
Trust, Risk, Perceived Usefulness, and Ease of Use on Intention to
Online Shopping Behavior
Aprilivianto, Dyah Sugandini, Mohamad Irhas Effendi
Universitas Pembangunan Nasional Veteran Yogyakarta
Keywords: Trust, perceived risk, perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, online shopping
Abstract: This study aims to analyze the influence of trust, risk perception, perceived usefulness, and perceived ease
of use together with buying interest online. This research is a quantitative study with an active student
population in the Special Region of Yogyakarta University. The sampling technique uses a purposive
sampling method with a sample size of 200 people. Data collection techniques using a questionnaire that has
been tested for validity and reliability. The data analysis technique used is the Multiple Linear Regression.
The results of this study indicate that trust, risk perception, perceived usefulness, and perceived ease of use
have a significant effect on the intention to buy online shop.
1 INTRODUCTION
Today, advances in technology and information are
experiencing very rapid development. The internet
has become one of the media facilities for social
interaction that is widely used today. The internet
connects one person to another, providing
information, as a means of entertainment, and as a
means of communication. But not only that, now the
internet raises a new phenomenon in the process of
buying and selling goods and services. Only by
opening a website, buyers can already see the
products offered. The ease of accessing the internet
gave birth to e-commerce, which has now become a
choice in shopping (Internet World Stats, 2018).
According to Internet World Stats (2018), in an
article with the headline InternetStatistics
Growthseen a significant increase in the growth of
internet users in the last five years, wherein
December 2014, there were 3.079 billion users,
equivalent to 42.4% of the human population. In
December 2015, there were 3.366 billion users,
equivalent to 46.4% of the human population. This
number continues to increase until, in June 2018,
there were 4,208 billion active internet users where
this number has touched 55.1% or more than half of
the total human population living on Earth.
In Indonesia alone, the number of internet users
continues to increase from year to year. Based on
data from the results of a survey conducted by the
Indonesian Internet Service Providers Association
(APJII) is 2017, the number of internet users in
Indonesia reached 54.68% of the total population of
Indonesia. The composition of internet users in
Indonesia is 51.43 percent male and 48.57 percent
female. Whereas, based on age, it is dominated by
internet users in the productive age range of 19-34
years, which is equal to 49.52%. Buying and selling
applications online become one of the services that
are often used by internet users in Indonesia. 32.19%
of services accessed by the people of Indonesia are
for purchasing goods, and 8.12% selling goods
online.
Along with the increasing use of the internet and
technology, several electronic media have emerged
that use it for business activities, which became
known as Electronic Commerce or e-commerce.
Sugandini et al. (2018a) revealed that e-commerce
refers to the use of the internet and websites to
conduct business transactions between organizations
and individuals. In Indonesia, e-commerce is
experiencing very rapid growth and is causing
Indonesian people to become interested and
interested in using e-commerce services.
One of the most important variables in
conducting online transactions is trust. According to
Koufaris & Hampton-sosa (2004), consumer trust in
e-commerce is one of the key variables in buying
and selling online (Sugandini et al., 2018b). Trust
has become the most important element in the
success of e-commerce. E-commerce companies
must build high trust in consumers to be interested
in making transactions through their sites. With the
trust of consumers in e-commerce companies, it is
Aprilivianto, ., Sugandini, D. and Effendi, M.
Trust, Risk, Perceived Usefulness, and Ease of Use on Intention to Online Shopping Behavior.
DOI: 10.5220/0009963302510256
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management (ICBEEM 2019), pages 251-256
ISBN: 978-989-758-471-8
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
251

expected to increase buying interest in e-commerce
companies.
Online buying interest is also influenced by the
perceived risk perceived by consumers. Kim et al.
(2008) define risk perception as consumer beliefs
about the potential for uncertain negative outcomes
from online transactions. According to Engel et al.,
(1995), the greater the risk perception, the greater
the possibility of consumer involvement in
purchases. If the realized risk is very high, the
consumer has a choice whether to avoid buying and
using it altogether or minimize the risk through the
search and evaluation of pre-purchase alternatives.
In addition to the problem of trust and risk
perception, the use of information systems is an
important problem faced by e-commerce users. One
theory related to the use of information systems is
the TAM (Technology Acceptance Model).
According to Andryanto (2016) and Sugandini et al.,
(2018a), TAM is an information systems theory
designed to explain how users understand and use
information technology. Also, TAM considers the
adoption of technology by the user to be determined
by two perceptions, namely the perceived usefulness
and perceived ease of use. Perceived usefulness to
the context of online shopping refers to the extent to
which consumers feel that shopping at web-based
stores will enhance their shopping experience (Wen
et al., 2011). The definition shows that perceived
usefulness will influence the decision-making
process.
The main reasons why people shop or do not
shop online are the factors of trust (trust) on the
shopping site in question, and the ease of applying
the shopping site (Mayer et al., 1995). Ease of use is
the extent to which consumers feel the ease of
interaction with e-commerce websites and can
receive product information that they need (Wen et
al., 2011; Cho & Sagynov (2015). Based on the
explanations described in this background, this study
aims to analyze the influence of trust, risk
perception, perceived usefulness, and perceived ease
of use on online buying interest (sugandini et al.,
2018a).
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Intention to Online Shopping
Behavior
Kinnear and Taylor (1995) define consumer
intention to buy as a component of consumer
behavior in consuming behavior, respondents'
tendency to act before buying decisions are correct
The purchase intention is an impetus that arises in a
person to buy goods or services in order to meet
their needs (McCarthy, 2002; Cho & Sagynov
(2015). Schiffman and Kanuk (2004) explain that
external influences, awareness of needs, the
introduction of products, and alternative evaluations
are things that can lead to consumer buying interest.
2.2 Trust
According to Mowen and Minor (1997), consumer
trust is all knowledge owned by consumers and all
conclusions made by consumers about objects,
attributes, and benefits. Ba and Pavlou (2002) define
trust as an assessment of one's relationship with
others who will carry out certain transactions by
expectations in an environment that is full of
uncertainty. This definition includes two important
attributes of trust: (1) expectations of trust include
the possibility of mutually beneficial results, (2)
uncertain environment indicates that the delegation
of authority from one party to another may have an
adverse effect on the deposit (Ba and Pavlou, 2002).
In the context of the e-commerce environment,
the role of trust is more important than the
traditional business due to the increased uncertainty
caused by the distance factor and impersonal other
(Wen et al., 2011; Cho & Sagynov (2015). The
success of the transaction on the internet to be
influenced by the presence of variable trust (Pavlou,
2003; Sugandini et al., 2018a; 2018b) Customer
trust is the basis of consumers in making a purchase,
especially in shopping online, Koufaris and
Hampton Sosa (2004) state that consumer trust in e-
commerce is one of the key factors in buying and
selling. Online. Faith has become the most important
element in the success of e-commerce. Therefore,
there must be mutual trust between seller and buyer
(Gefen, 2002; Sugandini et al., 2018b). With trust
will grow the interest of consumers to make buying
and selling activities online (Suh et al., 2015)
H1: Trust affects of intention to online shopping
behavior
2.3 Perceived Risk
Perceived Risk is defined by Olglethorpe (1994) as
consumers' perceptions of uncertainty and negative
consequences that may be received from the
purchase of a product or service. Mowen and Minor
(1997) define perceived risk as a negative overall
consumer perception of several actions based on an
assessment of negative results and the likelihood
that the results will occur. This definition includes
two main concepts: the negative outcome of a
decision and the probability that the outcome will
ICBEEM 2019 - International Conference on Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management
252

occur (Sugandini et al., 2018b). Kim et al. (2008)
define perceived risk as consumer beliefs about the
potential for uncertain negative outcomes from
transactions online. Kim et al. (2008) and Sugandini
et al. (2018a) state that consumers pay attention to
the risks faced when intending to conduct
transactions online so that it will negatively affect
consumers' intention to online shopping behavior.
H2: Perception of risk effects of intention to online
shopping behavior
2.4 Perceived Usefulness
Davis's(1989) and Venkatesh and Davis (2000)
define Perceived Usefulness (the perception of
benefits) as a level where someone believes that the
use of a particular system will improve the work
performance of that person). Perceived Usefulness
(PU) refers to a measure where someone believes
that using a particular system can improve the
performance of his work. Perceived usefulness of
having an important role in shaping the attitude
toward using (the attitude in use) and behavioral
intention to use (use of interest). According to Kim
et al., (2008); Cho & Sagynov (2015); Hasan,
Harun, Shaffran, Rashid (2015), perceived
usefulness are consumer beliefs about the extent to
which it will be better than transactions online with
certain websites. According to Adams et al. (1992),
most of the acceptance of information system users
are driven by perceived usefulness/benefits. The
perceived usefulness can be considered as a
subjective probability that the application of new
technology will improve the way the user completes
the given task (Davis, 1989; Sugandini et al.,
2018a).
H3: Perceived usefulness effects of intention to
online shopping behavior.
2.5 Perception of Ease of Use
Davis (1989) defines perceived ease of use as "the
degree to which people believe that using a
particular system would be free of effort." Ease of
use is defined as a level or condition in which a
person believes that the use of a particular system
will be free of effort. Ease of use refers to the user's
perception of the process towards the end of
transaction online, and ease is how easy it is to use
the internet as a means of buying and selling online
(Monsuwe et al., 2004). According to Wen et al.,
(2011); Cho & Sagynov (2015); Hasan, Harun,
Shaffran, Rashid (2015) perceived ease of use is the
extent to which consumers feel the ease of
interaction with e-commerce websites and can
receive product information that they need. The
intensity of use and interaction between the user
(user) with the system can also show the ease of use
(Adams et al., 1992).
H4: Perceived ease of use affects the intention of
online shopping behavior.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This study was included in the quantitative research.
Which is based on the philosophy of positivism?
This study with student respondents in the Special
Region of Yogyakarta. The sampling technique used
is Non-Probability Sampling. Non Probability
Sampling with criteria for students who have
shopped online. Assessment of respondents uses a
Likert scale with intervals of 1-5. Data Analysis
Techniques used in this study are Multiple Linear
Regression. F-test, according to Ghozali (2011), is
used to indicate whether all independent variables
included in the research model have an influence
simultaneously or together on the dependent
variable. This decision is made based on a
comparison of the calculated F value by looking at
the level of significance, then comparing it with a
predetermined significance level (5% or 0.05).
4 RESULTS
4.1 Characteristics of Respondents
The characteristics of respondents observed in this
study include gender, age, majors, income/allowance
per month, and many online shopping transactions.
A description of the characteristics of respondents is
presented as follows in table 1.
Table. 1 Characteristic of Respondents
Gender Percentage
(%)
Men 56%
Women 44%
Age
19 to 20 Years 7%
21 to 22 Years 52%
23 to 24 Years 41%
Origin of: UGM 30%
UPN 42%
UIN 11%
UNY 17%
Allowance Per Month
<Rp 1,000,000 35%
Rp 1,000,000 to Rp 2,000,000 46%
Trust, Risk, Perceived Usefulness, and Ease of Use on Intention to Online Shopping Behavior
253
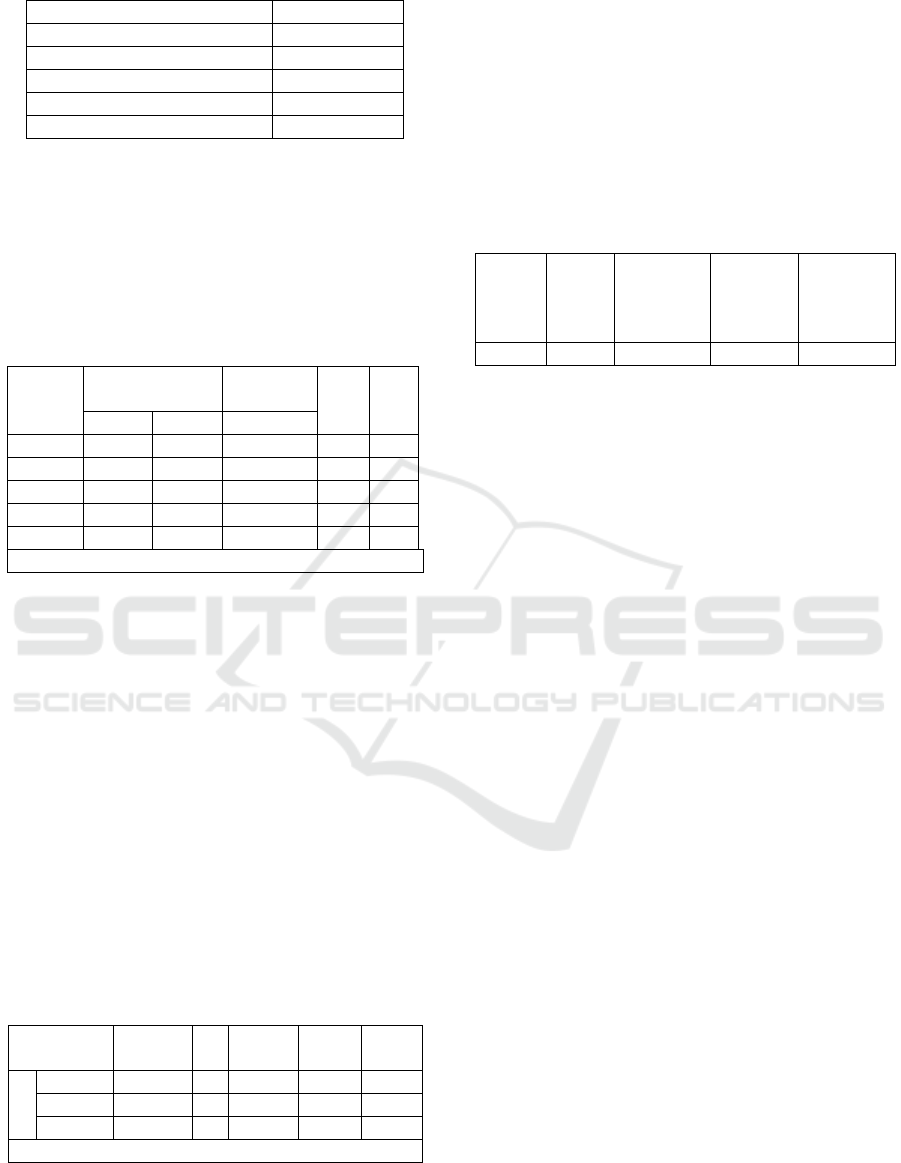
> Rp 2,000,000 19%
Amount of online shopping
1 time 33%
2 to 3 times 46%
4 to 5 times 7%
> 5 times 14%
4.2 Multiple Linear Regression
Analysis
The results of testing multiple linear Regression
models for variables that affect intention to online
shopping behavior can be seen in table 2.
Table 2. Results of Regression
MODEL
Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
t Sig.
B Std. Error Beta
Constant -0.742 2.245 - 0.330 0.740
Trust (X1) 0.435 0.117 0.454 3.720 0.000
Risk (X2) 0.194 0.083 0.144 2.345 0.021
PU 0.359 0.105 0.412 3.417 0.001
PEU ( X4) 0,287 0,117 0,148 2,459 0,016
Dependend variable: Intention to online shopping behavior
From the results of the regression analysis we
can find out the multiple regression equation as
follows:
Y = -0.742 + 0.435X1 + (-0.194) X2 + 0,359X3 + 0,287X4
Based on various parameters in the regression
regarding the variables of trust, risk perception,
perceived usefulness, and perceived ease of use that
affect intention to online shopping behavior.
a. F- test
The test aims to determine the effect of all
variables, including variables of trust, risk
perception, perceived usefulness, and perceived ease
use effects of intention to online shopping behavior.
The level of significance for this study was set at
0.05 (5%).
Table 3. F-test
Model Sum of
Square
df Mean
Square
F Sig.
1
Regression 1015,125 4 253,781 46,577 0,000b
Residual 517,625 95 5,449
Total 1532,750 99
Dependent Variable: Purchase Interest
Based on Table 3, it can be seen that the F value
is 46.577, with a significance of 0,000. Therefore the
significance value is smaller than 0.05 (0,000 <
0.05). The regression model of interest onshore data
is accepted.
b. Test The coefficient of determination (R
2
)
The coefficient of determination (R
2
) is used to
determine how far the model's ability to explain
variations in the dependent variable. Test results
R
2
shown by Table 4.
Table 4. Test Results from the coefficient of determination
(R2)
Model R R Square
Adjusted
R
Square
Standard
Error of
the
Estimate
1 0.814 0.662 0.648 2.334
Based on Table 4 can be seen the value of the
coefficient of determination (Adjusted R-square) of
0.648. This means that 64.8% of the variation in
buying interest can be explained by the four
independent variables consisting of trust, perceived
risk, perceived usefulness, and perceived ease of use
while the remaining 35.2% is explained by other
causes or influenced by other variables outside the
independent variable under study.
5 DISCUSSION
The results of this study indicate that trust has a
positive and significant effect on intention of online
shopping behavior. According to Pavlou (2003), the
success of large internet transactions is influenced
by the variable of trust. In transactions e-commerce,
the role of trust is more important compared to
traditional business because it is not met in person.
Consumers will tend to choose sites that they trust to
minimize the potential risk. The results of this study
are in line with research conducted by Suh et al.
(2015), which states that trust influences online
buying interest.
5.1 Perceived Risk and Intention to
Online Shopping Behavior
The results of this study indicate that perceived risk
has a negative and significant effect on buying
interest online. Gefen (2002) shows that consumers
with low-risk perceptions are more likely to engage
in purchasing activities than consumers with high-
risk perceptions. Kim et al. (2008) also show that
perceived risk is an important barrier for consumers
online when they buy products or services on the
Internet. The results of this study are in line with
ICBEEM 2019 - International Conference on Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management
254

research conducted by Ariffin et al. (2015), which
shows that the perceived risk of consumers
influences intention to buy.
5.2 Perceived Usefulness and
Intention to Online Shopping
Behavior
The results of this study indicate that the perceived
usefulness has a positive and significant effect on
buying interest online. Kim et al. (2008) state that
internet consumers make purchases on websites
because of perceived usefulness (for example,
increased comfort, cost savings, time savings,
increased variety of products to choose compared to
traditional shopping). The results of this study are in
line with research conducted by Hasan et al. (2015),
which shows that the perceived usefulness affects
the online buying interest.
5.3 Perceived Ease of Use and
Intention to Online Shopping
Behavior
The results of this study indicate that the perceived
ease of use has a positive and significant effect on
buying interest online. Davis (1989) defines the ease
of use as a level or condition where someone
believes that the use of a particular system will be
free of effort. The ease of applying shopping sites is
one of the reasons why people make purchases
online (Mayer et al., 1995). The results of this study
also support research conducted by Hasan et al.
(2015).
6 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the analysis and testing of
hypotheses on online consumers in the Special
Region of Yogyakarta, it can be concluded as
follows: Trust, perceived risk, perceived usefulness,
and perceived ease of use together have a significant
effect on the intention to online shopping behavior.
Trust has a positive and significant effect on
intention of online shopping behavior. Risk
perception has a negative and significant effect on
intention of online shopping behavior. Perceived
usefulness has a positive and significant effect on
the intention of online shopping behavior. Perceived
ease of use has a positive and significant effect on
the intention of online shopping behavior.
7 SUGGESTION
The trust variable is known to have a dominant
influence because it has the Standards Coefficients
Beta's highest value of 0.454. So it is better to
increase online consumer trust that can be done by
minimizing the possibility of fraud that can be
detrimental to consumers such as improving security
systems, improving after-sales service, and making
sure the product matches what is displayed on the
site. Online consumer trust about the accuracy of
fulfilling promises and commitments has the lowest
average value of the item (3.43), so online shopping
users should improve their systems and services,
such as securing transactions, speeding up the
delivery process, receiving complaints from
consumers, and disconnecting sellers who cheated.
This is because trust is the basis for consumers to
make a purchase, especially in shopping online. The
perceived risk with transaction security to protect
consumer privacy and to guarantee further improved
to avoid the possibility of fraud. Online sellers are
expected to provide clear and complete information
about products, sellers, after-sales services, and all
matters relating to online transactions.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We are thankful for the Directorate of Research and
Community Service, Ministry of Research and
Technology of the Republic of Indonesia (Direktorat
Riset dan Pengabdian Masyarakat – Kementerian
Riset, Teknologi dan Pendidikan Tinggi) for funding
this study in the Thesis Research Grant scheme
(Skema Hibah Tesis Magister) 2019. We are also
thankful for LPPM UPN Veteran Yogyakarta as the
institution that gave the approval to conduct this
research.
REFERENCES
Adams, DA, Nelson, RR, & Todd, PA (1992). “Perceives
Usefulness, Ease of Use, and Usage of Information
Technology: A Replication." MIS Quarterly. Vol. 16
No. 2
Andryanto, R (2016). “The Influence of Trust, Perception
of Benefits, and Perception of Ease of Use on Interest
in Buying in Online Stores (Empirical Study Made on
Olx.Co.Id in Yogyakarta)." Thesis. Faculty of
Economics. Yogyakarta State University
Ba, S., & Pavlou, PA (2002). “Evidence of the Effect of
Building Trust Technology in Electronic Markets:
Trust, Risk, Perceived Usefulness, and Ease of Use on Intention to Online Shopping Behavior
255

Price Premium and Buyer Behavior." MIS Quarterly.
26(3):243-268. DOI: 10.2307/4132332
Cho, Y. C & Sagynov, E. (2015). “Exploring Factors That
Affect Usefulness, Ease of Use, Trust, and Purchase
Intention In The Online Environment." International
Journal of Management & Information Systems. First
Quarter of 2015. Volume 19, Number 1.
Davis, F. D. (1986). “Technology Acceptance Model for
Empirically Testing New End-User Information
System Theory and Results." Dissertation.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
Davis, F. D. (1989). “Perceived Usefulness, Perceived
ease of use of Information Technology." Management
Information System Quarterly. Sep 1989; 13, 3;
ABI/INFORM Global pg. 319.
Gefen, D. (2000). “E-commerce: the role of familiarity
and trust." Omega,(28) 725 -737
Gefen, D. (2002). “Customer loyalty in E-commerce."
Journal of the association for information systems,
Volume 3, pp. 27-51
Ghozali, I. (2011). Multivariate Analysis Application with
SPSS Program. Issue 5. Semarang: Diponegoro
University.
Hasan, H, Harun, A & Rashid, MSZ (2015). “Factors
Influencing Online Purchase Intention In Online
Brands." International Journal of Business
Management & Research (IJBMR). Vol. 5, Issue 5.
Kim, D.J., Ferrin, D.L, & Rao, H.R. (2008). “A trust-
based consumer decision-making model in electronic
commerce: The role of trust, perceived risk, and their
antecedents." Decision Support Systems. 44, (2), 544-
564.
Koufaris, M., Hampton-Sosa, W. (2004). “The
development of initial trust in an online company by
new customers." Information and Management, 41,
377-397.
Mayer, R.C., Davis, J.H, Schoorman, F. D. (1995). “An
Integrative Model of Organizational Trust." Academy
of Management Review. Vol. 20. No. 3, 709-734
Mowen, John C & Minor, M. (1997). Consumer Behavior.
5th. Prentice Hall; Subsequent edition (July 24, 1997)
Pavlou, P. A. (2003). “Consumer Acceptance of
Electronic Commerce: Integrating Trust and Risk
With the Technology Acceptance Model."
International Journal of Electronic Commerce. 59,
(4), 69-103.
Schiffman, L., & Kanuk, L. L. (2004). Consumer
Behavior. 8th.(1000-01-01) [Paperback] (View
amazon detail page) ASIN: B009TUK8HW
Sugandini D., Sudiarto., Surjanti, J., Maroah, S., & Muafi.
(2018a). "Intention to delay: The context of
technology adoption based on android," International
Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology, Vol 9,
Issue 3, p. 736-746.
Sugandini D., Purwoko., Pambudi, A., Resmi, S., Reniati.,
Muafi., & Kusumawati, R.A (2018b). "The Role of
Uncertainty, Perceived Easy of Use, and Perceived
Usefulness Towards the Technology Adoption,"
International Journal of Civil Engineering and
Technology, Vol 9, Issue 4, p. 660-669.
Venkatesh, V., & Davis, F. D. (2000). “A Theoretical
Extension of the Technology Acceptance Model: Four
Longitudinal Field Studies." Management Science.
46(2):186-204. DOI:10.1287/mnsc.46.2.186.11926
Wen, Chao., Prybutok, V. R., & Xu, C. (2011). “An
integrated model for customer online repurchase
intention”. faculty research & Creative Activity. Paper
8. http://thekeep.eiu. edu/business_fac/8
------------------------------------------------------
Indonesian Internet Service Providers Association. (2017).
Indonesian Internet User Penetration Survey 2017.
Accessed from https://apjii.or.id on October 23, 2018.
Internet World Stats. (2017). Internet Growth Statistics.
Accessed from https:// www.internetworldstats. com
on October 23, 2018
iPrice. (2018). Map of Indonesian E-Commerce. Accessed
from https://iprice.co.id on October 25, 2018.
ICBEEM 2019 - International Conference on Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management
256
