
Assessing the Impact of OCR Quality on Downstream NLP Tasks
Daniel van Strien
3 a
, Kaspar Beelen
1 b
, Mariona Coll Ardanuy
1 c
, Kasra Hosseini
1 d
,
Barbara McGillivray
1,4 e
and Giovanni Colavizza
1,2 f
1
The Alan Turing Institute, London, U.K.
2
University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
3
The British Library, London, U.K.
4
University of Cambridge, Cambridge, U.K.
Keywords:
Optical Character Recognition, OCR, Digital Humanities, Natural Language Processing, NLP, Information
Retrieval.
Abstract:
A growing volume of heritage data is being digitized and made available as text via optical character recognition
(OCR). Scholars and libraries are increasingly using OCR-generated text for retrieval and analysis. However,
the process of creating text through OCR introduces varying degrees of error to the text. The impact of these
errors on natural language processing (NLP) tasks has only been partially studied. We perform a series of
extrinsic assessment tasks — sentence segmentation, named entity recognition, dependency parsing, information
retrieval, topic modelling and neural language model fine-tuning — using popular, out-of-the-box tools in order
to quantify the impact of OCR quality on these tasks. We find a consistent impact resulting from OCR errors on
our downstream tasks with some tasks more irredeemably harmed by OCR errors. Based on these results, we
offer some preliminary guidelines for working with text produced through OCR.
1 INTRODUCTION
Heritage organizations are rapidly digitizing collec-
tions and making them available in a machine readable
format through the use of optical character recogni-
tion (OCR) software (Terras, 2011). Text produced by
OCR — referred to in this paper as OCR’d text — is
used for a broad range of tasks including information
retrieval and text analysis. Increasingly, these analyses
are being carried out at scale.
The output of OCR software often contains errors
where text has been incorrectly transcribed. Errors
range from one character being incorrect, to entire
words, and consequently sentences being incorrectly
transcribed. Despite its central role in many tasks, the
impact of using OCR’d text has only been partially ex-
plored (Smith and Cordell, 2018). This paper extends
existing work by assessing the impact of OCR quality
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1684-6556
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7331-1174
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8455-7196
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4396-6019
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3426-8200
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9806-084X
on a range of NLP tasks common in digital libraries
and digital humanities research.
2 RELATED WORK
Digitization efforts mainly focus on materials contain-
ing text. The ENUMERATE report for the year 2017
states that 89% of heritage institutions included in the
survey possess analog text collections and 55% digital
ones. For libraries these numbers go up to 91% and
75%, respectively (Nauta et al., 2017). In between the
digitization and the use of textual collections, there
is a critical step: OCR, or the extraction of text from
images.
The importance of OCR cannot be understated.
Most search and mining on digitized collections are
performed using OCR’d texts. Unfortunately, OCR’d
texts often contain errors. Particularly for histori-
cal texts and despite notable improvements over time
(Smith and Cordell, 2018), error rates can be very high,
with largely unknown biasing consequences for end
users (Alex et al., 2012; Milligan, 2013; Strange et al.,
2014; Cordell, 2017; Jarlbrink and Snickars, 2017;
484
van Strien, D., Beelen, K., Ardanuy, M., Hosseini, K., McGillivray, B. and Colavizza, G.
Assessing the Impact of OCR Quality on Downstream NLP Tasks.
DOI: 10.5220/0009169004840496
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2020) - Volume 1, pages 484-496
ISBN: 978-989-758-395-7; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Traub et al., 2018; Cordell, 2019). Consequently, as-
sessing and improving OCR quality has been, and still
is, a key area for research and development (Alex and
Burns, 2014; Ehrmann et al., 2016; Smith and Cordell,
2018; Nguyen et al., 2019; Hakala et al., 2019).
Despite these known issues, there has been limited
efforts to systematically evaluate “errorful OCR” and
offer guidelines about “what kinds of research are pos-
sible within our current paradigm” (Smith and Cordell,
2018, 10). Only preliminary efforts have been made to
assess the practical impact of OCR errors on the use of
OCR’d corpora; efforts which would allow us to move
beyond the dichotomy between “clean transcriptions”
and “dirty OCR” (Smith and Cordell, 2018, 10-11)
and to overcome the widespread lack of a quantified
understanding of OCR quality (Traub et al., 2015).
Most OCR’d texts come with an estimation of their
“quality”. Typically, this quality is assessed through
an average confidence metric from the OCR software
which was used to perform OCR. This is an instance
of intrinsic OCR evaluation, where we only rely on the
OCR model to assess it(self). Such assessments are
unsatisfactory because they might not be comparable
when the software/provider changes and provide no
indication on how the OCR quality influences other
tasks or is related to other, external data or systems
(Hill and Hengchen, 2019). This is the broader scope
of extrinsic OCR evaluations.
The simplest examples of extrinsic OCR evalua-
tions are dictionary lookup and word-error rates. These
methods are still popular (Pletschacher et al., 2014),
yet they are often not optimal in the case of historical
texts due to language change phenomena. More gener-
ally, extrinsic evaluations encompass any use of a task
which takes as input the text output of an OCR model,
in order to assess the impact of OCR quality on the
task itself. We refer to these tasks as downstream tasks;
examples include: information extraction (e.g., named
entity recognition and detection), organization (e.g.,
document classification) and retrieval (e.g., document
ranking). Extrinsic evaluations are more involved but
also more informative, because they allow us to reason
about the practical use of OCR outputs. They also
require at least two versions of the same text: a clean
or high-quality one, alongside its OCR’d version. Task
results on the former are considered as “ideal” and are
compared to task results on the latter version of the
text.
Some work has been published on extrinsic OCR
evaluations, with an almost exclusive focus on English
and, to a lesser degree, French. Studies have con-
sidered information access and retrieval (Traub et al.,
2018), authorship attribution (Franzini et al., 2018),
named entity recognition (Hamdi et al., 2019), and
topic modelling (Nelson, 2020; Mutuvi et al., 2018).
Recently (Hill and Hengchen, 2019) compared dif-
ferent tasks on a corpus in English: topic modelling,
collocation analysis, authorship attribution and vec-
tor space modelling. From this study, a critical OCR
quality threshold between 70 and 80% emerged, where
most tasks perform very poorly below this threshold,
good results are achieved above it, and varying results
are achieved within, according to the task at hand.
There are many aspects of OCR’d texts and their
impacts on downstream tasks that remain to be ex-
plored, in particular, results assessing a wider range
of languages. Another element to be explored is the
impact of time, and consequently of the combined
effects of linguistic change and OCR quality on the
application of tools usually trained on contemporary
languages. Lastly, the range of tasks which are con-
sidered in previous work is limited, with comparisons
across tasks attempted in a single, seminal paper (Hill
and Hengchen, 2019). In this work, we start address-
ing these research questions by considering a larger set
of tasks and utilizing text drawn from a source which
poses many challenges for OCR: historic newspapers
(Pletschacher et al., 2014).
3 DATA AND METHODS
Building on previous work, we perform an extrinsic
assessment of the impact of OCR’d text via a number
of downstream NLP tasks.
1
We perform these tasks on
two versions of the same text: one produced through
OCR and one with human corrections. Through these
assessments we quantify the impact of OCR errors on
tasks which have a broad “real world” applicability.
The motivation of the assessment is to see to what ex-
tent there is a degradation in the performance of these
standard tools applied to OCR’d text as compared to
human-corrected text. These tools have been chosen
as they are used widely by scholars in the digital hu-
manities and researchers they collaborate with, e.g.,
digital librarians and curators, data scientists and com-
putational linguists.
2
Our evaluation tasks address a
number of use cases for working with digitized text,
including text pre-processing, retrieval and analysis.
The tasks work with text at different levels, from the
token level to document and corpus level, allowing for
a more comprehensive comparison of the impact of
1
In this paper we do not assess the impact of different
OCR software on the type of OCR error produced
2
For example spaCy (Honnibal and Montani, 2017) a
Python library for performing NLP tasks, is used in the
pipeline for Defoe, a tool utilised in digital humanities re-
search (Vicente et al., 2019).
Assessing the Impact of OCR Quality on Downstream NLP Tasks
485

OCR.
3.1 Available Data
There are a number of publicly available datasets
which can be used in extrinsic assessment tasks. This
includes two datasets produced as part of the 2017 and
2019 ICDAR Competitions on Post-OCR Text Correc-
tion (Rigaud et al., 2019; Chiron et al., 2017). These
datasets consist of OCR’d texts and a corresponding
gold standard.
Despite limitations we use the Overproof data
which contains a wider distribution of OCR qualities
in comparison to other datasets such as the ICDAR
competition data. Project Computing, a software com-
pany which develops a post-OCR correction software
service called ‘Overproof’, released data as part of a
paper evaluating their approach. The Overproof team
released three evaluation datasets (Evershed and Fitch,
2014). These datasets were drawn from a number of
sources. The first dataset is drawn from newspaper
text corrected from the National Library of Australia
Trove digitized newspaper collection. The Trove web-
site allows users to correct OCR errors as part of the
browsing interface. Currently, there are 330,484,635
lines of corrected text. Overproof sought to leverage
these corrections by identifying articles from the Syd-
ney Morning Herald, 1842-1945 which had extensive
corrections (at least 85% of the number of lines in the
article) and through the correction history accessing
the original uncorrected OCR’d text (Evershed and
Fitch, 2014, Section 6). We treat data released by
Overproof as a single dataset which we refer to in this
paper as the ‘Overproof dataset’.
3
3.2 Assessing OCR Quality
In order to quantify the impact of the OCR at a more
granular level, we perform a number of steps to prepare
our data. These include splitting the OCR portion of
our data into different quality bands and performing
token-level article alignment.
4
3.2.1 Word Error Rate
We calculate Levenshtein similarity (Levenshtein,
1966) between the two versions of the text calculated
as
(length − LD)/length
in which
length
is the num-
ber of characters in a text, and
LD
is the Levenshtein
3
Data available via http://overproof.projectcomputing.
com/datasets. We use all available data to ensure a range of
OCR quality is included in our evaluation.
4
Code for processing data and performing the evaluation
is available in a Zenodo repository via https://doi.org/10.
5281/zenodo.3611200.
Figure 1: Distribution of word-error rates (calculated via
Jaccard similarity) for articles in the four quality bands, es-
tablished via Levenshtein similarity.
distance between “ground truth” and OCR’d texts for
one article. If the lengths of “ground truth” and OCR’d
texts differ, the length of the longer text is used in-
stead. We treat a higher distance between the human-
corrected text and the OCR version as an indication of
lower quality OCR. We then use this score as a way
of allocating the OCR’d texts into four quality bands
using various thresholds of the Levenshtein score. Ta-
ble 1 illustrates these thresholds and the number of
articles into each quality band. In figure 1, we cal-
culate the Jaccard similarity between the OCR’d and
human-corrected version of the article using a bag-
of-words approach. The Jaccard similarity compares
the text at the word level as opposed to the character
level of Levenshtein similarity. When we plot the dis-
tribution of Jaccard similarity values across the OCR
quality bounds we see that there is some overlap in
distributions. However, we also see that the Jaccard
similarity decreases as the quality band decreases, sug-
gesting our approach is reasonable for determining
OCR quality.
Table 1: Summary of Overproof data by quality band (based
on human-corrected text).
Quality
band
Levenshtein
Distance
Articles Words
1 >0.9 11,461 4,024,217
2 >0.8 13,953 4,444,365
3 >0.7 3,600 1,019,422
4 60.7 1,495 404,054
Total NA 30,509 9,892,058
In Table 1, we see that the majority of articles fall into
quality band 2, with the worst OCR quality represent-
ing a smaller portion of the total data.
ARTIDIGH 2020 - Special Session on Artificial Intelligence and Digital Heritage: Challenges and Opportunities
486
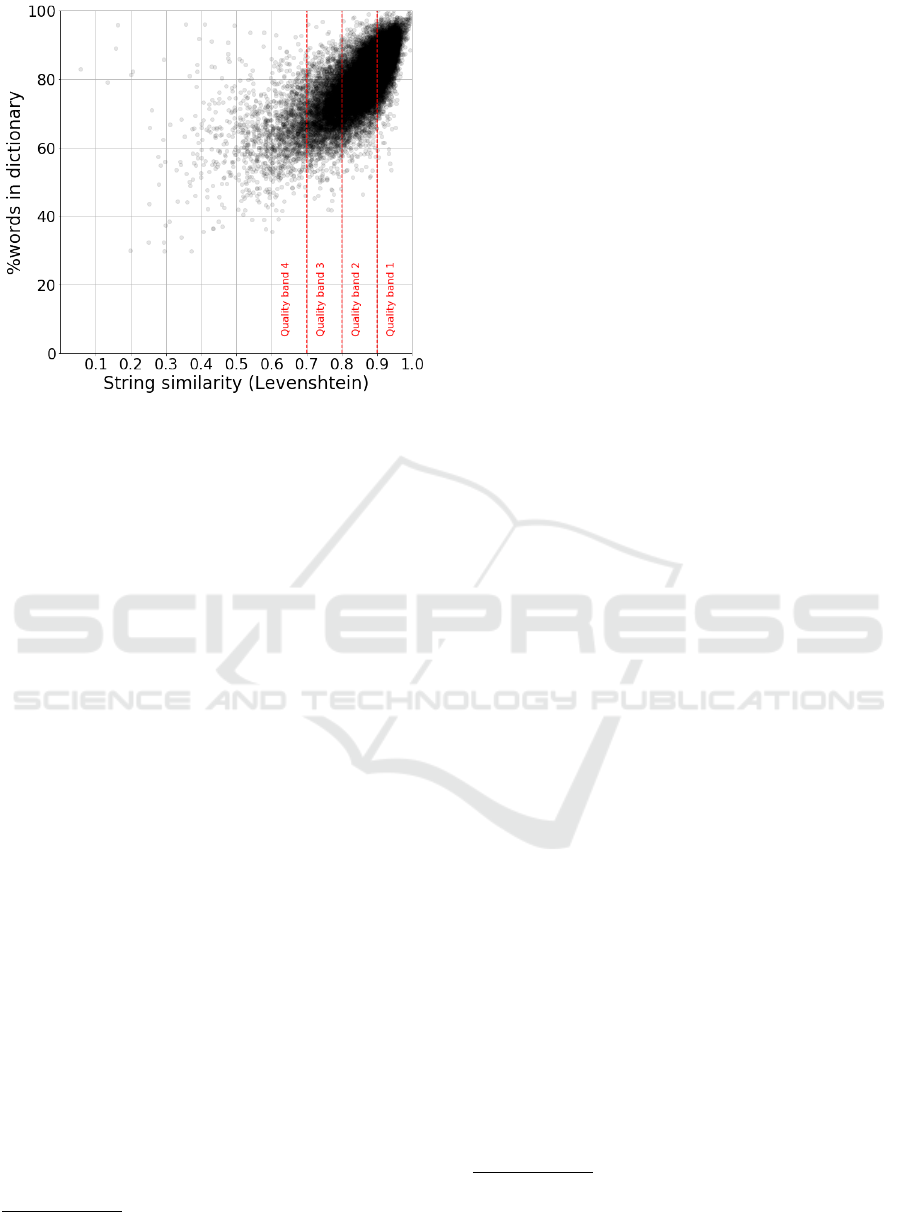
Figure 2: Percentage of words found in the dictionary, as a
function of the Levenshtein similarity measure. Each point
corresponds to one article.
3.2.2 Dictionary Lookup
Another approach to evaluating OCR quality is to use
a lookup of dictionary terms to count how many word
tokens in the OCR’d text are found in a dictionary. This
has the benefit of being possible without any externally
corrected versions of the text. It removes reliance
on the confidence measures from OCR software but
has other potential challenges, including choice of
dictionary, changing vocabulary, specialist vocabulary
and spelling variations. A direct lookup of a dictionary
will also provide an equal “score” to a word with one
mistaken character as to a word with many mistakes.
To assess how well dictionary lookup performs as
a proxy for OCR quality compared to a distance mea-
sure, we compared the percentage of words found in a
dictionary for an article to the string similarity between
OCR’d and human-corrected text. We used spaCy to
perform our dictionary lookup.
5
Figure 2 shows that
there is a correlation between the percentage of words
found in the dictionary and the string similarity mea-
sure. Therefore, although in this paper we use string
similarity to establish four OCR quality bands, our
results can be generalized due to its high correlation
with alternative methods to assess OCR quality. This
is particularly important when a ground truth is not
available.
5
Throughout this paper, we use the spaCy model for
English en_core_web_lg, see: https://spacy.io/models.
3.2.3 Text Alignment
The Overproof dataset aligns OCR’d and human-
corrected texts at an article level and, to a certain
degree, at a physical line level. Example 1 shows
the first four lines of an OCR’d article, and example
2 shows the same four lines of its human-corrected
version. For some of the tasks (e.g., linguistic pro-
cessing tasks), it is crucial that the linear sequence
of tokens is kept. With this in mind, we aligned the
dataset, both at an article level and at a token level, by
mapping tokens in the OCR’d text to their position in
the human-corrected version of the text.
(1) i NEW CALEDONIA.
’ Io the Editor of the Berala.
SIB,-Enclosed is a letter \
ooncernlug the expedition of the
’ »Governor, M. de Siisseî, tbiough \
the north of Caledonia, which
(2) NEW CALEDONIA.
To the Editor of the Herald.
SIR,-Enclosed is a letter \
concerning the expedition of the
Governor, M. de Saisset, through \
the north of Caledonia, which
We have taken a heuristic and conservative approach
to align the pairs of articles, by first mapping tokens
we are more confident about, in terms of:
•
length of the token to map (longer tokens are
mapped first),
•
string similarity between tokens (starting from
100% match and gradually decreasing to 70%
match, calculated as
2M/T
, where
M
is the num-
ber of matching characters and
T
is the total num-
ber of characters in both tokens), and
•
distance between the tokens’ first character posi-
tions in the texts.
We iteratively mapped the remaining tokens in order of
decreasing confidence, making sure that, if a token’s
position is between two aligned tokens in the human-
corrected text, this token’s position in the OCR’d text
should also be between the same two aligned tokens
in the OCR’d text. Table 2 shows an example of align-
ment between the OCR’d and the human-corrected
texts.
We have manually validated the alignments of 1266
tokens from articles from the four quality bands.
6
For the lowest quality band the accuracy of aligned
tokens is 98.4%, for the second lowest quality band it
6
We were unable to rely only on articles with additional
corrections from the Overproof researchers(total 159), since
this did not include a sufficient number of low OCR quality
articles.
Assessing the Impact of OCR Quality on Downstream NLP Tasks
487
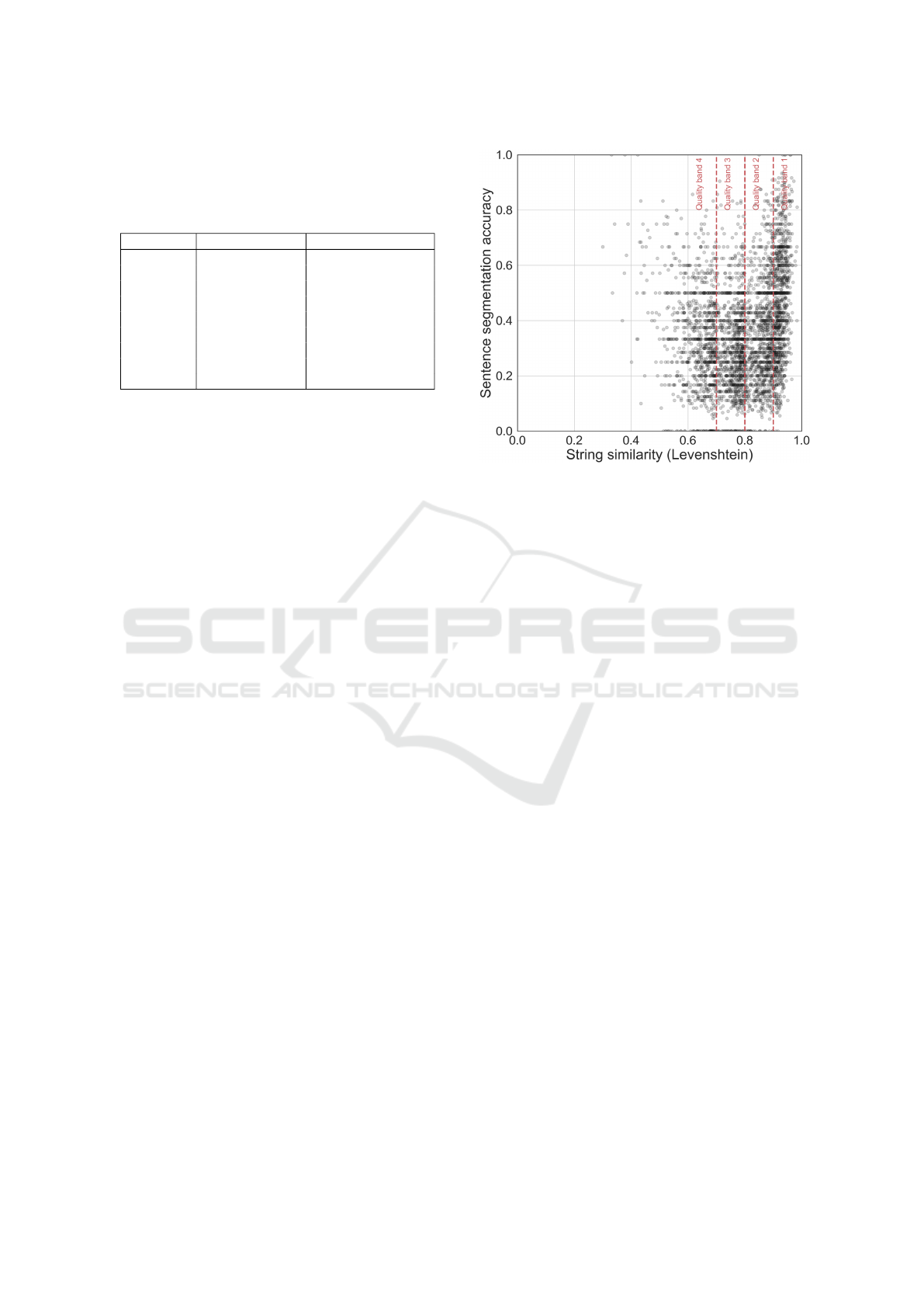
Table 2: Alignment of the first tokens of examples 1 and 2.
Uncertain elements are strings between aligned tokens that
the algorithm could not align. The numbers in parenthesis
correspond to the position of the first character of the string
in the OCR’d text and in the human-corrected text.
OCR’d text Human correction
Uncertain i NEW (0) NEW (0)
Aligned CALEDONIA. (6) CALEDONIA. (4)
Uncertain ’ Io the (17) To the (15)
Aligned Editor (26) Editor (22)
Aligned of (33) of (29)
Aligned the (36) the (32)
Aligned Berala. (40) Herald. (36)
Aligned SIB, (48) SIR, (44)
Aligned -Enclosed (53) -Enclosed (49)
is 99.9%, and for the best two quality bands it is 100%.
We have aimed at the highest precision possible even if
that meant having consequently considerably smaller
number of aligned tokens (from 30% in quality band 4
to 78% in quality band 1).
4 RESULTS
4.1 Linguistic Processing Tasks
We include a range of tasks which fall into common
NLP pipelines and are often required for other down-
stream tasks. Due to space limitations, in this section
we focus on just three tasks — sentence segmenta-
tion, named entity recognition, and dependency pars-
ing — and we analyze the impact of OCR errors on
spaCy. For each task, we consider spaCy’s output on
the human-corrected text to be the ground truth against
which we compare spaCy’s output on the OCR’d text,
therefore assuming that the highest performance we
can achieve on an OCR’d text is that which is achieved
on its human-corrected counterpart. In order to have
comparable quality bands, we have randomly down-
sampled the dataset to have the same number of articles
(950) in each quality band.
Considering the pervasive presence of OCR errors,
the comparison of the different methods’ performance
on the OCR’d text with respect to its human-corrected
counterpart is not straightforward. In the assessment
of the following tasks, we only take into consider-
ation those tokens which our algorithm has aligned
between OCR’d and human-corrected text. We are
aware that this approach neglects tokens containing a
large amount of OCR errors, which our algorithm does
not align. However, because linguistic processing is
heavily sequential, it is not only the presence of OCR
errors in the target token that has an impact on the
performance. This is an assumption that would benefit
Figure 3: Sentence segmentation accuracy of OCR’d with
respect to human-corrected articles, as a function of Leven-
shtein similarity. Each point corresponds to one article.
from further research.
4.1.1 Sentence Segmentation
Sentence segmentation is the task of detecting sen-
tence boundaries between the words in different sen-
tences (Palmer, ). It is the basis for many NLP appli-
cations, and is often regarded as a solved task. How-
ever, performance of sentence segmentation methods
has been shown to decrease when applied to noisy or
less formal text (Read et al., 2012). To assess the im-
pact of OCR errors on sentence splitting, we applied
spaCy’s sentence segmentation module to both texts
(human-corrected OCR’d text and original OCR’d text)
and considered a sentence as being correctly split if
both left and right boundaries enclose the exact same
aligned tokens.
Figure 3 shows that OCR errors can have a huge
impact on sentence segmentation. Indeed, a close
exploration of the segmentation informs that even a
one-character difference can trigger the splitting of a
sentence into two sentences. This results in a surpris-
ingly low performance of sentence segmentation, even
for OCR’d texts that are mostly correct.
4.1.2 Named Entity Recognition
Named entity recognition (NER) is the task of iden-
tifying mentions of entities in texts and classifying
them into predefined entity types (such as ‘person’,
‘organization’, or ‘currency’). For many tasks, includ-
ing information retrieval, named entities are arguably
the most important of lexical classes: an analysis of
ARTIDIGH 2020 - Special Session on Artificial Intelligence and Digital Heritage: Challenges and Opportunities
488
user queries on a historical corpus showed that most
popular search keywords were entities, in particular of
the location type (De Wilde and Hengchen, 2017). We
have considered a true result when an aligned token
has the same entity type tag and the same IOB tag,
which indicates the position of the token in the case of
a multi-token entity. Figure 4 shows the distribution of
each article’s named entity recognition accuracy plot-
ted against the string similarity between the OCR’d and
the human-corrected text. OCR errors show to have a
generally smaller impact in a named entity recognition
task than they have in sentence segmentation.
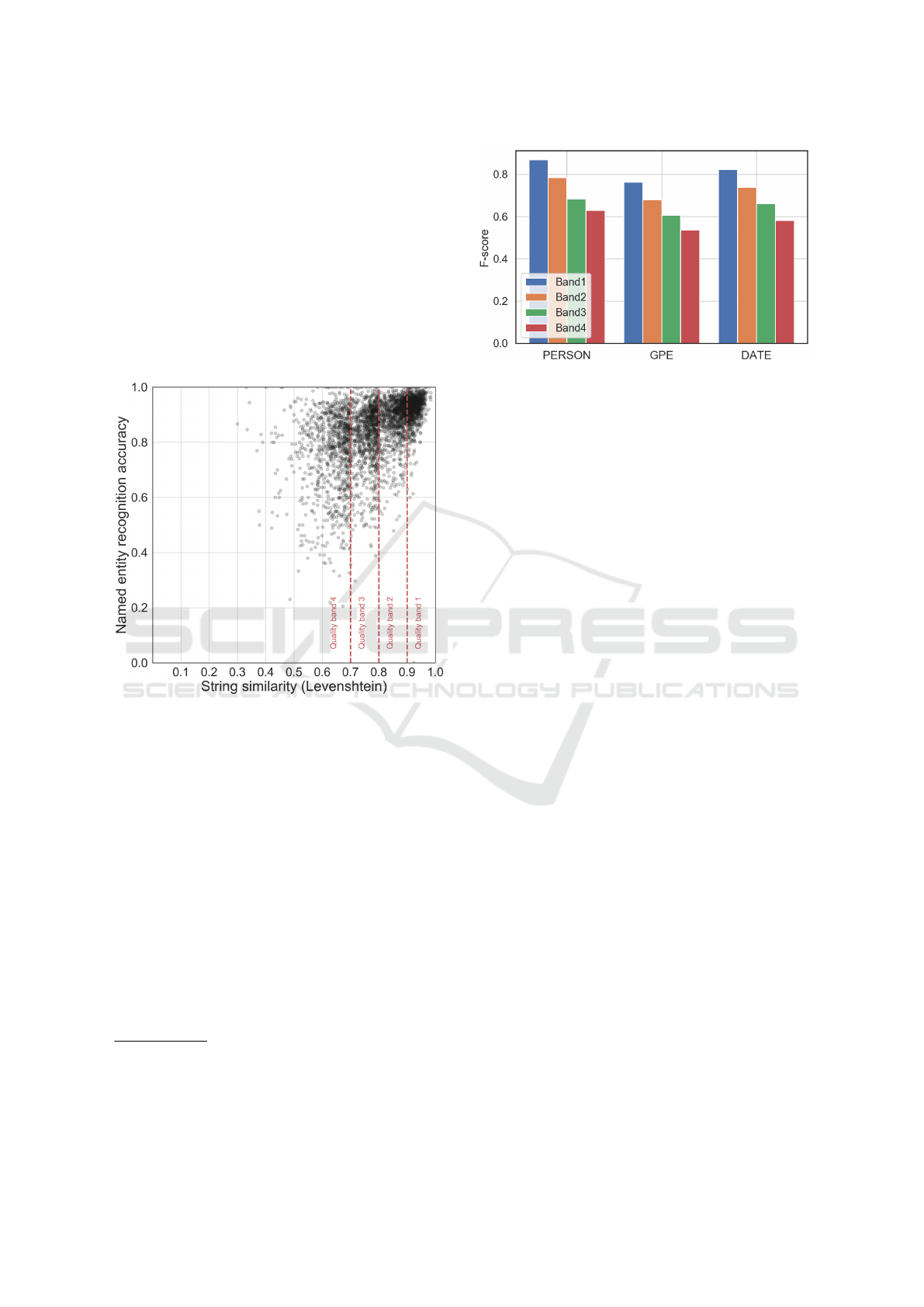
Figure 4: Named entity recognition accuracy of OCR’d
with respect to human-corrected articles, as a function of
Levenshtein similarity. Each point corresponds to one article.
In figure 5, we focus on three particular entity types,
namely
person
,
GPE
(geo-political entity), and
date
.
7
We can observe that the impact on person entities (0.87
and 0.63 average f-score in quality bands 1 and 4,
respectively) is less pronounced than on geo-political
entities, which are greatly affected by noisy OCR’d
text (0.76 and 0.54 average f-score in quality bands 1
and 4, respectively).
4.1.3 Dependency Parsing
Dependency parsing is the last and typically the most
complex of the linguistic processing tasks that we
cover in this paper. It is the task of finding the gram-
matical structure underlying a text in terms of syntactic
7
Person
and
GPE
are arguably the most relevant entity
types. The
date
entity type has very different characteristics
with respect to the other two, as it captures time expres-
sions, which are often sequences of several tokens, often
non-capitalized and containing numerical expressions.
Figure 5: Average f-scores for
person
,
GPE
, and
date
for
each quality band.
dependencies (i.e., head-dependent relationships) be-
tween the tokens in a sentence. Dependency parsing is
used in many downstream tasks, often for improving
their performance (Jie et al., 2018; Xia et al., 2019).
Figure 6 shows a clear impact of OCR errors in the
performance of dependency parsing.
Looking in more detail, we observe that the length
of the dependency relation is a very important factor,
as dependency relations between neighboring tokens
have an accuracy of 0.82 and 0.57 in quality band
1 and 4 respectively, whereas dependencies between
tokens that are separated by more than five tokens
have an accuracy of 0.57 and 0.09 in quality band 1
and 4 respectively. This is worth taking into account,
because it means that dependency types that tend to be
longer (such as the nominal subject
nsubj
dependency
type) will perform worse.
This analysis shows that the presence of OCR er-
rors in digitized text has different impact depending on
the task, and points to the importance of understanding
the data well and being cautious about the methods
used. There is a need for further research to better
understand how different tools cope with the presence
of errors, and to expand the analysis to other tasks.
4.2 Information Retrieval
OCR errors can negatively affect search and informa-
tion retrieval in digital collections. In this section, we
gauge how article OCR quality impacts (a) the arti-
cle ranking and (b) the retrievability of articles. For
the first task we measure the difference between two
rankings obtained by querying the same collection of
texts but varying in OCR quality. In this scenario, we
assume a user inspects the first
n
articles for a set of
queries
Q
. For each query
q
we compute the overlap
o(q)
between the two rankings.
r
corr
(q,n)
comprises
the ranking over the first
n
articles for query
q
, re-
trieved from the set of corrected articles. The length
Assessing the Impact of OCR Quality on Downstream NLP Tasks
489
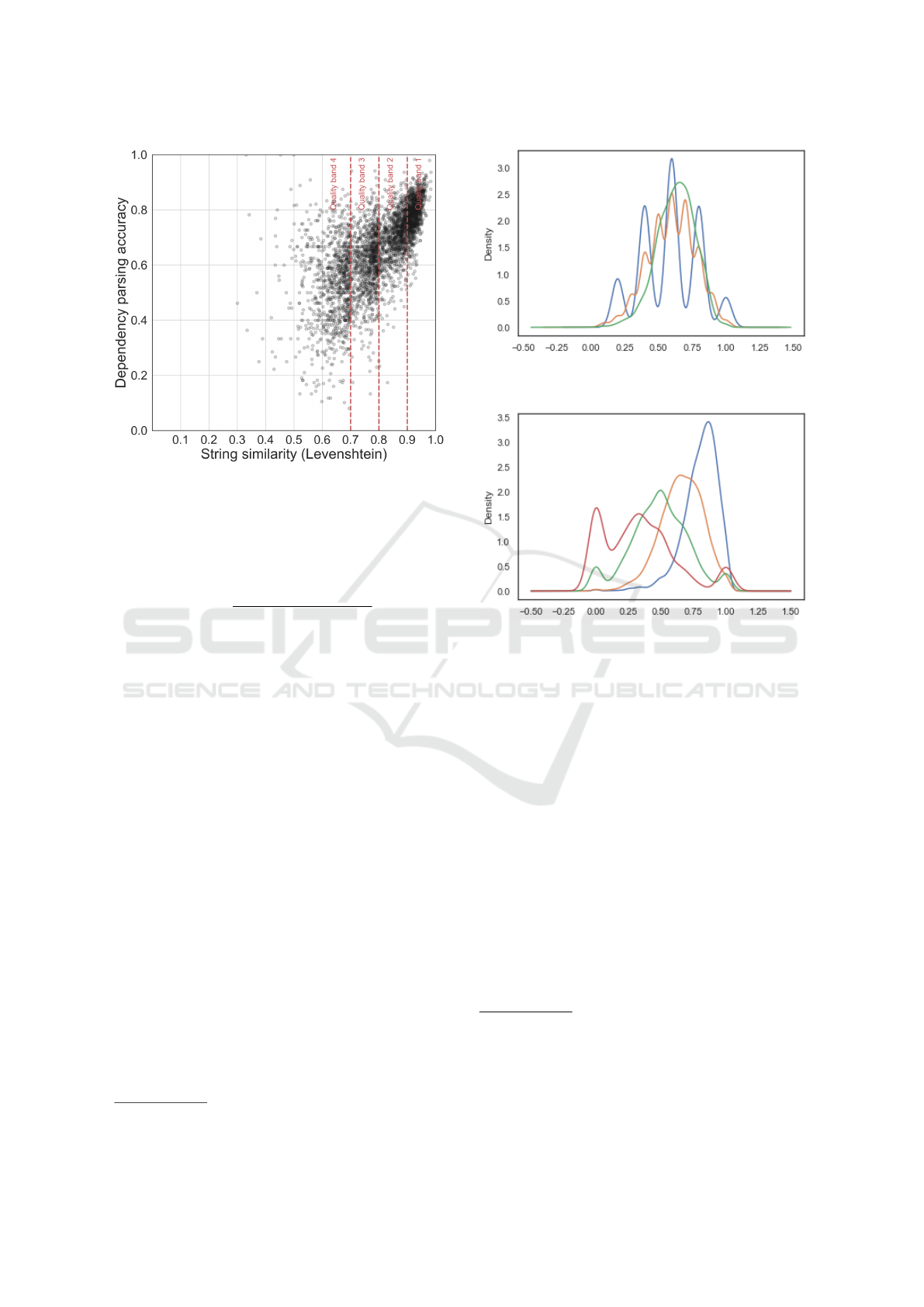
Figure 6: Dependency parsing accuracy of OCR’d with
respect to human-corrected articles, as a function of Leven-
shtein similarity. Each point corresponds to one article.
of the intersection is furthermore divided by the size
of r
corr
(q,n).
o(q) =
|r
corr
(q,n) ∩ r
ocr
(q,n)|
|r
corr
(q,n)|
We indexed both the OCR’d and human-corrected
articles with Elastic Search (using standard settings,
which utilise Luce’s Practical Scoring Function). As in
previous experiments, our choice was motivated by the
popularity of this tool in digital humanities research.
We simulated realistic search scenarios by col-
lecting query terms from two external resources: (a)
2,949 nouns collected from a sample of newspaper
articles (b) 2,231 Australian toponyms obtained from
WikiGazetteer (Ardanuy et al., 2019). This is a help-
ful approximation to understand how search for spe-
cific topics (nouns) or places (toponyms) might be
hampered by OCR. Below, we mainly discuss results
obtained using nouns as queries, but repeated all the
experiments with the toponyms to ensure that our find-
ings extend to other types of queries.
We first computed the
o(q,n)
based on the whole
collection of OCR’d and human-corrected articles. On
average, the size of the ranking (
n
) seems to slightly
increase the ratio of overlapping items (from 0.57 for
n=5 to 0.63 for n=25), but the differences remain min-
imal, as can be observed from Figure 7. Nonetheless,
these numbers do suggest that the rankings change as
a result of OCR error correction.
Figure 8 shows the average
o(q,n)
for different
quality bands.
8
The figure suggests a growing diver-
8
Given the different number of articles in each quality
Figure 7: Distribution of
o(q,n)
. Distribution of
o(q)
scores
for the ranking of size 5 (blue), 10 (orange) and 25 (green).
Figure 8: Distribution of
o(q,n)
scores for different quality
bands. n=25, blue=1, orange=2, green=3, red=4.
gence between the rankings as the quality decreases,
while the size of the ranking has only a minimal ef-
fect. It seems reasonable to conclude that “bad” OCR
produces “terrible” search results, but strictly speak-
ing this is not what the figure says. The shrinking
overlap doesn’t entail a loss in relevance, and in this
sense, the decline doesn’t convey that the lower qual-
ity bands produce “worse” results. However, an in-
spection of the number of items found suggests that
searching in bad quality text returns fewer articles.
For a set of queries
Q
we calculated
h
di f f
(Q)
as
h
corr
(Q)/[h
corr
(Q)+ h
ocr
(Q)]− 0.5
, with
h
c
(Q)
equal
to the number of articles found in corpus
c
. Table 3
shows that searching in messy data yields less infor-
mation. Similarly, we estimated the number of false
positives when querying the OCR’d data, by subtract-
ing (for each query) from the number of articles in the
human-corrected data (
h
corr
(q)
) those found in OCR’d
band, we replicated the result on a down-sampled corpus,
which has
≈
900 articles for each band. The trend is gen-
erally the same, but more volatile, as this measure is still
dependent on the content of texts (even though we try to
account for queries that fail to return a ranking by excluding
those for which we can’t find any articles in the human-
corrected corpus).
ARTIDIGH 2020 - Special Session on Artificial Intelligence and Digital Heritage: Challenges and Opportunities
490

Table 3:
h
di f f
and
f p
scores based on a comparison of
OCR’d versus human-corrected data.
quality 1 2 3 4
h
di f f
0.040 0.075 0.129 0.197
f p 0.011 0.017 0.029 0.046
Table 4: Gini coefficients computed on the retrievability
scores r(d).
topn 5 10 25
g
ocr
0.718 0.592 0.432
g
corr
0.711 0.579 0.413
texts (
h
ocr
(q)
). The total number of false positives is
then:
f p =
∑
q∈Q
min(h
corr
(q) − h
ocr
(q),0)
We divide the absolute value of
f p
by the total number
of found articles and report the results in Table 3.
To summarize, we observe that as the quality of
the data decreases, the rankings diverge, the number of
hits decline and the portion of false positives increases.
All combined, these indicators suggest that quality
does negatively effect search.
To measure the retrievability of articles, we used
the method proposed by (Azzopardi and Vinay, 2008).
It scores each article
r(d)
by counting how often it
occurs when inspecting the first
n
articles for queries
Q
.
f (k
d,q
)
is equal to 1 if article
d
appears within the
ranking of length
n
for the search term
q
. Following
(Traub et al., 2018), we treated all queries as equally
probable (effectively setting the individual weight for
each query (o
q
) to 1).
r(d) =
∑
q∈Q
o
q
· f (k
dq
,n)
Retrievability tracks how often articles are found for
a given set of queries. Comparing the retrievability
across quality bands is tricky, as the measure is influ-
enced by both the content and the number of articles.
However, we can assess the impact of the manual
correction by comparing human-corrected to OCR’d
articles. We report the Gini coefficients computed on
the distribution of retrievability scores to assess any
bias.
The results in Table 4 tie in with the findings of
(Traub et al., 2018), who observed consistently higher
Gini coefficients for the corrected articles, indicating
that increases in quality data decreases the bias. Com-
pared to them, however, we find that the differences are
only minimal, which could be caused by the imbalance
between the number of queries (ca. 2,000) and the size
of the corpus (ca. 30,000): when inspecting the distri-
bution of the retrievability scores on OCR’d text for
n = 25
, only 29% of the articles are found more than
once, and the maximum score is 12.
9
Even though the
impact of correction is small in our experiments, the
overall trend does confirm the previously reported link
between articles’ quality and retrievability bias.
4.3 Topic Modelling
We consider topic modelling next. Our experimental
setup is the following: we use an established method,
Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) (Blei et al., 2003)
in its by-now standard Gensim implementation (
ˇ
Re-
h˚u
ˇ
rek and Sojka, 2010). We find 15 to be a reasonable
number of topics using a coherence measure on the
human-corrected texts (Newman et al., 2010), for all
quality bands and despite their difference in size (see
Table 1). The comparison is made over four pairs
of LDA models, one per quality band (one to four),
and two per band (using human-corrected text, and its
OCR’d version). No sampling is done, as we use all
available articles to train each model.
We apply an aggressive clean-up to the texts before
topic modelling, in order to attempt to minimize the
impact of OCR quality as it would be done in a real
use case. The same pre-processing pipeline is used
for all corpora, both human and OCR and per quality
band, in order:
1.
Lowercasing, lemmatization and filtering of all
non-alphabetical tokens and all English stopwords,
replying on spaCy defaults.
2. Removal of tokens shorter than three characters.
3. Addition of bi-grams with minimum count of 25.
4.
Removal of infrequent (fewer than 5 occurrences)
or frequent words (appearing in more than half of
the articles).
We then train LDA models using ten passes over the
data and default parameters.
10
Firstly, we perform an intrinsic evaluation by as-
sessing each model’s perplexity and coherence (New-
man et al., 2010; Mimno et al., 2011). In agreement
with previous work (Mutuvi et al., 2018), we find that
OCR models have slightly lower (hence better) per-
plexity scores but also slightly lower (hence worse)
coherence scores. We do not find differences between
quality bands in this respect.
Next, we consider a matching between human-
corrected and OCR topics for every pair of models
9
Contrary to (Traub et al., 2018), we did not find a cor-
relation between article quality and retrievability, probably
also because of the imbalance between queries and articles.
10
The resulting vocabulary sizes are as follows. Quality
band 1: 19,227 (human-corrected), 27,171 (OCR); band 2:
21,447, 33,702; band 3: 9,062, 11,250; band 4: 4,938, 4,635.
Assessing the Impact of OCR Quality on Downstream NLP Tasks
491

within each quality band. The goal is to match each
OCR topic with its closest human-corrected topic (in
word distribution). To accomplish this, we consider
the 500 most distinctive (i.e., high probability) words
per topic, and construct a fully connected bipartite
graph between human-corrected and OCR topics re-
spectively. Edge weights between a human-corrected
topic i and OCR topic j are established as follows:
w
i j
= 1 −
∑
t∈V
i
∩V
j
p
i
(t)p
j
(t)
Where
w
i j
is the edge weight between topics
i
and
j
(the graph is bipartite, hence
i
and
j
must belong to
the set of human-corrected and OCR topics respec-
tively);
V
i
and
V
j
are the sets of 500 top words per
topic;
p
i
(t)
is the probability of word
t
under topic
model
j
, and similarly for
p
j
(t)
. Note that the sum
is capped above to 1, hence the weights of the graph
take values between 0 and 1 and must be interpreted
as distances, where 1 is maximum distance and 0 is
minimum distance between any two topics. We then
find a matching using Karp’s minimum weight algo-
rithm as implemented in NetworkX (Hagberg et al.,
2008). We find that topic matching is often imper-
fect, and degrades markedly with OCR quality. We
assess it using the Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence
of OCR topics from human-corrected topics (Steyvers
and Griffiths, 2007), whose distribution is shown in
Figure 9; we also show the number of overlapping
words in the top 500, as defined above, in Figure 10.
As it can be seen, results degrade as the OCR quality
lowers. A manual inspection of every match confirms
that, while within quality bands 1 and, to a lesser de-
gree, 2, most topics can still be matched, this is not
the case for bands 3 and 4. We further confirm this
result using a clustering approach. We assign an ar-
ticle to a cluster corresponding to its most probable
topic. We then assess what is the proportion of articles
which end in the matched clusters, i.e., which have as
most probable OCR topic the one matched with their
most probable human-corrected topic according to the
procedure described above. We find that, while OCR
quality always impacts clustering results negatively,
for bands 4 only 20% (median 11%) of articles end up
in the intended cluster, while the mean is up to 42%
(median 46%) for band 1.
We conclude the assessment of topic models by
considering the entropy of topic distributions over dif-
ferent top word vocabulary sizes.
11
We show results
for band 1 (Figure 11) and band 3 (Figure 12). As it
can be seen, lower OCR quality has an impact on the
top topic words. The impact increases from lower val-
ues of
V
(top words per topic), which likely contains
11
Shannon’s entropy of topic
i
is defined as
e
i
=
−
∑
t∈V
i
p
i
(t)log[p
i
(t)].
Figure 9: Per-quality band KL divergence of OCR topics
from Human-corrected topics, using a vocabulary of
V = 500
top words.
Figure 10: Per-quality overlap of top words (V = 500).
well-formed words, to the lower end of the topic’s
probability distribution, which likely contains more
OCR noise. OCR’d topics always have a higher en-
tropy than Human-corrected topics.
In summary, we find that OCR has an impact on
topic models, when compared to models trained on
clean text. OCR topic models increasingly diverge
from their human-corrected counterparts as the OCR
quality lowers. We find that, while quality bands 1 and,
to a lesser degree 2, still maintain a good fidelity with
their human-corrected counterparts, this is not the case
for bands 3 and, particularly, 4. The issue is not as
much that OCR topic models became meaningless but,
more subtly, that they retain their interpretability (Hill
and Hengchen, 2019) while becoming substantially
different from what they would be using clean texts.
Furthermore, we note that intrinsic evaluations, such
as perplexity and coherence, do not capture this effect,
and should thus be avoided for the purpose of assessing
the reliability of OCR topic models with respect to
their similarity to models trained on clean texts. It is
left for future work to study which countermeasures
could be taken to minimize the impact of OCR noise
on topic models, such as increasing the number of
topics to separate noise from signal. In conclusion, we
recommend to rely on topic modelling with OCR’d
ARTIDIGH 2020 - Special Session on Artificial Intelligence and Digital Heritage: Challenges and Opportunities
492

Figure 11: Quality band 1. Distribution of the entropy for
the top V words per topic, at varying values of V .
Figure 12: Quality band 3. Distribution of the entropy for
the top V words per topic, at varying values of V .
texts quality ideally above 90%, or at least above 80%.
4.4 Language Models
Language models (LMs) allow for the learning of a
useful representation of text without annotations. LMs
have resulted in massive gains in a broad range of
tasks including text classification (Howard and Ruder,
2018) and NER (Yadav and Bethard, 2018). LMs, in
particular Word2Vec, has also been directly used in
many digital humanities projects (Leavy et al., 2018).
Though minor OCR errors should not affect the
quality of LMs trained on a large corpus, poor qual-
ity texts may bias the LM in an irredeemable way.
Here, we use OCR’d and human-corrected texts to
quantify the impact of OCR errors on resulting LMs.
The amount of training data determines the stability
of LMs (i.e., small datasets result in unstable mod-
els). Therefore, in this task, we consider articles with
high and low OCR qualities. The first group contains
all the articles in quality bands 1-2 with
≈
10.5M
words. The second group is based on the articles in
quality bands 3-4 with
≈
1.9M words. To trace the
changes introduced by OCR errors, we use human
and OCR’d texts to fine-tune an existing pre-trained
model, Word2Vec LM (Mikolov et al., 2013) using
Figure 13: Impact of OCR errors on fine-tuning neural net-
work language models. The black and red lines correspond
to the texts with quality bands 1-2 and bands 3-4, respec-
tively. Fifty black lines for the high-quality group and one
red line for the low-quality group are plotted. See text for
discussion. Note that the x-axis is logarithmic.
the Gensim implementation. This skip-gram language
model was pre-trained using
≈
4.46 billion raw words
from
≈
49.4K historical books (1740-1900).
12
For the
low-quality group, we generated two new fine-tuned
LMs using human-corrected and OCR’d text. The two
models were then compared based on the similarity of
word vectors. First, the most frequent 1000 words in
the human-corrected text were selected, and for each
word and each LM, we extracted its neighboring words
as measured by cosine similarity. Next, we compared
the two lists of neighboring words using the Jaccard
similarity. The red line in Figure 13 shows the overlap
between the two lists for different numbers of queried
neighboring words. Interestingly, there is a high over-
lap between the two LMs for the closest neighbors. By
increasing the number of queried neighboring words,
the overlap decreases, and it reaches its lowest point at
1000 queried neighboring words. After this point, the
overlap increases as expected. This trend shows the
extent to which OCR’d text can affect the predicted
word vectors in widely used Word2Vec LMs.
A similar trend emerges in the case of high-quality
articles (black lines in Figure 13) but with higher Jac-
card similarity measures (5-10% higher) in almost all
the queries. We did not use all the 25,414 high-quality
articles in fine-tuning. Instead, we sampled 5,095 arti-
cles to have a comparable number of articles with the
low-quality group. We repeated the sub-sampling 50
times using random sampling with replacement, and
for each sub-sample, we generated two new fine-tuned
LMs using human-corrected and OCR’d texts. This
resulted in 100 fine-tuned LMs and 50 measures of Jac-
12
These books come from an open dataset of digitized
books from the British Library, available via https://doi.org/
10.21250/db14 (British Library Labs, 2014). The date range
was chosen based on the availability of training data. This
trained LM will be released alongside a forthcoming paper
which will include a full evaluation of this LM.
Assessing the Impact of OCR Quality on Downstream NLP Tasks
493

card similarity. The results of all 50 comparisons are
shown in Figure 13. All curves show a similar trend
in
#neighbors ≥ 5
which suggest a high-confidence
in their Jaccard similarity measures. The most vari-
able part of the trend is in the low number of queried
neighbor words.
These preliminary results show that the generated
word vectors by Word2Vec LMs can be substantially
affected by OCR errors when OCR’d text are used for
fine-tuning. However, LMs directly trained on large
OCR’d corpora may still yield robust word vectors.
They may even be able to position a word and its badly
OCR’d variants nearby in the vector space (Hämäläi-
nen and Hengchen, 2019). In such cases, LMs can be
used to identify OCR errors and possibly provide a
way to correct systematic OCR errors in a large corpus.
Future work will be required to assess the impact of
OCR on LMs at scale, as well as when LMs are used
as features in other models.
5 DISCUSSION
The use of OCR’d text has an impact on all of our
tasks, though the degree varies. OCR has an impact
even on tasks which are considered “solved”, such as
sentence segmentation. Though these pre-processing
tasks are not usually the end goal per se, they are often
required for other tasks in turn. NER progressively
worsens as OCR quality decreases, with a stronger
impact on the
GPE
entity type, followed by
date
and
person
. We suggest that this uneven impact on dif-
ferent entity types should be considered when using
NER on OCR’d text. We observe that dependency
parsing is impacted more severely as the length of
the dependency grows. This suggests that we should
be particularly cautious when applying dependency
parsing on low quality OCR texts.
In information retrieval, decreasing OCR quality
leads to a divergence in the ranking of retrieved articles
compared to the human-corrected text with the num-
ber of hits declining and an increasing number of false
positives. We find a smaller impact of improved OCR
quality on retrievability bias though this may be as a re-
sult of the size of our data and number of queries. Our
results accord with previous research on retrieval and
OCR and suggest caution in “trusting” retrieval results
on OCR’d text. This is particularly important when
search results are directly used to make arguments, for
example, by counting search results for a term over
time in a OCR’d corpus, since the variation may be a
proxy for OCR quality rather than a change in under-
lying usage of that term. This caution is particularly
important when OCR quality is unknown.
We find that worsening OCR quality leads to a
growing impact on topic models when compared to
those trained on the human-corrected text. Of note
is the subtle way in which topic models are impacted
by OCR quality: topics do not become meaningless,
but instead increasingly diverge from those trained on
human-corrected text. This means that this effect will
not be easily “spotted” when training topic models on
poor quality OCR’d text, particularly since intrinsic
evaluations do not capture this effect. From our results
we recommend a preference for high quality OCR
ideally above 90% and at least above 80%.
Lastly, our results suggest that the word vectors pre-
dicted by Word2Vec LMs can be significantly affected
by OCR errors when OCR’d texts are used for fine-
tuning. LMs directly trained on large OCR’d corpora
may still yield robust word vectors though we have
not fully test this assumption. The impact of OCR
on LMs is an area with promising paths for further
investigation which we partially outline below.
6 CONCLUSION
We have performed a large-scale analysis of the impact
of OCR errors on several NLP tasks. Promising areas
of future work include: using more data for perform-
ing assessment of OCR quality, establishing rigorous
heuristics for measuring OCR quality without reliance
on intrinsic confidence scores, and the post-correction
of OCR errors.
Language models have had a major impact on a
range of NLP tasks. However, whilst the impact of
OCR errors on these models is poorly understood, it
will be difficult for researchers and institutions work-
ing with OCR’d text to fully realize these benefits.
This is work we plan to begin soon.
Establishing evidenced-based best practices for
working with OCR’d will reap major benefits, par-
ticularly if these practices become more widely shared
across all researchers working with OCR’d text. This
is an area in which libraries and other heritage organi-
zations play an important advocacy role.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Work for this paper was produced as part of Living
with Machines. This programme, funded by the UK
Research and Innovation (UKRI) Strategic Priority
Fund, is a multidisciplinary collaboration delivered by
the Arts and Humanities Research Council (AHRC),
with The Alan Turing Institute, the British Library and
ARTIDIGH 2020 - Special Session on Artificial Intelligence and Digital Heritage: Challenges and Opportunities
494

the Universities of Cambridge, East Anglia, Exeter,
and Queen Mary University of London.
REFERENCES
Alex, B. and Burns, J. (2014). Estimating and rating the
quality of optically character recognised text. In Pro-
ceedings of the First International Conference on Digi-
tal Access to Textual Cultural Heritage - DATeCH ’14,
pages 97–102, Madrid, Spain. ACM Press.
Alex, B., Grover, C., Klein, E., and Tobin, R. (2012). Digi-
tised Historical Text: Does It Have to Be MediOCRe?
In Proceedings of the 9th Conference on Natural Lan-
guage Processing (KONVENS 2012).
Ardanuy, M. C., McDonough, K., Krause, A., Wilson, D.
C. S., Hosseini, K., and van Strien, D. (2019). Resolv-
ing places, past and present: Toponym resolution in
historical british newspapers using multiple resources.
In Proceedings of the 13th Workshop on Geographic
Information Retrieval, GIR ’19, New York, NY, USA.
Association for Computing Machinery.
Azzopardi, L. and Vinay, V. (2008). Retrievability: an evalu-
ation measure for higher order information access tasks.
In Proceedings of the 17th ACM conference on Infor-
mation and knowledge management, pages 561–570.
ACM.
Blei, D. M., Ng, A. Y., and Jordan, M. I. (2003). Latent
dirichlet allocation. the Journal of machine Learning
research, 3:993–1022.
British Library Labs (2014). Digitised Books. c. 1510 -
c. 1900. JSON (OCR derived text). Available via:
https://doi.org/10.21250/db14.
Chiron, G., Doucet, A., Coustaty, M., and Moreux, J. (2017).
Icdar2017 competition on post-ocr text correction. In
2017 14th IAPR International Conference on Docu-
ment Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR), volume 01,
pages 1423–1428.
Cordell, R. (2017). "Q i-jtb the Raven": Taking Dirty OCR
Seriously. Book History, 20:188–225.
Cordell, R. (2019). Why You (A Humanist) Should Care
About Optical Character Recognition. Blog available
via https://ryancordell.org/research/why-ocr.
De Wilde, M. and Hengchen, S. (2017). Semantic enrich-
ment of a multilingual archive with linked open data.
Digital Humanities Quarterly, 11(4).
Ehrmann, M., Colavizza, G., Rochat, Y., and Kaplan, F.
(2016). Diachronic Evaluation of NER Systems on
Old Newspapers. Proceedings of the 13th Conference
on Natural Language Processing (KONVENS 2016),
pages 97–107.
Evershed, J. and Fitch, K. (2014). Correcting noisy OCR:
Context beats confusion. In Proceedings of the First
International Conference on Digital Access to Textual
Cultural Heritage, pages 45–51. ACM.
Franzini, G., Kestemont, M., Rotari, G., Jander, M., Ochab,
J. K., Franzini, E., Byszuk, J., and Rybicki, J. (2018).
Attributing Authorship in the Noisy Digitized Corre-
spondence of Jacob and Wilhelm Grimm. Frontiers in
Digital Humanities, 5:4.
Hagberg, A. A., Schult, D. A., and Swart, P. J. (2008).
Exploring network structure, dynamics, and function
using networkx. In Varoquaux, G., Vaught, T., and
Millman, J., editors, Proceedings of the 7th Python
in Science Conference, pages 11 – 15, Pasadena, CA
USA.
Hakala, K., Vesanto, A., Miekka, N., Salakoski, T., and
Ginter, F. (2019). Leveraging Text Repetitions
and Denoising Autoencoders in OCR Post-correction.
arXiv:1906.10907 [cs]. arXiv: 1906.10907.
Hämäläinen, M. and Hengchen, S. (2019). From the paft
to the fiiture: a fully automatic nmt and word embed-
dings method for ocr post-correction. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1910.05535.
Hamdi, A., Jean-Caurant, A., Sidere, N., Coustaty, M., and
Doucet, A. (2019). An Analysis of the Performance of
Named Entity Recognition over OCRed Documents. In
2019 ACM/IEEE Joint Conference on Digital Libraries
(JCDL), pages 333–334.
Hill, M. J. and Hengchen, S. (2019). Quantifying the impact
of dirty OCR on historical text analysis: Eighteenth
Century Collections Online as a case study. Digital
Scholarship in the Humanities.
Honnibal, M. and Montani, I. (2017). spaCy: Natural lan-
guage understanding with Bloom embeddings, convo-
lutional neural networks and incremental parsing. To
appear.
Howard, J. and Ruder, S. (2018). Universal language model
fine-tuning for text classification. In Proceedings of
the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Com-
putational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pages
328–339, Melbourne, Australia. Association for Com-
putational Linguistics.
Jarlbrink, J. and Snickars, P. (2017). Cultural heritage as
digital noise: nineteenth century newspapers in the
digital archive. Journal of Documentation, 73(6):1228–
1243.
Jie, Z., Muis, A. O., and Lu, W. (2018). Efficient
dependency-guided named entity recognition. CoRR,
abs/1810.08436.
Leavy, S., Wade, K., Meaney, G., and Greene, D. (2018).
Navigating Literary Text with Word Embeddings and
Semantic Lexicons. In Workshop on Computational
Methods in the Humanities 2018, address = Luasanne,
Switzerland.
Levenshtein, V. I. (1966). Binary codes capable of correcting
deletions, insertions, and reversals. In Soviet physics
doklady, volume 10, pages 707–710.
Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., and Dean, J. (2013).
Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector
Space. arXiv preprint.
Milligan, I. (2013). Illusionary Order: Online Databases,
Optical Character Recognition, and Canadian History,
1997–2010. Canadian Historical Review, 94(4):540–
569.
Mimno, D., Wallach, H. M., Talley, E., Leenders, M., and
McCallum, A. (2011). Optimizing semantic coherence
in topic models. In Proceedings of the Conference on
Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing,
EMNLP ’11, pages 262–272, Stroudsburg, PA, USA.
Association for Computational Linguistics.
Assessing the Impact of OCR Quality on Downstream NLP Tasks
495

Mutuvi, S., Doucet, A., Odeo, M., and Jatowt, A. (2018).
Evaluating the Impact of OCR Errors on Topic Model-
ing. In Dobreva, M., Hinze, A., and Zumer, M., editors,
Maturity and Innovation in Digital Libraries, Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, pages 3–14. Springer In-
ternational Publishing.
Nauta, G. J., van den Heuvel, W., and Teunisse, S. (2017).
Survey Report on Digitisation in European Cultural
Heritage Institutions 2017. DEN Foundation (NL) on
behalf of Europeana/ENUMERATE.
Nelson, L. K. (2020). Computational Grounded Theory: A
Methodological Framework. Sociological Methods &
Research, 49(1):3–42.
Newman, D., Lau, J. H., Grieser, K., and Baldwin, T. (2010).
Automatic Evaluation of Topic Coherence. In Proceed-
ing of the Human Language Technologies: The 2010
Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of
the Association for Computational Linguistics, pages
100–108, Los Angeles, CA, USA. ACM.
Nguyen, T.-T.-H., Jatowt, A., Coustaty, M., Nguyen, N.-
V., and Doucet, A. (2019). Deep Statistical Analysis
of OCR Errors for Effective Post-OCR Processing. In
2019 ACM/IEEE Joint Conference on Digital Libraries
(JCDL), pages 29–38, Champaign, IL, USA. IEEE.
Palmer, D. D. A handbook of natural language processing. In
Robert Dale, H. M. and Harold Somers, e., editors, To-
kenisation and Sentence Segmentation. Marcel Dekker,
New York, NY.
Pletschacher, S., Clausner, C., and Antonacopou-
los, A. (2014). Europeana performance evalua-
tion report. Available via http://www.europeana-
newspapers.eu/public-materials/deliverables/.
Read, J., Dridan, R., Oepen, S., and Solberg, L. J. (2012).
Sentence boundary detection: A long solved problem?
In Proceedings of COLING 2012: Posters, pages 985–
994, Mumbai, India. The COLING 2012 Organizing
Committee.
ˇ
Reh˚u
ˇ
rek, R. and Sojka, P. (2010). Software Framework
for Topic Modelling with Large Corpora. In Proceed-
ings of the LREC 2010 Workshop on New Challenges
for NLP Frameworks, pages 45–50, Valletta, Malta.
ELRA.
Rigaud, C., Doucet, A., Coustaty, M., and Moreux, J.-P.
(2019). ICDAR 2019 Competition on Post-OCR Text
Correction. In 15th International Conference on Docu-
ment Analysis and Recognition, Sydney, Australia.
Smith, D. A. and Cordell, R. (2018). A Research Agenda for
Historical and Multilingual Optical Character Recog-
nition. Report available via http://hdl.handle.net/2047/
D20297452.
Steyvers, M. and Griffiths, T. (2007). Probabilistic topic mod-
els. Handbook of latent semantic analysis, 427(7):424–
440.
Strange, C., McNamara, D., Wodak, J., and Wood, I. (2014).
Mining for the Meanings of a Murder: The Impact
of OCR Quality on the Use of Digitized Historical
Newspapers. Digital Humanities Quarterly, 008(1).
Terras, M. M. (2011). The Rise of Digitization. In Rikowski,
R., editor, Digitisation Perspectives, volume 39, pages
3–20. Sense Publishers, Rotterdam.
Traub, M. C., Samar, T., van Ossenbruggen, J., and Hard-
man, L. (2018). Impact of Crowdsourcing OCR Im-
provements on Retrievability Bias. In Proceedings of
the 18th ACM/IEEE on Joint Conference on Digital
Libraries, JCDL ’18, pages 29–36. ACM.
Traub, M. C., van Ossenbruggen, J., and Hardman, L. (2015).
Impact Analysis of OCR Quality on Research Tasks in
Digital Archives. In Kapidakis, S., Mazurek, C., and
Werla, M., editors, Research and Advanced Technology
for Digital Libraries, volume 9316, pages 252–263.
Springer International Publishing, Cham.
Vicente, R. F., Jackson, M., Roubickova, A., Krause, A., Ter-
ras, M., Hauswedell, T., Nyhan, J., Beavan, D., Hobson,
T., Ardanuy, M. C., Colavizza, G., Hetherington, J.,
and Ahnert, R. (2019). Defoe: A Spark-based Toolbox
for Analysing Digital Historical Textual Data. In 2019
IEEE 15th International Conference on E-Science (e-
Science).
Xia, Q., Li, Z., Zhang, M., Zhang, M., Fu, G., Wang, R.,
and Si, L. (2019). Syntax-aware neural semantic role
labeling. CoRR, abs/1907.09312.
Yadav, V. and Bethard, S. (2018). A survey on recent ad-
vances in named entity recognition from deep learn-
ing models. In Proceedings of the 27th International
Conference on Computational Linguistics, pages 2145–
2158, Santa Fe, New Mexico, USA. Association for
Computational Linguistics.
ARTIDIGH 2020 - Special Session on Artificial Intelligence and Digital Heritage: Challenges and Opportunities
496
