
Discordance of Human Genotype of Papilloma Virus in Mother and
Toddler with Condyloma Acuminata
Sekar Sari Arum Palupi
1*
, Prasta Bayu Putra
1
, Kharisma Yuliasis
1
,
Dwi Retno Adi Winarni
1
, Didik Setyo Heriyanto
2
, Satiti Retno Pudjiati
1
1
Departmentof Dermatology and Venereology, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing Universitas Gadjah Mada
2
Anatomical Pathology Department Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing
Universitas Gadjah Mada
*Correspondence: +6281328479100, fax: (+62274) 885637,
Keywords: Human Papilloma Virus, Condyloma Acuminata, PCR, Genotype
Abstract: Condylomaacuminata (CA) is a Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) infection that is rarely found in children.
Transmission can be through vaginal contact, sexual abuse, auto or heteroinoculation or fomites.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) examination is the gold standard for determining the cause of HPV
genotype. This case report aimed to trace CA transmission to toddlers (ages <3 years). A female toddler has
warts around the anus with a history of vaginal delivery and no sign of sexual abuse. The mother has warts
on the genitals and between the fingers in pregnancy. The CA diagnosis was based on toddler's physical
examination, acetowhite tests, and perianal biopsies. The endocervical smear from the mother was in
accordance with the CA and the wart biopsy from the mother's fingers appropriate for verruca vulgaris. PCR
has examined 39 HPV genotypes in the mother and the child. In the child showed HPV genotype 11,
frommother’s cervical swab samplesshowed HPV genotype 87 and indeterminate result from the
mother'sfingers. The discordance of HPV genotypes in the mother and the child is likely due to
heteroinoculation transmission from the family who took care the child, or still possible from the mother but
not detected on PCR examination because it only can examine 39 types of HPV. Identification with whole
PCR is needed to ensure the source of transmission.
1 INTRODUCTION
Condyloma acuminata (CA) or genital warts are
infections of the Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)
which are rarely found in children. Until now, more
than 200 HPV genotypes have been identified using
the PCR method.
(Ghedira et al., 2016;Chen et
al.,2018,Sohrabi et al.,2017) More than 90% of
cases of perianal and anal CA in adults and children
are caused by HPV groups with low risk of
neoplastic namely HPV 6 or 11, but there is also
evidence that HPV 1, 2, 4, 7, 27, 57, 60 and 63 are
the causes Sohrabi et al,2017. Genotypes of HPV
types 16, 18, 31, and 33 are HPV groups with a
tendency to become intraepithelial neoplasia and
invasive squamous cell carcinoma.(Lacour et
al.,2012) Whereas, in HPV 87 there is still little
literature to discuss. This type of HPV is associated
with a tendency to occur in HIV patients.(Menzo et
al.,2001) CA transmission can be through contact
during vaginal delivery, sexual abuse, auto or
heteroinoculation, or through fomites. (Lacour et
al.,2012;Menzo et al.,2001;Tract et al.,2005)
Predilection of lesions in girls with CA is in the
vulva, perianal, vagina, and urethral regions whereas
in boys lesions are most often present in perianal and
rarely occur in the penis.(Boxman et al.,1999)
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) examination is
the gold standard in determining causative HPV
genotypes. (Sonnex et al.,2014)
Although common in adulthood, CA in children
is an unusual condition. In several studies reported
the dominance of female sex in children age with
CA with an average age ranging from 2.8 to 5.6
years. The prevalence of CA from epidemiological
data that occurs in Indonesia is around 5-19%, while
the prevalence in infants and children is less than
4.3%.(Jenison et al,2000) The incidence of CA in
adulthood in Dr. Sardjito Hospital for the past five
years was 605 cases while the toddlers (under three
338
Palupi, S., Putra, P., Yuliasis, K., Winarni, D., Her iyanto, D. and Pudjiati, S.
Discordance of Human Genotype of Papilloma Virus in Mother and Toddler with Condyloma Acuminata.
DOI: 10.5220/0009988203380342
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease (ICTROMI 2019), pages 338-342
ISBN: 978-989-758-469-5
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
years old) were only 1 case. This paper reports one
case of CA in toddlers who came to the
Dermatology and Venereology clinic of Dr. Sardjito
Hospital with complaints of warts on the perianal.
The purpose of this case report is to trace the
transmission possibilities.
2 CASE
A 15 months old girl came to the Dermatology and
Venereology clinic of Dr. Sardjito Hospital with the
chief complaint of warts appearing around the anal.
From heteroanamnesis and alloanamnesis found that
warts appeared since a few weeks ago, shaped rough
bumps, skin color, size less than 0.5 cm. It did not
feel itchy, painful, and there was no interference
with bowel movements. They said she never been
treated before. The patient was an only child,
bornwith appropriate gestational age, vaginal
delivery, with a head presentation. There were no
airway disorders, hoarseness, stridor, or eye
disorders. Every day the patient lived and was cared
for by her mother and grandmother, mother had the
habit of using towels alternately with her children to
clean their genitals after urinating and no history of
sexual abuse. Her parents were divorced, and her
father did not live at home.
A mother who was three months pregnant
had been diagnosed by dermatology, and
venereology specialist had genital warts in her
vagina and had been treated. The size of the wart
decreased but did not fall out until postpartum, and
the patient never attends follow up again. The
mother also had a wart with a diameter of 0.5 cm
between the index finger of her right hand.
Physical examination of children showed
right general conditions with vital signs within
normal limits, and there were no signs of sexual
abuse or enlarged lymph nodes. The perianal
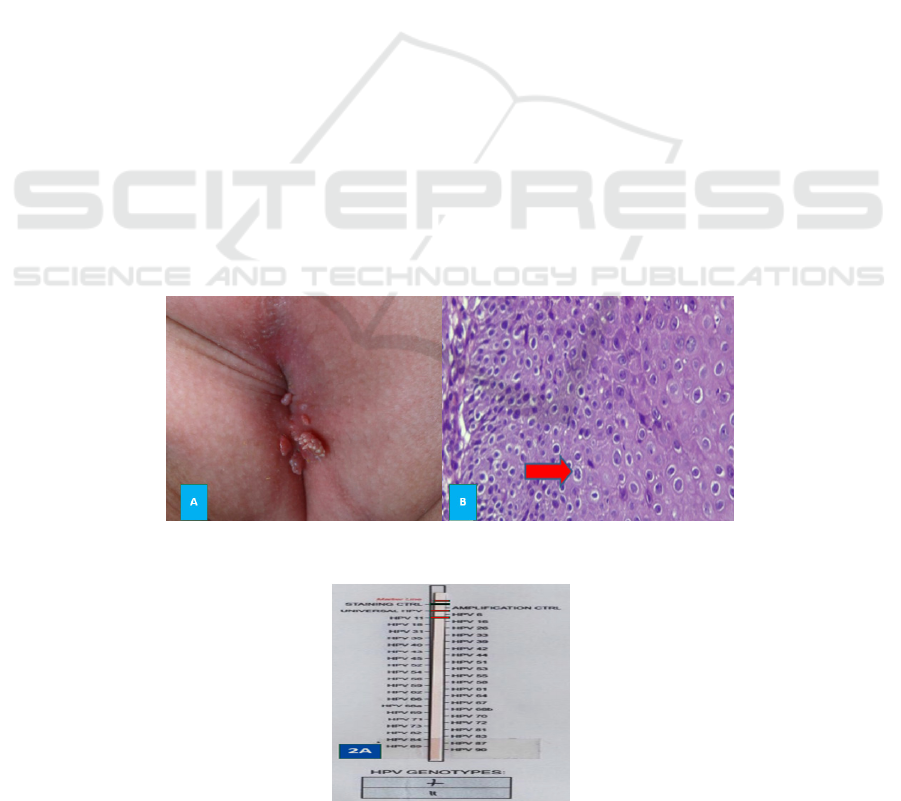
examination was revealed a verrucous papule, skin
color, multiple with a size of 0.2 cm-0.5 cm (Figure
1A). The acetowhite test showed positive results,
and on histopathological examination, with
Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) staining showed results in
the epidermis showed mild hyperkeratosis,
parakeratosis, partial hypergranulosis, spongiosis,
irregular acanthosis, parabasal hyperplasia, and little
lymphocyte acrositosis. Among them were
keratocytes with cytoplasm halo perinuclear and the
nucleus was slightly enlarged (coilocytosis). In the
dermis, there was quite a lot of lymphocytic and
periadnexal infiltration. There was no malignant
sign. Conclusion of perianal histopathology was in
accordance with CA (Figure 1B). PCR
examinationwas performed for 39 types of HPV.
Children and mother's HPV DNA was obtained from
the extraction of CA tissue in paraffin blocks. PCR
examination in perianal CA specimens of children
showed HPV 11 genotype (Figure 2A).
Figure 1: A: Perianal condyloma acuminata on the child; 1B: Histopathological examination with Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE)
staining revealed keratinocyte with halo perinuclear cytoplasm and the nucleus a bit enlarged or coilocytosis (arrow)
Figure 2: A. PCR CA of the child perianal resulted in HPV genotype 11
Discordance of Human Genotype of Papilloma Virus in Mother and Toddler with Condyloma Acuminata
339

The physical examination of the mother when
she came to the Dr.Sardjito Hospital showed no
vaginal CA, and on in speculum examination
(Figure 3A) the cervix appeared to be calm and no
discharge nor verucous papules were found, but
found a skin-colored verucous papule, a solitary size
of about 0.5cm in right manus interdigit II (Figure
3B).
Histopathological examination of verruca skin
tissue specimens with HE staining showed that the
epidermis appears hyperkeratotic, acanthosis,
papillomatosis, partly with hypergranulosis. Among
them were keratinocytes with cytoplasm halo
perinuclear and the nucleus was slightly enlarged
(coilocytosis). The dermis looks puffy with small
perivascular lymphocytes. There was no malignant
sign. Conclusions on histopathological biopsies were
in accordance with verruca vulgaris. (Figure 3C).
Histopathological examination of cervical swabs
appeared ectocervical cells in the form of many
intermediate cells and few parabasal cells. We
obtained a few endocervical epithelial cells and not
finding displaced metaplasia or malignant epithelial
cells. The background was erythrocytes, many
polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and few
lymphocytes. The conclusion to the Pap smear was
Papanicolaou Class I (non-peculiar inflammation,
Bethesda system: Negative for Intraepithelial Lesion
or Malignancy). PCR examination with cervical
swab showed HPV genotype 87 (Figure 4A),
whereas, with skin material, the lesions of verrucae
vulgaris on the fingers were undeterminated (Figure
4B).
Figure 3: A: Inspeculo examination to mother cervix showed calm cervix no discharge found nor verrucous papule. 3B:
Verrucous vulgaris on interdigit of mother hand. 3C: Histopathological examination with Hematoxylin Eosin (HE) of
verucous vulgais on the finger showed coilocyte (red arrow).
Figure 4: A. PCR of mother cervix showed HPV genotype 87.4B. PCR interdigit II manus dextra of the mother
showedundeterminated.
Patients are advised to be referred to an ENT
specialist and ophthalmology specialist to track the
presence or absence of laryngeal papillomatosis and
eye keratitis. Until this case report is made, it has not
been tracked due to limited costs.
3 DISCUSSION
Condylomaacuminata often referred to as chicken
combs or genital warts, is one of the sexually
transmitted infections caused by HPV. Human
Papilloma Virus is included in the papovaviridae
family, the genus polyomavirus. The clinical
manifestations of HPV infection in the genitals can
be classic symptoms, such as prominent cauliflower,
small smooth papules like flesh or hyperpigmented
papules that combine to form keratotic plaques or
papules or like verruca vulgaris The CA diagnosis in
perianal children, in this case, is confirmed by the
suitability of clinical features, histopathology and
the discovery of HPV genotype 11 on PCR
examination. In the mother, it can be concluded that
ICTROMI 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease
340

it has an asymptomatic CA on the cervix because
there is no lesion clinically, but on histopathological
examination and PCR examination shows HPV
infection genotype 87; while the diagnosis of
verruca vulgaris on the mother's finger is also
matched with the clinical and histopathological
features.
Condyloma acuminata in children can occur due
to transmission through vaginal delivery, sexual
abuse, auto or heteroinoculation, and fomites. In
cases, suspected transmission occurs during vaginal
delivery because CA lesions in children appear at
the age of 15 months while the mother emerges
vaginal CA at 3 months gestation, with an
incubation calculation of about 12 months. The
literature shows that HPV incubation ranges from 1-
12 months.(Chen et al.,2018,Sohrabi et al.,2017)
However, vaginal transmission is still questionable
because it turns out that the HPV genotype in
children is different from the HPV genotype in
mothers. Suspicion of transmission due to sexual
violence can be excluded because neither from
alloanamnesis nor physical examination shows signs
of sexual abuse. Suspicion of transmission through
autoinoculation can be excluded because the patient
does not have a CA at locations other than perianal.
Suspicion of heteroinculation transmission through
the mother's finger when cleaning the patient's anus,
or through fomites due to the habit of using towels
alternately with the patient to clean the genitals or
perianal is indisputable because on PCR
examination the warts on the fingers are
undeterminated or HPV is present but not in
accordance of 39 types of HPV examined. Veruca
vulgaris is a benign proliferation of the skin and
epidermal mucosa caused by HPV. The most
common type of HPV is types 1, 3, 27, and 57.
Whereas based on predilection, most often occur,
especially in places that often experience trauma
such as fingers, hands, and knees. HPV in the hands
and feet is usually typed 1, 2, 4, 27, 57 and 19.
Transmission of the perianal CA in children can be
through the caregiver's fingers to genitalia. .(Menzo
et al.,2001). Based on several studies, the
transmission of CA through fomites often occurs
through surgical equipment, gloves with less
sterilization, floor, toilet seat or through alternating
towels.(Lacour et al.,2012)
PCR examination is the gold standard in
determining HPV genotypes. The use of
ultrasensitive examination methods with real-time
PCR can detect≥ four dominant genotypes in 25% of
CA cases(Sonnex et al.,2014;Jenison et
al,2000;Hawkins et al.,2013)
PCR examination in this case used Ampliquality
Express type HPV with 99% instrument sensitivity
and 98.6% specificity that detected 39 types of HPV
genotypes, namely: 6, 11, 16, 18, 26, 31, 33, 35, 39,
40, 42 , 43, 44, 45, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 58, 59, 61,
62, 67, 68a, 68b, 70, 71, 72, 73, 81, 82, 83, 84, 87 ,
89, and 90.
6
The detection of vaginal transmission
from mother to child can actually be done if the
mother comes when there is still a vaginal CA.
However, when she came to follow up, her vaginal
CA was gone, so the sample was only taken from the
mother's cervical swab. The presence of laryngeal
papillomatosis and eye keratitis as a result of HPV
transmission during vaginal delivery cannot be
detected because the patient refuses to be referred.
The limitations of the PCR method with cervical
swab specimens were only detected by some of the
most dominant types of HPV because of the natural
competition between HPV genotypes of CA. The
types of specimens taken from the cervix also often
do not accurately describe the cause of the HPV
genotype, because some HPV genotypes are only
found in the basal cervical tissue. Skills and
techniques really determine the taking of test
specimens. Whereas, different results can be found
in HPV infections in the skin, where coinfection
caused by more than ten genotypes can be detected
even in deficient amounts.
4 CONCLUSION
One case of perianal CA on toddlers aged 15 months
with mothers suffering from asymptomatic CA in
the cervix and veruca vulgaris in the fingers is
reported, but there is no match for HPV genotypes
between the child and the mother. Thus,
transmission in children cannot be determined. HPV
genotype examination is needed with the whole PCR
method both in mother and child and screening to
the family who care for the child to identify the
transmission source.
REFERENCES
Boxman ILA, Hogewoning A, Mulder LHC, Nico JAN,
Bavinck B, Schegget JANTER. 1999. Detection of
Human Papillomavirus Types 6 and 11 in Pubic and
Perianal Hair from Patients with Genital Warts. J Clin
Microbiol.;37(7):2270–3.
Chen Z, Zhou J. 2018. Distribution of human
papillomavirus genotypes and its relationship to
clinicopathology in invasive cervical carcinoma in
Discordance of Human Genotype of Papilloma Virus in Mother and Toddler with Condyloma Acuminata
341

Zhejiang Province , China. J cancer Res
theraoetics.;780–4.
Ghedira R, Mahfoudh W, Hadhri S, Gabbouj S, Bouanene
I, Khairi H, et al. 2016. Human papillomavirus
genotypes and HPV- 16 variants distribution among
Tunisian women with normal cytology and squamous
intraepithelial lesions. Infect Agent Cancer
[Internet].;11:1–10. Available from:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13027-016-0109-2
Hawkin Mg,Winder DM,Ball SLR. Vaughan K, Sonnex
C, Stanley MA, et al. 2013. Detection of specific HPV
subtypes responsible for the pathogenesis of
condylomata acuminata. Virol J [Internet];10(1):1.
Available from: Virology Journal
Jenison SA, Yu X, Valentine JM, Koutsky LA,
Christiansen AE, Beckmann AM, et al. 2000.
Evidence of Prevalent Genital-Type Human
Papillomavirus Infections in Adults and Children. J
Infect Dis.;162:60–9.
Menzo S, Monachetti A, Trozzi C, Ciavattini A, Carloni
G, Varaldo PE, et al. 2001. Identification of Six
Putative Novel Human Papillomaviruses ( HPV ) and
Characterization
Sohrabi A, Hajia M, Jamali F, Kharazi F.2017.Is incidence
of multiple HPV genotypes rising in genital infections
J Infect Public Health [Internet].;xxx:4–7. Available
from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2016.10.006 of
Candidate HPV Type 87.;75(23):11913–9.
Sonnex C, Strauss S, Gray JJ. 2014.Detection of human
papillomavirus DNA on the fingers of patients with
genital warts. bmj;75:317–9
Tract R, Papillomavirus H, Transmission P, Abuse TS.
2005. Anogenital and Respiratory Tract Human
Papillomavirus Infections Among Children: Age,
Gender, and Potential Transmission Through Sexual
Abuse. Pediatrics.;116(4):815–25.
ICTROMI 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease
342
