
Digital Library "Scientific Heritage of Russia"
N. Kalenov
a
, K. Pogorelko
b
, I. Sobolevskaya
c
and A. Sotnikov
d
Joint Supercomputer Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences — Branch of Federal State Institution “Scientific
Research Institute for System Analysis of the Russian Academy of Sciences” (JSCC RAS — Branch of SRISA),
119334, Moscow, Leninsky av., 32 a, Russia
Keywords: Scientific Heritage, Digital Library, Russian Scientists, Information System, Network Technologies, Virtual
Exhibitions, Museum Objects, Digitization.
Abstract: The article discusses a new version of the digital library "Scientific Heritage of Russia" (DL SHR) presented
on the Internet at http://e-heritage.1gb.ru/. The DL SHR contains information about scientists of the 18th,
19th and first half of the 20th centuries who made a significant contribution to the development (Science in
Russia). These include both Russian scientists and foreign scientists who worked in Russia. DL content
includes structured metadata about scientists, their detailed biography, bibliography, portraits, and full texts
of their most important publications, museum and archival information related to them. The article presents
the principles underlying the filling of the DL SHR, the architecture of the Library, the blocks included in its
structure, describes the user interface, illustrated by examples.
1 INTRODUCTION
There are various renderings of terminology
associated with digital libraries (hereinafter referred
to as DL) and their components in computer science.
We will use the following definitions:
Definition 1: DL - structured information of
interest to them.
Definition 2: DL resources - full-text, audio and
video materials included in the DL.
Definition 3: Metadata - a set of formal features
by which resources are searched.
Definition 4: DL content - a set of metadata and
resources supported in DL.
In the modern information space, there are
thousands of digital libraries (DL) ranging from
universal ones containing metadata and full texts of
millions articles to small digital libraries contain the
employees works of individual scientific
organizations. For example:
https://www.elibrary.ru/defaultx.asp
https://www.scopus.com/home.uri
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5269-0988
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7598-8813
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9461-3750
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0137-1255
https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/digi
tal-library
http://zioc.benran.ru/).
Almost all of the world's largest publishers
provide users with access to digital versions of their
magazines and books. A number of large universities
and establishments create subject-oriented. For
example:
https://plato.stanford.edu/;
http://www.mathnet.ru/;
http://www.cas.org/.
Digital libraries are created at the national and
international levels. For example:
https://www.nibib.nih.gov/content/national-
science-digital-library-nsdl:
https://www.europeana.eu/en.
The absence of a scientific information resource
that solves the problem of preserving the scientific
heritage and creating the conditions for its effective
development, as well as the integration of the funds
of various memory institutions (libraries, archives
and museums) into a common digital information
resource is the main shortcoming of the information
retrieval platforms that exist today.
104
Kalenov, N., Pogorelko, K., Sobolevskaya, I. and Sotnikov, A.
Digital Library "Scientific Heritage of Russia".
DOI: 10.5220/0010106001040111
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications (CHIRA 2020), pages 104-111
ISBN: 978-989-758-480-0
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

In 2010, the DL "Scientific Heritage of Russia"
was created at the Russian Academy of Sciences. The
main purpose of creating the DL SHR is to provide
information on the outstanding scholars who worked
in Russia and who contributed to the development of
fundamental natural sciences and humanities through
the Internet in a free mode. Along with biographical
and bibliographic information about scientists, the
DL SHR includes full texts of the most significant
works published by them, as well as digital copies of
archival and museum materials related to the
professional activities of these scientists. In addition
to the fact that the placement of copies of documents
allows significantly expanding the circle of their
users, digitization of printed publications, archival
and museum materials that are of historical value,
allows ensuring their safety by minimizing the
circulation of their originals.
Thus, unlike most modern scientific DL, focused
on providing users with current information, the DL
SHR was faced with the task of ensuring at the
national level the popularization of the achievements
of domestic science and the preservation of rare
scientific documents.
Initially, the DL SHR was also tasked with
providing a multifaceted search and navigation
through heterogeneous resources, which is not typical
for most modern DLs that have a rather trivial search
interface.
Additional factors that distinguish DL SHR from
a variety of digital libraries are the principle of
selection of materials and the technology of forming
its content. Leading libraries, institutes, museums and
archives of the Russian Academy of Sciences
participate in the filling of the DL SHR. The software
and technological complex, which ensures the
formation of the DL SHR, provides for the
monitoring of data preparation processes and multi-
stage quality control of the input information.
Since 2010, the Joint SuperComputer Center
(JSCC) of the Russian Academy of Sciences – Branch
of Federal State Institution “Scientific Research
Institute for System Analysis of the Russian Academy
of Sciences” has been supporting the digital library
"Scientific Heritage of Russia" (DL SHR) in the
Internet (Kalenov N.E., 2016.).
The main goal of creating the DL SHR is to
provide information on outstanding scholars worked
in Russia and made a great advance in the
development of fundamental both natural and human
sciences.
Along with biographical and bibliographic
information about scientists, the DL SHR includes the
full texts of the most important works published by
them, as well as digital copies of archival and
museum materials related to the professional
activities of these scientists.
Digitalization of printed publications, archival
and museum materials, which are historical value,
allows to ensure their preservation by minimizing
their originals query.
The principle of coordinated decentralized
information generation in combination with
centralized data storage support and web single sign
on for users (Antopol'skij A.B., 2016) is the basis for
DL SHR database provisioning. DL SHR EB NNR is
part of the information support system for scientific
research (Kalenov N.E., 2015; Serebryakov V.A.,
2016) and an integral component of the project to
create a Single Digital Space of Scientific Knowledge
(Antopol'skij A.B., 2019).
This article is concerned with the structure of the
DL SHR and the services it provides for the search
and provision of its content.
2 THE DIGITAL LIBRARY
"SCIENTIFIC HERITAGE OF
RUSSIA" STRUCTURE
DL SHR is a complex that includes the following
units:
1. A resource management unit that supports the
following process technologies:
- selection of materials for inclusion into the DL;
- creation of a new resource;
- creation of metadata describing the resource;
- loading of resources and metadata in digital
documents, their correction and deletion.
2. User management unit that provides:
- registration of users with various access rights to
the digital library;
- adjustment, deletion of user data;
- authorization of users at the entrance to the DL.
3. The control unit of linguistic means (support for
dictionaries, classification systems, thesauruses, etc.).
4. The unit of access to the DL that provides:
- support for the user interface of the request
formation;
- query processing;
- information retrieval;
- navigation through the content of electronic
books.
5. The system administration unit that provides:
- installation, configuration, support of hardware
and software of electronic devices;
Digital Library "Scientific Heritage of Russia"
105

- archiving of information and recovery of
electronic devices after failures;
- monitoring DL (analysis of the demand for its
components).
6. The manager unit that solves administrative
tasks of current functioning and determines the main
directions of DL SHR development.
3 THE DIGITAL LIBRARY
"SCIENTIFIC HERITAGE OF
RUSSIA" ARCHITECTURE
The DL SHR is focused on distributed architecture in
which data sources (the storage of resources and
metadata) can be distributed geographically. Servers
that are providing digitized data storage, the main
web-portal of the DL SHR, data digitization centers
represent the general architectural components of the
system. DL SHR is built as a distributed information
system with a dedicated central node. The subsystems
are the entry points into the DL of the organizations
participating in the project on the one hand, and are
the information providers for the entire distributed
system on the other hand (Pogorelko K.P., 2015).
Consequently, the key principle of the
architecture is the independent development of digital
data by participating organizations and with the
simultaneous integration of data into a common
digital information space. This is achieved by
standardizing of metadata provision, data
presentation formats, search interfaces and
dictionaries (Kalenov N.E., 2012). These aspects are
relevant to this date (Ahmad K., 2019; Windhager F.,
2019). Thus, each digital library of the participating
organizations can store data in its own formats and
provide its own services, but at the same time, it must
provide the same interfaces for all mentioned above.
The system central node should provide
navigation, search and provision of data for all digital
libraries in accordance with unified formats and
services. The storage servers provide reliable storage
and backup of digital content. In addition, they
provide end-users an access to data redirected from
the central digital portal. The data storage servers also
provide the digitization centers with tools for data
automation placement and update. This approach is
applying today (Arshad H., 2020).
The main web-portal of DL SHR consolidates
metadata received from digitization centers within a
centralized repository, providing users with
centralized access (to them). Interacting with digital
storage servers, it is also an integrated point of access
to digital versions of scientific papers.
4 THE DIGITAL LIBRARY
"SCIENTIFIC HERITAGE OF
RUSSIA" METADATA
PROFILES
In the DL SHR the information partitioning about all
classes of objects is used. In particular, the various
bibliographic levels structuring of digital copies of
publications is used. (Baryshev R.A., 2020; Bonacchi
C., 2019). It avoids information duplication,
minimizes the number of misprints in the metadata
and presents the information to the user in a holistic
and consistent way. An application profile for
supporting museum activities has been developed.
The general survey of these specifics will be
examined in more detail.
For the object class “Museum Object” special
attributes are defined:
Condition (safety);
Year of collection;
Receipt date;
Affiliation of the collection.
Attributes such as "Title", "Description",
"Keywords", "Source", etc., are inherited from the
class common to museum objects and publications.
This profile allows to standardize the metadata of
physical museum items and multimedia (photo,
video, audio) resources.
As well as additions and changes were made to the
representations of the participating resources of the
main profile, such as "Persons", "Performance",
"Collections". In contrast to publications, the objects
descriptions in various museums may have their own
characteristics. It is impossible to provide a
comprehensive set of necessary properties here. In
this regard it is possible to determine additional
properties for these objects. Accordingly it is possible
to define additional properties of the object in the
system administrator’s interface. While
representations of the corresponding fields are
created in the data input and output interfaces. The
same problem is being considered today (Corrales
D.C., 2020; Zhmailo S.V., 2020). The entered values
of additional fields are displayed in full information
about the object, but they are not searched. Thus, the
administrator can add such properties as the "Number
of items", "Description author", "Collection author',
"Geography", "Dimensions", "Age", "Method of
receipt", "Preparations", etc.
CHIRA 2020 - 4th International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications
106

Museum objects more often than publications are
combined in collections. In this regard, the support
for nested objects of type "Collection" with attributes
(metadata) is implemented in the DL SHR:
Identifier;
Name;
Collection type;
Keywords;
Description;
Administrator;
The number of elements in the collection;
Storage;
Notice;
Elements of the collection.
Operations on collections are performed through
the following system forms:
Input and modification of information about
the collection;
Search and issue information about the
collection;
Issuing a list of collection objects;
Inclusion and exclusion of collection objects;
Collections removal;
Indication of the collection when entering
information about the object through an staging
database.
An additional profile of advanced data storage
support has been developed at the DL SHR. A
number of new entities have been introduced in this
profile. The main ones are:
- Class "Media Object". It is intended to describe
a media object as a single whole, consisting of
pieces of data with different functional load;
- Class "Part of the media object." This class
allows within a single media object, for
example, a museum subject, to have several
parts with different functional loads. In
particular, photographs from different angles, a
video clip, accompanying information
documents, etc.
5 THE DIGITAL LIBRARY
"SCIENTIFIC HERITAGE OF
RUSSIA" CONTENT
PREPARATION TECHNOLOGY
The following describes the distributed data
preparation technology for DL SHR.
Guided by the coordinated approaches to the
principles of digital books filling each organization
participating in the program determines the
publications from its funds, which it considers
appropriate to include in the electronic books (Wuttke
U., 2019; Freire N., 2018). After that, the registered
representative of this organization enters the dispatch
system and checks to see if this publication and its
author(s) are already registered in it. If there is no
publication in the system, metadata and information
about the author (if the author has not been entered
earlier) are entering into the proposed template its. In
this case, the “Current Status” template field assumes
the value “proposed for digitization”.
A representative of the editorial team periodically
enters the dispatch system and receives a list of
documents with the status “Proposed for
digitization”. The editorial team makes a decision on
each of them about the advisability of entering into
the digital library. If the document is to be digitized
the value of the “Current Status” field changes to
“Registered”, and the number of this document is
automatically entered into the record under which it
will be entered into the electronic document. In the
future, this number (“JSCC Number” field) is not
subject to change. If for any reason it is not practical
to digitize a document, the value of the “Current
Status” field changes to “No Digitization”.
A representative of the organization that forms he
digital content enters the scheduling system and
selects its records that have the current status of
“Registered”. After selecting publications and
sending them for digitization, their current status
changes - the value “In operation” is entered in this
field. After the digitization process is completed, the
status of the records changes to “Digitized”, after
being transferred to the JSCC editorial team, it is
“Surrendered”.
Thus, at each moment of time, the DL
administrative group can receive information on how
many and which publications are in operation, how
many and by whom it has been digitized, etc. Such
problems are being considered now (Fuchsgruber L.,
2019; Golub K., 2019; Munster S., 2019).
The technological field “Acceptance status” is
filled in by the staff of the editorial team. working
with this edition. Upon receipt of a digital copy of the
publication, the value “accepted for work” is entered
in this field. If there are no comments on the material,
it is transferred to the technical group, and the field
value changes to "accepted for uploading to the site",
after downloading the field takes the value
"published". If errors are detected in the material, the
editor sets the “Acceptance Status” field to “Problems
Detected”, fills in the “Missing Pages” and
“Comments on the Problem” fields and sends the
appropriate message to the contractor. The contractor
corrects the errors, accordingly changing the value of
Digital Library "Scientific Heritage of Russia"
107
the “Acceptance Status” field, after which the editor
transfers the publication for downloading to the
digital document.
Thus, the progress and timing of error correction
is controlled, and additional statistics on the operation
of the system can be obtained (Stegaeva M.V., 2020).
Metadata about persons and publications from the
technological system is downloaded to the digital
server automatically when downloading an electronic
publication (Samanta K.S., 2020; Silvis I.M., 2019).
6 THE DIGITAL LIBRARY
"SCIENTIFIC HERITAGE OF
RUSSIA" USER INTERFACE
DL SHR materials that have passed editorial control
are available on the public website http://e-
heritage.1gb.ru/.
The following navigation menu items are
available for users:
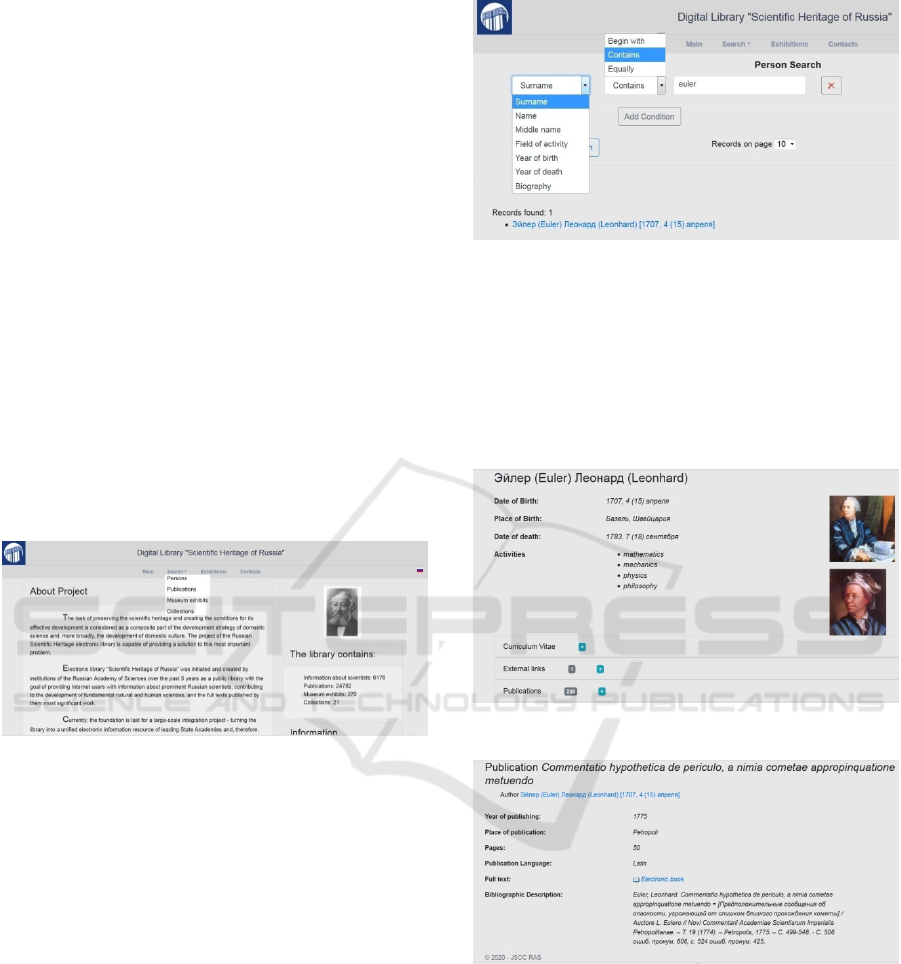
Main (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Page of the DL SHR website - “About the
project”.
Search. In the DL SHR, the search for objects
of “person”, “publication”, “museum objects”,
and “collections” has been implemented
(Figure 1).
A multi-faceted search (in particular, thematic,
scientific works, scholars, museum objects, by
fragment of surname, year or place of birth, etc.) can
be carried out in the DL SHR (Figure 2). One can use
several search attributes using Boolean logic. The
search result for a person by the surname “Euler” you
can see on the Figure 2.
Figure 2: Possibilities of person search queries.
Name of the person we found in the previous step
(in Cyrillic and Latin transcription) is an active link.
Clicking on it, the user gets to a page dedicated to
Leonhard Euler (Figure 3). On this page you can see
(pressing “+”) biography of the scientist, short list
with his bibliography and links to external sources
related to Euler.
Figure 3: Page dedicated to Euler.
Figure 4: Example of the book description.
CHIRA 2020 - 4th International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications
108
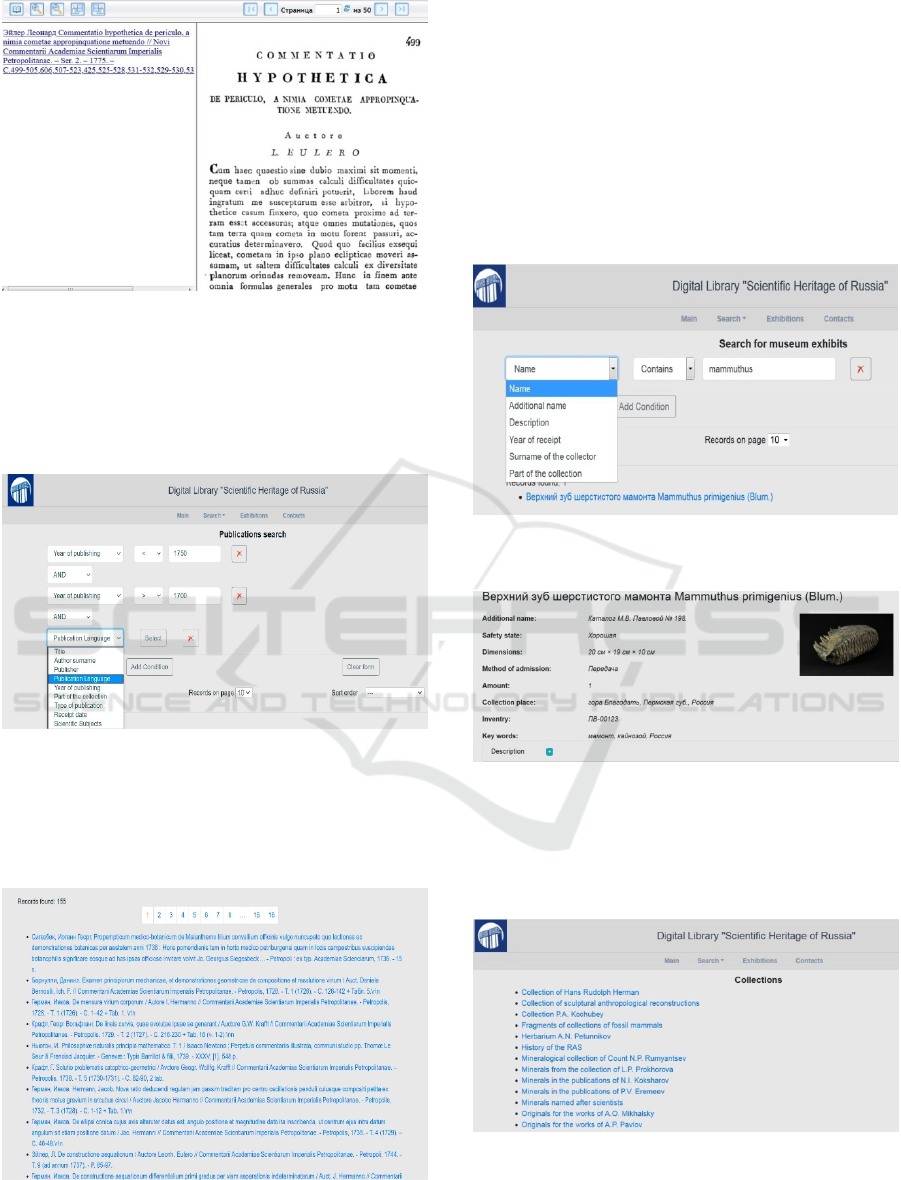
Figure 5: Full text visualisation.
Figure 6 shows the search capabilities for a fixed
both time frame and language of publication (e.g. it's
need to find publications in Latin published from
1700 to 1750). The search results are presented in
Figure 6.
Figure 6: Search for a both fixed time frame and language
of publication.
The surname of the author of each publication
(Figure 7) is an active link, by clicking on which you
can get information about the author.
Figure 7: Publication search result.
DLSHR allows to search for a museum object
both in full name and in its fragment. For example,
it's necessary to find all museum objects related to
mammoths. To do this, the name "
mammuthus" is
entered in the search query. On this query in the
collection is not only object "mammoth" but also an
object the "the upper of a woolly mammoth" related
to it.
Figures 8 and 9 show the possibilities and the
search result for a fragment of the name of the
museum object.
Figure 8: Search for the museum object name
“mammuthus”.
Figure 9: "The upper of a woolly mammoth's tooth" as a
search result for the name of the Museum object
"Mammuthus".
Figure 10 shows the fragment of list of collections
available in the DL SHR.
Figure 10: The list of collections available in the DL SHR.
Exhibitions.
DL SHR is an information resource allows to
create and present interdisciplinary multimedia
Digital Library "Scientific Heritage of Russia"
109
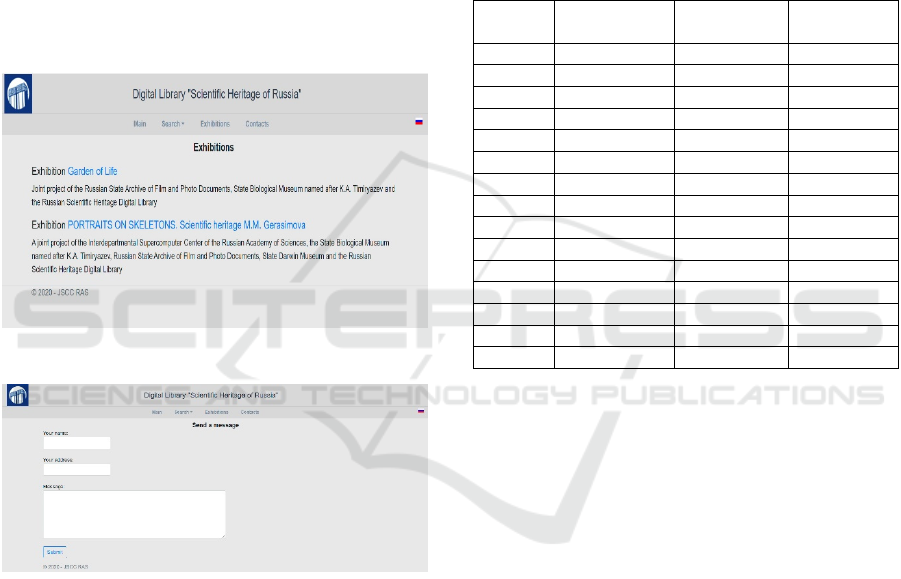
virtual exhibitions on its platform. A virtual
exhibition is an information resource that shows users
diverse information (digital copies of printed
materials, archival documents, museum items, etc.).
This information is united by certain signs. Due to the
fact that various types of materials are being
presented in the process of forming digital science
collections it becomes necessary to create multimedia
objects, in particular, digital 3D models of museum
objects and virtual reality objects (Sobolevskaya I.N.,
2019). There are several virtual exhibitions have been
implemented within the framework of the project on
filling the DL SHR. Among them those dedicated to
the 160th birthday of I.V. Michurin and the
development of genetics in Russia, as well as the
scientific heritage of M.M. Gerasimov (Figure. 11).
Figure 11: Virtual exhibitions carried out the DL SHR.
Figure 12: Contact form.
7 CONCLUSIONS
For now, data on more than 6,100 scientists working
in Russia since the 18th century have been entered
into the DL SHR and the full texts of more than
24,500 publications that are not subject to copyright
law are available. Scanned text is not recognized,
except for the table of contents, which provides
navigation within the publication. In addition, a
number of digital objects from natural science
museums are presented in the DL SHR. Along with
photographs, 3D models of some museum objects are
presented, including a collection of M.M.
Gerasimov’s anthropological reconstructions and I.V.
Michurin’s collection of fruits.
Although the resources of the DL SHR are
focused primarily on Russian users, as practice has
shown, many foreign specialists who are interested in
the problems of the development of science turn to
the DL SHR. Table 1 presents the "top 15"
distribution of demand for DL SHR by countries
(Pogorelko K.P., 2017).
Table 1: The "top 15" distribution of demand for DL SHR
by countries.
№ Сountry
Books
viewe
d
Pages
downloade
d
1 Russia 144573 5060276
2 Ukraine 28614 1228989
3 Belarus 6114 208723
4Bul
g
aria 2004 126883
5 Kazakhstan 3181 114877
6German
y
2701 107504
7 USA 2857 101974
8Polan
d
1707 65480
9Ital
y
1219 51838
10 Lithuania 778 50378
11 Azerbaijan 901 39964
12 Israel 1008 36345
13 Armenia 892 31501
14 Moldova 817 27751
15 France 756 28053
According to the data generated in the system
administration unit in 2019, 328.126 “effective” calls
to the DL SHR were received from 68.797 different
IP addresses (effective refers to the address during
which at least one page of the digital book was
downloaded).
Although (except Russia) the top 15 includes 7
CIS states a significant part of whose population is
fluent in Russian, representatives of a number of other
countries (Bulgaria, Germany, the USA) are also
quite active in the DL SHR and are at the top of the
ranked list .
Long term using of the DL SHR and its high
demand from users have shown that it fulfils its tasks
related to the preservation of the scientific heritage of
Russia and the popularization of scientific
achievements.
The experience gained during the development of
the Library and its content is supposed to be used in
the creation of a common digital space of scientific
knowledge in accordance with the concept given in
(Antopol'skij A.B., 2019).
CHIRA 2020 - 4th International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications
110

ACKOWLEDGEMENTS
The research is carried out by Joint Supercomputer
Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences – Branch
of Federal State Institution “Scientific Research
Institute for System Analysis of the Russian Academy
of Sciences” within the framework of the State task
0065-2019-0016.
REFERENCES
Ahmad K., Zheng JM., Rafi M., 2019. Librarian's
perspective for the implementation of big data analytics
in libraries on the bases of lean-startup model. In
Digital library perspectives. 36(1), pages 21-37.
Antopol'skij A.B., Kalenov N.E., Serebryakov V.A., 2016.
Edinaya sistema informacionnogo obsluzhivaniya
nauki FANO (Proekt koncepcii). In Informacionnye
resursy Rossii. № 5, pages 2-6.
Antopol'skij A.B., Kalenov N.E., Serebryakov V.A.,
Sotnikov A.N.. 2019. O edinom cifrovom prostranstve
nauchnyh znanij. In Vestnik Rossijskoj akademii nauk.
vol. 89(7), pages 728-735.
Arshad H., Jantan A., Hoon G.K., Abiodun I.O., 2020.
Formal knowledge model for online social network
forensics. In Computers & security. Vol. 89, UNSP
101675.
Baryshev R.A., Babina O.I., Tsvetochkina I.A.,
Manushkina M.M., 2020. Library and information
activities: theory and practice. In Nauchnye i
tekhnicheskie biblioteki-scientific and technical
libraries. 4, pages 13-36.
Bonacchi C., Krzyzanska M., 2019. Digital heritage
research re-theorised: ontologies and epistemologies in
a world of big data. In International journal of heritage
studies. Vol. 25(12), 1235-1247.
Corrales D.C., Ledezma, A., Corrales, J.C., 2020. A case-
based reasoning system for recommendation of data
cleaning algorithms in classification and regression
tasks. In Applied soft computing. Vol. 90, UNSP
106180.
Freire N., Voorburg R., Cornelissen R., de Valk S., Meijers
E., Isaac A., 2018. Aggregation of Linked Data in the
Cultural Heritage Domain: A Case Study in the
Europeana Network dagger. In Information. 10(8), №
252.
Fuchsgruber L., 2019. Museum Photo Archives and the
History of the Art Market: A Digital Approach. In Arts.
8(3). № 93.
Golub K., Tyrkko J., Hansson J., Ahlstrom I., 2019. Subject
indexing in humanities: a comparison between a local
university repository and an international bibliographic
service. In Journal of documentation.
Kalenov N.E., 2015. The Information Support of Basic
Research. In Automatic documentation and
mathematical linguistics. 49(2), pages 54-58.
Kalenov N.E., Pogorelko K.P., Serebryakov V.A., Sotnikov
A.N., 2016. Elektronnaya biblioteka «Nauchnoe
nasledie Rossii»: sostoyanie i perspektivy razvitiya. In
Nauchnyj servis v seti Internet: trudy XVIII
Vserossijskoj nauchnoj konferencii. pages 148-151.
Kalenov N.E., Savin G.I., Serebriakov V.A., Sotnikov
A.N., 2012. Principy postroeniya i formirovaniya
elektronnoj biblioteki "Nauchnoe Nasledie Rossii". In
programmnye produkty i sistemy. 4, id: 19685808.
Munster S., 2019. Digital Heritage as a Scholarly Field-
Topics, Researchers, and Perspectives from a
Bibliometric Point of View. In Acm journal on
computing and cultural heritage. 12(3), № 12.
Pogorelko K.P., 2015. Analiz vostrebovannosti elektronnoj
biblioteki "Nauchnoe nasledie Rossii". In
Informacionnoe obespechenie nauki: novye
tekhnologii: Sb-k nauchnyh trudov, pages 191-199.
Pogorelko K.P., 2017. Dinamika ispol'zovaniya elektronnoj
biblioteki "Nauchnoe nasledie Rossii". In
Informacionnoe obespechenie nauki: novye
tekhnologii: Sbornik nauchnyh trudov. BEN RAN,
pages 192-200.
Samanta K.S., Rath D.S., 2020. User-Generated Social
Tags Versus Librarian-Generated Subject Headings: A
Comparative Study in the Domain of History. In
Desidoc journal of library & information technology.
40(3), pages 176-184.
Silvis I.M., Bothma Theo J. D., de Beer Koos J. W., 2019.
Evaluating the usability of the information architecture
of academic library websites. In Library hi tech. 37(3),
pages 566-590.
Sobolevskaya I.N., Sotnikov A.N., 2019. Principles of 3D
Web-collections Visu-alization. In Proceedings of the
3rd Inter-national Conference on Computer-Human
Interaction Research and Appli-cation. SCITEPRESS.
Stegaeva M.V., 2020. Cataloguing in the digital epoch: b.
N. Yeltsin presidential library's experience. In
Nauchnye i tekhnicheskie biblioteki-scientific and
technical libraries. 2, pages 24-38.
Windhager F., Salisu S., Mayr E., 2019. Exhibiting
Uncertainty: Visualizing Data Quality Indicators for
Cultural Collections. In Informatics-basel. 6(3), № 29.
Wuttke U., Spiecker C., Neuroth H., 2019. PARTHENOS -
A Digital Research Infrastructure for eHumanities and
eHeritage. In Bibliothek forschung und praxis. 43(1),
pages 11-20.
Zhmailo S.V., Ulyanin O.V..2020. Sci-tech libraries within
the knowledge management system: from information
specialist's viewpoint. In Nauchnye i tekhnicheskie
biblioteki-scientific and technical libraries. vol. 2,
pages 9–23.
Digital Library "Scientific Heritage of Russia"
111
