
Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex
Lydia Kurniasari
1*
, Meiza
1
, Yosep Ferdinand Rahmat Sugianto
1
, Radityastuti
1
, Indra Wijaya
2
1
Departement of Dermatolovenereology,
Faculty of Medicine, Diponegoro University /
Dr. Kariadi Hospital Semarang
2
Department of Pathology Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Diponegoro University /
Dr. Kariadi Hospital Semarang
*
Corresponding author
Keywords: Epidermolysis bullosa simplex, skin blister, trauma avoidance
Abstract: Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS) is a rare blistering hereditary disease. It generally occurs in infants
and children. Fine (2010) stated the prevalence of EBS is 19.6 / 1 million live births, and 8.22 / 1 million
populations. This case report is aimed to establish the early diagnosis for prognosis assessment and parents’
education. A 1-month-old babygirl presented with blisters which became erosion on elbow and foot, and
nail dystrophy since birth. Skin biopsy result was in accordance to EBS. Patient was treated with normal
saline compress, topical antibiotic, and topical placenta extract. Treatment resulted in improvement of skin
lesion. The blisters of EBS is found intraepidermally on trauma-prone sites. The patient was followed up for
8 months. No secondary infection was found. The parent was satisfied with the result of treatment. EBS is a
lifelong condition which requires meticulate attention from the parents. Trauma avoidance is pivotal to
prevent the blisters. Genetic counselling might be needed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex (EBS), also known
as mechanobullous disease
1
is a genetic disorder
occurs in infants and children that cause the skin to
be very fragile and to blister easily without leaving
scars. Blister occurs in response to minor injury or
friction, such as rubbing or scratching and located
above the dermal-epidermal junctional layer. The
current name was “hereditary epidermolysis bullosa”
stated by Koebner in 1886 (Boediardja, 2002). As
reported by Fine (2010), the prevalence of EBS is
estimated around 19.6 per million live births and
8.22 per million general populations10. EBS covers
70% of all Epidermolysis Bullosa cases and EBS is
the mildest type (Fine et al, 2010; Lin et al, 1992;
Jennifer, 2017).
The four most common subtypes of EBS are
EBS localized (EBS-loc; previously known as
Weber-Cockayne type), EBS generalized
intermediate (EBS-gene intermed; previously known
as Koebner type), EBS with mottled pigmentation
(EBS-MP severe ( EBS-gen sev: previously known
as Weber ), EBS generalized severe ( EBS-gen sev:
previously known as Dowling Meara type ) (Paller
et al, 2011; Bashir et al, 2010).
EBS is inherited in
an autosomal dominant pattern and rarely occur in
an autosomal recessive pattern. EBS is typically
caused by mutations in the KRT5 and KRT14 genes
in which related to the formation of keratin 5 and
keratin 14, a type of protein that affects the strength
and elasticity of the epidermal layer (Paller et al,
2011; Marinkovich, 2012). Mutations will make the
epidermis to be easily damaged and injured. At other
cases new genes mutations also occur in people who
have no family history (Marinkovich, 2012).Clinical
features are characterized by fragility of the skin that
results in non-scarring blisters preceded by minor or
even no trauma, which usually heal without scar
tissue, blister appear on the hands and feet, in
annular or arch or group form, progressive brown
pigmentation interspersed with hypo-pigmented
spots on the trunk and extremities which often
disappears in adult life. The lession occurs in the
palmar region, hyperkeratosis in plantar, nail
dystrophy, and milia (Paller et al, 2011; Boediardja,
2002; Marinkovich, 2012; Ellen, 2016; Fine, 2014).
384
Kurniasari, L., Meiza, ., Sugianto, Y., Radityastuti, . and Wijaya, I.
Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex.
DOI: 10.5220/0009989703840388
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease (ICTROMI 2019), pages 384-388
ISBN: 978-989-758-469-5
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

EBS Therapy include: 1. Supportive care 2.
Prevention of secondary complications: topical and /
or systemic antibiotics or dressings or gels. 3.
Surveillance: for infection and proper wound
healing. 4. Agents / circumstances to avoid:
excessive heat, avoid poorly fitting or coarse-
textured clothing/footwear that traumatize the skin
(Ellen, 2016). Genetic counselling might be needed.
Genetic counseling is the process of providing
individuals and families with information on the
nature, inheritance, and implications of genetic
disorders to help them make informed medical and
personal decisions ((Ellen, 2016). The following
section deals with genetic risk assessment and the
use of family history and genetic testing to clarify
genetic status for family members
8
. The prognosis of
EB is highly dependent on the subtype of disease
that is present. Most EB patients, particularly those
with EBS , have normal life expectancies, but
significant morbidity may complicate some (Lin et
al, 1992; Jennifer, 2017).
2 CASE
A 1-month-old babygirl came to the dermatology
and venereology clinic of Dr. Kariadi Hospital
Semarang at September 2018 with skin peeling on
the elbows, fingers and feet, no nails growth on the
right and left fingers, and a brownish color on the
fingertips. Since birth, bullae appear from the
elbows, fingers and toes. Clothes friction can cause
ruptured bullae, then erosion occurs. Patients were
taken to the general practitioner in Jepara and given
antibiotic ointment. Based on the data told by the
patient's mother, there were no family history related
to this disease and no family relationship between
father and mother.
The patient showed good general condition, alert,
pulse are 130 beats per minute, respiration rate is 34
breaths per minute, temperature is 37
0
C. Physical
examination shows the weight is 3100 kg, head
circumference 33.5cm, body length 49cm,
examination of heart, lung, abdomen within normal
limits. Dermatology examination in the form of
linear erosion on the right and left elbow folds, right
and left foot, buttock and back ; right and left hand
nail dystrophy; right and left finger
hyperpigmentation (figure 1a).
Figure 1.a first observation on buttock and back erosion, elbows and fingers erosion, toes nail hyperpigmentation, nail
dystrophy, 1.b. Second observation (after 8 months). Healing in elbows erosion and nail hyperpigmentation but persistent
nail dystrophy
1a
1b
Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex
385
The result of consultation with pediatrics unit is
stunting. Laboratory results showed that
haemoglobin value: 8.4 g/dl, leukocytes: 13,000 /
uL, platelets: 980,000/uL, hematocrit: 27,7%,
albumin: 2,6 gr%, AST/ALT : 26/13 U/I, ureum/
creatinin: 14,5 mg% / 0,5 mg/dL
Histopathological section in elbow erosion
shows old lession, the feature are those of a cell free
sub-epidermal blister and are not specific ( the roof
in this blister is not seen on this section ) with the
base of fibrous stroma scatered with lymphocytes,
histiocytes, and macrophages, containing
hemosiderin pigments. No evidence of malignancy,
and histopathological consisten with the diagnosis
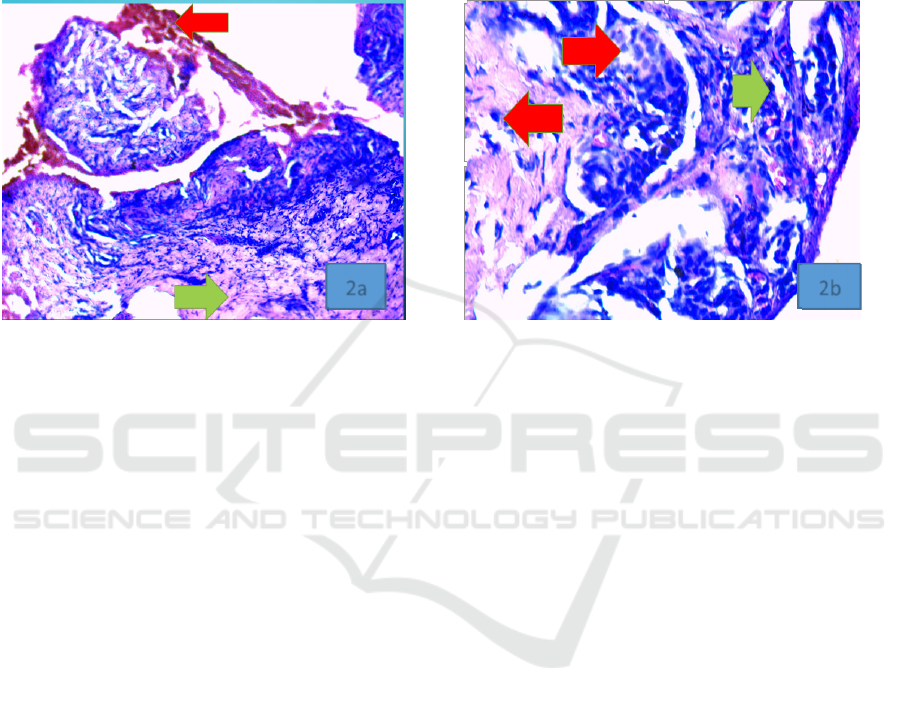
of epidermolysis bullosa simplex.( figure 2a,2b)
Figure 2a. Red arrow shows hemmorhage, green arrow shows fibrous stroma. H&E stain x 100, .2b. Red arrow shows
lymphocytes and histiocytes, green arrow shows hemosiderin pigments H&E stain x 400
The differential diagnosis in these patients is
Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica, epidermolysis
bullosa acquisita. The diagnosis in this patient is
epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Treatment for these
patients was Normal saline compresses for 15
minutes before topical cream therapy, topical
antibiotics, topically extracted placenta.
3 DISCUSSION
EBS diagnosis is based on history, physical and
histopathological examination. In this case, erosion
preceeded with bullae was found . Based on several
studies it was mentioned that there were points of
keratin K5 and K14 gene mutations on
chromosomes 12 and 17, also missense mutations in
the amino acid sequence in keratin K5 and K14.
Changes in these amino acids can cause changes in
the structure of the keratin. In result, disruption of
the formation of intercellular intermedia filament
tissue that extends from the nucleus to the plasma
membrane that connects the structure of hemi-
desmosomes and desmosomes with basal
keratinocytes occur(Lin et al., 1992;Pfender et
al,2007;Taboli,2009,Arnold,2009;Fine,2014).So that
intradermal bullae easily formed due to the trauma.
Supportive examination is needed to diagnose
and monitor possible complications that can occur.
Laboratory examination of blood in EBS is generally
normal and if anemia present, it is usually associated
with a growth disorder and mal-absorption. In this
case, the patient's Hb is low and the patient is
stunted. The lack of protein, iron and blood through
the open skin causes iron deficiency hypo-albumin
and lack of minerals (Taboli,2009). Consultation
with a nutritionistis expected to be able to maximise
calorie and protein intake and the provision of
special nutrients and vitamins such as iron, zinc, and
vitamin D3 (Taboli,2009). Nutritional support is
important to promote wound healing
14.
Histopathological examination with a light
microscope is not recommended. It is suggested to
use electron microscope. Both Hematoxolin Eosin
(HE) and Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS) staining can be
used to see the basal membrane, Examination of a
skin biopsy using immunofluorescence microscopy
and transmission electron microscopy may be
considered but can have limitations in the diagnosis
of EBS(Ellen,2016).
Histopathological section in elbow erosion
shows old lession, the feature are those of a cell free
sub-epidermal blister and are not specific ( the roof
in this blister is not seen on this section ) with the
base of fibrous stroma scatered with lymphocytes,
histiocytes, and macrophages, containing
hemosiderin pigments. No evidence of malignancy,
and histopathological consisten with the diagnosis
2a 2b
ICTROMI 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease
386

of epidermolysis bullosa simplex (Calonie et
al,2012).
EBS therapy is supportive and palliative, by
protecting itself from excessive friction or heat,
preventing abrasion and constriction, handling
secondary infections, supplementation and handling
of pain (Paller et al,2011;Marinkovich,2012)
For
skin care, an explanation and education is given to
the patient's family. Erosion is applied with
antibiotic cream or;ointment (Paller et
al,2011;Boediardja,2002;Pfender,2007;Fine,2008;El
len,2016). Administration of 0.9% normal saline
fluids compresses to wounds contribute to its
effectiveness as moist wound dressing promoting
granulation and epithelialization because normal
saline fluids can attract fluid from the wound
through osmosis and anti-inflammatory processes
(Bashir et al, 2010). Topical placenta extract used in
these patients contains fibroblasts, growth factors,
amino acids, nucleotides and vitamins that stimulate
biosynthesis of collagen (Tiwary,2015). Observation
after 8 months showed healing in elbows erosion
and nail hyperpigmentation, but persistent nail
dystrophy, In general, the result of therapy was good
(figure 1b).Genetic counseling is the process of
providing individuals and families with information
on the nature, inheritance, and implications of
genetic disorders to help them make informed
medical and personal decisions. Therefor, genetic
conseling might be needed for this patient
(Ellen,2016).
In the neonatal period it often causes death due
to the wide area of erosion that can cause sepsis, but
with the increasing age, the general condition will
get better with a quickly healed lesions without
leaving scar tissue and milia (Taboli,2009;
Marinkovich,2012;Fine,2014). Most EB patients,
particularly those with EBS, have normal life
expectancies, but significant morbidity may be
complicated (Lin et al,1992;Jennifer,2017). Those
indicate the prognosis of “dubia at bonam” due to
the better condition of the patient and significant
increase in activity.
4 CONCLUSION
An Epidermolysis bullous simplex case in a 1
month-old baby girl was reported. Diagnosis is
based on history of the disease, tracking family
history, physical examination and laboratory support
examinations and histopathology. Patient and family
are given genetic counseling and explanation of the
disease and skin care, prevention of the blister,
treatment and prevention of infections, nutritional
counseling to increase the quality of life of the
patients. And genetic counceling might be needed .
Prognosis in this case is dubia ad bonam.
REFERENCES
Arnold AW. 2009. Cetuximab therapy of metastasizing
cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma in patients with
severe recessive dystrophyic epidermolysis bullosa.
Dermatology 219(1): 80-83.
Bashir, Muhammad, afsal. 2010. Normal Saline and
Honey dressing in wound preparation for skin
grafting. 16(2)
Boediardja Sa. 2002. Epidermolisis bulosa Dalam :
Djuanda A, Hamzah M, Boediardjo SA, editor.Ilmu
penyakit Kulit dan Kelamin;edisi ke-3. Jakarta:
Bali.Penerbit FKUI. 200-7.
Calonje Eduardo; Brenn Thomas; Lazar Alexander;
McKee Phillip, editor. 2012. Of the skin. In: McKEE’s
Pathology Of The Skin With Clinical Correlations.
Fourth edition. British: Elsevier Saunders. p. 99–150.
Ellen GP. 2016. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex in from
URL: http:// www.Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books .Accessed
October 16
Fine JD. 2014. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa :Update
recommendations and diagnosis and classification. J
Am Acad Dermatol 70(6):1103-26
Fine JD, Johnson LB, Suchindran C. 2010. The
epidemiology of inherited epidermolysis bullosa:
finding in the Us, Canadian and European study
populations. In: Fine JD, Bauer EA, McGuire J,
Moshel A, eds Clinical, Epidemologic and laboratory
Advances and the Finding of the National
Epidermolysis Bullosa Registry. Baltimore: John
Hopkins University Press. 101-13
Fine JD. 2008. The classification of inherited
epidermolysis bullosa (EB): Report of the Third
International Consensus Meeting on Diagnosis and
Classification of EB. J Am Acad Dermatol 58:931-50
Jennifer B. 2017. Pain and quality of life evaluation in
patients with localied Epidermolysis bullosa simplex.
Orphanet Journal of Rare Disease 12:119
Lin AN, Carter DM. 1992. eds Epidermolysis bullosa
simplex: a clinical overview. In: Epidermolysis
Bullosa: Basic and Clinical Aspect. New York:
Springer. 89-117
Marinkovich MP. 2012. Inherited Epidermolysis Bullosa.
In: Goldsmith LA, Katz SI. Gilchrest BA, Paller AS,
Leffell DJ, Wolf K. Eds Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in
General Medicine. 8
th
ed. New York: McGraw-Hill.
p.649-664
Paller AS, Mancini AJ. 2011. Bullous disorders of
childhood. In: Hurwitz S. Clinical pediatric
dermatology, a textbook of skin disorders of childhood
and adolescence; fourth ed. Chicago, Illinois: Elsevier
saunders. P.303-313.
Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex
387

Pfendner EG. 2007. Basic science of Epidermolysis
Bullosa and diagnostic and molecular
characterization: proceedings of the IInd International
Symposium on Epidermolyis Bullosa, Santiago, Chile.
Int J Dermatol 46:781-794
Tabolli S. 2009. Quality of life in patients with
Epidermolysis Bullosa. Br J Dermatol 161:869-877
Tiwary SK. 2015. Effect of placental-extract gel and
cream on non healing wounds. J of wound care
15(7):325-8,
ICTROMI 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease
388
