
The Development of Conceptual Framework for the Leadership
of Sub-district Health Promoting Hospital Directors
Tarawadee Iasakul
1
, Wallapa Choeibuakaew
2
1
Graduate Student in Public Health, Faculty of Health and Sport Science, Thaksin University, Thailand
2
Lecturer, Faculty of Health and Sport Science Thaksin University, Thailand
Keywords: Leadership, Director, Sub-district Health Promoting Hospital (SHPH)
Abstract: SHPH works closely with community and under close supervision of District Public Health Office. SHPH
leadership is significant for SHPH effectiveness. However, the framework for SHPH leadership was never
developed in Thailand context. The purpose of this research was to develop the conceptual framework for the
leadership of SHPH directors by integrating the information from systematic review and data collected from
related stakeholders. Open-ended questions on “the required leadership of SHPH Directors” were asked to
8 SHPH directors, 2 local leaders, 4 public health district officers, 10 SHPH staff and 10 SHPH customers in
a selected district. The concept analysis (Walker and Avant, 1995) was used to frame the concept. The result
showed as follows: (1) Antecedents of the SHPH directors’ leadership were deep knowledge, intrinsic
motivation, organization culture, open environment, self-efficacy, and corporate social responsibility. (2)
Attributes of the SHPH directors’ leadership were individual competency to lead, intellectual skill,
management skill and connection to others. (3) The consequences were goal achievement, organization
growth, staff happiness and satisfaction, and sustainability. This conceptual framework will fit for SHPH
services in Thailand context. The suggestion for further investigation is to refine the conceptual framework
and develop the questionnaire for SHPH directors’ leadership (SHPH-D Lead).
1 INTRODUCTION
In Thailand, there are 4 levels of government
hospitals responding for 3 types of care. The four
levels consist of regional, province, district and sub-
district health promoting hospital (SHPH). The three
types of care are tertiary, secondary and primary care,
as summarized in figure 1. Primary care is the
services provided by SHPH, district, provincial, and
regional hospitals consisting of health promotion,
disease prevention, health rehabilitation, and
treatment. All services end at out-patient department
or day care services with or without physician
provider. Secondary care focuses on curing diseases
which provides by district, provincial and regional
hospitals. This level includes in-patient services and
requires physicians in a health care team. Tertiary
care concerns on the complication treatment or an
excellent center which provides by regional and
university hospitals. Sub specialty and specialty are
required. (Thai Health Coding Center: 2019).
Figure 1: Scope of three types of care in Thailand
SHPH is the smallest health care unit provided by
Ministry of Public Health. SHPH is categorized into
3 sizes (Ministry of Public Health: 2016) regarding to
the number of responded citizen: small (≤3,000
citizen), medium (3,001-8,000 citizen) and large
(>8,000 citizen). The major responsibility of the
SHPH is primary care consisting of health promotion,
basic treatment, disease prevention, health
rehabilitation and consumer protection (Public Health
Administration Office: 2016). SHPH service ends at
outpatient care. Health promotion is a major role
among all. SHPH plays a pivotal role in nationwide
primary healthcare. SHPH provides the service by
Iasakul, T. and Choeibuakaew, W.
The Development of Conceptual Framework for the Leadership of Sub-district Health Promoting Hospital Directors.
DOI: 10.5220/0009910407930797
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 793-797
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
793

public health officers and registered nurses led
directors. Some SHPH has more staff i.e. physicians,
public health technical officers, Thai traditional
medical doctors and hygiene dentists (Human
Resources Management Division Office of
Permanent Secretary: 2017). A director of SHPH is a
person who has been put into service and appointed
to serve by considering the knowledge and ability for
the benefits of government (Civil Service Act: 2008)
and been appointed by the provincial governor (State
Administration Act: 1992).
The disruptions caused by the rapid growth of
digital around the world, including changes in
Thailand itself affect the management and services of
SHPH (Office of the Civil Service Commission:
2015; College of Public Health Administration:
2561). Therefore, the leadership of SHPH's directors
is important to the growth and development of SHPH
in this era. However, there is no report on the
conceptual framework of the SHPH directors’
leadership. From the conducted observations, it is
found that all studies used one or more leadership
styles to assess SHPH directors’ leadership. Existing
leadership styles originate from Europe or the United
States. The purpose of this research, thus, was to
develop the conceptual framework of the SHPH
directors’ leadership by integrating data from
systematic review with information gathered from
SHPH staff and stakeholders.
‘True leadership is not a bullet which one uses to
kill and harm others. Rather, it is an instrument one
uses to serve others’ (Amera: 2008). Well known
leadership models were reviewed to guide this study.
Kurt Lewin’s concept is still influential over 60 years
after his death. In 1939, Lewin conducted a classic
study of leadership, involving three styles of
leadership: autocratic, democratic, and laissez-faire.
The three types are widely applied in management
environment and research (Lewin, Lippitt, and White:
1939 cited in Chou: 2012). Hersey and Blanchard
(1996) proposed a situational leadership model
explaining the balance of leadership style and the
readiness of the group members. There are 4
leadership styles: (1) telling- high task and low
relationship, (2) selling-high task and high
relationship, (3) participating- high relationship and
low task, (4) delegating- low relationship and low
task. Moreover, this model states that most effective
leadership style depends on the readiness of group
members. Readiness is divided for 4 levels: low
readiness, moderate, moderate to high, and high
readiness.
Fiedler’s contingency model was proposed by
Fiedler in 1967 concerning on the effectiveness of a
leader in an organization coming from leadership
style and situational favourableness. That matching of
leadership style and situational favourableness is
called “situational contingency”. There are 2 types of
leaders: relationship-oriented (aim to utilize the
emotional connection to maximize staff performance)
and task-oriented leader (aim to use the full potential
of staff to maximize performance). Servant leadership
is grounded in religious teaching; (Greenleaf, 1970)
consisting of empathy, listening, awareness, healing,
conceptualization, persuasion, stewardship, foresight,
community building and commitment to growth of
others. The servant leadership is value to be applied
for a director’s work. (Samut Chamnan, 2011).
The concept of transformational leadership is
widely applied. It was initially introduced by James
V. Downton. Then, a concept was further developed
by James MacGregor Burns. Later, Bernard M. Bass
expanded upon Burns' original ideas to develop what
is today referred to as ‘Bass Transformational
Leadership Theory’ (Wikipedia: 2019).
Transformational leadership enhances the
motivation, morale, and job performance of followers
through a variety of mechanisms. The mechanisms
sometimes referred to as the 4 I's: (1) idealized
Influence (II) – the leader serves as an ideal role
model for followers, (2) inspirational Motivation
(IM) –leader has the ability to inspire and motivate
followers through having a vision and presenting that
vision, and (3) individualized Consideration (IC) –
leader demonstrates genuine concern for the needs
and feelings of followers and help them self-
actualize, and (4) intellectual Stimulation (IS) – the
leader challenges followers to be innovative and
creative, they encourage their followers to challenge
the status quo.
The antecedents of leadership from diversity of
sources were collected. Thanakorn Eiempan (2013)
studied in the Thai air force and found the following
factors related to leadership: organization culture,
conscientiousness, procedures, operation and
openness. Kitikan Patibhan (2019) summarized
factors relating to creative leadership which were (1)
intrinsic motivation (goal setting, intensity,
persistence), open environment (independence,
challenge, trust and sincerity, and new paradigm),
deep knowledge (expert, experience and skill).
Jantana sansuk (2014) found self-efficacy, adaptive
capacity and corporate social responsibility affecting
leadership. She also reported the consequence of
leadership which was organizational effectiveness.
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
794

2 CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
The conceptual framework of this study was framed
based on literature review with the integration of
information from stakeholder’s opinion (figure 2).
Leadership in several professions were carefully
reviewed. In SHPH context, the roles and
responsibilities of SHPH directors were drawn from
notification of Ministry of Public Health (Ministry of
Public Health Issue Order No. 897/2559.2016). The
leadership of SHPH from the perspective of the
directors and staff of SHPH, sub-district leaders, and
SHPH customers were explored.
Figure 2: Conceptual framework for developing SHPH
directors’ leadership.
3 OBJECTIVES
The objective of this study was to develop a
conceptual framework for the sub-district health
promoting hospital (SHPH) directors’ leadership.
4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This descriptive study aimed at developing the
conceptual framework for SHPH directors’
leadership. A review of the literature was conducted
using several databases, including CINAHL, Google
Scholar, ScienceDirect, ThaiJo, and Emerald
management. The mentioned resources were
searched using the terms: 'leadership', 'director of
sub-district health promoting hospital', ‘director of
sub-district health promoting hospital & 'leadership',
and 'health care staff & 'leadership', and for studies
published from January 2000 to March 2019. Books,
articles; rules, regulation, policy and protocol enacted
by the Ministry of Public Health of Thailand relating
to SHPH director were reviewed.
(1) Systematic review on 2 major aspects: 1)
outstanding leadership models and related
research/article, on leadership and 2) roles and
responsibilities of SHPH directors.
(2) Data collection was conducted by answering
open-ended question “the required leadership of
SHPH directors” done by 8 SHPH directors, 2 local
leaders, 4 district public health officers, 10 SHPH
staff and 10 SHPH customers. The data was
thematically analyzed.
(3) Information from (1) and (2) were integrated
to conceptualize SHPH directors’ leadership by
applying the concept analysis suggested by Walker
and Avant (1995). There were 5 steps from 8 steps:
selecting a concept, determining the aim of analysis,
identify all uses of the concept, define attributes and
construct the case.
5 FINDINGS
The research findings were presented in figure 3 and
the details below:
(1) There were 4 antecedents of SHPH directors’
leadership, namely deep knowledge, intrinsic
motivation, organization culture, open environment,
self-efficacy, and corporate social responsibility.
(2) The attributes of SHPH director leadership
includes individual competency to lead, intellectual
skill, management skill and connection to others. The
sub-attributes were presented in table 1.
(3) The consequences were goal achievement,
organization growth, staff happiness, staff
satisfaction, and sustainability.
Figure 3: Antecedents, attributes and consequences of the
SHPH directors’ leadership.
The Development of Conceptual Framework for the Leadership of Sub-district Health Promoting Hospital Directors
795
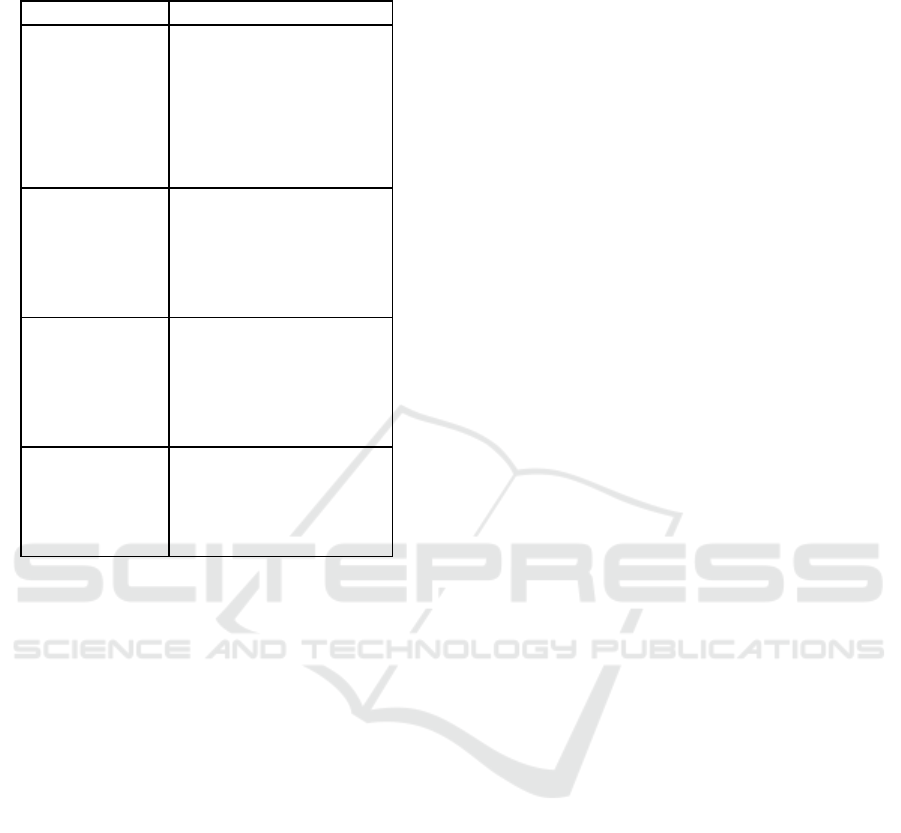
Table 4: Attributes and sub-attributes of SHPH the
directors’ leadership
6 CONCLUSION AND
RECOMMENDATION
The model case of the SHPH directors’ leadership
consisted of 5 antecedents, 4 attributes and 5
consequences. This is the first model developed for
the SHPH directors’ leadership. Thus, the refinement
of the model should be further examined. The
questionnaire measuring the SHPH directors’
leadership should be determined for psychometric
property which is an intellectual property of Thailand.
REFERENCES
Amera, D. 2008. The consequences of leadership.
Retrieved August 5. 2019. from
https://www.tigweb.org/youth-
media/panorama/article.html?ContentID=20695
Auareesuksakun, A., & Chuntuk, T. 2016.
Transformational Leadership: Changing Challenges to
Achieve Organization Sustainability. Veridian E-
Journal, Silpakorn University. 9(1), pp 845-860.
Chamnan. S., 2011. The servant leadership: New paradigm
in educational leadership. Journal of Educational
Administration Burapha university, 5(2), pp 1-14.
Chantuk, T., Nantharojphong, K., & Pasunon, Prasopchai.
2016. A Factor Analysis of Leadership in the Twenty
First Century of Student Organization Board. Journal of
Research Methodology, 29(2). pp 139-156.
Civil Service Act. 2008, Government Gazette, Volume 125
/ Episode 22k / Page 1/25 January 2008.
College of Public Health Administration Ministry of Public
Health. 2018. Retrieved August 10, 2019. from
http://www.cpha.ac.th/
Fiedler, F. (1967). A theory of leadership effectiveness.
New York: Mc Graw - Hill.
Government Administration Act, BE 2534, Government
Gazette, Volume 108 / Episode 156 / Special Edition,
Page 1/4 September 1991.
Greenleaf, R. K. 1970. Servant Leadership. Retrieved
August 5, 2019. from https://www.greenleaf.org/about-
us/robert-k-greenleaf-biography/
Hersey, P., Kenneth H. Blanchard., & Dewey E. Johnson,
1996. Management of Organizational Behavior:
Utilizing Human Resources. United States: Pearson
Education (US). 7th ed. pp. 188-223.
Human Resources Management Division Office of
Permanent Secretary, Ministry of Public Health. 2017.
Handbook of Structure and Framework of Authority for
Regional Administration in 2017-2021.
Iampan, T. 2016. Factors Affecting the Transformational
Leadership of Pilots in the Royal Thai Air Force. EAU
Heritage Journal Social Science and Humanity, 6(1). pp
98-110.
Kim, J. S., Kim, Y. M., Jang, K. S., Kim, B. N., & Jeong,
S. H. 2015. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm, 21(5), pp 575-
586.
Ministry of Public Health Issue Order No. 897/2559, 2016.
Subject assigned to government officials as supervisors
on May 19, 2016.
Ministry of Public Health. Thai Health Coding Center.
2019. Geographic Information System: GIS). Retrieved
August 3, 2019. from
http://www.thcc.or.th/download/GIS54.pdf
Office of the Civil Service Commission, 2015 Book no.
1008 / v 2 dated 19 February 2015 Re: Rules and
Conditions for Position Determination
Patiphan, K., Factor to Creative Leadership: Retrieved
August 5, 2019. pp. 51-62. from.
https://www.academia.edu/8635795/Factor_to_Creativ
e_Leadership
Public Health Administration Office, Ministry of Public
Health. 2016. Public Health Administration Office
Work manual: Health services (promote, prevent, cure
and protect consumers). Office of the Permanent
Secretary, Ministry of Public Health.
Sansuk, J. 2014. Antecedents and Consequence of Strategic
Leadership Capabilities of Higher Education Institute
in Thailand. Journal of the Association of Researchers,
19(1). pp 34-46.
Sarika, S. 2015. Leadership of the Director of the Sub-
District Health Promoting Hospital Ubon Ratchathani
Provincial Public Health Office. KKU Journal for
Public Health Research, 8(3). pp 21-27.
Attribute Sub attributes
Individual competency
to leadership
- visionary
- charisma
- EQ and social maturity
- recognition
- information technology skill
- social skill
- public mind
- service mind
- health care practice mastery
Intellectual skill - ability to learn and grow consisting
- individual consideration
- self- awareness
- adapting to change
- achievement drive
- problem solving skills
- decision making skill
Management skill
- good governance
- motivating and encouraging others
- risk management
- conflict management
- team building
- financial management
- role modelling
connecting to others -applying the King philosophy
of sufficiency
- understanding
-community engagement
-communication
- collaboration skill
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
796

Shih Yung Chou (2012) Millennials in the Workplace: A
Conceptual Analysis of Millennials’ Leadership and
Followership Styles. International Journal of Human
Resource Studies ISSN 2162-3058 2012, Vol. 2, No. 2,
pp 71-83.
Ministry of Public Health 2016. The criteria for dividing the
size of the civil servants, Manpower Board Resolution
the personnel committee, 16 December 2016. Retrieved
August 5, 2019 from
http://bps.moph.go.th/new_bps/sites/default/files/activi
ty/5.4%20KS.pdf
Walker. L., Avant. K .1995. Strategies for theory
construction in nursing, 2nd edition. London: Appleton
& Lange.
Watcharakate, S. 2014. Ten Principles of Servant
Leadership for Nurse Leaders. Journal of The Royal
Thai Army Nurses, 15(3), pp 44-48.
Wikipedia 2019. Transformational leadership. Retrieved
August 5, 2019. from
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transformational_leader
ship#Origins
The Development of Conceptual Framework for the Leadership of Sub-district Health Promoting Hospital Directors
797
