
Efficacy of Topical Β Blockers (0,25% Timolol Maleate Eye Drops
®
)
in Treatment of Infantile Hemangioma
Wizar Putri Mellaratna
1 *
, Deryne Anggia Paramita
1
1
Department of Dermato-Venereology, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Sumatera Utara, Dr, Mansur Street number 5,
Padang Bulan, Medan
Keywords: Infantile hemangioma, timolol maleate, eye drops, topical therapy
Abstract: Introduction: Infantile hemangioma (IH) is a benign vascular tumor, that occurs several weeks after birth.
Pathogenesis of IH considers an escalation of angiogenesis, vasculogenesis in proliferative phases and
apoptosis in regression phases. Since 2010, topical timolol maleate has used as a treatment of superficial
and non-ulcerated IH. Case: A 2 months 25 days infant admitted to our hospital with a history of bright red
swelling on his left forehead. The lesion appeared first like a mosquito bite swelling when the patient was
three weeks old, then lesion enlarged and the color became more erythematous.Dermatology examination
indicated solitaryerythematous nodule, size 0,7x0,3x0,05 cm
3
, stepping border, and cobblestone surface,
rubbery consistency, and warm on left temporal. The hemangioma severity scale (HSS) was six, and
hemangioma dynamic complication scale (HDCS) was 0. The patient was treated with topical β blocker
timolol maleate eye drop 0,25%
®
, one drop twice a day.Three months after treatment, the regression of the
lesion was significantwith size 0,5x0,1x0,01 cm
3
. Discussion: Topical β blocker indicated in our caseto
reduce the risk of functional compromise such as ulceration, scar, and risk for residual skin development
include telangiectasia, redundant skin, and fibrofatty tissue after involution phases. Timolol maleate 0,25%
1 drops two times a day resulted in regression of superficial IH, topical and lower concentration used
reduces the risk of side effects. Conclusions: Importance to determine the effective treatment for IH based
on some points include anatomic depth, morphology, and risk for complication, functional compromise, and
permanent disfigurement.
1 INTRODUCTION
Infantile hemangioma (IH) is a benign vascular
tumor characterized by increased endothelial
proliferation and epidermal turnover. Incidence of
IH approximately 5-10%, more common among
female infants, with female to male ratios
3:1.Although they occur in all races, IH is more
common in Caucasian (Laranjo et al, 2014). Based
on a prospective study of IH by Dickson, the risk
factors that strongly associated with IH are
premature infants, low birth babies (< 2500 gram),
babies conceived invitro fertilization (IVF), the
family history of IH (62,6%) ( Dickison et al, 2011).
Pathogenesis of IH have considered an escalation of
angiogenesis and vasculogenesis, and upregulated
expression of glucose transporter protein type-1
(GLUT-1), vascular endothelial growth factor
(VEGF), and fibroblast growth factor (FGF). GLUT-
1 is a specific marker for IH.Two phases of IH
include proliferation and involution. Proliferation
occurs several weeks after birth, characterized by
quick proliferation of endothelial cell and involution
starts by one year of age, characterize by reducing of
proliferation, increase apoptosis, and most lesions
flatten and shrink from the center outward (Callahan
et al, 2012).
Treatment of IH with systemic propranolol first
described by Leaute-Labreze et al. in 2008,
hypothesized mechanisms of action are decreased
nitrite oxide, vasoconstriction, blockage of VEGF
and FGF, and stimulation of apoptosis causing IH
regression (Chambers et al, 2012). Recently,
propranolol has become the first-line treatment for
complicated IH. Topical timolol maleate as a
nonselective β blocker agent, since February 2010,
has been reported as treatment of superficial and
non-ulcerated IH. Some studies report tumor
reduction up to 100% in superficial IH by using
timolol maleate 0,5%, 0,25% and propranolol 1%.
Efficacy of Topical Blockers (0,25 .
DOI: 10.5220/0009991404550459
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease (ICTROMI 2019), pages 455-459
ISBN: 978-989-758-469-5
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
455
Most previous studies described no systemic or only
minimal systemic absorption of topical β blocker,
but only one report by Weibel et al. concluded that
topical timolol is systemically absorbed, but the
impact of low serum timolol is not well studied
(Weibel et al, 2016). Here we report a case of IH
that was successfully treated with topical β blocker.
2 CASE
A 2 months 25 days old infant was admitted to our
hospital with two months history of bright red
swelling on his left forehead. The lesion appeared
first like a mosquito bite swelling, with a pale color
on the left forehead when the patient was three
weeks old, then lesion enlarged, became more
elevated with strawberry-like color. Baby’s birth
weight was 3,1 kg. Maternal pregnancy history
wasstandard. His father’s sister also had the same
history as a patient. Physical examination revealed
the patient was alert, and other vital signs were
typical. There was no abnormality of the airway,
cardiovascular, ocular, and motor movements of the
patient. The current baby’s weight was 5,1 kg.
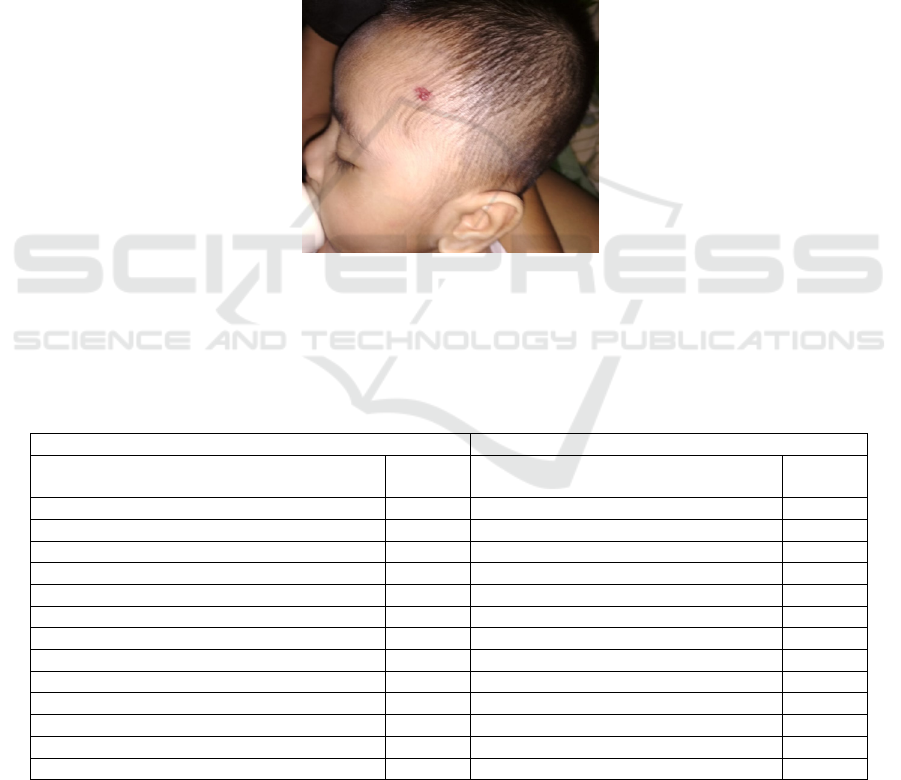
Dermatology examination indicated
solitaryerythematous nodule with size 0,7x0,3x0,05
cm
3
, stepping border, and cobblestone surface,
rubbery consistency on left forehead. Here is the
photo of the patient on the first visit.
Picture 1: Inspection: solitary erythematous nodule, size 0,7x0,3x0,05 cm3, stepping border, cobblestone surfaceon left
temporal. Palpation: Cobblestone surface, rubbery consistency, fixed and warm.
Examination results of IH severity using
hemangioma severity scale (HSS) and the risk of IH
complication using hemangioma dynamic
complication scale (HDCS) indicated:
Table 1. Results of HSS and HDCS
HSS HDCS
Parameter Score
Parameter Score
Objective items
Infection 0
Size (≤ 1 cm) 1 Ulceration 0
Location (peripheral face) 3 Feeding difficulties 0
Risk for associated structural anomalies 0 Torticollis 0
Complication 0 Cartilage distortion or destruction 0
Subjective items
Airway involvement 0
Pain 0 Visual compromise 0
Risk of disfigurement (telangiectasia) 2 Hypothyroidism 0
Anemia 0
Congestive heart failure 0
GI bleed 0
Hepatic dysfunction 0
TOTAL 6 TOTAL 0
The table was quoted with a little modification
from references number 9 and 10.
Differential diagnoses of this patient are an
infantile hemangioma, congenital hemangioma, and
pyogenic granuloma. Clinical diagnosis is infantile
hemangioma, and the patient was treated with
topical β blocker timolol maleate eye drop 0,25%
®
,
one drop twice a day. In addition, parents were
456
educated about a sign of hypothermia, bradycardia,
hypotension, hypoglycemia, and encouragethem to
feed the infant before each dose and do not
administer before bedtime without feeding. The
progress of this patient was followed monthly by a
dermatologist (to see the regression of the lesions)
and by a pediatrician (evaluating the
cardiopulmonary function and hypoglycemia).
One month after treatment, lesion became
smaller and lighter in color with size was
0,7x0,3x0,03 cm
3
, and the treatment was
stillcontinued because there were a good response
and no adverse effects. Two months from the first
visit, the size of the lesion was regressed, and the
size was 0,7x0,03x0,01, and there were no adverse
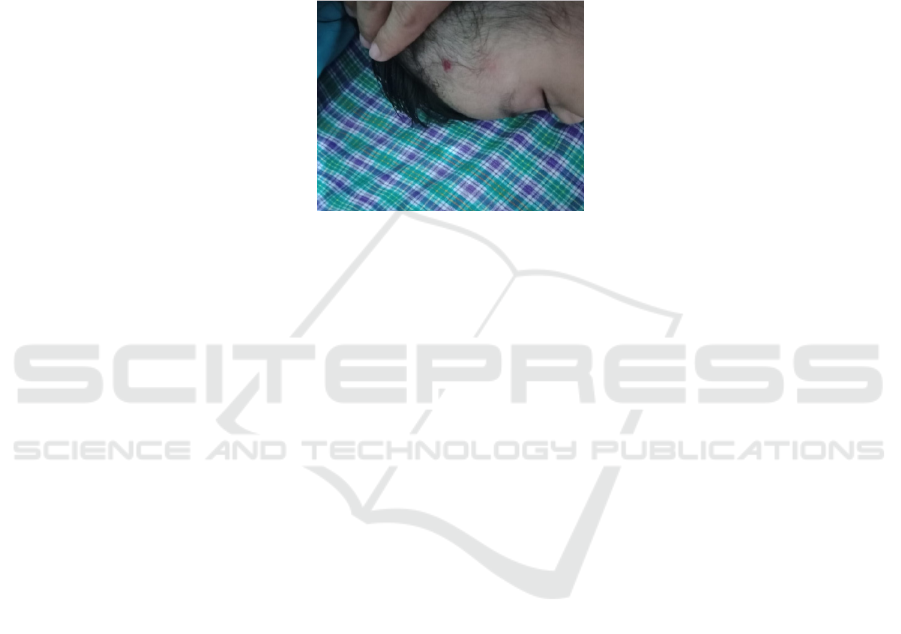
effects detected. Three months from the initial visit,
the regression of the lesion was more significant
with the current size was 0,5x0,1x0,01 cm
3
, and
there was no adverse effect occurred. Here is the
photograph of the patient in the last control:
Picture 2: Inspection: solitary pale erythematous nodule, size 0,5x0,1x0,01 cm3, firm border, pale on left temporal.
Palpation: smooth surface, rubbery consistency, fixed and warm nodules
Prognosis of this patient was considered suitable
because there were no systemic involvement, no risk
of complication or structural anomaly, and
permanent disfigurement.
3 DISCUSSION
Infantile hemangioma usually develops on the first 3
or 4 weeks of life. Phases of IH are proliferative and
involution. IH proliferate time depending on
morphology and configuration. Most growth is
completed by around five months.Clinical
appearance of IH in proliferative phases is
enlargement, elevated, with rubbery consistency,
surrounding pallor, and dilatation of surrounding
veins.The involution phases range from 1 year until
5-7 years of age, characterize by fading of the shiny
crimson color to a dull purplish hue, the surface
showed tiny white freckles, lesions softens, affected
skin becomes slightly wrinkled (Painter et al,
2019;Moyakine et al,2019).
In our case patient was
still in proliferative phases with typically red
noduleand rubbery consistency.
Based on lesion distribution and anatomic depth,
IH is classified into superficial, deep, and compound
type. Superficial IH describes as bright red papules,
plaques or nodule which are warm to touch,non-
tender with cobblestone or smooth surface, and also
known as strawberry type. Deep IH is lesion from
reticular dermis extends to subcutaneous tissues,
characterized by blue, appears as flesh-colored to
blue masses that are warm to touch. The mixed type
has no characteristics of superficial and deep IH. In
our cases, the patient showed superficial IH with
bright red nodule and warm to touch. Morphological
classification of IH is localized, segmental,
indeterminate, and multifocal. This classification is
often associated with some internal complications
and functional compromise. The localized lesion is
solitary discrete lesion and typically circular.
Segmental IH involves broad anatomic region, often
unilateral, and sharply demarcated. Segmental IH
has higher rate complication and increases the risk
for functional compromise if located on the face, it
is often associated with PHACE syndrome, and if it
is located on the lumbosacral and anogenital region,
is associated with LUMBAR syndrome. Multifocal
is numerous lesions (more than 10), discrete,
localized lesions present at more than one anatomic
sites and often associated with hepatic
hemangiomatosis. Indeterminate lesions are
notcharacterized as localized or
segmental.(Haggstrom et al,2019) In our case, this
patient has a localized IH with located in temporal
region, revealed a solitary nodule with size is less
than 1 cm, only superficial involvement based on the
erythematous color of the lesion, so there was no
risk for complication and functional compromise
according to location, morphology and anatomic
depth of the lesion.
Efficacy of Topical Blockers (0,25
457

The score of HSS and HDCS indicate outcome
measure, HSS measures the severity of lesion while
the HDCS assigns a grade for each complication in a
longitudinal use. Complication assed in HSS is
correlated with HDCS grade. Both of the scale
measure size changes, complications, and risk for
disfigurement. Study of Moyakine in 2017,
determined using HSS to facilitate treatment
decisions for IH, scores of 11 or higher as a marker
for propranolol treatment, scores of 6 or lower as a
marker for watchful waiting or topical β blocker
treatment, and children with HSS score higher than 6
and lower than 11, treatment decision should
consider other factors, including patient age, IH
type, and parental preferences.(Zheng et
al,2019;Rotter et al,2017) In our case, the HSS was
six, and HDCS was 0, based on HSS results, the
patient was treated with topical β blocker.
Diagnosis IH is based on clinical examination
and history. USG, MRI, and CT scan are only
required if there is systemic involvement. IH should
be differentiated with other vascular anomalies such
as congenital hemangioma and pyogenic granuloma.
This lesion occurred three weeks after birth, and the
lesion was rapidly progressed to eliminate the
diagnosis of congenital hemangioma. Location on
the face, tumor with red to brownish red color
manifested in pyogenic granuloma and IH, but
because in our case the lesion occurredseveral weeks
after birth and the surface of the lesion was not
easily bleeds and ulcerated, favor diagnosis as IH.
Treatment of IH has a purpose of preventing
complication, functional compromise, and
permanent disfigurement for this patient. In our case,
the lesion was superficial and localized, so the
primary purpose of administered treatment for this
patient was to reduce the risk of functional
compromise such as ulceration and scar and risk for
residual skin development include telangiectasia,
redundant skin, and fibrofatty tissue after involution
phases. Previous studies reported most 0,5% topical
timolol maleate, administered one drop two times a
day resulted in complete regression of superficial
IH, but only a few studies reported the use of lower
concentration (timolol maleate 0,25%) with the same
potential to reduce the lesion. Lower concentration
theoretically further reduce the risk of side effects,
such as hypotension, hypoglycemia, bradycardia,
and bronchoconstriction. (Chambers et al, 2012).
Prior before starting treatment, we examined
complete blood count (include blood glucose),
cardiovascular function, and pulmonary function.
Laboratory test and cardiopulmonary were regular
so that we started the treatment with topical β
blocker. Contraindication for β blocker includes AV
block (grade 2 and 3), congestive heart failure,
bronchospasm, hypoglycemia, hypotension, and
sinus bradycardia. Topical timolol maleate 0,5%
solutions or GSF consider safe treatment for
superficial IH in term infants receiving a dose less
than 0,2 mg/kg/day, with no adverse events reported.
Higher risk for systemic adverse events is
prematurity and low birth weight, baby. Adverse
events of β blocker usually reported by using
systemic propranolol, but only a few or almost no
adverse event reported by using topical β blocker.
Short-term adverse events include hypotension,
bradycardia, and hypoglycemia. Long-term adverse
events include emotional lability, sleep disturbance,
and other effects related to neural depressant effects.
In our case, the patient was a term baby with average
birth weight, and the lesion was superficial, non-
ulcerated, and located in the temporal region so that
the risk for systemic complication consider minimal
or none. Topical application of β blocker have a
higher risk for systemic complication if given on
mucosal surface (ocular, lips, anogenital), ulcerated
IH, and extend large IH. Evaluation of possible
systemic complication accomplished by educating
parents to evaluate sign and symptoms of adverse
events include lethargy, cyanosis, mottled/cold skin,
irritable, tremor, and excessive sweating. Monthly
evaluation of cardiopulmonary function and blood
glucose checks in hospital. In our case, during three
months of treatment, there wereno adverse effects
occur.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This case represents the treatment of superficial non-
complicated successfully, and non-ulcerated IH with
topical β blocker timolol maleate 0,25% eye drops
®
.
There were no adverse effects reported in this case.
It suggests an important to determine the effective
treatment for IH based on some points, include
anatomic depth, morphology, and risk for
complication, functional compromise, and
permanent disfigurement. The purpose of initial
administration treatment for superficial IH consider
to reduce the risk of functional compromise such as
ulceration and scar and risk for residual skin
development include telangiectasia, redundant skin,
and fibrofatty tissues.
458

REFERENCES
Callahan AB, Yoon MK. 2012. Infantile Hemangiomas: A
Review. AAO [internet]. [cited 2019 January
29];26:283-91. Available from:
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/255987798_
Infantile_hemangiomas_A_review DOI:
10.1016/j.sjopt.2012.05.004
Chambers CB, Katowitz WR, Katowitz JA, Binenbaum G.
2012. A Controlled Study of Topical 0,25% Timolol
Maleate Gel for the Treatment of Cutaneous Infantile
Capillary Hemangiomas. Ophthal Plast Surg
[internet]. [cited 2019 February 16]; 28(2): 103-6.
Available from:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22410658doi:1
0.1097/IOP.0b013e31823bfffb.
Dickison P, Student M, Christou E, Wargon O. 2011. A
Prospective Study of Infantile Hemangiomas with a
Focus on Incidence and Risk Factors. Pediatr
Dermatol [internet]. [cited 2019 February 20]; 28(6):
663-9. Available from:
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21995808doi:10.1111
/j.15251470.2011.01568.
Haggstrom AN, Beaumont JL, Lai SL, Adams DM, Droet
BA,Frieden IJ, et al. 2012. Measuring the Severity of
Infantile Hemangiomas. Arch Dermatol [internet].
[cited 2019 January 30]; 148(2):197-202. Available
from:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22351819
doi: 10.1001/archdermatol.2011.926.
Laranjo S, Costa G, Parames F, Freitas I, Martins JD,
Trigo C, et al. 2014. The role of propranolol in the
treatment of infantile hemangioma. Rev Port Cardiol
[internet]. [cited 2019 January 28];33(5):289-95.
Available
from:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24906291
doi:10.1016/j.repc. 2013.10.018
Moyakine AV, Koulil S, Vleuten CJM. 2017. Propanolol
treatment of infantile hemangioma is not associated
with psychological problems at 7 years of age. J Am
Acad Dermatol [internet]. July. [cited 2019 January
29];105-8. Available from:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28190620
doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.01.025.
Moyakine AV, Herwegen B, Vleuten CJM. 2017. Use of
the hemangioma Severity Scale to facilitate treatment
decisions for infantile hemangiomas. J Am Acad
Dermatol [internet]. August 14. [cited 2019 January
30];77(5):868-73. Available from:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28818436doi:
10.1016/j.jaad.2017.06.003
Painter SL, Hildebrand GD. 2016. Review of topical beta
blockers as treatment for infantile hemangiomas. Surv
Opthalmol [internet]. [cited 2019 January 29];61:51-8.
Available from:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26408055
doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2015.08.006.
Paller AS, Mancini AJ. 2016. Hurwitz Clinical Pediatric
Dermatology. Fifth edition. [cited 2019 February 3].
Chicago: Elsevier. pp: 279-95.
Rotter A, Najjar Z, Oliveira P. 2017. Infantile
hemangiomas: pathogenesis and mechanisms of action
of propranolol.JDDG [internet]. [cited 2019 January
29];1185-1190. Available from:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29193649
doi: 10.1111/ddg.13365
Weibel L, Barysch MJ, Scheer HS, Konigs I, Neuhaus K,
Schiestl C, et al. 2016. Topical Timolol for Infantile
Hemangiomas: Evidence for Efficacy and Degree of
Systemic Absorption. Peadtr Dermatol [internet].
[cited 2019 February 7]; 33(2):184-90. Available
from:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26840644
doi: 10.1111/pde.12767.
Zheng JW, Zhou Q, Mai HM, Wang YA, Fan XD, Qin
ZP. 2013. A practical guide to treatment of infantile
hemangiomas of the head and neck. Int J Clin Exp
Med [internet]. [cited 2019 January 31];6(10):851-60.
Available from:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24260591
Efficacy of Topical Blockers (0,25
459
