, derived from the Wiring platform, de-
signed to facilitate the use of electronics in vari-
ous fields. Arduino also simplifies the process of
working with a microcontroller. Here are the rea-
sons for the authors to use Arduino, as a signal
sensor to the controller, namely:
(a) Arduino prices are relatively low, ranging from
IDR 100,000, up to the cost of IDR 400,000, -
the price is cheaper than other professional mi-
crocontroller platforms.
(b) Arduino libraries are easy to get, available in
full on the Arduino website and even on other
Arduino community websites.
(c) Multi-platform, not only for Windows but also
suitable for working on Linux.
(d) Simple and easy programming, Arduino is easy
to use for beginners and flexible enough for
those who are already advanced. Arduino is
based on a processing programming environ-
ment, so if students or students are accustomed
to using processing, of course it will be easy to
use Arduino.
CONRIST 2019 - International Conferences on Information System and Technology
306
space
Figure 3: Arduino Uno R3
2.2 Previous Research
Some of the studies that correlate with this study are
summarized in Figure 4. There are several uses of
IoT in the same field with different methods and ap-
proaches.
Figure 4: Previous Research.
space
Figure 5: Previous Research(cont.).
Internet of Things in Overall Equipment Effectiveness Production System Applications
307
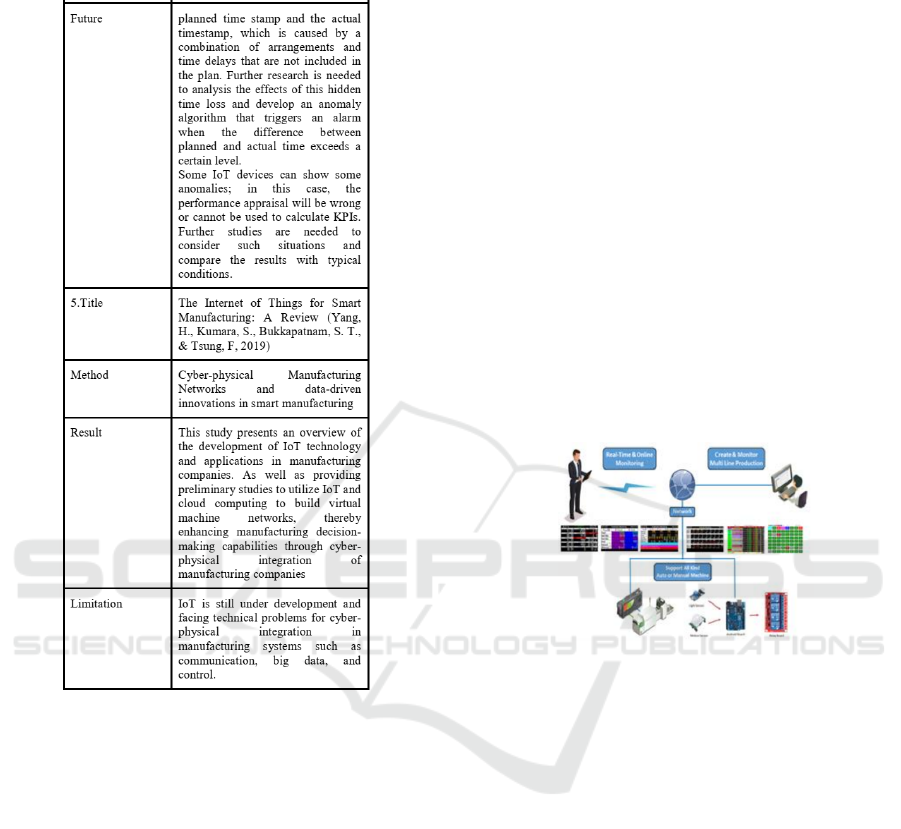
space
Figure 6: Previous Research(cont.).
Based on the literature review, the Internet of
things can be used to help make the whole process au-
tomatic, where devices can be controlled by programs
that can be run from various places, according to the
needs that are expected. The results of the research re-
view can also be used by the writer in understanding
the use of the Internet of Things in the manufactur-
ing and smart factory world where these influences to
provide support in real-time in the world of produc-
tion and improve OEE.
From study 1, the method used is the same,
namely by utilizing Arduino Uno and acting as an au-
tomation system, the difference lies in its use where
this thesis is used to support OEE applications at PT
Ultra Sakti. Study 3 also deals with improving OEE,
but the difference is that study 3 uses DMAIC & Sig
Sixma Approach. In Research 2, 4, and 5, the simi-
larities are discussed concerning the use of IoT in the
manufacturing and smart factory world.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The system built is to capture machine activity us-
ing internet technology, where the OEE process of
recording activity data from machine activity is done
automatically.
The process of implementing IoT (Internet of
Things) in the production process at PT. Ultra Sakti is
to use a digital input and digital output sensor system
and M2M Controller installed on the production ma-
chine, where the sensor system will send data through
the internet about the activities carried out by the de-
vice, starting from the engine running until it is turned
off. This process is carried out automatically by using
tools and data sent to the server, and then the data will
be processed into reports that can be used for various
analysis and strategy development to make the pro-
duction process more efficient and effective.
The following Figure 7 shows the business pro-
cess and IT infrastructure by utilizing IoT as a liaison
or identifier for several devices in the system is built.
Figure 7: Business process and IT infrastructure by using
IoT
And, to support the system to run better, it needs
several supporting devices such as (1) The server
computer (Figure 8) is used as a web server that func-
tions to receive requests that have been sent by the de-
vice or that are called through a browser application
and then respond to requests in the form of web pages
or more generally in HTML documents, (2) CON-
PROSYS M2M Controller (Figure 9) is used as a data
logger and receiver of signals sent by sensors or relays
from Arduino Uno R3 installed on the production ma-
chine, Sensors or relays installed are LOSS sensors,
DOWN sensors, GOOD sensors and NO GOOD sen-
sors, where the data triggers the OEE (Overall Equip-
ment Effectiveness) calculation, (3) Arduino UNO R3
(Figure 10) is used to receive digital input, and digi-
tal output signals which will then be transferred to the
M2M Controller and the data will be forwarded to the
webserver.
CONRIST 2019 - International Conferences on Information System and Technology
308

space
Figure 8: Computer server
Figure 9: CONPROSYS M2M Controller
Figure 10: Arduino UNO R3
As per Figure 7, the system generates informa-
tion that supports business processes that are better
and smarter. Intelligent information systems that are
formed produce information in real-time based on
data input from Arduino supported by IoT. Here are
some access and dashboard views for each system
user:
1. Management
Management has access to see all activities that
occur in the system; in general, management only
sees the whole system through the dashboard re-
port.
Figure 11: Management access
2. Division Head and Department Head (All Depart-
ments)
Division Heads and Department Heads have ac-
cess to view detailed data per production line, per
batch (lot), per item, and view by the target.
space
Figure 12: Report Line Per Lot
3. Production Supervisor & Admin
To make a schedule and configure the queue list
in the system is done by the supervisor & admin
of the production department.
Figure 13: Production Schedule
4. Production Staff & Operators
The user who interacts the most is the staff and op-
erators of the production department, where every
procedure for the process carried out follows the
conditions set by the system.
Figure 14: Daily Activity Machine
4 CONCLUSIONS
From the results of the ongoing system analysis, it
is known that the OEE calculation process, availabil-
ity, performance, quality, and achievement have sev-
eral problems so that all of these problems can lead to
an analysis process in dealing with issues and obsta-
cles that occur in the production department requires
a long time to find solutions and preventive mainte-
nance. So, in the research conducted by the author,
several results have been obtained, namely:
1. Industry 4.0 implementation by implementing
data processing automation between machine de-
vices and systems using IoT technology so that
it can improve effectiveness and can be appropri-
ately measured.
2. Communication between devices can be done us-
ing internet technology, where the tool sends a
signal to the server, and the data is processed into
the system.
3. M2M Controller can be made efficiently in a sim-
ple way, by developing a programming language
Internet of Things in Overall Equipment Effectiveness Production System Applications
309

that can give commands to the controller to pro-
vide the data needed by the system.
4. Web Application-based systems can support OEE
calculation processes, availability, performance,
quality and achievement faster than before, this
application system can be accessed by users
through a variety of devices and platforms.
5. OEE calculation system which previously took
3 hours to prepare documents and calculations.
However, the proposed system process that has
been developed, then it accelerates the calculation
process time in real time.
REFERENCES
Gunasekaran, M. and Periakaruppan, S. (2017). A hybrid
protection approaches for denial of service (dos) at-
tacks in wireless sensor networks. International Jour-
nal of Electronics, 104(6):993–1007.
Hashem, I. A. T., Chang, V., Anuar, N. B., Adewole,
K., Yaqoob, I., Gani, A., Ahmed, E., and Chi-
roma, H. (2016). The role of big data in smart
city. International Journal of Information Manage-
ment, 36(5):748–758.
Hwang, G., Lee, J., Park, J., and Chang, T.-W. (2017). De-
veloping performance measurement system for inter-
net of things and smart factory environment. Inter-
national journal of production research, 55(9):2590–
2602.
Madakam, S., Lake, V., Lake, V., Lake, V., et al. (2015).
Internet of things (iot): A literature review. Journal of
Computer and Communications, 3(05):164.
Mahalakshmi, G. and Vigneshwaran, M. (2017). Iot based
home automation using arduino. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Res.
Technol, 3(8):1–6.
Murad, D. F., Abbas, B. S., Trisetyarso, A., Suparta, W.,
and Kang, C.-H. (2018). Development of smart pub-
lic transportation system in jakarta city based on in-
tegrated iot platform. In 2018 International Confer-
ence on Information and Communications Technology
(ICOIACT), pages 872–878. IEEE.
Nasir, N., Hashim, A. B., Fauadi, M. H. F. M., and Ito, T.
(2018a). Statistical pattern recognition as an after ser-
vice for statistical process control. In Intelligent Man-
ufacturing & Mechatronics, pages 469–478. Springer.
Nasir, N., Ito, T., Hashim, A. B., and Fauadi, M. H. F. M.
(2018b). The development of graphical overall equip-
ment effectiveness interface. In Intelligent Manufac-
turing & Mechatronics, pages 671–683. Springer.
Ng, K.-C., Chong, K. E., and Goh, G. G. G. (2014). Im-
proving overall equipment effectiveness (oee) through
the six sigma methodology in a semiconductor firm:
A case study. In 2014 IEEE International Conference
on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Manage-
ment, pages 833–837. IEEE.
Tanwar, S., Tyagi, S., and Kumar, S. (2018). The role of in-
ternet of things and smart grid for the development of
a smart city. In Intelligent Communication and Com-
putational Technologies, pages 23–33. Springer.
Yang, H., Kumara, S., Bukkapatnam, S. T., and Tsung, F.
(2019). The internet of things for smart manufactur-
ing: A review. IISE Transactions, 51(11):1190–1216.
CONRIST 2019 - International Conferences on Information System and Technology
310
