
Generative Locomotion Model of Snake Robot with Hierarchical
Networks for Topological Representation
Yoonkyu Hwang and Masato Ishikawa
Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University, Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka, Japan
Keywords:
Locomotion, Generative Model, Topological Representation, Sequential Variational Inference, Hierarchical
Networks, User-oriented Interface.
Abstract:
We propose novel generative locomotion models for snake robots. Locomotion researches have been relied
on human experts with rich domain-knowledge and experience. Although recent data-driven approaches can
achieve explict controllers to make robots move, results often do not show enough interpretability with respect
to user-oriented interface. The proposed model focuses on interpretable locomotion generation to help intu-
itive locomotion planning by end-users. First, we introduce the topological shaping for time-series training
data. This allows us to bound the data to specific region, which leads to training/inference simplification,
intuitive visualization, and finally high generalization property for the proposed framework. Second, the dedi-
cated hierarchical networks were designed to propagate complex contexts in the snake robot locomotion. The
result shows that our generative locomotion models can be utilized as user-oriented interface for interpretable
locomotion design.
1 INTRODUCTION
Robot locomotion helps us to improve our intuition
about how the living things act, as well as general
control principle for animal-oriented robots includ-
ing humanoids, dog robots, and snake robots. How-
ever, studeis on robot locomotion have heavily re-
lied on human experts with multidisciplinary knowl-
edge/inspiration across system control theory, biol-
ogy, and neuroscience. The main difficulty is to
search and distinguish the structured input-output pat-
terns. Furthermore, the multi-modality between body
central pattern and joint pattern makes problem more
severe.
In this paper, the locomotion problem is de-
fined as the probabilistic generative process of an au-
tonomous agent having latent representations for lo-
comotion. The generative models are core machine
learning framework to learn data distribution (Good-
fellow et al., 2014) usually with low-dimensional la-
tent representation (Kingma and Welling, 2013). The
learned latent representation is utilized to generate the
desired novel observations which were not seen be-
fore. The generative process is actively studied also
in practical engineering problems. For example, the
inverse design problems such as (Sanchez-Lengeling
and Aspuru-Guzik, 2018) can be efficiently sovled by
searching complex, multi-modal patterns realizing the
desired goal.
Interpretability is an crucial factor as well as the
estimation error for all machine learning techniques
including generative models. The result having low
interpretability is not helpful for practical generation
work. Popular apporach in machine-learning frame-
work is to encdoe information to latent variables, and
improve information connection between the desired
effects and the specific latent variable. Most direct
way is to reveal the related metrics such as mutual in-
formation by direct estimation (Zhang et al., 2018b;
Hjelm et al., 2018; Poole et al., 2018) or some tech-
niques likes annealing (Dupont, 2018). Utilizing dis-
crete distribution (Maddison et al., 2016) in latent
variables also showed the interpretable results for the
target application having the discrete characteristics.
Another useful way to improve high-level interperta-
bility is based on hierarchical architectures. The hier-
archy helps information to be divided usually by over-
all meaning and residual information, which is called
as summary vector (Veli
ˇ
ckovi
´
c et al., 2018), context-
nuisance vector (Tomczak and Welling, 2018), and
sequence-segment level attributes (Hsu et al., 2017; Li
and Mandt, 2018). Our generative locomotion model
is based on the hierarchical configuration.
Modeling sequential data is a core part because a
194
Hwang, Y. and Ishikawa, M.
Generative Locomotion Model of Snake Robot with Hierarchical Networks for Topological Representation.
DOI: 10.5220/0008981401940202
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2020) - Volume 2, pages 194-202
ISBN: 978-989-758-395-7; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reser ved

great number of applications including robot locomo-
tion are operated and measured in time-series. Convo-
lutional neural networks have received huge attention
for time-series application such as motion recogni-
tion (Ha and Choi, 2016) and classification (Cui et al.,
2016). The convolution operation also can be utilized
in causal settings (van den Oord et al., 2016). Recur-
rent neural networks are considered as an ideal way to
estimate time-series data. However, for the sequences
having too long length or complex correlation suffers
from low modeling performance. Stochastic recurrent
networks introduce latent variable and temporal gen-
erational process. With the tractable variational infer-
ence (Chung et al., 2015), the latent variable at each
sequence-step improves modeling capacity, and can
be used by high-level information indicator.
On the other hand, the time-series can be changed
by other form via proper transformation such as
Fourier transform, which leads to dimensional reduc-
tion of raw data. In this paper, we transform our
time-series locomotion data to topological shape via
Fourier transfrom. Then, our aim is turned to learn
shape characteristics. To learn the representation of
topological shape (Li et al., 2017) in the transformed
locomotion data, We adopt the mentioned stochastic
recurrent neural networks with variational inference.
By the topological shape and stochastic recurrent neu-
ral networks, we can model complex shape pattern
with meaningful representation.
Locomotion and motion generation has been in-
tensively studied. Reinforcement Learning (Schul-
man et al., 2015) is widely used to make the robots to
move. In (Zhang et al., 2018a), the mode-adaptive lo-
comotion is searched. (Grochow et al., 2004) realize
inverse kinematics with style change for the desired
body pattern. Motion is generated for character in
(Holden et al., 2016), and for heterogeneous agents in
(Wampler et al., 2014). However, there remains prob-
lems about how to shape locomotion data to explore.
Futhermore, consideration on user-oriented interface
is limited.
This paper is organized as follows. In Section 2,
the variational inference for sequential data is briefly
introduced. In Section 3, the proposed generative lo-
comotion model is derived with the problem defini-
tion for snake robot. In Section 4, we show experi-
ments results including training fitness and locomo-
tion generation. Finally, the conclusion is given in
Section 5.
2 PRELIMINARIES
In this section, we briefly introduce the generative
model with sequential variational inference. Our goal
is to identify below data distribution p
θ
(x) with un-
derlying valuable latent representation z and model
parameter θ.
p
θ
(x) =
Z
p
θ
(x, z)z. (1)
However, the distribution is usually intractable be-
cause of the invisible latent variables. One of the
tractable alternatives can be obtained by variational
inference. It is called as the Evidence Lower Bound
(ELBO)L(θ, φ) with arbitrary alternative distribution
q
φ
(x) having model parameter φ.
log p
θ
(x) =log
Z
q
φ
(z|x)
p
θ
(x, z)
q
φ
(z|x)
= logE
q
φ
(Z|x)
≥ E
q
φ
(Z|x)
log
p
θ
(x, z)
q
φ
(z|x)
= L(θ, φ).
(2)
Although the ELBO has a few different representa-
tion ways (Hoffman and Johnson, ), we focus on the
below form which is decomposed as reconstruction
likelihood and Kullback-Leibler divergence D
KL
.
E
q
φ
(Z|X)
[log p
θ
(x|z)] − D
KL
q
φ
(z|x)kp
θ
(z)
. (3)
The variational method can be also expanded for the
sequential data x
1:K
with sequence length K and cor-
responding sequential latent variable z
1:K
.
p
θ
(x
≤K
, z
≤K
) =
K
∏
k=1
p
θ
(x
k
|z
≤k
, x
<k
) p
θ
(z
k
|x
<k
, z
<k
).
(4)
Using recurrent neural networks with hidden states h
k
, the information is propagated autoregressively.
h
k
= f(h
k−1
, x
k
, z
k
). (5)
Then, the ELBO for sequential data is defined as in
(Chung et al., 2015).
E
q
φ
(z
≤K
|
x
≤K
)
"
K
∑
k=1
log p
θ
(x
k
|
z
≤k
, x
<k
)−
D
KL
q
φ
(z
k
|
x
≤k
, z
<k
) k p
θ
(z
k
|
x
<k
, z
<k
)
(6)
, where the prior is conditioned on the hidden state h
k
.
Our generative locomotion model utilizes the ELBO
in the next section.
Generative Locomotion Model of Snake Robot with Hierarchical Networks for Topological Representation
195
3 PROPOSED GENERATIVE
LOCOMOTION MODEL
The locomotion of snake robot is formulated as gen-
erative models. Accordingly, the inference model and
trainable ELBO is derived. We start from the defini-
tion of system states and consider the representation
way of the measured data to be learned.
3.1 States Definition of Target Robot
The articulated snake robot in our setting has 8-
actuated joints. Two neighboring joints are perpen-
dicularly connected as drawn in Figure 1. The robot
has 8 motor angle position x
(J )
(1 : 8) as joint states
and 6 states of central body frame x
(B)
(1 : 6), which
means position in vertical, position in forward, posi-
tion in sideways, roll, pitch and yaw angle.
3.2 Data Representation
How to shape data is the critical part for the effi-
cient learning, plausible generation, and interpretabil-
ity. The robot states are measured in usually time-
series. However, one can utilize spectral transform
if the data is expected to have spectral information.
With the fact that locomotion is usually driven by
spectral joint pattern, we can promote spectral char-
acteristics of joint responses by injecting the group of
excitation signal having sparse spectral components
without loss of generality in both respect of time and
frequency-domain. The detailed explanation about
how we can achieve the excitation is given in the next
section with experiments settings.
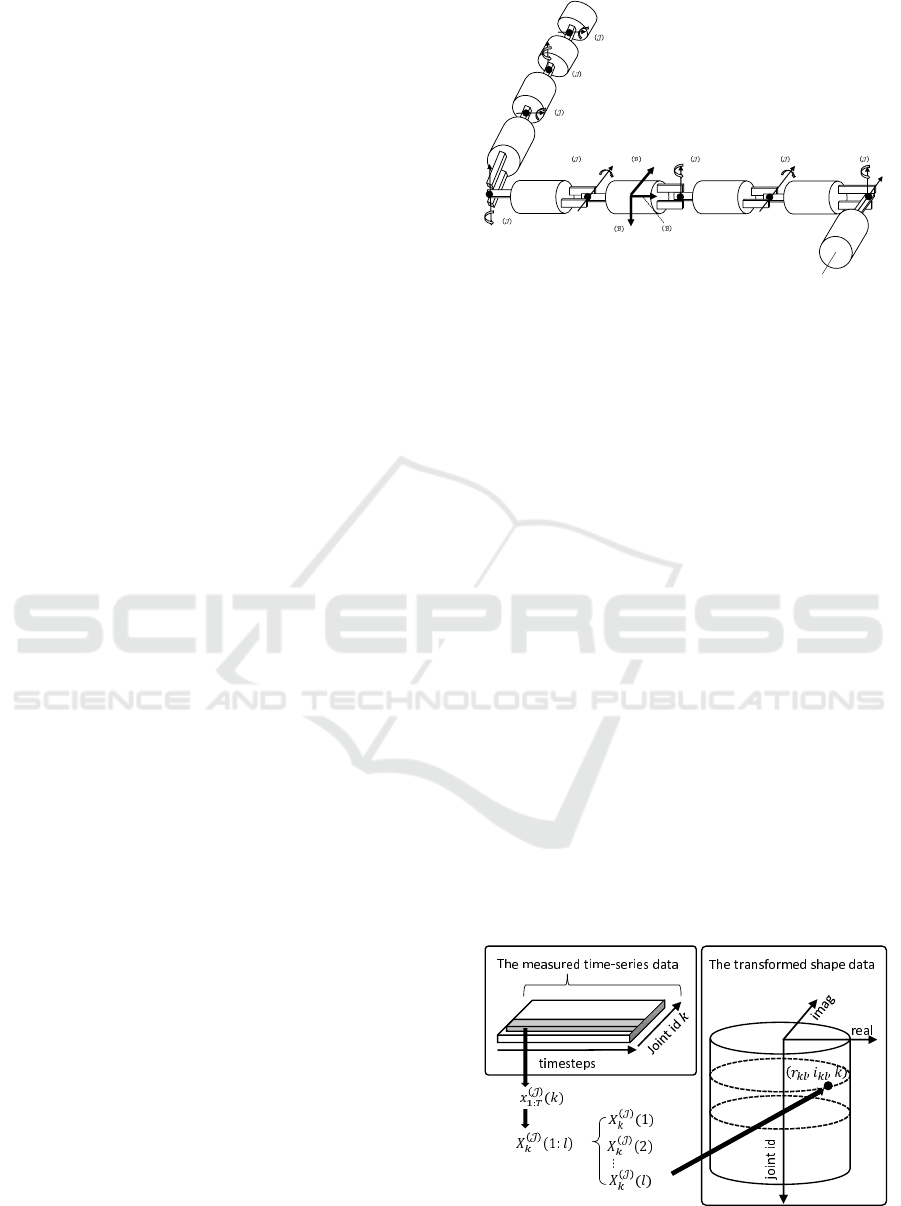
3.2.1 Topological Arrangement of Joint States
After Fourier transform for the measured time-series
of each joint angle state, the same length of spectral
vectors, that are complex values, are achieved. Filter-
ing out frequencies having too small power relative to
input power, we obtain more compact spectral vector.
Specifically, the L length spectral vector is obtained
for T length time-series for each joint angle, where
usually L << T with the filtering. The resulting spec-
tral vectors are defined as below.
X
(J )
k
(1 : L) = [c
k1
, c
k2
, . . . , c
kl
, . . . , c
kL
]
, where c
kl
= [r
kl
, i
kl
].
(7)
The terms of X
(J )
k
(l), c
kl
, r
kl
and i
kl
means the spec-
tral vector for k th joint angle, the spectral compo-
nents for l th frequency, and values corresponding
x 1x 2
x
6
x
7
x 8
x 5
x
4 x 3
x
1
x
2
x
3
Figure 1: The schematic of 3d snake robot system.
real and imaginary axis, respectively. Then, the set
of X
(J )
k
(l) is re-arranged as topological shape. The
spectral component c
kl
is mapped as the point in co-
ordinates (r
kl
, i
kl
, k), which is illustrated in Figure 2.
This approach turns our locomotion problem to one
to extract and generate meaningful pattern in point
cloud group that is topologically connected. Finally,
we can view locomotion data as the pair of the topo-
logical joint shape X
(J )
1:8
(1 : L) and jointly distributed
body pattern in time series x
(B)
.
3.3 Overall Architecture
The overall architecture of the proposed generative lo-
comotion model is illustrated in Figure 3. It is com-
posed of three parts (at top right box in Figure 3)
including the encoder of body states, the decoder of
body states, and sequential variational autoencoder
regarding topological joint shape. Again, the last part
is composed by hierarchically connected two stochas-
tic recurrent neural networks, which is written as
1
in Figure 3. We call centeral recurrent network that is
illustrated by large squares as root network and small
squares as child network in
1
. The X
(J )
k
(1 : L) is
Figure 2: Topological arrangement for time-series of joint
states.
ICAART 2020 - 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
196
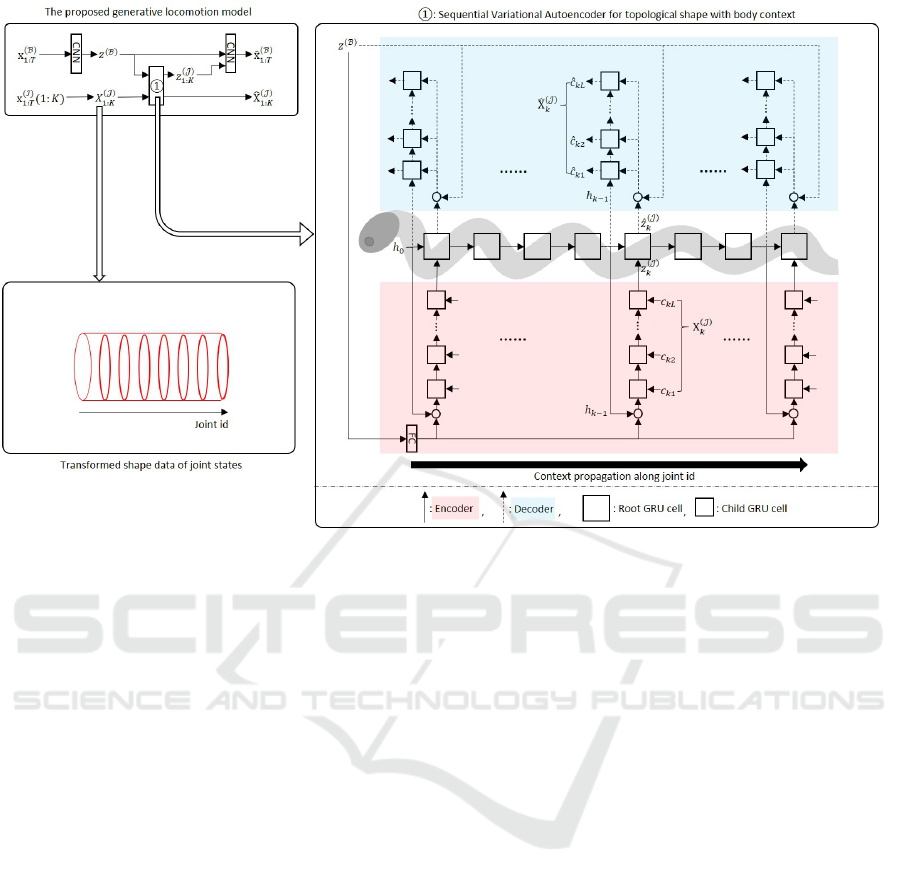
Figure 3: The overall architecture of the proposed generative locomotion model.
the topological joint shape for x
(J )
1:T
(k). The z
(B)
and
z
(J )
k
is the encoded latent variables for body states and
topological joint shape, respectively. Then, the hid-
den states h
k
of root network at k th step is updated as
following recurrence function.
h
k
= f
h
k−1
, X
(J )
k
, z
(J )
k
, z
(B)
. (8)
The child networks are propagated with three con-
text vector such as hidden states of root networks,
body latent variable, and joint shape latent variables.
For the encoder and decoder of body states, the con-
volutional neural networks are used. However, be-
cause the topological joint shape has small number of
spectral components and joint, the conventional pow-
erful convolutional neural networks-based approach
is difficult to be applied for small number of pixels.
Also, deeply stacked recurrent networks without the
stochastic generation at each sequence step is hard
to train practically regardless of hierarchical config-
uration. On the other hand, the proposed architec-
ture propagates latent context information autoregres-
sively and hierarchically.
3.4 Learning Objective
Our goal is to identify the locomotion data distribu-
tion with below decomposition.
p
θ
X
(J )
1:K
, x
(B)
1:T
, z
(J )
1:K
, z
(B)
. (9)
The generative model can be derived for the proposed
structure in Figure 3 with similar way in the explana-
tion of section 2.
p
θ
x
(B)
1:T
|z
(J )
1:K
, z
(B)
p
θ
z
B
×
K
∏
k=1
p
θ
X
(J )
k
|z
(J )
≤k
, z
(B)
p
θ
z
(J )
k
|z
(J )
<k
, z
(B)
.
(10)
By the proposed hierarchical architecture, the prior
distribution for body latent variable and joint latent
variables is defined as below.
z
(B)
∼ N (0, I). (11)
z
(J )
k
∼ N
µ
(J
prior
)
k
, σ
(J
prior
)
k
,
h
µ
(J
prior
)
k
, σ
(J
prior
)
k
i
= f
(prior)
h
k−1
, z
(B)
.
(12)
Also, for the proposed network, the inference model
is written by
q
φ
z
(B)
|x
(B)
≤T
K
∏
k=1
q
φ
z
(J )
k
|X
(B)
≤K
, z
(J )
<k
, z
(B)
. (13)
Generative Locomotion Model of Snake Robot with Hierarchical Networks for Topological Representation
197

Before the derivation of final training objectives, it
should be noted that the posterior collapse often oc-
curs in the variational representation learning frame-
works (Dai and Wipf, 2019; Alemi et al., 2017). The
problem states the posterior distribution q
θ
(z
|
x) tends
to q
θ
(z), which leads to uninformative representa-
tion learning. A few solutions are proposed such as
mutual information regularization, KL divergence an-
nealing, and the utilization of Maximum Mean Dis-
crepancy (MMD). The MMD can be alternative diver-
gence measure to KL divergence in original formula-
tion of variational inference as in (Tolstikhin et al.,
2017; Zhao et al., 2019). The MMD D
MM
is defined
with Gaussian kernel.
D
MM
(p(z) k q (z)) = E
p(z),p(z
0
)
κ
z, z
0
+
E
q(z),q(z
0
)
κ
z, z
0
− 2E
p(z),q(z
0
)
κ
z, z
0
.
(14)
, where Gaussian kernel κ(z, z0) = e
−
kz−z
0
k
2
2σ
2
. Finally,
the learning objective for our generative locomotion
model is derived by
E
q
φ
(z
|
x)
h
L
J
REC
+ αL
B
REC
− βL
J
MMD
i
− γL
B
MMD
, (15)
where:
q
φ
(z
|
x) = q
φ
z
(B)
, z
(J )
≤K
x
(B)
≤T
, X
(J )
≤K
,
L
J
REC
=
K
∑
k=1
log p
θ
X
(J )
k
z
(J )
≤k
, X
(J )
<k
, z
(B)
,
L
B
REC
= log p
θ
x
(B)
≤T
z
(J )
≤K
, z
(B)
,
L
J
MMD
= D
MM
q
φ
z
(J )
k
X
(J )
≤k
, z
(J )
<k
, z
(B)
k
p
θ
z
k
X
(J )
<k
, z
(J )
<k
, z
(B)
,
L
B
MMD
= D
MM
q
φ
z
(B)
x
(B)
≤T
k p
θ
z
(B)
.
The terms of L
J
REC
, L
B
REC
, L
J
MMD
, and L
B
MMD
respec-
tively represent reconstruction loss of joint states, re-
construction loss of body states, regularization term
on joint states distribution, and regularization term on
body states distribution. At the training phase, the to-
tal loss is weighted by hyperparameters of α, β, and γ.
4 EXPERIMENTS
The results are shown after describing the experi-
ments settings, the detailed network specification, and
the training settings.
4.1 Acquisition of Training Samples
The experiments were performed on virtual robot
simulator V-REP. For the acquisition of training
samples, the Rieman-equivalent excitation signal
(Schoukens et al., 2016) is injected as motor reference
angles for each joint. The excitation signal is known
for good alternative to Gaussian random noise exci-
tation, chirp, or the sum of multi-sines, because the
excitation shows the controlled amplitude distribu-
tion both in time-domain and frequency-domain with
small number of spectral components (Pintelon and
Schoukens, 2012). Specifically, below signal is in-
jected.
u
k
(t) =
L
∑
l=1
Usin(2π f
l
t + ϕ
l
) (16)
,where u
k
(t), U, f
l
, L, and ϕ
l
means reference input
of kth joint, amplitude constant, frequency, and phase
that is distributed randomly in [0, 2π], respectively.
In our experiments, the number of frequencies (L) is
8, the frequencies f
l
are selected in logarithmically
equal interval from 0.05 Hz to 3.0 Hz.The excitation
signal u
k=1,2,...,8
(t) ∈ [−2.2, 2.2] rad is obtained in
20 Hz sampling rate with 2000 timesteps and 4096
batch samples. After downsampling with 1/4 factor,
the topological joint shape is obtained by following
section 3. The topological shape and corresponding
body states are illustrated in Figure 4.
4.2 Network Specification
The 3 layers of convolutional neural networks are
stacked for the encoder and decoder of body states.
The body encoder has separable convolution neural
network layer for its first layer and the filter size is
increased two times with 1/2 average pooling layer
for each stacking. Global average pooling is done at
final layer of body encoder. Inversely, the decoder
of body states is upsampled two times with the de-
creased filter size for each stacking. For the hier-
archically connected two stochastic recurrent neural
networks, Gated Recurrent Unit is used for param-
eter efficiency. All child network shares parameters
between each other, and the root network has inde-
pendent parameters. The body and joint latent distri-
bution is isotropic Gaussian. For the body states en-
coder/decoder, the detailed architecture is illustrated
in Appendix.
ICAART 2020 - 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
198
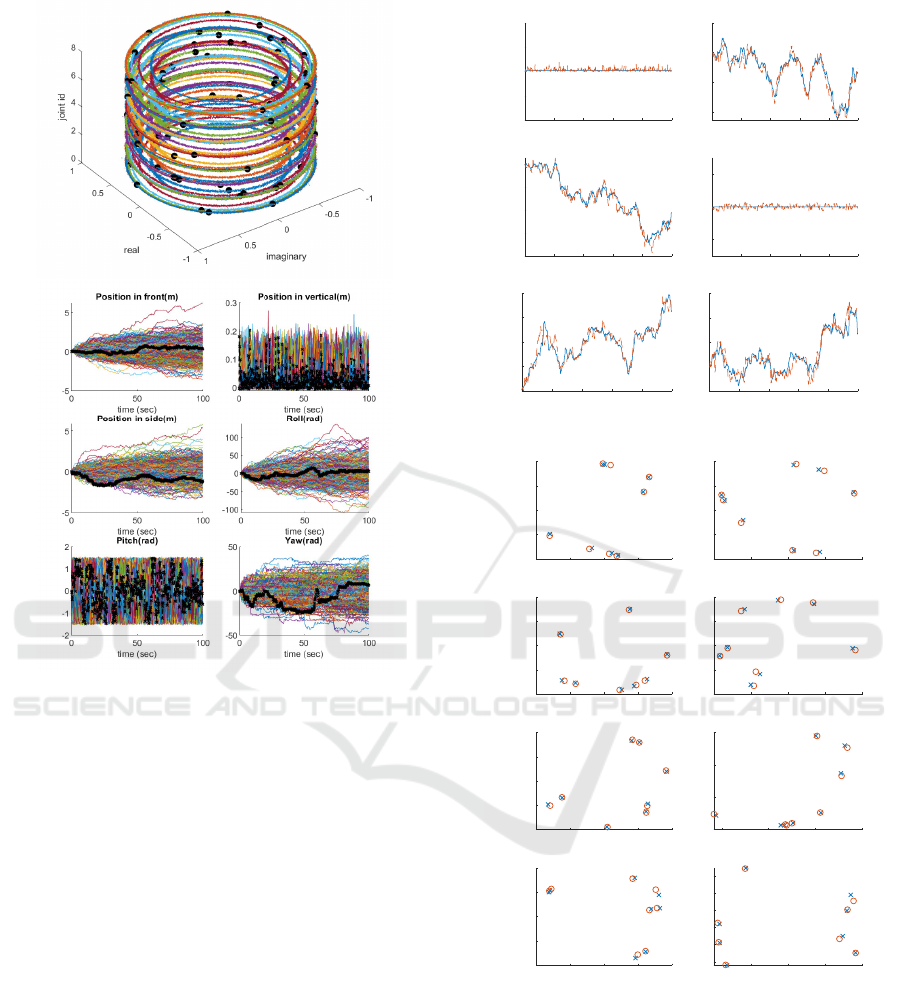
Figure 4: The topological joint shape of the measured train-
ing samples. In the top figure, the point group of black cir-
cles corresponds one example sample in all batch experi-
ments. In the bottom figure, the highlighted black line is
the paired body states corresponding to the black circles in
top figure.
4.3 Results
4.3.1 Training Results
The training was done by the Adam optimizer with
cyclic learning rate for faster convergence (Smith,
2017). The learning rate is cyclically repeated from
0.0002 to 0.004 in 800 epoch period with exponen-
tially decaying profile. The training results in Figure
5 show good fitting both in body states and topologi-
cal joint shape.
4.3.2 Locomotion Generation
We perform generation process for two different set-
tings. First, the body latent variable z
(B)
is randomly
sampled for the prior distribution with zero the joint
latent variables z
(J )
1:K
. The joint latent variable z
(J )
1:K
is
principally sampled by dynamic condition. However,
0 20 40 60 80 100
time (sec)
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
Position in vertical(m)
0 20 40 60 80 100
time (sec)
-2
-1.5
-1
-0.5
0
Position in front(m)
0 20 40 60 80 100
time (sec)
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
Position in side(m)
0 20 40 60 80 100
time (sec)
-20
-10
0
10
Roll(rad)
0 20 40 60 80 100
time (sec)
-10
0
10
Pitch(rad)
0 20 40 60 80 100
time (sec)
-5
0
5
10
15
Yaw(rad)
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1
real
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
imaginary
Joint 1
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1
real
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
imaginary
Joint 2
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1
real
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
imaginary
Joint 3
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1
real
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
imaginary
Joint 4
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1
real
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
imaginary
Joint 5
-0.5 0 0.5 1
real
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
imaginary
Joint 6
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1
real
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
imaginary
Joint 7
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1
real
-0.4
-0.2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
imaginary
Joint 8
Figure 5: The training result. For the topological joint shape
(bottom figure), the circle means experiments data, and the
cross does the estimated one. For the body states (top fig-
ure), the line means experiments data, and the dashed line
means the estimated one.
we set them as zero to identify the disentanglement
ability of body latent variables. Second, the joint la-
tent variables z
(J )
1:K
is sampled by the prior distribution
with the body latent variable z
(B)
fixed. The generated
samples are shown in Figure 6 for the first setting, and
in Figure 7 for the second setting. In the Figure 6, The
Generative Locomotion Model of Snake Robot with Hierarchical Networks for Topological Representation
199

generation result of first settings shows that the body
latent variable z
(B)
efficiently spans across sequence
level that is represented as variation in vertical direc-
tion. It means that we can design locomotion based on
the intuitive body latent variables. The result of sec-
ond setting in Figure 7 indicates that two body pattern
have inter-sequence variation, not the intra-sequence
variation. The same result also can be found samples
of spectral joint shape in Figure 8. Thus, we can gen-
erate locomotion stably for the desired intuitive body
pattern with corresponding topological joint shape.
The results from two different settings, the proposed
generative locomotion model has user-oriented inter-
face to help locomotion design.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We introduced the generative locomotion model.
Compared with the conventional works that were re-
lied on human expert or specific domain-knowledge,
the proposed approach provides user-oriented high
level intuition/interface. In our model, one can gen-
erate complex locomotion by selecting intuitive body
patterns. The advantages come from two methods.
Topological shaping allows locomotion data to be
bounded in shape, which leads to generalize datasets.
The designed hierarchical networks efficiently esti-
mated complex contexts via latent information prop-
agation. We expect that our generative model ap-
proach on locomotion proposes alternative ways for
conventional locomotion studies, and the method can
be adopted for other robot locomotion researches.
0 20 40 60 80 100
time (sec)
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
Position in vertical(m)
0 20 40 60 80 100
time (sec)
-2
0
2
4
Position in front(m)
0 20 40 60 80 100
time (sec)
-2
-1
0
1
2
Position in side(m)
0 20 40 60 80 100
time (sec)
-50
0
50
100
Roll(rad)
0 20 40 60 80 100
time (sec)
-10
0
10
Pitch(rad)
0 20 40 60 80 100
time (sec)
-20
-10
0
10
20
Yaw(rad)
Figure 6: The body latent variable is randomly sampled
with zero joint latent variables.
Figure 7: Two differnt latent variables of body state were
sampled. For each body latent variable, 8 different joint la-
tent variables were sampled. The shaded region represents
trajectories for same body latent variable. In the shaded re-
gion, 8 different joint latent sample trajectories were drawn.
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1
real
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
imaginary
Joint 1
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1
real
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
imaginary
Joint 2
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1
real
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
imaginary
Joint 3
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1
real
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
imaginary
Joint 4
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1
real
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
imaginary
Joint 5
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1
real
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
imaginary
Joint 6
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1
real
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
imaginary
Joint 7
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1
real
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
imaginary
Joint 8
Figure 8: For two different body latent variables in Figure
7, independet 8 joint samples were drawn. The symbols
’o’ and ’x’ respectively represents two differnt body latent
varaibles. For the symbol ’o’ or ’x’, independent joint latent
samples were illustrated by differnt colors.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partially supported by CREST, JST,
and Komatsu MIRAI construction institute, Osaka
University.
ICAART 2020 - 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
200

REFERENCES
Alemi, A. A., Poole, B., Fischer, I., Dillon, J. V., Saurous,
R. A., and Murphy, K. (2017). Fixing a broken ELBO.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.00464.
Chung, J., Kastner, K., Dinh, L., Goel, K., Courville, A.,
and Bengio, Y. (2015). A Recurrent Latent Variable
Model for Sequential Data. pages 1–9.
Cui, Z., Chen, W., and Chen, Y. (2016). Multi-Scale Con-
volutional Neural Networks for Time Series Classifi-
cation.
Dai, B. and Wipf, D. (2019). Diagnosing and enhancing vae
models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1903.05789.
Dupont, E. (2018). Learning disentangled joint continuous
and discrete representations. In Advances in Neural
Information Processing Systems, pages 710–720.
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B.,
Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., and Ben-
gio, Y. (2014). Generative adversarial nets. In
Advances in neural information processing systems,
pages 2672–2680.
Grochow, K., Martin, S. L., Hertzmann, A., and Popovi
´
c,
Z. (2004). Style-based inverse kinematics. In ACM
transactions on graphics (TOG), volume 23, pages
522–531. ACM.
Ha, S. and Choi, S. (2016). Convolutional neural net-
works for human activity recognition using multi-
ple accelerometer and gyroscope sensors. In 2016
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks
(IJCNN), pages 381–388. IEEE.
Hjelm, R. D., Fedorov, A., Lavoie-Marchildon, S., Gre-
wal, K., Bachman, P., Trischler, A., and Bengio,
Y. (2018). Learning deep representations by mu-
tual information estimation and maximization. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1808.06670.
Hoffman, M. D. and Johnson, M. J. ELBO Surgery: Yet
another way to carve up the evidence lower bound.
Holden, D., Saito, J., and Komura, T. (2016). A deep
learning framework for character motion synthesis
and editing. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG),
35(4):138.
Hsu, W.-N., Zhang, Y., and Glass, J. (2017). Unsupervised
learning of disentangled and interpretable representa-
tions from sequential data. In Advances in neural in-
formation processing systems, pages 1878–1889.
Kingma, D. P. and Welling, M. (2013). Auto-encoding vari-
ational bayes. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.6114.
Li, J., Xu, K., Chaudhuri, S., Yumer, E., Zhang, H., and
Guibas, L. (2017). Grass: Generative recursive au-
toencoders for shape structures. ACM Transactions
on Graphics (TOG), 36(4):52.
Li, Y. and Mandt, S. (2018). Disentangled sequential au-
toencoder. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.02991.
Maddison, C. J., Mnih, A., and Teh, Y. W. (2016). The con-
crete distribution: A continuous relaxation of discrete
random variables. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.00712.
Pintelon, R. and Schoukens, J. (2012). System identifica-
tion: a frequency domain approach. John Wiley &
Sons.
Poole, B., Ozair, S., van den Oord, A., Alemi, A. A.,
and Tucker, G. (2018). On variational lower bounds
of mutual information. In NeurIPS Workshop on
Bayesian Deep Learning.
Sanchez-Lengeling, B. and Aspuru-Guzik, A. (2018). In-
verse molecular design using machine learning: Gen-
erative models for matter engineering. Science,
361(6400):360–365.
Schoukens, J., Vaes, M., and Pintelon, R. (2016). Linear
system identification in a nonlinear setting: Nonpara-
metric analysis of the nonlinear distortions and their
impact on the best linear approximation. IEEE Con-
trol Systems Magazine, 36(3):38–69.
Schulman, J., Moritz, P., Levine, S., Jordan, M., and
Abbeel, P. (2015). High-Dimensional Continuous
Control Using Generalized Advantage Estimation.
pages 1–14.
Smith, L. N. (2017). Cyclical learning rates for training
neural networks. In 2017 IEEE Winter Conference on
Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pages 464–
472. IEEE.
Tolstikhin, I., Bousquet, O., Gelly, S., and Schoelkopf, B.
(2017). Wasserstein auto-encoders. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1711.01558.
Tomczak, J. M. and Welling, M. (2018). VAE with a vamp-
prior. International Conference on Artificial Intel-
ligence and Statistics, AISTATS 2018, pages 1214–
1223.
van den Oord, A., Dieleman, S., Zen, H., Simonyan,
K., Vinyals, O., Graves, A., Kalchbrenner, N., Se-
nior, A., and Kavukcuoglu, K. (2016). Wavenet:
A generative model for raw audio. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1609.03499.
Veli
ˇ
ckovi
´
c, P., Fedus, W., Hamilton, W. L., Li
`
o, P., Bengio,
Y., and Hjelm, R. D. (2018). Deep graph infomax.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.10341.
Wampler, K., Popovi
´
c, Z., and Popovi
´
c, J. (2014). Gener-
alizing locomotion style to new animals with inverse
optimal regression. ACM Transactions on Graphics
(TOG), 33(4):49.
Zhang, H., Starke, S., Komura, T., and Saito, J. (2018a).
Mode-adaptive neural networks for quadruped mo-
tion control. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG),
37(4):145.
Zhang, Y., Galley, M., Gao, J., Gan, Z., Li, X., Brockett,
C., and Dolan, B. (2018b). Generating informative
and diverse conversational responses via adversarial
information maximization. In Advances in Neural In-
formation Processing Systems, pages 1810–1820.
Zhao, S., Song, J., and Ermon, S. (2019). Infovae: Balanc-
ing learning and inference in variational autoencoders.
In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial
Intelligence, volume 33, pages 5885–5892.
Generative Locomotion Model of Snake Robot with Hierarchical Networks for Topological Representation
201

APPENDIX
The Layer Architecture of Body States
Encoder/Decoder
Figure 9: The stacked architecture for body states in Figure
3.
ICAART 2020 - 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
202
