
In Vitro Study of Reduction of Oral Enterococcus faecalis Biofilm on
Application of Combination of Chrysomya megacephala Maggot
Extract and Sodium Hypochlorite
Rizka Hidayati
1 a
, Ari Asnani
2b
, Muhamad Salman Fareza
3c
and Dwi Utami Anjarwati
4d
1
Magister of Biomedicine, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Jenderal Soedirman, Purwokerto,Indonesia
2
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Universitas Jenderal
Soedirman, Purwokerto, Indonesia
3
Department of Biochemistry, Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Health Sciences, Universitas
Jenderal Soedirman, Purwokerto, Indonesia
4
Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Jenderal Soedirman, Purwokerto, Indonesia
Keywords: Antibiofilm, Root Canal Irrigant, Blowfly Larvae, Endodontic Treatment
Abstract: The tooth's infected root canal relates to the bacteria invasion, such as Enterococcus faecalis. The eradication
of the bacteria using single root canal irrigants becomes difficult because of the formed biofilm. We aimed to
investigate the effectiveness of a combination of C. megacephala maggot extract with the common irrigant,
sodium hypochlorite 3%, on the biofilm reduction of E. faecalis. The C. megacephala maggot extract was
tested at concentrations 25%, 50%, and 100%, and the combination of each extract concentration with sodium
hypochlorite in a volume ratio of 1:1; 1:2, 1:3, 2:1, and 3:1. All treatments were performed three times of
replication with incubation time for 1 hour and 3 hours. Antibiofilm effect was measured with crystal violet
staining and the optical density reading. Data was analyzed with the Statistical Package for the Social
Sciences Statistic Version 22. The least biofilm formation was observed in combination of maggot extract
25% with sodium hypochlorite (2:1) for 1 hour incubation (p=0,05) and combination of maggot extract 25%
(1:1) for 3 hours incubation (p=0,000). This combination effectively inhibits the biofilm of E. faecalis. This
study identified the protease enzymes in C. megacephala maggot extract and investigated C. megacephala
maggot extract's antibiofilm effect combine with the other root canal irrigant.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the bacteria found in the root canal of the
infected tooth is Enterococcus faecalis. These
bacteria are persistent and can form biofilms.
Therefore they are difficult to be removed. The
bacteria in the root canal treatment are eradicated by
applying root canal irrigant. The agent commonly
used as root canal irrigant is sodium hypochlorite
(NaOCl), with 1,25-5% (Mulyawati, 2011). NaOCl
effectively removes planktonic bacteria, but it is less
effective in reducing biofilms produced by bacteria
(Dunavant et al., 2006). NaOCl is usually combined
with other irrigation solution such as chlorhexidine
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5351-752X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8569-2565
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2414-1249
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8394-2543
(CHX) to increase the antibacterial and antibiofilm
effects.
Several researchers have also carried out the
combination of root canal irrigant with natural agents.
Geethapriya et al. (2016) combined chitosan with
EDTA against E. faecalis biofilms with a ratio of 1: 1
in their study, which showed effective results in
inhibiting E. faecalis biofilm formation (Geethapriya
et al., 2016). Other studies combined chitosan with
chlorhexidine (CHX), whose results showed the same
effect with 5% NaOCl in inhibiting E. faecalis biofilm
(Jaiswal et al., 2017). Other studies regarding the
combination of NaOCl with natural agents have never
been done.
98
Hidayati, R., Asnani, A., Fareza, M. and Anjarwati, D.
In Vitro Study of Reduction of Oral Enterococcus faecalis Biofilm on Application of Combination of Chrysomya megacephala Maggot Extract and Sodium Hypochlorite.
DOI: 10.5220/0010488400980103
In Proceedings of the 1st Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference in conjunction with the 5th Annual Scientific Meeting (Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia
(JIMC 2020), pages 98-103
ISBN: 978-989-758-499-2
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Maggot extract is material from natural sources
that have not been studied as root canal irrigant. Some
maggots, such as maggot Lucilia sericata contain
proteolytic enzyme components that can degrade
bacterial biofilms' extracellular matrix (Chen et al.,
2012). Chymotrypsin in L. sericata secretion can
affect bacterial biofilms' adhesion (Harris et al.,
2013). Other types of maggots, such as Chloroprocta
sp. contain protease enzymes that can reduce the
extracellular biofilm matrix in Staphylococcus
epidermidis (Anjarwati et al., 2017). Another maggot
extract, such as Chrysomya megacephala maggot
extract, has an excretory and secretory. This product
contains serine (trypsin and chymotrypsin), an
antibacterial effect on Escherichia coli,
Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacillus subtilis (El-
Ebiarie et al., 2012; Mohamed 2015a, 2015b).
In this study, the maggot was taken from the
maggot Chrysomya megacephala, a local maggot that
is quite common in Indonesia (Putri, 2018).
Combination of maggot extract C. megacephala with
3% NaOCl as root canal irrigant is expected to
increase the reduction of E. faecalis biofilm.
2 METHODS
2.1 Material
This experimental laboratory study conducted the E.
faecalis biofilm test. The materials used were C.
megacephala maggot extract with a concentration of
25%, 50%, 100% and a combination of each
concentration of maggot extract with 3% NaOCl with
a volume ratio of 1: 1, 1: 2, 1: 3, 2: 1 and 3: 1, 3%
NaOCl as a positive control, tryptic soy broth (TSB)
and sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) as
negative controls. Each treatment was replicated three
times. Biofilm reduction was measured by added 1%
crystal violet with optical density measured at a
wavelength of 595 nm (OD595) using a microtiter
plate reader at the Cancer and Stem Cell Research
Center Laboratory, Muhammadiyah University,
Purwokerto.
2.2 Bacterial Strains
The sample used in this study is that the colony is E.
faecalis ATCC 29212, a moderate biofilm-producing
bacteria. The colony has been isolated and cultured
with Mueller Hinton Agar (MHA) media in the
Microbiology Laboratory of the Faculty of Medicine,
Universitas Jenderal Soedirman, Purwokerto. The
powder of MHA with 12 grams was solved with 240
mL of aquadest and poured into the culture tray (20
mL/tray). The media was sterilized in an autoclave for
15 minutes (2 atm, 121oC), then put in an incubator
for 24 hours to check if there is contamination or not.
The E. faecalis were cultured in sterile media with an
anaerobic environment. The bacteria's growth colony
was taken and diluted with NaCl 0,9% until the
concentration equal to 106 CFU/mL (CFU: Colony
Forming Unit) or 0,5 Mc Farland Standard (Howarto
et al., 2015).
2.3 Rearing Maggot and Collecting
Maggot Extract
The process of collecting C. megacephala maggot
extract was carried out at the Faculty of Medicine,
Universitas Jenderal Soedirman. The rearing of the
maggot C. megacephala was done by installing traps
of flies that have been given raw fish (fish waste).
After one day, the fly eggs that have been collected in
fish waste were transferred to fresh raw fish and left
to grow into a maggot. After growing into a maggot,
the maggot at the end of the second instar and the
beginning of the third instar was collected in a vessel
and washed using ethanol and distilled water three
times (Arora et al., 2010).
Figure 1: Soaking C. megacephala maggot in Phosphate
Buffered Saline (PBS).
Every 1 gram of maggot was immersed in 1 ml of
sterile PBS solution for 1 hour at room temperature in
a dark room (Figure 1). Continued Soaking was for
24 hours (moved to room light). Then maggot in PBS
was incubated at 37
o
C for 48 hours. Then the maggot
and liquid were separated, then the liquid was
centrifuged at 25
o
C, with 10,000 rpm for 15 minutes.
In Vitro Study of Reduction of Oral Enterococcus faecalis Biofilm on Application of Combination of Chrysomya megacephala Maggot
Extract and Sodium Hypochlorite
99

The supernatant obtained from the centrifuge process
was collected and sterilized with a 0.2 µm membrane
filter. Maggot extract obtained from this process was
stored at -20
o
C (Honda et al., 2011).
2.4 Biofilm Reduction Measurement by
Administering Chrysomya
megacephala Maggot Extract and
Its Combination with Sodium
Hypochlorite
The biofilm of E. faecalis (ATCC 29212) was
measured using 96-well microtiter plates. The
bacteria were transferred from Mueller Hinton Agar
(MHA) media into Tryptic Soy Broth (TSB) and
incubated for 24 hours under anaerobic conditions,
which remained at 37 oC. The culture was diluted
with 1: 100 on the medium. Then 20 µl of bacterial
culture was inoculated with 200 µl TSB in each well,
dispensed into 96-well microtiter plates with a flat
bottom. After anaerobic incubation at 37 °C for 24
hours, the planktonic bacteria from each well were
disposed of carefully by using a micropipette slowly
until the bottom of the well looked clear. Each well
was washed with 300 µl phosphate-buffered saline
(PBS) 2 times slowly.
As many as 100 μL of maggot extract filled into
each well of the 96-well microtiter plate was filled
with at different concentrations (25%, 50%, 100%)
and a combination of maggot extract and 3% NaOCl
with a ratio of 1: 1, 1: 2, 2: 1, 1: 3, and 3: 1. The 96-
well microtiter plate that has been inserted maggot
extract and a combination of maggot extract and
NaOCl are then incubated for 1 hour and 3 hours.
After incubation, the biofilm is examined by giving a
dye of 200 µL of 1% crystal violet solution in water
for 30 minutes and washed with distilled water. Wells
are reversed and dried on paper towels and dry air.
Then, 200 µL of 5% acid isopropanol was added to
each well to remove biofilm colour. The optical
density was measured at 595 nm (OD595) using a
microtiter plate reader (Pierce et al., 2010).
Table 1: The result of optical density reading in 1 hour and 3 hours incubation.
No. Treatment
Mean of absorbance
1 hour 3 hours
1. TSB with E. faecalis (control of bacteria) 0,851 3,064
2. C. megacephala maggot extract 25% 0,253 2,966
3. C. megacephala maggot extract 50% 0,319 2,902
4. C. megacephala maggot extract 100% 0,424 2,927
5. Combination of C. megacephala maggot extract 25%, and NaOCl 3% (1:1) 0,214
0,176
6. Combination of C. megacephala maggot extract 50%, and NaOCl 3% (1:1) 0,756 2,809
7. Combination of C. megacephala maggot extract 100%, and NaOCl 3% (1:1) 0,619 2,915
8. Combination of C. megacephala maggot extract 25%, and NaOCl 3% (1:2) 0,268 0,294
9. Combination of C. megacephala maggot extract 50%, and NaOCl 3% (1:2) 0,501 0,211
10. Combination of C. megacephala maggot extract 100%, and NaOCl 3% (1:2) 0,190 2,998
11. Combination of C. megacephala maggot extract 25%, and NaOCl 3% (1:3) 0,209 0,212
12. Combination of C. megacephala maggot extract 50%, and NaOCl 3% (1:3) 0,232 0,216
13. Combination of C. megacephala maggot extract 100%, and NaOCl 3% (1:3) 0,176 2,830
14. Combination of C. megacephala maggot extract 25%, and NaOCl 3% (2:1)
0,155 0,294
15. Combination of C. megacephala maggot extract 50%, and NaOCl 3% (2:1) 0,498 2,925
16. Combination of C. megacephala maggot extract 100%, and NaOCl 3% (2:1) 0,664 2,273
17. Combination of C. megacephala maggot extract 25%, and NaOCl 3% (3:1) 0,343 2,918
18. Combination of C. megacephala maggot extract 50%, and NaOCl 3% (3:1) 0,273 2,962
19. Combination of C. megacephala maggot extract 100%, and NaOCl 3% (3:1) 1,395 2,920
20. PBS with E. faecalis 0,317 2,982
21. NaOCl 3% with E. faecalis 0,157 0,194
Table 2: The calculating of the value of MBRC
50
and MBRC
80
in biofilm test with 1 hour and 3 hours incubation.
Time of
incubation
OD of
Bacterial
control
OD of
Blank
MBRC
50
(OD of bacterial control –OD of
blank) x 50%
MBRC
80
(OD of bacterial control –OD of
blank) x 20%
1 hour 0,851 0,097 0,394 0,151
3 hours 3,064 0,109 1,477 0,591
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
100
2.5 Statistical Analysis
The effects of various maggot extract concentrations
and their combinations with sodium hypochlorite in
reducing biofilms were analyzed using one-way
ANOVA and Post hoc LSD (Least Significant
Difference) tests by using The Statistical Package for
the Social Sciences Statistic Version 22.
3 RESULTS
From all treatment groups with 1-hour incubation, the
most extensive treatment group in reducing E.
faecalis biofilm was a combination of 25% maggot
extract and sodium hypochlorite with a ratio of 2: 1
(reducing 81.75% of biofilm production produced
from the bacterial control, p < 0,05) ). The
combination of maggot extract (25%) and sodium
hypochlorite (2:1) reduced biofilm better than 3%
sodium hypochlorite only. The Post hoc LSD test
showed that the combination of 25% maggot extract
and sodium hypochlorite with ratio 2:1 does not have
a different effect than 3% sodium hypochlorite in
reducing the biofilm of E. faecalis (p>0,05).
In 3 hours of incubation, the most extensive
treatment group in reducing E. faecalis biofilm was a
combination of 25% maggot extract and sodium
hypochlorite with a ratio of 1: 1 (reducing 94.25% of
biofilm production produced from bacterial control, p
<0.001) (Table 1). The 25% maggot extract and
sodium hypochlorite application (ratio 1:1) showed
more effect than 3% sodium hypochlorite only. The
Post hoc LSD test also showed that the combination
of 25% maggot extract and sodium hypochlorite with
ratio 1:1 does not have a different effect than 3%
sodium hypochlorite in reducing the biofilm of E.
faecalis (p>0,05).
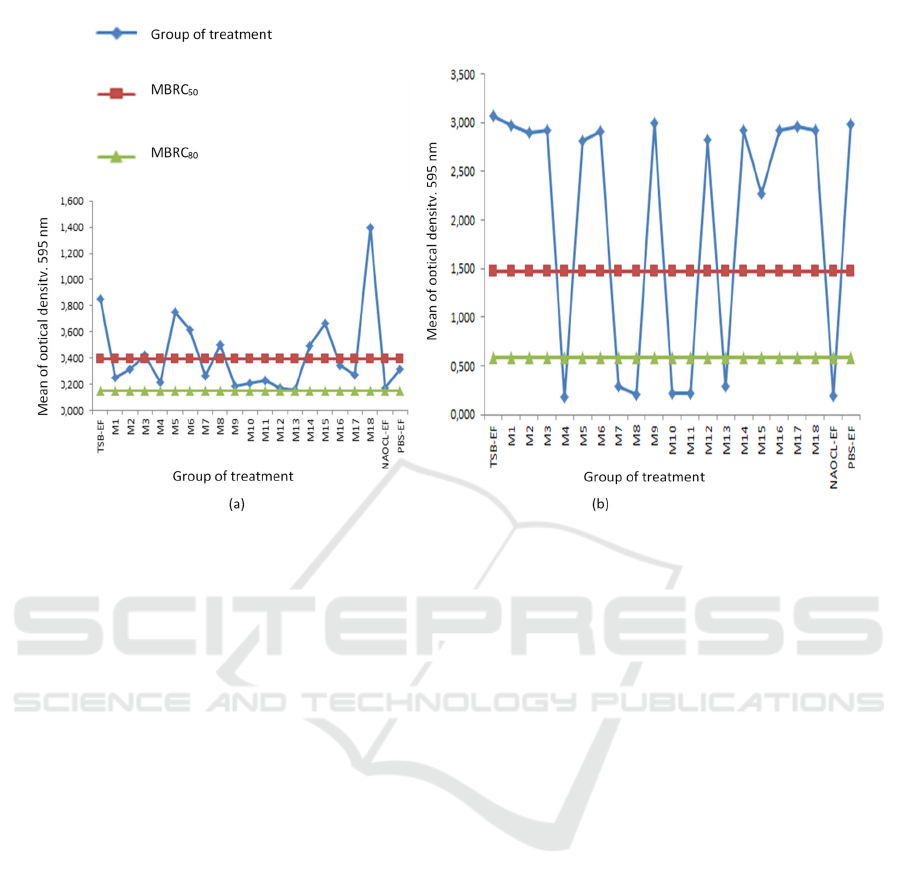
In 1 hour incubation, the value of MBRC50 in
this research is 0,394 and MBRC80 is 0,151 (Table
2). In 1 hour incubation, MBRC50 could be found in
maggot extract 25%, 50%, combination of maggot
extract 25% (1:1), 25% (1:2), 100% (1:2), 25% (1:3),
50% (1:3), 25% (2:1), 25% (3:1), and50% (3:1).
Meanwhile, the value of MBRC80 could not be found
in all the treatment in 1 hour incubation (Figure 1). In
3 hours incubation, the value of MBRC50 is 1,477
and the value of MBRC80 is 0,591 (Table 2). In 3
hours incubation, MBRC50 and MBRC80 could be
found in the same treatment which are the
combination of maggot extract 25% (1:1), 25% (1:2),
50% (1:2), 25% (1:3), 50% (1:3), and 25% (2:1)
(Figure 2).
Figure 2 showed that in 1-hour incubation,
MBRC50 could be reached of maggot extract
application (concentration 25%, 50%, the
Figure 2. The effect of Chrysomya megacephala maggot extract on biofilm reduction of Enterococcus faecalis ATCC
29212 for 1-hour incubation (a) and 3 hours incubation (b)
In Vitro Study of Reduction of Oral Enterococcus faecalis Biofilm on Application of Combination of Chrysomya megacephala Maggot
Extract and Sodium Hypochlorite
101

combination of 25% maggot extract (1:1), 25%
maggot extract (1:2), 100% maggot extract (1:2),
25% maggot extract (1:3), 50% maggot extract (1:3),
25% maggot extract (2:1), 25% maggot extract (3:1),
and 50% maggot extract (3:1)). Meanwhile,
MBRC80 could not be found in 1-hour of incubation.
4 DISCUSSION
Compared to the results of biofilm reduction at 1-hour
incubation (maggot extract 25% (2:1)), there was a
decrease in the concentration of maggot extract
needed to reduce biofilms for a longer time (3 hours),
namely with extract concentration of 25% (1:1). Due
to a decrease in maggot extract protease activity, the
possibility is as time increases, therefore at 3 hours
incubation. The possibility of more significant
antibiofilm activity is due to the combination of 3%
sodium hypochlorite and maggot extract (Łaba et al.,
2010).
Compared with the effect of giving 3% sodium
hypochlorite, the combination of 25% (1:1) maggot
extract (1 hour) and a combination of 25% (2: 1) (3
hours) maggot extract had no different effects on
Enterococcus faecalis biofilm reduction (p>0.05).
This result shows that an evaluation in the research
process is needed to increase the antibiofilm effect to
be more maximal. In PBS solvent with E. faecalis,
compared with a combination of 25% 2: 1 maggot
extract (1-hour incubation) and 25% (1:1) (3 hours
incubation) combination of maggot extract, there
were no significant differences in antibiofilm effects.
This result showed that the presence of PBS as a
solvent in making maggot extract is not a factor that
influences the reduction of bacterial biofilms.
However, the antibiofilm effect produced comes from
the extract of the maggot.
This study also showed that the C. megacephala
maggot extract's antibiofilm effect was more effective
at 3 hours incubation (p <0.001). In other studies,
incubation time also significantly affected the
reduction of extracellular biofilm matrix after maggot
extract. This is thought to be due to proteases
requiring time to break down proteins into dissolved
proteins in exopolysaccharide (EPS) on bacterial
walls. Protease is one type of enzyme contained in
maggot extract. The effect of enzyme damage is
directly proportional to the length of time the
interaction of environmental exposure to the enzyme.
The longer the exposure to the environment will
damage the enzyme's structure, so that a decrease in
enzyme activity Łaba et al., 2010)
5 CONCLUSIONS
C. megacephala maggot extract and its combination
with sodium hypochlorite affect the reduction of
biofilms produced by E. faecalis. Further research is
needed to develop C. megacephala maggot extract,
such as identifying other protease enzymes in C.
megacephala maggot extract to reduce other bacterial
biofilms and determine the antibacterial and
antibiofilm effects of C. megacephala maggot extract
with a combination of other root canal irrigation
materials.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper can be arranged by support from many
people. Therefore, we are grateful to Dr. Warsinah,
M.Si., Apt, Dr. Oedjijono, M.Sc, and Dr. dr. Lantip
Rujito, M.Si. Med for the advice to make this paper
better.
REFERENCES
Anjarwati DU, Nuryastuti T, Riwanto I, Wahyono H.
Effects of Chloroprocta sp. maggot filtrates on
extracellular matrix reduction and embedded
Staphylococcus epidermidis viability. Malaysian
Journal of Microbiology. 2017; 3(3) : 235-243.
Arora S, Lim CS, Baptista C. Antibacterial activity of
Lucilia cuprina maggot extracts and its extraction
techniques. International Journals of Integrative
Biology. 2010; .9(1): 43-48.
Chen Y, Norde W, Mei HC, Busscher, HJ. Bacterial Cell
Surface Deformation under External Loading.
American Society For Microbiology. 2012; 3(6): 1-7.
Dunavant TR, Regan JD, Glickman GN, Solomon ES,
Honeyman AI. Comparative evaluation of endodontic
irrigants against Enterococcus faecalis biofilms. J.
Endod. 2006; 32 (6): 527-531.
El-Ebiarie AS, Taha N. Molecular characterization of
serine proteases from both first and third larval instars
of Chrysomya megacephala. Life Science Journal.
2012; 9(3): 2086-2093.
Geethapriya N, Subbiya A, Padmavathy K, Mahalakshmi
K, Vivekanandan P, Sukumaran VG. Effect of
chitosan-ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid on
Enterococcus faecalis dentinal biofilm and smear layer
removal. J. C. D. 2016; 19: 472-477.
Harris LG, Nigam Y, Sawyer J, Mack D, Pritchard DI.
Lucilia sericata Chymotrypsin Disrupts Protein
Adhesin-Mediated Staphylococcal Biofilm Formation.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013; 79(4): 1393-1395.
Honda, K, Okamoto, K, Mochida Y, Ishioka K, Oka M,
Maesato K., et al. A novel mechanism in maggot
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
102

debridement therapy: protease in excretion/secretion
promotes hepatocyte growth factor production. Am. J.
Physiol. 2011; 301: C1423-C1430.
Howarto SM, Wowor PM, Mintjelungan CN. Uji
efektivitas antibakteri minyak atsiri sereh dapur sebagai
bahan medikamen saluran akar terhadap
bakteriEnterococcus faecalis. Jurnal e-Gigi. 2015;
Vol.3 (2), 432-438.
Jaiswal N, Sinha DJ, Singh UP, Singh K, Jandial UA, Goel
S, Evaluation of antibacterial efficacy of chitosan,
chlorhexidine, propolis, and sodium hypochlorite on
Enterococcus faecalis biofilm: an in vitro study. J. Clin.
Exp. Dent. 2017; 9 (9): e1066-1074.
Łaba W, Rodziewicz A. Keratinolytic Potential of Feather-
Degrading Bacillus polymyxa and Bacillus cereus.
Polish Journal of Environmental Studies. 2010; 19(2):
371-378.
Mohamed NT. Activity of two serine proteases and
antibacterial studies on both excretory/secretory
products and whole body homogenates of third instar
larvae of Chrysomya megacephala. International
Journal of Advanced Research. 2015b; Vol. 3 (4), 451-
459.
Mohamed NT. Fractionation and purification of bioactive
peptides in excretory/ secretory products of third instar
larvae of Chrysomya megacephala (Calliphoridae:
Diptera). International Journal of Applied and Pure
Science and Agriculture. 2015a; Vol.01, 129-136.
Mulyawati E. Peran bahan desinfeksi pada perawatan
saluran akar. Maj. Ked. Gi. 2011; 18 (2): 205-209.
Pierce, CG, Uppuluri P, Tummala S, Lopez-Ribot JL. A 96
Well Microtiter Plate-based Method for Monitoring
Formation and Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of
Candida albicans Biofilms. Journal of Visualized
Experiments. 2010; 44: 1-4.
Putri YP. Taksonomi lalat di pasar induk Jakabaring kota
Palembang. Sainmatika: Jurnal Ilmiah Matematika dan
Ilmu Pengetahuan Alam. 2018; 15(2): 105-111.
In Vitro Study of Reduction of Oral Enterococcus faecalis Biofilm on Application of Combination of Chrysomya megacephala Maggot
Extract and Sodium Hypochlorite
103
