
Predicting a Song Title from Audio Embeddings on a Pretrained
Image-captioning Network
Avi Bleiweiss
BShalem Research, Sunnyvale, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Image Captioning, Audio Spectrogram, Neural Networks, Long Short-term Memory, Beam Search.
Abstract:
Finding the name of a song from a piece played without the lyrics remains a long-standing challenge to music
recognition services. In this work, we propose the use of a neural architecture that combines deep learned
image features and sequence modeling to automate the task of predicting the song title from an audio time
series. To feed our network with a visual representation, we transform the sound signal into a two-dimensional
spectrogram. Our novelty lies in model training on the state-of-the-art Conceptual Captions dataset to generate
image descriptions, jointly with inference on the Million Song and Free Music Archive test sets to produce
song titles. We present extensive quantitative analysis of our experiments and show that using k-beam search
our model achieved an out-domain BLEU score of 45.1 compared to in-domain performance of 61.3.
1 INTRODUCTION
Music Information Retrieval (MIR) is a growing field
of research that recently underwent a profound mind
shift from the use of handcrafted audio features to-
ward representation learning to increase performance.
Deep neural architectures have been proposed for
a variety of MIR tasks, including speech denoising
(Germain et al., 2018), mood detection (Delbouys
et al., 2018), and the more widely explored topic,
genre classification (Oramas et al., 2018). In this pa-
per, we propose a deep learning approach to automate
song naming, a task that generates a natural language
short-phrase with an attempt to faithfully represents
the content of an audio time sequence. In practice,
automatic song title can benefit a diverse real-world
application domains, including audio indexing, musi-
cal gaming, and personal memory assistant.
In the past decade, most prominent music descrip-
tors used in MIR research were the Mel-frequency
cepstral coefficients (MFCC) and chroma vectors (Ur-
bano et al., 2014) that capture complementary tim-
bral and tonal information from the underlying audio
signal, respectively. The computation of the descrip-
tors conforms to the same principle as they extract a
time-frequency representation of the audio, filter out
noise, map this representation to vectors, and accumu-
late them over time. This style of engineered features
benefit effective machine learning, but is labor inten-
sive and moreover is prone to extract discriminate
data variability that is essential for building tailored
predictors. In contrast, applying deep representation
learning to automatic annotation and ranking of mu-
sic audio (Hamel et al., 2011; Choi et al., 2017) and
to polyphonic transcription (Boulanger-Lewandowski
et al., 2012) had shown to considerably outperform
models that use manual feature extraction.
Deep convolutional neural networks (CNN) have
proved to greatly benefit many tasks in the domain
of image understanding (He et al., 2016; Szegedy
et al., 2016). This had subsequently motivated MIR
researchers to express the input audio signal in a vi-
sual representation and learn musical features from
a pretrained neural network on the large ImageNet
dataset (Russakovsky et al., 2015). Recent musically
inspired architectures have hence seen migrated to
the use of a widely accepted audio format of a two-
dimensional time-frequency spectrogram that is fed
to a CNN (Pons et al., 2016; Oramas et al., 2018).
Unlike an image that is an array of pixels interpreted
spatially, the orthogonal dimensions of a spectrogram,
time and frequency, makes the design of filters in the
CNN top layer less intuitive. Respectively, audio fil-
ters learn proportional temporal dependencies on one
axis, and timbral features on the other.
Recently, automatic description generation from
images attracted broad attention from the natural
language processing (NLP) and computer vision re-
search communities. Among the diverse approaches,
Vinyals et al. (2015) proposed an encoder-decoder ar-
Bleiweiss, A.
Predicting a Song Title from Audio Embeddings on a Pretrained Image-captioning Network.
DOI: 10.5220/0008939004830493
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2020) - Volume 2, pages 483-493
ISBN: 978-989-758-395-7; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
483

LSTM
LSTM
LSTM
LSTM
⋯
LSTM
<start>
sandcastle
beach
sky
sandcastle
beach
on
<end>
ResNet
RNN
Visual
Embedder
Text
Generator
7x7 conv
3x3 conv
⋮
3x3 conv
avg pool
3x3 conv
Figure 1: Neural model architecture: ResNet, a deep convolutional neural network is used to create a semantic representation
of an image, which we then decode using an LSTM network. The vectorized image representation is fed into the network,
followed by a special start-of-sentence token. The hidden state produced is then used by the LSTM to predict or generate the
caption for the given image word-embeddings.
chitecture that uses a recurrent neural network (RNN)
to generate captions conditioned on image features
learned by a CNN. Alternately, Fang et al. (2015)
explored a compositional neural model that detects
words likely to be contained in a caption by apply-
ing CNN to image tiles, and then re-ranks a set of
high-likelihood candidate sentences using learned lin-
ear weights. In their excellent surveys, Bernardi et
al. (2016) and Hossain et al. (2019) offer an ex-
haustive critical review of model evolution, dataset
choices and properties, and a discussion on evaluation
metrics. Our neural model for generating song titles
followed the Show-And-Tell (Vinyals et al., 2015) ar-
chitecture, and leveraged the residual version of the
Inception network (ResNet) (Szegedy et al., 2016) for
the CNN module as shown in Figure 1.
We trained our model on the state-of-the-art Con-
ceptual Captions dataset (Sharma et al., 2018) that
has an order of magnitude more images than the most
studied dataset to date, MS-COCO (Lin et al., 2014).
Unlike the human curated MS-COCO, Conceptual
Captions organizes samples as pairs of an image url
and a description that were collected from a billion of
English web pages and are thus by far more diversi-
fied. The initial image annotations are picked up from
the alternative text attribute (alt) of a web page that is
commonly supplied to an image.
1
However, alt-text
sequences are free–form and tend to contain proper
names that would make the training of song title gen-
eration a major challenge. In filtering the Conceptual
Captions dataset, one of the more appealing processes
to our task is the removal of noun modifiers and sub-
1
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alt attribute
stituting named-entities with their hypernym.
In our baseline audio inference, we used a subset
of the Million Song Dataset (MSD) (Bertin-Mahieux
et al., 2011), a large-scale dataset that contains meta-
data and audio analysis for a million of contempo-
rary tracks, which are legally available to Echo Nest
(Jehan and Whitman, 2005). This exploratory subset
is published on the UCI repository (Dua and Graff,
2017) and was originally targeted for the task of pre-
dicting the release year of a song from timbral fea-
tures. In our work, we first associate a song title with
its audio features, and then convert the timbral data
to a tensor that we feed directly to the text generator,
thus bypassing the ResNet stage all together.
In end-to-end evaluation of our neural model, we
used the Free Music Archive (FMA) dataset (Deffer-
rard et al., 2017). FMA provides full-length and high
quality audio for over one hundred thousand tracks
from thousands of artists. The song collections from
this archive are distributed in variable counts of mp3-
encoded audio data of either balanced or unbalanced
genres. We used a group of 8,000 music tracks, each
of a 30-second play time, gathered from eight top gen-
res evenly with one thousand clips per genre. In our
framework, we convert an mp3 song to a wave object
from which we produce a spectrogram that is param-
eterized by the number of time frames and frequency
bins. A consistent clip length for each track warrants
a fixed-size input to the ResNet stage of our model.
The main contribution of our work is the learn-
ing of audio representations from a pretrained neural
model that automatically generates descriptions from
images, to predict musical titles. We hypothesize that
image captioning and song naming are similar in con-
ICAART 2020 - 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
484

Train
Image/Caption
Pairs
Random
Weights
Train
Song/Title
Pairs
Image-Trained
Weights
Inference
Song/Title
Pairs
Finetuned
Weights
BLEU
Score
Figure 2: Our two-step training process for adapting the source visual domain to the target auditory cues.
text and thus make a constructive knowledge transfer
plausible. To the extent of our knowledge, we are the
first to propose a multi-domain collaboration of audio,
natural language, and vision to solve a MIR task.
The rest of this paper is structured as follows. In
Section 2, we introduce our baseline and end-to-end
neural model architectures for predicting song titles.
Proceeding to Section 3, we review the image cap-
tioning and audio datasets we used for training and
inference, respectively. Section 4 provides initial data
analyses, details our training methodology, and pur-
sues domain similarity intuition. We then present ex-
tensive quantitative results of our experiments for var-
ious scenarios of representation learning, in Section
5. Discussion, summary, and identified avenues for
prospective research are drawn in Section 6.
2 MODEL
Many proposed models that use deep neural networks
(DNN) for image description generation (Vinyals
et al., 2015; Fang et al., 2015; Ding and Soricut, 2017)
were inspired by recent advances in neural machine
translation (NMT). NMT architectures have shown
state-of-the-art results in both the form of a pow-
erful sequence model (Sutskever et al., 2014; Cho
et al., 2014; Bahdanau et al., 2015), and more re-
cently using the cross-attention ConvS2S (Elbayad
et al., 2018) and the self-attention based Transformer
network (Vaswani et al., 2017).
The task of image captioning uses a similar ap-
proach to NMT, but instead of encoding a variable-
length text sequence to a fixed dimensional vector
that is decoded to an output sentence, an image rep-
resented as a two-dimensional tensor (Paszke et al.,
2017) is translated to its description. Moreover, rather
than RNN, images are encoded using deep CNN.
In our work, we used the most recent residual ver-
sion 2 of the Inception architecture (He et al., 2016;
Szegedy et al., 2016) to produce image embeddings,
and follow Vinyals et al. (2015) with a Long Short-
term Memory (LSTM) (Hochreiter and Schmidhuber,
1997; Chung et al., 2014) variant of recurrent net-
works to generate natural language descriptions.
In Figure 1, we review our neural model archi-
tecture for predicting song titles. Using a very deep
ResNet, the model creates a semantic representation
of either a natural image or an audio spectrogram that
is then decoded in an LSTM network for generat-
ing variable-size text sequences. Our framework uses
a two-step process depicted in Figure 2 to train our
model and adapt the source visual domain to the tar-
get auditory cues by tuning network hyperparameters.
In training, we feed the model with images
drawn from urls provided by the Conceptual Captions
dataset (Sharma et al., 2018). The dataset retains im-
ages of which both dimensions are greater than 400
pixels that we randomly crop each into a consistent
two-dimensional array of 256 × 256 pixels sampled
from the raw image or its horizontal reflection. Each
pixel renders a mean-subtracted 3-channel intensity.
We used deep visual representation that enjoyed
great success in large-scale image and video recog-
nition tasks (Simonyan and Zisserman, 2015). Pre-
trained on the large ImageNet dataset (Russakovsky
et al., 2015), extremely deep residual networks
(ResNets) prove significant accuracy gains from con-
siderably increased network depth (He et al., 2016).
Moreover, deep ResNets have an appreciable lower
computational complexity compared to a much shal-
lower VGGNet architecture (Simonyan and Zisser-
man, 2015).
Wave
to
Timbre
Text
Generator
Song Title
Figure 3: Baseline inference model: timbral engineered fea-
tures are extracted from an audio signal and fed via a back-
door to the language generator.
Our model applies a residual network with a depth of
152 layers to encode an image into a 512 × 1 tensor.
We strip off the last 1000-way fully-connected layer
that produces probabilities through a softmax activa-
tion, and expose the global average-pooling stage of
which we extract the image features. Following Ioffe
and Szegedy (2015), we chose to invoke batch nor-
malization in training our ResNet without requiring
Predicting a Song Title from Audio Embeddings on a Pretrained Image-captioning Network
485

Visual
Embedder
Text
Generator
Wave
to
Spectrogram
Song Title
Figure 4: Mainline inference model: the audio signal is converted to a spectrogram that is fed to the visual embedder and
follows the processing path of a natural image.
dropout to regulate the network. More formally, given
a natural image denoted by I, the image embedding
tensor, I
e
, extracted by ResNet reduces to
I
e
= ResNet152(I).
On the NLP side, we constructed a vocabulary
V from the textual image descriptions provided by
the Conceptual Captions train set. We used a dense
d-dimensional representation of word embeddings
(Pennington et al., 2014) that are stored in the ma-
trix E ∈ R
|V|×d
and are looked up to feed the LSTM
cells of the text generator. Special word embeddings
were added to indicate the begin and end delimiters
of a text sequence (Figure 1), and an unknown to-
ken that identifies out-of-vocabulary words. We use
the colon notation v
i: j
to denote a sequence of vectors
(v
i
, v
i+1
, . . . , v
j
). Let x
0:T −1
be the word embeddings
to enter the LSTM network, thus the output probabil-
ity of the next word is defined by
p
t+1
= LST M(x
t
). t ∈ {0, . . . , T − 1}.
The ResNet pipeline and the embedding matrix E
map the image and words of its description text se-
quence to the same vector space, respectively. To
avoid more easily overfitting to the image noisy con-
tent, we feed the image tensor I
e
once as the first input
of a dynamic length LSTM at time t = −1 (Figure 1).
In inference, we are given an audio signal and our
goal is to predict a song title using a pretrained image
caption network as the source domain. This is mainly
motivated by the abundance of available image net-
works (Russakovsky et al., 2015; Simonyan and Zis-
serman, 2015) and on the other hand, the shortage of
networks trained on audio data. We contrast title pre-
diction quality of a baseline model that uses a hand-
crafted feature set with a mainline model that lets the
network learn the features.
In Figure 3, we show our baseline model. Timbral
(MFCC like) engineered features are extracted from
an audio signal, upscaled to match the dimensions
of the ResNet output tensor (512 × 1), and then fed
through a backdoor as input to the RNN text-sequence
generator. Although proven highly effective in audio
classification tasks at extremely reduced data rates,
MFCC is a lossy representation and thus less optimal
in a producer type environment we employ.
To synthesize high-quality sound for our gener-
ative network, a lossless representation of the audio
signal is essential. In Figure 4, we show our mainline
inference model that has the audio signal converted
to a spectrogram, a time-frequency matrix representa-
tion S ∈ R
F×T
, where F is the number of frequency
bins and T the number of time frames. Spectrograms
are commonly perceived as two-dimensional images
with pixel intensities representing the strength of a
frequency component at a given time frame (Wyse,
2017). Hence a spectrogram representation is favor-
ably suggestive that vision-purposed networks, like
ResNet, may apply directly to sound.
In a generative neural model, k-beam search is
widely used to improve the output language quality.
Our study compares inference performance and run-
time of a greedy search (k = 1), which selects at each
timestep the most likely word in the output sequence,
with beam search of varying k > 1 that returns a list of
the best k candidate sequences up to time t with length
t + 1 and discards the non-promising alternatives. We
hypothesize that greedy search impacts performance
adversely and analyze the runtime cost incurred with
increased beam size. Both time and space complexi-
ties of beam search are linear with the number of the
most promising k nodes to expand the graph per layer,
and thus O(kd), where d is the depth of the search.
3 DATA
In this section, we summarize the datasets we used
in our experiments to train and evaluate our neural
model for predicting song titles.
3.1 Conceptual Captions
Our model is trained on the recently published Con-
ceptual Captions dataset (Sharma et al., 2018). The
dataset version released contains over three million
image urls paired with natural language descriptions,
2
as the link between visual importance and descrip-
tions inherently leads to the problem of text sum-
2
https://github.com/google-research-datasets
ICAART 2020 - 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
486

0
50000
100000
150000
200000
10 20 30 40 50
Word Length
Number of Examples
(a) Conceptual Captions
0
50000
100000
150000
200000
250000
0 10 20 30 40
Word Length
Number of Examples
(b) Million Songs
0
20000
40000
0 10 20 30
Word Length
Number of Examples
(c) Free Music Archive
Figure 5: Description distribution for (a) Conceptual Captions, (b) Million Song, and (c) Free Music Archive datasets.
Table 1: Statistics of description distribution across source and target datasets.
Dataset Examples Min Length Max Length Mean Length StdDev Length
Conceptual Captions 1,000,000 4 50 10.31 4.67
Million Songs 515,576 1 135 3.09 1.86
Free Music Archive 106,573 1 28 2.98 2.11
marization in natural language processing. Concep-
tual Captions is by far the largest dataset introduced
to date for the task of automatic visual description
compared with one million captioned photographs in
Im2Txt (Ordonez et al., 2011) and 328,000 images in
the most broadly used MS-COCO (Lin et al., 2014).
3
Image annotations in Conceptual Captions were au-
tomatically distilled to avoid named-entities and re-
sult in a fairly concise vocabulary of slightly over fifty
thousands unique tokens. This is prominent to effec-
tively use the dataset as a source domain for trans-
fer learning from large-scale vision data to a more
constraint auditory space in generating waveform-
originated song titles without proper names.
The Conceptual Captions dataset contains a total
of 3,346,732 examples of which 3,318,333 are for
training, 15,840 for validation, and 12,559 for test.
We note that the test split is hidden and intended pri-
marily for a challenge competition. In Figure 5a, we
provide distribution of caption word length over a ran-
dom sample of one million training examples. About
93.8 percent of the captions are of fifteen words or
less and on average a caption is comprised of ten to-
kens, as evidenced in the statistics shown in Table 1.
3.2 Million Songs
To evaluate our baseline model (Figure 3), we used
two complementary subsets of the Million Song
dataset (Bertin-Mahieux et al., 2011), a collection of
audio features and metadata for million western-style
contemporary tracks. Originally intended for the task
3
https://github.com/cocodataset/cocoapi
of estimating the release year of a song based on its
audio features, the data of timbral features is publicly
available on the UCI Machine Learning Repository
(Dua and Graff, 2017),
4
and the correlated metadata
set contains a list of all tracks that have the year infor-
mation over a time span of almost ninety years, from
1922 till 2011.
5
To properly serve our purpose, we
dropped the track release-year field from the feature
set and appended to it a song title column that we ex-
tracted from the metadata set.
Our working dataset comprises 515,576 examples
made of pairs of timbre features and song titles of
which we randomly drew target samples for testing
the baseline model (Figure 3). Manual-made MFCC-
like features are represented each as a two-way vector
of ninety elements. The first twelve coefficients of the
feature vector are the canonical mean vector over all
the audio segments, and the remaining 78 elements
represent the covariance matrix.
In Figure 5b, we show word length distribution of
song titles over the entire working set. Song title se-
quences of one to five words inclusive make up about
ninety percent of over half a million tracks. The mean
title length is of about three words, and while the max-
imum title size is of 135 tokens (Table 1), there is
only one song of this word length and the immedi-
ately largest title to follow is of 45 tokens.
4
http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets
5
http://millionsongdataset.com/pages/tasks-demos/
Predicting a Song Title from Audio Embeddings on a Pretrained Image-captioning Network
487
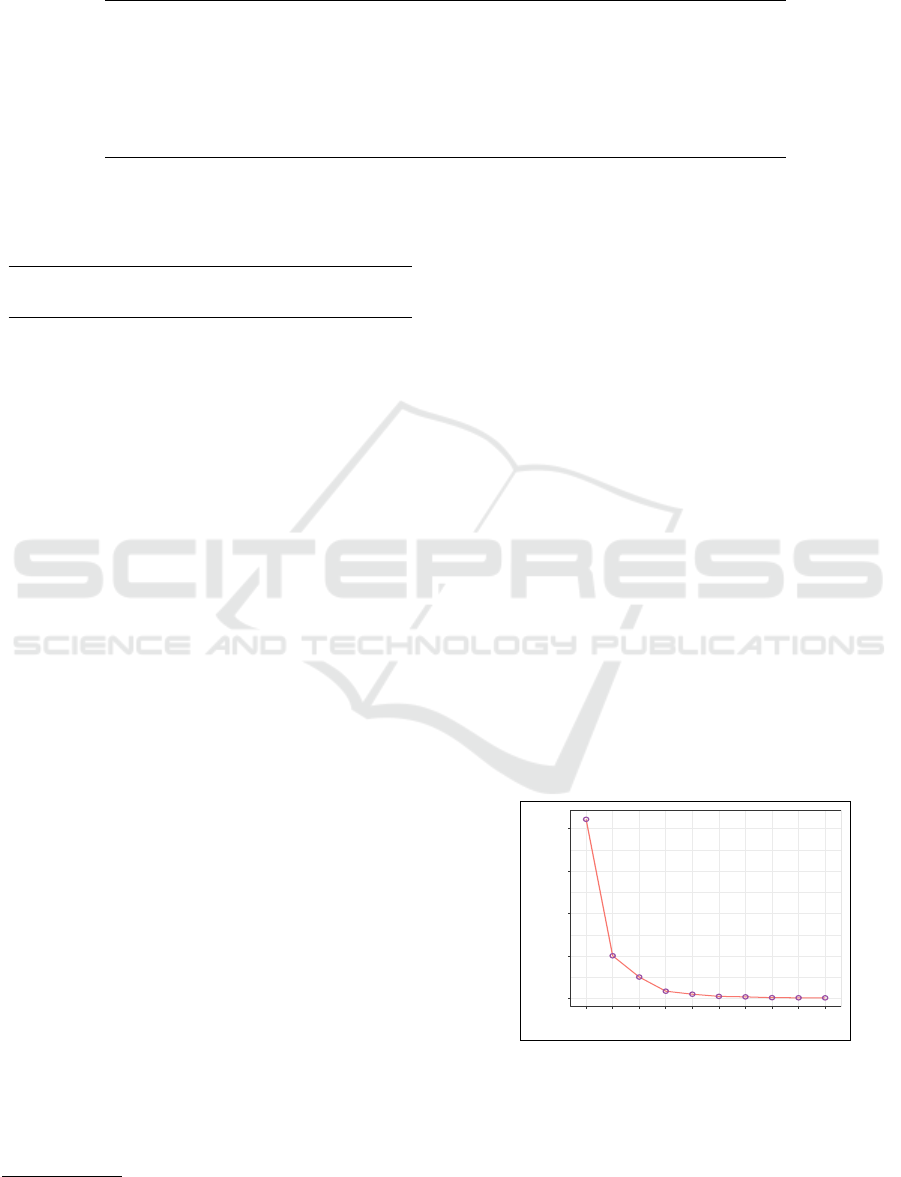
Table 2: A sample of song titles from the Million Song and Free Music Archive datasets. All tokens are lowercased.
Million Songs Free Music Archive
• trouble in mind
• warm and sunny day
• all i want is a spoonful
• georgia man
• the world does not revolve around you
• peel back the mountain sky
• where is your love
• queen of the wires
• space power over-watch destroying evil rats
• too happy
Table 3: Vocabulary token distribution in song titles for total
tracks and 1000-track test sets across audio collections.
Million Songs Free Music Archive
Total 153,588 79,085
Test 966 1,573
3.3 Free Music Archive
We used the large-scale Free Music Archive (Deffer-
rard et al., 2017),
6
to evaluate our end-to-end main-
line model (Figure 4). The data contains both high-
quality mp3-encoded audio and metadata for over one
hundred thousand tracks, and is legally available for
music analysis tasks. Most of the tracks have a sam-
pling rate of 44,100Hz, a bit rate of 320Kbits/sec, and
were produced in stereo. FMA offers a variety of
downloadable collections based on size. In our work,
we used an eight-balanced genre set of 8,000 tracks,
each of thirty seconds play time. We built our target
dataset for inference by randomly choosing mp3 file
indices that we paired with the song title we extracted
from the all-track metadata FMA provides.
The distribution of song title length across all
106,573 FMA tracks is illustrated in Figure 5c. Con-
sistent with the title distribution in MSD, FMA song
titles of five words or fewer take up about 89 percent-
age points of the tracks. Moreover, identical to MSD,
average title length is about three words and is smaller
than the mean caption word-length of ten. This length
disparity between a song title and an image caption is
at least suggestive to benefit transfer learning from vi-
sion to auditory domains. The maximum title length
in FMA is of 28 tokens and thus spans the shortest
description range of all the three datasets (Table 1).
4 SETUP
We measure song title quality by comparing the pre-
dicted title to a reference target, and chose to report
unigram BLEU precision for our performance metric
6
https://github.com/mdeff/fma
(Papineni et al., 2002). In the BLEU metric, higher
scores indicate better performance.
4.1 Corpora
The datasets we used throughout our experiments un-
derwent numerous cleanup steps. To tailor the Con-
ceptual Captions source dataset to fit our task, we pre-
processed the provided image urls and pruned ones
that were either nonexistent or denied permission to
user access. We found about ten percent of the raw
training pairs to be unavailable. The caption vocabu-
lary of the train set has 51,201 unique tokens and is
sufficiently large compared to 996 and 1,573 distinct
symbols for the target MSD and FMA song titles in
their respective test sets of one thousand tracks each,
as shown in Table 3. Using named-entity recognition
with the Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK), we re-
viewed all song titles for the presence of any type of a
named-entity. Given their short text sequence (Table
1), clips with named-entity titles were excluded from
the test set. Similarly, tracks with titles that included
words out of the English vocabulary were removed.
In Table 2, we show lowercased samples of clean title
text-sequences from MSD and FMA datasets.
0
200
400
600
800
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Epoch
Perplexity
Figure 6: Epoch perplexity progression in in-domain train-
ing of our neural model.
Audios from the FMA dataset are in mp3 format
and in the process of transforming them to spectro-
grams, we first created an R wave object (R Core
Team, 2013). FMA tracks are consistently sampled
ICAART 2020 - 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
488

native image timbre features
(a) Timbre-Image similarity
native image spectrogram
(b) Spectrogram-Image similarity
Figure 7: Audio-Visual similarity for (a) timbre-image and (b) spectrogram-image feature projection.
at 44,100Hz with 16-bit depth per sample, and as all
clips are of a thirty-second play time, each thus spans
roughly 1,323,000 samples. Sound waves have two-
channel representation and stereo signals are con-
verted to mono by either averaging both channels or
selecting one of left or right, and then proceeding with
the removal of DC offset by subtracting the mean. We
used 1024 FFT points, a window size of 512, and an
overlap of half the window points to generate a spec-
trogram from the finalized wave object. The spectro-
gram matrix of which we produce a sound image has
256 frequency bins and about 2,580 time frames. The
number of time frames varies slightly across objects,
as the play time is close to but not precisely 30 sec-
onds for all tracks.
4.2 Training
In our work, we used domain adaptation to learn from
descriptions bound to the visual content of a native
image and predict song titles based on representations
derived from auditory cues. We trained and validated
our neural model (Figure 1) on the in-domain train
and validation subsets of the Conceptual Captions
dataset, and evaluated our baseline (Figure 3) and
mainline (Figure 4) networks on out-domain test sets
sampled from the MSD and FMA audio datasets, re-
spectively. In-domain training parameters were fine-
tuned after they were initialized to out-domain image-
based weights.
We used PyTorch (Paszke et al., 2017) version 1.0
as our deep-learning research platform to train and
evaluate our model for the task of description text
generation. Embedding and hidden dimensions were
set uniformly to 512, using a single-layer LSTM with
a dropout of 0.2 to avoid train set overfitting. In train-
ing we minimized the cross-entropy loss and used the
Adam optimizer (Kingma and Ba, 2014) with an ini-
tial learning rate of 0.001, as batch parameter updates
were distributed across four CPU workers. Variable-
length target descriptions are initially padded to the
maximum sequence length in a train set, and then
subsequently sequences are packed for efficiency. In
Figure 6, we show the progression of perplexity in
in-domain training across the first ten epochs, as the
descent subsides at around the seventh epoch.
4.3 Domain Similarity
In this section, we analyze qualitatively the closeness
between auditory and visual features, hypothesizing
that similar source and target domains is one prereq-
uisite to establish constructive transfer learning. We
chose the embedding representation that feeds the text
generator of our model in the form of a 512 × 1 ten-
sor, as both sound spectrograms and native images
conform to this interface format once they are pro-
cessed by the ResNet pipeline. However, MSD fea-
tures bypass the ResNet altogether (Figure 3) and thus
involved the reshape of the ninety-dimensional raw
timbre-vector to the 512 × 1 tensor shape, using ran-
dom permutation of replicating indices.
We used t-distributed stochastic neighbor embed-
ding (t-SNE) to project the large dimensional tensor
space onto a two-dimensional extent (van der Maaten
and Hinton, 2008) for visualization. We show pro-
portional train and test set positional distributions of
timbral and native image tensors in Figure 7a, and
correspondingly spectrogram and native image ten-
sors in Figure 7b. Upscaled timbral tensors appear
fully contained in the visual cluster, while some sound
image tensors are outliers or borderline at best and
thus might be perceived as less optimal to knowledge
transfer.
Predicting a Song Title from Audio Embeddings on a Pretrained Image-captioning Network
489
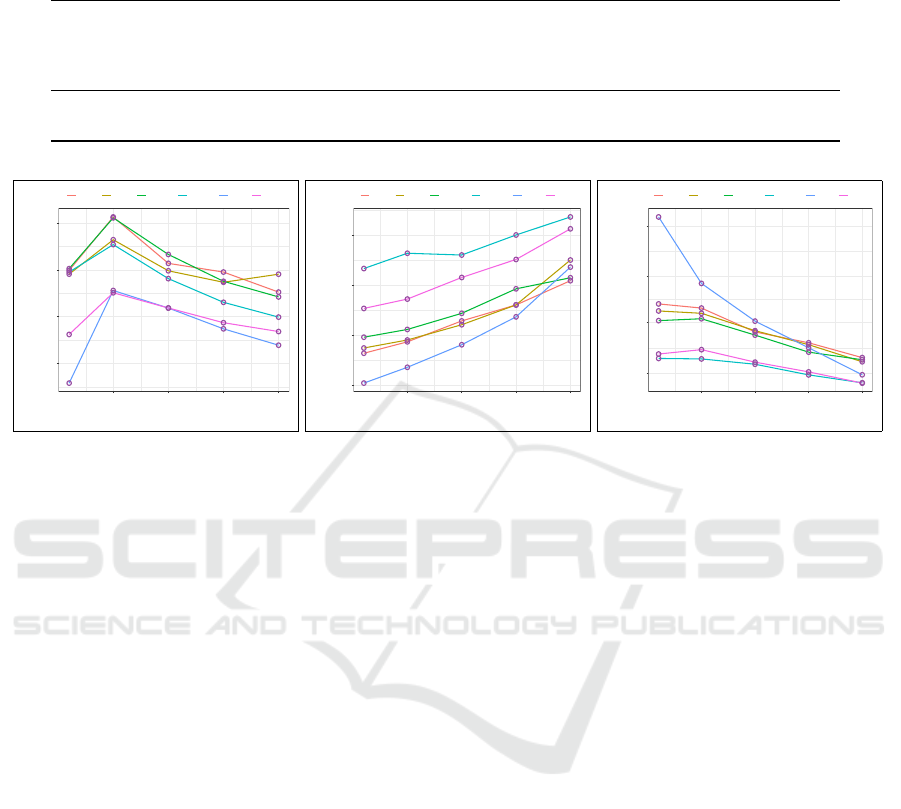
Table 4: BLEU performance scores in percentage points for in-domain and out-domain scenarios as a function of non-
descending beam sizes (k = 1 implies greedy search).
Dataset Tile Size Tiles 1-beam 5-beam 10-beam 15-beam 20-beam
Conceptual
Captions
32 × 32 64 49.9 61.3 51.4 49.6 45.3
64 × 64 16 49.1 56.4 49.8 47.4 49.1
128 × 128 4 50.3 61.1 53.3 47.6 44.2
256 × 256 1 49.5 55.4 48.2 43.1 39.9
MSD NA NA 25.8 45.6 41.9 37.4 33.9
FMA NA NA 36.2 45.1 41.9 38.7 36.9
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
5 10 15 20
Beam Size
BLEU
cc32 cc64 cc128 cc256 msd fma
(a) BLEU Scores
0
50
100
150
5 10 15 20
Beam Size
Seconds
cc32 cc64 cc128 cc256 msd fma
(b) Running Time
0.3
1.0
3.0
10.0
5 10 15 20
Beam Size
BLEU/Second
cc32 cc64 cc128 cc256 msd fma
(c) BLEU Rates
Figure 8: Model performance for in-domain and out-domain scenarios. Showing side-by-side (a) normalized BLEU scores,
(b) running time cost, and (c) BLEU rates as a function of increased beam sizes.
5 RESULTS
We report quantitative quality of predicting song ti-
tles using hand-curated timbral features and spectro-
gram representations feeding our baseline (Figure 3)
and mainline (Figure 4) neural models, respectively.
Throughout our experiments, we contrast the sub-
optimal greedy search that selects the highest scoring
word at every stage of title generation with k-beam
search that returns a list of the most likely candidate
text sequences.
Depicted in percentage points, the rendered BLEU
scores of our neural models are summarized in Table
4 for both in-domain and out-domain transfer scenar-
ios. The scores are further parameterized by five dis-
crete choices of beam sizes ∈ {1, 5, 10, 15, 20}, where
k = 1 sets greedy prediction mode. In-domain scenar-
ios use a subset of the Conceptual Captions valida-
tion set for inference and were evaluated for different
number of image tiles arranged in a randomly selected
crop size of 256 × 256 pixels from the larger raw im-
age. Tiles are fed to the ResNet module individually
and the final caption generation performance is the
mean of all individual tile scores. Our best achieved
in-domain score has 61.3 BLEU for an image config-
uration of 8 × 8 tiles, each an array of 32 × 32 pixels.
Out-domain performance is only moderately lower
than the top in-domain score by about 15.7 BLEU, as
MSD timbral features has a slight edge over the sound
image representation from FMA, with 45.6 and 45.1
BLEU, respectively.
Our results for varying beam search sizes in gen-
erating song titles are shown graphically in Figure 8.
Consistently across all the transfer scenarios, predic-
tion quality of song titles peaks for a beam size of five
as presented in Figure 8a. Out-domain curves that are
laid out distinctly at the bottom of the plot, initially
climb precipitously from greedy search to a beam size
of five, raising scores from about 0.25 to 0.45 BLEU,
and then follow a fair descent as the beam size in-
creases. In striking contrast to in-domain scores that
sustain a more controlled upward slope. Then in Fig-
ure 8b, we review running time cost corresponding
with each transfer scenario and beam size setting. As
expected, running time cost increases linearly with
a larger beam size. From a rather different perspec-
tive, BLEU-per-second derivative rates are shown on
a logarithmic scale in Figure 8c. Out-domain MSD
features render the sharpest decline in BLEU rates of
roughly 4.9X as k increases from one to five, how-
ever this drop is rewarded with a marked performance
boost of about 1.8X. In all, this quality-runtime trade-
off is deeply rooted in the beam search algorithm and
confirms its complexity.
ICAART 2020 - 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
490

Table 5: Comparative model performance of text generation
derived from audio signals, shown in BLEU scores.
Features
AudioCaps Our Model
k = 1 k = 1 k = 5
MFCC 34.1 25.8 45.6
Spectrogram 44.2 36.2 45.1
The task of generating natural language descriptions
to music audio is unusually understudied in earlier re-
search. Related to our work is the recent study by
Kim et al. (2019) that creates text solely from au-
dio input. They address the void of audio captioning
by contributing the AudioCaps dataset that consists
of 46K pairs of audio clips captured from YouTube
video frames and newly collected human-annotated
text descriptions. Kim et al. (2019) research evaluates
numerous audio-captioning models for efficacy using
both MFCC features and high-level spectrogram rep-
resentations pretrained on VGGNet (Hershey et al.,
2017). Unlike the captioning methods on the Audio-
Caps dataset that use 1-nearest search with audio fea-
tures, our model emphasizes the tradeoffs of apply-
ing beam search to generated commentary. In Table
5, we show comparative performance as our model
is slightly behind the AudioCaps captioning frame-
work on greedy search, but present an advantage of
11.5 and 0.9 BLEU for MFCC and spectrogram rep-
resentations, respectively, when using beam search of
k = 5. Although unable to evenhandedly contrast our
model against, these results on their own appear to
substantiate our transfer learning approach.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we proposed to leverage learning of im-
age embeddings that capture semantics for caption-
ing to aid in predicting song titles from both timbral
and spectrogram audio representations. We showed
that by adapting visual descriptions to the auditory
domain, our model performed in line with in-domain
state-of-the-art vision data. Moreover, applying beam
search over greedy predictions proved remarkable
gains at a reasonable running time cost, however, ex-
tending the beam size to greater than ten drew a quali-
fied diminishing return on performance. To the extent
of our knowledge, the work we presented is the first
attempt at a MIR task that translates sound cues to
natural language sequences.
A key challenge to our work was the striking dis-
parity between training and inference for conducting
supervision steps to create descriptive input text to
our model. The process of captioning a multimedia
source is often governed by a visual bias attributed
to a human judge, and hence captions tend to be ex-
tremely diverse, highly expressive, and correlate with
either the image or audio clip they are paired with. In
contrast, song titles are rather a loose summarization.
They may be based on either the lyrics or the tune,
and in many cases the song title is given before the
music has been composed, or even edited later by the
performing artist.
We envision several directions as a natural pro-
gression to improve our work. The use of additive at-
tention in the recurrent text generator only marginally
improved performance for image captioning systems,
however, replacing the LSTM network of our model
with the self-attention transformer architecture is wor-
thy of pursuing and potentially gaining efficiency.
Using the most deepest pretrained ResNet available
have incurred the cost of increased inference time
and memory footprint, thus exploring a shallower net-
work is a reasonable step to benefit our model runtime
with no apparent performance loss. Although the mu-
sic category was discarded and set for future Audio-
Caps exploration, training our model on the Audio-
Caps dataset is likely to boost semantic similarity be-
tween source and target domains and thus benefit the
quality of song title generation. Lastly, constructing
a music dataset that associates the song title with the
lyrics for each audio clip adds an essential dimension
in evaluating our task.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for
their insightful suggestions and feedback.
REFERENCES
Bahdanau, D., Cho, K., and Bengio, Y. (2015). Neural ma-
chine translation by jointly learning to align and trans-
late. In International Conference on Learning Repre-
sentations, (ICLR), San Diego, California.
Bernardi, R., Cakici, R., Elliott, D., Erdem, A., Erdem, E.,
Ikizler-Cinbis, N., Keller, F., Muscat, A., and Plank,
B. (2016). Automatic description generation from im-
ages: A survey of models, datasets, and evaluation
measures. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research
(JAIR), 55(1):409–442.
Bertin-Mahieux, T., Ellis, D. P., Whitman, B., and Lamere,
P. (2011). The million song dataset. In Proceedings of
the 12th International Conference on Music Informa-
tion Retrieval (ISMIR 2011), pages 591–596, Miami,
Florida.
Boulanger-Lewandowski, N., Bengio, Y., and Vincent, P.
(2012). Modeling temporal dependencies in high-
Predicting a Song Title from Audio Embeddings on a Pretrained Image-captioning Network
491

dimensional sequences: Application to polyphonic
music generation and transcription. In Proceedings
of the International Conference on Machine Learning
(ICML), pages 1159–1166, Edinburgh, Scotland.
Cho, K., van Merrienboer, B., Gulcehre, C., Bahdanau,
D., Bougares, F., Schwenk, H., and Bengio, Y.
(2014). Learning phrase representations using RNN
encoder–decoder for statistical machine translation. In
Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing
(EMNLP), pages 1724–1734, Doha, Qatar.
Choi, K., Fazekas, G., Sandler, M., and Cho, K. (2017).
Convolutional recurrent neural networks for music
classification. In IEEE International Conference on
Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP),
pages 2392–2396, New Orleans,Luisiana.
Chung, J., G
¨
ulc¸ehre, C¸ ., Cho, K., and Bengio, Y. (2014).
Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural net-
works on sequence modeling. CoRR, abs/1412.3555.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.3555.
Defferrard, M., Benzi, K., Vandergheynst, P., and Bresson,
X. (2017). Fma: A dataset for music analysis. In Pro-
ceedings of the International Society for Music Infor-
mation Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), page 316–323,
Suzhou, China.
Delbouys, R., Hennequin, R., Piccoli, F., Royo-Letelier,
J., and Moussallam, M. (2018). Music mood detec-
tion based on audio and lyrics with deep neural net.
In Proceedings of the International Society for Music
Information Retrieval (ISMIR), pages 370–375, Paris,
France.
Ding, N. and Soricut, R. (2017). Cold-start reinforcement
learning with softmax policy gradient. In Guyon,
I., Luxburg, U. V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fer-
gus, R., Vishwanathan, S., and Garnett, R., editors,
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems
(NIPS), pages 2817–2826. Curran Associates, Inc.
Dua, D. and Graff, C. (2017). UCI machine learning repos-
itory. http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml.
Elbayad, M., Besacier, L., and Verbeek, J. (2018). Per-
vasive attention: {2D} convolutional neural networks
for sequence-to-sequence prediction. In Proceedings
of the 22nd Conference on Computational Natural
Language Learning (CONLL), pages 97–107, Brus-
sels, Belgium.
Fang, H., Gupta, S., Iandola, F., Srivastava, R. K., Deng, L.,
Doll
´
ar, P., Gao, J., He, X., Mitchell, M., Platt, J. C.,
Zitnick, C. L., and Zweig, G. (2015). From captions
to visual concepts and back. In The IEEE Conference
on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR),
pages 1473–1482.
Germain, F. G., Chen, Q., and Koltun, V. (2018).
Speech denoising with deep feature losses. CoRR,
abs/1806.10522. https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.10522.
Hamel, P., Lemieux, S., Bengio, Y., and Eck, D. (2011).
Temporal pooling and multiscale learning for auto-
matic annotation and ranking of music audio. In Pro-
ceedings of the International Society for Music Infor-
mation Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), page 729–734,
Miami, United States.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., and Sun, J. (2016). Deep resid-
ual learning for image recognition. In 2016 IEEE Con-
ference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
(CVPR), pages 770–778, Las Vegas, Nevada.
Hershey, S., Chaudhuri, S., Ellis, D. P. W., Gemmeke,
J. F., Jansen, A., Moore, R. C., Plakal, M., Platt,
D., Saurous, R. A., Seybold, B., Slaney, M., Weiss,
R. J., and Wilson, K. (2017). Cnn architectures for
large-scale audio classification. In International Con-
ference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing
(ICASSP), pages 131–135, New Orleans,Louisiana.
Hochreiter, S. and Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-term
memory. Neural Computation, 9(8):1735–1780.
Hossain, M. Z., Sohel, F., Shiratuddin, M. F., and Laga, H.
(2019). A comprehensive survey of deep learning for
image captioning. ACM Computing Surveys, 51(6):1–
36.
Ioffe, S. and Szegedy, C. (2015). Batch normalization: Ac-
celerating deep network training by reducing internal
covariate shift. In International Conference on Ma-
chine Learning, ICML, pages 448–456, Lille, France.
Jehan, T. and Whitman, B. (2005). Echo nest.
https://developer.spotify.com.
Kim, C. D., Kim, B., Lee, H., and Kim, G. (2019). Au-
dioCaps: Generating captions for audios in the wild.
In Conference of the North American Chapter of the
Association for Computational Linguistics (NAACL),
pages 119–132, Minneapolis, Minnesota.
Kingma, D. P. and Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A method
for stochastic optimization. CoRR, abs/1412.6980.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980.
Lin, T., Maire, M., Belongie, S. J., Bourdev, L. D., Gir-
shick, R. B., Hays, J., Perona, P., Ramanan, D., Doll
´
ar,
P., and Zitnick, C. L. (2014). Microsoft COCO:
common objects in context. CoRR, abs/1405.0312.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1405.0312.
Oramas, S., Barbieri, F., Nieto, O., and Serra, X. (2018).
Multimodal deep learning for music genre classifica-
tion. Transactions of the International Society for Mu-
sic Information Retrieval (ISMIR), 1(1):4–21.
Ordonez, V., Kulkarni, G., and Berg, T. L. (2011). Im2text:
Describing images using 1 million captioned pho-
tographs. In Shawe-Taylor, J., Zemel, R. S., Bartlett,
P. L., Pereira, F., and Weinberger, K. Q., editors,
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems
NIPS, pages 1143–1151. Curran Associates, Inc.
Papineni, K., Roukos, S., Ward, T., and Zhu, W.-J. (2002).
BLEU: a method for automatic evaluation of machine
translation. In Annual Meeting of the Association
for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pages 311–318,
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Paszke, A., Gross, S., Chintala, S., Chanan, G., Yang, E.,
DeVito, Z., Lin, Z., Desmaison, A., Antiga, L., and
Lerer, A. (2017). Automatic differentiation in py-
torch. In Workshop on Autodiff, Advances in Neu-
ral Information Processing Systems (NIPS) ), Long
Beach, California.
Pennington, J., Socher, R., and Manning, C. (2014). Glove:
Global vectors for word representation. In Empirical
Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP),
pages 1532–1543, Doha, Qatar.
Pons, J., Lidy, T., and Serra, X. (2016). Experimenting with
musically motivated convolutional neural networks.
ICAART 2020 - 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
492

In International Workshop on Content-Based Multi-
media Indexing (CBMI), pages 1–6, Bucharest, Ro-
mania.
R Core Team (2013). R: A Language and Environment
for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Sta-
tistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-
project.org/.
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S.,
Ma, S., Huang, Z., Karpathy, A., Khosla, A., Bern-
stein, M., Berg, A. C., and Fei-Fei, L. (2015). Im-
agenet large scale visual recognition challenge. In-
ternational Journal of Computer Vision, 115(3):211–
252.
Sharma, P., Ding, N., Goodman, S., and Soricut, R. (2018).
Conceptual captions: A cleaned, hypernymed, im-
age alt-text dataset for automatic image captioning.
In Annual Meeting of the Association for Compu-
tational Linguistics (ACL), pages 2556–2565, Mel-
bourne, Australia. Association for Computational Lin-
guistics.
Simonyan, K. and Zisserman, A. (2015). Very deep con-
volutional networks for large-scale image recognition.
In International Conference on Learning Representa-
tions, ICLR, San Diego, California.
Sutskever, I., Vinyals, O., and Le, Q. V. (2014). Se-
quence to sequence learning with neural networks. In
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems
(NIPS), pages 3104–3112. Curran Associates, Inc.,
Red Hook, NY.
Szegedy, C., Ioffe, S., and Vanhoucke, V. (2016). Inception-
v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual
connections on learning. CoRR, abs/1602.07261.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1602.07261.
Urbano, J., Bogdanov, D., Herrera, P., G
´
omez, E., and
Serra, X. (2014). What is the effect of audio qual-
ity on the robustness of mfccs and chroma features?
In Proceedings of the International Society for Mu-
sic Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), page
573–578, Taipei, Taiwan.
van der Maaten, L. and Hinton, G. E. (2008). Visualizing
data using t-sne. Journal of Machine Learning Re-
search (JMLR), 9(Nov):2579–2605.
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones,
L., Gomez, A. N., Kaiser, L. u., and Polosukhin, I.
(2017). Attention is all you need. In Advances in
Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), pages
5998–6008. Curran Associates, Inc., Red Hook, NY.
Vinyals, O., Toshev, A., Bengio, S., and Erhan, D. (2015).
Show and tell: A neural image caption generator. In
The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition (CVPR), pages 3156–3164, Boston,
Massachusetts.
Wyse, L. (2017). Audio spectrogram represen-
tations for processing with convolutional
neural networks. CoRR, abs/1706.09559.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.09559.
Predicting a Song Title from Audio Embeddings on a Pretrained Image-captioning Network
493
