
The Necessity and Pitfall of Augmentation in Deep Learning:
Observations During a Case Study in Triplet Learning for Coin Images
Daniel Soukup
AIT Austrian Institute of Technology GmbH, Center for Vision, Automation & Control, Vienna, Austria
Keywords:
Deep Embedding Learning, Triplet Learning, Augmentation, Interpolation, Novelty-aware Classification.
Abstract:
We conducted a case study on a subset of the MUSCLE CIS image benchmark of modern coins with the goal
to assess the potential of deep embedding learning for generating representative CNN feature vectors of coin
images, which are clustered class by class. In the course of training our models (CNN), we applied algorithmic
rotational augmentation to the coin images to enforce rotational invariance. While augmentation is a usual
procedure for regularizing deep learning models towards more geometric invariance, exactly that procedure
revealed an interesting yet precarious pitfall in deep embedding learning: its susceptibility to interpolation
errors. That interpolation bias results in distorted and ambiguous representation clusters of coin classes in the
feature space, jeopardizing classification capabilities.
1 INTRODUCTION
Image recognition of modern coins is an interesting
industrial task. It is a many-class problem with hun-
dreds of different currencies, thousands of coin de-
nominations, each coin with two faces, various types,
and versions. The so-called dies on the coin faces
with their stamped reliefs contain the most charac-
teristic patterns for recognizing a coin type. How-
ever, due to wear and soiling, those can exhibit con-
siderable intra-class appearance variations (Fig. 1).
On the other hand, modern coins are all perfectly
produced metal discs with mostly circular contours
which entails a quite low inter-class shape variation.
Ancient coins are different in this regard as they con-
tain more geometrical intra-class variations. They
have been specifically treated providing support for
the management and safety of cultural heritage (Za-
harieva et al., 2007; Huber-M
¨
ork et al., 2008; Kampel
et al., 2009; Huber-M
¨
ork et al., 2010). (N
¨
olle et al.,
2003) presented a coin recognition and sorting system
for modern coins, which could handle hundreds of
classes. Moreover, from their efforts, N
¨
olle and Han-
bury extracted a comprehensive coin image database,
the MUSCLE Coin Images Seibersdorf (CIS) bench-
mark (N
¨
olle and Hanbury, 2006) (Fig. 1). That data
set was used for further efforts in image classifica-
tion of modern coins, e.g. (Reisert et al., 2006; Reisert
et al., 2007; N
¨
olle et al., 2006). A good overview over
coin classification and identification in the pre-deep-
learning era is given by (Huber-M
¨
ork et al., 2012).
For image classification it is essential to determine
representative features derived from those images. In
conventional image processing and computer vision,
such features were e.g. Fourier transforms (N
¨
olle
et al., 2003), Eigen images (Huber-M
¨
ork et al., 2005),
or SIFT (Lowe, 2004). Nowadays, usually a CNN is
trained, which implicitly comes up with relevant fea-
tures directly from the image data.
Such end-to-end CNN classifiers perform well in
the classification task itself. However, these methods
have no reliable mechanism to be novelty-aware, i.e.
recognizing when an object class is presented which
was not part of the training set. Novelty-awareness
is crucial for a coin classification system, since there
are so many coin types in a potential real-world ap-
plication and the likelihood of being presented a coin
type which has not been trained is high. Recognizing
such an incident would increase a coin classification
system’s reliability. End-to-end CNN classifiers are
not appropriate in that aspect. Implementing novelty-
awareness requires a different (i.e. distance-based)
classification mechanism.
Deep embedding learning provides those tools to
enforce the generation of advantageous class-wise,
distance-based data clusters in the feature space. We
were inspired by FaceNet (Schroff et al., 2015).
There, embeddings of face images in the feature space
were trained with the so-called triplet loss ((Chechik
et al., 2010); cmp. Sec. 4.1). Based on such fea-
Soukup, D.
The Necessity and Pitfall of Augmentation in Deep Learning: Observations During a Case Study in Triplet Learning for Coin Images.
DOI: 10.5220/0008910303870394
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM 2020), pages 387-394
ISBN: 978-989-758-397-1; ISSN: 2184-4313
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
387
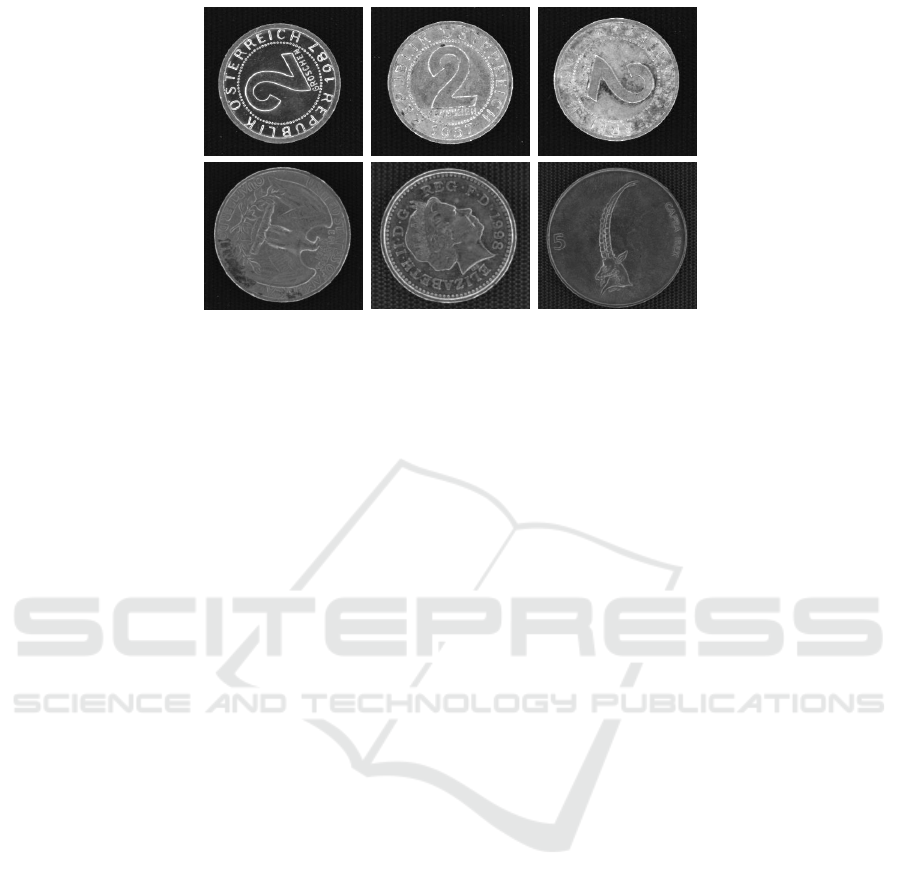
a b c
d
e f
Figure 1: Cropped example coins from MUSCLE CIS database. Top row: strong effects of wear and soiling within coin
classes. Bottom row: various coin classes showing effects of database inherent image pre-processing, e.g. visible conveyor
belt structure.
ture embeddings generated from face images, a sim-
ple person recognition problem could be realized by
kNN classification in that feature space. Meanwhile,
a lot of effort has been put into elaborating on that ba-
sic concept, all aiming to improve achieved clustering
properties, e.g. (Wang et al., 2017; Snell et al., 2017;
Yang et al., 2018; Gosh et al., 2019).
We initiated a case study on coin images from the
MUSCLE CIS database to fathom the feasibility of
a novelty-aware classification system by using triplet
learning. The MUSCLE CIS coin images had been
acquired in arbitrary angles and the available data per
class often only contain a handful of those randomly
rotated samples. Thus, we had to use rotational data
augmentation during training to enforce rotational in-
variance. While that is common practice in training
machine learning systems, we encountered a critical
pitfall, potentially caused by an improper choice of
interpolation method for image augmentation. In this
work, we solely focus on presenting and discussing
that observed impact of interpolation methods during
data augmentation. The classification system itself is
only sketched to clarify the role of the feature space.
The crucial point is that an unwise choice of the
interpolation method for augmentation has distorting
effects on the underlying data distributions. Since
augmentation only takes place during training, only
the training images would be affected. In the in-
ference phase, one would operate on original im-
ages. If they were from a different distribution than
the training images, those deviations would perpetu-
ate through the CNN to the feature space, ultimately
causing diminished classification accuracies.
We begin with a description of the used data set in
Sec. 2, emphasize the necessity for image augmenta-
tion in Sec. 3, and shortly explain the core idea of the
coin classification system in Sec. 4. After setting the
ground, we detail the experiments targeting to high-
light the effects of interpolation methods on the distri-
bution of feature vectors (Sec. 5). Finally, we discuss
the results and draw conclusion in Sec. 6.
2 COIN DATA SAMPLE
In 2003 a coin sorting device called Dagobert was
built at ARC Seibersdorf research GmbH, Aus-
tria (N
¨
olle et al., 2003). The coins which originate
from far more than 100 countries were sorted by
Dagobert within two years. From those data, the Coin
Images Seibersdorf (CIS) - Benchmark has been de-
veloped as a part of the MUSCLE benchmarking ini-
tiative (N
¨
olle and Hanbury, 2006). It contains 693
coin types for training and testing. Each coin is rep-
resented by two 640 × 576 pixel images, whereas of-
ten the conveyor belt structure is clearly visible in the
background.
For deep learning, multiple images per class are
required. So, we had to restrict ourselves solely to
the classes with sufficient samples and treated each
coin side as an individual coin class. We collected
275 coin classes with at least 15 sample images, 10
for training and at least 5 remaining samples to vali-
date / test, which is still a rather scarce class represen-
tation. All together, we had 2750 training and 5478
test images. The coins were cropped and rescaled to
256 × 256 pixels.While cropping eliminates the de-
ceptive background, it focuses the neural networks’
attention to the coins’ pure die patterns. Moreover,
we normalized the images by mean and standard de-
viation and set all background pixels to zero.
ICPRAM 2020 - 9th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
388

3 DATA AUGMENTATION IS
ESSENTIAL
With only 10 images per coin class, a lot of informa-
tion was missing in our training image set, most no-
tably the rotational variation. During acquisition, the
coins had been acquired at random rotation angles.
A machine learning model for handling coin images
must be rotational invariant, which is commonly ac-
complished by image augmentation. Each coin im-
age is algorithmically rotated by a random angle each
time it is touched during the training process. In this
way, rotation invariant feature codes are learned.
While rotational augmentation is a key step for
training a rotation invariant classification system, ex-
actly that is where we encountered a crucial pitfall: a
wrong choice of interpolation method causes a slight
distortion of the augmentation data w.r.t. the origi-
nal image data. In the inference phase, only unrotated
images would be processed. Eventually, that differ-
ence causes deviations in the feature space between
augmented and un-augmented images, which leads to
declined classification accuracies (see Sec. 5).
4 A NOVELTY-AWARE COIN
CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM
Our concept of a novelty-aware coin classification
system consists of two major parts:
• Feature model and
• Cluster model (in feature space).
The feature model (Sec. 4.1) is learned with triplet
learning to obtain an appropriate feature space, where
coins cluster together class by class, i.e. the similarity
of coin dies is reflected by the L2 distance of coin
images’ feature vectors in that feature space.
Based on those coin features, a cluster model
(Sec. 4.2) can be developed enabling distance-
based classification by measuring the distances w.r.t.
coin class clusters in that feature space. Novelty-
awareness is inherently achievable, as coin features of
not trained classes would comprise a significant larger
distance to their closest clusters than the cluster mem-
bers mutually have.
For both models, algorithmic rotational augmen-
tation of the training images is a critical ingredient,
which is required to ensure the entire system’s rota-
tional invariance.
4.1 Data-appropriate Feature Model
The triplet loss was introduced independently of neu-
ral networks (Chechik et al., 2010). We give a formu-
lation for the L
2
-norm, but any norm is applicable:
L
trip
2
=
∑
i
max{0, M −||a
i
− n
i
||
2
+ ||a
i
− p
i
||
2
}. (1)
Anchor
Negative
Positive
Anchor
Negative
Positive
LEARNING
Figure 2: Visualization borrowed from and caption freely
after (Schroff et al., 2015): the Triplet Loss minimizes the
distance between an anchor and a positive, both of the same
object (coin) class, and maximizes the distance between the
anchor and a negative of a different object (coin) class.
The sum in Equ. 1 is taken over a batch of triplets
(a
i
, p
i
, n
i
), where a
i
is the triplet’s anchor, i.e. a sam-
ple of a certain class. An anchor is compared to a
negative n
i
(a sample of a different class) and a pos-
itive p
i
(a different sample, but of the same class).
L
trip
2
shall be minimized, that means positives shall be
dragged nearer to the anchors, while negatives shall
be dragged away from them (Fig. 2). M serves as a
safety margin.
Since we aim to learn CNN features with opti-
mized triplet loss, we have to consider the CNN func-
tion in the formulation of Equ. 1. Let f
Ξ
: R
n
→ R
m
be
a function from the n-dim image space to the m-dim
feature space represented by a CNN with parameters
Ξ. Then the triplet loss is:
L
trip
2
=
∑
i
max{0, . . .
. .. M − || f
Ξ
(a
i
) − f
Ξ
(n
i
)||
2
+ || f
Ξ
(a
i
) − f
Ξ
(p
i
)||
2
},
(2)
with a
i
, n
i
, p
i
∈ R
n
, i.e. anchors, negatives, and pos-
itives being coin images. We found M = 1 to be an
optimal margin. As outlined in (Wang et al., 2017),
the features have to be L
2
-normalized for triplet learn-
ing ( f
Ξ
(x) ≡ 1). Thus we learn to project coin images
onto a unit hypersphere in the feature space in such a
way, that the coin images’ feature vectors cluster to-
gether class by class, where we found m = 256 to be
appropriate.
Note, as already argued in Sec. 3, we made exten-
sive use of image augmentation of all training images,
whenever they were used in the triplet training phase.
The Necessity and Pitfall of Augmentation in Deep Learning: Observations During a Case Study in Triplet Learning for Coin Images
389

4.2 Cluster Model in Feature Space
Eventually, the CNN has converged and coin images
are projected to the unit hypersphere in the feature
space, where they form clusters class by class. In
order to be able to actually perform classification in
that feature space, a cluster model must be developed.
Such a cluster model requires to have a description of
each coin class cluster, so that the similarity / dissim-
ilarity of a feature vector w.r.t. each class cluster can
be calculated.
In a first simple model, we decided to use Nearest
Centroid (NC) classification. For each cluster (each
coin class), we calculated the cluster’s center of grav-
ity as the cluster’s prototype. A coin image’s feature
would be assigned to the class of the cluster with the
closest cluster (class) prototype.
Naturally, the feature vectors of the training im-
ages have to be used to derive those cluster proto-
types for each coin class. Still, the computation of
the prototype should not only rely on those 10 origi-
nal training images per class. A good description of
the clusters’ shapes in the feature space should as well
take feature positions of rotated versions of the train-
ing images into account. That would make the de-
scriptions more explicit in terms of possible cluster
memberships. Hence, like for the training procedure
of the CNN, also for setting up the cluster model, aug-
mentation is required.
For a better cluster model, i.e. a better approx-
imation of the clusters’ shapes, we used probabilis-
tic Principle Components Analysis (PCA) (Tipping
and Bishop, 1999). There, PCA is formulated within
a maximum-likelihood framework, based on a spe-
cific form of a Gaussian latent variable model, which
leads to a well-defined mixture model for probabilis-
tic PCA. We used that method with local dimension-
ality reduction for cluster description in the feature
space. We found that by means of a 10D PCA la-
tent subspace of the triplet feature space, each cluster
could be modeled in a characteristic way.
5 EXPERIMENTS
To compare the effects of interpolation methods, we
trained three triplet CNNs
1
(Sec. 4.1), each with a dif-
1
All CNNs have the same VGG*-inspired (Simonyan
and Zisserman, 2014) architecture, i.e. 5 conv. blocks, each
block with 2 conv. layers with ReLU and batchnorm, each
block followed by spatial downsampling by 2 and doubling
the number of feature maps. Finally, one conv. layer pro-
jecting to the 256D triplet feature space. Processing was
performed with TensorFlow 1.13.1 (Abadi et al., 2015) on
ferent interpolation method for rotationally augment-
ing the training data (coin images), i.e. NEAREST
(neighbor), LINEAR (i.e. bilinear, from 2 × 2 neigh-
bor pixels), and BICUBIC (from 4 × 4 neighbor pix-
els) interpolations
2
. We refer to the corresponding
CNNs as
• NEAREST CNN,
• LINEAR CNN, and
• BICUBIC CNN.
As outlined in Sec. 4.2, we also need to use aug-
mented training data for obtaining a possibly rota-
tional invariant cluster model as basis for distance-
based classification in those triplet feature spaces.
Also for that second augmentation step, we applied
NEAREST (neighbor), LINEAR, and BICUBIC in-
terpolations, in fact for the feature spaces of each of
the 3 triplet CNNs. So that we obtained 9 different
cluster models to be compared. To ensure a fluid pre-
sentation, we introduce a naming convention of ab-
breviations to refer to the individual cluster models
in Tab. 1.
We performed two types of analyses in order to
compare the effects of interpolation methods in triplet
training and cluster modeling:
• assessing the quality of class by class train-
ing cluster separation in the features spaces
(Sec. 5.1), and
• determining distance-based classification accura-
cies (Sec. 5.2) on the basis of the 9 cluster models.
5.1 Influence of Interpolation on
Cluster Separation
For each of the 9 cluster models, we aim to deter-
mine how well the features of the training images
are clustered on the hypersphere in the feature space.
Let F
train
be the set of features obtained by pro-
cessing the original training images through a triplet
CNN. As basis for calculating the cluster model,
we rotated each training image by rotational angles
Ψ = {0
◦
, 15
◦
, 30
◦
, ...,345
◦
}, whereas ψ = 0 repre-
sents no rotation. A set of features for one triplet CNN
obtained for such an augmented training set will be re-
ferred to as F
train
Ψ
. Note, that F
train
⊂ F
train
Ψ
. That aug-
mentation step was performed for NEAREST (neigh-
bor), LINEAR, and BICUBIC interpolations, yielding
9 types of F
train
Ψ
sets (see Tab. 1).
Optimally, the feature sets F
train
Ψ
form com-
pact, well-separated clusters class by class. The
an NVIDIA Titan RTX gpu.
2
For all interpolation operations, we used OpenCV 4.1.0
algorithms (Bradski, 2000).
ICPRAM 2020 - 9th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
390

Table 1: Naming convention to refer to the analyzed 9 different cluster models by abbreviations. The columns represent the 3
different triplet CNNs and stand for the interpolation methods used for augmentation in the respective triplet training stages.
The rows represent interpolation methods used for augmentation in the cluster modeling steps.
naming convention triplet (feature) learning
for interp. method NEAREST LINEAR BICUBIC
comb. in augm. steps CNN CNN CNN
clust. m.
NO augm. NEA/NO LIN/NO BIC/NO
NEAREST NEA/NEA LIN/NEA BIC/NEA
LINEAR NEA/LIN LIN/LIN BIC/LIN
BICUBIC NEA/BIC LIN/BIC BIC/BIC
General Discrimination Value (GDV), introduced
by (Schilling et al., 2018), is a measure for assessing
how well data classes / clusters are separated. The
GDV is a combination of averaged intra-class and
inter-class distances into a single value. The smaller
the GDV of a data set, the better the cluster separa-
tion. A value ≤ 0 is desirable, −1 is considered very
good separation.
Tab. 2 shows the GDV for all 9 cluster models.
Following observations can be made:
• optimal cluster separation is achieved for cluster
model NEA / NEA,
• GDV optima appear on / near the diagonal
(BIC/LIN only slightly better than BIC/BIC),
• along the diagonal, GDV aggravates with increas-
ing interpolation order,
• GDV for F
train
and F
train
Ψ
are equal only for
NEA / NEA cluster model (!), or in other words,
• the use of any interpolation method other than
NEAREST in triplet learning or cluster modeling
causes a worse GDV for F
train
Ψ
compared to F
train
.
Note, that for NEA / NEA, despite of augmentation,
the separation quality is preserved w.r.t. the origi-
nal images’ feature distribution. We ascribe the de-
terioration of cluster separation quality for LINEAR
and BICUBIC interpolations to the image smoothing
and overshooting effects due to local weighted aver-
aging of pixel values, whereas in NEAREST interpo-
lation only original pixel values are sampled. Interpo-
lation artifacts apparently change the image distribu-
tions and cause the CNN filter kernels to respond to
different levels of image sharpness.
5.2 Effects of Interpolation on
Distance-based Classification
The analysis of the separation quality of the coin class
clusters in the individual features spaces revealed that
higher order interpolation methods in augmentation
operations alter the distributions of training image
features in the triplet feature spaces. But how does
that actually affect classification performance? We
conducted distance-based classification experiments
on the cluster models from Sec. 5.1, whereas we in-
vestigated following classification strategies:
• Nearest Centroid (NC) based on L
2
norm,
• max. PCA scores, essentially indicating Maha-
lanobis distances w.r.t. cluster centroids.
While NC assumes circular and equally large cluster
distributions of features around the respective cluster
centers in the feature space, PCA also takes into ac-
count that those cluster shapes probably might com-
prise different variances along different dimensions.
Moreover, PCA allows for further dimensionality re-
duction w.r.t. the feature space. In our experiments, a
sub-space dimension of 10 was appropriate. We used
the probabilistic PCA method of (Tipping and Bishop,
1999), which yields cluster membership likelihoods
rather than explicit Mahalanobis distances by evalu-
ating a certain latent space formulation with an EM
optimizer.
5.2.1 Classification Performances for Different
Interpolation Methods in Augmentation
We determined classification accurracies for the train-
ing images as well as the test set, which has not been
used either in triplet training or for cluster modeling.
In order to contrast different influences of interpola-
tion artifacts, we generated augmented data sets for
training and test images. We did that in the same
fashion as described for cluster modeling. However,
here we used a different set of image rotation an-
gles Φ = {0
◦
, 10
◦
, 20
◦
, ...,360
◦
}, i.e. angle step of
10
◦
. Consequently, F
train
⊂ F
train
Φ
represent features
of original training images and feature vectors ob-
tained for augmented training images, respectively.
Knowing full well, that, for a real-world system, ro-
tational augmentation only makes sense for training
images, we also augmented the test images yielding
F
test
⊂ F
test
Φ
. So we were able to measure interpola-
The Necessity and Pitfall of Augmentation in Deep Learning: Observations During a Case Study in Triplet Learning for Coin Images
391

Table 2: GDV for the 9 different cluster models. Columns represent the 3 triplet CNNs trained with different interpolation
methods in augmentation. The rows represent interpolation methods used to calculate F
train
and F
train
Ψ
for cluster modeling.
GDV
augm. interp. meth., triplet (feature) learning
triplet learning and NEAREST LINEAR BICUBIC
cluster modeling CNN CNN CNN
clust. m.
F
train
- NO augm. -0.578 -0.566 -0.567
F
train
Ψ
- NEAREST -0.578 -0.555 -0.530
F
train
Ψ
- LINEAR -0.548 -0.561 -0.556
F
train
Ψ
- BICUBIC -0.533 -0.539 -0.554
tion effects on data, that have not been involved in any
part of the training phase.
First, we took a look at the achievable NC classifi-
cation accuracies of F
train
Φ
and F
test
Φ
for the 9 different
cluster models (Tab. 3).
Similar points can be recognized as already ob-
served for GDV. All observations hold true for train-
ing and test data, i.e. F
train
Φ
and F
test
Φ
, respectively:
• highest classification accuracies are achieved for
the NEA / NEA cluster model,
• classification optima appear on / near the diag-
onal (again, BIC / LIN is slightly better than
BIC / BIC),
• along the diagonal, higher interpolation orders en-
tail worse classification accuracies.
Obviously, the presence of interpolation artifacts in
the course of augmentation directly affects the NC
classification performances negatively.
Tab. 4 shows the respective recognition rates for
PCA classification based on maximization of cluster
membership likelihoods. In contrast is to be recog-
nized:
• training accuracies are all equal and almost per-
fect,
• test accuracies are significantly improved in all
cases,
• LIN / LIN cluster model performs equally well as
NEA / NEA,
• still, mixing interpolation methods in triplet learn-
ing and cluster modeling tendentiously causes
losses in classification accuracies.
Evidently, the effects of higher order interpolation on
the cluster’ distributions in the feature spaces can be
factored out by PCA to a significant amount by fo-
cusing on those dimensions that contain most of the
clusters’ variances.
5.2.2 No Interpolation Artifacts vs.
Interpolation Artifacts
We split the augmentation angle set Φ and extracted
the set of angles, which are integer multiples of 90
◦
,
i.e. Φ
mult90
⊂ Φ. For those angles, no interpolation
method causes smoothing or ringing on accordingly
rotated images due to the accordance of pixel grid po-
sitions in the original and rotated images. Naturally,
the complementary set Φ \ Φ
mult90
contains rotation
angles ensuing various amounts of interpolation arti-
facts. Note, that |Φ \ Φ
mult90
| >> |Φ
mult90
|. By pro-
cessing the augmented images through a triplet CNN,
we obtain feature vectors F
train
Φ
mult90
, F
train
Φ\Φ
mult90
, F
test
Φ
mult90
,
F
test
Φ\Φ
mult90
, which refer to images with and without in-
terpolation artifacts, respectively.
For that last experiment, we solely present the NC
classification accuracies in Tab. 5, whereas the same
interpolation methods were used in triplet learning
and cluster modeling. Following observations hold
true for training and test images, F
train
∗
and F
test
∗
, re-
spectively:
• equal classification results for both types of
interpolation angles are only achieved for the
NEA / NEA cluster model, while
• higher order interpolation methods show sig-
nificant worse performances for rotation angles
ϕ ∈ Φ
mult90
.
Since the Φ \ Φ
mult90
features outweigh the Φ
mult90
features, the cluster models predominantly rather rep-
resent their distributions in the feature spaces. A
worse classification rate for F
train
Φ
mult90
and F
test
Φ
mult90
indi-
cates, that features of images with no interpolation ar-
tifacts at least slightly deviate from that cluster model.
Another indication that the higher order interpolation
methods contort the underlying image distributions.
In the inference phase, where no augmentation takes
place, a diminished classification performance is to
be expected, when interpolation methods other than
NEAREST are used for augmentation operations.
ICPRAM 2020 - 9th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
392
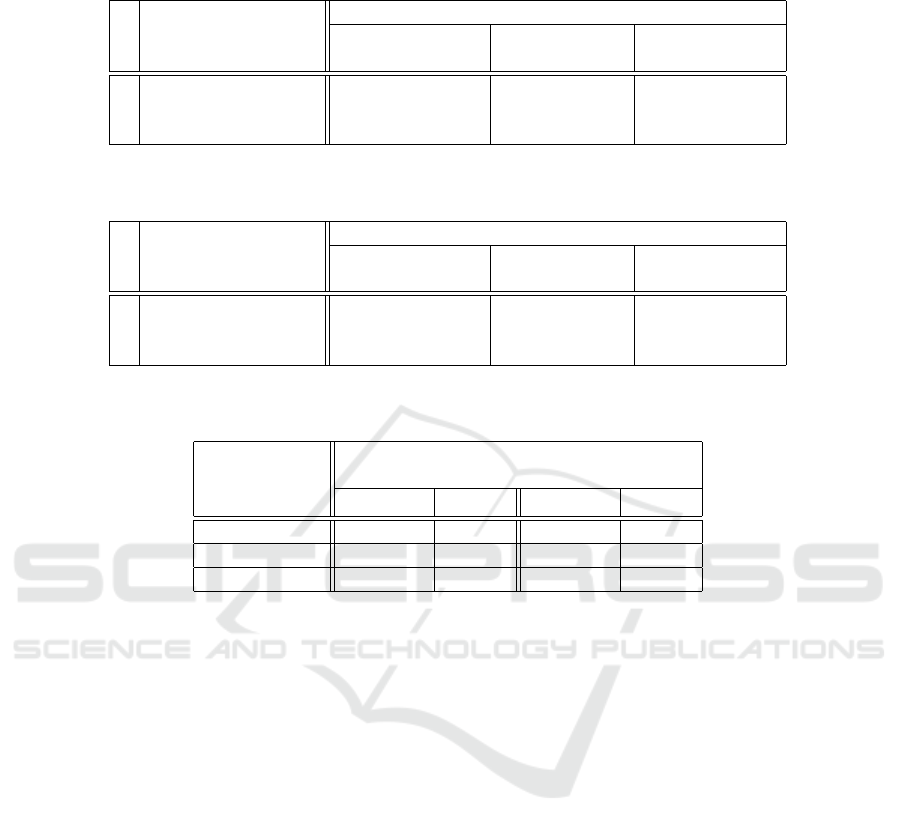
Table 3: NC classification accuracies for the 9 different cluster models. Columns represent the 3 triplet CNNs. The rows
represent interpolation methods used to calculate F
train
Φ
and F
test
Φ
for cluster modeling.
NC
augm. interp. meth., triplet (feature) learning
triplet learning and NEAREST CNN LINEAR CNN BICUBIC CNN
cluster modeling F
train
Φ
/ F
test
Φ
F
train
Φ
/ F
test
Φ
F
train
Φ
/ F
test
Φ
clust.
NEAREST 0.953 / 0.891 0.927 / 0.867 0.912 / 0.848
LINEAR 0.911 / 0.839 0.939 / 0.874 0.939 / 0.874
BICUBIC 0.887 / 0.815 0.897 / 0.835 0.933 / 0.871
Table 4: PCA classification accuracies for the 9 different cluster models. Columns represent the 3 triplet CNNs. The rows
represent interpolation methods used to calculate F
train
Φ
and F
test
Φ
for cluster modeling.
PCA
augm. interp. meth., triplet (feature) learning
triplet learning and NEAREST CNN LINEAR CNN BICUBIC CNN
cluster modeling F
train
Φ
/ F
test
Φ
F
train
Φ
/ F
test
Φ
F
train
Φ
/ F
test
Φ
clust.
NEAREST 0.999 / 0.928 0.999 / 0.923 0.999 / 0.918
LINEAR 0.999 / 0.916 0.999 / 0.928 0.999 / 0.926
BICUBIC 0.999 / 0.914 0.999 / 0.920 0.999 / 0.924
Table 5: Separate evaluation of NC classification accuracies for features from augmentation images according to rotation
angles ϕ ∈ Φ
mult90
and ϕ ∈ Φ \ Φ
mult90
. Configuration naming according to Tab. 1.
Cluster model
acc. to augm. NC classification accuracies
configuration F
train
Φ\Φ
mult90
F
train
Φ
mult90
F
test
Φ\Φ
mult90
F
test
Φ
mult90
NEA / NEA 0.95 0.95 0.89 0.89
LIN / LIN 0.96 0.80 0.89 0.75
BIC / BIC 0.96 0.79 0.90 0.71
6 CONCLUSIONS
We conducted a case study for evaluating the useful-
ness of deep embedding learning for generating ad-
vantageous feature distributions of modern coin im-
ages with a CNN, i.e. triplet learning. Our initial goal
was to achieve features that cluster together class by
class, whereas coin class membership is represented
by feature vector proximity in the feature space. Con-
sequently, as distance-based classification system was
feasible, which also comprised a certain degree of
novelty-awareness. However, for training such a coin
classification system, extensive use of image augmen-
tation is required in order to achieve rotation invari-
ance. That algorithmic image rotation involves inter-
polation operations which cause different types and
amounts of interpolation errors around each pixel. In
conventional image processing, one strives to choose
a possibly high degree of interpolation to achieve a
realistic impression, but linear and bicubic interpola-
tions produce certain amounts of smoothing and / or
ringing artifacts.
As desired as higher order interpolation is in con-
ventional image processing, we found that in deep
embedding learning it tends to change the images’
distributions. That distortion may be small, but def-
initely measurable when it comes to fitting clus-
ter models to the coin classes in the CNN feature
space. Those respective interpolation errors, intro-
duced through image rotation in the course of aug-
mentation, obviously cause slightly different CNN fil-
ter responses. Those alter the resulting feature vec-
tors’ positions in the feature space.
Augmentation is only required in the training
phase. In inference, the input images would not be
rotated at all, but plainly processed through the sys-
tem. If the augmentation in the training phase had
altered the expected image distribution, the system
would comprise an unknown bias compromising its
accuracy and reliability.
We showed effects of different interpolation meth-
ods on the quality of cluster separation in triplet fea-
ture spaces and demonstrated that those transfer to di-
minished classification accuracies.
However, there is a simple and computationally
performant way to conserve the original images’ dis-
tribution during augmentation in the first place: using
nearest neighbor interpolation. Nearest neighbor in-
The Necessity and Pitfall of Augmentation in Deep Learning: Observations During a Case Study in Triplet Learning for Coin Images
393

terpolation merely re-samples the pixel values from
the original pixel value set, so that no smoothing or
ringing artifacts are produced. Nearest neighbor in-
terpolation demonstrably preserves the distribution of
augmentation images within the original image distri-
bution, which is apparent in preserved feature separa-
tion quality and classification capability.
It is not surprising news that one has to be very
thorough compiling and maintaining a training data
set for a deep learning system. But, since CNNs
are very powerful approximators of high-dimensional
data distributions, one has also to be wary when
choosing an interpolation method for image augmen-
tation. We showed that the wrong choice leads to de-
viations w.r.t. the original image distributions, caus-
ing distortions of the feature distributions, which di-
rectly affect classification performance and system re-
liability.
REFERENCES
Abadi, M., Agarwal, A., Barham, P., Brevdo, E., Chen, Z.,
Citro, C., Corrado, G. S., Davis, A., Dean, J., Devin,
M., Ghemawat, S., Goodfellow, I., Harp, A., Irving,
G., Isard, M., Jia, Y., Jozefowicz, R., Kaiser, L., Kud-
lur, M., Levenberg, J., Man
´
e, D., Monga, R., Moore,
S., Murray, D., Olah, C., Schuster, M., Shlens, J.,
Steiner, B., Sutskever, I., Talwar, K., Tucker, P., Van-
houcke, V., Vasudevan, V., Vi
´
egas, F., Vinyals, O.,
Warden, P., Wattenberg, M., Wicke, M., Yu, Y., and
Zheng, X. (2015). TensorFlow: Large-scale machine
learning on heterogeneous systems. Software avail-
able from tensorflow.org.
Bradski, G. (2000). The OpenCV Library. Dr. Dobb’s Jour-
nal of Software Tools.
Chechik, G., Sharma, V., Shalit, U., and Bengio, S.
(2010). Large scale online learning of image similarity
through ranking. J. Mach. Learn. Res., 11:1109–1135.
Gosh, S., Singh, R., and Vatsa, M. (2019). On learning
density aware embeddings. In The IEEE Conference
on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
Huber-M
¨
ork, R., N
¨
olle, M., Rubik, M., H
¨
odlmoser, M.,
Kampel, M., and Zambanini, S. (2012). Automatic
coin classification and identification. In Kypraios, I.,
editor, Advances in Object Recognition Systems, chap-
ter 7. IntechOpen, Rijeka.
Huber-M
¨
ork, R., Ramoser, H., Mayer, K., Penz, H., and
Rubik, M. (2005). Classification of coins using an
eigenspace approach. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 26(1),
pages 61–75.
Huber-M
¨
ork, R., Zaharieva, M., and Czedik-Eysenberg, H.
(2008). Numismatic object identification using fusion
of shape and local descriptors. In Proc. Symp. on Vi-
sual Computing, pages 368–379.
Huber-M
¨
ork, R., Zambanini, S., Zaharieva, M., and Kam-
pel, M. (2010). Identification of ancient coins based
on fusion of shape and local features. Machine Vision
and Applications.
Kampel, M., Huber-M
¨
ork, R., and Zaharieva, M. (2009).
Image-based retrieval and identification of ancient
coins. In IEEE Intell. Syst. 24(2), pages 26–34.
Lowe, D. (2004). Distinctive image features from scale-
invariant keypoints. Int. J. of Comput. Vision 60(2),
pages 91–110.
N
¨
olle, M. and Hanbury, A. (2006). Muscle coin images
seibersdorf (cis) benchmark competition 2006. In
IAPR Newsletter 28(2), pages 18–19.
N
¨
olle, M., Penz, H., Rubik, M., Mayer, K., Holl
¨
ander, I.,
and Granec, R. (2003). Dagobert – a new coin recog-
nition and sorting system. In Proc of Int. Conf. on
Digital Image Computing – Techniques and Applica-
tions, pages 329–338.
N
¨
olle, M., Rubik, M., and Hanbury, A. (2006). Re-
sults of the muscle cis coin competition 2006. In
Proc. of the Muscle CIS Coin Competition Work-
shop,Berlin,Germany.
Reisert, M., Ronneberger, O., and Burkhardt, H. (2006). An
efficient gradient based registration technique for coin
recognition. In Proc. Muscle CIS Coin Competition
Workshop, pages 19–31.
Reisert, M., Ronneberger, O., and Burkhardt, H. (2007). A
fast and reliable coin recognition system. In Proc. of
DAGM, pages 415–424.
Schilling, A., Rietsch, J., Gerum, R., Schulze, H., Metzner,
C., and Krauss, P. (2018). How deep is deep enough?
- optimizing deep neural network architecture. CoRR,
abs/1811.01753.
Schroff, F., Kalenichenko, D., and Philbin, J. (2015).
Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition
and clustering. CoRR, abs/1503.03832.
Simonyan, K. and Zisserman, A. (2014). Very deep con-
volutional networks for large-scale image recognition.
CoRR, abs/1409.1556.
Snell, J., Swersky, K., and Zemel, R. (2017). Prototyp-
ical networks for few-shot learning. In Guyon, I.,
Luxburg, U. V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R.,
Vishwanathan, S., and Garnett, R., editors, Advances
in Neural Information Processing Systems 30, pages
4077–4087. Curran Associates, Inc.
Tipping, M. E. and Bishop, C. M. (1999). Mixtures of prob-
abilistic principal component analyzers. Neural Com-
putation, 11:443–482.
Wang, F., Xiang, X., Cheng, J., and Yuille, A. L. (2017).
Normface: L2 hypersphere embedding for face verifi-
cation. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM International
Conference on Multimedia, MM ’17, pages 1041–
1049, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Yang, H., Zhang, X., Yin, F., and Liu, C. (2018). Robust
classification with convolutional prototype learning.
CoRR, abs/1805.03438.
Zaharieva, M., Huber-M
¨
ork, R., N
¨
olle, M., and Kampel, M.
(2007). On ancient coin classification. In Proc. of Int.
Symp. on Virtual Reality, Archaeology and Cultural
Heritage, pages 55–62.
ICPRAM 2020 - 9th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
394
