
Characteristics, Effective Reproduction Number (Rt), and Spatial
Modelling of Covid-19 Spread at Magetan District, East Java,
Indonesia
Yudhi Wibowo
1
a
, Nendyah Roestijawati
1
b
Atik C. Hidajah
2
c
Agoes Y. Purnomo
3
d
and Tutiek Herlina
4
e
1
Department of Public Health and Community Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Jenderal Soedirman,
Purwokerto, Indonesia
2
Department of Epidemiology, Faculty of Public Health, Airlangga University, Surabaya, Indonesia
3
District Health Office, Magetan, Indonesia
4
Poltekes of Health Ministry, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Characteristics, Effective Reproduction Number (Rt), Spatial Modelling, Covid-19.
Abstract: Covid-19 has been rapidly spreading to various regions in Indonesia including to Magetan District
which has the 3rd highest cases (0.91%) in East Java Province. This study was aimed to determine the
characteristics, effective reproduction number (Rt) and spatial modelling of Covid-19 spread in the Magetan
District. This was a cross-sectional study which included 43 patients with confirmed Covid-19. Univariate
analysis was used to describe the characteristics of Covid-19. Epiestim was used to calculate Rt while the
spread of Covid-19 cases was spatially modelled using Crimestat. On June 28, 2020, Magetan had 96
suspected cases, 104 confirmed cases with 75 cases were recovered and 4 people died. Most of the confirmed
cases were at the age group of 40-49 years (22.6%), male (54%), and symptomatic (91.5%). Fever was the
most commonly found symptom (81.7%). The Rt for the period March 10, 2020-June 28, 2020 was 1.27
(0.85-1.82; 95% CrI). Spatial analysis showed that the distribution of confirmed cases was widespread in 15
sub-districts. The Covid-19 outbreak was still out of control and still ongoing in Magetan. Therefore, a strong
implementation of health protocol is recommended.
1 INTRODUCTION
Corona virus disease-19 (Covid-19) is an infectious
disease caused by Severe Acute Respiratory
Syndrome-Corona Virus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) formerly
known as 2019-nCov. This disease was firstly
identified from 41 cases of pneumonia with unknown
cause in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China on December
30, 2019. It was reported that the disease related to
the contact with the seafood market (Isaac I. Bogoch,
Alexander Watts, Andrea Thomas-Bachli, Carmen
Huber, 2020; Lu, Stratton and Tang, 2020; WHO,
2020a, 2020c).
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7523-2170
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4232-062X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9797-1887
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8860-8787
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4238-9574
On March 11, 2020, World Health Organisation
(WHO) declared a global Covid-19 pandemic due the
rapid increase in the number of cases (13 times) and
affected countries (three times) within two weeks
(Cucinotta and Vanelli, 2020; Sohrabi et al., 2020).
As of May 5, 2020, the Covid-19 pandemic has
spread to 215 countries and territories. Globally there
were 3,525,116 confirmed Covid-19 cases and
243,540 deaths (WHO, 2020b).
While in Indonesia as of May 6, 2020, there were
12,071 confirmed Covid-19 and 872 deaths. East Java
Province is the second epicenter of Covid-19 cases in
Indonesia after DKI Jakarta (Kemenkes R, 2020).
Magetan District had 69 positive people with 4 people
Wibowo, Y., Roestijawati, N., Hidajah, A., Pur nomo, A. and Herlina, T.
Characteristics, Effective Reproduction Number (Rt), and Spatial Modelling of Covid-19 Spread at Magetan District, East Java, Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0010487100210027
In Proceedings of the 1st Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference in conjunction with the 5th Annual Scientific Meeting (Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia
(JIMC 2020), pages 21-27
ISBN: 978-989-758-499-2
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reser ved
21

died which make this district had the third highest
confirmed cases in East Java Province. Furthermore,
Magetan District has relatively high population
mobility due to tourism attractions which increase the
risk of Covid-19 spread in this area.
At present, most countries, including Indonesia,
are preparing for a new normal life, as well as the
Magetan District. WHO has issued public health
criteria to adjust public and social health measures in
the context of Covid-19. According to WHO, the
covid-19 outbreak can be considered as “in
controlled” if the Rt <1 for at least 2 weeks.(World
Health Organisation, 2020) This study aims to
determine the characteristics, effective reproduction
number and spatial modeling of Covid-19 spread in
Magetan District, East Java Province, Indonesia.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Research Design and Population
This study was an observational study using a cross-
sectional design. This study used secondary data from
the Magetan District Health Office. Suspect and
confirmed cases of Covid-19 between the period of
period March 10 to June 28, 2020 were included in
this study. Suspect and confirmed cases were define
according to WHO definition (WHO. World Health
Organization, 2020).
The sample size was calculated using the
assumptions of (i) level of significant = 0.05, (ii) the
power of the study = 80%, (iii) the case proportion p
= q = 0.5, which yielded a minimum sample size of
43 people. The total sample size included in this study
was 71 confirmed cases and 392 suspected cases. The
data were collected by the Magetan District Health
Office through a survey which include demographic
characteristics, geographical location, date of onset,
symptoms and signs, as well as travel history from /
to outside city.
This study has undergone ethics review and
received ethics approval from Health Research Ethics
Committee, Faculty of Medicine, Jenderal Soedirman
University (Reference number 137/KEPK/VI/2020).
2.2 Data Analysis
The basic characteristics of the confirmed cases were
described according to age group, sex, travel history
to / from out of town, symptoms and signs.
The effective reproduction number (Rt) is an
important parameter to find out whether outbreak
control is effective or additional interventions are
needed (Nishiura and Chowell, 2009). Rt values
represent the number of new secondary cases that are
infected from one infective case at time t. If Rt> 1, the
possibility of disease will become epidemic, if Rt = 1,
the disease becomes endemic and if Rt <1, the
possibility of disease will disappear from circulation
(Camacho et al., 2015). In this study, Rt was
calculated using EpiEstim software based on Excel
developed by Cori et al in 2013(Cori et al., 2013), and
corrected by Thomson et al in 2019 (Thompson et al.,
2019). The mean serial interval (SI) and standard
deviation (SD) from of Tindale et al were used in this
study with the average SI = 4.56 and SD = 0.95
(Tindale et al., 2020).
The standard deviational ellipse (SDE) was used
to analyze trends and patterns of dispersion of
confirmed Covid-19 cases. Standard deviation ellipse
is a summary of central tendency and dispersion in
two dimensions, as well as a directional trend. Two
points were used as the basis for the distribution of
point locations on SDE which were central tendency
and dispersion. Central tendency uses the center of
the mean while dispersion refers to the spread of the
center mean bounded by the ellipse. Standard
deviational ellipse models can be used to gain a better
understanding of the geographical aspects of the
phenomenon and identify the cause of an event, based
on specific geographic patterns (Lai, So and Chan,
2008). The spatial analysis was conducted using
Crimestat software.
3 RESULTS
Magetan District is one of the districts in East Java,
Indonesia. Magetan District consists of 18 sub-
districts and 235 villages with land area of 688.8 km2
and total population of 628,924. During the period
from March 10 to June 28, 2020, there were 104
confirmed cases, and 4 cases died due to covid-19.
The characteristics of 104 confirmed cases when
first treated are presented in Table 1. The confirmed
cases were predominantly at the age group of 15-24
years (30.8%) and male (69.2%). Only 20.2% of
confirmed cases were symptomatic with main
symptoms were cough (12.5%) and fatigue (6.7%).
The proportion of confirmed cases with comorbidities
were 17.3% with pneumonia (8.7%) and hypertension
(5.8%) were the most frequent comorbidities. The
number of deaths among confirmed cases was four
people which resulted in mortality rate of 4.8%. Most
of deaths were occurred at the age of 35-64 years and
3 out of 4 cases had comorbid diseases.
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
22

Table 1: The characteristics of confirmed Covid-19 cases.
Characteristics Recovere
d
Die
d
Total
n%n%n %
Gende
r
Male 4 100 68 68 72 69.2
Female 0 0 32 32 32 30.8
Age Group
0-<5 00222 1.9
5-14 00222 1.9
15-24 0 0 32 32 32 30.8
25-34 0 0 17 17 17 16.3
35-44 2 50 11 11 13 12.5
45-54 1 25 20 20 21 20.2
55-64 1 25 11 11 12 11.5
65-74 00444 3.8
75-84 00111 1
Citizenship
Indonesian 4 100 78 78 82 78.8
Forei
g
ne
r
0 0 22 22 22 21.2
S
y
m
p
toms
Yes 4 100 17 17 21 20.2
No 0 0 83 83 83 79.8
Type of symptoms
Feve
r
250224 3.8
Histor
y
of feve
r
375336 5.8
Cou
g
h 2 50 11 11 13 12.5
Flue 00333 2.9
Sore throat 00222 1.9
Dyspnoea 3 75 2 2 5 4.8
Shiverin
g
00111 1
Headache 00111 1
Fati
g
ue 250557 6.7
Myalgia 00222 1.9
Nauseous vomit 1 25 2 2 3 2.9
Abdominal
p
ain 125223 2.9
Comorbidities
Yes 3 75 15 15 18 17.3
No 1 25 85 85 86 82.7
Type of comorbidities
Diabetes Mellitus 00333 2.9
H
yp
ertension 1 25 5 5 6 5.8
Cance
r
00111 1
Liver diseases 00111 1
COPD 00222 1.9
Tuberculosis 00111 1
Pneumonia 2 50 7 7 9 8.7
The trends of effective reproduction number (Rt)
for the period March 10 to June 28, 2020, is shown in
figure 1. From the calculation, the average Rt during
this period was 1.27 (95% CrI: 0.85-1.82). The trends
of Rt are further detailed in the table 3. In the last 14
days of the the observation period from 15-28 June
2020, the Rt for several days are below 1. However,
the upper bond of the Rt is still above 1 in all of the
observation days.
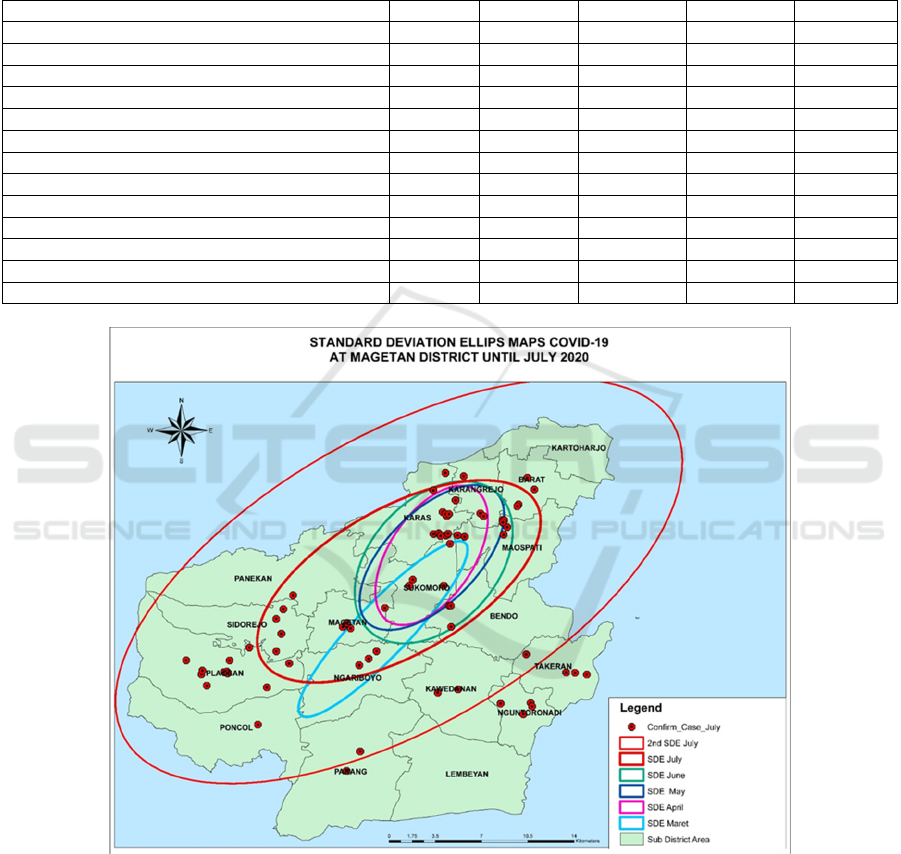
The results of the spatial modelling of the spread
of covid-19 for the period March-July 2020 in
Magetan district are presented in Table 3 and Figure
2. According to Table 3, it is found that the counter
clockwise shifted from 43.81
○
to 60.10
○
, SD x from
0.02 km to 0.05 km and SD y from 0.08 km to 0.11
km. Based on Figure 2, the trend of the spread is
predicted to be towards the southwest and the
northeast and counter clockwise.
Characteristics, Effective Reproduction Number (Rt), and Spatial Modelling of Covid-19 Spread at Magetan District, East Java, Indonesia
23
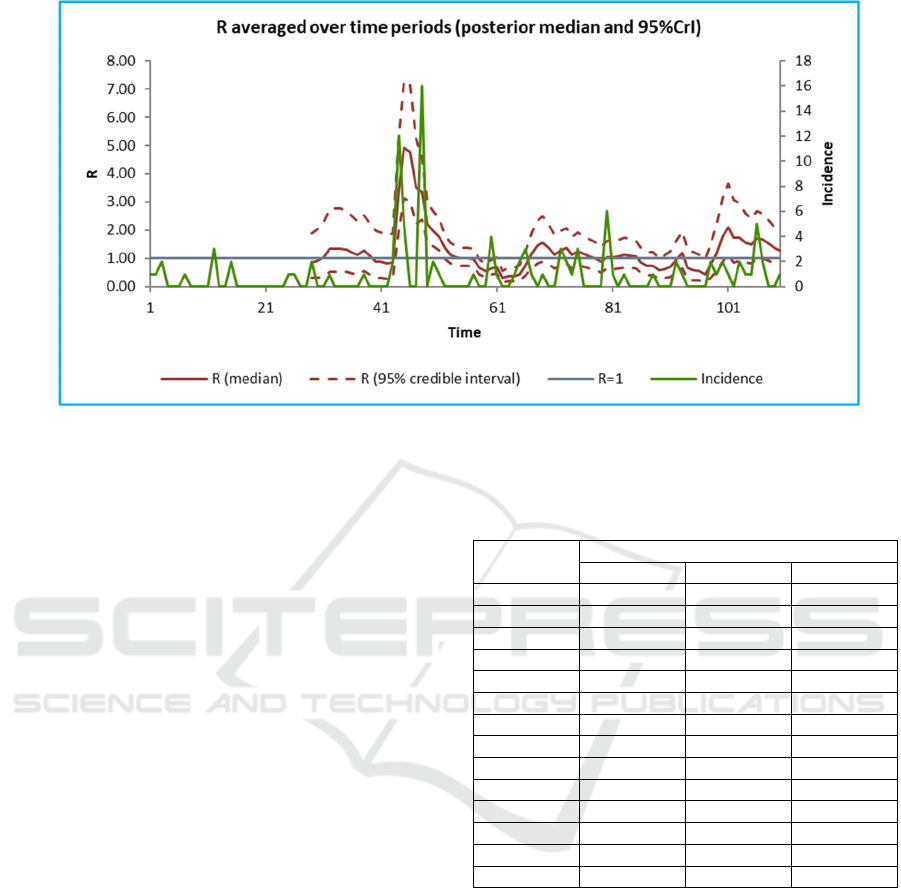
Figure 1: Trends of Effective Reproductive Number (Rt) of Covid-19 in Magetan District, Period March 10 to June 28, 2020.
4 DISCUSSION
Our research aims to determine the characteristics,
effective reproduction number (Rt), and spatial
modeling of Covid-19 spread in Magetan district. The
confirmed cases in Magetan District were
predominantly occurred in the age group of 15-24.
Covid-19 affects individuals in all age groups
(Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020).
The high number of confirmed cases in this age of
group related to outbreak which were happened in the
Islamic boarding school located in Magetan District.
At the beginning of the outbreak, no action has yet
been taken to close the learning activity in school and
resulted to rapid transmission of Covid-19 among the
students. One of the Islamic boarding schools had
students from Malaysia which explain a significant
proportion of the confirmed cases were foreign
citizens. The existence of foreign students with travel
history inside and outside of the city increase the risk
of Covid-19 transmission. Previous study shows that
travelling and people mobility increase the risk of
Covid-19 transmission (Bi et al., 2020).
The confirmed Covid-19 cases in this study were
mostly men which are consistent to the findings in
many studies. Men have higher susceptibility to
Covid-19 likely due to exposure of major risk factor
such as smoking. Furthermore, compare to women,
men have less protection the X chromosome and sex
hormones which play an important role in innate
immunity and adaptation (Jaillon, Berthenet and
Garlanda, 2019; Cai, 2020; Chen et al., 2020).
Table 2: Trends of effective reproductive numbers (Rt) of
covid-19 for the last 14 days.
Onset
Rt
Q 5% Median Q 95%
15/06/2020 0.19 0.44 0.87
16/06/2020 0.37 0.76 1.35
17/06/2020 0.60 1.15 1.98
18/06/2020 0.99 1.77 2.88
19/06/2020 1.22 2.12 3.36
20/06/2020 0.98 1.74 2.83
21/06/2020 1.04 1.74 2.72
22/06/2020 0.95 1.56 2.40
23/06/2020 0.92 1.49 2.25
24/06/2020 1.11 1.71 2.50
25/06/2020 1.11 1.69 2.43
26/06/2020 1.01 1.53 2.21
27/06/2020 0.90 1.37 1.98
28/06/2020 0.85 1.27 1.82
In this study, the mortality rate of Covid-19
confirmed cases is 4.7% which is relatively high
compare to global mortality rate. The death cases
were occurred in the age group of 35-64 years and
most of them had comorbidities. Older individual and
individuals with comorbidities such as chronic
disease have been known to have the higher fatality
risk of Covid-19. However, when individuals are 80
years old or older, the risk of fatality are more and
less the same disregard to the presence of
comorbidities (Chen et al., 2020; Onder, Rezza and
Brusaferro, 2020). According to the Centers for
Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the risk of
fatality is significantly higher for the age group of ≥65
years and for all age groups with comorbidities such
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
24
as chronic lung disease, moderate-severe asthma,
heart disease, and immunocompromised patient
(cancer treatment, smoking, organ transplantation) or
bone marrow, immune deficiency, uncontrolled HIV
/ AIDS, prolonged use of corticosteroids, and other
treatments that weaken the immune system), severe
obesity, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease,
and liver disease, increase the risk of suffering from
severe covid-19.(Centers for Disease Control and
Prevention, 2020)
Table 3: Results of Spatial Modeling of Spread of Covid-19 in Magetan District, Period March-July, 2020.
March April May June July
Sample size 9 46 56 60 122
Clockwise an
g
le of Y-axis rotation
(
°
)
43.81 33.90 44.95 43.11 60.10
Ratio of the lon
g
to the short axis after rotation 4.46 1.87 1.99 1.50 2.17
Standard deviation alon
g
the new X axes
(
km
)
0.02 0.03 0.03 0.04 0.05
Standard deviation along the new Y axes (km) 0.08 0.05 0.06 0.06 0.11
X-axes length 0.04 0.06 0.06 0.09 0.10
Y-axes len
g
th 0.16 0.11 0.12 0.13 0.22
Area of the elli
p
se defined b
y
these axes
(
km
2
)
0.00 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.02
Standard deviation alon
g
the X axes
(
km
)
0.04 0.06 0.06 0.09 0.10
Standard deviation along the Y axes (km) 0.16 0.11 0.12 0.13 0.22
X-axes length for a 2× SDE 0.07 0.11 0.13 0.17 0.20
Y-axes length for a 2× SDE 0.32 0.21 0.25 0.26 0.43
Area of the 2× elli
p
se defined b
y
these axes
(
km
2
)
0.02 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.07
Figure 2: Results of SDEs Map of Covid-19 in Magetan District, Period March-July, 2020.
The effective reproduction number (Rt) in the last
14 observation days (June 15, 2020 to June 28, 2020)
was still above one. This indicates that the Covid-19
outbreak in Magetan Districs are still not under
controlled (World Health Organisation, 2020).
Spatial modeling of spread covid-19 found that
the prediction of the spread of covid-19 to the
southwest and northeast in a counter clockwise
direction. This can be seen from the results of the
analysis of the standard deviation ellipse (SDE). SDE
and mean center visually form spatial and temporal
movement of disease explicitly. The spatiotemporal
analysis of this disease estimates future disease
patterns based on previous disease trends. This has
Characteristics, Effective Reproduction Number (Rt), and Spatial Modelling of Covid-19 Spread at Magetan District, East Java, Indonesia
25

implications for policy development and resource
planning according to the groups most at risk (Lai, So
and Chan, 2008). Therefore, efforts to increase
discipline on health protocols such as wearing face
masks properly, maintaining distance from others at
least 1-2 meters, and handwashing regularly. In
addition of that, contact tracing, testing and treatment
need to be continued and improved, as well as
protection for the vulnerable groups.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The covid-19 outbreak in Magetan Districs is still not
under controlled. Therefore, it is still necessary to
strictly implement health protocols and other
prevention efforts. Tracing contacts, testing and
treatment need to be strengthened as well as effort to
protect the vulnerable groups.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thank hhe Institute for Research and
Community Service, Faculty of Medicine, Jenderal
Sudirman University, and Magetan District Health
Office for their cooperation and assistance.
REFERENCES
Bi, Q., Wu, Y., Mei, S., Ye, C., Zou, X., Zhang, Z., Liu, X.,
Wei, L., Truelove, S. A., Zhang, T., Gao, W., Cheng,
C., Tang, X., Wu, X., Wu, Y., Sun, B., Huang, S., Sun,
Y., Zhang, J., … Feng, T. (2020). Epidemiology and
Transmission of COVID-19 in Shenzhen China:
Analysis of 391 cases and 1,286 of their close contacts.
MedRxiv.
https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.03.20028423
Cai, H. (2020). Sex difference and smoking predisposition
in patients with COVID-19. In The Lancet Respiratory
Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-
2600(20)30117-X
Camacho, A., Kucharski, A., Aki-Sawyerr, Y., White, M.
A., Flasche, S., Baguelin, M., Pollington, T., Carney, J.
R., Glover, R., Smout, E., Tiffany, A., Edmunds, W. J.,
& Funk, S. (2015). Temporal changes in ebola
transmission in sierra leone and implications for control
requirements: A real-time modelling study. In PLoS
Currents (Vol. 7, Issue OUTBREAKS).
https://doi.org/10.1371/currents.outbreaks.406ae55e83
ec0b5193e3085
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020). People
who are at higher risk for severe illness | CDC. In
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Chen, N., Zhou, M., Dong, X., Qu, J., Gong, F., Han, Y.,
Qiu, Y., Wang, J., Liu, Y., Wei, Y., Xia, J., Yu, T.,
Zhang, X., & Zhang, L. (2020). Epidemiological and
clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel
coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive
study. The Lancet. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-
6736(20)30211-7
Cori, A., Ferguson, N. M., Fraser, C., & Cauchemez, S.
(2013). Package ‘EpiEstim’ July. In American Journal
of Epidemiology. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwt133
Cucinotta, D., & Vanelli, M. (2020). WHO declares
COVID-19 a pandemic. In Acta Biomedica.
https://doi.org/10.23750/abm.v91i1.9397
Isaac I. Bogoch, Alexander Watts, Andrea Thomas-Bachli,
Carmen Huber, M. U. G. K. and K. K. (2020).
Pneumonia of unknown aetiology in Wuhan, China:
potential for international spread via commercial air
travel. Journal of Travel Medicine.
Jaillon, S., Berthenet, K., & Garlanda, C. (2019). Sexual
Dimorphism in Innate Immunity. In Clinical Reviews in
Allergy and Immunology.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-017-8648-x
Kemenkes R. (2020). Situasi Terkini Perkembangan
Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) 5 Mei 2020.
Lai, P. C., So, F. M., & Chan, K. W. (2008). Spatial
epidemiological approaches in disease mapping and
analysis. In Spatial Epidemiological Approaches in
Disease Mapping and Analysis.
https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420045536
Lu, H., Stratton, C. W., & Tang, Y. W. (2020). Outbreak of
pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, China: The
mystery and the miracle. In Journal of Medical
Virology. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25678
Nishiura, H., & Chowell, G. (2009). The effective
reproduction number as a prelude to statistical
estimation of time-dependent epidemic trends. In
Mathematical and Statistical Estimation Approaches in
Epidemiology. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-
2313-1_5
Onder, G., Rezza, G., & Brusaferro, S. (2020). Case-
Fatality Rate and Characteristics of Patients Dying in
Relation to COVID-19 in Italy. In JAMA - Journal of
the American Medical Association.
https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.4683
Sohrabi, C., Alsafi, Z., O’Neill, N., Khan, M., Kerwan, A.,
Al-Jabir, A., Iosifidis, C., & Agha, R. (2020). World
Health Organization declares global emergency: A
review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19). In
International Journal of Surgery.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.02.034
Thompson, R. N., Stockwin, J. E., van Gaalen, R. D.,
Polonsky, J. A., Kamvar, Z. N., Demarsh, P. A.,
Dahlqwist, E., Li, S., Miguel, E., Jombart, T., Lessler,
J., Cauchemez, S., & Cori, A. (2019). Improved
inference of time-varying reproduction numbers during
infectious disease outbreaks. Epidemics.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epidem.2019.100356
Tindale, L., Coombe, M., Stockdale, J. E., Garlock, E., Lau,
W. Y. V., Saraswat, M., Lee, Y. B., Zhang, L., Chen,
D., Wallinga, J., & Colijn, C. (2020). Transmission
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
26

interval estimates suggest pre-symptomatic spread of
COVID-19. MedRxiv.
https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.03.20029983
WHO. World Health Organization. (2020). Global
Surveillance for human infection with coronavirus
disease (COVID-19). Interim Guidance, February, 27–
29.
WHO. (2020a). Coronavirus. WHO.
WHO. (2020b). Coronavirus disease. In World Health
Organization (Vol. 2019, Issue March, p. 2633).
https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.2633
WHO. (2020c). Naming the coronavirus disease (COVID-
19) and the virus that causes it. World Health
Organization.
World Health Organisation. (2020). Considerations in
adjusting public health and social measures in the
context of COVID-19. World Health Organisation,
May, 1–7.
Characteristics, Effective Reproduction Number (Rt), and Spatial Modelling of Covid-19 Spread at Magetan District, East Java, Indonesia
27
