
Effect of Giving Fatimah Grass (Anastatica Hierochuntica)
Immersion Water to Uterine Contractions in Maternity Mother
Yunita Syahputri Damanik*, Utami Diah Armi, M. Dasril Samura, Friska Ernita Sitorus, Nur Mala
Sari
Departement Of Public Health, Health Institute Of DELI HUSADA Deli Tua,
Keywords : Grass Fatimah (Anastatica Hierochuntica), Uterine Contractions, Maternity Mother.
Abstract : Fatimah grass (Anastatica Hierochuntica) is a plant that contains phytochemical ingredients, namely
flavonoids. Flavonoids are natural ingredients that have a structure resembling endogenous steroid
hormones, namely estradiol and show estrogenic activity. The purpose of this study was to analyze the
effect of giving fatimah grass (Anastatica Hierochuntica) immersion water to the uterine contractions of
maternal mothers. This research is an experimental study using Paired T-Test (pre-test and post-test). The
number of samples in this study were 20 women who were divided into 2 groups, namely the control group
and the case group who were given 500 cc of water with 100 grams of Fatimah grass (Anastatica
Hierochuntica). The results of this study indicate the results obtained from the control group with an average
value of uterine contractions of maternity mothers at 2.90 (116 seconds) with Std. Deviation of 1.449.
Whereas in the treatment group, the mean value of uterine contractions of maternal mothers was 4.40 (176
seconds) with Std. Deviation of 1.265. The average difference between the control group and the treatment
group was 1.8 (72 seconds). From the results of statistical tests using the Wilcoxon test obtained a P-Value
of 0.025, it can be concluded that there is a difference between the control and treatment groups (pretest and
posttest) and it can be concluded that there is an effect of giving fatimah grass soaking water (Anastatica
Hierochuntica) to uterine contractions in maternity mothers.
1 INTRODUCTION
Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR) is an indicator of a
country's health. AKI in the world globally is 830
every day, in Indonesia 38 mothers per 305 mothers
give birth died due to illness or complications
related to pregnancy and childbirth. Factors that
cause mothers to die after giving birth are heavy
bleeding, infection, preeclampsia, parturition or
disability and unsafe abortion (Achadi, Health and
University, 2019).
In Arab countries and among Malaysians 63.9%
use the Fatimah grass plant (Anastatica
Hierochuntica) as a traditional herbal that is believed
to facilitate labor, postpartum care and
breastfeeding. Beliefs in developing countries,
including Indonesia's Fatimah (Anastatica
Hierochuntica) grass immersion water, are also used
hereditary during pregnancy, especially before
delivery, which is believed to facilitate labor, reduce
uterine bleeding, accelerate labor and postnatal care
(Baker RK, 2013).
Childbirth is a physiological process that occurs
in all pregnant women. This physiological process
can turn pathological if the treatment is not handled
properly. Complications in labor often arise
suddenly and this must be anticipated to ensure the
safety of the mother and fetus. Labor is defined as
regular uterine contractions that cause cervical
thinning and dilatation so that the results of
conception can exit the uterus. The exact trigger of
labor is unknown.
Normal childbirth is a process of fetal
expulsion, born spontaneously with the presentation
of the back of the head, followed by removal of the
placenta and membranes from the mother's body,
without complications of both the mother and fetus.
Childbirth is the process of expulsion from the
conception (fetus and placenta) that has reached the
age of the month or can live outside the womb
through the birth canal or through another way
(caesarean), with help or without help (own
strength). This process begins with true labor
contractions, which are characterized by progressive
580
Damanik, Y., Armi, U., Samura, M., Sitorus, F. and Sari, N.
Effect of Giving Fatimah Grass (Anastatica Hierochuntica) Immersion Water to Uterine Contractions in Maternity Mother.
DOI: 10.5220/0009976205800587
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology (ICHIMAT 2019), pages 580-587
ISBN: 978-989-758-460-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

changes in the cervix and ends with birth. Maternity
is the process of expulsion from the conception
(fetus and uri) that has been quite months and can
live outside the womb through the birth canal or
through other roads with help or without help or
strength alone. Normal childbirth is the process of
expulsion from the conception that can live from
inside the uterus through the vagina to the outside
world that occurs in term pregnancy (37-42 weeks)
with marked uterine contractions that cause thinning,
cervical dilatation, and push the fetus out through
the road born with a percentage of the back of the
head without tools or help (spontaneous birth) and
no complications in the mother and fetus (Widia,
2015).
The factors that stimulate birth (birth) in
humans are very complex and reflect a series of
endocrine-related events that take place in sync. As
estrogen increases during pregnancy, this hormone
stimulates an increase in oxytocin receptors in the
fetus. The consequences of estrogen deficiency are
prolonged labor and death in the uterus, unless a C-
section is performed.
This inadequate uterine contractions prolong the
time of I. In general, the primigravida of the old time
I was 13-14 hours and multigravida of the old time I
which was 6-7 hours. The duration of labor will be
longer if the mother experiences interruption of
uterine contractions, causing a prolonged labor. Old
parturition is labor that lasts more than 24 hours in
primigravida, and more than 18 hours in
multigravida. Old parturition is a latent phase of
more than 8 hours. The absence of uterine
contractions during childbirth can result in
prolonged parturition which can also have an impact
on the mother and fetus, namely intrapartum
infection, uterine rupture, succutanous head and fetal
head molasses. Old parturition contributes to
maternal mortality and newborn mortality. The
average parturition in the world causes maternal
deaths by 8% and in Indonesia by 9%, while
newborns account for 26% for the world and 30%
for Indonesia
Belief in developing countries, fatimah grass
soaking water (Anastatica hierochuntica) or also
known as Rose Jericho is used as medicine during
pregnancy, especially before delivery, which is
believed to facilitate labor and reduce bleeding.
Indonesian people for generations have known and
used fatimah grass to accelerate labor. You do this
by soaking dried Fatimah grass in warm water, then
drinking the immersion water.
Fatimah grass contains flavonoid phytochemical
which is a natural material with a structure similar to
estradiol and shows estrogenic activity. High levels
of estrogen push the connective signal in uterine
smooth muscle cells. The formed connexes are
inserted in the myometrial plasma membrane to
form fissure links that electrically unite the uterine
smooth muscle cells so that they are able to contract
coordinately. These changes in myometrium cause
increased responsiveness of the uterus to oxytocin
which ultimately triggers labor. High estrogen levels
also encourage the formation of prostaglandins
which play a role in cervical maturation by
stimulating cervical enzymes that locally break
down collagen fibers. Fatimah grass is believed to
accelerate labor because of its phytoestrogen and
other minerals. Physiologically, the hormone
estrogen is proliterative so that it can increase the
number of myometrial cells and oxytocin receptors
in the myometrium. Thus it can increase the
sensitivity of myometrium against oxytocin and
increase the effectiveness of myometrial
contractions.
Fatimah grass is believed to accelerate labor
because of its phytoestrogen and other minerals.
Physiologically, the hormone estrogen is
proliferative so that it can increase the number of
myometrial cells and oxytocin receptors in the
myometrium. Thus it can increase the sensitivity of
myometrium to oxytocin and increase the
effectiveness of myometrial contractions (Herman
and Serudji, 2017).
Based on the results of the Indonesian
Demographic and Health Survey (2012), it is known
that the maternal mortality rate is 102 per 100,000
live births and the infant mortality rate is 23 per
100,000 live births. The most common causes of
maternal death in Indonesia are caused by direct
obstetrics namely bleeding, preeclampsia /
eclampsia and infection resulting from the absence
of significant uterine contractions associated with
prolonged labor. One direct cause of maternal death
in Indonesia is prolonged labor, which is influenced
by inadequate uterine contractions (his). Some of the
direct causes of maternal mortality in Indonesia are
still dominated by birth canal such as vaginal
rupture, perineal rupture and uterine rupture. For
16%, rupture of the birth canal is the first cause of
bleeding after uterine atony. According to Desiyani
Nani 2009, giving Fatimah grass (Anastatica
Hierochuntica) immersion water can increase the
number of active oxytocin receptors in the uterine
muscle so that it can help reduce maternal mortality
due to no uterine contractions. (SDKI, 2012).
The main physiological strength during labor is
uterine contractions. Uterine contractions are
Effect of Giving Fatimah Grass (Anastatica Hierochuntica) Immersion Water to Uterine Contractions in Maternity Mother
581

rhythmic contractions of the smooth muscle of the
uterine wall that starts from the uterine fundus
region. These contractions occur in the third
trimester and medics often mistake the strong
Braxton Hicks contractions for the initial
contractions of labor. Braxton Hicks strong
contractions can be mistaken as an early sign of
labor, and this is known as fake labor. The initial
contraction time must be more than one hour and if
the contraction occurs in close proximity and lasts a
long time, maybe the mother will soon experience
childbirth (Elisabeth Siwi Walyani, Amd.Keb, Th.
Endang Purwoastuti, S.Pd, 2015).
Childbirth is a physiological process that occurs
in all pregnant women. This physiological process
can turn into pathological if management is not
handled properly. Normal childbirth is a process
when a woman's body expels an existing baby that
has been fully developed or has a womb of less than
9 months or 40 weeks, as long as the womb develops
gradually in the womb (Karinta Ariani Setia Putri,
2019). Infant mortality due to infection caused by
Caput Succedaneum, according to WHO in 2012
amounted to 0.05%.
Whereas in Indonesia the infant mortality rate
from Caput Succedaneum infection in 2012 was
11% of 35 per 1000 live births. Based on
Baishideng, in 2013, Caput Succedaneum was
relatively common at birth, but was rarely diagnosed
in the womb.
Fatimah grass is known as a grass that can help
accelerate the labor process, it is known that fatimah
grass contains an oxytocin-like substance which is a
hormone that is widely used in labor induction drugs
and serves to trigger or accelerate the rate of uterine
contractions (Ajeng Anastasia Kinanti, 2019).
Novianty 2017, analyzed the effects of water
immersion in Fatimah grass on estrogen hormone
levels in pregnant white rats. The results of this
study showed that there were significant differences
(p <0.05) of estrogen hormone levels between the
control group (55.51 ± 7.60) with the P2 group
(67.37 ± 7.14) and P3 (68.13 ± 7, 33) at a dose of 20
gr and 40 gr. The conclusion of this research is that
there is a significant increase in the level of the
hormone estrogen after giving Fatimah grass
immersion water to pregnant white rats (Herman and
Serudji, 2017).
The provision of fatimah grass soaking water
had previously been done quite a lot by labor
assistants, but have not been exposed to many other
labor assistants because of the process, way of
giving, the number and processing of fatimah grass
that they do not know well yet.
Based on the above problems, researchers
consider it necessary to conduct further research on
the Effect of Fatimah Grass Immersion Water
(Anastatica Hierochuntica) on Uterine Contractions
in Maternity Mothers. This is necessary to prevent
complications that have a negative impact on the
health of maternity mothers. This is needed to
prevent complications that can occur in maternal
health. Based on the experiences that have been
faced by researchers in this study related to uterine
contractions during labor especially not the normal
contraction during childbirth and after the release of
the baby into the placenta, causing complications
when labor is increasingly giving a strong impetus to
researchers to conduct this research.
2 METHOD
Research design is a method used in the process of
collecting research data so that research results can
be proven. This research is an experimental research
that is research in which the researcher deliberately
raises the occurrence of an event or condition, in
other words experimental research is a way to look
for a causal relationship (causal effect). The
experimental method used was a quasi-experimental
method using the Wilcoxon test. The population in
this study were all women who were going to deliver
at the Klinik Bersalin Astuti in Percut Sei Tuan, Deli
Serdang, which numbered 20 people. The sampling
technique in this study is purposive sampling, which
is a probability sampling method that is carried out
with certain criteria with the number of samples in
this study is 20 people, with a control group division
of 10 people and an intervention group of 10 people.
The method for treating Fatimah grass
(Anastatica Hierochintica) soaking water is as
follows:
a. Take Fatimah grass as much as 100 grams,
then wash it cleanly, this washing aims to
remove all dirt that may stick during the
storage process.
b. After washing, then enter and soak the grass of
Fatimah (Anastatica Hierochuntica) into the
warm water into a container such as a bowl or
glass containing 500 cc of warm water.
c. Make sure the Fatimah grass is submerged
with warm water as a whole.
d. Leave it for a few moments until the grass
withers and does not soak the grass for too
long. Immersion in the long term can make the
oxytocin content even higher so that it poses a
danger to mother and baby.
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
582

e. After the immersion process is finished, give it
to the mother who will deliver after opening 1
cm to be drunk immediately.
f. Evaluate the results of giving the fatimah grass
soaking water after 1 hour of administration.
Figure 1: How to treat water immersion in Fatimah
Grass (Anastatica Hierochuntica).
3 RESULTS
Based on the frequency distribution, it can be seen
that the Influence of Fatimah Grass (Anastatica
Hierochuntica) Immersion Water Against Uterine
Contractions in Maternal Mothers is more common
in mothers aged 18-19 years as many as 14 samples
(70%). Whereas maternity mothers with the age of
20-21 years were 6 samples (30%). The Influence of
Fatimah Grass (Anastatica Hierochuntica)
Immersion Water Against Uterine Contractions in
Maternal Mothers occurred in mothers who worked
as housewives in 18 samples (90%) also occurred in
mothers who worked as entrepreneurs as many as 2
samples (10%). The Influence of Fatimah Grass
(Anastatica Hierochuntica) Immersion Water
Against Uterine Contractions in Maternal Mothers
occurs in mothers with junior high school education
of 2 samples (10%), also occurs in mothers with
high school education of 18 samples (90%).
Data on oxytocin levels were analyzed using a
computer program. In this study a normality test for
oxytocin levels was performed using the Shapiro
Wilk test. The results of data normality are presented
in Table 2.
In this study, of the 20 samples, there were
women who gave birth to the first study (primipara)
and women who received 18-21 years. Demographic
data of the respondents consisted of parietas, age,
occupation and education.
Based on Table 1, it is known that the Influence
of Fatimah Grass (Anastatica Hierochuntica)
Immersion Water Against Uterine Contractions in
Maternal Mothers is more common in mothers aged
18-19 years, as many as 13 samples (65%). While
mothers with age 20-21 years were 7 samples (35%).
The Influence of Fatimah Grass (Anastatica
Hierochuntica) Immersion Water on Uterine
Contractions in Maternal Mothers occurred in
mothers who worked as housewives in 17 samples
(85%) also occurred in mothers who worked as
entrepreneurs as many as 3 samples (15%). The
Influence of Fatimah Grass (Anastatica
Hierochuntica) Immersion Water Against Uterine
Contractions in Maternal Mothers occurs in mothers
with junior high school education of 2 samples
(10%), also occurs in mothers with high school
education of 18 samples (90%).
Effect of Giving Fatimah Grass (Anastatica Hierochuntica) Immersion Water to Uterine Contractions in Maternity Mother
583
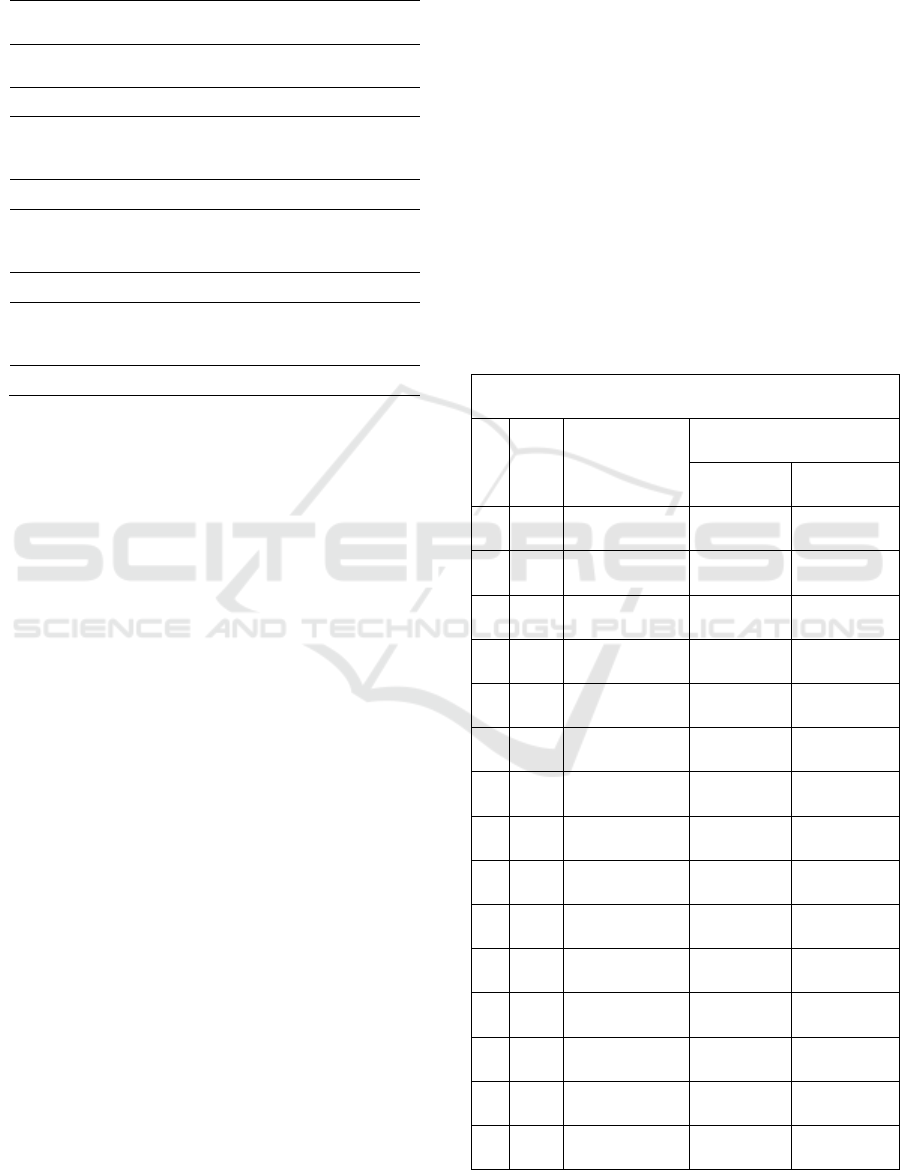
Table 1: Frequency Distribution Effect of Giving
immersion water Fatimah Grass (Anastatica
Hierochuntica) Against Uterine Contractions.
No Characteristics of
Respondents
N Percentage
(%)
1 Parity
1. Primipara
20
100 %
n 20 100 %
2 Age
1. 18-19
2. 20-21
14
6
70 %
30 %
n 20 100%
3 Profession
1. Housewife
2. Private sector worker
18
2
90 %
10 %
n 20 100%
4 Education
1. Middle School
3. High School
2
18
10 %
90 %
n 20 100%
Based on Table 2, Observation of the Influence
of Fatimah Grass (Anastatica Hierochuntica)
Immersion Water Against Uterine Contractions in
Maternity after cervical opening 1 Cm, there were 8
people from the control group who were given water
immersed in fatimah grass which underwent normal
uterine contractions (Contraction of 5x10 '> 40 " )
and 2 people from the control group who were given
water immersed in fatimah grass experiencing
abnormal uterine contractions (2x10 '<20
"contraction) while from the intervention group who
were not given water immersed in fatimah grass
found 2 people experienced normal uterine
contractions (5x10' contraction> 40 ") and 8 people
experienced abnormal uterine contractions (2x10
'<20" contraction). Observation was carried out
after 1 hour of giving fatimah grass immersion water
to 10 people from the control group.
Observation was carried out after 1 hour of
giving fatimah grass immersion water to 10 people
from the control group, observation after 1 hour was
carried out in the hope that the fatimah grass soaking
water had an effect on 10 mothers who would give
birth soon with a contraction. Then see again
whether the contractions are normal or not. The gift
is not required to be done at the same time to 10
mothers, the important thing is to pay attention to
the time of administration, the amount of fatimah
grass immersion water that is given and observe 1
hour later,and the most important thing is to pay
attention to your condition at the time of childbirth
while still checking your physical condition and vital
signs.
Based on Table 3, the test results for normality
of uterine contractions, p values <0.05 means that
data on oxytocin levels are not normally distributed.
So the test that meets the requirements is the
Wilcoxon test. Based on Table 4, it is known that in
the control group the mean value of uterine
contractions of maternal women was 2.90 (116
seconds) with Std. Deviation of 1.449. Whereas in
the intervention group, the mean value of uterine
contractions of maternal mothers was 4.40 (176
seconds) with Std. Deviation of 1.265. The mean
difference between the control group and the
intervention group was 1.8 (72 seconds). From the
results of statistical tests using the Wilcoxon test, a
P-value of 0.025 is obtained, so it can be concluded
that there are differences between the control and
intervention groups (pretest and posttest).
Table 2: Frequency distribution of 20 maternity mother.
Uterine Contractions After Cervical Opening 1 cm
No Code
Giving
Fatimah Grass
immersed
water
1 Hour After Giving
Uterine
contraction
s
the results
1 K was given
Contraction
5x10’>40”
Normal
2 K was given
Contraction
5x10’>40”
Normal
3 K was given
Contraction
5x10’>40”
Normal
4 K was given
Contraction
5x10’>40”
Normal
5 K was given
Contraction
2x10’<20”
Abnormal
6 K was given
Contraction
5x10’>40”
Normal
7 K was given
Contraction
5x10’>40”
Normal
8 K was given
Contraction
5x10’>40”
Normal
9 K was given
Contraction
2x10’<20”
Abnormal
10 K was given
Contraction
5x10’>40”
Normal
11 I Not given
Contraction
5x10’>40”
Normal
12 I Not given
Contraction
2x10’<20”
Abnormal
13 I Not given
Contraction
2x10’<20”
Abnormal
14 I Not given
Contraction
2x10’<20”
Abnormal
15 I Not given
Contraction
5x10’>40”
Normal
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
584

16 I Not given
Contraction
2x10’<20”
Abnormal
17 I Not given
Contraction
2x10’<20”
Abnormal
18 I Not given
Contraction
2x10’<20”
Abnormal
19 I Not given
Contraction
2x10’<20”
Abnormal
20 I Not given
Contraction
2x10’<20”
Abnormal
Table 3: Test Results for Normality of Uterine
Contractions.
Shapiro-Wilk
Statistic df Sig.
Pre Test
.594 10 .000
Post Test
.509 10 .000
Table 4: Frequency Distribution of Influence of Fatimah
Grass (Anastatica Hierochuntica) Immersion Water
Against Uterine Contractions.
Group N Mean
Std.
Deviation
P-Value
(Sig.2
tailed)
Control 10
2.90 1.449
0,025
Intervention 10
4.40 1.265
n 20
4 DISCUSSIONS
Effects of consuming Fatimah Grass (Anastatica
Hierochuntica) Immersion Water on Uterine
Contractions in Maternity after cervical opening 1
Cm, there were 8 people from the control group who
were given Fatimah grass immersion water which
experienced normal uterine contractions (5x10 '> 40
"Contraction) and 2 people from the control group
was given fatimah grass immersion water which
experienced abnormal uterine contractions (2x10
'<20 "contraction) while from the intervention group
that was not given fatimah grass immersion water it
was found 2 people experienced normal uterine
contractions (5x10'> 40" contraction) and 8 people
experience abnormal uterine contractions (2x10 '<20
"contraction).
The results of the analysis showed that there
was an effect of giving fatimah grass (Anastatica
Hierochuntica) immersion water to uterine
contractions in maternal. Based on the results of the
analysis, it can be interpreted that the mother who
consumes water from the grass of Fatimah grass
(Anastatica Hierochuntica) will help increase uterine
contractions when the mother gives birth. The
results of this study showed that in the control group
the mean value of uterine contractions of maternal
women was 2.90 (116 seconds) with Std. Deviation
of 1.449. Whereas in the treatment group, the mean
value of uterine contractions of maternal mothers
was 4.40 (176 seconds) with Std. Deviation of
1.265. The average difference between the control
group and the treatment group was 1.8 (72 seconds).
From the results of statistical tests using the
Wilcoxon test obtained a P-Value of 0.025, it can be
concluded that there are differences between the
control and treatment groups (pretest and posttest)
and it can be concluded that there is an effect of
giving fatimah grass immersion water (Anastatica
Hierochuntica) to uterine contractions in maternity
mother.
Increased uterine contractions that occur after
giving fatimah grass immersion water is a very
positive thing that is expected for medical workers
who help with the labor process, because fatimah
grass soaking water is not much different from
drinking water normally consumed by mothers will
not complicate the process of giving. Fatimah grass
soaking water that will be easier blessed by Mother
because how to consume it is also very easy to do, it
also really helps the labor process of labor continues
to run well, given the considerable number of cases
of childbirth that cause death because there are no
contractions during labor.
The results of this study also did not fully affect
the contraction process after giving Fatimah grass
soaking water, because there were also some
mothers who were given fatimah grass immersion
water did not get a good response from the results of
the submerged water, however, more women
experience normal contractions compared to those
given but do not experience normal contractions. As
in this study of 10 mothers who will give birth, there
were 8 mothers who experienced normal
contractions and there were 2 mothers who
experienced abnormal contractions after being given
water bathed with fatimah grass.
This is very helpful for birth attendants to
continue to provide support to mothers who are
about to give birth and of course to help mothers
who experience fear and worry during labor due to
complications that occur during childbirth such as
not contracting the uterus normally. Based on the
Effect of Giving Fatimah Grass (Anastatica Hierochuntica) Immersion Water to Uterine Contractions in Maternity Mother
585

results of this study, fatimah grass immersion water
can provide a positive response to the occurrence of
uterine contractions in mothers who will give birth
and is believed to accelerate labor, because the
fatmah grass (Anastatica Hierochuntica) contains
phytoestrogens and other minerals.
During the research process, 10 mothers who
were sampled in this study were afraid that if
something bad happened to their baby after drinking
fatimah grass soaking water, but with the
explanation given by the researcher, as well as
evidence that this has also previously been given to
mothers who will give birth and even make the
delivery process quickly and safely and mothers do
not feel pain for a long time and then they feel calm
and can receive well. In line with the process of
providing immersion water, researchers still provide
a sense of calm and comfort to the mother by still
inviting her to communicate.
The results of this study are in line with the
Novianty 2017 study, which analyzes the effect of
giving fatimah grass immersion water on estrogen
hormone levels in pregnant white rats. The results of
this study showed that there were significant
differences (p <0.05) of estrogen hormone levels
between the control group (55.51 ± 7.60) with the P2
group (67.37 ± 7.14) and P3 (68.13 ± 7, 33) at a
dose of 20 gr and 40 gr. Conclusion, there was a
significant increase in estrogen hormone levels after
giving Fatimah grass immersion water to pregnant
white rats (Herman and Serudji, 2017).
The results of this study are in line with
research on the effect of aqueous extract of
anastatica hierochuntica on some hormones in
mouse females to obtain the results of fatimah grass
immersion in female rats showed a significant
increase (p <0.05) in the levels of the hormones LH,
FSH, Prolactin and progesterone. However, no
studies to date have been able to clearly show an
increase in LH, FSH, prolactin, and progesterone in
female rats with extracts or water immersion in
fatimah grass, so more research must be done to
confirm it (Safitri and Yantri, 2019) .
Paired t-test results showed a significant
difference between frequencies without and with
oxytocin 0.01 IU stimulation in estradiol (p = 0.032),
RF10 group (p = 0.026), RF20 (p = 0.001), and
RF40 (p = 0.027) . It can be concluded that water
soaked by Fatimah grass (Anastatica hierochuntica
L) can increase the frequency of contraction of
smooth muscle of the rattus norvegicus Sprague
Dawley uterus in the estrous phase. increase the
number of active oxytocin receptors in the uterine
muscle. It is proven by the increasing frequency of
contraction as a form of mechanical activity
response from the increasing number of oxytocin
bonds with oxytocin receptors in the uterine muscle
(Nani, 2009).
5 CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study indicate the effect of giving
Fatimah grass (Anastatica Hierochuntica) immersion
to the uterine contractions of maternal mothers can
be concluded that there are significant differences
between the results of giving Fatimah grass
immersion water among respondents who were
given Fatimah grass soaking water (Anastatica
Hierochuntica) with those not given to maternity
mother.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This Research Was Supported By Health Institute Of
Deli Husada, Health Institute Of Medistra Lubuk
Pakam, Sembiring General Hospital Foundation,
And Medistra Foundation, Indonesia.
REFERENCES
Achadi, E. L., Kesehatan, F. and Universitas, M. (2019)
‘Kematian Maternal dan Neonatal di Indonesia’.
Ajeng Anastasia Kinanti (2019) ‘Manfaat Rumput
Fatimah Jelang Persalinan’, p. 6.
Baker RK. The Effect Of Aqueous Extract Of Anastatica
Hierochuntica On Some Hormones In Mouse Females.
Ibn Al-Haitham Journal For Pure and Applied
Science. 2013;26(2):198-205.
Elisabeth Siwi Walyani, Amd.Keb, Th. Endang
Purwoastuti, S.Pd, A. (2015) ‘Asuhan Persalinan dan
Bayi Baru Lahir’.
Glessner-fischer, A. D. (2018) ‘The Role of Sex
Hormones in Inducing Maternal Uterine Remodeling
and Vasodilation During Pregnancy’.
Herman, R. B. and Serudji, J. (2017) ‘Pengaruh Pemberian
Air Rendaman Rumput Fatimah (Anastatica
Hierochuntica) Terhadap Kadar Hormon Estrogen
Pada Tikus Putih (Rattus Norvegicus) (Effect of
Giving Water of Fathimah Grass (Anastatica
hierochuntica) Toward The Level of Estrogen
Hormone’,2 (November), pp. 109–113.
Karemore, M. N. and Nagpur, R. T. M. (2017) ‘No Title’,
8(12), pp. 5326–5335. doi: 10.13040/IJPSR.0975-
8232.8(12).5326-35.
Karinta Ariani Setia Putri (2019) ‘Melahirkan Normal
Proses dan Tahapan’, p. 10.
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
586

Nani, D. (2009) ‘Pengaruh air rendaman rumput fatimah
(Anastatica hierochuntica L) Terhadap Frekuensi
Kontraksi Otot Uterus Tikus Galur Sprague Dawley
Pada Fase Estrus’, Jurnal Keperawatan Soedirman
(The Soedirman Journal of Nursing), 4(1), pp. 1–8.
Noviyanti, Herman, R. B. and Serudji, J.(2017) ‘Pengaruh
Pemberian Air Rendaman Rumput Fatimah
(Anastatica Hierochuntica) Terhadap Kadar Hormon
Estrogen Pada Tikus Putih (Rattus Norvegicus) (Effect
of Giving Water of Fathimah Grass (Anastatica
hierochuntica) Toward The Level of Estrogen
Hormone’, 2 (November), pp. 109–113.
Safitri, Y. and Yantri, E. (2019) ‘Artikel Penelitian
Pengaruh Pemberian Air Rendaman Rumput Fatimah
(Anastatica Hierochuntica) Terhadap Kadar Hormon
Oksitosin dan Hormon Prolaktin Pada Tikus Putih
(Rattus Norvegicus) Menyusui Perbandingan’, 8
(Supplement 1), pp. 31–35.
SDKI (2012) ‘Survey Demografi Dan Kesehatan
Indonesia Program Perencanaan Persalinan Dan
Pencegahan Komplikasi (P4K .akses 20 Mei 2016).’
Widia Shofa, Ilmiah. Buku Ajar Asuhan Persalinan
Normal, Yogyakarta: Nuha Medika, 2015.
Effect of Giving Fatimah Grass (Anastatica Hierochuntica) Immersion Water to Uterine Contractions in Maternity Mother
587
