
Green Synthesis of 4-Hydroxy-4-Methoxychalcone by Grinding
Techniques
Elfi Susanti V. H. and Sri Mulyani
The Chemical Education Study Program of FKIP Universitas Sebelas Maret, Surakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Green Synthesis, 4-Hydroxy-4-Methoxychalcone, Grinding Techniques
Abstract: The synthesis of the 4-hydroxy-4-methoxychalcone has been synthesized by grinding techniques. This
compound was synthesized by reacting 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde with 4-methoxy acetophenone using NaOH
catalyst in a mortar for 30 minutes at room temperature. The reaction product was monitored by TLC and then
recrystallized from ethanol, and golden yellow crystals were obtained. Characterization of synthesized
compounds with
1
H-NMR and
13
C-NMR.
1
H-NMR (CDCl3, δ ppm): 3,86 (3H, s, H-OCH
3
), 6.86 (2H, d, J=10,
Ar-H), 7,07 (2H, d, J=5 Hz, Ar-H), 7,66 (1H, d, J=15, H-Cα), 7,75 (1H, d, J=7, H-Cβ), 7,73 (2H, d, Ar-H),
8,14 (2H, d, J=9 Hz, Ar-H), 10,09 (1H, s, UH-OH).
13
CNMR (CDCl
3
, δ, ppm): 187,28 (C=O), 163.04 (C4),
160,01 (C4), 143,70 (C=C-β), 130,95 (C2 dan C6), 130,82 (C2 dan C6), 130,77 (C1), 125,98 (C1), 118,44
(C=C-α), 115,84 (C3 dan C5), 113,99 (C3 dan C5), 55,57 (-OCH
3
). The results of
1
H-NMR and
13
C-NMR
characterization showed that the synthesized compound had been formed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Chalcone (1,3-diphenyl propenone) is an intermediate
agent in synthesising various heterocyclic compounds
(Patil, et al., 2009). Chalcone can be synthesized
using Claisen-Schmidt condensation, a condensation
reaction between aromatic aldehydes and aromatic
ketones to form α, β-unsaturated ketones. Claisen-
Schmidt condensation can occur in an acid or base.
The use of acid catalysts in condensation reactions
(e.g., HCl, BF
3
, B
2
O
3
) generally gives low yields (10-
40%) (Patil, et al., 2009). The KOH catalyst in the
synthesis reaction of chalcone through the Claisen-
Schmidt reaction obtained an 88-94% yield (Zangade,
et al., 2011). The use of Ba(OH)
2
in the synthesis of
chalcone derivatives was obtained with a yield of 88-
98% (Rateb, Zohdi, 2009), and the NaOH catalyst
obtained a yield of 90-96% (Mogilaiah, et al., 2010).
The Claisen-Schmidt reaction in the synthesis of
chalcone with NaOH catalyst gave better results
(yield 93-98%) than using KOH, NaOAc, and
NH
4
OAc (yield 81-85%) (Rahman, et al., 2012).
Moreover, the Claisen-Schmidt reaction is essential in
synthetic organic chemistry. The synthesis of
chalcone through the Claisen-Schmidt condensation
reaction has been widely used (Prasad, et al., 2008).
Susanti (Susanti, et al., 2012 and 2014) have
synthesized hydroxy chalcone from hydroxy
acetophenone and methoxy benzaldehyde through
conventional Claisen-Schmidt condensation using
ethanol solvent. Their results revealed that the
formation of hydroxy chalcone compounds requires a
strong base (50%), a long reaction time (24 hours),
and a low yield (40-70%). Thus, this current research
will develop a new chalcone synthesis design through
the green chemistry approach, namely solvent-free
synthesis using grinding techniques (Susanti, et al.,
2014).
The grinding technique in synthesis is the
development of chalcone synthesis, which is very
profitable because it uses very simple equipment,
namely pestle and mortar. Chalcone synthesis was
modified using grinding techniques to synthesize
chalcone compounds from 2-acetyl-1-naphthol and
benzaldehyde (Zangade, et al., 2011). Meanwhile,
synthesized chalcone with this technique running
without solvent, short reaction time (4-8 minutes),
and high yields (84-95%). Grinding techniques have
also been used to synthesize chalcone from
cyclohexanone and benzaldehyde, giving 96-98%
yield. Susanti have also synthesized three derivatives
of hydroxy chalcone compounds using this technique
and yielded 70-84% (Susanti, et al., 2014). However,
this grinding technique has not been performed to
V. H., E. and Mulyani, S.
Green Synthesis of 4-Hydroxy-4’-Methoxychalcone by Grinding Techniques.
DOI: 10.5220/0010801900003317
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Science, Technology, and Environment (ICoSTE 2020) - Green Technology and Science to Face a New Century, pages 167-170
ISBN: 978-989-758-545-6
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
167
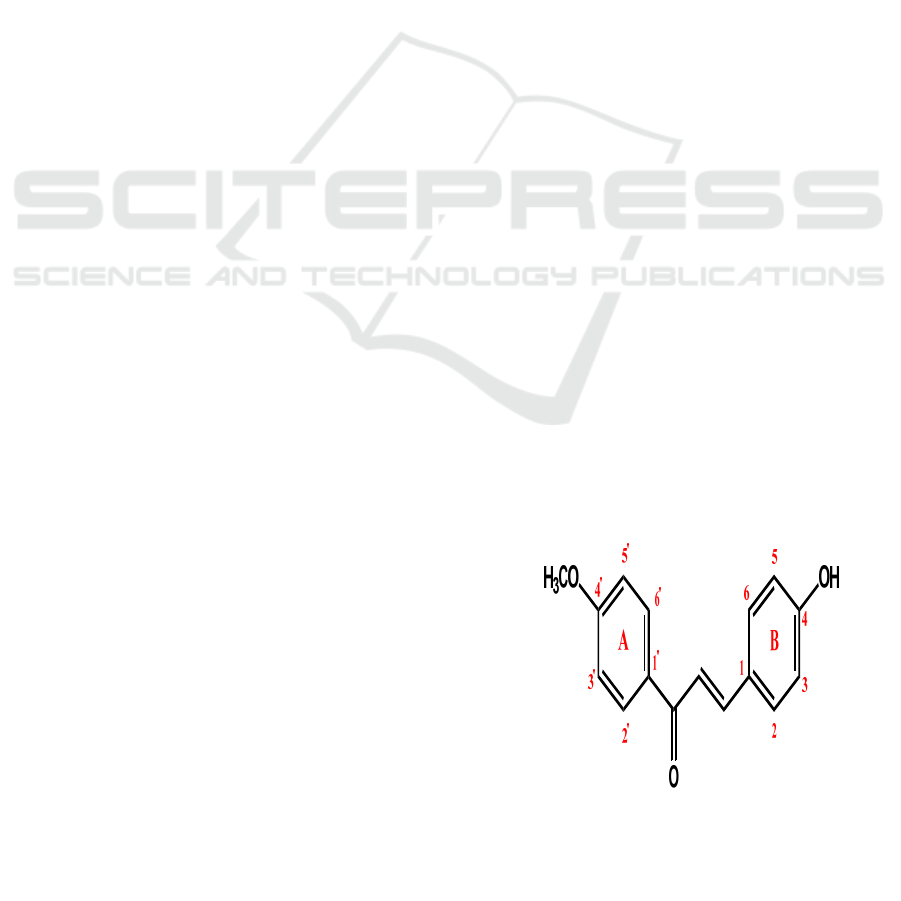
synthesize the chalcone derivative of 4-
methoxyacetophenone with substituted
benzaldehyde. In this study, a new chalcone
derivative of 4-methoxyacetophenone and 4-
hydroxybenzaldehyde will be synthesized.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
2.1 Materials
The materials used in this study had analytical grade
quality from E-Merck, including 4-
hydroxybenzaldehyde, 4-methoxyacetophenone,
sodium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid,
acetone, ethyl acetate, ethanol, n-hexane, chloroform,
methanol, dichloromethane, and anhydrous sodium
sulfate.
2.2 Instrumentation
Instruments in this study were laboratory glassware,
analytical scales (Libror EB330 Shimadzu), magnetic
stirrer, chromatography column, reflux device,
desiccator, magnetic stirring plate, Buchi evaporator,
254 nm UV lamp, Whatman paper no 1, test tube,
callipers, magnetic resonance spectrometer Proton
core (1H-NMR, 500 Mhz) and carbon (13C-NMR,
125 MHz), and JEOL-MY500.
2.3 Procedure
The chalcone compound was synthesized by grinding
4-methoxyacetophenone with 4-bromobenzaldehyde
in a mortar and pestle at room temperature for several
minutes. The completeness of the reaction was
monitored by Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC).
The reaction mixture was then diluted with cold
water, neutralized with a cold solution of HCl 10%
(v/v), then filtered. Purification was carried out by
employing recrystallization. The synthetic products
were then characterized using
1
H- and
13
C-NMR
spectrometers.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Synthesis of Chalcone by Grinding
Techniques
The synthesis of chalcone compounds using grinding
techniques was carried out by grinding 4-
methoxyacetophenone, 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, and
solid NaOH in mortar. This grinding process was
performed at room temperature for 30 minutes. In this
process, friction energy was generated from local heat
due to collisions between reactants, which accelerate
the reaction to form products. The monitoring of the
results of the synthesized compounds was conducted
using Thin Layer Chromatography. The synthesis
results in yellow crystals as much as 0.8 g (32.5%
yield) were obtained after the recrystallization
process using ethanol. Characterization of chalcone
compounds was done using a
1
H-NMR spectrometer.
The
1
H-NMR spectrum of the NMR chalcone
compounds, as presented in Figure 1, showed 14
protons in the synthesized compound. The absorption
peak at the chemical shift (δ) of 3.85 ppm was thought
to be a proton signal from the methoxy group with a
singlet and 3-integrated appearance. The singlet
appearance indicates that no neighboring protons
were coupling these protons. The absorption at 6.84
ppm chemical shift with a doublet's appearance was a
signal from the protons from C3 and C5 in the
aromatic ring B. This doublet appearance occurred
because the protons in C3 and C5 were one
neighbouring proton.
The chemical shift at 7.06 ppm was the proton
signal owned by C3 'and C5' (aromatic ring A). This
assumption was strengthened because the peak at 7.06
ppm had a doublet appearance, revealing that the
protons C3' and C5' had the same environment, one
neighbouring proton. A peak with a similar
appearance also occurred at the chemical shift of 7.73
ppm (the protons in C2 and C6) and 8,14 ppm (the
protons in C2' and C6'). Olefin protons of α, β-ketone
unsaturated were observed at the chemical shift of
7.64 and 7.75 ppm with coupling constants J = 9 and
15 Hz, respectively. It revealed that the chalcone
formed had a trans structure. The peak at 10.09 ppm
has a singlet appearance which is the unprotected
absorption of hydroxy protons due to the induction of
the electronegative O atom. The results of chalcone
1
H-NMR spectral analysis are presented in Table 1.
Figure 1a.
1
H -NMR spectrum of chalcone
ICoSTE 2020 - the International Conference on Science, Technology, and Environment (ICoSTE)
168
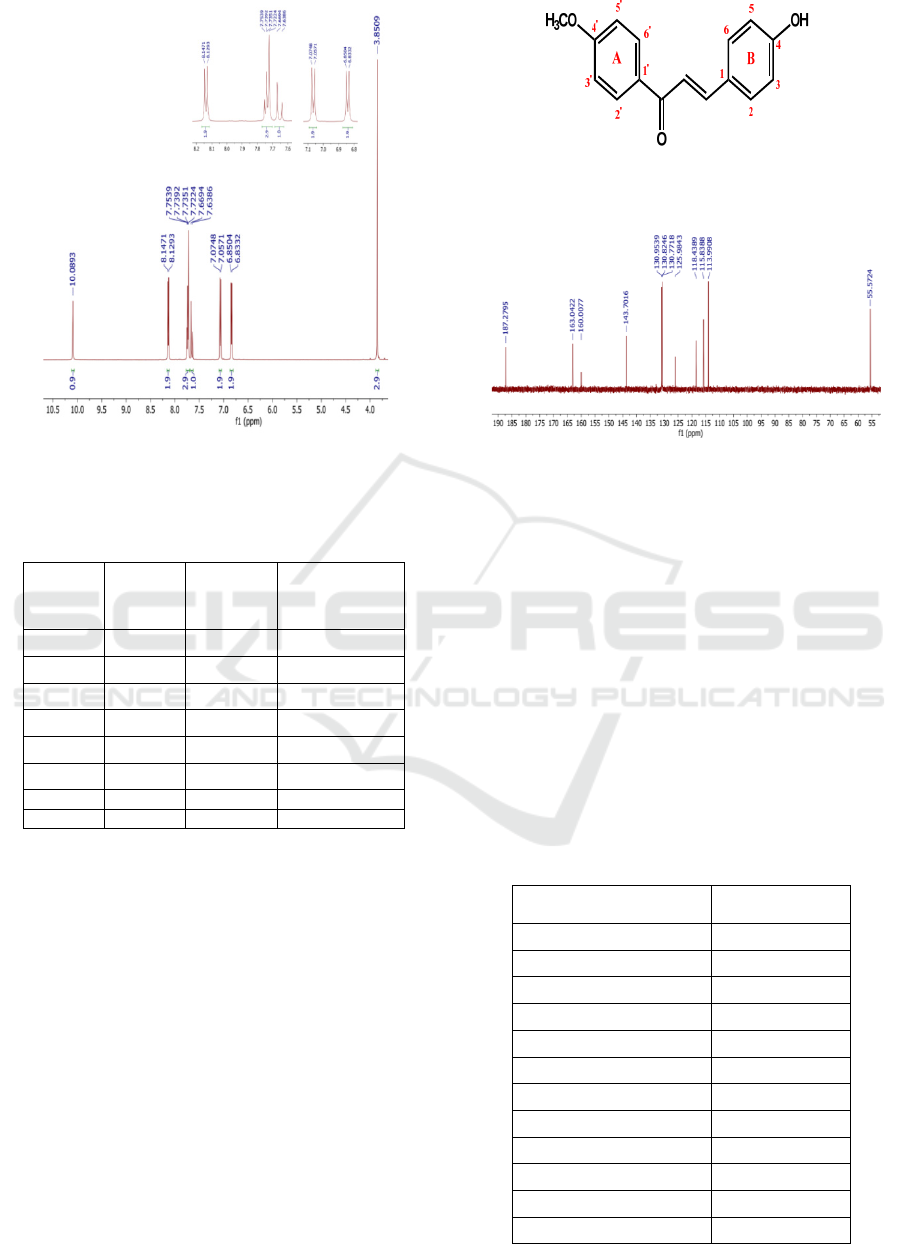
Figure 1b.
1
H -NMR spectrum of chalcone
Table 1. Results of the
1
H -NMR spectral analysis of
chalcone 1
The structural characterization of the synthesized
compounds was further strengthened by the
13
C-NMR
analysis (Figure 2), which exhibited 12 signals and
indicated the presence of 12 different carbons. The
absorption for methoxy carbon was observed at a
chemical shift of 55.65 ppm. The carbonyl band
(C=O) was shown at a far chemical shift (deshielding
area), at chemical shift 187.28 ppm. It is following
Mostaher who asserted that the carbonyl carbon from
chalcone usually appears in the area of 170-194.6
ppm (Mostahar et al., 2007). The carbon is bonded
directly to the O atom, which has a large
electronegativity so that the electrons around the C
atom increasingly unprotect the nucleus of the C atom
due to being attracted by the O atom.
Figure 2a.
13
C-NMR Spectrum of chalcone
Figure 2b.
13
C-NMR Spectrum of chalcone
Carbon with the same environment will appear
as one peak in the 113.9 ppm chemical shift, which is
the absorption of C3 dan C5. The same thing
happened to absorption at 115.8 ppm (C3 and C5),
130.8 ppm (C2 and C6), and 114,09 (C2 and C6).
The absorption of Cα was observed at a chemical shift
of 119.4 ppm, while Cβ was at 143.7 ppm. The C-β
peak appeared more downfield than the C-α atom. It
is aligned with Mostahar et al. research (2007), which
uncovered that the C-β absorption of chalcone
compounds appeared in a more remarkable chemical
shift than C-α. In detail, the results of the chalcone
13
C-NMR spectral analysis are presented in Table 2.
Table 2. Results of the
13
C-NMR spectral analysis of
chalcone
Chemical
Shift δ
(ppm)
Appea
rance
Coupling
Constants
J (Hz)
Number and
Type of Proton
3,86 singlet 3H, -OCH
3
6,84
doublet
10
2H at C3 & C5
7,07
doublet
5
2H at C3' & C5'
7,66
doublet
15
1H at C-α
7,73
doublet
7,5
2H at C2 & C6
7,75
doublet
7
1H at C-β
8,14 double
t
9 2H at C2' & C6'
10,09
s
ingle
t
1H at OH
Chemical Shift δ (
pp
m) T
yp
e of Carbon
187,28 C=O
163,04 C4'
160,01 C4
143,70 C-β
130,95 C2' dan C6'
130,82 C2 dan C6
130,77 C1'
125,98 C1
118,44 C-α
115,84 C3 dan C5
113,99 C3' dan C5'
55,57 C-OCH
3
Green Synthesis of 4-Hydroxy-4’-Methoxychalcone by Grinding Techniques
169

Based on the
1
H- and
13
C-NMR analysis results
that have been carried out, it could be stated that
chalcone, namely 4-hydroxy-4-methoxychalcone,
has been formed from the results of the Claisen-
Schmidt condensation process between 4-
methoxyacetophenone and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde.
The synthesized product was a yellow crystal. The
chalcone formation reaction was assumed to follow
the condensation aldol reaction mechanism. The
reaction started from an acid-base reaction, where the
base took a proton from the α carbon of 4-
methoxyacetophenone to form an enolate ion, which
stabilized by resonance. The nucleophilic addition of
carbanions from 4-methoxyacetophenone then
occurred to the carbonyl carbon of 4-
bromobenzaldehyde, followed by releasing water
molecules with acids' help form double bonds (Figure
3).
Synthesis of chalcone using grinding techniques
is a strategic breakthrough because it considers the
principle of green chemistry, namely reducing the use
of solvents in the synthesis process. Solvents in the
synthesis of many compounds are toxic and cause
environmental problems. Therefore, it is vital to
develop a method of compound synthesis without a
solvent. In the grinding process, all reactants are
crushed in a mortar. The collision between the
reactants occurs and creates friction energy from local
heat, accelerating the reaction to form chalcones.
Figure 3. Reaction Mechanism in Chalcone Synthesis
4 CONCLUSION
The development of environmentally friendly
synthesis methods needs to be developed
continuously. The use of grinding techniques in
chalcone synthesis is a route with great potential to be
developed. Researchers have successfully synthesised
4-hydroxy-4'-methoxy-chalcone by reacting 4-
methoxyacetophenone and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde
through a green chemistry approach with grinding
techniques. The study of this compound application
as an active antibacterial compound is ongoing.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I would like to thank the Universitas Sebelas Maret,
for provided funding for implementing this research.
REFERENCES
Manage, S., Singh, H.P., Gupta D., and Moorthy H.R.,
2007, Synthesis and Characterization of Some
Chalcone Derivatives, Trend Applied Sci. Res., 2, 52-
56.
Mogilaiah, K., Swami, T.K., Chandra, A.V., Srivani, N.,
and Vidya, K., 2010, Claisen Schmidt Condensation
under Solvent-Free Conditions, Indian J. Chem., 49B,
382-385.
Patil, C.B., Mahajan S.K., and Katti, S.A., 2009, Chalcone:
A Versatile Molecule, J. Pharm. Sci. & Res., 1(3), 11-
22.
Prasad, Y. R., Lakshmana, A. R., and Rambabu, R., 2008,
Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Some
Chalcone Derivatives, E-J. Chem., 5(3), 461-466.
Rahman, M. A. F. M., Ali, R., Jahng, Y., and Kadi, A. A.,
2012, A Facile Solvent Free Claisen-Schmidt
Reaction: Synthesis of α,α′-bis-(Substituted-
benzylidene) cycloalkanones and α,α′-bis-
(Substituted-alkylidene)cycloalkanones, Molecules,
17, 571-583.
Rateb, N.M., Zohdi, H.F., 2009, Atom-Efficient, Solvent
Free, Green Synthesis of Chalcone by grinding,
Synthetic Communications, 39, 2789-2794.
Salwar, Y.S., Sayyed, M. A., Mokle, S.S., Zanwar, P.R.,
and Vibhute, Y. B., 2009, Synthesis and Insect
Antifeedan Activity of Some New Chalcones Against
Phenacocus Solenopsis, World J. Chem., 4(2), 123-
126.
Susanti, E.V.H., Matsjeh, S., Wahyuningsih, T.D., Mustofa,
and Redjeki, T., 2014, Improved Synthesis Of 2',6'-
Dihydroxy-3,4-Dimethoxy Chalcone By Grinding
Technique To Synthesize 5-Hydroxy-3',4'-Dimethoxy
Flavone, Indo. J. Chem., 4 (2), 174 – 178.
Susanti, E.V.H., Matsjeh, S., Wahyuningsih, T.D., Mustofa,
and Redjeki, T., 2014, Syntheses And Antioxidant
Activities Of Some Hydroxy Dimethoxy Chalcone
Derivatives, Indonesian J. Pharm. 25 17–24.
Susanti, E.V.H., Matsjeh, S., Wahyuningsih, T.D., Mustofa,
and Redjeki, T., 2012, Synthesis, Characterization
And Antioxidant Activity of 7-Hydroxy-3',4'-
Dimethoxyflavone , Indo. J. Chem., 12(2), 146-151.
Zangade, S., Mokle, S., Vibhute, A., Vibhute, Y., 2011, An
Efficient and Operationally Simple Synthesis of Some
New Chalcones by Using Grinding Technique, Chem.
Sci. J., 13, 1-6.
ICoSTE 2020 - the International Conference on Science, Technology, and Environment (ICoSTE)
170
