
Relationship of Reliability, Responsiveness, and Nurse Empathy to
Inpatient Satisfaction
Riaty Simbolon, Ermi Girsang and Ali Napiah Nasution
Faculty of Medichine, Universitas Prima Indonesia, Indonesia
Keywords: Patient Satisfaction, Reliability, Responsiveness, Empathy.
Abstract: Surveysof patient satisfaction about unprofessional nurses providing in services still often sound unfriendly
and inattentive to their patients. Nurses in quantity are the most workers in the hospital, amounting to 60.55%
and providing 24-hour services directly related to patients. The purpose of this study was to analyze the
relationship of reliability, responsiveness, and empathy towards inpatient satisfaction. This research was an
analytic study with cross sectional approach, with a population of 865 people and a sample of 190 repondents.
The tools used in this research were instruments (questionnaires) that have been tested for validity and
reliability. Furthermore, data were processed using univariate analysis, bivariate with chi-square test, and
multivariate with multiple logistic regression at a 95% confidence level ( = 0.05). The results showed that
the variables of reliability, responsiveness, and empathy were significantly associated with inpatient
satisfaction, p <0.05. The most significant variable related to inpatient satisfaction was empathy with Exp (B)
/ OR = 8,132 meaning that patients who stated that nurses empathized had a chance of being satisfied 8.1
times higher than patients who stated nurses lack empathy.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Ministry of Health has issued regulations that
determine patient satisfaction standards in health
services that are set nationally. Based on the
Regulation of the Ministry of Health of the Republic
of Indonesia in 2016 concerning minimum service
standards for patient satisfaction that is above 95%
(Ministry of Health Republic of Indonesia, 2016).
Health services with a level of patient satisfaction
<95% are considered not to meet minimum standards
or are not satisfactory.
Patient satisfaction surveys about officers who
are not professional in providing health services are
still oftenly heard (complains officers which are not
friendly and lack attention to their patients) (Isnindar,
Saputra, & Robiyanto, 2018).
The quality of nursing care services provided to
inpatients can be assessed based on the service quality
theory developed by Parasuraman, Zeithaml, and
Berry which consists of dimensions of physical
evidence (tangibles), reliability (reliability),
responsiveness (responsiveness), assurance
(assurance), and empathy (empathy) (Tjiptono and
Chandra, 2015). In their study the quality of service
studied is related to reliability, responsiveness, and
empathy.
According to Griffith (2017), in order to increase
loyalty can be done by adding value to what is
offered.Adding value can be done in ways such as
increasing the speed and responsiveness of service.
(Yu and Kirk 2009) Empathy is considered essential
to the provision of quality care. Research by Simbala
et al. (2013) shows a probability value of (p = 0.001
<0.05) which means there is a significant relationship
between nurse empathy services and patient
satisfaction.
Research Purwanti, Prastiwi, & Rosdiana (2017)
found that good service provided by nurses from
empathy factors almost all patients felt nurses lack
understanding of patient problems such as giving
personal attention to asking complaints experienced
by patients. “Being empathic has a significant place
in nursing within the therapeutic relationship. The
studies reviewed demonstrated that it is possible to
increase nurse’s empathic ability from a range of
clinical specialties and at both undergraduate and
postgraduate levels.”
(Brunero and Coates 2010).
Al-Damen's research results (2017) in Jordan
show that there is an impact of perceived health
service quality on overall patient satisfaction.
Simbolon, R., Girsang, E. and Nasution, A.
Relationship of Reliability, Responsiveness, and Nurse Empathy to Inpatient Satisfaction.
DOI: 10.5220/0010286700510057
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics, Medical, Biological Engineering, and Pharmaceutical (HIMBEP 2020), pages 51-57
ISBN: 978-989-758-500-5
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
51

Reliability has the most influence, followed by
empathy and assurance. Ozlii and Uzun, (2015) found
that there were differences in patient satisfaction in
various hospitals in Turkey related to the educational
background, profession, hospital where the patient
lived and previous hospital experience. Shan et al.
(2016) found a lack of trust as a source of patient
dissatisfaction in Heilongjiang, China. Devi and
Muthuswamy (2016) who examined in India, found
that physical evidence, reliability and responsiveness
were the three most important dimensions in
increasing patient satisfaction. Cunico, et al, (2012).
Empathy is the quality responsible for creating a
caring environment. Several nursing theorists have
identified empathy as a crucial component of caring.
Yousapronpaiboon and Johnson (2013), who
examined in Thai private hospitals, found that
assurance is the most dominant dimension, followed
by empathy, responsiveness, tangibles and reliability
in influencing patient satisfaction. The service quality
dimensions Empathy of nursing staff and Assurance
impact positively on both Loyalty and Cumulative
satisfaction (Gray and Boshoff, 2004.)
Furthermore, research (Essiam, 2013) examining
in state university hospitals in Ghana obtained results
that patient satisfaction is best explained by
responsive variables, followed by variables of
empathy, assurance, physical evidence, and
reliability.
Dissatisfaction felt by patients related to nurse
services which sometimes comes a long time when
called, nurses often play mobile phones, nurses are
less friendly, nurses less explain about the treatment
of illness in patients. This indicates that the
performance of some nurses is still not satisfying the
patient and family. One of the most important factors
for patient survival is to keep using hospital services
or encourage others to come to the same hospital
depending on the level of patient satisfaction in
getting services from the performance of nurses,
especially patients and families get services in the
inpatient room.
Based on the description above, the researcher is
interested in taking the title “Relationship Of
Reliability, Responsiveness, And Nurse Empathy To
Inpatient Satisfaction”
It is increasingly important that nursing care be
associated with measurable patient outcomes. A
correlational study examined relationships between
nurse‐expressed empathy and two patient outcomes:
patient perceived empathy and patient distress.
(Olson, 1995).
2 METHOD
This research was conducted at Stella Maris Hospital
in Medan in November 2019. The study population
was all inpatients with an average of 865 people per
month, and samples were obtained as many as 190
people. The research sampling technique was
accidental sampling. Characteristics of the majority
of respondents aged <39 years (50.5%), aged> 39
years (49.5%), all women (100.0%), educated
diploma (48.9%), minority educated high school
people (21, 1%). The majority of respondents were
private employees (40.0%), a minority worked as
housewives (8.4%). Based on the length of stay, the
majority had been treated for 2 days (45.3%), the
minority had been treated for 4 days (25.8%). Data
was collected by distributing questionnaires to
inpatients who will go home as in Figure1.
Univariate data analysis, bivariate using chi-
square test, and multivariate using multiple logistic
regression tests with a confidence level of 95%. The
research instrument was a questionnaire that had been
tested for validity and reliability with a sample of 20
people at Sarah's Hospital. The result was that all
instruments are valid (> 0,361) and reliable (> 0,600)
as shown in Table 1.
Univariate data analysis, bivariate using chi-
square test, and multivariate using multiple logistic
regression tests with a confidence level of 95% were
applied. Multiple logistic regression is a multiple
regression model if the dependent variable is
dichotomous data. Dichotomy means in the form of
categories with a total of 2 categories. The scheme of
entire reseach proses is decribed n Figure 1.
Table 1: Validity and reliability test results.
No Variables r-count r-table
Cronbach
Alpha
1 Reliability 1-10 0.436 0.361 0.733
2
Responsiveness 1-
10
0.465 0.361 0.725
3 Empathy 1-10 0.505 0.361 0.739
4
Patient
Satisfaction 1-10
0.532 0.361 0.745
Based on figure 1, the research process begins
with a sample application for approval to each
respondent through filling out the consent form. After
getting approval, the respondents filled out a research
questionnaire where the questionnaire had been tested
for its validity and reliability at Sarah's hospital to 20
respondentsThe questionnaire consists of
independent variables (reliability, responsiveness,
empathy) and dependent variables (Inpatient
HIMBEP 2020 - International Conference on Health Informatics, Medical, Biological Engineering, and Pharmaceutical
52
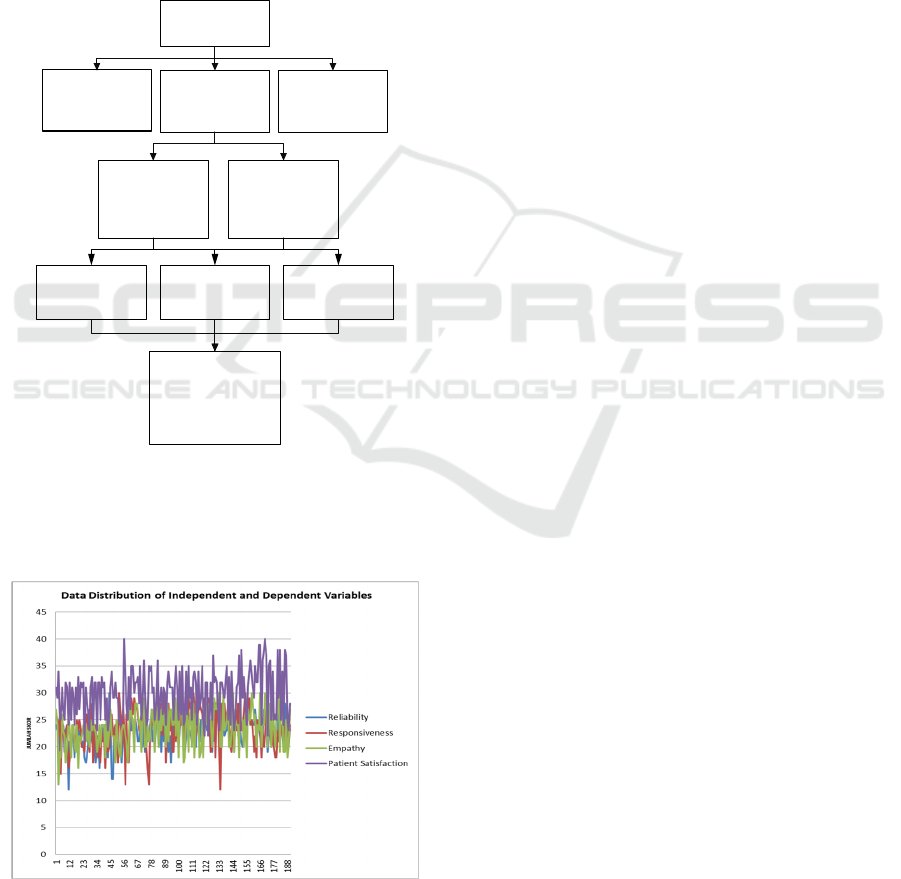
Satisfication).The study population was 865 people
located at Stella Maris Hospital. The sample is part of
the population and with the Lameshow formula, a
sample of 190 people is obtained. This research is an
analytical study with a cross sectional approach. The
data analysis methods used were univariate, bivariate
(Chi Square), and multivariate (Multiple Logistic
Regression). The result of multivariate analysis with
multiple logistic regression test shows that 3
variables, namely reliability, responsiveness and
empathy are all related to patient satisfaction, where
empathy is the variable that has the greatest
relationship with inpatient satisfaction.
Informed of Consent
Questionnaire
Validity and
Reliability Test
Location: Sarah Hospital
Samples: 20 Respondents
Independent
variables : reliability ,
responsiveness ,
empathy
Dependent variable:
Inpatients
Satisfaction
Population: 865
people
Samples: 190
Research Type: Analytic
study
Design: Cross sectional
Location: Inpatient at
Stella Maris Hospital
DataAnalysis :Univariate,
Bivariate(ChiSquare),
Multivariate(MultipleLogistics
Regression)
Multivariateresults :reliability,
responsiveness,empathyand
inpatientsatisfaction
Figure 1: The Scheme of the Research Process.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSIONS
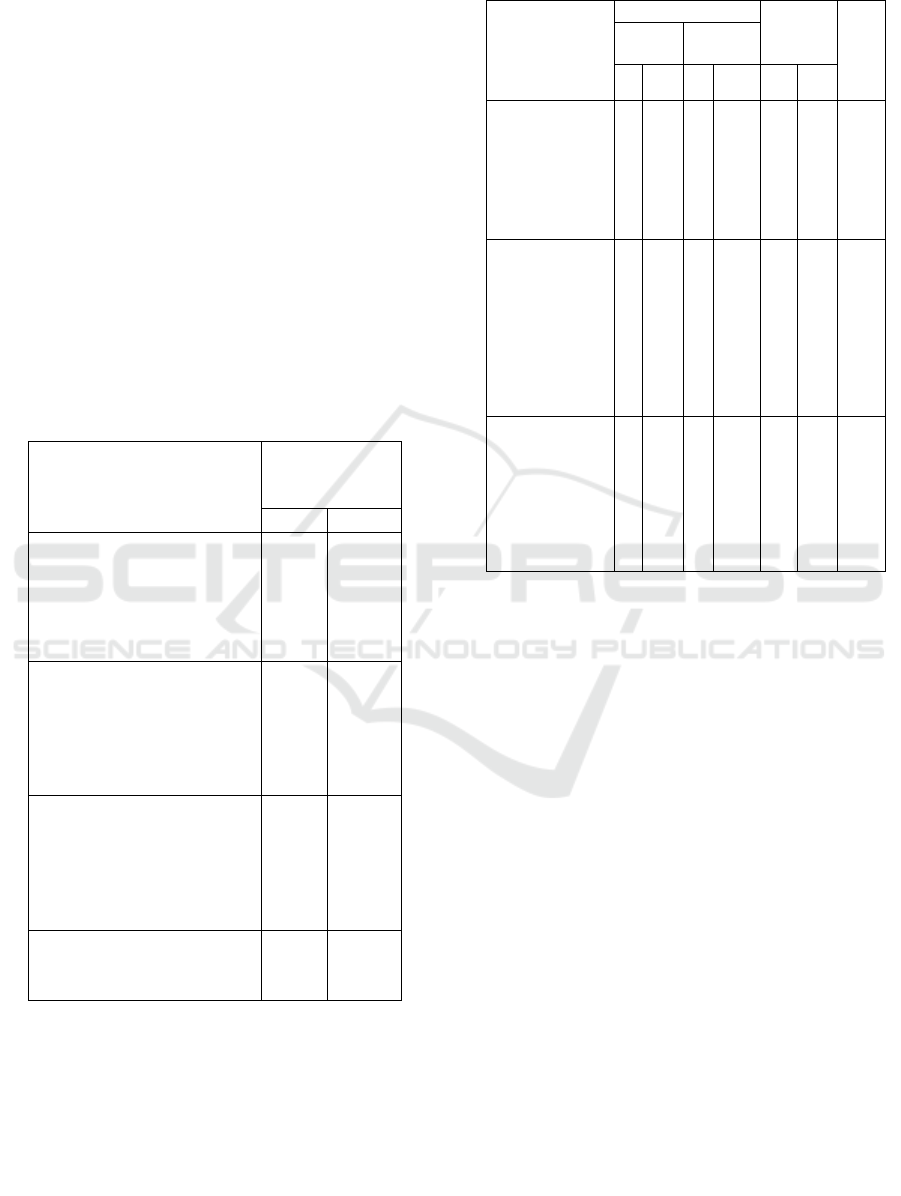
Figure 2. Data of recorded quessionare data from 190
respondents.
Figure 2 was the measured data of each variable
from the quessionare instrument. In the Figure 2. X
and Y axis areindicates the number of scores
respondents, respectively. Independent and
dependent variables data distribution shows that the
mean value of reliability was 22, Responsiveness was
23, empathy was 24, and patient satisfaction was 30.
All the results of the questionnaire were ploted
according to the variable namely: reliability,
Responsiveness, empathy, and satisfication with each
of 10 questions (the option in the quessionare were
Yes (score 3), Sometimes (score 2), and No (score
1)). The lowest score was 10, the highest score was
30. Good if score 21 - 30 (category 1) and Less if
score 10-20 (category 0). As for Patient Satisfaction
variable with 10 questions with answer choices Very
Satisfied (score 4), Satisfied (score 3), dissatisfied
(score 2), Very Dissatisfied (score 1), the lowest score
was 10 and the highest score was 40, so it says
Satisfied: if the results are 26-40 (category 1), Less
Satisfied 10 - 25 (category 0).
Found some differences in the results of the
respondents' scores for each variable, among others:
Reliability variable, the lowest score is 12. This result
was because during the treatment period respondents
did not get nurses who were always responsive when
need in help, did not pay attention to cleanliness of
the body and the area of the inpatient ward, less do
infusion control and sometimes do not routinely
check health conditions, likewise drug administration
is not timely while the highest score was 30 where
respondents get reliable nurse services which were
always responsive to all tested variables.
Responsibility variable found the lowest score
was 15, this is likely due to nurses never discussing
about health conditions, illness or continued care at
home, not checking health conditions, not providing
moral support, sometimes even nurses want to show
cooperation and want to help if needed. While the
highest score was 30, where nurses are quick to
respond to the complaints and the needs of
respondents. The Empathy variable found to be the
lowest score was 13, this is due to the nurses not
showing a sense of empathy towards the respondent,
only inviting communication about conditions but not
explaining their rights and obligations as well as
regulatory rules and not even asking for approval of
every action to be performed, explaining the
procedure difficult to understand, answering
questions that do not match the answers, even do not
treat with friendly and polite so that patients feel
uncomfortable. While the highest score was 30 where
a nurse has carried out her services with empathy
through good communication, explaining in language
Relationship of Reliability, Responsiveness, and Nurse Empathy to Inpatient Satisfaction
53
that was easy to understand both about the rules,
rights and obligations, all actions are asked for
approval, full of courtesy and courtesy, each
communicates a feeling of security and
comfortable.In the variable patient satisfaction found
the lowest score was 22, this is still found in
hospitalization, especially nursing services that are
not reliable, unresponsive and not empathetic in
carrying out their daily work, while the high score
was 40 where a nurse in his service has includes
nurses who are reliable, responsive and empathetic so
that respondents feel comfortable and safe.
Based on the univariate analysis, the results
showed that the majority of respondents grade the
reliability, responsiveness, and empathy with good
were ranged between 72.1% -76.3%, while those that
stated were not good between 23.7% -27.9%. For the
satisfaction variable, 74.7% of satisfied inpatients and
25.3% less satisfied, as shown in
Table 2: Variable Frequency Distribution (n = 190).
Variables
Quantity
N
%
Reliability:
Good
Not Good
145
45
76,3
23,7
Responsiveness:
Good
Not Good
144
46
75,8
24,2
Empathy:
Good
Not Good
137
53
72,1
27,9
Satisfications
Satisfied
N
ot Satisfie
d
142
48
74,7
25,3
Furthermore, based on the results of the bivariate
analysis, all independent variables were significantly
related to inpatient satisfaction, namely reliability (p
= 0.021), responsiveness (p = 0.016), and empathy (p
= 0.001). The complete Chi-Square statistical test
results can be seen in Table 3.
Table 3: Relationship of Each Independent and Dependent
Variables.
Variables
Patient Satisfaction
Qty
p-
value
Satisfied
Not
Satisfie
d
n % n % N %
Reliability:
Good
N
ot Goo
d
124
18
85,5
40,0
21
27
14,5
60,0
145
45
100
100
0,021
Responsiveness:
Good
N
ot Goo
d
124
18
86,1
39,1
20
28
13,9
60,9
144
46
100
100
0,016
empathy:
Good
N
ot Goo
d
121
21
88,3
39,6
16
32
11,7
60,4
137
53
100
100
0,001
The results of multivariate analysis with multiple
logistic regression tests showed that about 3 variables
as model candidates, all were related to inpatient
satisfaction which area reliability, responsiveness,
and empathy as in Table 4 (B is beta value, sig.
(significant), Exp (B) was exponential beta is read as
an OR (Odds ratio) value, and 95% CI for exp (B) was
a 95% confidence level for exponential beta values
for the upper and lower limits).
The variable that has the greatest relationship with
patient satisfaction for inpatients was the empathy
variable which has a value of Exp (B) / OR = 8.132
by mean that patients who have empathy were good
nurses, have the opportunity to feel satisfied by 8.1
times higher than patients who expressed empathy
nurses were not good.
The variable responsiveness (responsiveness)
which has a value of exp (B) / OR = 7.483 means that
patients with good nurse responsiveness have a 7.8
times higher chance of being satisfied than patients
who think that nurses' responsiveness is not good.
The variable reliability (reliability) which has a
value of Exp (B) / OR = 4.973 means that patients
who say the reliability of nurses are good, have a
chance to feel satisfied by 4.9 times higher than
patients who say that their reliability is not good.
HIMBEP 2020 - International Conference on Health Informatics, Medical, Biological Engineering, and Pharmaceutical
54

Table 4: Results of Multiple Logistic Regression Tests.
Variable B Sig. Exp(B)
95%CI for
Exp(B)
Reliability
Responsiveness
Empathy
Constants
1,604
2,060
2,096
-2,696
0,001
0,000
0,000
0,000
4,973
7,843
8,132
1,987-12,447
3,126-19,679
3,328-19,868
3.1 Reliability
The results showed that there was a relationship with
reliability on inpatient satisfaction. Patients who
stated good nurse reliability, had a 4.9 times higher
chance of being satisfied compared to patients who
expressed poor nurse reliability.
This study is in line with the results of research
conducted by Simbala, Rattu, & Sondakh (2013)
showing the probability value (p = 0.002 <0.05)
indicates that there is a significant relationship
between the service of nurses' responsiveness and
patient satisfaction. The results of research conducted
by Mubin & Jalal (2017), found that the assessment
of the quality of nursing services: high reliability
category is 45 respondents (45%), moderate category
is 52 respondents (52%), and low category is 3
respondents (3%). The quality of nursing services on
the reliability dimension is significantly related to
inpatient satisfaction. From those results of the
regression analysis can be concluded that the
reliability variable has a positive and significant
relationship to patient satisfaction.
In hospital services, nurses are very much in the
spotlight, because it is closely related to patient and
family satisfaction. Even the presence and touch of
nurse services have the largest proportion of services
in hospitals, so without ignoring the services of other
officers, the nurse service with its reliability in
providing nursing care is certainly a service that
should get more attention for management at the
hospital. Reliability That is the ability to provide the
promised service immediately, accurately and
satisfactorily, honestly, safely, on time, availability.
According to the researchers' assumptions, the
results of this study prove that nurse reliability is
related to inpatient satisfaction. This shows that if
nurses demonstrate reliability in providing nursing
care to patients, the satisfaction felt by inpatients also
increases. According to the researchers' assumptions,
the reliability of nurses perceived by inpatients while
being treated is that nurses are always responsive
when asked by patients for help, keep the room clean
and quiet, pay attention to cleanliness and maintain
the peace of the room, the bed linen is replaced
immediately if it looks dirty or wet, conducts an
examination of conditions patients from morning to
night even though carried out alternately by nurses,
routinely control the infusion that is placed on the
patient, do physical examinations especially vital
signs in accordance with the specified time.
Patients also stated that nurses' reliability was still
not good because nurses paid less attention to the
patient's body hygiene during treatment. Usually the
patient's family wipes the patient's body because the
patient is not allowed to take a shower. Others that
patients felt less well were the nurse also does not
help the patient on taking the medication but assisted
by the family. Nurses got medical checks in late, since
the nurses work baed on the shifts and also the nurses'
behavior varies from one to another, especially in
providing services to inpatients.
3.2 Responsiveness
Based on the study results indicate that there was a
relationship between responsiveness to the inpatient
satisfaction. Patients who stated that nurses
'responsiveness were good, had a 7.8 percent higher
chance of being satisfied than stated not good. The
responsiveness variable is associated with inpatient
satisfaction. Demands for services that address
various complaints from the forms of service
provided become a positive assessment of the
responsiveness of the providers and receiver of the
services. The party providing the service should find
that the person being served lacks understanding of
the various procedures or mechanism requirements, it
is necessary to provide a clear and wise
understanding,also provide various alternative
facilities to follow the correct service conditions.
Therefore, the impression of the customers or
responds to the customer desires of being served.
Responsiveness is the desire of an employees to
help consumers and provide services that are
responsive to the needs of a consumers, quickly pay
attention and address the needs.According to the used
assumptions, the results of this study indicate that
nurses' responsiveness in providing nursing care was
related to inpatient satisfaction. Also, the more
responsive of the nurses to the inpatientscomplaints
and needs, the more satisfied the inpatients feel.
Inpatient satisfaction with nurses' responsiveness
because nurses immediately come when called (less
than 5 minutes), nurses help eat/drink patients if
unable to do it themselves, nurses provide moral
support (enthusiasm) for healing inpatients, discuss
patient problems with the family in performing
Relationship of Reliability, Responsiveness, and Nurse Empathy to Inpatient Satisfaction
55

nursing actions, the nurse also explained about further
care at home. Those makes the patient feel satisfied
and feel comfortable during treatment.
The study also found that some patients felt that
nurses' responsiveness was still lacking, such as the
nurse does not immediately check the patient's
condition after treatments. Patients expect that
after a treatment from a nurse or a doctor, the
patient wish the nurse to always check the patient's
condition but there are some patients who do not
get such attention. There are also patients who say
that nurses do not provide moral support /
enthusiasm for patient recovery. This causes the
patient to feel less satisfied with the nurse's
responsiveness service.
3.3 Emphaty
It was found that the empathy variable has a
relationship with inpatient satisfaction. Patients who
expressed good nurse empathy were more likely to be
satisfied by 8.1 times higher than patients who stated
nurse empathy was not good. Empathy or concern
includes ease in making good communication
relationships and understanding consumer needs that
are manifested in attention to each consumer, serving
friendly and attractive, understanding consumer
aspirations, communicating well and correctly and
behaving sympathetically.
It has been proven that empathy is related to the
satisfaction felt by inpatients. According to the
Assumption, nurses' empathy is obtained by showing
concern and sympathy for what the patient feels,
communicating about the patient's condition,
explaining hospital regulations, and taking care of
nursing in a friendly and polite manner. Empathy is
the variable most related to inpatient satisfaction.
This means that empathy has a positive and
significant relationship to patient satisfaction. The
better the patient's perception of nurse empathy, the
patient satisfaction will be higher, and if the patient's
evaluation of nurse empathy is not good, the patient
satisfaction will be lower.
The things that make some patients feel that the
empathy of nurses less than good was some patients
assume that nurses do not provide satisfactory
answers to the questions asked. Also the nurses did
not provide opportunities for patients to express the
patientsfeelings or complaints. In addition, some
patients feel that nurses were not easily contacted if
needed.
4 CONCLUSIONS
From the results of a study of a number of
respondents, it was found that patients who felt less
satisfied were 25.3%, while those who were satisfied
were 74.7%. Patients' good perceptions about
reliability, responsiveness and empathy ranged from
72.1% -76.3%, while unfavorable between 23.7% -
27.9%. The reliability, responsiveness, and empathy
of nurses are related to inpatient satisfaction. The
most dominant variable related to inpatient
satisfaction is empathy. Patients who state that nurses
empathize have a chance of being satisfied 8.1 times
higher than patients who lack empathy.
REFERENCES
Al-Damen, R. (2017) Health Care Service Quality and Its
Impact on Patient Satisfaction “Case of Al-Bashir
Hospital, International Journal of Business and
Management, 12(9), pp. 136–152. doi:
10.5539/ijbm.v12n9p136.
Brunero, S., Lamont, S. and Coates, M., (2010). A review
of empathy education in nursing. Nursing inquiry,
17(1), pp.65-74.
Devi, K. V and Muthuswamy, P. R. (2016) A Study on
service Cunico, L., Sartori, R., Marognolli, O. and
Meneghini, A.M., 2012. Developing empathy in
nursing students: a cohort longitudinal study. Journal of
clinical nursing, 21(13-14), pp.2016-2025.
Essiam, J. (2013) Service Quality and Patients Satisfaction
with Healthcare Delivery: Empirical Evidence from
Patients of the Out Patient Department of a Public
University Hospital in Ghana, European Journal of
Bussiness and Managment, 5(28), pp. 52–59.
Gray, B. and Boshoff, C., (2004) The relationships between
service quality, customer satisfaction and buying
intentions in the private hospital industry. South
African journal of business management, 35(4), pp.27-
37.
Isnindar, Saputra, I. and Robiyanto (2018) Analisis Tingkat
Kepuasan Pasien Rawat Inap Di Ruangan Penyakit
Dalam Terhadap Pelayanan Di Instalasi Farmasi
Rumah Sakit Periode Desember 2011-Februari 2012,
Jurnal Manajemen dan Pelayanan Farmasi, 3(4), pp.
231–248.
Olson, J.K., 1995. Relationships between nurse‐expressed
empathy, patient‐perceived empathy and patient
distress. Image: The Journal of Nursing Scholarship,
27(4), pp.317-322.
Ozlii, Z. K. and Ozge Uzun (2015) Evaluation of
Satisfaction with Nursing Care of Patients
Hospitalaized in Surgical Clinics of Different
Hospitals, International Journal of Caring Sciences,
4(2), pp. 21–29.
Purwanti, S., Prastiwi, S. and Rosdiana, Y. (2017)
Hubungan Pelayanan Perawat Dengan Kepuasan
HIMBEP 2020 - International Conference on Health Informatics, Medical, Biological Engineering, and Pharmaceutical
56

Pasien Rawat Jalan Di Puskesmas Wisata Dau Malang,
Nursing News, 2(2), pp. 688–699. Available
at:https://publikasi.unitri.ac.id/index.php/fikes/article/
view/514/432.
Shan, L. et al. (2016) Patient satisfaction with hospital
inpatient care: Effects of trust, medical insurance and
perceived quality of care, PLoS ONE, 2(1), pp. 1–18.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164366.
Simbala, W., Rattu, A. J. M. and Sondakh, R. C. (2013)
Hubungan Antara Kualitas Jasa Pelayanan Perawat
Dengan Tingkat Kepuasan Pasien Di Ruang Rawat
Inap Rumah Sakit Islam Sitti Maryam Kota Manado.
Fakultas Kesehatan Masyarakat Universitas Sam
Ratulangi. Available at: http://fkm.unsrat.ac.id/wp-
content/uploads/2014/08/JURNAL_Wiwien_Simbala_
080112068_AKK.pdf.
Tjiptono, F. and Chandra, G. (2015) Service, Quality &
Satisfaction, in Edisi 4. Yogyakarta: ANDI. doi:
10.3389/fgene.2015.00293.
Warda, A., Junaid and Fachlevy, A. F. (2016) Hubungan
Persepsi Mutu Pelayanan Dengan Tingkat Kepuasan
Pasien Puskesmas Perumnas Di Kota Kendari Tahun
2016, Naskah Publikasi Halu Oleo, 1(1), pp. 3–9.
Yousapronpaiboon, K. and Johnson, W. C. (2013) Out-
patient Service Quality Perceptions in Private Thai
Hospitals, International Journal of Business and Social
Science, 4(2), pp. 57–66.
Yu, J. and Kirk, M., (2009) Evaluation of empathy
measurement tools in nursing: systematic review.
Journal of advanced nursing, 65(9), pp.1790-1806
Relationship of Reliability, Responsiveness, and Nurse Empathy to Inpatient Satisfaction
57
