
The Effect of Well-informed Minorities and Meritocratic Learning in
Social Networks
Marwa Shekfeh and Ali A. Minai
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH 45221-0030, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Associative Learning, Social Learning, Cognitive Agents, Misinformation.
Abstract:
A significant amount of information acquisition in human groups occurs through social learning, i.e., individ-
uals learning through communication with their peers. Since people communicate what they know and their
information is not completely accurate, such peer-to-peer learning can lead to the spread of both knowledge
and misinformation over social networks. How much of each occurs depends on many factors, including the
quality of knowledge in the group as a whole, its initial distribution over the network, and the learning styles
of individuals. The number of configurations in which these factors can occur is infinite, but multi-agent net-
work models provide a promising way to explore plausible scenarios. In this paper, we use such a model to
consider the joint effect of two factors: 1) The proportion of initially well-informed and ill-informed agents
in the population; and 2) The choice of each group to learn in one of two plausible ways. The simulations
reported find that both factors have a large effect.
1 INTRODUCTION
The spread of misinformation in social networks has
recently been a topic of major interest because of
the increasingly important role social media is play-
ing in politics and policy (Del Vicario et al., 2016;
Allcott and Gentzkow, 2017; Shu et al., 2017; Wal-
drop, 2017; Vosoughi et al., 2018; Oliveira and Chan,
2018; Tambuscio et al., 2018). However, the social
propagation of misinformation has been part of hu-
man society since time immemorial, and methods to
counter it have become part of the social mores and
codes in virtually all societies. The challenge being
faced at the present time arises from the sudden, ex-
ponential, and non-geometric amplification of social
networking with the advent of the Internet. It has,
therefore, become very important to understand the
factors that contribute to the spread of misinforma-
tion or can mitigate such spread. Of course, this is
an extremely complex issue that can be addressed at
many different levels using a variety of approaches.
In this paper, we describe a simple, abstract multi-
agent model called MANILA (Multi-Agent Network
for the Implicit Learning of Associations) to explore
the implicit social propagation of false conceptual as-
sociations. We apply this model to look at the effect of
two factors on the spread of such misinformation: 1)
The presence of an extremely well-informed minority
in the population; and 2) The preference of individu-
als to attend to peers based on their perceived like-
mindedness versus their reputation for being well-
informed. The model considers both the quality and
quantity of information, and attempts to capture the
implicit nature of social learning as well as some of
its cognitive complexities.
2 MOTIVATION
Human knowledge is necessarily imperfect, and the
ubiquity of social learning makes it inevitable that
false information would spread to some degree in hu-
man populations (Buntain and Golbeck, 2017; Men-
doza et al., 2010; Castillo et al., 2013). However, not
all individuals are equally well- or ill-informed, and
it is interesting to consider how the presence of ex-
ceptionally well-informed individuals in a population
influences the quality of knowledge in the larger, less
well-informed sub-population. Here, one can con-
sider varying degrees of being well- or ill-informed as
well as a varying presence of each class in the overall
population. Exploring this entire space of possibili-
ties is practically impossible even in a computational
model, but a few canonical cases can be considered.
One of these is when the population is divided into
those who only have accurate information and those
104
Shekfeh, M. and Minai, A.
The Effect of Well-informed Minorities and Meritocratic Learning in Social Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0008980201040115
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2020) - Volume 1, pages 104-115
ISBN: 978-989-758-395-7; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

whose information is tainted to some plausible degree
by inaccuracies. The proportion of each group in the
population can then be varied systematically, as is the
case in the present study.
A second interesting factor is which peers the
agents in each sub-population learn from. Again,
there are many possibilities, but the MANILA model
includes three pure strategies for accepting informa-
tion received from a peer: 1) Based on the strength
of the social connection; 2) Based on perceived like-
mindedness; and 3) Based on the empirically ob-
served reputation of the peer for having accurate in-
formation. Well-defined mixtures of these strate-
gies are also possible. In this paper, we consider
the canonical situation where well-informed agents
prefer to learn from high-quality peers whereas the
less well-informed agents prefer to learn from like-
minded ones. We then consider whether the mixture
of some quality preference in the latter population can
have a significant effect.
3 BACKGROUND
The two main features of MANILA are the spread
of information in the social network and the im-
plicit learning of (true and false) associations that re-
sults from it. This section relates these features of
MANILA to prior work.
The diffusion of information in social networks
has been studied empirically for a long time, result-
ing in several models (Granovetter, 1978; Liggett,
1985; Kempe et al., 2003). Many other models have
also been developed for the diffusion and spreading
of ideas, innovations, information, and disease on
social networks (Adar and Adamic, 2005; Leskovec
et al., 2006; Leskovec et al., 2007; Watts and Dodds,
2007; Liben-Nowell and Kleinberg, 2008; Golden-
berg et al., 2008). The effect of model structure on
the spread of information (and misinformation) has
also been studied (Weng et al., 2013). Lamberson
(Lamberson, 2010) proposed the term “cognitive ad-
vantage” as a factor in how one should study idea
propagation, and criticized previous models that took
into consideration only the underlying structure of the
social networks without looking at the cognitive and
psychological profile of agents diffusing information
or ideas through the social network. MANILA also
incorporates the cognitive preferences and reputation
of agents in the model.
Though learning and adaptation are not part of all
multi-agent models (MAS), in most cases the phe-
nomenon of interest does require the inclusion of
adaptation – often in the form of reinforcement learn-
ing (Sutton and Barto, 1998), where agents learn to
improve their choices based on positive or negative
feedback from the environment or a critic. Learning
in MAS is a natural extension of classic reinforcement
learning, but adds a crucial social component, with
learning depending not only on rewards, but also on
communication, attention and information diffusion
(Weiss (ed.), 1999). In almost all cases, however, re-
inforcement learning is explicit, with each action or
sequence of actions eliciting a direct, visible reward
from a critic. MANILA, in contrast, uses a type of
reinforcement learning that differs from the classic
paradigm because it uses reward only implicitly and
indirectly.
Bayesian models of learning in social networks
have been studied by several researchers (Gale and
Shachar, 2003; Rosenberg et al., 2009; Acemoglu
et al., 2011; Lobel and Sadler, 2012; Mueller-Frank,
2013). These models are complex, and focus mainly
on proving the convergence of beliefs to the truth.
However, most of them do not model the dynamics
of learning and information diffusion, or the asso-
ciative nature of knowledge. In contrast, MANILA
takes into consideration the representation of knowl-
edge as epistemic networks, the communication of
this knowledge, and the flow of ideas over a social
network with a specific structure – albeit in a simple,
idealized way.
Implicit learning (Reber, 1967; Seger, 1994)
refers to learning that occurs incidentally and with-
out awareness of learning. Most work on this – in-
cluding computational models (Dienes, 1992; Mathis
and Mozer, 1994) – focuses on individuals without
reference to social factors (Berry, 1997; Dienes and
Berry, 1997). In MANILA, however, the term refers
to the acquisition or loss of conceptual associations
by agents as a side-effect of their communication with
each other, and incorporates both social and cognitive
factors.
4 MODEL DESCRIPTION
4.1 Overview
MANILA is a system with cognitive and generative
agents who receive and learn associative informa-
tion implicitly from interaction with their peers in a
social network. The social network is assumed to
have a small-world (SW) architecture as proposed by
Watts and Strogatz (Watts and Strogatz, 1998). The
knowledge of each agent, i, is represented as an epis-
temic network (EN), E
i
, whose nodes represent con-
cepts and edges indicate associations between con-
The Effect of Well-informed Minorities and Meritocratic Learning in Social Networks
105

cepts. Therefore, This system has a network-of-
networks structure with two levels of networks: The
social network connecting the agents, each of whom
has an epistemic network. To mimic natural dis-
course, agents are assumed to communicate not in
terms of concepts, but ideas, which are combinations
of concepts, as postulated in most models of ideation
(Campbell, 1960; Mednick, 1962; Brown et al., 1998;
Paulus, 2002; Fauconnier and Turner, 2003; Simon-
ton, 2003; Simonton, 2010). Formally, an idea is de-
fined as a 0.5-quasi-clique (Brunato et al., 2008) of
6 to 10 concept nodes in the EN. Concepts and ideas
are defined purely in abstract terms to perform sys-
tematic simulations, but a lexical network based on a
text corpus could be used as well.
Agents in MANILA generate and express ideas,
i.e., combinations of concepts, based not on their ex-
pectation of reward – which they have no model to
calculate – but on their subjective assessment of the
idea’s coherence within their own mind, which they
use as a surrogate for its value. This models the nat-
ural situation in human expression where individuals
express ideas based on their own convictions rather
than on a calculation of external reward, with the tacit
assumption that those convictions, in fact, represent
real value or truth.
Similarly, when an agent receives an idea from a
peer, it assimilates that idea into its own mind based
not on some explicit reward that the idea has visibly
generated, but based on its esteem and regard for the
peer from whom it came. This esteem, in turn, can be
based on several factors, including those that have no
bearing on the veracity of the idea or the agent.
The Oracle
Since the focus of this work is on false associations,
there needs to be a criterion of true associations, and
a mechanism by which the correctness or incorrect-
ness of expressed ideas can be perceived in the so-
cial network. In keeping with the abstract nature of
the model, we assume that there is a fixed large ideal
epistemic network (IEN) of concepts and true associa-
tions known only to an Oracle, which thus represents
the ground truth. Agents’ initial ENs represent par-
tial, noisy samples from the IEN, reflecting the fact
that an individual agent’s information is typically in-
complete and possibly inaccurate. Whenever an agent
expresses an idea, it is evaluated by the Oracle and
elicits a reward to the agent based on the idea’s con-
sistency with the Oracle’s IEN. Thus, the Oracle plays
the role of the critic in classic reinforcement learning.
However, in this case, the reward represents only the
implicit benefit and reputation an agent acquires for
being right, and is not publicly visible or linked ex-
plicitly to a specific idea in the generating agent’s per-
ception. Agents accumulate the rewards they receive
with a decay factor, and the cumulative reward of an
agent at a given time is visible to other agents as an
indication of the agent’s merit status. Thus, over time,
every agent can see which of their peers are more (or
less) well-informed in an aggregate sense.
In a real-world situation, the role of the Oracle
would be played by fact-checkers, news reporters, ex-
perts, and the general social consensus on what is or
is not acceptable as fact. In MANILA, the Oracle pro-
vides a purely abstract but fixed (and therefore objec-
tive) reference against which the correctness of asser-
tions can be evaluated.
The Social Network
The social network in MANILA is defined by a sym-
metric small-world adjacency matrix C = [c
i j
], where
c
i j
∈ {0, 1} indicates whether there is a social connec-
tion from A
j
to A
i
.
Epistemic Network Initialization
The initial EN for agent A
k
is constructed in three
steps:
1. A set of ideas is sampled randomly from the Ora-
cle’s idea repertoire.
2. The selected ideas are superposed to create an
epistemic network with N edges, all of which are
true by construction (because they came from the
IEN).
3. Next, qN true edges are removed and the same
number of false edges are added, giving the ini-
tial EN for A
k
as a partial and noisy version of
the IEN, with q ∈ [0, 1] controlling the degree of
misinformation (incorrect associations) in the fi-
nal EN.
4.2 Bayesian Model for Learning
Association Weights
For each Agent, A
k
, if there is an edge e
k
i j
= 1 between
concept nodes i and j in its EN, it has a weight w
k
i j
,
representing the agent’s confidence in the association
between the concepts represented by nodes i and j.
The weights are initially chosen independently from
a uniform distribution between 0 and 1, and change
based on an agent’s learning process using a Bayesian
formulation.
Idea Generation and Expression
Each agent potentially generates an idea at each time
ICAART 2020 - 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
106
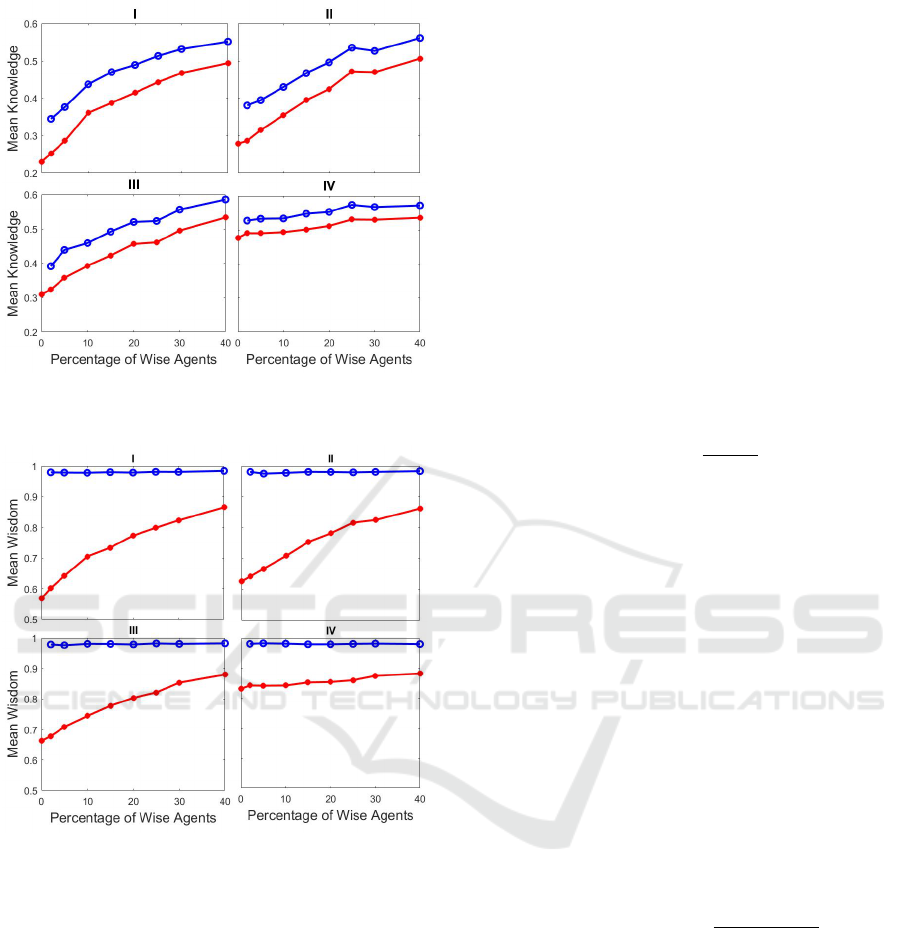
Figure 1: Mean Agent Knowledge after 1000 epochs for
wise agents (upper blue curve) and normal agents (lower
red curve) for various percentages of wise agents.
Figure 2: Mean Agent Wisdom after 1000 epochs for wise
agents (upper blue curve) and normal agents (lower red
curve) for various percentages of wise agents.
step by sampling its EN via an attentional search pro-
cess. The edges in the generated idea are binary rather
than weighted:The agent is asserting which associ-
ations exist or do not exist in the idea, and not in-
dicating how strongly it believes each association in
its own mind. However, the association weights are
taken into account by the agent in the process of gen-
erating ideas. Idea generation and expression occurs
as follows:
1. Attentional Focus: This step identifies the con-
cepts and associations that agent A
s
currently has
in mind. A seed set of nodes is identified in the
EN of the source agent A
s
. This is then used to
obtain the biased set of nodes via spreading acti-
vation. After removal of low-degree nodes, this
gives the sub-network, E
s
B
(t), which is designated
the current attended epistemic network (AEN) of
the agent at time t, and represents the internal at-
tentional focus of the agent (Iyer et al., 2009; Iyer
et al., 2010).
2. Generation of Potential Ideas: This step gener-
ates the set G
s
(t) of all possible potential ideas,
g
s
i
(t), within the AEN by applying the quasi-
clique search algorithm, with the number of nodes
per idea restricted to be between 6 and 10.
3. Evaluation of Potential Ideas: Once agent A
s
has generated the set of potential ideas, G
s
(t) =
{g
s
i
(t)}, it evaluates the coherence, q
s
i
(t), of each
idea based on the density of its internal connec-
tivity and weight of its edges in its AEN. For an
idea g
s
i
with nodes N
s
i
and edges E
s
i
, the weighted
coherence is given by:
z
s
i
=
n
s
∏
e∈E
s
i
w
e
(1)
where w
e
is the weight of the edge e and n = |E
s
i
|
Thus, more densely connected ideas with higher
weights are considered more coherent. Coherence
is the agent’s subjective assessment of the quality
of an idea.
Coherence values below a threshold φ are set to 0.
The result is a coherence vector Z
s
(t) = {z(g
s
i
(t))}
for the set of ideas in G
s
(t). If no idea meets
threshold φ, the coherence vector is null, and the
agent remains silent in that time-step.
4. Idea Selection and Expression: One of the ideas
from G
s
(t) is chosen for expression by using a
roulette wheel algorithm based on the coherence
of the ideas, i.e., the probability of choosing idea
g
s
m
(t) for expression is:
p
comm
(g
s
m
(t)) =
z
s
m
(t)
∑
u∈G
s
(t)
z
s
u
(t)
(2)
Once A
s
decides to express the idea, it broadcasts
it to all its immediate neighbors in the social net-
work.
The seed set is also continually updated by the nat-
ural dynamics of the system based on recently gener-
ated ideas and what the agents hears from others (see
(Shekfeh, 2017) for details.)
Idea Evaluation and Reward
Ideas expressed by agents are evaluated by the Oracle
based on the number of true and false associations in
it. If an idea g is expressed by agent A
s
at time t, it
The Effect of Well-informed Minorities and Meritocratic Learning in Social Networks
107

generates a reward using the function R that is com-
puted by the Oracle as follows:
R(χ(g)) =
0.5[1 − (χ(g))
1−µ
] i f χ(g) ≤ 0
0.5[1 + (χ(g))
1−µ
] i f χ(g) > 0
(3)
where µ is the reward selectivity parameter and χ(g)
represents the Oracle’s quality evaluation function for
ideas. Given an idea g, its quality is calculated as :
χ(g) =
e
true
− e
f alse
e
total
(4)
where e
total
is the number of edges in g, e
true
is the
number of edges in g that are also present in the IEN,
and e
f alse
is the number of edges present in the g but
not in the IEN.
The merit of agent k is then computed as follows:
ξ
s
(t + 1) = (1 − σ)ξ
s
(t) + σR(χ(g)) (5)
where σ ∈ (0, 1) is the merit adaptation rate parame-
ter and is set to a small value. Thus, the more accurate
the ideas expressed by an agent, the more merit it ac-
quires over time.
Idea Reception and Assimilation
Idea Reception: When a receiving agent A
r
receives
an idea from source agent A
s
, it can choose to ig-
nore it or assimilate it into its own EN, thus learning
that idea. The idea is assimilated with a probability
based on the receiving agent’s general receptivity to
ideas and its specific attentiveness towards the send-
ing agent A
s
. The attentiveness of A
r
towards A
s
de-
pends on three possible factors: 1) The social weight,
ϕ
rs
, between the agents; 2) The empirical epistemic
affinity, ψ
rs
, that A
r
has inferred with A
s
(see below);
and 3) The merit differential, ξ
s
− ξ
r
, of A
r
and A
s
.
The attentiveness of agent A
r
towards agent A
s
is rep-
resented by the esteem of A
r
for A
s
:
Λ
rs
= c
r
S
f
S
(ψ
rs
) + c
r
E
f
E
(ϕ
rs
) + c
r
R
f
R
(ξ
s
− ξ
r
) (6)
where f
S
( ), f
E
( ), and f
R
( ) are monotonically in-
creasing sigmoid functions with range 0 to 1, and
c
r
S
, c
r
E
and c
r
R
, are parameters representing the so-
cial, epistemic, and perceptual components of the
attentiveness function, respectively. These are de-
fined on the simplex c
r
S
+ c
r
E
+ c
r
R
= 1, so that the tu-
ple (c
r
S
, c
r
E
, c
r
R
) defines the learning style of agent A
r
.
There are three pure learning styles:
1. Social Learning Style (1, 0, 0), where the agent
learns preferentially from those to whom it has
strong social connections. The social selectivity
function determines how esteem depends on so-
cial weight with the source agent. It is defined as:
f
S
(ϕ) =
0.5[1 − (1 − 2ϕ)
1−α
] i f ϕ ≤ 0.5
0.5[1 + (2ϕ − 1)
1−α
] i f ϕ > 0.5
(7)
where α is the social selectivity parameter. If
α = 0 , f
S
has linear dependence on social weight.
As α increases towards 1, f
S
(ϕ(r, s)) approaches
a threshold function at ϕ(r, s) = 0.5, so the agent
accepts ideas only from peers with social connec-
tion ϕ(r, s) > 0.5.
2. Like-Minded Learning Style (0, 1, 0), where the
agent learns preferentially from agents that have
previously expressed ideas similar to its own. This
function determines how esteem depends on epis-
temic affinity that the receiving agent perceives
with the source agent. It is defined as:
f
E
(ψ) =
0.5[1 − (1 − 2ψ)
1−β
] i f ψ ≤ 0.5
0.5[1 + (2ψ − 1)
1−β
] i f ψ > 0.5
(8)
where β is the epistemic selectivity parameter. If
β = 0, f
E
becomes a linear function of epistemic
affinity. As β increases towards 1, f
E
(ψ(r, s)) ap-
proaches a threshold function at ψ(r, s) = 0.5, so
the agent accepts ideas only from peers with epis-
temic affinity ψ(r, s) > 0.5 .
3. Meritocratic Learning Style (0, 0, 1), where the
agent learns preferentially from those who have
higher accumulated merit than itself. The f
R
func-
tion determines how esteem depends on the dif-
ference between the merit status of the receiving
agent and the source agent. It is defined as:
f
R
(∆) =
0.5[1 − |∆|
1−γ
] i f ∆ ≤ 0
0.5[1 + |∆|
1−γ
] i f ∆ > 0
(9)
where the differential status, ∆ = ξ
s
−ξ
r
is the dif-
ference in current merit status between the receiv-
ing agent and the source agent, and γ is the merit
status selectivity parameter. If γ = 0, f
R
is a linear
function of reward status. As γ increases towards
1, f
R
(∆) approaches a threshold function at ∆ = 0,
so ideas from an agent with higher status are al-
ways accepted and those from agents with lower
status are not.
The probability of agent A
r
accepting an idea from
agent A
s
is:
P
accept
(r, s) = κ
r
Λ
rs
(10)
where κ
r
∈ [0, 1] is the general receptivity of
agent r to ideas from others. We use κ
r
= 1 for all
agents.
ICAART 2020 - 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
108

Idea Assimilation: Once the receiving agent A
r
has
decided to accept an idea, g, from the source agent A
s
,
it must be assimilated into A
r
’s EN. The process of
assimilating a new idea involves updating the weights
of edges using a Bayesian model. The process for
updating the edge between concept nodes i and j in
the received idea comprises the following steps:
• If i and j are connected (disconnected) in both
g and E
r
, they remain connected (disconnected)
in E
r
. However, in the connected case, the edge
weight is adjusted according the weight adjust-
ment rule which is described in the following sec-
tion.
• If i and j are connected in g but not in E
r
, A
r
con-
nects them with a small weight, w
ε
, with proba-
bility p
add
= Λ
rs
– the esteem for agent A
s
.
• If i and j are not connected in g but are connected
in E
r
, the weight in E
r
is decreased by an amount
∆w
i j
which is also described in the Learning Rule
section
Thus, the result is to make E
r
more consistent with
the received idea g. Both addition of associations and
weight adjustment of edges is possible, which is cru-
cial for improving initially noisy ENs.
The Learning Rule
The association weights in the ENs of individual
agents change based on the ideas they assimilate from
their peers, which increase or decrease the agents’
confidence in each received association. A single
weight update equation is as follows:
w
r
i j
(t + 1) =
¯e
s
i j
"
(1 − λ)w
r
i j
(t) + λ
ρ
sr
w
r
i j
(t)
(1 − w
r
i j
(t)) + ρ
sr
w
r
i j
(t)
#
+ (1 − ¯e
s
i j
)
"
(1 − λ)w
r
i j
(t) + λ
w
r
i j
(t)
ρ
sr
(1 − w
r
i j
(t)) + w
r
i j
(t)
#
where: w
r
i j
(t) is the belief at time t of agent A
r
that the
edge is True; ¯e
s
i j
≡ the state of the edge in the message
sent by agent A
s
; e
r
i j
≡ the state of the edge in the EN
of receiving agent A
r
: e
r
i j
= 1 means the edge exists,
else 0; λ is the learning rate; and ρ
sr
is the odds ratio
of A
r
believing an association received from A
s
. The
last quantity is computed from Λ
sr
, the esteem that
Agent A
r
has for Agent A
s
, as follows:
ρ
sr
= 1 − log(1 −Λ
sr
) (11)
Thus, an esteem of Λ
sr
= 0 implies ρ
1
sr
= 1, i.e., Agent
A
r
thinks that Agent A
s
is just as likely to be wrong in
its assertion of e
∗
i j
= 1 as it is to be right, it will learn
nothing from Agent s and has no esteem for it.
Of course, it is necessary that 0 < λ < 1. For the
complete derivation of this equation, see (Shekfeh,
2017).
Two points should be noted here. First, that the
esteem of A
r
for A
s
determines both whether the for-
mer accepts an idea from the latter and the degree to
which the idea changes its own beliefs. Second, the
learning happening here is implicit in that informa-
tion elements (conceptual associations) are learned as
a side-effect of assimilating ideas rather than individ-
ually, and that the agents are not trying explicitly to
become wiser or more knowledgeable: It simply oc-
curs as an implicit consequence of communication,
attention, and influence among agents.
Activation and Forgetting
Not all knowledge in a person’s mind is equally ro-
bust: Things must be brought to mind somewhat reg-
ularly, or may be forgotten entirely. This effect is
modeled in the system by processes of activation and
forgetting.
An association (edge) in an agent’s EN is acti-
vated when it receives the agent’s attention in the pro-
cess of searching for ideas to express, or is updated
via a received idea, that is:
1. If the two concepts occur in an idea received from
another agent.
2. If the agent thinks of the two concepts as part of
an idea it generates.
If the association is not activated at a time step, its
strength changes as follows:
w
i j
(t + 1) =
(1 − ε
−
)w
i j
(t) i f w
i j
(t) ≤ θ
m
w
i j
(t) else
(12)
where ε
−
is a small memory decay rate parameter.
Thus, if the absolute strength of the association
between concepts i and j falls below θ
m
, it begins to
be forgotten and requires activation in order to sur-
vive. Through this process, both correct and incor-
rect associations can, in principle, disappear from the
agent’s mind – and from the entire population – over
time. Recently activated concepts also provide the
seed for idea search in the agent’s mind.
Epistemic Affinity Update
The epistemic affinity, ψ
sr
, that agent A
r
perceives for
agent A
s
is based on the ideas it has seen from A
s
,
and quantifies the degree to which A
s
says things that
A
r
agrees with. Initially, ψ
rs
is set to 0.5 , i.e., neutral
The Effect of Well-informed Minorities and Meritocratic Learning in Social Networks
109

affinity. Every time A
r
receives an idea, g, from A
s
, A
r
calculates the raw similarity, S
r
(g), of the idea with
its own EN as:
S
r
(g) =
e
present
− e
absent
e
total
(13)
where e
present
is the number of edges in g that are also
present in EN
r
, e
absent
is the number of edges in g
that are not present in EN
r
, and e
total
is the number of
edges in g . Thus, if all the associations in g are al-
ready found in the receiving agent’s EN, the raw sim-
ilarity is +1, and if none are, the raw similarity is -1.
A normalized familiarity value is then calculated as:
Γ(S) =
0.5[1 − (S)
1−ν
r
] i f S ≤ 0
0.5[1 + (S)
1−ν
r
] i f S > 0
(14)
where ν
r
is a small value ∈ (0, 1). A comparison with
Eqns. (3) and (4) shows that the familiarity of idea
g for agent A
r
is a subjective version of the Oracle’s
objective reward metric: They represent an estimate
of the perceived truth of the idea by the agent and the
Oracle, respectively.
Then the epistemic affinity of agent A
r
for A
s
is
updated as:
ψ
rs
(t + 1) = ψ
rs
(t) + η[Γ(S) − ψ
rs
(t)] (15)
where η ∈ (0, 1) is a small adaptation rate parameter.
The n × n matrix ψ(t) = [ψ
rs
(t)] is defined as the
epistemic affinity matrix.
4.3 Metrics of Agent Information
Agents are evaluated in terms of their information via
two metrics:
1. Knowledge: This measures the quantity of cor-
rect information that the agent has in its EN com-
pared to the Oracle’s IEN, with a penalty for in-
correct knowledge. The performance of agent A
k
in time step t is computed as:
K
k
(t) =
e
true
− e
f alse
e
total
(16)
where e
total
is the number of edges in IEN, e
true
is the number of true edges in EN
k
, and e
f alse
is
the number of false edges in EN
k
. Thus, if an
agent knows all the true associations but no false
associations, its knowledge is 1. If it has as many
false associations as true ones, its knowledge level
is 0, and when the number of false associations
exceed true ones, knowledge becomes negative.
This metric is similar in spirit to the standard re-
call metric, but allows for negative values.
2. Wisdom: This measures the quality of an agent’s
information regardless of its quantity. For an
agent A
k
, this is measured as:
W
k
(t) =
e
true
e
true
+ e
f alse
(17)
Thus, it is identical to the standard precision met-
ric.
5 SIMULATIONS AND RESULTS
The simulations reported in this study use an undi-
rected small-world social network with n = 500
agents and average degree of 20. All agents begin
with ENs of approximately the same size, generated
as described below. A fraction n
w
of agents in the
network are initialized as wise agents, i.e., q = 0 and
all the associations in their initial EN are true. The
remaining fraction 1 − n
w
of agents are initialized as
normal agents, with 5% false edges in their initial EN
(q = 0.05). All the wise agents are assumed to always
learn in the pure meritocratic style, while the learn-
ing styles of the normal agents are varied as described
below.
5.1 Scenarios and Parameters
The simulations explore the effect of two factors on
implicit learning in the network: 1) The fraction of
wise agents, n
w
; and 2) The learning style of the nor-
mal agents. The following 9 values of n
w
are sim-
ulated: n
w
= 0 (baseline case with no wise agents),
0.02, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, and 0.4. For each of these
cases, four different learning style scenarios are sim-
ulated for the normal agents:
• Case I: All normal agents learn in the pure like-
minded (0, 1, 0) style.
• Case II: 5% of normal agents learn in the pure
meritocratic (0, 0, 1) style and the remaining 95%
in the pure like-minded (0, 1, 0) style.
• Case III: All normal agents have a mixed (0, 0.95,
0.5) learning style: Mostly like-minded with a
small degree of meritocratic learning.
• Case IV: All normal agents learn in the purely
meritocratic (0,0,1) style – as do the wise agents.
Thus, in all there are 36 different simulation sce-
narios, with results averaged over 10 independent tri-
als for each one. The knowledge and wisdom of each
agent is tracked over time in each run. The struc-
ture of the social network is fixed across all simu-
lations, but the positions of wise and normal agents
ICAART 2020 - 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
110
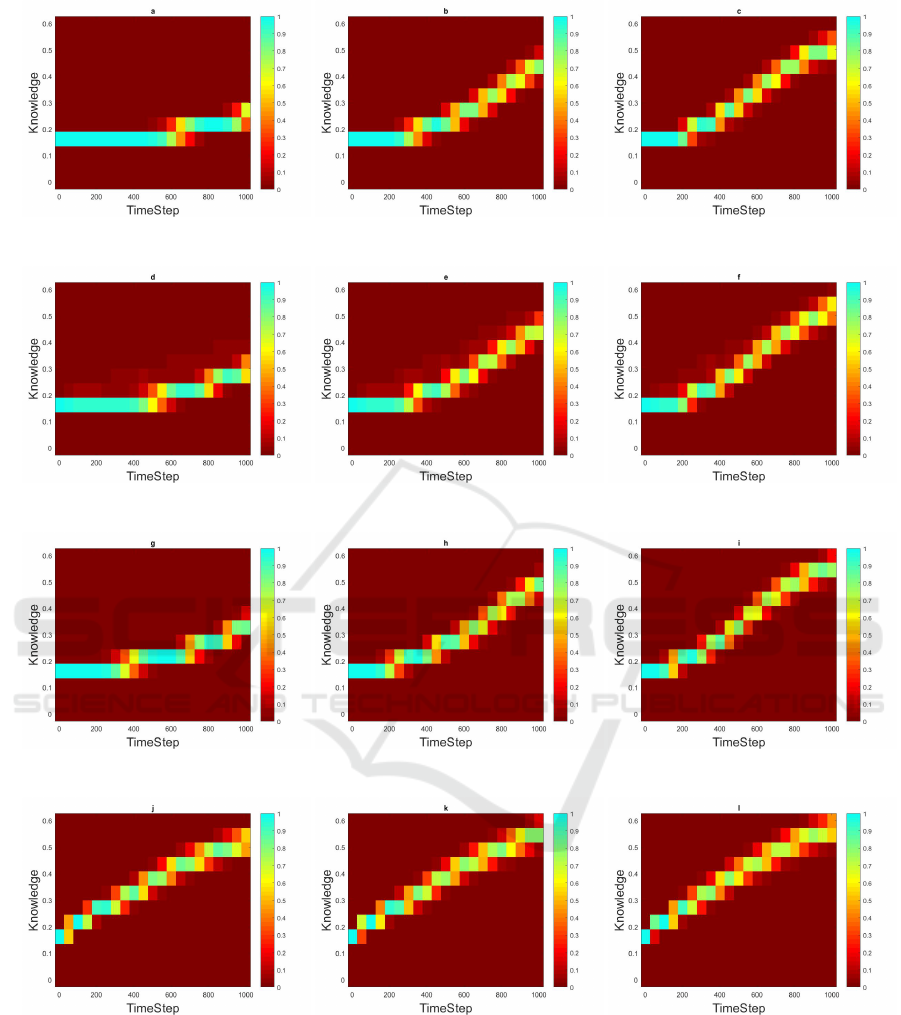
(a) 0% Wise Agents (b) 20% Wise Agents (c) 40% Wise Agents
(d) 0% Wise Agents (e) 20% Wise Agents (f) 40% Wise Agents
(g) 0% Wise Agents (h) 20% Wise Agents (i) 40% Wise Agents
(j) 0% Wise Agents (k) 20% Wise Agents (l) 40% Wise Agents
Figure 3: Distribution of Knowledge in the normal agent population over time for Case I (top row); Case II (second row);
Case III (third row); and Case IV (bottom row). In each image, the leftmost column shows the color-coded histogram of initial
Knowledge distribution, and subsequent columns show the same at the end of successive a 50-epoch intervals.
(and learning style assignments in Case II) are varied
randomly over trials. A total of 1, 000 epochs are run
in each trial, where an epoch comprises giving each
agent the opportunity to generate and express an idea.
5.2 System Initialization
The initial ENs are set up at the start of each simu-
lation trial by randomly selecting a set of true ideas
from the ideas pool gathered a priori by parsing the
The Effect of Well-informed Minorities and Meritocratic Learning in Social Networks
111

(a) 0% Wise Agents (b) 20% Wise Agents (c) 40% Wise Agents
(d) 0% Wise Agents (e) 20% Wise Agents (f) 40% Wise Agents
(g) 0% Wise Agents (h) 20% Wise Agents (i) 40% Wise Agents
(j) 0% Wise Agents (k) 20% Wise Agents (l) 40% Wise Agents
Figure 4: Distribution of Wisdom in the normal agent population over time for Case I (top row); Case II (second row); Case
III (third row); and Case IV (bottom row). In each image, the leftmost column shows the color-coded histogram of initial
Wisdom distribution, and subsequent columns show the same at the end of successive a 50-epoch intervals.
IEN and collecting all possible ideas in it. The indi-
vidual EN of a normal agent is then parsed again to
remove some true edges and add as many false ones
to reach the noise level q as defined in the agent pa-
rameters. Wise agents do not have any noise, so all
their associations are true. Then, the initial status of
each agent is computed according to the wisdom for-
mula. So the wisdom of normal agents is initialized as
the number of correct ideas after adding noise divided
by the original number of correct ideas when the EN
ICAART 2020 - 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
112

is created. Accordingly, the merit status of all wise
agents is initialized to 1.
Finally, the initial epistemic similarity is com-
puted between all pairs of agents by calculating the
overlap between their initial ENs.
5.3 Results
Figures 1 and 2 plot the final levels of mean knowl-
edge and wisdom attained by each agent group as
a function of n
w
and the learning cases for normal
agents. The following observations can be made:
• In the absence of wise agents (left-most data point
in each graph), by far the best strategy for nor-
mal agents is to learn from better informed peers
(lower right graph in each figure.)
• Introducing even a small fraction of wise individ-
uals into the population improves the learning of
the whole community.
• Increasing the fraction of the wise minority in
the population improves the learning of the nor-
mal population dramatically, except when the nor-
mal agents adopt a meritocratic learning strategy,
in which case the presence of more wise agents
makes only a modest difference. This suggests
that the effect of more wise agents is not mainly
due to the greater available volume of correct
knowledge they bring, but due to the greater num-
ber of connections to wise peers available to nor-
mal agents.
• of the two non-pure learning cases for the normal
majority (Cases II and III), it is better for all nor-
mal agents to have a small meritocratic element in
their learning rather than having a small fraction
of normal agents learn purely meritocratically.
• Interestingly, the wise minority shows exactly the
same pattern of improvement in their final knowl-
edge level with higher n
w
as is seen for the nor-
mal majority – albeit with an increment reflecting
their edge in initial knowledge due to the absence
of false associations. This can be explained by
the fact that, since the wise agents follow a pure
meritocratic strategy, they learn mostly from their
wise peers and hardly ever from the normal major-
ity. As such, increasing n
w
increases the pool of
peers from whom each wise agent can learn, lead-
ing to faster learning. And since the normal agents
do not pay much attention to the merit status of
their peers (except in Case IV), the learning pat-
tern for the wise minority simply passes through
to the normal majority.
• The general pattern of knowledge and wisdom is
similar for the normal majority across all scenar-
ios. Of course, the wise minority always retains its
perfect wisdom because wise agents learn with a
purely meritocratic strategy, and thus hardly ever
accept an idea from less well-informed peers. It
will be interesting to see how wise agents fare if
some of them adopt a different learning style.
Figures 3 and 4 show the time evolution of the dis-
tribution of knowlegde and wisdom among the nor-
mal agents when n
w
is 0, 0.2, and 0.4. The most no-
table feature of all these plots is that normal agents all
learn together: There are no stragglers or any bifur-
cation. The figures also show that the added benefit
from a larger wise minority start showing up early.
In the beginning, the distribution remains quite stable
around the initial distribution for both knowledge and
wisdom. But it then reaches a breakout point where
learning suddenly takes off. Interestingly, the delay
before breakout depends greatly not only on the size
of the wise minority (horizontal comparisons) but also
on the learning style of the normal majority (vertical
comparisons). This effect is stronger with knowledge
than with wisdom. The adoption of a purely meri-
tocratic learning style by the normal agents leads to
a qualitatively different learning pattern, with break-
out occurring almost immediately, a very linear rise in
performance, and much higher final level of both wis-
dom and knowledge. The latter effect is very small if
the wise minority is larger.
Many other things can be analyzed based on the
simulations (e.g., the spread or disappearance of indi-
vidual true/false edges in the social network), but this
will be discussed in future reports.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, a multi-agent network of generative cog-
nitive agents was used to look at the effect of having
a well-informed wise minority in a larger population
of normal agents that carry a certain amount of false
information. It was found that the size of the minor-
ity has a direct effect on the implicit learning perfor-
mance of normal agents. The study also found that
the performance depends very strongly on the learn-
ing style adopted by the normal agents. In particular,
this is seen in the transition of learning from an initial
flat phase to a breakout with rapid learning.
The MANILA model is versatile and powerful
enough to be useful for exploring many other issues
related to the spread and learning of information in
human networks, including the spread of false infor-
mation – a critical problem at this time. Such issues
will be addressed in future studies.
The Effect of Well-informed Minorities and Meritocratic Learning in Social Networks
113

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partly supported by National Science
Foundation INSPIRE grant BCS-1247971 to Ali Mi-
nai.
REFERENCES
Acemoglu, D., M.Dahleh, Lobel, I., and Ozdaglar., A.
(2011). Bayesian learning in social networks. The
Review of Economic Studies, 78:1201–1236.
Adar, E. and Adamic, L. A. (2005). Tracking information
epidemics in blogspace. IEEE/WIC/ACM Interna-
tional Conference on Web Intelligence (WI’05), pages
207–214.
Allcott, H. and Gentzkow, M. (2017). Social media and
fake news in the 2016 election. Journal of Economic
Perspectives, 31:211–36.
Berry, D., editor (1997). How Implicit Is Implicit Learning?
Oxford University Press.
Brown, V., Tumeo, M., Larey, T., and Paulus, P. (1998).
Modeling cognitive interactions during group brain-
storming. Small Group Research, 29:495–526.
Brunato, M., Hoos, H. H., and Battiti, R. (2008). On ef-
fectively finding maximal quasi-cliques in graphs. In
In Proceedings of 2nd Learning and Intelligent Opti-
mization Workshop.
Buntain, C. and Golbeck, J. (2017). I want to believe:
Journalists and crowdsourced accuracy assessments in
twitter. CoRR, abs/1705.01613.
Campbell, D. T. (1960). Blind variation and selective re-
tention in creative thought as in other knowledge pro-
cesses. Psychol. Rev., 67:380–400.
Castillo, C., Mendoza, M., and Poblete, B. (2013). Pre-
dicting information credibility in time-sensitive social
media. Internet Research: Electronic Networking Ap-
plications and Policy, 23.
Del Vicario, M., Bessi, A., Zollo, F., Petroni, F., Scala,
A., Caldarelli, G., Stanley, H. E., and Quattrocioc-
chi, W. (2016). The spreading of misinformation on-
line. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sci-
ences, 113(3):554–559.
Dienes, Z. (1992). Connectionist and memory-array mod-
els of artificial grammar learning. Cognitive Science,
16(1):41–79.
Dienes, Z. and Berry, D. (1997). Implicit learning: Below
the subjective threshold. Psychnomic Bulletin and Re-
view, 4:3–23.
Fauconnier, G. and Turner, M. (2003). The Way We Think:
Conceptual Blending And The Mind’s Hidden Com-
plexities. Basic Books.
Gale, D. and Shachar, K. (2003). Bayesian learning in social
networks. Games and Economic Behavior, 45:329–
346.
Goldenberg, J., Han, S., Lehmann, D. R., and Hong, J. W.
(2008). The role of hubs in the adoption processes.
Journal of Marketing, American Marketing Associa-
tion.
Granovetter, M. (1978). Threshold models of collective be-
havior. American Journal of Sociology, 83(6):1420–
1443.
Iyer, L. R., Doboli, S., Minai, A. A., Brown, V. R., Levine,
D. S., and Paulus, P. B. (2009). Neural dynamics of
idea generation and the effects of priming. Neural Net-
works, 22:674–686.
Iyer, L. R., Venkatesan, V., and Minai, A. A. (2010).
Neurcognitive spotlights:configuring domains for
ideation. In Proceedings of WCCI 2010, pages 3026–
3033.
Kempe, D., Kleinberg, J., and Tardos, E. (2003). Maximiz-
ing the spread of influence through a social network.
In In Proceedings of the 9th ACM SIGKDD Interna-
tional Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data
Mining.
Lamberson, P. J. (2010). Social learning in social networks.
The B.E. Journal of Theoretical Economics, 10:36.
Leskovec, J., McGlohon, M., Faloutsos, C., Glance, N., and
Hurst, M. (2007). Cascading behavior in large blog
graphs. In SDM07: Proc. of the SIAM Conference on
Data Mining.
Leskovec, J., Singh, A., and Kleinberg, J. M. (2006). Pat-
terns of influence in a recommendation network. In
Proc. of the 10th Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowl-
edge Discovery and Data Mining (PA-KDD’06),
pages 380–389.
Liben-Nowell, D. and Kleinberg, J. M. (2008). Tracing the
flow of information on a global scale using internet
chain-letter data. In Proc. of the National Academy of
Sciences, volume 105(12), pages 4633–4638.
Liggett, T. M. (1985). Interacting Particle Systems.
Springer.
Lobel, I. and Sadler, E. (2012). Social learning and aggre-
gate network uncertainty. Working Paper.
Mathis, D. W. and Mozer, M. C. (1994). On the computa-
tional utility of consciousness. In Proceedings of the
7th International Conference on Neural Information
Processing Systems (NIPS’94), pages 11–18.
Mednick, S. (1962). The associative basis of the creative
process. Psychological Review, 69(3):220–232.
Mendoza, M., Poblete, B., and Castillo, C. (2010). Twitter
under crisis: Can we trust what we rt? In Proceed-
ings of the First Workshop on Social Media Analytics,
pages 71–79.
Mueller-Frank, M. (2013). A general framework for ra-
tional learning in social networks. Theoretical Eco-
nomics, 8:1–40.
Oliveira, D. F. M. and Chan, K. S. (2018). The effects of
trust and influence on the spreading of low and high
quality information. Physica A, 525:657–663.
Paulus, P. B. (2002). Social and cognitive influences
in group brainstorming. predicting production gains
and losses. European Review of Social Psychology,
12:299–325.
Reber, A. S. (1967). Implicit learning of artificial gram-
mars. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behav-
ior, 6(6):855 – 863.
ICAART 2020 - 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
114

Rosenberg, D., Solan, E., and Vieille, N. (2009). Infor-
mational externalities and emergence of consensus.
Games and Economic Behavior, 66:979–994.
Seger, C. (1994). Implicit learning. Psychological Bulletin,
115:163–196.
Shekfeh, M. (2017). MANILA: A Multi-Agent Framework
for Emergent Associative Learning and Creativity in
Social Networks. PhD thesis, University of Cincinnati,
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer
Science.
Shu, K., Sliva, A., Wang, S., Tang, J., and Liu, H. (2017).
Fake news detection on social media: A data mining
perspective. SIGKDD Explor. Newsl., 19:22–36.
Simonton, D. K. (2003). Scientific creativity as constrained
stochastic behavior: the integration of product, per-
son, and process perspectives. Psychological Bulletin,
129:475–494.
Simonton, D. K. (2010). Creative thought as blind-variation
and selective-retention: Combinatorial models of ex-
ceptional creativity. Physics of Life Reviews, 7:156–
179.
Sutton, R. S. and Barto, A. G. (1998). Reinforcement Learn-
ing: An Introduction. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA.
Tambuscio, M., Oliveira, D. F. M., Ciampaglia, G. L., and
Ruffo, G. (2018). Network segregation in a model of
misinformation and fact-checking. Journal of Compu-
tational Social Science, 1:261–275.
Vosoughi, S., Roy, D., and Aral, S. (2018). The spread of
true and false news online. Science, 359:1146–1151.
Waldrop, M. M. (2017). News feature: The genuine
problem of fake news. Proceedings of the National
Academy of Sciences, 114:12631–12634.
Watts, D. and Strogatz, S. (1998). Collective dynamics of
”small-world” networks. Nature, 393:440–442.
Watts, D. J. and Dodds, P. (2007). Influentials, networks,
and public opinion formation. Journal of Consumer
Research, 34:441–458.
Weiss (ed.), G. (1999). Multiagent Systems: A Modern
Approach to Distributed Artificial Intelligence. Cam-
bridge, MA: MIT Press.
Weng, L., Menczer, F., and Ahn, Y.-Y. (2013). Virality pre-
diction and community structure in social networks.
Scientific Reports, 3:2522.
The Effect of Well-informed Minorities and Meritocratic Learning in Social Networks
115
