
Students Satisfaction in using Mobile Learning at Higher
Educational Institution
Asri Safrinawati, Mega Mayasari
Department of Business Management, Batam State Polytechnic, Batam, Indonesia
Keywords: Mobile Learning, Ease of Use, Internet Speed, Smartphone Portability, Design Layout
Abstract: This study aims to examine the factors that influence student satisfaction in using mobile learning. This study
also examines whether there were differences in satisfaction between students from public and private college.
Data collection techniques used were survey to participant. The sampling technique uses purposive sampling.
The research took sample from 186 students from Batam State Polytechnic and Putera Batam University. The
analytical tool used is multiple regression and Independent sample t-Test. The results show that ease of use,
internet speed and layout design affect to student satisfaction. Smartphone portability does not affect student
satisfaction. The results indicate there is not any difference in satisfaction between state and private college
students in using mobile learning. The results of this study are expected to provide input and evaluation to
faculty to improve e-learning systems and appearance. These will increase student satisfaction of e-learning
use by smartphone.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays the development of technology is rapidly
change. The rapid development of technology has
made the learning system in Higher Education
significantly changed. Learning system is not only
done manually, but it can perform using technology.
This learning system is also called E- learning.
Learning management system (LMS) with moodle
can be accessed via personal computer and the laptop.
Currently E learning can be accessed from mobile. E
learning is a web-based learning ecosystem for the
dissemination of information, communication, and
knowledge for education and training, Cidral,
Oliveira, Felice, & Aparicio, (2018). E-learning has
many benefits in the world of education. Students can
access E-learning with their mobile without having to
be on campus. E-learning access that can be reached
anywhere makes it easier for students to get
information about courses materials. Satisfaction is
inseparable from the expectations, desires and needs.
The Reaserch of Eliyanora, Andriani, & Zahara
(2010) proved that the level of student satisfaction
with educational services can be known by comparing
expectations with the reality they get.
In an era of rapidly developing technology like
today, research is needed on students who have used
their smartphones to access e-learning. Whether there
is learning using mobile learning students feel
satisfaction. There are currently many colleges that
use E-learning as a tool for teaching and learning. The
Ministry of Research, Technology and Higher
Education (Menristekdikti) explained that tertiary
institutions are targeted to conduct learning in
accordance with technological developments. An
online learning system is needed for students'
readiness to face technology that is developing so
quickly.
Advances in E-learning technology have also
made Batam State Polytechnic implement electronic-
based learning since 2007. Students use E-learning to
get material from lecturers, do quizzes and
examinations using E-learning, and can upload
assignments on E-learning. The existence of this
facility makes it easier for students to learn without
having to meet face to face in class. Not only in Batam
State Polytechnic, several private colleges in Batam
use E-learning for teaching and learning but also the
Putera Batam University. Students Batam State
Polytechnic and Putera Batam University always
access e-learning using smartphones to get
information about their learning. No need to come to
campus, students can immediately see the latest
information from the lecturer for learning. Students
Safrinawati, A. and Mayasari, M.
Students Satisfaction in using Mobile Learning at Higher Educational Institution.
DOI: 10.5220/0010357401330141
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science (ICAESS 2020) - Shaping a Better Future Through Sustainable Technology, pages 133-141
ISBN: 978-989-758-517-3
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
133

also enjoy learning through e-learning without having
to face to face in class.
The prior research related to the technology in
education has been studied are Basidious & Lange
(2009) examined the impact and use of information
and communication technology on accounting
student learning outcomes. The results of the research
that the existence of information and communication
technology makes accounting students do not
understand well. Dimitrios, Labros, Nikolaos, Maria,
& Athanasios (2013) their research about identifies
and presents views about teaching accounting
internationally using information and communication
technology. The results of the studies are students
prefer teaching methods that are centered by
personalized instructors. Students recommend that
the internet and various computer programs,
simulations, case studies in real and virtual work
environments become tools supporting traditional
methods rather than being the main tool.
Research related to the topic in Indonesia has been
discussed, the results show that E-learning has a
significant and positive effect on the quality of
student learning, Karwati, (2014). Faoziah &
Sembiring (2017) shows that learning using E-
learning with Ease of Use, form, accuracy, speed of
responding and privacy security has a positive effect
on student satisfaction, and a significant effect on the
speed of responding and privacy security variables.
Research on E-learning using mobile is not new
research but research related to this topic continues to
be developed using different variables. Alqahtani &
Mohammad (2015). The results of the study indicate
that there is a positive relationship between mobile
applications and perceptions of the performance,
satisfaction and behavior of the students involved.
Paricio, Bacao, & Oliveira (2017) proposes a
theoretical model of learning grit as a determinant of
the success of E-learning systems. The results of the
study indicate that grit has a positive effect on
individual student satisfaction and performance,
enhance E-learning strategies and understand E-
learning success. Sulaiman & Dashti (2018), their
research about satisfaction and factors in using
Mobile Learning (ML). The findings of the research
show that female students and Kuwaiti Nationality
students were more satisfied with their ML compared
to students who were not Kuwaiti nationals. The
factors used to Internet speed, smartphone portability,
smartphone skills, screen size, gender, nationality,
and college.
Result of the research performed by Cidral,
Oliveira, Felice, & Aparicio (2018) shows that the use
and satisfaction of E-learning users are
interdependent, and both have a significant effect on
individual performance. The success of E-learning in
Brazil has a positive impact. Sarker, Mahmud, Islam,
& Islam (2019) examine the suitability of
implementing effective E-learning through learning
management system (LMS) at the private university
in Bangladesh. The findings of the research reveal
that E-learning has been well accepted by most of the
students as they are found routinely spending time on
the LMS on a regular basis for watching lecture
videos, viewing course information, reading postings
of the fellow students in the forum. However, there
are constraints as well since the learning materials are
poorly designed that do not allow much interaction
between students and lecturers. There are also some
technical problems such as poor internet connection
which restrict access to E-learning platforms.
This research idea came from Sulaiman & Dashti
(2018) The difference between this research and the
prior research such as samples and variable used.
Previous studies used a sample of general students
and Informatics majors in Banglades and Kuwait.
Sample in this research are business student at the
Batam State and Private Higher Educational
Institution. Variable ease of use obtained from
Theory Acceptance Model (TAM) internet speed,
layout design, smartphone portability from Sulaiman
& Dashti (2018). Based on previous research
comparing public and private universities, the
researcher also compared two groups of universities
but used a sample of business accounting students. To
measure the level of satisfaction between two
different universities, are there differences in
satisfaction. The purpose of this study is the first, to
examine the factors that influence satisfaction of
using mobile learning. Second, to consider whether
there is a difference between the use of mobile
learning between students at State and Private Higher
Educational Institution.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW AND
HYPOTHESIS
2.1 Theory
2.1.1 Technology Acceptance Model
Davis (1986) describing usability and ease of use is a
significant determinant of technology acceptance or
adoption. Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) can
explain the main factors of information technology
user information on the acceptance of information
technology users. This theory explains if the use of
ICAESS 2020 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
134

information systems will be influenced by the
benefits and ease of use variables, both of which have
high determinants and empirically tested validity.
TAM believes that the use of information systems can
improve the performance of individuals or
organization, in addition, the use of information
systems is easier to use. According to the TAM
model, perceived benefits and perceived ease of use
determine an individual's attitude, which will
determine an individual's intention to use a system.
2.1.2 The Counstructivsm Learning Theory
Brune (1966) states that the concept of the theory of
constructivism is an active process of students in
building new ideas according to present and past
knowledge. Constructivism is an extremely broad
theory, has aspects such as social, physical,
evolutionary, information, processing, Murphy
(1997). Constructivism theory focuses on creating a
learning environment that is centred on students in
what they learn. Learners are actively involved in the
learning process supported by existing infrastructure.
One of the main features of the theory of
constructivism is motivation and satisfaction in
learning, Hein, (1991). This research is also based on
constructivism learning theory, how students have
knowledge by using a system and can feel satisfaction
with the system.
2.2 Literature Review
Research on the use of e-learning and mobile learning
has been widely studied before. An explanation of the
previous research will be discussed in the literature
review. Previous research, Basidious & Lange,
(2009) examined the impact and use of information
and communication technology on accounting
student learning outcomes. The results of this
research that the existence of information and
communication technology makes accounting
students do not understand well.
Dimitrios, Labros, Nikolaos, Maria, & Athanasios
(2013) which identifies and presents views on the
teaching of accounting internationally using
information and communication technology (ICT).
The results of these studies are students prefer
teaching methods that are centered by personalized
instructors. Students recommend that the internet and
various computer programs, simulations, case studies
in real and virtual work environments become tools
supporting traditional methods rather than being the
main tool.
Research Tîrziua & Vrabie, (2015) aims to
provide a framework for teachers to interact with
electronic good to students. The results of the study
are effective for presenting face-to-face material in an
online environment that makes students achieve
higher levels of learning satisfaction and more
understanding of the subject matter.
Research on e-learning using mobile researched
by Alqahtani & Mohammad, (2015). The research
sample used 118 students from Computer Science and
Information Systems in Higher Education at Al Imam
Muhammed Bin Saud Islamic University. The results
of this study indicate there is a positive relationship
between mobile applications and perceptions of
performance, satisfaction and behavior of students
involved.
Research Aparicio, Bacao, & Oliveira, (2017)
proposes a theoretical model of learning grit as a
determinant of the success of e-learning systems. The
results of the study indicate that grit has a positive
effect on individual student satisfaction and
performance, enhance e-learning strategies and
understand e-learning success. Research Cidral,
Oliveira, Felice, & Aparicio, (2018) that shows
understanding of satisfaction, use, and success in e-
learning at universities in Brazil. The results of the
study indicate that the use and satisfaction of e-
learning users are interdependent, and both have a
significant effect on individual performance. The
success of e-learning in Brazil has a positive impact.
Research Sulaiman & Dashti, (2018) regarding
satisfaction and factors of using Mobile Learning
(ML), shows the results that female students and
Kuwaiti nationality students are more satisfied with
ML for education compared to students who are not
Kuwaiti nationals. The factors used to predict student
satisfaction are user convenience, internet speed,
smartphone portability and layout design. Research
Sarker, Mahmud, Islam, & Islam, (2019) critically
examines the appropriateness of the application of
effective e- learning through Learning Management
Systems (LMS) in Bangladeshi educational
institutions. The results of the study showed that most
students were very enthusiastic about e-learning.
Research related to the topic of e-learning in
Indonesia was conducted by Karwati, (2014) who
analyzed how electronic learning in FKIP UNINUS,
how the quality of learning in FKIP UNINUS, and to
find out whether electronic learning affects the
quality of student learning in FKIP UNINUS. The
results showed that e-learning had a significant and
positive effect on the quality of student learning.
Research Fauziah & Sembiring, (2017) shows that
learning using e-learning with user convenience,
Students Satisfaction in using Mobile Learning at Higher Educational Institution
135

form, accuracy, speed of responding and privacy
security has a positive effect on student satisfaction,
and significantly influences the speed of responding
and privacy security variables.
2.3 Hypothesis
2.3.1 User Ease Influences Satisfaction
Davis (1986) explain the benefits obtained and
facilitate the use determined by determining the
individual, which will determine the individual's
intention to use a system. System users who do not
need a burden and easily use this system, including
those involving Ease of Use Faoziah & Sembiring,
(2017). Previous research explains user ease
influences student satisfaction, Faoziah & Sembiring,
(2017). Systems that are easy to use by users will
continue to be used so that the creation of satisfaction
in using the system. Based on the explanation, the
hypothesis is:
H1: Ease of use influences satisfaction
2.3.2 Internet Speed Has an Effect on
Satisfaction
Davis (1986) explain TAM can explain the main
factors of information technology user behavior
towards the acceptance of information technology
users. Internet speed is one of the factors of user
satisfaction in using mobile learning Sulaiman &
Dashti, (2018). The satisfaction of using mobile
learning is inseparable external supporting factors,
one of which is internet speed. Internet speed will
affect the satisfaction of mobile learning users. Based
on the explanation, the hypothesis is:
H2: Internet Speed influences satisfaction
2.3.3 Smartphone Portability Influences
Satisfaction
Davis (1986) explains that TAM can explain the main
factors of information technology user behavior
towards the acceptance of information technology
users. Smartphone portability is a factor of user
satisfaction in using mobile learning Sulaiman &
Dashti, (2018). Satisfaction of the use of mobile
learning is inseparable from the facilities that support
mobile learning facilities and external supporting
factors, one of which is smartphone portability.
Smartphone portability will affect the satisfaction of
mobile learning users. Based on the explanation, the
hypothesis is:
H3: Smartphone portability has an effect on
satisfaction
2.3.4 Layout Design Has an Effect on
Satisfaction
Davis (1986) explains that usability and ease of use
are significant determinants of technology acceptance
or adoption. TAM can explain the main factors of
information technology user behaviour towards the
acceptance of information technology users.
Interesting useruser interestinseparable from the
design that has been created to attract the attention of
users. Technology can be accepted if it is interesting
and easy to understand Alqahtani & Mohammad,
(2015). The layout design will affect the satisfaction
behaviour of mobile learning users. Based on the
explanation, the hypothesis is:
H4: Layout design influences satisfaction
2.3.5 The Difference in Satisfaction of the
Use of Mobile Learning between
Students in Public and Private College
in Batam
Brune (1966) explained that motivation in sample
according to learning by using the system will cause
users to feel satisfaction with the system. The
satisfaction of using mobile learning is inseparable
from the facilities that support mobile learning
facilities. That students in public and private
universities were satisfied using mobile learning, that
female students were more satisfied with ML than
male students. Moreover, Kuwaiti students were
more satisfied than non-Kuwaitis Sulaiman & Dashti,
(2018). The difference in satisfaction is inseparable
from the factors that influence the use of the mobile
learning Based on the explanation, the hypothesis is:
H5: There is difference in satisfaction of the use of
mobile learning between students in public and
private college in Batam. Based on the hypotheses
that have been presented, the research model is
obtained as follows:
ICAESS 2020 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
136
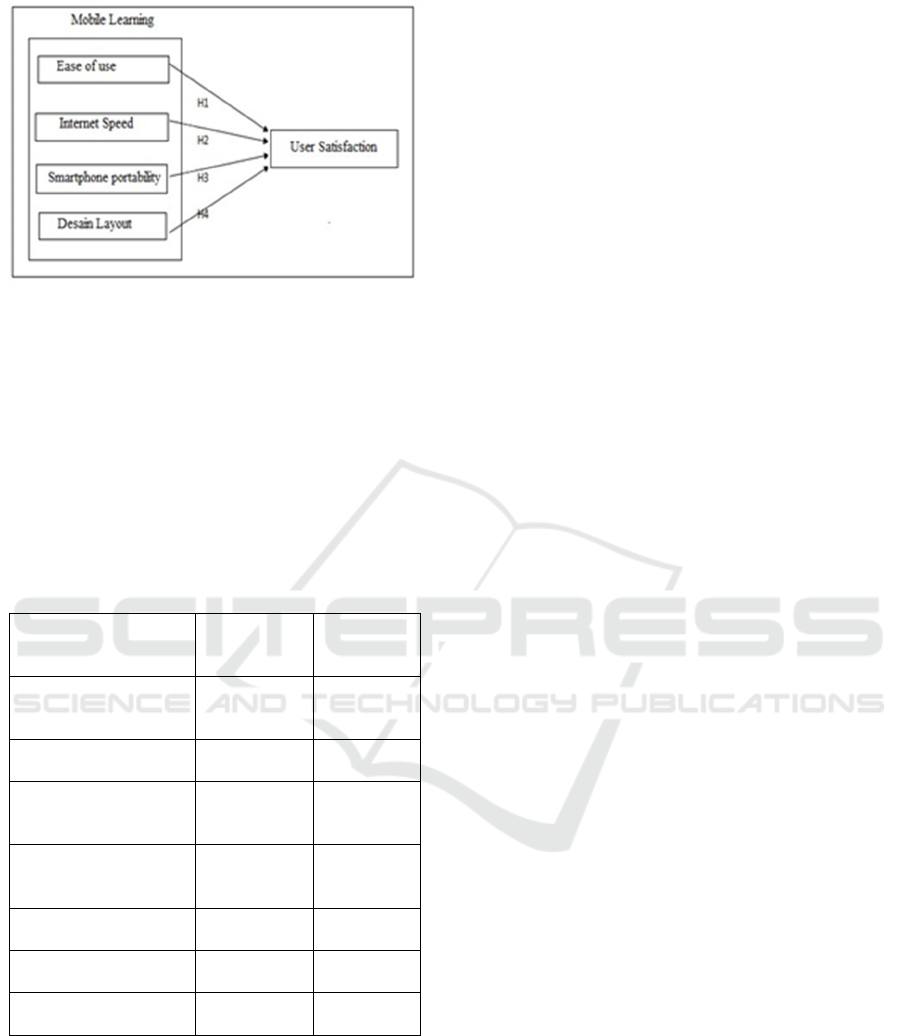
Figure 1: Research model
3 METHOD
The research method used in this study is a
quantitative approach to testing hypotheses. Sample
in this research are student from Batam State
Polytechnic the Number of samples in this study use
the Slovin formula with an error level of 10%. The
minimum sample is 184 respondents
Table 1: Data Questionnaires
Information Batam State
Polytechnic
Putera
Batam
Universit
y
Total student
population is based on
forlap Dikti Data
1266 1015
Sample according to
slovin formula
93 91
Questionnaires are
filled out via google
form
105 66
The questionnaire is
filled in throught print
out
8 33
Questionnaire that did
not return
(2) (17)
Inappropriate
res
p
ondents
(19) (7)
Questionnaire that can
b
e processe
d
94 92
Source: Processed data
Sampling in this study uses purposive sampling
judgment with the criteria of students who have been
studying for at least one year and who frequently
access E-learning through smartphones. The
questionnaire in this study consisted of two parts. The
first part is the contents of the questionnaire which
contained 21 question items about student satisfaction
using mobile learning. The second part contains the
general data of respondents. In accordance with the
research variables, the source of the contents of the
questionnaire was adapted from Alqahtani &
Mohammad, (2015) and Sulaiman & Dashti, (2018).
3.1 Independent Variable
Mobile learning is an electronic technology that is
used to send, support, assess, and improve teaching
and learning or learning Faoziah & Sembiring,
(2017). The definition of mobile learning in this study
refers to e-learning accessed through student
smartphones, so it is referred to as mobile learning.
There are 4 dimensions in measuring satisfaction in
using mobile learning. Ease of use, internet speed,
smartphone portability and layout design.
3.1.1 Ease of Use
User Ease is a belief about new technology that
affects personal attitudes towards using that
technology Alqahtani & Mohammad, (2015). Ease of
use is related to how users can easily accept the new
technology provided to improve performance. The
ease of use in this study is related to the ease of users
in using E-learning. Criteria that need to be
considered in measuring Ease of Use are usability,
attitudes, interests and behavior Faoziah &
Sembiring, (2017). Measuring using five items of
questions were adapted from Alqahtani &
Mohammad, (2015).
3.1.2 Internet Speed
Internet speed is the speed of accessing data using the
internet. Internet speed in this study is related to speed
in accessing mobile learning. Internet speed is an
external factor that can affect the satisfaction of using
mobile learning. Internet speed is also related to the
signal from WIFI and the availability of WIFI
networks Sulaiman & Dashti, (2018). Criteria that
need to be considered in measuring internet speed are
the availability of WIFI, speed in accessing
information and speed in doing things with mobile
learning. Measuring using three question items in the
questionnaire were adapted from Sulaiman & Dashti,
(2018).
3.1.3 Smartphone Portability
Smartphone portability is the convenience of users in
bringing smartphones anywhere Sulaiman & Dashti,
(2018). Smartphone portability is also inseparable
from the user's skills in using the smartphone.
Indicators that measure smartphone portability are the
Students Satisfaction in using Mobile Learning at Higher Educational Institution
137
ease of carrying a smartphone, the ability to use a
smartphone, and the ease of students charging.
Measuring using three question items in the
questionnaire were adapted from Sulaiman & Dashti,
(2018). There is one question has a negative
statement, so the likert scale used on the smartphone
portability variable in the question is reversed to 1-5
3.1.4 Layout Design
Layout design can incorporate typographic elements,
which can connect meaning Alqahtani &
Mohammad, (2015). Layout design is related to how
things look that can make technology users
comfortable and easy to use. The layout design in this
study is related to the layout design and appearance
of the mobile which can make it easy for users to use
it. Indicators that measure layout design are user
preferences with user friendly appearance and
applications. There are five question items on the
questionnaire to measure layout design variables
adapted from Alqahtani & Mohammad, (2015).
3.2 Dependent Variable
Table 3 show that Responden Characteristics.
Table 3: Responden Characteristics
Responden
Characteristics F %
Gender
Male 47 25.3
Female 139 74.7
College
Politeknik Negeri Batam 94 50.5
Universitas Putera Batam 92 49.5
Source: Processed data
3.2.1 User Satisfaction
User satisfaction refers to the extent to which users
feel comfortable with the system to achieve their
goals Sulaiman & Dashti, (2018). User satisfaction of
human-computer interaction refers to the expression
of affection obtained from interacting with the
system. User satisfaction is related to the convenience
of users in interacting with the system. Indicators that
measure user satisfaction are user satisfaction,
repeated use, and recommendations that users give to
others to use technology or systems. There are five
question items on the satisfaction variable adapted
from Sulaiman & Dashti, (2018) and Alqahtani &
Mohammad, (2015) which will be used to measure
satisfaction from the use of mobile learning.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Result
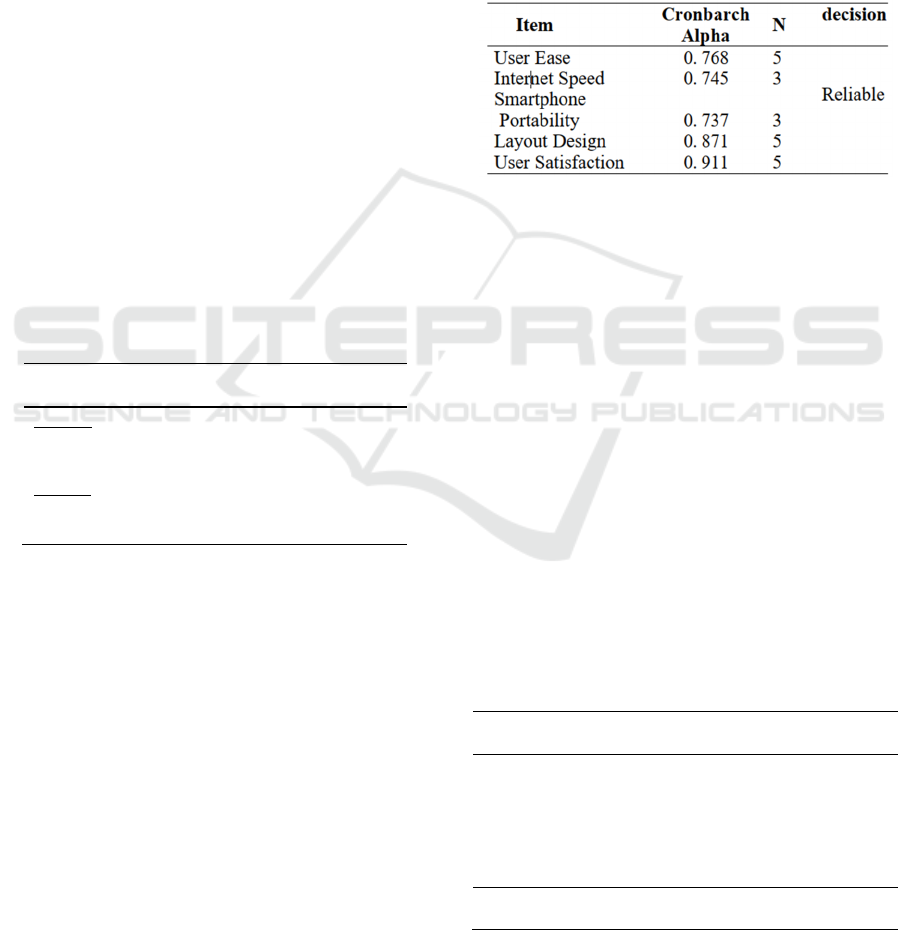
4.1.2 Variable Validity and Reliability
The question items that represent the variables in
this research is stated to be exceptionally reliable
reliable based on the value of Cronbach Alpha> 0.7.
The result displayed in table 2.
Table 2: Analysis Reliability Variabel
Source: Processed Data
About their validity. Question items to be valid if r
count> r table, with the number n = 30 respondents,
then obtained degree of freedom (df) = 28 and r table
= 0.4629 at alpha = 0.01. So that the item is said to be
valid if r count> 0.4629. The question items in this
study represent variables of Ease of Use, internet
speed, smartphone portability, layouts design and
user satisfaction expressed as valid with a value of
rcount> 0.4629.
4.2 Result and Discussion
Data in this research processed using SPSS. Data
were analyzed using multiple linear regression
analysis to test first hypothesis to the hypothesis. The
fifth hypothesis used independent sample t-test
analysis to find differences in satisfaction between
students in public and private college in Batam. Table
4 show that the result of the hypothesis testing.
Table 4: The Result of Multiple Regression.
Variable Regression
Coefficient
t
count
Sig.
Konstanta 2.629 1.76 0.080
Ease of Use 0.207 2.87 0.005**
Internet Speed 0.334 3.73 0.000**
Smartphone
Portabilit
y
0.098 1.02 0.308
Layout Design 0.385 6.15 0.000**
F count = 43.007
R
2
= 0.487
Sig α ** = 5% Source: Processed data
ICAESS 2020 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
138

From table 4, obtained the multiple linear
regression equation is as follows.
The multiple regression test produced an R2
value of 0.487 which showed that the independent
variables of Ease of Use, internet speed, smartphone
portability, and layout design simultaneously formed
48.7% of the variations in student satisfaction. That a
positive constant value of 2,629 shows the positive
influence of the independent variables of Ease of Use,
internet speed, smartphone portability and layout
design. If the independent variable goes up, the user
satisfaction variable will also go up.
The value of the regression coefficient on the
user ease variable on user satisfaction is 20.7%
which means, if the user ease variable has increased
by one unit, then user satisfaction will increase by
20.7%. The results of the multiple regression test in
the table 3 show that the Ease of Use variable has a t
value of 2.866 with a significant value of 0.005
which is below 0.05 so it can be concluded that H1
is supported. The results of this study indicate that
ease of use influences student satisfaction in
using mobile learning. Davis (1986) explains that
the right benefits and proper use determine
individual attitudes, which will determine the
individual's intention to use a system. Ease of use of
good mobile learning will increase student
satisfaction. Students also find it easier to learn and
more efficient by using smartphones, coupled with
easy-to-use mobile learning.
The regression coefficient on the internet speed
variable to user satisfaction is 33.4% which means, if
the internet speed variable has increased by one unit,
then user satisfaction will increase by 33.4%. The
results of the multiple regression test in the table show
that the internet speed variable has a t-value of 3,734
with a significance value of 0,000 which is below
0.05 so it can be concluded that H2 is supported. This
study also found that internet speed affects student
satisfaction. Davis (1986) explains that TAM can
explain the main factors of information technology
user behavior on the acceptance of information
technology users. Internet speed is one of the factors
for user satisfaction in using mobile learning,
Sulaiman & Dashti, (2018).
The regression coefficient on the internet speed
variable to user satisfaction is 33.4% which means,
if the internet speed variable has increased by one
unit, then user satisfaction will increase by 33.4%.
The results of the multiple regression test in the table
show that the internet speed variable has a t-value of
3,734 with a significance value of 0,000 which is
below 0.05 so it can be concluded that H2 is
supported. This study also found that internet speed
affects student satisfaction. Davis (1986) explains
that TAM can explain the main factors of
information technology user behavior on the
acceptance of information technology users. Internet
speed is one of the factors for user satisfaction in
using mobile learning, Sulaiman & Dashti, (2018).
The regression coefficient on the smartphone
portability variable to user satisfaction is 9.8%,
which means that if the smartphone portability
variable increases by one unit, user satisfaction will
increase by 9.8%. The results of the multiple
regression test in the table indicate that the
smartphone portability variable has a calculated
value of 1.022 with a significance value of 0.308
which is above 0.05 so it can be concluded that H3
is not supported. In addition, this study also proves
that smartphone portability does not affect student
satisfaction. Causing that smartphone portability
variable is not a factor that can affect student
satisfaction in using mobile learning. This is because
in the indicators of students' ease of charging,
students state that they feel they disagree with
statements if they have problems charging their
smartphones on campus. From the answers of
students who often access e-learning, they have no
problems when charging their smartphone on
campus. Students can still access e-learning easily
without having problems with charging on campus.
Research using smartphone portability variables was
first investigated by Sulaiman & Dashti, (2018).
Research by them which states that smartphone
portability affects student satisfaction. The
satisfaction of using mobile learning is inseparable
from the facilities that support mobile learning
facilities as well as external supporting factors, one of
which is smartphone portability. Smartphone
portability will affect mobile learning user
satisfaction.
The regression coefficient on the layout design
variable to the user's decision is 38.5% which
means, if the layout design variable has increased by
one unit, the user satisfaction will increase by
38.5%. The results of the multiple regression test in
the table above show that the layout design variable
has a calculated value of 6,153 with a significance
value below 0.05 so it can be concluded that H4 is
Supported. Layout design affects student
satisfaction. The better the layout design of the
mobile learning display, it will increase the
satisfaction of students who use mobile learning.
Students Satisfaction in using Mobile Learning at Higher Educational Institution
139

Davis (1986) explains that usability and ease of use
are significant determinants of technology
acceptance or adoption. TAM can explain the main
factors of information technology user behavior
towards acceptance of information technology users.
Attracting user interest cannot be separated from the
design that has been made to attract the attention of
users.
The results of the free sample t-test to test the
fifth hypothesis are listed in table 5, as follows:
Table 5: The Result of Independent sample t-test
Source: Processed data
The fifth hypothesis states that there is
difference in satisfaction of the use of mobile
learning between state and private tertiary education
students in Batam. The results of data processing are
in table 5. To test the fifth hypothesis, an
independent sample t-test was used with a
significance <0.05. From table 5, it can be explained
that the test results not significance value of 0.113
which can be concluded that there is not any
difference in satisfaction between state college
students and private college students which means
H5 is not supported. Brune (1966) explained that
motivation in learning using the system will result in
users feeling satisfaction with the system. Currently
the use of a smartphone is a necessity so that it is
inherent in students. Students feel ease of use the
mobile learning and is not related to the facilities
provided by the campus. this has caused not any
difference in satisfaction between public or private
campuses. The summary hypothesis testing show in
table 6.
Table 6: Hypothesis testing result summary
Hypothesis Result
H1: Ease of use has an effect
on satisfaction
Supported
H2: Internet Speed has an
effect on satisfaction
Supported
H3: Smartphone portability has
an effect on satisfaction
not supported
H4: Layout design has an effect on
satisfaction
Supported
H5: There is difference in
satisfaction of the use of mobile
learning between students in public
and private college in Batam
not supported
5 CONCLUSIONS
The main objective of this study is to determine the
factors that influence student satisfaction in using
mobile learning with ease of use, internet speed,
smartphone portability and layout design to the
satisfaction of students of states and private colleges
in Batam and examine the diferrences between the
two groups.This study also found that there were not
any differences in satisfaction between students of
state and private college in Batam. So, it can be said
that state and private college students feel the same
satisfaction in using mobile learning. Implication of
the current research as an evaluation material to
colleges to continues improvement the system, the
appearance of e- learning so that users are satisfied
with the use of e- learning through smartphones
Future studies are recommended to increase the
number of samples in the study. Reducing the
standard of error in determining the number of
samples. In addition, further research is expected to
add other college to be used as research samples. And
the next research should involve other factors that can
affect student satisfaction in using mobile learning.
REFERENCES
Alqahtani, M., & Mohammad, H. (2015). Mobile
Applications’ Impact on Student Performance and
Satisfaction. The Turkish Online Journal of Educational
Technology, 102-112.
Aparicio, M., Bacao, F., & Oliveira, T. (2017). Grit in The
Path to E-learning Success. Computers in Human
Behavior, 388-399.
Basidious, I. G., & Lange, P. D. (2009). An assessment of
the learning benefits of using a Web-based Learning
Environment when teaching accounting. Advances in
Accounting, Incorporating Advances in International
Accounting, 13-19.
Cidral, W. A., Oliveira, T., Felice, M. D., & Aparicio, M.
(2018). E-learning success determinants: Brazilian
empirical study. Computers & Education, 273-290
Dimitrios, B., Labros, S., Nikolaos, K., Maria, K., &
Athanasios, K. (2013). Traditional Teaching Methods
vs Teaching Through the Application of Information
and Communication Technologies in The Accounting
Field: Quo Vadis? European Scientific Journal, 74-101.
Eliyanora, Andriani, W., & Zahara. (2010). Pengukuran
Tingkat Kepuasan Mahasiswa Terhadap Pelayanan
Pendidikan di Politeknik Negeri Padang. Jurnal
Akuntansi & Manajemen, 81-88.
Faoziah, R. A., & Sembiring, J. (2017). Pengaruh
Implementasi Sistem Pembelajaran E- Learning
Terhadap Kepuasan Mahasiswa Universitas Telkom
(Studi Kasus Fakultas Informatika dan Fakultas
ICAESS 2020 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
140

Rekayasa Industri. E-Proceeding of Management,
2547-2554.
Ghozali, I. (2018). Aplikasi Analisis Multivariate dengan
Program IBM SPSS 25 Edisi 9. Semarang: Badan
Penerbit - Undip.
Jaiyeoba, O. O., & Iloanya, J. (2019). E-learning in tertiary
institutions in Botswana: apathy to adoption. The
International Journal of Information and Learning
Technology, 157-168.
Karwati, E. (2014). Pengaruh Pembelajaran Elektronik (E-
learning) terhadap mutu belajar mahasiswa. Jurnal
Penelitian Komunikasi, 41-54.
Lloyd, A. (2006). Information Literacy Lanscape: An
Emerging Picture. Journal of Documentation, 570-583.
Moses, O. O. (2008). Improving mobile learning with
enhanced Shih’s model of mobile learning. Online
Submission, 22-28.
Roscoe, J. T. (1975). Fundamental Research Statistics for
the Behavioral Science (2nd Editio.). New York: Holt,
Rinehart, and Winston.
Santoso, S. (2018). Mahir Statistik Parametrik. Jakarta: PT
Elex Media Komputindo.
Sarker, M., Mahmud, R., Islam, M., & Islam, M. (2019).
Use of E-learning at Higher Educational Institutions in
Bangladesh: Opportunities and Challenges. Journal of
Applied Research in Higher Education, 210-223.
Sekaran
Uma. 1992. “Research Methods for Business”. Third
Edition. Southern Illionis University.
Strayer, J. F. (2012). How learning in an inverted classroom
influences cooperation, innovation, and task
orientation. Learning Environments Research, 171-193.
Suddaby, G., & Milne, J. (2008). Cordinated,
Collaborative, and Cohrent: Developing and
Implementing E-learning Guidelines within a National
Tertiary Education System. Campus Wide Information
System, 114-122.
Sugiyono. (2013). Metode penelitian Kuantitatif, Kualitatif
dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sugiyono. (2015). Metode Penelitian Manajemen.
Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sujarweni, V. W. (2014). Metodologi Penelitian.
Yogyakarta: Pustaka Baru Press.
Sulaiman, A., & Dashti, A. (2018). Student' Satisfaction
and Factors in Using Mobile Learning among College
Students in Kuwait. EURASIA Journal of
Mathematics, Science and Technology Education,
3181- 3189.
Tîrziua, A.-M., & Vrabie, C. (2015). Education 2.0: E-
Learning Methods. Procedia - Social and Behavioral
Sciences, 376-380.
Tseng, M. L., Lin, R. J., & Chen, H. P. (2011). Evaluating
the effectiveness of e-learning system in uncertainty.
Industrial Management & Data Systems, 869-889.
Students Satisfaction in using Mobile Learning at Higher Educational Institution
141
