
Cognitive Modeling in Computational Rhetoric: Litotes, Containment
and the Unexcluded Middle
Jelena Mitrovi
´
c
1 a
, Cliff O’Reilly
2 b
, Randy Allen Harris
3 c
and Michael Granitzer
1 d
1
Faculty of Computer Science and Mathematics, University of Passau, Germany
2
Birkbeck College, University of London, U.K.
3
Department of English Language and Literature, University of Waterloo, Canada, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Litotes, Computational Rhetoric, Cognitive Modeling, Ontology, Image Schema, Unexcluded Middle.
Abstract:
The focus of our study is the rhetorical figure litotes and its cognitive modeling. This figure is formed by a
contrary term that emphatically accentuates a positive, e.g. He is not exactly an idiot (said of Albert Einstein).
Lawrence Horn’s illumination of the Law of Excluded Middle and its relationship to litotes by creating an
Unexcluded Middle is central to our ideas and we correlate this to Image Schema theories developed by Mark
Johnson, George Lakoff and Rafael N
´
u
˜
nez – specifically the schema of CONTAINMENT. The distinction be-
tween contrary and contradictory opposition is described. We extend the assessment of the Excluded Middle
from the perspective of Image Schema theory into the realm of the Unexcluded Middle and draw a represen-
tation of the layout of containers and analogous concept-activation. Lastly, we create and present an OWL
ontology and publish it online.
1 INTRODUCTION
We argue for the integration of rhetorical studies,
cognitive science, computational modeling, and Nat-
ural language processing (NLP), by way of an ex-
tended example, the unjustly neglected rhetorical fig-
ure, litotes.
Litotes is a figure in which we say less but mean
more (“minus dicimus et plus significamus” (Miguel,
1990)) and can be placed in the Pragmatic context un-
der Implicature – the difference between what is said
by a speaker and what is intended
1
. Litotes is as ubiq-
uitous as any of the more famous rhetorical figures
such as metaphor and irony, and yet not well studied
from a computational perspective. Despite this ne-
glect, we hold that research on its function, role and
importance promises headway in the rich new field
of figure analysis in Computational Rhetoric, an area
of study which brings together computer scientists,
rhetoricians, psychologists, philologists, literary crit-
ics and information scientists working on the detec-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3220-8749
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8002-5336
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9324-1879
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3566-5507
1
For a defining overview of rhetorical figures including
litotes see (Harris and Di Marco, 2017)
tion and understanding of rhetorical figures, their as-
sociated cognitive machinery and computational ap-
plicability.
In this paper we connect the realm of rhetorical
studies to the domain of Image Schema theory. As
Dewell has said: “...language plays a much greater
role in the development of image schemas than is of-
ten assumed, contributing not only to cross-linguistic
variation but also to some universal similarities in
the structure of image schemas” (Dewell, 2005). We
are especially concerned with the universal schema
known as containment, which gives a valuable pur-
chase on litotes.
The Law of the Excluded Middle is a primary el-
ement of logical thought and a variant extension of
this law – named the Unexcluded Middle – effectively
bridges litotic understatement and cognitive concept-
activation, i.e. the neuronal activity resulting in con-
scious or subconscious understanding of a concept.
In section 2 we offer some background on litotes,
a more detailed analysis of the Unexcluded Middle,
the Image Schema CONTAINMENT and the onto-
logical approach to modeling litotes. Section 3 gives
an analysis of how these concepts are intertwined in
litotes while in section 4 we provide an OWL ontol-
ogy of litotes. Conclusions and Future work consid-
erations are given in the last two sections of the paper.
806
Mitrovi
´
c, J., O’Reilly, C., Harris, R. and Granitzer, M.
Cognitive Modeling in Computational Rhetoric: Litotes, Containment and the Unexcluded Middle.
DOI: 10.5220/0009104908060813
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2020) - Volume 2, pages 806-813
ISBN: 978-989-758-395-7; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Litotes
Litotes is a rhetorical figure in which a state-
ment is made emphatic by denying a con-
trary. A straightforward example from Henry
Peacham’s The Garden of Eloquence (1593) is
“he is not the wisest man in the world” which has a
meaning similar to “he is a fool” (Lanham, 1991).
It is a form of understatement, also known as
Deminutio to Latin pre-Christian scholars, but the
term comes to us from the Greek meaning “smooth”
or “plain”: λιτοτης. An example of litotes appears in
the early handbook erroneously attributed to Cicero,
the Rhetoric ad Herennium (Cicero, 1954):
“his father left him a patrimony that was – I
do not wish to exaggerate – not the smallest”
Cicero expresses the point of mitigating a posi-
tive but nevertheless getting across the message in-
tended, i.e. that the legacy in question was large in-
deed. There is, in short, some level of irony at work
with litotes, and interpretation requires a reconstruc-
tion of the speaker’s intention. The impact of litotes
derives from speaking plainly about a subject while,
at the same time, contradicting a negative term to
enhance the positive. Its usefulness as a means for
understatement, modesty and insult leads to signifi-
cant usage and an almost ubiquitous position in lan-
guage and culture (Shovel, 2015). Its prominence has
brought a few interesting studies in more recent times
(Hermann et al., 2013; Yuan, 2017)
Horn examines the figure in great detail (Horn,
2017) and differentiates between two important con-
cepts - contrariety and contradiction. A contradictory
opposition is binary, e.g. black versus white or green
versus not green, whereas a contrary opposition can
allow room for things to lie in-between, e.g. truthful
versus untruthful or comfortable versus uncomfort-
able. Nuance, context and vagueness are important
factors that determine the impact of the differences in
contrary oppositions.
Litotes aligns both with the principles of logic (the
negation of a negative is a positive) and the prin-
ciples of style (no repetition is null). Repetitions
work chiefly in an additive way, but the main is ad-
ditive, familiar in the iconicity principle of quantity –
more language corresponds to more conceptual mat-
ter (Givon, 1991). That is where the emphasis comes
in. The two negatives in this case are not just positive,
they are emphatically positive. Denotatively, “not the
smallest” means that there is at least one other quan-
tity that is smaller, the not cancelling out the superla-
tive. Rhetorically, it means something more like “the
biggest”, or at least “really big”. Sometimes, how-
ever, repeating the negative has less emphatic sense.
For instance, compare the two sentences, “Lupita Ny-
ong’o is not unattractive” (with a negator and a negat-
ing prefix) and “Lupita Nyong’o is not ugly” (with a
negator and a negatively valenced adjective). The first
one is mildly complimentary about her appearance,
the second more emphatic. And with the following
example, which pushes the disavowal of the adjective
to an extreme, the compliment approaches perfection:
“Lupita Nyong’o is the furthest thing from ugly.”
Computational modeling of litotes has to take into
consideration its many characteristics, negation being
the most prominent. Negation has been treated differ-
ently in Linguistics and Rhetoric, as well as in Prag-
matics, where it has a strong effect (Taboada et al.,
2017). Likewise, a rhetorical figure such as Antithesis
has been seen as very effective and even persuasive,
precisely due to the presence of negation, as well as
opposition. We see litotes as a figure that can also
play a persuasive role in arguments, therefore its de-
tection should be included in argument mining sys-
tems (Mitrovi
´
c et al., 2017).
2.2 Unexcluded Middle
In logic, the Law of Excluded Middle, dating at
least to Aristotle’s discussion of the principle of non-
contradiction in On Interpretation (Aristotle, 1938),
states that for any proposition, either that proposition
is true or its negation is true. It is the third of the three
classic laws of thought. This, now (in)famous quote
from a former United States’ president illustrates us-
age of the excluded middle in modern practice :
(1) Either you are with us or you are with the
terrorists (George W. Bush)
Using propositional logic notation to reflect the logic
of the terms and arguments involved we can say that
P ∨ Q becomes P ∨ ¬P (P represents being “with us”
and Q represents being “with the terrorists”). By im-
plication anyone not with “us” must be with “the ter-
rorists”. We illustrate this in Figure 1 – we transi-
tion from a three member set {us,terrorists,neither us
nor terrorists} to a two-member set {us,terrorists} and
the middle is effectively excluded from being (“po-
lar contraries p and q become mutually exhaustive as
well as mutually inconsistent” (Horn, 2017)).
Figure 1: Transition to Excluded Middle.
Cognitive Modeling in Computational Rhetoric: Litotes, Containment and the Unexcluded Middle
807

There is a further twist to this pattern called the
Unexcluded Middle. This aspect of the litotic form
can be seen in the following example:
(2) I’m not happy but I’m not unhappy about
it. (The History Boys, Alan Bennett)
The speaker is neither happy nor unhappy which vio-
lates the law of non-contradiction, but rhetorically the
meaning is that happiness is irrelevant to the situa-
tion. Pragmatically, we may also say that (despite the
binary nature of the adjectives) happiness can form
a contrary opposition, not contradictory one, so that
the speaker can be seen to articulate a midpoint on a
continuum, neither positive (happy) nor negative (un-
happy), the negator and the negative affix cancelling
each other out. Figure 2 shows a representation of the
Unexcluded Middle and the creation of a new state
that is in-between happy and not happy. We could
graphically represent this in a number of ways, but
choose this three-member set for simplicity.
Figure 2: Representation of the Unexcluded Middle.
Reinhard Blutner describes this phenomenon as
“double negation” and draws it slightly differently
(Figure 3) (Blutner et al., 2004). Blutner also reflects
that “it’s an interesting exercise to introduce more
than three states of happiness...More importantly, in
the context of litotes, it seems necessary to account
for the effect of gradient acceptability and continuous
scales” (Blutner et al., 2004).
Horn states that “To depict individuals (or their
marriages and routines) as ’not unhappy’ yet – by
implication – not (exactly) happy either is to tac-
itly invoke a scale <not unhappy, happy> in accor-
dance with which a weaker property is affirmed or
conceded but a stronger alternative implicitly denied”
(Horn, 2017). The key term for us here is “by im-
plication” since it is the mental process of blending
knowledge about what happiness in marriage is like
which can give rise to opposition. What is implied by
understanding of words, contexts, stereotypes, Scripts
(Schank and Abelson, 1975), Frames (Fillmore et al.,
1982) etc. affects what happens in the balancing of
terms.
Figure 3: When two negatives don’t make a positive, repro-
duced from (Blutner et al., 2004).
Just as regarding affixal negation (the
“notorious not un- construction” (Horn, 2017))
such as “not unhappy”, we can include a similar
description of a term that creates a contradictory
opposition. In the example phrase, below, by Roger
Penrose, the Unexcluded Middle is created between
the possible and impossible.
(3) Quantum entanglement is a very intriguing
issue, but it is not impossible. (Roger Penrose)
Possibility should not be able to be defined in this way
(Frege’s assertion that “clothing a thought in dou-
ble negation does not alter its truth value” (Frege
and Beaney, 1997) should hold true for proposi-
tional logic), however this example shows another
Unexcluded Middle where understanding the sub-
ject (Quantum Entanglement) is in some way nei-
ther possible nor impossible. This case could be for
the purposes of understatement or simply a play on
the concept of impossibility given that the perceived
difficulty of understanding Quantum Theory is well
known. Horn’s analysis defines a symbolic represen-
tation for this phenomenon:
1. ¬(
c
[
adj
X])
2. ¬(¬[
adj
X])
(
c
represents contrary opposition, ¬ represents con-
tradictory opposition and [
adj
X] represents an adjec-
tival term.)
2.3 Image Schemata
Image Schemata are “structures by which we are able
to have coherent experience that we can comprehend”
(Johnson, 1987), but “they can be seen as the con-
ceptual building blocks for metaphoric and abstract
thought” (Hedblom et al., 2015). Image Schemata
provide a framework which we can use to describe
complex structures of understanding and cognition in
many domains. We focus herein on the linguistic,
but also take into account that the underlying mecha-
nisms are neurological, develop from infancy and are
sensori-motor in origin (Cuccio and Gallese, 2018).
ICAART 2020 - 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
808

Figure 4: Venn-style diagram representing CONTAINER
objects.
2.3.1 The Schema CONTAINMENT
There are many recognized Image Schemata, one fun-
damental example being CONTAINMENT. Johnson
discusses the structure of this schema. Based on ex-
perience of the world (grounded or embodied), a re-
curring organization of structure, spatially bounded,
a three-dimensional container is experientially salient
and can be thought of as an “in-out orientation”
(Johnson, 1987).
Lakoff and N
´
u
˜
nez approach core concepts in
mathematics from the direction of Image Schema the-
ory (Lakoff and N
´
u
˜
nez, 2000). Of particular interest
to us is the treatment of CONTAINMENT mapped to
fundamental inferential laws of logic and especially
the Law of Excluded Middle. Also the link estab-
lished between visual processing in the brain (a root
for Image Schema theory) and concept-activation ap-
plied to non-visual stimuli, gives us a basis for the
arguments in this paper and therefore a thesis that the
underlying mechanisms of language understanding –
especially the complex and rich domain of rhetoric
– are predicated on the same brain structures (or at
least connected to them) that give rise to visual pro-
cessing and conceptualizations; “...it makes neurolog-
ical sense that structures in the visual system can be
used for conceptual purposes” (Lakoff and N
´
u
˜
nez,
2000). As argued further in their work, the capacity
for perceiving the world in terms of contained struc-
tures gives rise to a sort of Folk Boolean Logic which
can be associated to a Venn diagram, such as in Fig-
ure 4. Container A represents a concept. Object B is
within the container and therefore adheres to the con-
cept of A.
Each region in the diagram is related to a con-
cept that maps to a Container element (either in or
out of the container). Lakoff and N
´
u
˜
nez develop a
Law of Container Schemas which evolves from the
mapping of structural constraints (from the physical
process of containment and exclusion) to inferential
structures which are conceptual in nature, but fol-
low analogous “rules”, e.g. an object inside a con-
tainer maps to a member of the category represented
by the container. This gives rise to the Conceptual
Metaphor Categories Are Containers. Table 1 shows
the progression through logic from the CONTAINER
schema to a symbolic representation of the Law of
Excluded Middle.
2.4 Ontological Approach
Ontologies are ideal for representing ideas as com-
plex as rhetorical figures, which have specific prop-
erties and are often interrelated (Harris et al., 2017).
The figure of Anadiplosis, for example, has the prop-
erty of repeating lexemes across clause boundaries
and litotes, as we have seen, is centred on spe-
cific phrases (lexemes) in well-defined orientations
(double-negation). Furthermore, rhetorical figures
have a tendency to co-occur which makes linking con-
cepts within and across distinct ontology models a
useful tool for extending understanding and also for
inferential knowledge discovery.
Our ontology of litotes is modeled and developed
in OWL
2
which enables us to utilize the power of log-
ical inference and validation with tools such as Pro-
tege
3
. It also enables significant re-use within the Se-
mantic Web movement since, by publishing the on-
tology files online, we enable others to benefit from
our work. We create links via OWL properties to on-
tologies already part of the Semantic Web and this po-
tentially allows inference and computation across the
combined set of data we hope to create in the near
future.
There are numerous recent works that develop
an ontological perspective on image schemata (Kim-
mel, 2005; Kuhn, 2007; Hedblom et al., 2014; Hed-
blom et al., 2018), however, to our knowledge, few
OWL ontologies exist that describe the cognitive as-
pects of rhetorical figure sub-structure (a number of
taxonomically-focussed ontologies have been devel-
oped however, e.g. the Ontology of Rhetorical fig-
ures for Serbian (Mladenovi
´
c and Mitrovi
´
c, 2013)
and the Ontology focusing on the figure Antimetabole
(O’Reilly and Harris, 2017).
3 ANALYSIS
Similar to Bennett & Cialone’s analysis of geomet-
rical constraints through their “Eight kinds of sur-
rounding” (Bennett and Cialone, 2014) we explore
the Venn-style representation of the container/concept
analogy. Lakoff and N
´
u
˜
nez represent the Container
Schema logic for Excluded Middle as a container with
2
https://www.w3.org/OWL/
3
https://protege.stanford.edu/
Cognitive Modeling in Computational Rhetoric: Litotes, Containment and the Unexcluded Middle
809
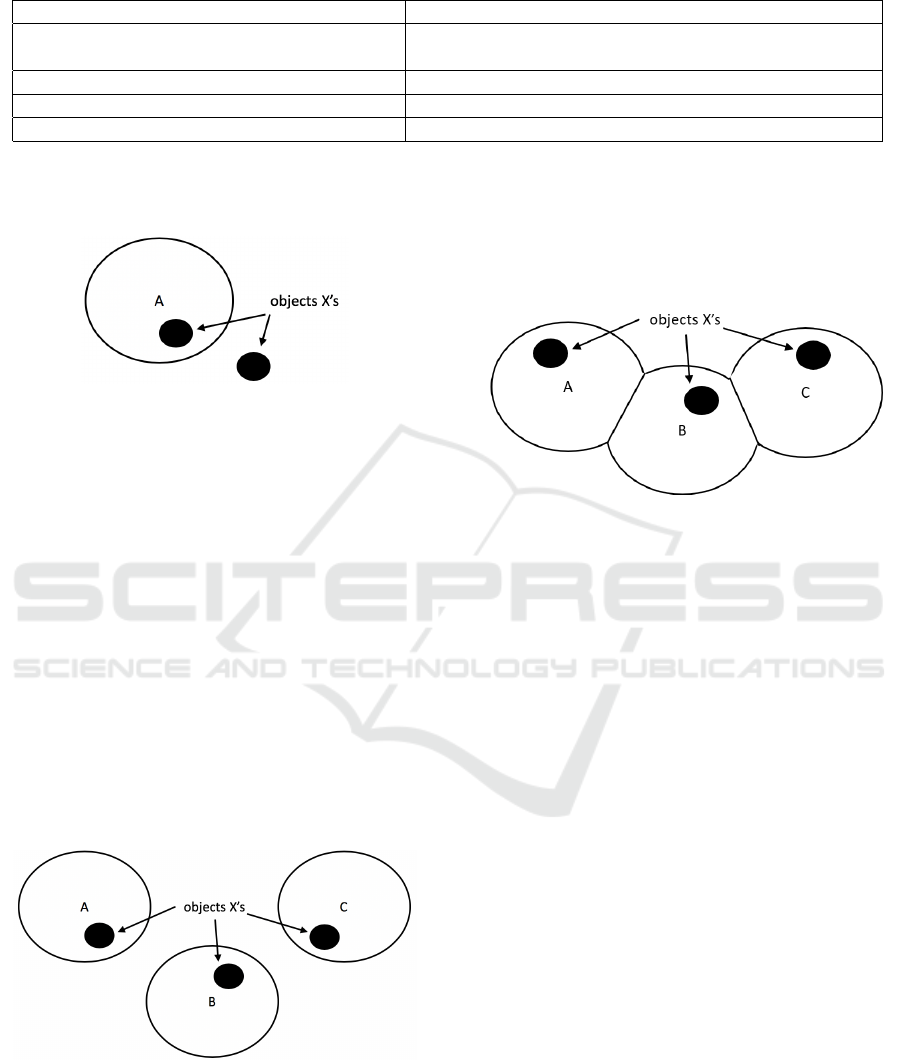
Table 1: Logic and Law progression for Excluded Middle (from (Lakoff and N
´
u
˜
nez, 2000).
Logic Law
Embodied Container Schemata Every object X is either in Container schema A or out of
Container schema A
Mapped classes Every entity X is either in category A or out of category A
Propositions mapped from classes Every proposition P is either true or not true
Symbolic form mapped from propositions P ∨ ¬P
an entity X either in or out of the container A – Figure
5.
Figure 5: Container Schema representation for Excluded
Middle, reproduced from (Lakoff and N
´
u
˜
nez, 2000).
To follow our previous example of an utterance cred-
ited to the former US President Bush, we might say
that the container A represents the category terrorist
and for entity X to be positioned in the container is to
be a terrorist and outside the container is to belong to
us as presented in the infamous quote given in Section
2.2 of this paper.
In considering the Unexcluded Middle we extend
this analogy and diagramming method. Figure 6
shows a view of container and entity orientation in re-
spect to the Unexcluded Middle. To follow the exam-
ple from Penrose again, an opposition is created be-
tween possible and impossible, but because the “se-
mantic contradictory is also a virtual (or coerced)
contrary” (Horn, 2017) we have to consider three cat-
egories and therefore three containers.
Figure 6: Container Schema representation #1 for Unex-
cluded Middle.
The process of double negation similar to those de-
scribed herein leads to concept-activation (again, we
are not referring exclusively to the creation of a novel
concept representation) and a conceptual leap that re-
sults in added complexity and ambiguity. Container
A could be possible, container B impossible and con-
tainer C could represent not impossible (the so-called
Unexcluded Middle). The entity X is either in con-
tainer A, B or C.
Figure 7: Container Schema representation #2 for Unex-
cluded Middle.
We contend that in reality it is plausible that some
form of all three concepts (containers) are activated
especially where concepts are not completely con-
trary or if there is a particularly large contextual over-
lap. We show this alternative representation in Fig-
ure 7. The key difference between Figures 6 and 7
is that the containers are merged or in contact (John-
son lists MERGING and CONTACT as separate im-
age schemata (Johnson, 1987) which indicates some
overlap or connection between the concepts.
4 ONTOLOGY
We take the previous insights gained from coalesc-
ing the image schema of CONTAINMENT, our un-
derstanding of linguistic entities, and the concept-
activation process we have termed the Unexcluded
Middle and develop an OWL ontology representation.
We draw a graph showing the main concepts and re-
lations and display it in the Figure 8.
We describe the linguistic entity Lexeme which
may be proximal-to any other lexeme and each of
which may evoke a Sememe. The sememe being a
semantic unit and lexeme being a lexical unit – these
terms reflect linguistic standards. A sememe can be
situated-in either an Exterior or Interior of a Con-
tainer which itself is bounded-by a Boundary. In-
ICAART 2020 - 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
810

Figure 8: Ontology of the rhetorical figure litotes.
stances of the class of litotes are composed-of in-
stances of Sememe which themselves are part-of the
class of Signified. Signified is a linguistic term and
represents the set of concepts (in semantic terms, se-
memes) that are evoked by lexical units. Tying to-
gether the container, signified and litotes entities is
the UnexcludedMiddle class. We argue that this entity
activates a container (through a neurological process
not understood well and not described herein) and the
specific order or direction of this relationship is de-
batable.
From image schema theory we say that a container
entails the concept (signified). This is a metaphoric
action, i.e. signifieds are not actually in anything (ex-
cept, debatably, in our heads), but since we grasp em-
bodied experience intuitively we can use our physical
and spatial understanding of the world to set concepts
in metaphoric bounded containers. Due to the syn-
chrony between containers and signifieds, the unex-
cluded middle class creates a signified and, further, it
is the unexcluded middle that develops the existence
of the figure of litotes.
Lastly, we contend that the Unexcluded Middle
is itself invoked by the Contrariety that exists be-
tween sememes (Sememes are subject-to Contrari-
ety). There is further work in this area that should in-
volve the other invoking mechanisms around the Un-
excluded Middle such as the context or knowledge of
the thinker.
The ontology is deliberately underspecified which
allows for more flexibility in the descriptions we pro-
vide. We have yet to apply this model to many exam-
ples of real-world figures of litotes, however because
we are modelling at a high level and underspecifying
properties we do not believe this is a problem to be
fixed. We do, however, anticipate that future work
would include greater specificity and the use of this
ontology in computational applications.
We publish our OWL representation (in XML for-
mat) online
4
.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper we argue that litotes is a rhetorical figure
that develops a novel middle ground located between
an opposition of terms. The middle ground can be de-
scribed in concept-activation terms and can be consid-
ered in the light of Image Schema theory – especially
the schema of CONTAINMENT. This contrasts with
the logical view of the Law of the Excluded Middle
where concepts are definitively bounded. Still, there
is a more complex conceptual arrangement involved
where litotes is used and we show a model for the ac-
tivation of new concepts (and Containers) to account
for this novel middle ground(s).
To make this point clearer we must show various
strengths of the figure – that are reflected in the rel-
ative strengths of Implicature. Two further examples
are given, below.
(4) “Not a bad day’s work on the whole,”
he muttered, as he quietly took off his mask,
and his pale, fox-like eyes glittered in the red
glow of the fire. “Not a bad day’s work.”
4
http://repositori.com/sw/onto/litotes.owl
Cognitive Modeling in Computational Rhetoric: Litotes, Containment and the Unexcluded Middle
811

(Baroness Emmuska Orczy, The Scarlet Pim-
pernel, 1905)
(5) Are you also aware, Mrs. Bueller, that Fer-
ris does not have what we consider to be an
exemplary attendance record? (Jeffrey Jones
as Principal Ed Rooney, Ferris Bueller’s Day
Off, 1986)
In (4) the intent is understatement (a good day’s work
is implied as having been done), but the phrase is a
commonly-used one and usually reflects an alterna-
tive and modest way to congratulate someone. In (5),
however, the implication here is that Ferris has a poor
attendance record. It is an understatement again, but
considering that we can picture the scene in the Prin-
cipal’s office with all of the context, we might believe
that this second example is a stronger understatement
and reflects more weight of intention to make an em-
phatic point about attendance, but without expressly
uttering it.
In summary, litotes creates categorical structures
which map to Containers, and therefore to neural
structures – it is these that give rise to the ability for
litotes to work at all. Furthermore, the balancing of
negated terms versus a contrary – and therefore the
construction of strong or weak opposites – defines the
figure of litotes. This balancing force comes about
through the context or wider semantics of the words
in use. Therefore litotes gains strength by the use of
terms with significant semantic baggage that allows
the balancing forces to appear.
The power and ubiquity of litotes are evident to
anyone giving modern language usage even just a
brief analysis. This, coupled with the complexity
of the meaning, makes it a very interesting and use-
ful research area. For example in the modern world
of all-pervading social media and a post-truth aspect,
litotes is sometimes used to carry meaning that, due to
its complexity, evades direct computational analysis.
Notably we could look for its presence in hate-speech
in a pejorative sense — which we could call hidden
hate-speech — the speaker is not being hateful in a
direct way, e.g. He is not the smartest pea in the pod.
Our research aims include highlighting the cog-
nitive mechanisms which underlie the figure in order
to attract greater interest and understanding. Through
more awareness and comprehension we hope to en-
courage more research. A further motivation is to
create computational models of the figure in order
to drive automated discovery and analysis in a cur-
rently sparse field. Our ontological models are pub-
lished online and usable by anyone wanting to per-
form logical inference across linguistic data sets. We
are currently developing further computational mod-
els in this area.
6 FUTURE WORK
Much research has been done in the domain of Image
Schema theory and cognitive understanding, however
there is more to be done (“The cognitive processes
underlying concept invention are still largely unex-
plored ground” (Hedblom et al., 2015)). The perspec-
tive from which we approach these issues is slightly
different and we bring a wealth of rhetorical research
behind us. The following are some areas that we be-
lieve will be important for future research in the cross-
domain territory we are continuing to explore:
1. Our view is that the semantic and pragmatic
weight of a word or phrase can impact the ex-
tent to which conceptual middles can be formed.
We would like to follow this research direction
through exploratory computational corpora anal-
yses.
2. Taking into consideration the characteristics of
litotes and its relation to negativity and Image
Schemata, it is possible to build upon the ontolog-
ical modeling of litotes as a rhetorical figure, as it
was done in the RetFig project (Mladenovi
´
c and
Mitrovi
´
c, 2013) and for the schema of BALANCE
in (O’Reilly and Harris, 2017), and to further use
this new model as a part of argument structure as
envisioned in (Mitrovi
´
c et al., 2017)
3. Many detailed studies of Image Schemata and
especially CONTAINMENT have been done
(Lakoff and N
´
u
˜
nez, 2000; Dewell, 2005; Bennett
and Cialone, 2014; Hedblom et al., 2018). We
aim at research that would combine more of these
deeper theories and alternative methods of under-
standing them with the linguistic domain along
which we have already started.
4. Our ontological representation is deliberately un-
derspecified which means the definitions are flex-
ible. This can bring problems in terms of in-
ference, but it can also make the ontology more
pliable to mapping to well-developed upper on-
tologies such as SUMO (Niles and Pease, 2001)
which would allow for inferencing on different
levels of complexity. Our goal is to define in
more detail the properties of the various entities
we have modeled and to apply this to real-world
examples within computer applications.
REFERENCES
Aristotle (1938). On Interpretation. Harvard University
Press.
ICAART 2020 - 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
812

Bennett, B. and Cialone, C. (2014). Corpus guided sense
cluster analysis: a methodology for ontology devel-
opment (with examples from the spatial domain). In
FOIS, pages 213–226.
Blutner, R. et al. (2004). Pragmatics and the lexicon. Hand-
book of pragmatics, 488-514.
Cicero, M. T. (1954). Cicero Ad C. Herennium de ratione
dicendi:(Rhetorica ad Herennium), volume 403. Har-
vard University Press.
Cuccio, V. and Gallese, V. (2018). A peircean account of
concepts: grounding abstraction in phylogeny through
a comparative neuroscientific perspective. Phil. Trans.
R. Soc. B, 373(1752):20170128.
Dewell, R. (2005). Dynamic patterns of containment. From
perception to meaning: Image schemas in cognitive
linguistics, pages 369–393.
Fillmore, C. J. et al. (1982). Frame semantics. Cognitive
linguistics: Basic readings, pages 373–400.
Frege, G. and Beaney, M. (1997). The Frege Reader. Black-
well Oxford.
Givon, T. (1991). Isomorphism in the grammatical code:
Cognitive and biological considerations. Studies in
Language, 15(1):85–114.
Harris, R., Di Marco, C., Mehlenbacher, A. R., Clapper-
ton, R., Choi, I., Li, I., Ruan, S., and O’Reilly, C.
(2017). A cognitive ontology of rhetorical figures. In
Proceedings of AISB Annual Convention 2017, pages
228–235.
Harris, R. A. and Di Marco, C. (2017). Rhetorical figures,
arguments, computation. Argument & Computation,
8(3):211–231.
Hedblom, M., Kutz, O., and Neuhaus, F. (2014). On the
cognitive and logical role of image schemas in com-
putational conceptual blending. CEUR-WS.org.
Hedblom, M. M., Gromann, D., and Kutz, O. (2018). I n, o
ut and through: formalising some dynamic aspects of
the image schema c ontainment. In Proceedings of the
33rd Annual ACM Symposium on Applied Computing,
pages 918–925. ACM.
Hedblom, M. M., Kutz, O., and Neuhaus, F. (2015). Choos-
ing the right path: image schema theory as a founda-
tion for concept invention. Journal of Artificial Gen-
eral Intelligence, 6(1):21–54.
Hermann, K. M., Grefenstette, E., and Blunsom, P. (2013).
”not bad” is not ”bad”: A distributional account of
negation. Proceedings of the ACL Workshop on Con-
tinuous Vector Space Models and their Composition-
ality.
Horn, L. (2017). Lie-toe-tease: double negatives and un-
excluded middles. Philosophical Studies, 174(1):79–
103.
Johnson, M. (1987). The body in the mind: The bodily
basis of imagination, reason, and meaning. The body
in the mind: the bodily basis of imagination, reason
and meaning.
Kimmel, M. (2005). Culture regained: Situated and com-
pound image schemas. From perception to meaning:
Image schemas in cognitive linguistics, pages 285–
311.
Kuhn, W. (2007). An image-schematic account of spatial
categories. In International Conference on Spatial In-
formation Theory, pages 152–168. Springer.
Lakoff, G. and N
´
u
˜
nez, R. E. (2000). Where mathematics
comes from: How the embodied mind brings mathe-
matics into being. Basic Books.
Lanham, R. A. (1991). A handlist of rhetorical terms. Uni-
versity of California Press Berkeley.
Miguel, L. H. (1990). Hoffman, maria, e.:” negatio con-
trarii. a study of latin litotes” (book review). Emerita,
58:346.
Mitrovi
´
c, J., O’Reilly, C., Mladenovi
´
c, M., and Handschuh,
S. (2017). Ontological representations of rhetorical
figures for argument mining. Argument & Computa-
tion, 8(3):267–287.
Mladenovi
´
c, M. and Mitrovi
´
c, J. (2013). Ontology of
rhetorical figures for serbian. In Text, Speech, and Di-
alogue, pages 386–393. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Niles, I. and Pease, A. (2001). Towards a standard upper
ontology. In FOIS.
O’Reilly, C. and Harris, R. A. (2017). Antimetabole and
image schemata: Ontological and vector space mod-
els. In JOWO.
Schank, R. C. and Abelson, R. P. (1975). Scripts, plans, and
knowledge. In IJCAI, pages 151–157.
Shovel, M. (2015). Litotes, the most common
rhetorical device you’ve never heard of. https:
//www.theguardian.com/media/mind-your-language/
2015/mar/26/litotes-the-most-common-rhetoric\
\al-device-youve-never-heard-of). Accessed:
2018-10-28.
Taboada, M., Trnavac, R., and Goddard, C. (2017). On be-
ing negative. Corpus Pragmatics, 1:57–76.
Yuan, Y. (2017). The argumentative litotes in the analects.
Argument & Computation, 8:253–266.
Cognitive Modeling in Computational Rhetoric: Litotes, Containment and the Unexcluded Middle
813
