
Antibiotic Sensitivity Test Gentamicin in Bacteria Staphylococcus
aureus with Incubation Temperature 33ºC and 35ºC
Vincentia Ade Rizky
1
, Mei Rositasari
2
, Visensius Krisdianilo
1
, Julia Damayanti
2
and Sa’adah Siregar
1
1
Faculty of Pharmacy, Institut Kesehatan Medistra Lubuk Pakam,, North Sumatera, Indonesia
2
Faculty of Health Sciences, Universitas Katolik Musi Charitas, Palembang, Indonesia
Keywords: Sensitivity Test, antibiotic Gentamicin, Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract: Staphylococcus aureus is one of the bacteria that causes infection but is very resistant to various antibiotics
Many factors affect the results of this antibiotic sensitivity test, one of which is the temperature factor.
According to CLSI (2014) the incubation temperature for the sensitivity test used was 35 ± 2ºC, whereas
according to WHO (2004) the temperature used for this test was 35ºC temperature, temperatures higher than
35ºC of the culture seemed sensitive, whereas at temperatures lower than 35ºC resistant colonies will grow
inside the inhibition zone. This type of research is analytic observation. The research sample used was a pure
strain of Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923. The study sample was taken after fulfilling the inclusion and
exclusion criteria. Staphylococcus aureus bacteria that have been inoculated were planted on the Mueller
Hinton Agar media and antibiotics were added by the Kirby-Bauer method, then incubated at 33ºC and 35ºC
respectively. The inhibition zone yield is measured in mm. The measurement data then tested the hypothesis
by the Wilcoxon test with a 0.05 consecutive confidence level. The results showed the mean zone of inhibition
at 33ºC gentamicin 21.67 mm while at 35ºC gentamicin 21.67 mm. These data were analyzed and showed no
difference in the zone of inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus at 33°C and 35°C incubation temperatures.
Based on the results of the study it can be concluded that the difference in incubation temperature of 33ºC and
35ºC can be done in the examination of the Susceptibility Test because there is no difference between the
results of the zone of inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria with variations in incubation temperature.
1 INTRODUCTION
The bacteria Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterial
pathogen that can cause infections and disorders of
the skin include impetigo and folliculitis (Radji,
2010). The spread of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria
in the world is known as Methycillin Resistant
Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). MRSA is an
infection of the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus
which is very resistant to various antibiotics that
causes new problems in the world of health. The last
overall report of the prevalence of Staphylococcus
and MRSA in Indonesia in 2006 reached 23.5%
(Ramadhani, 2014). Bacterial sensitivity test is a
method to determine the level of bacterial
susceptibility to antibacterial substances and to find
out the pure, antibacterial activity. The principle of
this method is inhibition of the growth of
microorganisms, which is a zone of obstacles will be
seen as a clear area around discs containing
antibacterial substances (antibiotics). The Diameter
of the bacterial growth barrier zone indicates bacterial
sensitivity to antibacterial substances. Furthermore,
the wider diameter of the zone of obstacles formed by
the bacteria is increasingly sensitive (Waluyo, 2008).
The sensitivity test result, as reported to the
Clinisi, is the classification of these microorganisms
into one of two or more sensitivity categories. The
simplest system consists of only two categories that
are sensitive and resistant. This classification has
many advantages for statistical and epidemiological
purposes, too rigid to be used by Clinilians.
Therefore, often used classification of three
categories. The Kirby-Bauer method and its
modifications are often used to determine the
sensitivity of the bacteria using three categories of
sensitivity, clinicians and laboratory workers must
understand the exact definition and clinical
significance of those categories (WHO, 2003). Many
factors affect the results of this antibiotic sensitivity
528
Ade Rizky, V., Rositasari, M., Krisdianilo, V., Damayanti, J. and Siregar, S.
Antibiotic Sensitivity Test Gentamicin in Bacteria Staphylococcus aureus with Incubation Temperature 33
o
C and 35
o
C.
DOI: 10.5220/0009974305280535
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology (ICHIMAT 2019), pages 528-535
ISBN: 978-989-758-460-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

test, including environmental factors. Environmental
factors that affect growth include abiotic and biotic
factors. Abiotic factors include temperature, osmose
pressure, drying, and ions from electricity. Biotic
factors are among the factors found in the bacteria
itself (Gultom, 2015). Temperature is the most
important factor in influencing the rate of bacterial
growth. Sometimes temperature is not much noticed
in growth and of bacterial identification. Laying
bacterial isolation at room temperature when
incubators are being used for the safety of other
bacteria often done. Temperature analytic procedures
should be observed to diagnosis in the breeding of
bacteria is acceptable. Influence incubation
temperature may result in an error analytic procedure
to fault inhibition zone results (Safety, 2015).
The optimum growth temperature for
Staphylococcus aureus is 35-37ºC. This sensitivity
test was incubated at 35ºC for optimal growth. If the
temperature is lowered, the time needed for effective
growth will lengthen and produce a wider zone. At
temperatures of 35ºC or lower, colonies can grow
inside the inhibition zone. The incubation time is 16-
18 hours (for rapid diagnosis), but you should use a
conventional 24 hour time for optimum results
(Vandepitte et al., 2010). The bacterial temperature
metabolism Stapylococcus aureus is when the
temperature rises, the metabolic rate in the form of
macromolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, in
Stapylococcus aureus bacteria will suffer damage
permanent (Abrar et al., 2013). When lowered, the
metabolic rate descending (Brooks et al., 2005).
According to Madigan et al (2012) the bacterial
growth temperature can be divided into psychophilic
bacteria (15ºC-20ºC), mesophilic bacteria (20ºC-
40ºC) and thermophilic bacteria (50ºC-60ºC).
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria whose growth is
optimal in temperatures of 35-37ºC are included in
mesophilic bacteria (Vandepitte et al., 2010).
According to WHO on Basic Laboratory the
incubation temperature used for the optimal
sensitivity test is 35ºC with a time of 16-18 hours or
24 hours
(WHO, 2003)
. CLSI on Performance Standards
for Antimicrobial Suceptibility suggests using a
temperature of 35 ± 2ºC (CLSI, 2014). Previous
research stated that temperatures of 37ºC and 40ºC
were effective for the growth of Staphylococcus
aureus toxins and enterotoxins (Vandenbosch et al.,
1973). Other studies on the isolation and
characterization of Staphylococcus aureus of Milk of
Ettawa Crossbred Goat, were inoculated on the
Mueller Hinton media in temperature 37 ºC to obtain
intermediet results (Purnomo, 2006). Antibiotic
sensitivity test according to CLSI uses a temperature
of 35 ± 2ºC (33ºC and 37ºC). According to WHO on
Basic Laboratory the temperature used is 35ºC, at
temperatures higher than 35ºC the culture appears
sensitive, whereas at temperatures lower than 35ºC
the resistant colony will grow inside the inhibition
zone (WHO, 2003).
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
The study was conducted at the Microbiology
Laboratory at Grandmed Lubuk Pakam Hospital. This
Research uses the Wulcoxon Test statistical analysis.
In this research the tools and materials used include:
Ose, Autoclave, Bunsen, sterile cotton swab, test
tube, ruler/ calipers, Nutrient Agar, Mueller Hinton
Agar, Antibiotic Gentamicin, NaCl 0.9% sterile,
Incubator. Media MRVP, Media Lactose, Media
Maltose, H
2
O
2
3%, Coagulase Test, DHO, Mac-
Farland 0,5, Gentian Violet, Lugol/Iodium, Alkohol
96%, and Safranin.
The first step in this research is sterilize the tools
and materials. The tools used must be sterile. The tool
is sterilized using a Dry Heat Oven (DHO) at a
temperature of 160ºC for 2 hours. Then, the materials
used for testing and bacterial growth after being made
in accordance with the specified composition are then
sterilized using an autoclave at 121ºC for 15 minutes.
The next step is to do sterility and quality test of the
media. Steps to do the media sterility test is put the
media Mueller Hinton Agar, Nutrient Agar, Lactose,
Maltose to the incubator at 35ºC for 18-24 hours.
Then proceed witd testing the quality of the media is
create Staphylococcus aureus bacterial suspense with
Mac Farland turbidity level 0.5, the do 10.000
dilution suspensions. Then obtained 10
2
dilutions or
equivalent to the number of colonies from 100-200.
The media to be tested is 10% of the amount of media.
After obtaining the media to be tested then take 100
µL suspense that has been diluted then inoculated in
the media using the spread plate method. Incubate for
18-24 hours at 35ºC. The next steps is making the
suspension bacteria, take 1 ose of bacterial suspense.
Scratch the Nutrient Agar media evenly with the
Streak method. Incubate for 18-24 hours at 35ºC.
2.1 Bacteria Standard Test
Catalase Test. Procedure catalase test (Figure 1) is
Apply one drop of H
2
O
2
3% on a object glass, then
transfer the Staphylococcus aureus bacterial colony
with a loop to the H
2
O
2
solution, then mix. Catalase
positif reaction:evident by immediate effervescence
(air bubble formation), and then catalase negatif
Antibiotic Sensitivity Test Gentamicin in Bacteria Staphylococcus aureus with Incubation Temperature 33
o
C and 35
o
C
529

reaction: no bubble formation (no catalase enzyme to
hydrolyze the hidrogen peroxide. The catalase test is
primarily used to distinguish among gram positive
cocci: members of the genus Staphylococcus are
catalase positif, and members of genera Steptococcus
and Enterococcus are catalase negatif (Tankeshwar,
2013).
Figure 1: Catalase Test (Vetbatch, 2017)
Microscopic Test. Make bacterial suspense from
bacterial colonies that grow on agar nutrient media.
Make preparations slide of bacteria, then do gram
staining. The steps of gram staining (Figure 2) : (a)
fixation of the slide, (b) apply a crystal violet stain for
1 minute, (b) wash slide in a gentle and indirect
stream of tap water for 2 seconds, (c) flood slide with
the iodine wait 1 minute, (d) wash slide in a gentle
and indirect stream of tap water for 2 second, (e) flood
slide with decolorizing agent (alcohol decolorizer)
wait 10-15 second or add drop by drop to slide until
decolorizing agent running from the slide runs clear,
(f) flood slide with a counterstain with safranin, wait
30 second to 1 minute, (g) wash slide in a gentile and
indirect stream of tap water until no color appears in
the effluent and then blot dry with absorbent paper,
(h) observe the resulth of the staining procedure under
oil immersion using a microscope (Tankeshwar,
2015). The result of gram staining is gram negatif
bacteria will stain pink/red and gram positif bacteria
wil stain blue/purple.
Figure 2: Gram Staining (Prajapati et al., 2018)
The next step of bacteria standart test is
biochemical characterization. Potential isolate were
characterized by different biochemical methods like
lactose and maltose test, MR (Methyl red) and VP
(Voges Proskauer) test, and Coagulase test. Sugar
Test (Lactose and Maltose) : Take 1 ose of bacterial
suspense and put it in a sugar medium (lactose and
maltose). Mix evenly. Incubate at 35ºC for 18-24
hours. Methyl Red (MR) Test : Take 1 ose bacterial
suspense, insert into MR media, mix evenly, incubate
at 35ºC for 18-24 hours. After incubating to find out
the reaction, add the Methyl red reagent. Positive
results are indicated by a change in color from yellow
to red. Voges Proskauer Test (VP) :
Take 1 ose
bacterial suspense, insert into the VP media, mix
evenly, incubate at 35ºC for 18-24 hours. After
incubating to find out the reaction, add the KOH and
α-Naphthol reagents. Positive results are indicated by
a change in color from yellow to red. Coagulase Test
: This test is used to determine the presence of free
coagulase by means of 200 µL plasma aseptically
inserted into a sterile test tube. Take 3-5 bacterial
colonies of Staphylococcus aureus , put them in the
test tube, mix carefully. Incubate at 35ºC for 18-24
hours.
The next step is prosedure of antibiotic
sensitivity test. The first Making the Inoculum
(Suspension) : Take 3-5 ose Staphylococcus aureus
bacteri colonies of the same size in the media using
an ose (loop) that has been incanded above Bunsen.
Then insert the colony into a test tube that contains
sterile 0.9% NaCl solution, then homogeneous.
Compare this with turbidity suspension of
Staphylococcus aureus with 0.5 Mac-Farland
comparison solution. NB: Turbidity Bacterial
suspension should be equivalent to Mac-Farland 0.5.
And then, step of Antibiotic Sensitivity Test
(Susceptibility Test) : Inoculation using the Kirby-
bauer method and place the antibiotic in the middle of
the media surface. Incubate the media at 33ºC and
35ºC for 18-24 hours. And then, record and measure
each zone formed around the antibiotic (disc paper).
The resulting inhibition is measured in mm
(millimeters), show procedure in Figure 3.
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
530
3 RESULT
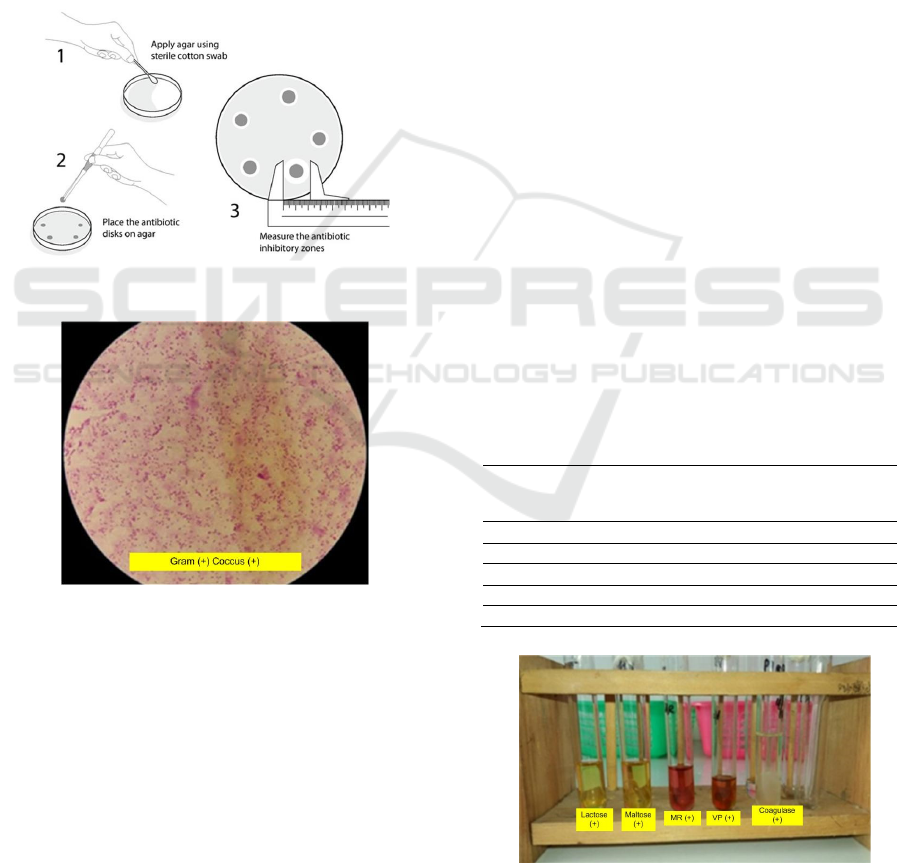
Identification of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria can
be microscopic and biochemical test of bacteria. On
microscopic examination found Gram (+) cocci (+).
These bacteria are round like a ball or spherical,
clustered and purple. The results obtained are the
same as the results of microscopic examination by
Holt et al (1994) which states that the Staphylococcus
aureus bacteria are gram-positive coccus bacteria that
are spherical in shape like a ball. These bacteria are
purple because it is the first absorbing dye is gentian
violet. The result of microscopic test show in Figure
4 below.
Figure 3: Step Antibiotic Test (ACS, 2020)
Figure 4: Microscopic Test
Biochemical tests used to test further
identification of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. This
test is carried out on confectionery media namely
lactose and maltose, Methyl Red (MR), Voges
Proskauer (VP), Catalase Test and Coagulase Test.
The results can be seen in Table 1 and Figure 5. The
Result of Staphylococcus aureus bacterial
biochemistry test carried out in confectionery media,
namely lactose and maltose, showed positive results
with a marked change in green to yellow, indicating
that the bacteria were able to ferment lactose and
maltose. Patty research states that the test of lactose
and maltose sugars of the bacterium Staphylococcus
aureus get positive results that are marked by a
yellow discoloration, this shows that the bacteria
tested are able to ferment the type of sugars tested
(Patty et al., 2016).
In the Methyl Red and Voges Proskauer tests,
positive results were obtained with a change from the
deep red yellow which indicates the presence of
acetoin in the solution produced by bacteria. Dewi’s
research states that the positive results of the Methyl
Red and Voges Proskauer tests are characterized by a
change in color from yellow to red indicating the
presence of glucose fermentation in Staphylococcus
aureus from the formation of acetilmetilcarbinol
(acetoin) (Dewi, 2013). Catalase test is a test to
distinguish between groups of Staphylococcus aureus
or Steptococcus bacteria. The results obtained in the
catalase test are positive which is marked by the
presence of air bubbles (O
2
). Toelle’s research states
that the Staphylococcus aureus bacterial catalase test
with positive results because these bacteria produce
enzymes capable of hydrolyzing hydrogen peroxide
(H
2
O
2
) into water (H
2
O) and air bubbles (O
2
) (Toelle
& Viktor, 2014). On the examination of the coagulase
test positive results were indicated by the presence of
lumpy white jelly. Purnomo’s research states that
Staphylococcus aureus can agglutinate blood,
bacause it has a coagulase reacting factor, the role of
coagulase produced by germs is used as a determinant
of Stapylococcus aureus species that make white clots
like jelly that show positive results (Purnomo, 2006).
Table 1: Test Results for Identification of Staphylococcus
aureus Bacteria
Figure 5: Biochemical Test
Identification Test Results
Lactose Test (+) Positive yellow
Maltose Test (+) Positive yellow
Metyl Red Test (+) Positive red color
Voges Proskauer (+) Positive red color ring
Catalase Test (+) Positive air bubbles
Antibiotic Sensitivity Test Gentamicin in Bacteria Staphylococcus aureus with Incubation Temperature 33
o
C and 35
o
C
531

Sterility test in this study was carried out on Nutrient
Agar Media and Muller Hinton Agar Media. This test
is performed by non-cultivation of Staphylococcus
aureus. The media standard will be tested by means
incubated at 37
0
C for 24 hours. The purpose of the
media sterility test is to determine whether there is
growth of bacteria and fungi of other microorganisms
that can affect the results of research. The results of
sterility media test can be seen in Table 2 and Figure 6.
Table 2: Media Sterility Test
Media Test result Sterile / Not steril
Nutrient Agar Does not
grow
Sterile
Mueller Hinton
Agar
Does not
grow
Sterile
Figure 6: Nutrient Agar Media and Mueller Hinton Agar
Media for media sterility test result
Media quality test performed to determine the growth
of bacteria on a medium which will be used, whether
the media can be overgrown with fertile bacteria or
not. This test is performed on Nutrient Agar and
Mueller Hinton Agar. The results can be seen in Table
3, Figure 7 and Figure 8.
Table 3: Media Fertility Test
Media Test result
(Colonies)
Good/
Not Good
Nutrient Agar Grow Good
Mueller Hinton
Agar
Grow Good
Figure 7: The results of the agar nutrient media quality test
Figure 8: The results of the agar Mueller hinton media
quality test (Mueller Hinton Agar with Gentamicin
Antibiotic Media is shown in the image on the left
3.1 Results of Gentamicin Antibiotic
Sensitivity Test (Susceptibility Test)
Susceptibility test or antibiotic sensitivitty test is used
to determine the inhibitory zone produced from an
antibiotic. Inhibition zone was used as the diagnosis
result if the antibiotics are sensitive or resistant to
these bacteria. The results of the Staphylococcus
aureus bacteria inhibition zone on Gentamicin
antibiotics with an incubation temperature of 33ºC
(Figure 9) and 35ºC (Figure 10) for 24 hours are
presented in Table 4.
Table 4: Results of inhibition zones of Staphylococcus
aureus bacteria on Gentamicin antibiotics with an
incubation temperature of 33ºC and 35ºC.
No
Gentamicin Antibiotic Zone
(mm)
Information
Temperature
of 33ºC
Temperature
of 35ºC
1 21 22 Sensitive
2 22 22 Sensitive
3 21 21 Sensitive
4 21 22 Sensitive
5 22 22 Sensitive
6 21 21 Sensitive
7 22 22 Sensitive
8 22 22 Sensitive
9 23 21 Sensitive
Average 21.67
21.67
Sensitive
Description :
Sensitive ≥ 15mm; Resistance <12mm
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
532

Figure 9: The result of inhibition zone of antibiotic
gentamicin at a temperature 33ºC
Figure 10: The result of inhibition zone of antibiotic
gentamicin at a temperature 35ºC
3.2 Data Analysis
The results of the examination of the zone of
gentamicin antibiotic inhibition of bacteria
Staphylococcus aureus that have been collected, then
processed and then presented in tabular form and
analyzed the data through several stages, namely
normality test and hypothesis testing.
3.2.1 Normality Test
In this study the normality test was carried out using
the Kolomogorov-Smirnov test because the number
of samples used was less than 50 with a significance
level of 95% (=0.05). The following are normality
test results presented in Table 5 below:
Table 5: Normality Test Results
Kolomogorov-Smirnov
Statistic Df Sig
Temp33 ,272 9 ,054
Temp35 ,414 9 ,000
Based on Table 5 the p value (sig) obtained for the
temperature of 33ºC gentamicin antibiotic is 0.054,
for temperature 35ºC gentamicin antibiotic is 0,000.
From the values above there is 1 data that is normally
distributed at 33ºC, while at 35ºC the data is not
normally distributed. Because there is one data that is
not normally distributed, it is followed by a non-
parametric statistical test.
3.2.2 Hypothesis Testing
The Wilcoxon Test is a test used to test differences in
sample pairs in 2 groups (Dahlan, 2014). The results
of data analysis are obtained as shown in Table 6.
Table 6: Wilxocon Test Results
Temp 33 -
Temp 35
Z
,000
Asymp. Sig. 1,000
From the analysis of the data obtained, it can be seen
that the significant value in the Table above is 0,000.
Based on the specified conditions if it is significantly
greater than the alpha value of 0.05 then Ho is
accepted, whereas if it is significantly smaller than the
alpha value of 0.05, Ho is rejected. So it can be seen
that the asymp.sig value obtained is 1,000 is greater
than the alpha value of 0.05 then Ho is accepted.
Thus, it can be concluded that "There is no difference
in the inhibition zone in the Gentamicin Antibiotic
Sensitivity Test for Staphylococcus a ureus Bacteria
for Incubation Temperature Variations of 33ºC and
35ºC".
4 DISCUSSION
In this study, a number of preliminary tests were
carried out including sterility tests, quality tests, and
bacterial standard tests. Sterility tests are carried out
with the aim of ensuring that the media used are not
contaminated with bacteria or other microorganisms.
Fertility test or media quality test is a test used to see
that the media used is good for bacterial growth.
Bacterial standard tests are also used to identify or
confirm tests that the bacteria used are
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria.
Identification of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria
can be done with microscopic tests and bacterial
biochemical tests. On microscopic examination, gram
(+) coccus (+) was obtained. These bacteria are round
like a ball or spherical, clustered and purple. The
results obtained are the same as the results of
microscopic examination by which states that the
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria are gram-positive
positive coccus bacteria that are spherical in shape
like a ball. This bacterium is purple because it absorbs
the first dye, gentian violet (Holt et al., 1994).
Staphylococcus aureus bacterial biochemistry test
carried out on confectionery media, namely lactose
and maltose, showed positive results with a marked
change in green to yellow, indicating that the bacteria
Antibiotic Sensitivity Test Gentamicin in Bacteria Staphylococcus aureus with Incubation Temperature 33
o
C and 35
o
C
533

were able to ferment lactose and maltose. In the
Methyl Red and Voges Proskauer tests positive results
were obtained with a change in color from yellow to
red mangosteen which showed the presence of
acetoin in the solution produced by bacteria. Catalase
test is a test to distinguish between Staphylococcus
and Streptococcus bacteria groups , in this test
positive results are indicated by marked bubbles when
dripped with H
2
O
2.
In the examination of the
coagulase test obtained positive results in the
presence of lumpy white jelly. The results obtained
are the same as the results of Dewi's research (Dewi,
2013).
In this study the results of gentamicin antibiotic
inhibition zones, each incubated at 33
o
C and 35
o
C,
showed no difference because the temperature range
used in the growth temperature range of
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria was either used or
commonly called mesophilic temperature. According
to the research of James H. Jorgensen et al the
optimum growth of Staphylococcus aureus at 35
o
C
for 16-24 hours with vancomysin, daptomycin, and
linezolid antibiotics (James et al., 2009). According
to the Clinical and Laboratory Standars Institute
(2014) sensitivity test or antimicrobial susceptibility
test using temperatures of 35 ± 2ºC (33ºC, 35ºC and
37ºC). Meanwhile, according to WHO on Basic
Laboratory, it is recommended that the temperature
sufficiency test be used for 35 ° C for 24 hours,
because at the most optimal temperature it can reduce
the risk of contamination of other bacteria that will
grow (WHO, 2003).
Analysis of the data used in this study is
Wilxocon. Based on Wilxocon test results, it is
known that there is no difference in the zone of
inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on
gentamicin antibiotics with incubation temperatures
of 33ºC and 35ºC. The results obtained are seen from
the value of sig. 1,000 is greater than the alpha value
(1,000> 0.05).
5 CONCLUSION
Based on the results and discussion carried out it can
be concluded as follows;
a. The average zone of inhibition of the antibiotic test
for gentamicin in Staphylococcus aureus with an
incubation temperature of 33ºC was 21.67 mm
b. The average zone of inhibition of the antibiotic test
for gentamicin in Staphylococcus aureus with an
incubation temperature of 35ºC was 21.67 mm
c. From the results of gentamicin antibiotic inhibition
zones that have been carried out statistical tests, it
can be concluded that there is no difference in the
zone of inhibition in the antibiotic sensitivity test of
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria to the incubation
temperature variations of 33ºC and 35ºC.
REFERENCES
Abrar M. Wibawan. Priossoeryanto. Soedarwanto and
Pasaribu. 2013. Peranan Hemaglutinin Staphylococcus
aureus dalam Proses Adhesi Pada Sel Epitel Ambing
Sapi Perah. J. Veterinary medicine. 7 (1): 4346.
ACS Distance Education. 2020. Phamaceuticals and
Microbiology. [Online],
Available:https://www.acs.edu.au/info/sciences/chemi
cal-sciences/phamaceuticals-and-microbiology.aspx
[2020, January 28].
Brooks GF, Butel JS, dan Morse, SA (2005). Mikrobiologi
Kedokteran Jawetz, Melnick dan Adelberg. Jakarta:
Salemba Medika.
Clinical and Laboratory Standars Institute.
2014.Performance Standards for Antimicrobial
Seceptibility Testing; Twenty-Fourth Informational
Supplement. USA. ISBN1-56238-898-3:1(34)
Dahlan MS (2014) Statistik Untuk Kedokteran dan
Kesehatan: Deskriptif, Bivariat, dan Multivariat,
Dilengkapi Dengan Menggunakan SPSS Edisi 6.
Jakarta : Epidemiologi Indonesia
Dewi AK (2013). Isolasi, Identifikasi dan Uji Sensitivitas
Staphylococcus aureus Terhadap Amoxilin dari Sampel
Susu Kambing Peranakan Ettawa (PE) Penderita
Mastitis di Wilayah Giri Mulyo, Kulon Progo,
Yogyakarta. ISSN : (2) 0126 – 042
Gultom DR (2015). Faktor – Faktor yang Mempengaruhi
Perkembangan Mikroorganisme. Magelang :
Universitas Tidar.
Holt JG. NR Krieg. PHA Sneath. JT Staley. and ST
William. 1994. Bergeys’s manual of determinative
bacteriologi 9
th
ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins.
P:532.
James H. Jorgensen, and Ferraro. 2009. Antimicrobial
susceptibility testing : A review principles and
contemporary practices.
Madigan MT, Martinko JM, Stahl DA & Clark DP (ed).
2012. Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 13
th
edition.
Benjamin Cummings. San Fransisco, pp: 129-131; 134-
139.
Patty RF, Fatimawali, Wewekang DS (2016). Identifikasi
dan Uji Sensitivitas Bakteri yang Diisolasi dari Sputum
Penderita Pneumonia di RSUP Prof.DR. R. D. Kandau-
Manado Terhadap Antibiotik Ampicillin, Sefixim, dan
Xefixime, dan Siprofloksasin. ISSN : 5 (1) 2302-249.
Prajapati V, Karen, Prajapati PH, Sen DJ, and Patel. 2018.
Chemistry and Histochemistry of Gram Staining of
Dyes on Bacterial Peptidoglycan. World Journal of
Pharmaceutical Research. ISSN 2277-7105. 7(16), 490-
535
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
534

Purnomo (2006). Isolasi dan Karakterisasi Staphylococcus
aureus Asal Susu Kambing Peranakan Ettawa. Media
Kedokteran Hewan : 22 (3)
Radji M (2010). Buku Ajar Mikrobiologi Panduan
Mahasiswa Farmasi & Kedokteran. Jakarta : EGC.
Ramadhani PNU (2014). Profil Pasien Berkaitan dengan
Kolonisasi Staphylococcus aureus Methicillin Resisten
Staphylococcus aureus di Ruang Rawat Inap Paska
Bedah Cendana 1 pada April-Juni 2014. Yogyakarta:
Universitas Gajah Mada.
Safety S. 2015. Pengaruh Variasi Suhu Inkubasi Terhadap
Tingkat Pertumbuhan Bakkteri Staphylococcus aureus.
Palembang: Fakultas Ilmu Kesehatan, UKMC
Tankeshwar A. 2013. Catalase test: Principle, Procedure,
Result and Applications. [Online], Available:
https://microbeonline.com/catalase-test-principle-uses-
procedure-results/ [2020, February 12]
Tankeshwar A. 2015. Gram Staining: Principle, Procedure
and Result. [Online], Available :
https://microbeonline.com/gram-staining-principle-
procedure-results/ [2020, February 12]
Toelle NN, Viktor Lenda (2014). Identifikasi dan
Karakteristik Staphylococcus aureus dari infeksi
Ovarium Pada Ayam Petelur Komersial. Jurnal Ilmu
Ternak: 1 (7), 32-37.
Vandenbosch LL. Fung Daniel YC. and Widomski M.
1973. Optimum Temperature for Enterotoxin
Production by Staphylococcus aureus S-6 and 137 in
Liquid Media. Spplied Microbiology, 25 (3).
Vandepitte et al., (2010). Prosedur Laboraturium Dasar
untuk Bakteriologi Klinis. Jakarta : EGC. 29-34.
Vetbatc. 2017. Catalase Test. [Online],
Available:www.vetbact.org/index.php?biochemtest=1
#maincontainer [2020, January 28]
Waluyo L (2008). Teknik dan Metode Dasar Dalam
Mikrobiologi. Malang. UMM Press.
World Health Organization. 2003. Basic Laboratory
Procedures In Clinical Bacteriology, 2
rd
Ed.
Switzerland : Geneva.
Antibiotic Sensitivity Test Gentamicin in Bacteria Staphylococcus aureus with Incubation Temperature 33
o
C and 35
o
C
535
