
On Satisfisfiability Modulo Theories in
Continuous Multi-Agent Path Finding: Compilation-based and
Search-based Approaches Compared
Pavel Surynek
Faculty of Information Technology, Czech Technical University in Prague, Th
´
akurova 9, 160 00 Praha 6, Czech Republic
pavel.surynek@fit.cvut.cz
Keywords:
Multi-Agent Path Finding (MAPF), Satisfiability Modulo Theory (SMT), Continuous Time, Continuous
Space, Makespan Optimal Solutions, Geometric Agents.
Abstract:
Multi-agent path finding (MAPF) in continuous space and time with geometric agents, i.e. agents of various
geometric shapes moving smoothly between predefined positions, is addressed in this paper. We analyze
a new solving approach based on satisfiability modulo theories (SMT) that is designed to obtain makespan
optimal solutions. The standard MAPF is a task of navigating agents in an undirected graph from given
starting vertices to given goal vertices so that agents do not collide with each other in vertices or edges of
the graph. In the continuous version (MAPF
R
), agents move in a metric space along predefined trajectories
that interconnect predefined positions. Agents themselves are geometric objects of various shapes occupying
certain volume of the space - circles, polygons, etc. For simplicity, we work with circular omni-directional
agents having constant velocities in the 2D plane where positions are interconnected by straight lines. As
agents can have different shapes/sizes and are moving smoothly along lines, a movement along certain lines
done with small agents can be non-colliding while the same movement may result in a collision if performed
with larger agents. Such a distinction rooted in the geometric reasoning is not present in the standard MAPF.
The SMT-based approach for MAPF
R
called SMT-CBS
R
reformulates the well established Conflict-based
Search (CBS) algorithm in terms of SMT. Lazy generation of decision variables and constraints is the key
idea behing SMT-CBS. Each time a new conflict is discovered, the underlying encoding is extended with new
variables and constraints to eliminate the conflict. We compared SMT-CBS
R
and adaptations of CBS for the
continuous variant of MAPF experimentally.
1 INTRODUCTION AND
BACKGROUND
In multi-agent path finding (MAPF) (Kornhauser
et al., 1984; Ryan, 2008; Sharon et al., 2015; Sharon
et al., 2013a; Silver, 2005; Surynek, 2009; Wang and
Botea, 2011) the task is to navigate agents from given
starting positions to given individual goals. The prob-
lem takes place in undirected graph G = (V,E) where
agents from set A = {a
1
,a
2
,...,a
k
} are placed in ver-
tices so that there is at most one agent per vertex. The
initial configuration of agents in vertices of the graph
can be written as simple assignment α
0
: A → V and
similarly the goal configuration as α
+
: A → V . The
task of navigating agents can be then expressed as a
task of transforming the initial configuration of agents
α
0
: A → V into the goal configuration α
+
: A → V .
In the standard MAPF, movements are instanta-
neous and are usually possible into vacant neighbors
assuming no other agent is entering the same tar-
get vertex
1
. We usually denote the configuration of
agents at discrete time step t as α
t
: A → V . Non-
conflicting movements transform configuration α
t
in-
stantaneously into next configuration α
t+1
so we do
not consider what happens between time steps t and
t + 1.
In order to reflect various aspects of real-life appli-
cations variants of MAPF have been introduced such
as those considering kinematic constraints (H
¨
onig
et al., 2017), large agents (Li et al., 2019), or dead-
lines (Ma et al., 2018) - see (Ma et al., 2017) for
more variants. Particularly in this work we are deal-
ing with an extension of MAPF introduced only re-
cently (Andreychuk et al., 2019b; Andreychuk et al.,
1
Different versions of MAPF permit entering a vertex
being simultaneously vacated by another agent excluding
the trivial case when agents swap their position across an
edge.
2019a; Walker et al., 2018) that considers contin-
uous time and space and continuous movements of
agents between predefined positions placed arbitrar-
ily in the metric space. The continuous version will
be denoted as MAPF
R
. It is natural in MAPF
R
to
assume geometric agents of various shapes that oc-
cupy certain volume in the space - circles in the 2D
space, polygons, spheres in the 3D space etc. In con-
trast to MAPF, where the collision is usually defined
as the simultaneous occupation of a vertex by two
(or more) agents, collisions are defined as any spa-
tial overlap of agents’ bodies in MAPF
R
. Agents in
MAPF
R
move along predefined trajectories that in-
terconnects predefined positions. Assuming certain
individual speed of an agent we can assign the agent a
position in the space at any moment. Different shapes
of agents’ bodies play a role. Hence for example a
movement along two distinct trajectories that is colli-
sion free when done with small agents may turn into
a collision if performed with large agents. For sim-
plicity we will assume agents moving along straight
lines but the the presented techniques are applicable
to different trajectories as well.
The motivation behind introducing MAPF
R
is the
need to construct more realistic paths in many appli-
cations such as controlling fleets of robots or aerial
drones (Janovsky et al., 2014; C
´
ap et al., 2013) where
continuous reasoning is closer to the reality than the
standard MAPF.
The contribution of this paper consists in show-
ing how to apply satisfiability modulo theory (SMT)
reasoning (Bofill et al., 2012; Nieuwenhuis, 2010) in
MAPF
R
solving. The SMT paradigm constructs deci-
sion procedures for various complex logic theories by
decomposing the decision problem into the proposi-
tional part having arbitrary Boolean structure and the
theory part that is restricted on the conjunctive frag-
ment.
1.1 Related Work and Organization
Our SMT-based approach focuses on makespan opti-
mal MAPF solving and builds on top of the Conflict-
based Search (CBS) algorithm (Sharon et al., 2012;
Sharon et al., 2015). Makespan optimal solutions
minimize the overall time needed to relocate all
agents into their goals.
CBS tries to solve MAPF lazily by adding con-
flict elimination constraints on demand. It starts with
the empty set of constraints. The set of constraints is
iteratively refined with new conflict elimination con-
straints after conflicts are found in solutions for the in-
complete set of constraints. Since conflict elimination
constraints are disjunctive (they forbid occurrence of
one or the other agent in a vertex at a time) the refine-
ment in CBS is carried out by branching in the search
process.
CBS can be adapted for MAPF
R
by implement-
ing conflict detection in continuous time and space
while the high-level framework of the CBS algorithm
remains the same as shown in (Andreychuk et al.,
2019b; Andreychuk et al., 2019a).
In the SMT-based approach we are trying to build
an incomplete propositional model so that if a given
MAPF
R
Σ
R
has a solution of a specified makespan
then the model is solvable (but the opposite impli-
cation generally does not hold). This is similar to
the previous SAT-based (Biere et al., 2009) MAPF
solving (Surynek, 2012; Surynek et al., 2016) where
a complete propositional model has been constructed
(that is, the given MAPF has a solution of a specified
makespan if and only is the model is solvable).
The propositional model in the SMT-based ap-
proach in constructed lazily through conflict elimina-
tion refinements as done in CBS. The lazy approach
of propositional model construction for the standard
MAPF was first introduced in (Surynek, 2019). Here
we further generalize the SMT-based approach for
MAPF
R
. Similar techniques for lazy introduction of
constraints are also known in integer programming
and were succesfully applied in the standard MAPF
solving as well (Lam et al., 2019).
The incompleteness of the model is inherited from
CBS that adds constraints lazily. This is in contrast to
SAT-based methods like MDD-SAT (Surynek et al.,
2016) where all constraints are added eagerly result-
ing in a complete model. We call our new algorithm
SMT-CBS
R
. The major difference of SMT-CBS
R
from CBS is that instead of branching the search we
only add a disjunctive constraint to eliminate the con-
flict in SMT-CBS
R
. Hence, SMT-CBS
R
does not
branch the search at all at the high-level. The proposi-
tional model is incrementally refined at the high-level
instead.
Similarly as in the SAT-based MAPF solving we
use decision propositional variables indexed by agent
a, vertex v, and time t with the meaning that if the
variable is TRUE agent a appears in v at time t. How-
ever the major technical difficulty with the continuous
version of MAPF is that we do not know all necessary
decision variables in advance due to continuous time.
After a conflict is discovered we may need new de-
cision variables to avoid that conflict. For this reason
we introduce a special decision variable generation al-
gorithm that generates decision variables on demand.
The paper is organized as follows: we first intro-
duce MAPF
R
formally. Then we recall a variant of
CBS for MAPF
R
. Details of the novel SMT-based

solving algorithm SMT-CBS
R
follow. Finally, an ex-
perimental evaluation of SMT-CBS
R
against the con-
tinuous version of CBS is shown. We also show a
brief comparison with the standard MAPF.
1.2 MAPF with Continuous Time
We follow the definition of MAPF with continu-
ous time denoted MAPF
R
from (Andreychuk et al.,
2019b) and (Walker et al., 2018). MAPF
R
shares
several components with the standard MAPF: the un-
derlying undirected graph G = (V,E), set of agents
A = {a
1
,a
2
,...,a
k
}, and the initial and goal configu-
ration of agents: α
0
: A → V and α
+
: A → V .
Definition 1. (MAPF
R
) Multi-agent path finding
with continuous time (MAPF
R
) is a 5-tuple Σ
R
=
(G = (V,E), A,α
0
,α
+
,ρ) where G, A, α
0
, α
+
are from
the standard MAPF and ρ determines continuous ex-
tensions as follows:
• ρ.x(v), ρ.y(v) for v ∈ V represent the position of
vertex v in the 2D plane; to simplify notation we
will use x
v
for ρ.x(v) and y
v
for ρ.x(v)
• ρ.velocity(a) for a ∈ A determines constant veloc-
ity of agent a; simple notation v
a
= ρ.velocity(a)
• ρ.radius(a) for a ∈ A determines the radius of
agent a; we assume that agents are circular discs
with omni-directional ability of movements; sim-
ple notation r
a
= ρ.radius(a)
Naturally we can define the distance between a
pair of vertices u, v with {u,v} ∈ E as dist(u,v) =
p
(x
v
− x
u
)
2
+ (y
v
− y
u
)
2
. Next we assume that agents
have constant speed, that is, they instantly accelerate
to v
a
from an idle state. The major difference from
the standard MAPF where agents move instantly be-
tween vertices is that in MAPF
R
continuous move-
ment of an agent between a pair of vertices (posi-
tions) along the straight line interconnecting them
takes place. Hence we need to be aware of the pres-
ence of agents at some point in the 2D plane on the
lines interconnecting vertices at any time.
As we will see in the definition of collisions hav-
ing predefined positions interconnected by straight
lines is used for simplification only. Any fixed trajec-
tory that allows us to map an agent from continuous
time to a position in the trajectory is possible.
Collisions may occur between agents due to their
size which is another difference from the standard
MAPF. In contrast to the standard MAPF, collisions
in MAPF
R
may occur not only in a single ver-
tex or edge but also on pairs of edges (on pairs of
lines/trajectories interconnecting vertices). If for ex-
ample two lines are too close to each other and si-
multaneously traversed by large agents then such a
condition may result in a collision. Agents collide
whenever their bodies overlap
2
.
We can further extend the set of continuous prop-
erties by introducing the direction of agents and the
need to rotate agents towards the target vertex be-
fore they start translation movement towards the tar-
get (agents are no more omni-directional). The speed
of rotation in such a case starts to play a role. Also
agents can be of various shapes not only circular discs
(Li et al., 2019).
For simplicity we elaborate our solving concepts
for the above basic continuous extension of MAPF
with circular agents only. We however note that all
developed concepts can be adapted for MAPF with
more continuous extensions like directional agents
which only adds another dimension to indices of
propositional variables.
A solution to given MAPF
R
Σ
R
is a col-
lection of temporal plans for individual agents
π = [π(a
1
),π(a
2
),...,π(a
k
)] that are mutu-
ally collision-free. A temporal plan for agent
a ∈ A is a sequence π(a) = [((α
0
(a),α
1
(a)),
[t
0
(a),t
1
(a))); ((α
1
(a),α
2
(a)), [t
1
(a),t
2
(a)));
...;((α
m(a)−1
,α
m(a)
(a)), [t
m(a)−1
,t
m(a)
))] where m(a)
is the length of individual temporal plan and each
pair (α
i
(a),α
i+1
(a)),[t
i
(a),t
i+1
(a))) in the sequence
corresponds to the traversal event between a pair
of vertices α
i
(a) and α
i+1
(a) starting at time t
i
(a)
(including) and finished at t
i+1
(a) (excluding).
It holds that t
i
(a) < t
i+1
(a) for all i =
0,1,..., m(a)−1. Moreover consecutive vertices must
correspond to edge traversals or waiting actions, that
is: {α
i
(a), α
i+1
(a)} ∈ E or α
i
(a) = α
i+1
(a); and
times must reflect the speed of agents for non-wait
actions, that is:
α
i
(a) 6= α
i+1
(a) ⇒ t
i+1
(a) − t
i
(a) =
dist(α
i
(a),α
i+1
(a))
v
a
.
In addition to this, agents must not collide with
each other. One possible formal definition of a geo-
metric collision is as follows:
Definition 2. (Collision) A collision between
individual temporal plans π(a) = [((α
i
(a),
α
i+1
(a)), [t
i
(a),t
i+1
(a)))]
m(a)
i=0
and π(b) =
[((α
i
(b),α
i+1
(a)),[t
i
(b),t
i+1
(b)))]
m(b)
i=0
occurs if
the following condition holds:
• ∃i ∈ {0, 1,...,m(a)} and ∃ j ∈ {0,1, ...,m(b)} such
that:
– dist([x
α
i
(a)
, y
α
i
(a)
; x
α
i+1
(a)
, y
α
i+1
(a)
]; [x
α
j
(b)
,
y
α
j
(b)
; x
α
j+1
(b)
, y
α
j+1
(b)
]) < r
a
+ r
b
2
In our current implementation we followed a more cau-
tious definition of the collision - it occurs even if agents ap-
pear too close to each other.
– [t
i
(a),t
i+1
(a))∩ [t
j
(b), t
j+1
(b)) 6=
/
0
(a vertex or an edge collision - two agents simulta-
neously occupy the same vertex or the same edge
or traverse edges that are too close to each other)
The distance between two lines P and
Q given by their endpoint coordinates
P = [x
1
,y
1
;x
2
,y
2
] and Q = [x
0
1
,y
0
1
;x
0
2
,y
0
2
] denoted
dist([x
1
,y
1
;x
2
,y
2
];[x
0
1
,y
0
1
;x
0
2
,y
0
2
]) is defined as the
minimum distance between any pair of points p ∈ P
and q ∈ Q: min{dist(p,q) | p ∈ P ∧ q ∈ Q}. The defi-
nition covers degenerate cases where a line collapses
into a single point. In such a case the definition of
dist normally works as the distance between points
and between a point and a line.
The definition among other types of collisions
covers also a case when an agent waits in vertex v and
another agent passes through a line that is too close
to v. We note that situations classified as collisions
according to the above definition may not always re-
sult in actual collisions where agents’ bodies overlap;
the definition is overcautious in this sense. Alterna-
tively we can use more precise definition of collisions
that reports collisions if and only if an actual over-
lap of agents’ bodies occurs. This however requires
more complex equations or simulations and cannot be
written as simple as above. The presented algorithmic
framework is however applicable for any kind of com-
plex definition of collision as the definition enters the
process as an external parameter.
The duration of individual temporal plan π(a) is
called an individual makespan; denoted µ(π(a)) =
t
m(a)
. The overall makespan of MAPF
R
so-
lution π = [π(a
1
),π(a
2
), ...,π(a
k
)] is defined as
max
k
i=1
(µ(π(a
i
))). In this work we focus on finding
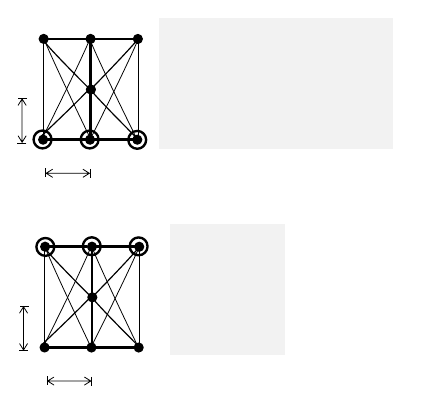
makespan optimal solutions. An example of MAPF
R
and makespan optimal solution is shown in Figure
1. We note that the standard makespan optimal so-
lution yields makespan suboptimal solution when in-
terpreted as MAPF
R
.
Through the straightforward reduction of MAPF
to MAPF
R
it can be observed that finding a makespan
optimal solution with continuous time is an NP-hard
problem (Ratner and Warmuth, 1990; Surynek, 2010;
Yu and LaValle, 2015).
2 SOLVING MAPF WITH
CONTINUOUS TIME
We will describe here how to find optimal solution
of MAPF
R
using the conflict-based search (CBS)
(Sharon et al., 2015). CBS uses the idea of resolv-
ing conflicts lazily; that is, a solution of MAPF in-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1.0
1.0
a
1
a
2
a
3
α
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1.0
1.0
a
1
a
2
a
3
α
+
π(a
1
):
1 → 1 [0.000, 1.414)
1 → 2 [1.414, 2.414)
2 → 7 [2.414, 4.650)
π(a
3
):
3 → 6 [0.000, 2.236)
6 → 5 [2.236, 3.236)
5 → 5 [3.236, 4.650)
μ = 4.650 (MAPF
R
)
π(a
2
):
2 → 4 [0.000, 1.000)
4 → 4 [1.000, 3.236)
4 → 6 [3.236, 4.236)
6 → 6 [4.236, 4.650)
π(a
1
)
1 → 6
6 → 3
3 → 7
π(a
2
)
2 → 4
4 → 1
1 → 6
π(a
3
)
3 → 7
7 → 2
2 → 5
μ = 3 (MAPF)
μ = 6.472 (MAPF
R
)
ρ.speed = 1.0 ρ.radius = 0.2
MAPF
R
MAPF
Figure 1: An example of MAPF
R
instance on a
[3,1,3]−graph with three agents and its makespan optimal
solution (an optimal solution of the corresponding standard
MAPF is shown too).
stance is not searched against the complete set of
movement constraints. Instead of forbidding all pos-
sible collisions between agents, we start with ini-
tially empty set of collision forbidding constraints that
gradually grows as new conflicts appear. CBS that
was originally developed for MAPF, can be modified
for MAPF
R
as shown in (Andreychuk et al., 2019a):
let us denote the modification CBS
R
.
2.1 Conflict-Based Search
CBS
R
is shown using pseudo-code in Algorithm 1.
The high-level of CBS
R
searches a constraint tree
(CT) using a priority queue (ordered according to the
makespan or other cumulative cost) in the breadth first
search manner. CT is a binary tree where each node
N contains a set of collision avoidance constraints
N.constraints - a set of triples (a
i
,{u,v}, [t
0
,t
+
)) for-
bidding occurrence of agent a
i
in edge {u,v} (or in
vertex u if u = v) at any time between [t
0
,t
+
), a solu-
tion N.π - a set of k individual temporal plans, and the
makespan N.µ of the current solution.
The low-level process in CBS
R
associated with
node N searches temporal plan for individual agent
with respect to set of constraints N.constraints. For
given agent a
i
, this is the standard single source
shortest path search from α
0
(a
i
) to α
+
(a
i
) that at
time t must avoid a set of edges (vertices) {{u,v} ∈
E | (a
i
,{u,v}, [t
0
,t
+
)) ∈ N.constraints ∧ t ∈ [t
0
,t
+
)}.
Various intelligent single source shortest path algo-
rithms can be applied here such as A*(Hart et al.,
1968).

Algorithm 1: Basic CBS
R
algorithm for solving
MAPF with continuous time.
1 CBS
R
(Σ
R
= (G = (V, E),A,α
0
,α
+
,ρ))
2 R.constraints ←
/
0
3 R.π ← {shortest temporal plan from α
0
(a
i
) to
α
+
(a
i
) | i = 1,2, ..., k}
4 R.µ ← max
k
i=1
µ(N.π(a
i
))
5 OPEN ←
/
0
6 insert R into OPEN
7 while OPEN 6=
/
0 do
8 N ← min
µ
(OPEN)
9 remove-Min
µ
(OPEN)
10 collisions ← validate-Plans(N.π)
11 if collisions =
/
0 then
12 return N.π
13 let (a
i
,{u,v},[t
0
,t
+
)) ×
(a
j
,{u
0
,v
0
},[t
0
0
,t
0
+
)) ∈ collisions
14 [τ
0
,τ
+
) ← [t
0
,t
+
) ∩ [t
0
0
,t
0
+
)
15 for each
(a,{w,z}) ∈ {(a
i
,{u,v}),(a
j
,{u
0
,v
0
})}
do
16 N
0
.constraints ← N.constraints ∪
{(a,{w,z},[τ
0
,τ
+
))}
17 N
0
.π ← N.π
18 update(a, N
0
.π, N
0
.con f licts)
19 N
0
.µ ←
∑
k
i=1
µ(N
0
.π(a
i
))
20 insert N
0
into OPEN
CBS
R
stores nodes of CT into priority queue
OPEN sorted according to the ascending makespan.
At each step the algorithm takes node N with the low-
est makespan from OPEN and checks if N.π represent
non-colliding temporal plans. If there is no collision,
the algorithm returns valid MAPF
R
solution N.π.
Otherwise the search branches by creating a new pair
of nodes in CT - successors of N, each resolving the
collision by diverting one of the colliding agents.
Assume that a collision occurred between agents a
i
and a
j
when a
i
traversed {u, v} during [t
0
,t
+
) and
a
j
traversed {u
0
,v
0
} during [t
0
0
,t
0
+
). This collision
can be avoided if either agent a
i
or agent a
j
does
not occupy {u,v} or {u
0
,v
0
} respectively during
[t
0
,t
+
) ∩ [t
0
0
,t
0
+
) = [τ
0
,τ
+
) or more precisely we can
calculate unsafe time interval for each agent so that
whenever the agent commences the movement during
this time interval the movement will result in a colli-
sion assuming the other agent following its original
plan. These two options correspond to new successor
nodes of N: N
1
and N
2
that inherit set of conflicts
from N as follows: N
1
.con f licts = N.con f licts
∪{(a
i
,{u,v}, [τ
0
,τ
+
))} and N
2
.con f licts =
N.con f licts ∪{(a
j
,{u
0
,v
0
},[τ
0
,τ
+
))}. N
1
.π and
N
1
.π inherit plans from N.π except those for agent a
i
and a
j
respectively that are recalculated with respect
to the new sets of conflicts. After this N
1
and N
2
are
inserted into OPEN.
Definition of collisions comes as a parameter to
the algorithm though the implementation of validate-
Plans procedure. We can switch to the less cautious
definition of collisions that reports a collision after
agents actually overlap their bodies. This can be done
through changing the validate-Plans procedure while
the rest of the algorithm remains the same.
2.2 A Satisfiability Modulo Theory
(SMT) Approach
A close look at CBS reveals that it operates simi-
larly as problem solving in satisfiability modulo theo-
ries (SMT) (Bofill et al., 2012; Nieuwenhuis, 2010).
The basic use of SMT divides a satisfiability problem
in some complex theory T into an abstract proposi-
tional part that keeps the Boolean structure of the de-
cision problem and a simplified decision procedure
DECIDE
T
that decides fragment of T restricted on
conjunctive formulae. A general T -formula Γ being
decided for satisfiability is transformed to a proposi-
tional skeleton by replacing its atoms with proposi-
tional variables. The standard SAT-solving procedure
then decides what variables should be assigned TRUE
in order to satisfy the skeleton - these variables tells
what atoms hold in Γ. DECIDE
T
then checks if the
conjunction of atoms assigned TRUE is valid with re-
spect to axioms of T . If so then the satisfying as-
signment is returned and we are finished. Otherwise
a conflict from DECIDE
T
(often called a lemma) is
reported back to the SAT solver and the skeleton is
extended with new constraints resolving the conflict.
In a more general case, not only new constraints are
added to resolve the conflict but also new variables
i.e. atoms can be added to Γ.
The above observation inspired us to the idea to
rephrase CBS
R
in terms of SMT similarly as it has
been previously done with CBS and its reformula-
tion in SMT suggested in (Surynek, 2019). T will
be represented by a theory with axioms describing
movement rules of MAPF
R
; a theory we will denote
T
MAPF
R
3
.
A plan validation procedure known from CBS will
act as DECIDE
MAPF
R
and will report back a set of
conflicts found in the current solution. The propo-
sitional part working with the skeleton will be taken
from existing propositional encodings of the stan-
3
The formal details of the theory T
MAPF
R
are not rel-
evant from the algorithmic point of view so we will omit
them here. Nevertheless let us note that the signature of
T
MAPF
R
consists of non-logical symbols describing agents’
positions at a time such as at(a,u,t) - agent a at vertex u at
time t.

dard MAPF such as the MDD-SAT (Surynek et al.,
2016) provided that constraints forbidding conflicts
between agents will be omitted (at the beginning). In
other words, we only preserve constraints ensuring
that propositional assignments form proper paths for
agents but each agent is treated as if it is alone in the
instance (we only forbid agents to jump but we ignore
collisions between them).
2.3 Decision Variable Generation
MDD-SAT introduces decision variables X
t
v
(a
i
) and
E
t
u,v
(a
i
) for discrete time-steps t ∈ {0, 1,2,...} de-
scribing occurrence of agent a
i
in v or the traversal
of edge {u,v} by a
i
at time-step t. We refer the reader
to (Surynek et al., 2016) for the details of how to en-
code constraints of top of these variables. As an ex-
ample we show here a constraint stating that if agent
a
i
appears in vertex u at time step t then it has to leave
through exactly one edge connected to u or wait in u.
X
t
u
(a
i
) ⇒
_
v | {u,v}∈E
E
t
u,v
(a
i
) ∨ E
t
u,u
(a
i
), (1)
∑
v | {u,v}∈E
E
t
u,v
(a
i
) + E
t
u,u
(a
i
) ≤ 1 (2)
Vertex collisions expressed for example by the fol-
lowing constraint are omitted when the encoding is
being built lazily in the SMT-style. The constraint
says that in vertex v and time step t there is at most
one agent.
∑
a
i
∈A | v∈V
X
t
v
(a
i
) ≤ 1 (3)
A significant difficulty in MAPF
R
is that we need
decision variables with respect to continuous time.
Fortunately we do not need a variable for any possible
time but only for important moments.
If for example the duration of a conflict in neigh-
bor v of u is [t
0
,t
+
) and agent a
i
residing in u at t ≥ t
0
wants to enter v then the earliest time a
i
can do so is
t
+
since before it would conflict in v (according to the
above definition of collisions). On the other hand if
a
i
does not want to waste time (let us note that we
search for a makespan optimal solution), then waiting
longer than t
+
is not desirable. Hence we only need
to introduce decision variable E
t
+
u,v
(a
i
) to reflect the
situation.
Generally, when having a set of conflicts we need
to generate decision variables representing occur-
rence of agents in vertices and edges of the graph at
important moments with respect to the set of conflicts.
The process of decision variable generation is for-
mally described as Algorithm 2. It performs breadth-
first search (BFS) on G using two types of actions:
Algorithm 2: Generation of decision variables in
the SMT-based algorithm for MAPF
R
solving.
1 generate-Decisions
(Σ
R
= (G = (V, E),A,α
0
,α
+
,ρ), a
i
, con f licts,
µ
max
)
2 VAR ←
/
0
3 for each a ∈ A do
4 OPEN ←
/
0
5 insert (α
0
(a),0) into OPEN
6 VAR ← VAR ∪ {X
t
0
α
0
(a)
(a)}
7 while OPEN 6=
/
0 do
8 (u,t) ← min
t
(OPEN)
9 remove-Min
t
(OPEN)
10 if t ≤ µ
max
then
11 for each v such that {u,v} ∈ E do
12 ∆t ← dist(u, v)/v
a
13 insert (v,t + ∆t) into OPEN
14 VAR ←
VAR ∪{E
t
u,v
(a),X
t+∆t
v
(a)}
15 for each v such that
{u,v} ∈ E ∪ {u,u} do
16 for each (a,{u, v}, [t
0
,t
+
)) ∈
con f licts do
17 if t
+
> t then
18 insert (u,t
+
) into
OPEN
19 VAR ←
VAR ∪{X
t
+
u
(a)}
20 return VAR
edge traversals and waiting. The edge traversal is the
standard operation from BFS. Waiting is performed
for every relevant period of time with respect to the
end-times in the set of conflicts of neighboring ver-
tices.
As a result each conflict during variable genera-
tion through BFS is treated as both present and absent
which in effect generates all possible important mo-
ments.
Procedure generate-Decision generates decision
variables that correspond to actions started on or be-
fore specified limit µ
max
. For example variables cor-
responding to edge traversal started at t < µ
max
and
finished as t
0
> µ
max
are included (line 10). Variables
corresponding to times greater than µ
max
enable de-
termining what should be the next relevant makespan
limit to test (see the high-level algorithm for details
how the makespan limit is used). Assume having a
decision node corresponding to vertex u at time t at
hand. The procedure first adds decision variables cor-
responding to edge traversals from u to neighbors de-
noted v (lines 11-14). Then all possible relevant wait-
ing actions in u with respect to its neighbors v are gen-
erated. Notice that waiting with respect to conflicts in

u are treated as well.
2.4 Eliminating Branching in CBS by
Disjunctive Refinements
The SMT-based algorithm itself is divided into two
procedures: SMT-CBS
R
representing the main loop
and SMT-CBS-Fixed
R
solving the input MAPF
R
for
a fixed maximum makespan µ. The major difference
from the standard CBS is that there is no branching
at the high-level. The set of conflicts is iteratively
extended during the entire execution of the algorithm
whenever a collision is detected.
Procedures encode-Basic and augment-Basic
build formula F (µ) over the decision variables gener-
ated using the aforementioned procedure. The encod-
ing is inspired by the MDD-SAT approach but ignores
collisions between agents. That is, F (µ) constitutes
an incomplete model for a given input Σ
R
: Σ
R
is solv-
able within makespan µ then F (µ) is satisfiable.
Conflicts are resolved by adding disjunctive con-
straints (lines 13-15 in Algorithm 4). The collision is
avoided in the same way as in the original CBS that is
one of the colliding agent is diverted from performing
the action leading to the collision. Consider for ex-
ample a collision on two edges between agents a
i
and
a
j
as follows: a
i
traversed {u, v} during [t
0
,t
+
) and a
j
traversed {u
0
,v
0
} during [t
0
0
,t
0
+
).
These two movements correspond to decision
variables E
t
0
u,v
(a
i
) and E
t
0
0
u
0
,v
0
(a
j
) hence elimination of
the collision caused by these two movements can be
expressed as the following disjunction: ¬E
t
0
u,v
(a
i
) ∨
¬E
t
0
0
u
0
,v
0
(a
j
). At the level of propositional formula
there is no information about the semantics of a con-
flict happening in the continuous space; we only have
information in the form of above disjunctive refine-
ments. The disjunctive refinements are propagated at
the propositional level from DECIDE
MAPF
R
that ver-
ifies solutions of incomplete propositional models.
The set of pairs of collected disjunctive conflicts
is propagated across entire execution of the algorithm
(line 16 in Algorithm 4).
Algorithm 3 shows the main loop of SMT-CBS
R
.
The algorithm checks if there is a solution for given
MAPF
R
Σ
R
of makespan µ. The algorithm starts at
the lower bound for µ that is obtained as the duration
of the longest temporal plan from individual temporal
plans ignoring other agents (lines 3-4).
Then µ is iteratively increased in the main loop
(lines 5-9). The algorithm relies on the fact that the
solvability of MAPF
R
w.r.t. cumulative objective like
the makespan behaves as a non decreasing monotonic
function. Hence trying increasing makespans eventu-
Algorithm 3: High-level of the SMT-based MAPF
R
solving.
1 SMT-CBS
R
(Σ
R
= (G = (V, E),A,α
0
,α
+
,ρ))
2 con f licts ←
/
0
3 π ← {π
∗
(a
i
) a shortest temporal plan from
α
0
(a
i
) to α
+
(a
i
) | i = 1,2, ..., k}
4 µ ← max
k
i=1
µ(π(a
i
))
5 while TRUE do
6 (π,con f licts, µ
next
) ←
SMT-CBS-Fixed
R
(Σ
R
, con f licts, µ)
7 if π 6= UNSAT then
8 return π
9 µ ← µ
next
ally leads to finding the optimal makespan in case of
solvable MAPF
R
provided we do not skip any rele-
vant makespan µ. The next makespan to try will then
be obtained by taking the current makespan plus the
smallest duration of the continuing movement (line
19 of Algorithm 4). The iterative scheme for trying
larger makespans follows the idea used in MDD-SAT
(Surynek et al., 2016) and before introduced in SAT-
based classical planning algorithm SATPlan (Kautz
and Selman, 1992).
3 EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION
In this section we present results of the first experi-
mentation with SMT-CBS
R
. We implemented SMT-
CBS
R
in C++ to evaluate its performance
4
.
SMT-CBS
R
was implemented on top of Glucose
3 SAT solver (Audemard and Simon, 2009) which
ranks among the best SAT solvers according to recent
SAT solver competitions (Balyo et al., 2017). When-
ever possible the SAT solver was consulted in the in-
cremental mode.
It turned out to be important to generate decision
variables in a more advanced way than presented
in Algorithm 2. We need to prune out decisions
from that the goal vertex cannot be reached under
given makespan bound µ
max
. That is whenever we
have a decision (u,t) such that t + ∆t > µ
max
, where
∆t = dist
estimate
(u,α
+
(a))/v
a
and dist
estimate
is a
lower bound estimate of the distance between a pair
of vertices, we rule out that decision from further con-
sideration. Moreover we apply a postprocessing step
in which we iteratively remove decisions that have
4
The complete source codes will be made available
to enable reproducibility of presented results on the au-
thor’s website: http://users.fit.cvut.cz/surynpav/research/
icaart2020.
Algorithm 4: Low-level of the SMT-based MAPF
R
solving.
1 SMT-CBS-Fixed
R
(Σ
R
, con f licts, µ)
2 VAR ← generate-Decisions(Σ
R
, con f licts, µ)
3 F (µ) ← encode-Basic(VAR, Σ
R
,con f licts, µ)
4 while TRUE do
5 assignment ← consult-SAT-Solver(F (µ))
6 if assignment 6= UNSAT then
7 π ← extract-Solution(assignment)
8 collisions ← validate-Plans(π)
9 /* DECIDE
MAPF
R
*/
10 if collisions =
/
0 then
11 return (π,
/
0,UNDEF)
12 for each (a
i
,{u,v},[t
0
,t
+
)) ×
(a
j
,{u
0
,v;},[t
0
0
,t
0
+
)) ∈ collisions do
13 Y ← (u = v) ? X
t
0
u
(a
i
) : E
t
0
u,v
(a
i
)
14 Z ← (u
0
= v
0
) ? X
t
0
0
u
0
(a
j
) :
E
t
0
0
u
0
,v
0
(a
j
)
15 F (µ) ← F (µ) ∪ {¬Y ∨ ¬Z}
16 [τ
0
,τ
+
) ← [t
0
,t
+
) ∩ [t
0
0
,t
0
+
)
17 con f licts ← con f licts ∪
{(a
i
,{u,v},[τ
0
,τ
+
)),
(a
j
,{u
0
,v
0
},[τ
0
,τ
+
))}
18 VAR ← generate-Decisions(Σ
R
,
con f licts, µ)
19 F (µ) ← augment-
Basic(F (µ), VAR,Σ
R
,con f licts, µ)
20 µ
next
← min{t | X
t
u
(a
i
) ∈ VAR ∧t > µ)}
21 return (UNSAT, con f licts, µ
next
)
no successors. The propositional model is generated
only after this preprocessing.
In addition to SMT-CBS
R
we re-implemented in
C++ CBS
R
, currently the only alternative solver for
MAPF
R
based on own dedicated search (Andreychuk
et al., 2019a). The distinguishing feature of CBS
R
is
that at the low-level it uses a more sophisticated sin-
gle source shortest path algorithm that searches for
paths that avoid forbidden intervals, a so-called safe-
interval path planning (SIPP) (Yakovlev and Andrey-
chuk, 2017).
Our implementation of CBS
R
used the standard
heuristics to improve the performance such as the
preference of resolving cardinal conflicts (Boyarski
et al., 2015). Without this heuristic, CBS
R
usually
exhibited poor performance. In the preliminary tests
with SMT-CBS
R
, we initially tried to resolve against
single cardinal conflict too but eventually it turned out
to be more efficient to resolve against all discovered
conflicts (the presented pseudo-code shows this vari-
ant).
5
5
All experiments were run on a system with Ryzen 7 3.0
GHz, 16 GB RAM, under Ubuntu Linux 18.
3.1 Benchmarks and Setup
SMT-CBS
R
and CBS
R
were tested on synthetic
benchmarks consisting of layered graphs, grids, game
maps (Sturtevant, 2012). The layered graph of height
h denoted [l
1
,l
2
,...,l
h
]-graph is a special contruct en-
abling detailed stuty of movements of agents in con-
tinuous space. The layered graph consists of h lay-
ers of vertices placed horizontally above each other in
the 2D plane (see Figure 1 for [3,1,3]-graph). More
precisely the i-th layer is placed horizontally at y = i.
Layers are centered horizontally and the distance be-
tween consecutive points in the layer is 1.0. Size of
all agents was 0.2 in radius.
We measured runtime and the number of deci-
sions/iterations to compare the performance of SMT-
CBS
R
and CBS
R
. Small layered graphs consisting of
2 to 5 layers with up to 5 vertices per layer were used
in tests. Three consecutive layers are always fully in-
terconnected by edges. There is no edge across more
than three layers of the graphs. That is in graphs with
more than 3 layers agents cannot go directly to the
goal vertex.
In all tests agents started in the 1-st layer and fin-
ished in the last h-th layer. To obtain instances of var-
ious difficulties random permutations of agents in the
starting and goal configurations were used (the 1-st
layer and h-th layer were fully occupied in the start-
ing and goal configuration respectively). If for in-
stance agents are ordered identically in the starting
and goal configuration with h ≤ 3, then the instance
is relatively easy as it is sufficient that all agents move
simultaneously straight into their goals.
We also used grids of sizes 8 × 8 and 16 × 16
with no obstacles in our tests. Initial and goal con-
figuration of agents have been generated randomly.
In contrast to MAPF benchmarks where grids are 4-
connected we used interconnection with all vertices
in the neighborhood up to certain distance called 2
k
-
neighborhood in (Andreychuk et al., 2019a). A simi-
lar setup has been used in game maps (Dragon Age).
The difference here is that the game maps are larger
and contain obstacles.
Ten random instances were generated for individ-
ual graph. The timeout for all tests has been set to 1
minute in layered graphs and small grids and 10 min-
utes for game maps. Results from instances finished
under this timeout were used to calculate average run-
times.
3.2 Comparison of MAPF
R
and MAPF
Solving
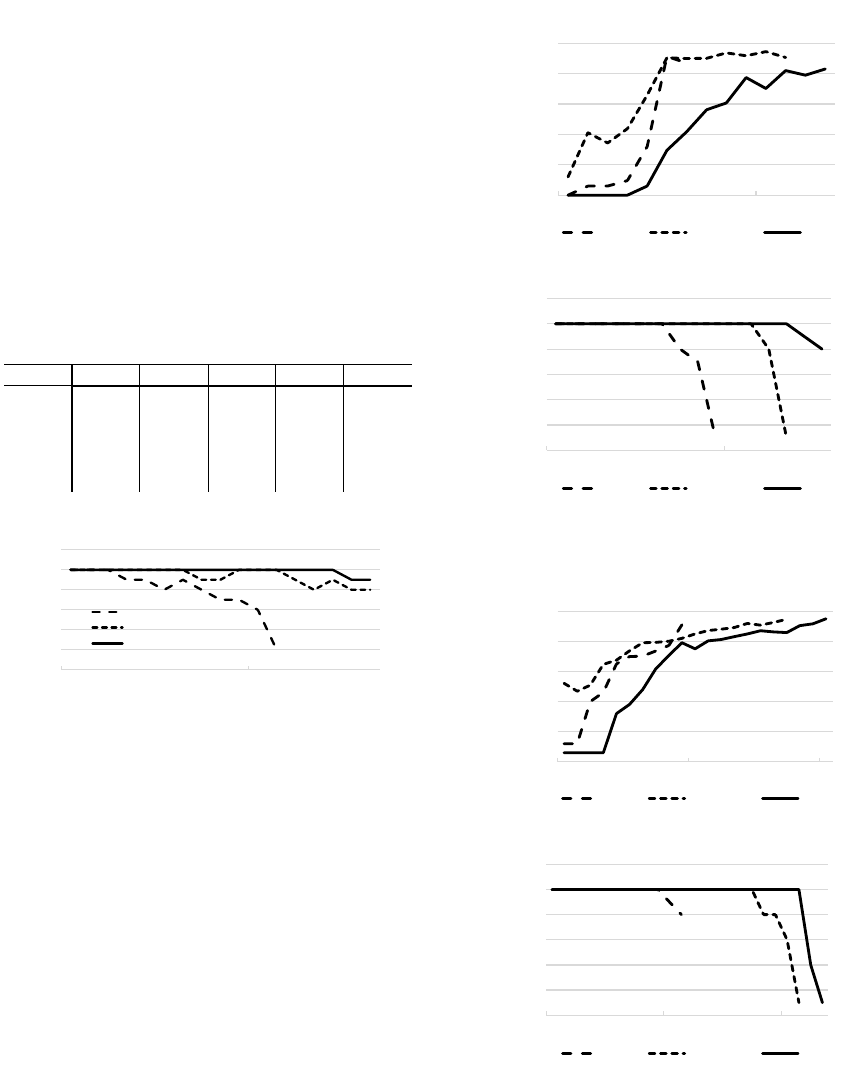
Part of the results obtained in our experimentation
with layered graphs is shown in Figure 2. The
general observation from our runtime evaluation is
that MAPF
R
is significantly harder than the standard
MAPF. When continuity is ignored, makespan opti-
mal solutions consist of fewer steps. But due to re-
garding all edges to be unit in MAPF, the standard
makespan optimal solutions yield significantly worse
continuous makespan (this effect would be further
manifested if we use longer edges).
Average runtime and makespan (μ) on selected layered graphs
Graph
CBS
R
SMT-CBS
R
μ MAPF
R
CBS
μ MAPF
[2,2]
2.78
1.22
2.41
0.01
2.00
[3,1,3]
17.91
2.33
3.65
0.02
2.75
[4,2,2,4]
19.34
4.78
3.80
0.02
2.67
[5,3,1,3,5]
57.23
6.11
6.78
0.03
3.15
[5,3,5,3,5]
-
19.93
5.39
0.03
3.75
0,00
0,20
0,40
0,60
0,80
1,00
1,20
4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
Success rate
|V|
Success rate (layered graphs)
CBS-R
SMT-CBS-R
CBS
Figure 2: Comparison of CBS
R
and SMT-CBS
R
in terms
of average runtime, makespan, and success rate on layered
graphs. The standard CBS on the corresponding standard
MAPF is shown too (times are in seconds). Makespan is
shown for the case when the instance is interpreted as the
standard MAPF and as MAPF
R
.
SMT-CBS
R
outperforms CBS
R
on tested in-
stances significantly. CBS
R
reached the timeout
many more times than SMT-CBS
R
. In the absolute
runtimes, SMT-CBS
R
is faster by factor of 2 to 10
than CBS
R
.
In terms of the number of decisions, SMT-CBS
R
generates order of magnitudes fewer iterations than
CBS
R
. This is however expected as SMT-CBS
R
shrinks the entire search tree into a single branch in
fact. We note that branching within the search space
in case of SMT-CBS
R
is deferred into the SAT solver
where even more branches may appear.
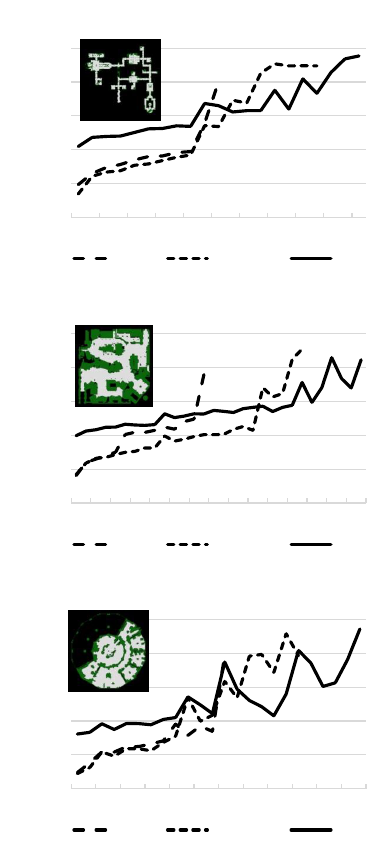
In case of small grids and large maps (Figures 3,
4 and 5), the difference between CBS
R
and SMT-
CBS
R
is generally smaller but still for harder in-
stances SMT-CBS
R
tends to have better runtime and
success rate. We attribute the smaller difference be-
tween the two algorithms to higher regularity in grids
0,00
0,01
0,10
1,00
10,00
100,00
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Runtime (seconds)
|A|
Average runtime (grid 8x8)
CBS-R SMT-CBS-R CBS
0,00
0,20
0,40
0,60
0,80
1,00
1,20
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
Success rate
|A|
Success rate (grid 8x8)
CBS-R SMT-CBS-R CBS
Figure 3: Comparison of CBS
R
and SMT-CBS
R
on 8 × 8
grid with 2
k
neighborhood (k = 3).
0,00
0,01
0,10
1,00
10,00
100,00
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22
Runtime (seconds)
|A|
Average runtime (grid 16x16)
CBS-R SMT-CBS-R CBS
0,00
0,20
0,40
0,60
0,80
1,00
1,20
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24
Success rate
|A|
Success rate (grid 16x16)
CBS-R SMT-CBS-R CBS
Figure 4: Comparison of CBS
R
and SMT-CBS
R
on 16×16
grid with 2
k
neighborhood (k = 3).
compared to layered graphs that exhibit higher com-
binatorial difficulty.
0,01
0,1
1
10
100
1000
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22
Runtime (seconds)
|A|
Average runtime (Brc202d)
CBS-R SMT-CBS-R CBS
0,01
0,1
1
10
100
1000
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30
Runtime (seconds)
|A|
Average runtime (Den520d)
CBS-R SMT-CBS-R CBS
0,01
0,1
1
10
100
1000
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24
Runtime (seconds)
|A|
Average runtime (Ost003d)
CBS-R SMT-CBS-R CBS
Figure 5: Comparison of CBS
R
and SMT-CBS
R
on game
maps (Dragon Age) with 2
k
neighborhood (k = 3).
4 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSION
We suggested a novel approach for the makespan op-
timal solving of the multi-agent path finding problem
with continuous time and space based on satisfiability
modulo theories (SMT). Our approach builds on the
idea of treating constraints lazily as suggested in the
CBS algorithm but instead of branching the search af-
ter encountering a conflict we refine the propositional
model with the conflict elimination disjunctive con-
straint. The major obstacle in using SMT and propo-
sitional reasoning is that decision variables cannot be
determined in advance straightforwardly in the con-
tinuous case. We hence suggested a novel decision
variable generation approach that enumerates new de-
cisions after discovering new conflicts. The proposi-
tional model is iteratively solved by the SAT solver.
We call the novel algorithm SMT-CBS
R
.
We compared SMT-CBS
R
to the only previous
approach for MAPF
R
that modifies the standard CBS
algorithm (Andreychuk et al., 2019a) and uses dedi-
cated search on a number of benchmarks. The out-
come of our comparison is that SMT-CBS
R
is faster
than CBS
R
. We observed the best performance of
SMT-CBS
R
on layered graphs that constitute com-
binatorially difficult case on a small graph - this is
the case where SMT-CBS
R
relies mostly on the SAT
solver and less on decision variable generation and
other other high-level mechanisms. We attribute the
better runtime results of SMT-CBS
R
to more effi-
cient handling of disjunctive conflicts in the underly-
ing SAT solver through propagation, clause learning,
and other mechanisms.
Comparison with the standard MAPF version in-
dicate that continuous reasoning is harder to solve but
on the other hand provides more realistic solutions.
Closer analysis of assumptions introduced by the
definition of MAPF
R
shows the importance of prede-
fined interconnections between positions in the space.
Currently neither CBS
R
nor SMT-CBS
R
can handle
agents that are moving freely in the space along any
trajectory. Such a less restrictive variant of continu-
ous MAPF takes place in completely different search
space and hence searching for a solution would re-
quire different reasoning.
For the future work we assume extending the con-
cept of SMT-based approach for MAPF
R
with other
cumulative cost functions other than the makespan
such as the sum-of-costs (Sharon et al., 2013b). We
also plan to extend the node generation scheme to di-
rectional agents where we need to add the third di-
mension in addition to space (vertices) and time: di-
rection (angle). We also regard the work in MAPF
R
as stepping-stone to multi-robot motion planning in
continuous configuration spaces (LaValle, 2006).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper has been supported by the Czech Science
Foundation (application number 19-17966S). The au-
thor would like to thank anonymous reviewers for
their effort to provide valuable comments.
REFERENCES
Andreychuk, A., Yakovlev, K., Atzmon, D., and Stern, R.
(2019a). Multi-agent pathfinding (MAPF) with con-
tinuous time. CoRR, abs/1901.05506.
Andreychuk, A., Yakovlev, K. S., Atzmon, D., and Stern,
R. (2019b). Multi-agent pathfinding with continuous
time. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth Interna-
tional Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJ-
CAI 2019, pages 39–45. ijcai.org.
Audemard, G. and Simon, L. (2009). Predicting learnt
clauses quality in modern SAT solvers. In IJCAI,
pages 399–404.
Balyo, T., Heule, M. J. H., and J
¨
arvisalo, M. (2017). SAT
competition 2016: Recent developments. In AAAI,
pages 5061–5063.
Biere, A., Biere, A., Heule, M., van Maaren, H., and Walsh,
T. (2009). Handbook of Satisfiability: Volume 185
Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications.
IOS Press.
Bofill, M., Palah
´
ı, M., Suy, J., and Villaret, M. (2012). Solv-
ing constraint satisfaction problems with SAT modulo
theories. Constraints, 17(3):273–303.
Boyarski, E., Felner, A., Stern, R., Sharon, G., Tolpin,
D., Betzalel, O., and Shimony, S. (2015). ICBS:
improved conflict-based search algorithm for multi-
agent pathfinding. In IJCAI, pages 740–746.
C
´
ap, M., Nov
´
ak, P., Vokr
´
ınek, J., and Pechoucek, M.
(2013). Multi-agent RRT: sampling-based coopera-
tive pathfinding. In International conference on Au-
tonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, AAMAS
’13, 2013, pages 1263–1264.
Hart, P. E., Nilsson, N. J., and Raphael, B. (1968). A for-
mal basis for the heuristic determination of minimum
cost paths. IEEE Transactions on Systems Science and
Cybernetics, SSC-4(2):100–107.
H
¨
onig, W., Kumar, T. K. S., Cohen, L., Ma, H., Xu, H.,
Ayanian, N., and Koenig, S. (2017). Summary: Multi-
agent path finding with kinematic constraints. In Pro-
ceedings of the Twenty-Sixth International Joint Con-
ference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI 2017, Mel-
bourne, Australia, August 19-25, 2017, pages 4869–
4873.
Janovsky, P., C
´
ap, M., and Vokr
´
ınek, J. (2014). Finding co-
ordinated paths for multiple holonomic agents in 2-d
polygonal environment. In International conference
on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, AA-
MAS ’14, 2014, pages 1117–1124.
Kautz, H. A. and Selman, B. (1992). Planning as satisfiabil-
ity. In Proceedings of the 10th European Conference
on Artificial Intelligence, ECAI 1992, pages 359–363.
John Wiley and Sons.
Kornhauser, D., Miller, G. L., and Spirakis, P. G. (1984).
Coordinating pebble motion on graphs, the diameter
of permutation groups, and applications. In FOCS,
1984, pages 241–250.
Lam, E., Bodic, P. L., Harabor, D. D., and Stuckey, P. J.
(2019). Branch-and-cut-and-price for multi-agent
pathfinding. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth In-
ternational Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence,
IJCAI 2019, 2019, pages 1289–1296. ijcai.org.
LaValle, S. M. (2006). Planning algorithms. Cambridge
University Press.
Li, J., Surynek, P., Felner, A., Ma, H., and Koenig, S.
(2019). Multi-agent path finding for large agents. In
AAAI. AAAI Press.
Ma, H., Koenig, S., Ayanian, N., Cohen, L., H
¨
onig, W.,
Kumar, T. K. S., Uras, T., Xu, H., Tovey, C. A.,
and Sharon, G. (2017). Overview: Generalizations
of multi-agent path finding to real-world scenarios.
CoRR, abs/1702.05515.
Ma, H., Wagner, G., Felner, A., Li, J., Kumar, T. K. S.,
and Koenig, S. (2018). Multi-agent path finding with
deadlines. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh In-
ternational Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence,
IJCAI 2018, July 13-19, 2018, Stockholm, Sweden.,
pages 417–423.
Nieuwenhuis, R. (2010). SAT modulo theories: Getting the
best of SAT and global constraint filtering. In Prin-
ciples and Practice of Constraint Programming - CP
2010 - 16th International Conference, CP 2010, St.
Andrews, Scotland, UK, September 6-10, 2010. Pro-
ceedings, pages 1–2.
Ratner, D. and Warmuth, M. K. (1990). Nxn puzzle
and related relocation problem. J. Symb. Comput.,
10(2):111–138.
Ryan, M. R. K. (2008). Exploiting subgraph structure in
multi-robot path planning. J. Artif. Intell. Res. (JAIR),
31:497–542.
Sharon, G., Stern, R., Felner, A., and Sturtevant, N.
(2015). Conflict-based search for optimal multi-agent
pathfinding. Artif. Intell., 219:40–66.
Sharon, G., Stern, R., Felner, A., and Sturtevant, N. R.
(2012). Conflict-based search for optimal multi-agent
path finding. In AAAI.
Sharon, G., Stern, R., Goldenberg, M., and Felner, A.
(2013a). The increasing cost tree search for optimal
multi-agent pathfinding. Artif. Intell., 195:470–495.
Sharon, G., Stern, R., Goldenberg, M., and Felner, A.
(2013b). The increasing cost tree search for opti-
mal multi-agent pathfinding. Artificial Intelligence,
195:470–495.
Silver, D. (2005). Cooperative pathfinding. In Proceedings
of the First Artificial Intelligence and Interactive Dig-
ital Entertainment Conference, 2005, pages 117–122.
AAAI Press.
Sturtevant, N. R. (2012). Benchmarks for grid-based
pathfinding. Computational Intelligence and AI in
Games, 4(2):144–148.
Surynek, P. (2009). A novel approach to path planning
for multiple robots in bi-connected graphs. In 2009
IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Au-
tomation, ICRA 2009, pages 3613–3619. IEEE.
Surynek, P. (2010). An optimization variant of multi-robot
path planning is intractable. In Proceedings of the
Twenty-Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelli-
gence, AAAI 2010. AAAI Press.
Surynek, P. (2012). Towards optimal cooperative path
planning in hard setups through satisfiability solving.
In PRICAI 2012: Trends in Artificial Intelligence -
12th Pacific Rim International Conference on Artifi-
cial Intelligence, 2012. Proceedings, volume 7458 of
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 564–576.
Springer.
Surynek, P. (2019). Unifying search-based and
compilation-based approaches to multi-agent path
finding through satisfiability modulo theories. In
Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth International Joint
Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI 2019,
2019, pages 1177–1183. ijcai.org.
Surynek, P., Felner, A., Stern, R., and Boyarski, E. (2016).
Efficient SAT approach to multi-agent path finding un-
der the sum of costs objective. In ECAI, pages 810–
818.
Walker, T. T., Sturtevant, N. R., and Felner, A. (2018). Ex-
tended increasing cost tree search for non-unit cost
domains. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh In-
ternational Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence,
IJCAI 2018., pages 534–540.
Wang, K. and Botea, A. (2011). MAPP: a scalable multi-
agent path planning algorithm with tractability and
completeness guarantees. JAIR, 42:55–90.
Yakovlev, K. and Andreychuk, A. (2017). Any-angle
pathfinding for multiple agents based on SIPP al-
gorithm. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh In-
ternational Conference on Automated Planning and
Scheduling, ICAPS 2017., page 586.
Yu, J. and LaValle, S. M. (2015). Optimal multi-robot
path planning on graphs: Structure and computational
complexity. CoRR, abs/1507.03289.
