
Test the Effectiveness of Durian Skin Briquettes in Reducing
Zinc Content (Zn) in Well Water
Samuel Marganda Halomoan Manalu, Fithri Handayani Lubis, Friska Ernita Sitorus, Astriana
Fransiska Butarbutar
Institut Kesehatan DELI HUSADA Deli Tua
Keywords: effectiveness test, durian skin briquettes, zinc content, well water.
Abstract: Water has a very important role for human survival. Well water is a source of ground water. Well water in
general contains several types of minerals one of which is often found is the mineral zinc (Zn). Excessive
consumption of Zn can lead to other mineral deficiencies. A dose of zinc consumption (Zn) of 2 grams or
more can cause vomiting, diarrhea, fever, extreme fatigue, anemia, and reproductive disorders. One of the
treatment techniques that can be used to reduce Zn content in well water is absorption, using briquette media.
The absorbent used is durian skin briquettes as one of the filter media in the filtering. The purpose of this
study was to determine the effectiveness of durian skin briquettes in reducing Zn levels in well water. This
type of research used is quasi-experimental research designs with pre and post test design. Samples in the
form of well water with filtering treatment with 15 cm gravel filter media, 20 cm sand and durian skin
briquettes with a thickness of 45 cm, 50 cm, 55 cm and 60 cm durian skin briquettes. Each repetition is done
3 times. Where the water is filtered as much as 6 L and takes 18 minutes during filtering. The results showed
that the sample before filtering well water had zinc levels of 21.38 mg / l. In screening with briquette thickness
of 45 cm, 50 cm, 55 cm and 60 cm respectively the average levels of Zn were 8.66 mg / l, 8.05 mg / l, 7.47
mg / l and 6.97 mg / l. Briquette layer with a thickness of 60 cm is most effective in reducing the level of Zn
with a value before filtering at 21.38 mg/l and after a screening of 6.97 mg/L. Reduction of zinc levels after
screening was conducted at 14.41 mg/l with a percentage of 67.39%. In the results of the filtering there is a
decrease in the Zn content of well water, so it can be concluded that the use of durian skin briquettes as a filter
media is effective in reducing Zn levels. The obstacle that was found during the implementation of filtering
well water with durian skin briquettes is that it takes a long time in the screening proces.
1 INTRODUCTION
Water is a substance that has a very important role
for human survival. One source of water that is
sourced from groundwater groups which is still
widely used as well water. Water sources on earth
come from surface water which is water from rivers
and lakes. The quality of ground water depends on its
depth can be called shallow ground water or deep
ground water. As well as space water, which is water
that comes from the atmosphere, such as rain and
snow. The quality of various water sources varies
according to natural conditions and human activities
that are around (Slamet, 2018).
Over time, the development of civilization and
increasing population will increase life activities that
increase water pollution (Sutrisno, 2017). In certain
areas, the available water does not meet health
requirements, so simple and modern repair efforts are
needed (Kusnaedi, 2018). One effort that can be taken
to optimize the use of water resources, especially to
produce energy is to optimize the treatment of water
resources (Nuraeni, 2019).
Ground water is a portion of rainwater that reaches
the earth's surface and absorbs into the soil layer and
becomes ground water (Chandra, 2017). Deep ground
water is generally classified as clean because it has
natural filtering.
One of the chemicals in ground water is Zn.
Excessive Zn levels in water in addition to causing
health effects can also cause a yellow color on
clothes,sinks and floors in the bathroom, a bad taste
in water, precipitation on the turbidity wall of the
water.Zn is needed by the body for metabolic
processes, but in high levels it can be toxic (Slamet,
2018). Zn dose of 2 grams or more can cause
588
Halomoan Manalu, S., Lubis, F., Sitorus, F. and Butarbutar, A.
Test the Effectiveness of Durian Skin Briquettes in Reducing Zinc Content (Zn) in Well Water.
DOI: 10.5220/0009976705880595
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology (ICHIMAT 2019), pages 588-595
ISBN: 978-989-758-460-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
vomiting, diarrhea, fever, fatigue, anemia, and
reproductive disorders. Zn supplements can cause
poisoning, as well as acidic foods and stored in cans
coated with Zn (Almatsier, 2017). Zn metal is
actually not toxic but in an ionic state, Zn free has
high toxicity. Zinc shakes are caused by inhalation of
Zn-oxide during the galvanization process or the
joining of Zn-containing materials. Although Zn is an
essential element for the body, in high doses Zn can
be dangerous and toxic. Excessive consumption of Zn
can cause other mineral deficiencies.Zn toxicity can
be acute and chronic. Zn intake of 150-450 mg / day
causes a decrease in Cu levels, alteration of Fe
function, reduction of body immunity, and reduction
of high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels
(Widowati, 2018). Zn contamination sources can
come from various human activities that produce
waste in the form of polluter. These pollutants are
transported by rainwater and water movement from
the sea and freshwater waters to the river mouth
which is a meeting place for sea and fresh waters. If
it is known that the Zn level has exceeded the quality
standard, then it is necessary to do a follow-up in
preventing interference caused by the Zn metal
(Amriani, 2016). According to the Republic of
Indonesia Minister of Health Regulation No. 416 /
MENKES / PER / IX / 1990 the maximum allowable
Zn level is 15 mg / L. One way of water treatment is
by absorption technique, the media used is activated
carbon or charcoal. The most widely used absorbent
to absorb heavy metals is activated carbon.
Activated carbon is a kind of absorbent
(absorbent) black, granular, pellet or powder
(Kusnaedi, 2017). Activated carbon is the most
commonly used absorbent for the adsorption process
because of its high adsorption capacity.
Commercially available activated carbon has a high
price. Therefore, a lot of development is being done
to find alternative absorbents.
In this study the absorbent used was durian skin.
Local durian production in Indonesia reaches 600,000
tons per year and the skin reaches 400,000 per year
(Trubus, 2017). Skin weights reach 70% of the total
weight of the fruit, the greater durian fruit waste
comes from the skin (Untung, 2017). To overcome
the increased production of solid waste that can cause
environmental problems, durian skin can be
processed into briquettes that are used as absorbents
in water filtration.
Based on research, durian skin proportionally
contains high cellulose (50-60%), lignin (5%), and
low starch content (5%) (Hatta, 2017). The use of
cellulose can be applied because this material can
bind metal materials (Soekardjo, 2018).
Research on the use of durian peel which is used
as activated carbon as an absorbent material has been
done previously, namely as an absorbent of heavy
metals Pb in electroplating liquid waste (Basaltico, et
al, 2016), as a raw material for making bioethanol (Al
Hidayat, 2017), as ion adsorbent Cadmium metal
(Marlinawati, 2018) and HCl activator (Wardani,
2017). While Suci (2018) conducted research on the
effect of the concentration of activator Potassium
Hydroxide (KOH) on the synthesis of durian skin
activated carbon. Based on the description above, the
writer wants to develop the use of durian skin into
briquettes which are used as a medium in reducing
zinc (Zn) levels in well water.
2 MANUSCRIPT PREPARATION
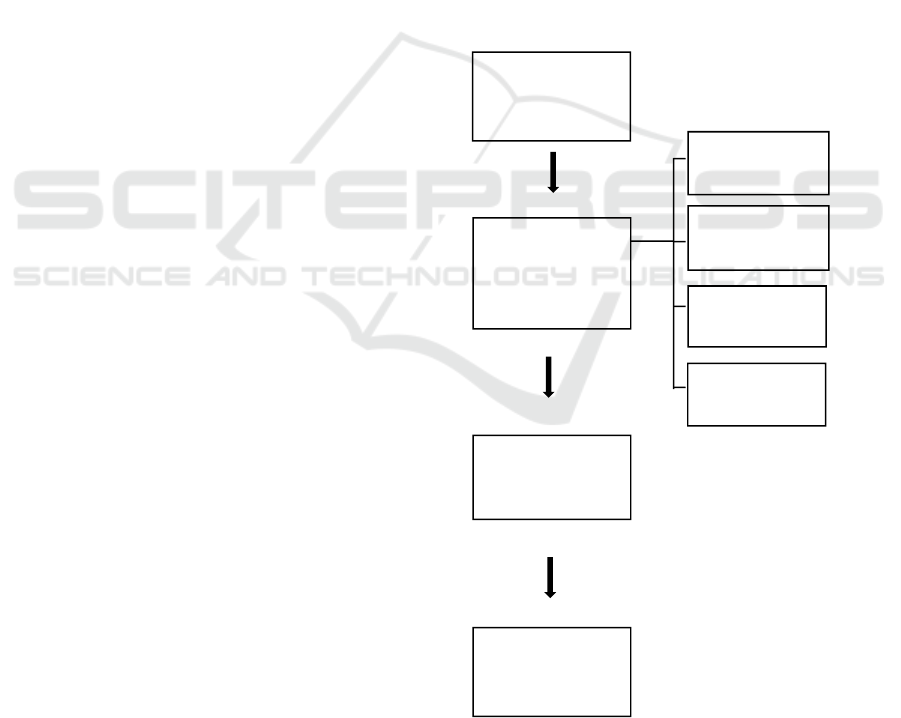
Broadly speaking, research can be seen in the
flowchart below:
.
Figure 1. Chart of research flow
60 cm
Thickness
45 cm
Thickness
50 cm
Thickness
Making Durian
Leather
Briquettes
55 cm
Thickness
Examination of
Zn Water Well
Levels
Well Water
Filtration
Zn levels of
well water
Test the Effectiveness of Durian Skin Briquettes in Reducing Zinc Content (Zn) in Well Water
589

2.1 Tools
The tools used in the study include scissors, knives,
rulers, water reservoirs, stirrers, AYI IO photometer
water test kits, test tubes.
2.2 Ingredients
Materials used in the study included durian skin,
starch, water, 4 inch pvc pipe, ¼ inch, ½ inch, 4 inch
pvc DOP (lid), durian skin briquettes, gravel sand,
well water, 1 bottle of Zn reagent -1k, 1 sheet round
sticker for numbering test tubes, tissue.
3 RESEARCH PROCEDURE
3.1 Zn Level Check for Well Water
Check the pH of well water (the pH of the water
should be around 1-10), if it is not in the above range
you can add sodium hydroxid solution or sulfuric
acid. Samples that have Zn levels greater than 4 mg /
l should be diluted with distilled water.Enter 5 ml of
sample water into each test tube, cover with a screw
cap and mix. Add 1 measure of Zn-1K blue
microspoon, cover the tube with a screw cap.Shake
the test tube firmly to dissolve the solid. Let the
solution react for 3 minutes. Place the test tube into
the test tube chamber, align the markings on the test
tubes with the markings on the AYI-IO photometer
water test kit. Then read the results.
3.2 Making Durian Skin Briquettes
Cut the Durian’s skin into pieces of smaller parts.
Then dry the durian skin that has been cut. But before
that, put straw or twigs. Furthermore, burned into
charcoal. After the combustion process is complete,
the combustion results are removed and separated,
then the durian skin charcoal is crushed to be smooth
and evenly distributed. The next step is to knead the
starch with charcoal from burning.Starch is mixed
with water and cooked until it changes color. When
it's ready, the glue is cooled first, then put in a
containercontaining crushed charcoal.
Figure 1. The Dried Durian Skin
Figure 2: Durian Skin Burning Process
Figure 3: Durian Charcoal
Figure 4: Process of mixing adhesive and powder
The comparison is 600 cc of liquid glue mixed with
1kg of crushed charcoal.
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
590

Figure 5: Process of Durian leather briquette printing
The next stage is printing, the mold is made of 1 inc
pvc pipe cut 5 cm long. Dough or mixture of glue with
crushed charcoal is added little by little into the mold
until it is full. Then removed by being pushed . Then
dry the mold in the sun for 2-3 days or until dry.
During drying the briquettes are turned over to dry
together.
Figure 6: The drying process of durian leather briquette
3.3 Filtering Well Water with Durian’s
Skin Briquettes
Cut pvc pipe to 4 inc with a length of 1-1.2 meters.
On one side a hole 1 / 2inc diameter is made with a
distance of 10 cm from the bottom of the pipe. This
hole is for the 1 / 2inc faucet stop. Then attach the
DOP (lid) pvc pipe 4 inc at the bottom of the pipe.
After that, fill the activated carbon filter media as
follows: The bottom layer is gravel (5-10 mm
diameter) with a thickness of 10-15 cm. Above the
gravel layer is a layer of sand with a thickness of 20
cm, and above the sand layer is a durian skin briquette
with various thicknesses as follows:
A. The thickness of the durian skin briquettes is 45
cm so that the thickness of the filter media layer
is 80 cm
B. The thickness of the durian skin briquettes is 50
cm so that the thickness of the filter media layer
is 85 cm
C. The thickness of the durian briquette is 55 cm so
that the thickness of the filter media layer is 90
cm
D. The thickness of the durian briquette is 60cm so
that the thickness of the filter media layer is 95
cm.
Then drain / enter water into the filter and then open
the faucet on the filter. After that take water as a
sample to be examined for zinc (Zn) levels in the
laboratory. Do three repetitions for each treatment.
Figure. 7 Filter section and screener Media composition
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Effectiveness Test Results
The results of the Effectiveness Test showed that the
ability of all durian skin briquettes used for filtering
well water was based on different thicknesses.
Test the Effectiveness of Durian Skin Briquettes in Reducing Zinc Content (Zn) in Well Water
591

Table 1: Zn Test Results Before and After Screening
Briquett
e
thickness
Zinc(Zn)Mg/l Averag
e
(Mg/l)
Zn
Qual
ity
Stan
dard
(mg
/l)
Repetition
1 2 3
‐ 21.38‐ ‐ 21.38 15,0
45cm 8.70 8.66 8.62 8.66
50cm 8.08 8.04 8.03 8.05
55cm 7.52 7.48 7.42 7.4
60cm 7.01 6.98 6.93 6.97
Table 2: Percentage Decrease in Zinc Level (Zn) Before and
After Screening
Briquette
thickness
ZincMg/l Difference
inZn
Mg/l
Differ
ence
in Zn
%
Before After
45cm 21.38 8.66 12.72 59.49
50cm 8.05 13.33 62.34
55cm 7.47 13.91 65.06
60cm 6.97 14.41 67.39
4.2 Discussion
The results were obtained from the results of
laboratory tests conducted on well water, before and
after the use of filtering using durian skin briquettes.
Based on tables 1 and 2 it can be seen that the zinc
content (Zn) prior to screening is 21.38 mg / l and
does not meet the quality standards according to the
Republic of Indonesia Ministerial Regulation No.416
of 1990. Filtering is carried out with a 15 cm gravel
filter media structure, 20 cm sand , durian leather
briquettes 45 cm, 50 cm, 55 cm and 60 cm. Where the
average decrease in zinc (Zn) each was 8.66 mg / l,
8.05 mg / l, 7.47 mg / l, and 6.97 mg / l. Percentage
of reduction in zinc (Zn) levels afterscreening. This
study is in line with research conducted by Aulia
(2016) about decreasing levels of Fe and Zn metals in
leachate using activated carbon and zeolite as
adsorbents. Which proves the reduction in Zns metal
concentration by 60.06% by active charcoal media
with the most effective residence time of 300minute.
In addition there are still many studies that use
durian skin as an adsorbent of cadmium metal ions
(Marlinawati, 2018), as an absorbent of Pb heavy
metals in electroplating liquid waste (Basaltico, et al,
2006), as a raw material for making bioethanol (Al
Hidayat, 2017), as cadmium metal ion adsorbent
(Marlinawati, 2018) and HCl activator (Wardani,
2017). While Suci (2018) conducted research on the
effect of the concentration of activator Potassium
Hydroxide (KOH) on the synthesis of durian skin
activated carbon.
The thickness of the filter media layer is also very
influential on the quality of filtered water. Where the
thickness of the effective filter media layer generally
ranges between 80-120 cm (Asmadi, 2018). In the
results of the study (Sri, 2016) there was an effect of
variations in thickness of sand and activated carbon
on slow sand filter media to decrease Fe and Mn
levels so that the conclusion was that the greater the
thickness of sand and activated carbon, the higher the
decrease in Fe and Mn levels in well water . The time
needed to spend 6 liters of water put into the filter is
18 minutes.
The presence of zinc elements in water is needed to
meet the body's needs for these elements. Zn is
needed by the body for metabolic processes, but in
high levels it can be toxic (Slamet, 2018). Heavy
metals are harmful if they enter a creature's metabolic
system in amounts exceeding the threshold. The
threshold for each type of heavy metal and for each
type of living creature is different. Importation of
heavy metals into human and animal metabolic
systems can be directly or indirectly. Direct intake
occurs simultaneously with drinking water
(Notohadiprawiro, 2017).
The source of heavy metal Zn contamination can
come from various human activities that produce
waste in the form of pollutants. These pollutants are
transported by rainwater and water movement from
the sea and fresh water to the river mouth which is
where the waters and fresh water meet. Zn metal in
water is concentrated through biological and
chemical-physical processes. Bioaccumulation and
biomagnification are biological processes that are
able to precipitate metals in the body of organisms
through the food chain. In the physical chemical
process, heavy metals are dissolved and deposited in
sediments and can also be absorbed in suspended
substances.
The presence of zinc elements in water is needed to
meet the body's needs for these elements. Zn is
needed by the body for metabolic processes, but in
high levels it can be toxic (Slamet, 2018). Heavy
metals are harmful if they enter a creature's metabolic
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
592

system in amounts exceeding the threshold. The
threshold for each type of heavy metal and for each
type of living creature is different. Importation of
heavy metals into human and animal metabolic
systems can be directly or indirectly. Direct intake
occurs simultaneously with drinking water
(Notohadiprawiro, 2017).
The source of heavy metal Zn contamination can
come from various human activities that produce
waste in the form of pollutants. These pollutants are
transported by rainwater and water movement from
the sea and fresh water to the river mouth which is
where the waters and fresh water meet. Zn metal in
water is concentrated through biological and
chemical-physical processes. Bioaccumulation and
biomagnification are biological processes that are
able to precipitate metals in the body of organisms
through the food chain. In the physical chemical
process, heavy metals are dissolved and deposited in
sediments and can also be absorbed in suspended
substances.
If it is known that the Zn metal content has
exceeded the quality standard, then it is necessary to
do a follow-up in preventing interference that can be
caused by the Zn metal (Amriani, 2018). Zinc metal
(Zn) tends to form ions when it is in water. Zinc (Zn)
ions are easily absorbed in sediments and soils and
the solubility of heavy metals Zinc (Zn) in water is
relatively low in water, heavy metals tend to follow
the flow of water and the effect of dilution when there
is water inlet, such as rainwater, contributes to a
decrease in heavy metal concentrations on water.
The concentration of heavy metals in water will
also affect the concentration of heavy metals present
in the sediment. The tendency to increase the
concentration of heavy metals in sediments is due to
the high concentration of heavy metals in water.
Zinc is a micromineral that is everywhere in human
/ animal tissue and is involved in the function of
various enzymes in the metabolic process. The adult
human body contains 2-2.5 grams of zinc. Three-
quarters of that amount is in the bones and
mobilization is very slow. In high concentrations zinc
is also found in iris, retina, liver, pancreas, kidney,
skin, muscles, testes and hair, so zinc deficiency
affects these tissues. In the blood zinc is mainly found
in red blood cells, little is found in white blood cells,
platelets and serum. Approximately 1/3 of serum zinc
binds to albumin or the amino acid histidine and
cysteine. In 100 ml of blood there are 900 ml of zinc
and in 100 ml of plasma there are 90-130 mg of zinc.
Zinc is involved in more than 90 enzymes related to
carbohydrate and energy metabolism, protein
degradation / synthesis, nucleic acid synthesis, heme
biosynthesis, CO2 transport (carbonic anhydrase) and
other reactions.
The most obvious effects are on metabolism,
function and maintenance skin, pancreas and male
reproductive organs, especially on the change of
testosterone to active dehydrotestosterone. In the
pancreas, zinc has to do with the amount of protease
secretion needed for digestion.
The presence of zinc elements in water is needed to
meet the body's needs for these elements. Zn is
needed by the body for metabolic processes, but in
high levels it can be toxic (Slamet, 2018). Heavy
metals are harmful if they enter a creature's metabolic
system in amounts exceeding the threshold. The
threshold for each type of heavy metal and for each
type of living creature is different. Importation of
heavy metals into human and animal metabolic
systems can be directly or indirectly. Direct intake
occurs simultaneously with drinking water
(Notohadiprawiro, 2017).
The source of heavy metal Zn contamination can
come from various human activities that produce
waste in the form of pollutants. These pollutants are
transported by rainwater and water movement from
the sea and fresh water to the river mouth which is
where the waters and fresh water meet. Zn metal in
water is concentrated through biological and
chemical-physical processes. Bioaccumulation and
biomagnification are biological processes that are
able to precipitate metals in the body of organisms
through the food chain. In the physical chemical
process, heavy metals are dissolved and precipitated
in sediments and can also be absorbed in suspended
substances. If it is known that the Zn metal content
has exceeded the quality standard, then it is necessary
to do a follow-up in preventing interference that can
be caused by the Zn metal (Amriani, 2018).
Zinc metal (Zn) tends to form ions when it is in water.
Zinc (Zn) ions are easily absorbed in sediments and
soils and the solubility of heavy metals Zinc (Zn) in
water is relatively low in water,heavy metals tend to
follow the flow of waterand the effect of dilution
when there is water inlet, such as rainwater,
contributes to a decrease in heavy metal
concentrations on water.
The concentration of heavy metals in water will
also affect the concentration of heavy metals present
in the sediment. The tendency to increase the
concentration of heavy metals in sediments is due to
the high concentration of heavy metals in water.
Zinc is a micromineral that is everywhere in human
/ animal tissue and is involved in the function of
various enzymes in the metabolic process. The adult
human body contains 2-2.5 grams of zinc. Three-
Test the Effectiveness of Durian Skin Briquettes in Reducing Zinc Content (Zn) in Well Water
593

quarters of that amount is in the bones and
mobilization is very slow. In high concentrations zinc
is also found in iris, retina, liver, pancreas, kidney,
skin, muscles, testes and hair, so zinc deficiency
affects these tissues. In the blood zinc is mainly found
in red blood cells, little is found in white blood cells,
platelets and serum. Approximately 1/3 of serum zinc
binds to albumin or the amino acid histidine and
cysteine. In 100 ml of blood there are 900 ml of zinc
and in 100 ml of plasma there are 90-130 mg of zinc.
Zinc is involved in more than 90 enzymes related to
carbohydrate and energy metabolism, protein
degradation / synthesis, nucleic acid synthesis, heme
biosynthesis, CO2 transport (carbonic anhydrase) and
other reactions.
The most obvious effects are on metabolism,
function and maintenance skin, pancreas and male
reproductive organs, especially on the change of
testosterone to active dehydrotestosterone. In the
pancreas, zinc has to do with the amount of protease
secretion needed for digestion.
A dose of zinc consumption (Zn) of 2 grams or
more can cause vomiting, diarrhea, fever, extreme
fatigue, anemia, and reproductive disorders. Zinc
supplementation (Zn) can cause poisoning, as well as
acidic foods and stored in zinc-coated cans (Zn)
(Almatsier, 2001 in Anonymous, 2017). One reported
case of someone consuming 4 g of Zn-gluconate (570
mg of Zn elements) ) which after 30 minutes results
in nausea and vomiting. A single dose of 225-500 mg
Zn can cause vomiting, while supplementation with a
dose of 50-150 mg / day results in digestive pain.
Excessive consumption of Zn over a period of time
can lead to Cu deficiency. Total Zn intake of 60 mg /
day (50 mg of Zn supplement and 10 mg of Zn from
food) can result in Cu deficiency. Zn consumption of
more than 50 mg / day for several weeks can interfere
with the biological availability of Cu, while high
consumption of Zn can affect the synthesis of Cu
protein or metalotionin bonds in theintestine.
Excessive consumption of Zn will disrupt the
metabolism of other minerals, especially Fe and Cu
(Widowati, 2018).
Based on the description above, it needs to be done
an Basedair treatment effort to meet health
requirements. One of them is filtering. From the
research carried out it turns out that the filter media
can reduce Zn levels in well water. This shows that
the tool has worked to reduce the Zn content
contained in the well water. The use of briquettes in
this study serves as an absorbent, which is effective
in reducing color and eliminating odor and taste. The
process of absorption is the ion by activated carbon.
Chemical substances bind to activated carbon or
briquettes to form a precipitate. From the results of
the study note that the use of filters based on the
thickness of the briquettes affect the quality of the
filtering results. The thicker the briquette layer used,
the greater the reduction in zinc (Zn) levels in well
water. This is caused by the length of well water
contact with the filter media
5 CONCLUSIONS
The use of durian skin briquettes can reduce zinc (Zn)
levels in spring water, but there are differences in the
filtering power produced. Briquette layer with a
thickness of 60 cm is most effective in reducing the
level of Zn with a value before filtering at 21.38 mg/l
and after a screening of 6.97 mg/L. Reduction of zinc
levels after screening was conducted at 14.41 mg/l
with a percentage of 67.39%. Thus, it was concluded
that the thicker the briquette layer used in filtering,
the higher the level of zinc (Zn) reduction in well
water.
6 SUGGESTIONS
It is recommended for further researchers to conduct
research with different samples and thicknesses to see
the effectiveness of filtering using durian skin
briquettes to reduce Zn levels with other samples.
REFERENCES
Almatsier, S. (2017). Prinsip Dasar Ilmu Gizi. PT
Gramedia Pustaka Utama: Jakarta.
Al Hidayat (2018). Pemanfaatan Limbah Selulosa dalam
Kulit Durian sebagai Bahan Baku PembuatanBioetanol
melalui Proses Fermentasi. Institut Agama Islam
Negeri: Palangkaraya.
Amriani (2017). Bioakumulasi Logam Berat Timbal (Pb)
dan Seng (Zn) pada Kerang Darah (AnadaraGranosa
L.) dan Kerang Bakau (Polymesoda Bengalensis L.) di
Perairan Teluk Kendari. [Tesis], Universitas
Diponegoro, Semarang.
Granosa L.) dan Kerang Bakau (Polymesoda Bengalensis
L.) di Perairan Teluk Kendari. [Tesis], Universitas
Diponegoro, Semarang.
Asmadi (2016). Teknologi Pengolahan Air Minum.
Penerbit Gosyen Publishing. Yogyakarta.
Aulia, R. (2016). Penurunan Kadar Logam Berat Fe dan
Zn pada Air Lindi Menggunakan Media Karbon Aktif
dan Zeolit sebagai Adsorben. Jurnal. Universitas
Hasanuddin: Makasar.
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
594

Basaltico, R. S. (2016). Pemanfaatan Kulit Durian sebagai
Absorben Logam Berat Pb pada Limbah Cair
Elektroplating. Universitas Pembangunan Nasional
“Veteran”: Jawa Timur.
Departemen Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. (1990).
Peraturan Menteri Kesehatan Republik Indonesia
No.416/MenKes/PER/IX/1990.Departemen Kesehatan
Republik Indonesia: Jakarta.
Hatta, V. (2017). Manfaat KulitDurian Selezat Buahnya.
Jurnal: UNLAM Sutrisno,C.T(2002).Teknologi
Penyediaan Air Bersih. Jakarta: PT.Rineka Cipta.
Kusnaedi (2018). Mengolah Air Kotor untuk Air Minum.
Penebar Swadaya: Jakarta.
Marlinawati (2017). Pemanfaatan Arang Aktif dari Kulit
Durian sebagai Adsorben Ion Logam Kadmium. Jurnal
Kimia Mulawarman. Vol 13. Unmul: Samarinda.
Notohadiprawiro (2018). Pengelolaan Kesuburan Tanah
dan Peningkatan Efisiensi Pemupukan. Ilmu Tanah
UGM: Yogyakarta.
Nuraeni, Y. (2016). Metode memperkirakan debit air yang
masuk ke waduk dengan metode stokastik chain
maskov. Jurnal Teoritis dan Terapan Bidang Rekayasa
Sipil, 18 (2), 15-20.
Slamet, J. S. (2016). Kesehatan Lingkungan. Yogyakarta:
UGM-Press.
Slamet, J. S. (2018). Kesehatan Lingkungan. Gajah Mada
University Press: Yogyakarta.
Soekardjo (2016). Kimia Anorganik. PT Rineka Cipta:
Jakarta.
Sri, A. N. (2019). Pengaruh Variasi Ketebalan Pasir dan
Karbon Aktif pada Media Saringan Pasir Lambat
terhadap Penurunan Kadar Besi (Fe) dan Mangan
(Mn) pada Air Sumur. Jurnal: Gorontalo.
Suci, M (2016). Sintesis Karbon Aktif dari Kulit Durian
untuk Pemurnian Air Gambut. Jurnal Fisika. Vol 3.
Unand: Padang.
Trubus (2017). 100 Plus Herbal Indonesia Bukti Ilmiah dan
Racikan. Vol 11. Trubus Swadaya: Jakarta.
Untung, O. (2018). Durian untuk Kebun Komersial dan
Hobi. PT. Penebar Swadaya: Jakarta.
Wardani, S. P. (2016). Pengaruh Konsentrasi Asam
Klorida terhadap Kualitas Karbon Aktif dari Kulit
Durian sebagai Adsorben Logam Cu. Politeknik Negeri
Sriwijaya: Palembang.
Widowati (2018). Efek Toksik Logam : Pencegahan dan
Penanggulangan Pencemaran. Penerbit Andi:
Yogyakarta
Test the Effectiveness of Durian Skin Briquettes in Reducing Zinc Content (Zn) in Well Water
595
