
Study of Preference for Stereo Recording Techniques of a
Pelog-based of Gamelan Gender, Bonang, and Peking Ensemble
Nyoman Kieran Sebastian, Jack A. Simanjuntak
Conservatory of Music, Pelita Harapan University, Karawaci, Tangerang, Indonesia
Keywords: Stereo Recording Techniques, A Pelog-based of Gamelan Gender Bonang and Peking.
Abstract: The layout of gamelan ensemble produce stereo imaging, instrument separation, and sound clarity. Until now,
for music production purposes, gamelan ensemble recording uses spot-based microphone technique, which
produces more individual sound, while the stereo microphone technique is able to produce the characteristics
of gamelan ensemble, either in instrument separation, sound clarity, or stereo imaging. No previous study has
investigated on preference for stereo recording techniques of a pelog-based of gamelan gender, bonang, and
peking ensemble. Techniques that applied in this research were XY stereo recording technique, NOS, ORTF,
and AB. This research uses qualitative method, using statistical calculation. There were four stages, collecting
data, which consists of assign the player, analyze the characteristics of the ensemble, choose the song to be
recorded, decide the layouts of the ensemble and the microphones, and create the questionnaire. The second
stage was recording process. The third stage was sample test and interview. These findings is clearly indicate
that NOS stereo recording technique is the most prefered stereo recording techniques of a pelog-based
gamelan gender, bonang, and peking ensemble.
1 INTRODUCTION
Gamelan is a traditional musical instrument in the
form of ensemble from Java Island, Indonesia. The
instruments are made of metal, wood, or bamboo, that
creates sound by hitting it. It is also classified as an
idiophone musical instrument (Tjahyanto et al, 2011).
Gamelan has its own characteristics. Each
instrument of gamelan was created with frequency
range and with different roles (Suyatno et al, 2013).
The characteristics influence the layout of gamelan
ensemble. The layout of gamelan ensemble produces
wide stereo imaging (Suyatno et al, 2013). The
impression of wide stereo image was created by
stereo microphone techniques.
Until now, for music production purposes,
gamelan ensemble recording uses spot-based
microphone technique. No previous study has
investigated on preference for stereo recording
techniques of a pelog-based of gamelan gender,
bonang, and peking ensemble.
The stereo microphone technique is able to
produce the characteristics of gamelan ensemble,
either in instrument separation, sound clarity, or
stereo imaging. For example, Spaced-Pair (AB)
stereo microphone technique is able to produce a
clear stereo image, which makes listener able to
differentiate the position of each sound source, and
determine the boundaries of a room (Bates, 2016).
But when compared with spot-based microphone
technique, the spot-based microphone technique
produces more individual sound.
Other than that, gamelan is also still less well-
known in general, even by Indonesian people
themselves. Iswara (2010) stated that the
insufficiency of gamelan preservation is caused by
the lack of government's participation, foreign
culture, and gamelan which is still rarely known by
Indonesian society, and the lack of interest towards
the gamelan itself (Iswara 2017).
The aim of this research is to analyse four stereo
recording techniques of a pelog-based of gamelan
gender, bonang, and peking ensemble.
2 METHODOLOGY
There are four stereo recording techniques used on
this research:
▪ XY 90°;
▪ NOS 90°;
540
Sebastian, N. and Simanjuntak, J.
Study of Preference for Stereo Recording Techniques of a Pelog-based of Gamelan Gender, Bonang, and Peking Ensemble.
DOI: 10.5220/0009911105400546
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Interdisciplinary Arts and Humanities (ICONARTIES 2019), pages 540-546
ISBN: 978-989-758-450-3
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

▪ ORTF 110°;
▪ Spaced Pair (AB).
2.1 Data Collection
2.1.1 Instrument Players
There are three players and three instruments on this
research:
▪ Gender: Roban Eko Putranto;
▪ Bonang: Rusli;
▪ Peking: Anastasia Emmanoela Putri.
2.1.2 Ensemble Characteristics Analysis
2.1.3 Song Selection
The song chosen for this study was Gundul-Gundul
Pacul, written by R. C. Hardjosubroto. Music score
courtesy of Rusli.
2.1.4 Ensemble Layout Planning
There are five ensemble layouts used throughout the
recording process. One layout uses the standard
ensemble layout (as 1), and the other four layouts are
adjusted to the characteristics of each stereo recording
techniques (as 2).
2.1.5 Microphone Layout Planning
For the research, the microphone that was used is a
pair of Neumann KM184 as a stereo microphone and
also stand mics. There are 24 microphone layouts that
were used on the recording process (three of each
ensemble layout and stereo recording technique).
Three microphones were placed to the midpoint of all
the ensemble layout with a distance of:
▪ Two point five meter (2,5 m) as A;
▪ Three meters (3 m) as B;
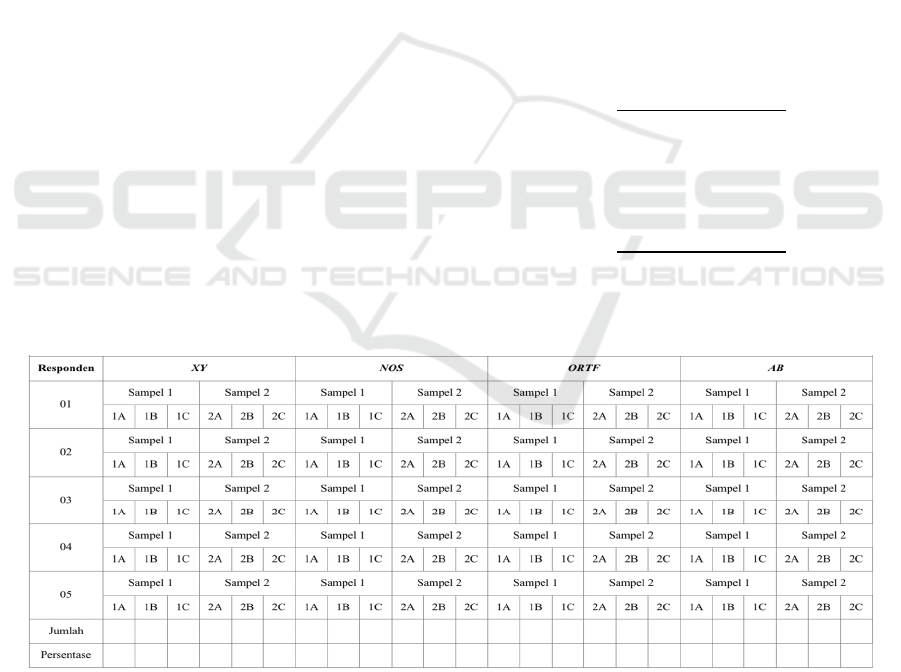
▪ Three point five meter (3,5 m) as C.
So, there were six names for each stereo recording
techniques, namely 1A, 1B, 1C, and 2A, 2B, 2C.
2.1.6 Questionnaire Making
The questionnaire sheet was divided into several
section. The sections consist of application section,
‘statement of being a respondent’ section, explanation
and interview section, as well as the interview
questions (can be found in appendix B essay). The
questionnaire was divided into three stages:
▪ First stage, is to find out the respondents'
preferences for microphone distance towards
gamelan ensemble for all ensemble layouts
(first and second);
Respondents had to choose one out of the three
given audio samples of first layout and one of the
three audio samples of second layout, therefore
respondents had to choose eight out of 24 given audio
samples.
▪ Second stage, is to find out the respondents'
preferences for gamelan ensemble layouts for
all stereo recording techniques;
Respondents had to choose one of two audio
samples from the previous selected audio samples,
therefore respondents had to choose four of eight
audio samples
▪ Third stage, is to find out the respondents'
preferences for stereo recording techniques of
gamelan gender, bonang, and peking ensemble.
Respondents had to choose one of four audio
samples from the previous selected audio samples.
2.2 Recording Process
2.2.1 Recording Process
Devices being used on the recording process:
▪ Universal Audio Digital Apollo 8 audio
interface, by using first and forth channel, and
the amplitude of 40 dB;
▪ Mac Pro Server, mid 2010, 2.8 GHz Quad-Core
Intel Xeon processor, 8 Gb 1066 MHz DDR3
memory, OS Sierra version 10.12.3;
▪ Yamaha HS8 speaker;
▪ Logic Pro X version 10.4.1;
▪ Two pieces of microphone stands;
▪ One pieces of carpet with 159 cm length and
123 cm width.
Audio samples have been recorded and bounced
with 48 kHz 24 bits sample rate. The audio that was
produced from the microphone was directed to the
left and panned as much as minus 64 degrees (-64°)
and the audio that was produced from the microphone
was directed to the right and panned as much as plus
63 degrees (+63°).
2.2.2 Preparation of Audio Samples
The devices being used on the recording process:
▪ MacBook Pro Retina, Retina, 13-inch, mid
2014, processor 2.6 GHz Intel Core i5, memory
8 Gb 1600 MHz DDR3, OS High Sierra version
10.13.5;
▪ Headphone Sennheiser HD 280 Pro 64 ohm;
▪ Logic Pro X version 10.4.1.
Study of Preference for Stereo Recording Techniques of a Pelog-based of Gamelan Gender, Bonang, and Peking Ensemble
541
Format of the audio samples is wav, with 48 kHz
24 bits sample rate.
2.3 Samples Test
2.3.1 Questionnaire
The respondents were divided into two categories:
▪ Professional, gamelan instrumentalist and
sound engineer with minimum five years
experiences;
▪ Non-Professional, musician and non-musician
with age range 16 until 30 years.
The quantitative data collection was done by
letting respondents listen to the audio samples that
have been recorded. After respondents listen to the
audio samples, respondents were asked to fill the
questionnaire. After that, respondents were
interviewed to find out the reasons of their choices
before.
The devices being used to listen on the recording
results:
▪ Focusrite Scarlett 2i2 interface, amplitude on
12 o'clock;
▪ MacBook Pro Retina, Retina, 13-inch, mid
2014, processor 2.6 GHz Intel Core i5, memory
8 Gb 1600 MHz DDR3, OS High Sierra version
10.13.5;
▪ Speaker Sennheiser HD 280 Pro 64 ohm;
▪ QuickTime Player version 10.4 (928.13).
2.3.2 Interview
After filling in the questionnaire, the respondents
were also going to be interviewed.
Qualitative data collection was done by preparing
interview's questions, sound recording device, and
stationery. Interview was done with semi structured
format, with two questions. First question, "why did
the respondents choose the option?". Second
question, "what are the factors that influence the
respondents choices?"
Devices being used on the recording process:
▪ Iphone 6S, 2015, iOS 11.4.1 handphone;
▪ Stationery.
2.4 Data Analysis
2.4.1 Questionnaire
The questionnaire results on the first stage
questionnaire is compiled and analysed on Table 2.1
𝐹𝑂𝑅𝑀𝑈𝐿𝐴:
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑅𝑒𝑠𝑝𝑜𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠
100%
The questionnaire results on the second stage
questionnaire is compiled and analyzed on Table 2.2
𝐹𝑂𝑅𝑀𝑈𝐿𝐴:
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑅𝑒𝑠𝑝𝑜𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠
100%
Table 2.1: Analysis table from first stage questionnaire.
ICONARTIES 2019 - 1st International Conference on Interdisciplinary Arts and Humanities
542

Table 2.2: Analysis table from second stage questionnaire.
The questionnaire results on the third stage
questionnaire is compiled and analyzed on Table 2.3
𝐹𝑂𝑅𝑀𝑈𝐿𝐴:
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐿𝑖𝑘𝑒
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑅𝑒𝑠𝑝𝑜𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠 𝐿𝑖𝑘𝑒
100%
𝐹𝑂𝑅𝑀𝑈𝐿𝐴:
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐷𝑖𝑠𝑙𝑖𝑘𝑒
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑅𝑒𝑠𝑝𝑜𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠 𝐷𝑖𝑠𝑙𝑖𝑘𝑒
100%
Table 2.3: Analysis table from third stage questionnaire.
2.4.2 Interview
The interview results (qualitative data) have been
processed with three stages:
▪ Evaluation Coding;
Evaluation coding is a systematic data collection
process to increase the effectiveness of the research.
This method focuses on patterned observation or
respondents' answer from detail's quality. This
method also allows the researcher to know which
participator has given positive or negative response.
▪ Data Presentation;
Reduced data was grouped and took the action to
be presented at data conclusion. This stage allows the
researcher to take further actions if there were less
information to understand the interview data analysis
▪ Data Conclusion.
On this stage, all data preparation should be done,
so that data can be presented by bar chart.
3 ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Preference Analysis of Stereo
Recording Techniques based on
Professional Preferences
3.1.1 First Stage
The first stage most liked stereo recording technique
by professional category preference is XY 2A (50%),
NOS 2C (50%), ORTF 1A (50%), and ORTF 2C
(50%), followed by XY 1B (42.9%), XY 1C (42.9%),
and AB 2C (42.9%).
At the same time, the first stage most disliked
stereo recording technique by professional category
preference is NOS 1A (35.7%), NOS 1C (35.7%), AB
1A (35.7%), and AB 1C (35.7%).
3.1.2 Second Stage
The second stage most liked stereo recording
technique by professional category preference is NOS
2 (85.7%), followed by AB 1 (71.4%), and ORTF 2
(64.3%).
At the same time, the second stage most disliked
stereo recording technique by professional category
preference is XY 1 (50%) and XY 2 (50%).
3.1.3 Third Stage
The most liked stereo recording technique by
professional category preference is NOS (71.42%),
on Figure 3.1. There are several factors:
Study of Preference for Stereo Recording Techniques of a Pelog-based of Gamelan Gender, Bonang, and Peking Ensemble
543

▪ The sound of the gamelan blends together;
▪ Enough reverb;
▪ Clear and balance stereo image;
▪ Clear separation instruments;
▪ Clear gamelan's sound;
▪ Balance loudness;
▪ Cleaner sound;
▪ Comfortable to hear;
▪ Optimal harmonic content;
▪ Balance of gamelan's sound;
▪ The performance;
▪ Tempo;
▪ Stable tone.
Figure 3.1: Diagram value on the third stage of professional
respondent percentage.
The most disliked stereo recording technique by
professional category preference is XY (64.29%), on
Figure 3.1. There are several factors:
▪ Too much noise;
▪ Too much reverb;
▪ Narrow stereo image;
▪ The sound of gamelan does not blend together;
▪ The worst clarity sound;
▪ Less high frequency;
▪ The sound cracked;
▪ The sound was too smooth;
▪ Harmonics at certain frequencies was
annoying;
▪ Less balance;
▪ The performances are not stable;
▪ The dynamics doesn't sound comfortable.
3.2 Preference Analysis of Stereo
Recording Techniques based on
Non-professional Preferences
3.2.1 First Stage
The first stage most liked stereo recording technique
by non-professional category preference is NOS 2C
(64.2%), followed by XY 1B (50%) and ORTF 2A
(50%). At the same time, the first stage most disliked
stereo recording technique by non-professional
category preference is NOS 1B (35.7%) and NOS 1C
(35.7%), followed by XY 2A (42.8%), ORTF 1B
(42.8%), AB 1A (42.8%), AB 2B (42.9%), and AB
2C (42.9%).
3.2.2 Second Stage
The second stage most liked stereo recording
technique by non-professional category preference is
ORTF 2 (78.5%), followed by XY 1 (71.4%) and AB
1 (71.4%). At the same time, the second stage most
disliked stereo recording technique by non-
professional category preference is NOS 1 (57.1%).
3.2.3 Third Stage
The most liked stereo recording technique by non-
professional category preference is NOS (71.42%),
on Figure 3.2. There are several factors:
▪ Comprehensive reverb;
▪ Perfect melody and accompaniment separation;
▪ The sound of gamelan blends together;
▪ Clear melody and accompaniment;
▪ Clear transient;
▪ Balance range frequency;
▪ Sound of the reflection effect from hitting
gamelan;
▪ Balance melody and accompaniment loudness.
The most disliked stereo recording technique by
non-professional category preference is XY (64.29%)
and ORTF (64.29%), on Figure 3.2. There are several
factors:
▪ Too much noise;
▪ Less separation balance;
▪ The sound of gamelan does not blend together;
▪ Too wide stereo image;
▪ Less direct and reflected sound balance;
▪ Annoying resonance;
▪ Less melody sound;
▪ Too much high frequency;
▪ Too rough, sharp, and piercing sound;
▪ Too much noise.
ICONARTIES 2019 - 1st International Conference on Interdisciplinary Arts and Humanities
544

3.3 Preference Analysis of Stereo
Recording Techniques Based on All
Respondent Category Preferences
Figure 3.2: Diagram value on the third stage of non-
professional respondent percentage.
3.3.1 First Stage
The first stage most liked stereo recording technique
by all category preference is NOS 2C (57.1%). At the
same time, the first stage most disliked stereo
recording technique by all category preference is
NOS 1C (35.7%) and ORTF 2A (35.7%), followed by
ORTF 1A (39.2%), AB 1A (39.2%), AB 2C (42.9%),
XY 1B (46.4%) and XY 2A (46.4%).
3.3.2 Second Stage
The second stage most liked stereo recording
technique by all category preference is ORTF 2
(71.4%) and AB 1 (71.4%), followed by NOS 2
(64.2%). At the same time, the second stage most
disliked stereo recording technique by all category
preference is XY 1 (60.7%).
3.3.3 Third Stage
The most liked stereo recording technique by all
category preference is NOS (71.42%), on Figure 3.3.
There are several factors:
▪ The sound of gamelan blends together;
▪ Enough reverb;
▪ Clear gamelan's sound;
▪ Balance loudness;
▪ Cleaner sound;
▪ Noise were not disturbed by the gamelan's
sound.
The most disliked stereo recording technique by
all category preference is XY (64.29%), on Figure
3.3. There are several factors:
Figure 3.3: Diagram value on the third stage of all
respondent percentage.
▪ Too much noise;
▪ Less clear sound;
▪ Less high frequency;
▪ Very less balance;
▪ The performance are not stable.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This research has shown that preference for stereo
recording technique of a pelog-based of gamelan
gender, bonang, and peking ensemble is NOS stereo
recording technique. NOS stereo recording technique
has high definition. However, it has long reverb time.
A long reverb time is the characteristic of gamelan.
There is no sound of gamelan instruments that is
covering one another. Frequency ranges that are
relatively balanced, there are no dominant or less
frequency ranges. Gamelan performances are smooth
and stable. In the majority of NOS samples, there is
no high noise and sound of other disturbances that
disturb the sound of the gamelan. This shows that the
respondents likes the sound of the gamelan which
replicated the room image factor, instrument
separation, and the clarity of gamelan sound during
the live performance.
There is a focus difference between the categories
of professional gamelan respondents, professional
sound engineer respondents and non-professional
respondents. The professional gamelan respondents
focus into the quality of the performance while the
sound engineer and non-professional respondents
categories tends to focus accordance with the research
Study of Preference for Stereo Recording Techniques of a Pelog-based of Gamelan Gender, Bonang, and Peking Ensemble
545

topic, namely the analysis of stereo recording results.
This is because gamelan's professional respondents
plays the gamelan from five years to 40 years,
different from sound engineer professional
respondents who have at least sound experience for
five years, and non-professional respondents who do
not have any experience for gamelan musical
instrument and are not sound engineers for at least
five years. Vocabulary and responses from gamelan
professional respondents are also based on
perceptions, instead of sound engineer professional
respondents who are based on technical matters.
The result of this research indicates that space,
timbre, and quality factors are the aspects which the
professional gamelan respondents focuses, while
space, timbre, quality, and defects are the main focus
of non-professional respondents.
Further research might explore room acoustics
parameter measurements for gamelan's ensemble,
because the room acoustics parameter measurements
affects the gamelan's sound and the recording results.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thank you for Bapak Jack Simanjuntak, Kevin, Olin,
and Cung.
REFERENCES
Aris Tjahyanto, Yoyon K Suprapto, dan Diah Puspito
Wulandari, 2011. Model Analysis-By-Synthesis
Aplikasi Pembangkit Suara Gamelan Sintetik. In
Seminar Nasional Aplikasi Teknologi Informasi 2011,
1907-5022.
Suyatno et al., 2013. Karakteristik Akustik Gamelan Jawa
Studi Kasus Gamelan Milik PSTK ITB. In Seminar
Fisika dan Aplikasinya 2013, 2086-0773.
Suyatno et al. 2013. Pengaruh Tata Letak Instrumen
Gamelan Jawa di Panggung Pendhapa ISI Surakarta
Terhadap Parameter Akustik Bagi Penggendang.
Tom Bates, 2016. Coincident or Near-Coincident Mic
Placement Techniques, DPA Microphones Online
Publications.
Noor Hidyat Iswara, 2017. Dinamika Kesenian Gamelan
pada Fungsi dan Pelestarian Kesenian Gamelan dalam
Sanggar Budaya Singhasari di Kecamatan Singosari,
Kabupaten Malang, Jawa Timur. In Universitas
Airlangga, Skripsi Sarjana 1.
ICONARTIES 2019 - 1st International Conference on Interdisciplinary Arts and Humanities
546
