
Antibacterial Activity of Synthesized Silver Nanoparticle using
Langsat Leaf Extract (Lansium domesticum var. pubescen Kooders et
Valeton) as Bioreductor against Escherichia coli and
Staphylococcus aureus
Khairunnida Rahma
1a
, Agung Dwi Wahyu Widodo
2b
, Rebekah Juniati Setiabudi
2c
,
Retno Indrawati Roestamadji
3d
, Maftuchah Rochmanti
4e
, Pudji Lestari
5f
1
Basic Medical Science Study Program, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
2
Department of Medical Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
3
Department of Oral Biology, Faculty of Dental Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
4
Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
5
Department of Public Health-Preventive Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords:
Antibacterial Activity, Escherichia coli, Green Synthesis, Lansium domesticum, Silver Nanoparticles,
Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract: The emerging of antimicrobial resistance has caused the urgency to find new alternative agents. The
application of silver in the form of silver nanoparticles (AgNP) began to be studied again. The less toxic and
ecofriendly method to synthesize AgNP is through the green synthesis approach using plant extract. Langsat
is one of the endemic plants of South Kalimantan and its leaf provides secondary metabolites substances to
help the synthesize of AgNP. The synthesis of AgNP was prepared and AgNO
3
using Langsat Leaf (LL)
extract as the bioreductor. The synthesized LL-AgNP was then characterized by UV-Vis spectrophotometer
on 575 nm. The MIC study was done using broth dilution method with 6 different concentrations ranged from
3.125% to 100% and 2 controls, followed by the MBC study on MHA plates. The LL-AgNP successfully
inhibited the growth of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus in concentration of 6.25% and 25%,
respectively. The LL-AgNP also showed bactericidal activity against Escherichia coli in concentration of
25% but showed no activity on Staphylococcus aureus. This result indicates that LL-AgNP has potential as
an antibacterial agent against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus.
1 INTRODUCTION
Infection caused by microorganisms is one of the
main causes of chronic infection and even death
(Linlin, Chen, & Longquan, 2017). There are more
than 200 known diseases that can be transmitted from
bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microbes to human
(Ganesan et al., 2017). It increases from time to time
and becomes a real threat for the community.
Antibiotics are currently used as preferred method for
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6089-3619
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3449-768X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2171-8743
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4597-6782
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9222-9376
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4725-4676
bacterial infection treatment because they are
considered to be more effective in cost and have
proven to give strong and clear results.
However, nowadays, the use of antibiotics has
also started to cause other dangerous phenomena. The
emergence of bacteria causing antibacterial resistance
has increased quite rapidly throughout the world
(Ventola, 2015). The limitation of new antibiotics in
nature to replace antibiotic agents that are no longer
effective raises the urgency to develop new
298
Rahma, K., Wahyu Widodo, A., Setiabudi, R., Roestamadji, R., Rochmanti, M. and Lestari, P.
Antibacterial Activity of Synthesized Silver Nanoparticle using Langsat Leaf Extract (Lansium domesticum var. pubescen Kooders et Valeton) as Bioreductor against Escherichia coli and
Staphylococcus aureus.
DOI: 10.5220/0010491702980304
In Proceedings of the 1st Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference in conjunction with the 5th Annual Scientific Meeting (Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia
(JIMC 2020), pages 298-304
ISBN: 978-989-758-499-2
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

antibiotics to strengthen the effectiveness of existing
antibiotic agents (World Health Organization, 2014).
There are many types of precious metals that are
used in the medical world, especially in antimicrobial
research. One of them is silver metal (Ag). Ag has
been used to demonstrate antibacterial effects and has
been frequently used in medicine including
orthopedics (Castiglioni, Cazzaniga, Locatelli, &
Maier, 2017). The advantage of Ag utilization is that
it can be formed into silver nanoparticles (AgNP).
AgNP gives promising potential as antibiotic
alternatives because AgNP has better
physicochemical and biological properties than
whole silver (Qing et al., 2018). One of the methods
to create AgNP is the green synthesis approach. This
approach is seen from the biology perspective,
especially the utilization of natural organisms has
offered a method that is reliable, simple, non-toxic,
and environmentally friendly (Velusamy, Kumar,
Jeyanthi, Das, & Pachaiappan, 2016). In green
synthesis, many sources from nature such as plants,
bacteria, and fungi can be used in the process.
Indonesia is a country which has rich biodiversity.
This provides a good opportunity and potential to
develop the synthesis of nanoparticles that is more
environmentally friendly using plant extracts from
various plants in Indonesia. One of the endemic plants
found in South Kalimantan, especially Tabalong, is
Langsat. Langsat (Lansium domesticum var.
Pubescen Kooders et Valeton) is a plant that comes
from Meliaceae family. Every fruiting season,
Langsat produces a lot of fruits but people in South
Kalimantan only eat the fruits, despite the results of
previous research proving that other parts such as
bark, fruit skin, and leaf have potential as traditional
medicine.
To the best of our knowledge, the synthesis of
AgNP using Langsat leaf has been hardly explored
until now. This fact supports the research of
antibacterial activity using silver nanoparticles
synthesized by biological methods using a
bioreductor from Langsat leaf extract (Lansium
domesticum var. Pubescen Kooders et Valeton) in
vitro as one of the endeavor to find the potential of
new antibacterial agents in the future.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
This research is a true experiment and was done with
randomized post-test only control group design.
There were 6 different LL-AgNP concentrations and
2 controls (positive and negative). Silver Nitrate
(AgNO
3
) 99% from Merck was used for the synthesis
of silver nanoparticle. Langsat (Lansium domesticum
var. pubescen Kooders et Valeton) leaf were collected
from a private plantation in Tabalong District, South
Kalimantan, Indonesia. Bacterial strain of Gram-
negative Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Gram-
positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus ATCC
25923 were purchased from Center of Health
Laboratory (BBLK) Surabaya, East Java, Indonesia.
The research was conducted in Microbiology
Laboratory Faculty of Medicine, Universitas
Airlangga Surabaya, East Java Indonesia.
2.1 Preparation of Leaf Extract
The fresh Langsat leaves were collected from
Langsat trees and wiped gently using dry paper towel
to remove dust on surface. The Langsat leaves were
then washed thoroughly with running water and were
tapped gently with paper towels afterward. The leaves
were dried using a microwave at medium temperature
for 6 minutes. The dried leaves were chopped using
blender and were sifted with 60 mesh strainer. The
extraction process was following the maceration
steps. First, 100 grams of fine dried leaves were
weighed and added by ethanol 96% until the volume
reached 1000 ml. The mixture was left for 24 hours
and was strained after that. The process was repeated
for 3 times and was evaporated using vacuum rotary
evaporator until a thick extract was obtained.
2.2 Silver Nanoparticles Synthesis
Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Langsat Leaf
extract (LL-AgNP) was done using the green
synthesis method. The ratio of AgNO
3
solution and
the extract was 1:10. Around 15 ml of the extract was
mixed with 150 ml AgNO
3
solution inside a beaker
glass that has been covered with aluminum foil to
prevent light intrusion. The solution was then warmed
inside a water bath at 60
o
C and was stirred once in a
while. The discoloration is one of the indications that
the synthesis of LL-AgNp has been done.
2.3 Silver Nanoparticles
Characterization
The characterization of synthesized LL-AgNP was
done using UV-Vis Spectrophotometer. As much as
1 ml of LL-AgNP solution was scanned between 300
- 650 nm for determining the wavelength peak. The
scan was done 4 times; right after the synthesis
process (D+0) and one month after watching the
stability of LL-AgNP (D+37, D+44, D+51, and
D+58) with the same steps as mentioned above. The
Antibacterial Activity of Synthesized Silver Nanoparticle using Langsat Leaf Extract (Lansium domesticum var. pubescen Kooders et
Valeton) as Bioreductor against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus
299

result from LL-AgNP characterization was then used
to calculate its size using a formula described by
Amirjani, Firouzi, & Haghshenas, (2020).
Nanoparticle size 0,78 𝜆
266
(1)
2.4 Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
Assay
The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) assay
was done by the broth dilution method. First, 5 ml
MHB sterile was pipetted to 8 different test tubes and
were given labels; tube 1-5, Control (+), and Control
(
–
). Then, 2 ml of LL-AgNP was added to the first
tube and homogenized. After being homogenized, 1
ml of the solution from tube 1 was pipetted and was
moved to the second tube and was vortexed. This step
was done until the fifth tube and from tube 5, 1 ml of
the solution was discharged and became the lowest
concentration.
Aquadest was used as negative control, while
Meropenem and Vancomycin were used as the
positive control for Escherichia coli and
Staphylococcus aureus, respectively. The tubes were
vortexed well and were incubated on an incubator for
24 hours at 35
o
C. The color of the solution on each
tube was observed after the incubation. Tubes with
color turbidity imminent with turbidity on positive
control were then noted and the lowest concentration
was decided as MIC. The tubes were proceeded to
MBC assay. This assay was done in triplicate. The
result was noted and analyzed descriptively.
2.5 Minimum Bactericidal
Concentration Assay
One loop of the solution from tubes that has been
selected from previous MIC assay was taken and was
streaked to the Mueller-Hinton Agar plates. The
plates were then incubated on an incubator for 24
hours at 35
o
C. The colony growth was observed after
the incubation period. Plates without any colony
growth observed were then noted and the lowest
concentration of it was decided as MBC. The result
was noted and analyzed descriptively.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Silver Nanoparticles Synthesis
The Langsat leaf (LL) extract had a dark brown color
after the extraction process was done. Meanwhile,
AgNO
3
had no color with a clear solution just like the
solvent used. After both of the components were
mixed with ratio 1:10 of AgNO
3
1 mM solution and
LL extract, discoloration was observed. The mixed
solution showed a yellowish color and slightly turbid.
Based on the color changes, it could indicate the
formation of silver nanoparticles. However, a further
test was done in order to make sure the silver
nanoparticles were successfully synthesized.
Figure 1: AgNO
3
solution before the synthesis process (left)
and LL-AgNP after the synthesis process (right).
3.2 Silver Nanoparticles
Characterization
The solution was then run through the
spectrophotometer UV-Vis reading to get the
wavelength peak in order to confirm the formation of
LL-AgNP. The reading was done at λ 300 - 650 nm.
Based on the reading process, the peak of LL-AgNP
was observed at λ 398 nm with an absorbance value
of 0.92. This result confirmed that LL-AgNP has been
synthesized and reflected on Figure 1.
Figure 2: Characterization of LL-AgNP.
The recorded wavelength of LL-AgNP was then
calculated with the formula to roughly estimate its
size. Based on the calculation, a 44 nm LL-AgNP was
synthesized. As stated in Khodashenas & Ghorbani
(2019), AgNP shape with the size similar to the
synthesized AgNP would be spherical. Biological
methods for AgNP synthesis are still under
development. Nanoparticles with shapes other than
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
300
spherical and cubic could only be synthesized through
physical or chemical methods.
One month after the synthesis, another reading on
the spectrophotometer was done to measure the
current absorbance value and the stability of LL-
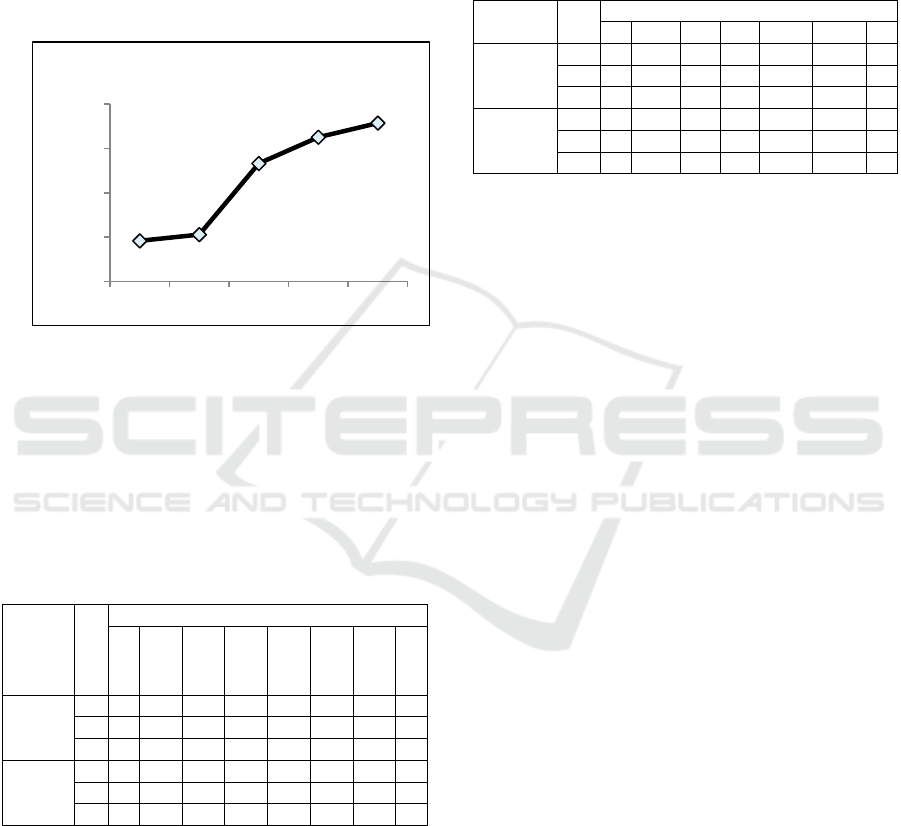
AgNP. The LL-AgNP absorbance value shifted from
0.92 (D+0) to 1.06 (D+37), 2.66 (D+44), 3.25
(D+51), and 3.57 (D+58) (Figure 3). It could indicate
the LL-AgNP has agglomerated and alteration of size
and shape has occurred.
Figure 3: The LL-AgNP stability observation on several
days after the initial synthesys.
3.3 Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
Assay
The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) result
of various LL-AgNP concentrations presented on
table 1.
Table 1: MIC of LL-AgNP.
Isolate
s
R
LL-AgNP Concentration (%)
+
100
50
25
12.5
6.25
3.125
–
E. coli 1
–
–
–
–
–
–
++
2
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
+
3
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
+
S.
aureus
1
–
–
–
–
+ + ++
2
–
–
–
–
–
–
++
3
–
–
–
–
–
–
++
R (replication), + (Meropenem for Escherichia coli and
Vancomycin for Staphylococcus aureus), – (Aquadest)
Based on the data in table 1, LL-AgNP could
inhibit the growth of Escherichia coli at concentration
6.25% and Escherichia coli ESBL at 12.5%.
Meanwhile, on the Gram-positive bacteria, the
growth of Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA
inhibited by LL-AgNP at concentration 25%.
3.4 Minimum Bactericidal
Concentration Assay
The Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
result of previously obtained from MIC assay
presented on tablr 2.
Tabel 2: MBC of LL-AgNP.
Isolates R
LL-A
g
NP Concentration (%)
+ 100 50 25 12.5 6.25
–
E. coli 1
–
–
–
–
+ ++
2
–
–
–
–
–
–
+
3
–
–
–
–
–
–
+
S.
aureus
1
–
++ + + ++
2
–
++ + + ++
3
–
++ + + ++
R (replication), + (Meropenem for Escherichia coli and
Vancomycin for Staphylococcus aureus), – (Aquadest)
Based on the data in table 2, LL-AgNP showed
bactericidal activity against Escherichia coli at
concentration 25% and Escherichia coli ESBL at
12.5%. Discrepant with the result of Gram-negative
bacteria, there was no bactericidal activity observed
against Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA.
4 DISCUSSION
Langsat leaf extract was proven can be used as
bioreductor on silver nanoparticle synthesis. This
could happen because Langsat leaf extract contains
secondary metabolites that act as a reduction agent.
Phytochemical screening of Langsat leaf was done
previously by Mayanti et al. (2015), Yunus, Boddhi,
& Queljoe (2018), and Matsumoto et al. (2019). The
results showed Langsat leaf posses phenolic
compounds, saponin, and triterpenoid/steroid. The
phenolic compound on Langsat leaf has the potential
as metal salt reducer and agent to stabilize the
nanoparticles from agglomeration.
Pal, Rai, & Pandey (2019) explained reduction
and stabilization of silver ions by biomolecule
combination like protein, amino acid, polysaccharide,
secondary metabolites, and vitamin that plant has,
will serve as the easiest and cheapest way to
synthesize NP. Generally, plant leaf has high
polyphenol level. The phenolic compound has
hydroxyl and ketonic group that has the ability to
bond with metal and reduces metal salt and gives
stability from agglomeration. Kawas (2016)
described the process of secondary metabolites as a
reducer of silver nitrate is AgNO
3
will detach into
Ag+ and NO
3
- form and greatly influenced by
0,92
1,06
2,66
3,25
3,57
0
1
2
3
4
Day 0 Day 37 Day 44 Day 51 Day 58
Absorbance (AU)
Antibacterial Activity of Synthesized Silver Nanoparticle using Langsat Leaf Extract (Lansium domesticum var. pubescen Kooders et
Valeton) as Bioreductor against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus
301

temperature and light. During the process, it is
necessary to seal the beaker glass with a cover like
aluminum foil to make the beaker dark. The plant
extract also gives proteins and enzymes to AgNO
3
solution in which the Ag+ ion will combine with
enzymes to make enzyme-substrate complex. The
enzymes released from plant extract work on silver
ion and release nanoparticles as the product (Prasad,
2014). This formation is not just through covalent
bond, but also because of the existence of protein
attraction through hydrogen bond, electrostatic, or
other supramolecular interactions (Ballottin et al.,
2016).
Characterization of synthesized nanoparticles is
one of the important steps. This has to be done in
order to ensure the formation of nanoparticles. Noah
(2019) explained that AgNP shows strong absorbance
band and specific colors on its solution. The
synthesized LL-AgNP color is yellowish and slightly
turbid. The color variation occured because of the
variety of phytochemical compounds on plant extract
that used for the AgNP synthesize process (Ovais,
2016). Moreover, the variety of shape and size of the
formed AgNP also will contribute to the AgNP
solution color diverseness (González, Noguez,
Beránek, & Barnard, 2014). Beside color observation,
a more quantitative test needs to be done as part of NP
characterization. One of the methods us
spectrophotometer Uv-Vis. The LL-AgNP shows a
wavelength peak at λ 398 nm. According to Seifipour,
Nozari, & Pishkar (2020), AgNP that successfully
synthesized has a peak observed at around 370 nm -
500 nm. With this result, it can be considered that LL-
AgNP has formed.
Almost all AgNP is prone to agglomeration and it
is a commonly found phenomenon. Agglomeration is
a process when nanoparticles lose their nano
characteristic (Bae, Lee, Kim, Choi, & Yi, 2013).
Based on the finding result, one month after the LL-
AgNP was formed, agglomeration was observed.
AgNP stability can be monitored from time to time.
The wavelength will shift and it indicates the change
of absorbance spectrum on the UV-Vis area. Badiah,
Seedeh, Supriyanto, & Zaidan (2019) explained that
large surface tension force causes greater cohesion
force. This causes the interaction between AgNPs to
become greater as well. Over time, the particles will
become larger in size due to the formation of groups
amongst AgNPs.
Silver nanoparticles are stabler, more consistent in
size, and not toxic to human tissues compared to
silver in metal form. It affects the effectiveness of
AgNP as antibacterial (Nolan, 2018). AgNP can
penetrate to microbe cell wall easier because of its
smaller size than the microorganism (Siddiqi, Husen,
& Rao, 2018). Based on the obtained result, it is
known that synthesized LL-AgNP has potential as an
antibacterial agent against Escherichia coli and
Staphylococcus aureus. The LL-AgNP could inhibit
the growth of said bacteria.
The MIC and MBC assay showed that LL-AgNP
works better against Escherichia coli than
Staphylococcus aureus. In line with the result,
according to Qing et al. (2018), AgNP gives a
stronger effect on Gram-negative bacteria. One of the
theories that support this finding is because Gram-
negative bacteria have thinner peptidoglycan cell
walls, while Gram-positive bacteria have thicker cell
walls (Sizar & Unakal, 2020). Kailasa, Park, Rohit, &
Koduru (2019) also mentioned the amount of Ag+
ions that successfully penetrate into the Gram-
positive bacteria is fewer. It shows that there is a
strong interaction between AgNP and Gram-negative
bacteria.
The specific mechanism of AgNP for each
bacteria is still under investigation. Generally, AgNP
mechanisms as antibacterial are similar, both on
Gram-negative and Gram-positive (Baptista et al.,
2018). The observed mechanisms are inhibition of
cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, and nucleic acid
synthesis. Furthermore, damage on the cell surface
and respiration chin are also known.
There are several mechanisms of synthesized
AgNP using plant extract as the reducer that has been
explained by experts. The AgNP will release silver
ions (Ag+) and it will directly penetrate into the
bacteria cell wall (Rajeshkumar & Bharath, 2017).
Wong and Liu (2010) in Durán et al. (2016) also
explained that AgNP has wide surface area to come
into contact with bacteria. This makes AgNP possible
to adhere to the cell membrane and easily get into the
bacteria. The released Ag+ ion has strong
antibacterial properties. The Ag+ ion will interact
with the bacteria cell membrane and cell wall
components. This is one of the crucial mechanisms of
AgNP toxicity towards bacteria (Liu et al., 2020).
Silver nanoparticles have positive charge. It will
cause the electrostatic attraction between AgNP and
bacteria cell membrane that has negative charge. The
bacteria cell wall has negative charge because of
electron release that is caused by catalysis activity on
cell respiration. This charge interaction will help
AgNP to attach to the cell membrane (Abbaszadegan
et al., 2015). Hence, the antibacterial effect could be
enhanced by altering the surface charge of AgNP so
that stronger obstruction will be obtained (Mandal et
al., 2016).
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
302

5 CONCLUSIONS
Nanoparticles were successfully synthesized using
AgNO
3
and Langsat leaf extract with the recorded
wavelength peak at 398 nm. The approximate size of
the LL-AgNP is 44 nm. Based on the results that are
obtained, we conclude that the LL-AgNP shows
antibacterial activity against Gram-negative bacteria
Escherichia coli and Gram-positive bacteria
Staphylococcus aureus. The LL-AgNP MIC is
observed at 6.25% on Escherichia coli and 25% on
Staphylococcus aureus. The MBC is observed at 25%
on Escherichia coli but no bactericidal activity is
observed on Staphylococcus aureus. Further tests
with different strains, concentrations, and methods
are suggested to add more diversity from the findings
of this study.
REFERENCES
Abbaszadegan, A., Ghahramani, Y., Gholami, A.,
Hemmateenejad, B., Dorostkar, S., Nabavizadeh, M., &
Sharghi, H. (2015). The Effect of Charge at the Surface
of Silver Nanoparticles on Antimicrobial Activity
against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria: A
Preliminary Study. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2015,
720654. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/720654
Amirjani, A., Firouzi, F., & Haghshenas, D. F. (2020).
Predicting the Size of Silver Nanoparticles from Their
Optical Properties. Plasmonics.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01121-x
Badiah, H. I., Seedeh, F., Supriyanto, G., & Zaidan, A. H.
(2019). Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and the
Development in Analysis Method. IOP Conference
Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 217(1).
https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/217/1/012005
Bae, E., Lee, B. C., Kim, Y., Choi, K., & Yi, J. (2013).
Effect of agglomeration of silver nanoparticle on
nanotoxicity depression. Korean Journal of Chemical
Engineering, 30(2), 364–368.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-012-0155-4
Ballottin, D., Fulaz, S., Souza, M. L., Corio, P., Rodrigues,
A. G., Souza, A. O., … Tasic, L. (2016). Elucidating
Protein Involvement in the Stabilization of the Biogenic
Silver Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Research Letters,
11(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1538-y
Baptista, P. V., McCusker, M. P., Carvalho, A., Ferreira, D.
A., Mohan, N. M., Martins, M., & Fernandes, A. R.
(2018). Nano-strategies to fight multidrug resistant
bacteria-"A Battle of the Titans". Frontiers in
Microbiology, 9(JUL), 1–26.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01441
Castiglioni, S., Cazzaniga, A., Locatelli, L., & Maier, J. A.
M. (2017). Silver nanoparticles in orthopedic
applications: New insights on their effects on
osteogenic cells. Nanomaterials, 7(6).
https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7060124
Durán, N., Durán, M., de Jesus, M. B., Seabra, A. B.,
Fávaro, W. J., & Nakazato, G. (2016). Silver
nanoparticles: A new view on mechanistic aspects on
antimicrobial activity. Nanomedicine:
Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine, 12(3), 789–
799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2015.11.016
Ganesan, P., Reegan, A. D., David, R. H. A., Gandhi, M.
R., Paulraj, M. G., Al-Dhabi, N. A., & Ignacimuthu, S.
(2017). Antimicrobial activity of some actinomycetes
from Western Ghats of Tamil Nadu, India. Alexandria
Journal of Medicine, 53(2), 101–110.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajme.2016.03.004
González, A. L., Noguez, C., Beránek, J., & Barnard, A. S.
(2014). Size, Shape, Stability, and Color of Plasmonic
Silver Nanoparticles. The Journal of Physical
Chemistry C, 118(17), 9128–9136.
https://doi.org/doi:10.1021/jp5018168
Kailasa, S. K., Park, T.-J., Rohit, J. V., & Koduru, J. R.
(2019). Antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles.
In Nanoparticles in Pharmacotherapy.
https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-816504-1.00009-0
Kawas, H. (2016). How Plant Extract Affect and Reduce
AgNO3? Retrieved February 21, 2020, from Reserach
Gate website:
https://www.researchgate.net/post/how_plant_extract_
affect_and_reduce_AgNO3
Khodashenas, B., & Ghorbani, H. R. (2019). Synthesis of
silver nanoparticles with different shapes. Arabian
Journal of Chemistry, 12(8), 1823–1838.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.12.014
Linlin, W., Chen, H., & Longquan, S. (2017). The
antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: present situation
and prospects for the future. International Journal of
Nanomedicine, 12, 1227–1249.
https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S121956
Liu, X., Cai, J., Chen, H., Zhong, Q., Hou, Y., Chen, W., &
Chen, W. (2020). Antibacterial activity and mechanism
of linalool against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbial
Pathogenesis, 141, 1469–1487.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2020.103980
Mandal, D., Kumar Dash, S., Das, B., Chattopadhyay, S.,
Ghosh, T., Das, D., & Roy, S. (2016). Bio-fabricated
silver nanoparticles preferentially targets Gram positive
depending on cell surface charge. Biomedicine &
Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine &
Pharmacotherapie, 83, 548–558.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.07.011
Noah, N. (2019). Green synthesis: Characterization and
application of silver and gold nanoparticles. In Green
Synthesis, Characterization and Applications of
Nanoparticles. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-
102579-6.00006-x
Nolan, R. (2018). Colloidal Silver vs Nano Silver.
Retrieved August 14, 2020, from
https://elementasilver.com/blog/colloidal-silver-vs-
nano-silver/
Ovais, M. (2016). The Reason for Green Colour of Silver
Nanoparticle. Retrieved February 17, 2020, from
Antibacterial Activity of Synthesized Silver Nanoparticle using Langsat Leaf Extract (Lansium domesticum var. pubescen Kooders et
Valeton) as Bioreductor against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus
303

Reserach Gate website:
https://www.researchgate.net/post/What_is_the_reason
_for_green_colour_of_silver_nanoparticle
Pal, G., Rai, P., & Pandey, A. (2019). Green synthesis of
nanoparticles: A greener approach for a cleaner future.
In Green Synthesis, Characterization and Applications
of Nanoparticles. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-
102579-6.00001-0
Prasad, R. (2014). Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles in
Photosynthetic Plants. Journal of Nanoparticles, 2014,
1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/963961
Qing, Y., Cheng, L., Li, R., Liu, G., Zhang, Y., Tang, X.,
… Qin, Y. (2018). Potential antibacterial mechanism of
silver nanoparticles and the optimization of orthopedic
implants by advanced modification technologies.
International Journal of Nanomedicine, 13, 3311–
3327. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S165125
Rajeshkumar, S., & Bharath, L. V. (2017). Mechanism of
plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles – A
review on biomolecules involved, characterisation and
antibacterial activity. Chemico-Biological Interactions,
273, 219–227.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2017.06.019
Seifipour, R., Nozari, M., & Pishkar, L. (2020). Green
Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles using Tragopogon
Collinus Leaf Extract and Study of Their Antibacterial
Effects. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic
Polymers and Materials, (0123456789).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01441-9
Siddiqi, K. S., Husen, A., & Rao, R. A. K. (2018). A review
on biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and their
biocidal properties. Journal of Nanobiotechnology,
16(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-018-0334-5
Sizar, O., & Unakal, C. G. (2020). Gram Positive Bacteria.
Retrieved July 20, 2020, from StatPearls Publishing
website:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470553/
Velusamy, P., Kumar, G. V., Jeyanthi, V., Das, J., &
Pachaiappan, R. (2016). Bio-inspired green
nanoparticles: Synthesis, mechanism, and antibacterial
application. Toxicological Research, 32(2), 95–102.
https://doi.org/10.5487/TR.2016.32.2.095
Ventola, C. L. (2015). The antibiotic resistance crisis:
causes and threats. P&T Journal, 40(4), 277–283.
https://doi.org/Article
World Health Organization. (2014). Antimicrobial
resistance. In Antimicrobial Resistance Global Report
on Surveillance. Retrieved from
https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/11264
2/9789241564748_eng.pdf;jsessionid=21594BEE3EF
1AEF1C7D2D04FB31FD78C?sequence=1
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
304
