
Impact of Developers Sentiments on Practices and Artifacts in Open
Source Software Projects: A Systematic Literature Review
Rui Santos Carige Junior
1
and Glauco de Figueiredo Carneiro
2 a
1
Federal Institute of Bahia (IFBA), Seabra - BA, Brazil
2
Universidade Salvador (UNIFACS), Salvador - BA, Brazil
Keywords:
Sentiment Analysis, Systematic Literature Review, Open Source Software Projects.
Abstract:
Context: Sentiment Analysis proposes the use of Software Engineering techniques for automated identifica-
tion of human behavior. There is a growing interest in the use of Sentiment Analysis in topics related to
Computing, more specifically in Software Engineering itself. Objective: Analyze the impact of developers
sentiments on software practices and artifacts in open source software projects. Methods: We conducted a
Systematic Review to collect evidence from the literature regarding the impacts of developers sentiments on
software practices and artifacts. Results: We have found that the growing number of studies in this area
provides greater visibility of the direct influence of developers sentiments on software practices. Practices
associated with developers productivity and collaboration, along with source code, are the most vulnerable
to sentiments variation. Conclusions: With the results presented, we hope to contribute to the discussion
about the potential of improvement the social environment quality of software projects, as the sentiments of
developers can positively or negatively impact software practices and artifacts.
1 INTRODUCTION
There has been a growing interest in the use of Sen-
timent Analysis (SA) in topics related to Comput-
ing, including Software Engineering (SE). The way
programmers interact among themselves through dif-
ferent types of messaging in different development
environments can reveal perceptions and behaviors
that can have some sort of relationship with software
projects choices and results in which they work. This
relationship would not be trivially unveiled through
the use of traditional data analysis techniques.
Many researches have dedicated their best efforts
to deepen the discussion on human aspects related
to Software Engineering (Asri et al., 2019) (Grazi-
otin et al., 2017) (Cheruvelil and C. da Silva, 2019).
The literature has provided results based on the effect
of developers personality traits on software projects.
These results use approaches that consider a holistic
view of the subject, in this case, the developers.
Although studies analyzing developers sentiments
have widely adopted several types of perspectives and
areas to focus the analysis, it lacks a proper under-
standing of how these individual studies contribute to
the entire field of software engineering. To the best
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6241-1612
of our knowledge, there is no secondary study that in-
vestigates how data related to developers interactions
have been used by the research community. For this
reason, we conducted a Systematic Literature Review
study (SLR) to gather evidence provided by papers
published in peer-reviewed conferences and journals
from January 2000 to August 2019. We found 229
papers as a result of the applied search strings in spe-
cific electronic databases, from which we selected 11
studies to answer the stated research question. Find-
ings suggest that there is a gap in effective solutions
to deal with variation of developers sentiments data
throughout the software life cycle, especially the im-
pact of this variation on software practices and arti-
facts. This indicates the need to motivate researchers
to conduct studies in this subject.
This SLR study is part of a larger joint project,
which aims to propose a road map on how to iden-
tify, collect and analyze the impact of developers sen-
timents on practices and artifacts of open source soft-
ware and an technological infrastructure to support
the accomplishment of these goals. As a first step of
this project, we endeavour to characterize the impacts
analyzed by the researchers. The Research Question
(RQ) of this SLR is as follows: “What is the impact of
sentiments in adopted software practices and artifacts
Carige Junior, R. and Carneiro, G.
Impact of Developers Sentiments on Practices and Artifacts in Open Source Software Projects: A Systematic Literature Review.
DOI: 10.5220/0009313200310042
In Proceedings of the 22nd Inter national Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2020) - Volume 2, pages 31-42
ISBN: 978-989-758-423-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
31

produced by programmers in open source software
projects?”. This research question is in line with the
goal of this review. The motivation behind the stated
RQ is to understand to which extent sentiments of de-
velopers can positively or negatively affect the quality
of the software. We hope to strengthen the discussion
to understand the possible roots and conditions that
promote both positive and negative sentiments in the
context of open source software projects.
The remainder of this paper is organized as fol-
lows: Section 2 contextualizes Open Source Software
(OSS) projects. The Section 3 presents the methods
we adopted to conduct this research. The Section 4
reports the results collected from evidence of selected
papers. We discuss these results in Section 5, present-
ing the answer to the stated research question. Section
6 discusses the threats to the validity of this research.
Finally, we conclude and mention future work in Sec-
tion 7.
2 OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE
PROJECTS
While stability and economic benefits are the main
criteria for commercial software, open source soft-
ware projects explicitly consider the satisfaction of
users of great influence in the prioritization of is-
sues and its corresponding implementation (Singh
et al., 2017). Successful practices and products from
OSS projects have attracted attention for several rea-
sons (Michlmayr et al., 2015). Companies can draw
lessons from open source software projects by study-
ing their best practices and applying them internally
(Stol and Fitzgerald, 2015) (Michlmayr et al., 2015).
Developers in OSS projects not only focus on code,
they also dedicate efforts to review code from their
counterparts to provide feedback, assure quality at-
tributes, among others activities (Santos et al., 2013).
To accomplish these tasks, programmers need to in-
teract and communicate among themselves. They
usually interact through text messages registered in
issue comments, wikis, forums, just to name a few.
This raises the need to investigate this interaction
expressed through comments to unveil details, chal-
lenges and the rationale behind decisions of OSS
projects.
In fact, beyond the communication itself, com-
ments can provide hints regarding the sentiments of
programmers during the software life cycle. Initia-
tives have been taken to examine this in the context
of software engineering. The term Behavioral Soft-
ware Engineering (BSE) was proposed as an attempt
to fill the gap in which most research on software pro-
cess improvement focused on the actual change rather
than the people that will have to change their behav-
ior (Lenberg et al., 2015). Recent results from the
literature indicate that the BSE research area is grow-
ing and considering an increasing number of concepts
that range from psychology to social science (Lenberg
et al., 2015). More recently, a SLR characterized pub-
lished works concerning software developers’ emo-
tions and indicators to assess them. The selected stud-
ies searched for empirical evidence of the intersection
of emotions and software engineering using a holistic
view on the subject (S
´
anchez-Gord
´
on and Colomo-
Palacios, 2019). The same authors highlighted the
need for a deeper analysis and comparison between
the primary studies, with particular emphasis on un-
derstanding the effect of emotions on the software de-
velopment process expressed in terms such as per-
formance, productivity, quality, and well-being. We
tackle this issue in the SLR presented in the follow-
ing sections.
Another SLR was conducted to investigate the ef-
fect of personality traits and team climate on software
team performance (Soomro et al., 2016). The authors
selected 35 primary studies that discussed this effect
and concluded that team climate comprises a wide
range of factors that fall within the fields of manage-
ment and behavioral sciences (Soomro et al., 2016).
In the preliminary findings from a SLR about Person-
ality in Software Engineering (Cruz et al., 2011), Cruz
et al. identified the methods used, topics addressed,
personality tests applied, and the main findings pro-
duced in the research about personality in software
engineering. In an extended version of the previous
secondary study, the same authors found that research
related to pair programming, education, team effec-
tiveness, software process allocation, software engi-
neer personality characteristics, and individual perfor-
mance concentrated over 88% of 90 studies selected,
while team process, behavior and preferences, and
leadership performance were topics not focused by
the majority of researchers (Cruz et al., 2015).
We decided to conduct this research focusing on
open source projects due to the intrinsic contribution
of this initiative to the academic field. The advent of
OSS projects made possible the provision of data to
be scrutinized for research purposes. Moreover, shar-
ing the results of the analysis of these data contributes
to open source development.
Another reason for choosing to research the senti-
ments of developers in open source projects is linked
to collaborative development. Open source projects
enable the participation of programmers from differ-
ent parts of the world, contributing to the plurality of
the origins of sentiments.
ICEIS 2020 - 22nd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
32
3 RESEARCH DESIGN
We conducted a Systematic Literature Review to find
evidence for the impact of sentiments on practices and
artifacts in open source software projects. The fol-
lowing subsections describe the research design we
adopted.
3.1 Planning
We conducted this SLR based on a protocol com-
prised of objectives of the review, criteria for consid-
ering papers, research questions, selected electronic
databases and its search strings, selection procedures
and exclusion, inclusion and quality criteria to select
the studies from which we aim to answer the stated
research questions (Wohlin et al., 2012). The proto-
col of this SLR and related artifacts are available in a
public GitHub repository
1
. The goal of this study is
presented in Table 1 according to the GQM approach
(Basili and Rombach, 1988).
Table 1: The Goal according the GQM approach.
Analyze sentiments
for the purpose of identification of its impact
with respect to adopted practices as well as
software artifacts produced
from the point of programmers
view of
in the context of open source software projects
The Research Question (RQ) is “What is the impact of
sentiments in adopted software practices and artifacts
produced by programmers in open source software
projects?”. This research question is in line with the
goal of this review, and has been derived into two spe-
cific research questions, as follows: Specific Research
Question 1 (SRQ1): What is the impact of sentiments
of programmers in open source software projects in
adopted software practices? Specific Research Ques-
tion 2 (SRQ2): What is the impact of sentiments of
programmers in open source software projects arti-
facts?
The motivation behind the research question is
due to the relevance of understanding to which ex-
tent the sentiments of developers can positively or
negatively affect the quality of the software through
their practices and artifacts produced. The specific
research questions have the goal to gather evidence to
support the answer of the stated RQ. We considered
the PICO criteria (Stone, 2002) to define the search
strings, as shown in Table 2. The search strings are
1
https://github.com/impactsentimentanalysis/
iceisExploratoryStudy2020
based on this criteria for the selective process of pa-
pers for this review.
Table 2: PICO Criteria for Search Strings.
(P)opulation software engineering papers focusing on open source
software projects
(I)ntervention influence of sentiments in adopted software practices
and artifacts produced by programmers
(C)omparison not applicable
(O)utcomes impacts (positive and negative) of the influence of
sentiments on software practices and artifacts
The formation of the search string applied in the elec-
tronic databases is shown in Tables 3 and 4. The Table
3 refers to the major terms for the research objectives,
built using the PICO criteria. We also considered the
use of alternative terms and synonyms of these major
terms. For example, the term sentiment can be associ-
ated with terms such as feeling, emotion, and opinion
mining. These alternative terms, as shown in Table 4,
are also included in the search string. We built the fi-
nal search string by joining the major terms with the
boolean “AND” and joining the alternative terms to
the main terms with the boolean “OR”. The formed
search strings aimed at focusing on papers targeting
the research questions of this systematic review.
Table 3: Major terms for the research objectives.
Criteria Major Terms
(P)opulation AND ”software engineering”
AND ”open source software project”
(I)ntervention AND ”sentiment”
(C)omparison not applicable
(O)utcomes AND ”software practice” AND ”software artifact”
Table 4: Alternative terms from majors terms.
Major Term Alternative Terms
“open source software project”
“Free and open-source software”
OR “free/libre and open-source software”
OR “OSS” OR FOSS” OR “F/LOSS”
OR “FLOSS”
“sentiment”
“feeling” OR “emotion”
OR “opinion mining”
“software practice”
“software activity”
“software artifact”
“software asset”
Table 5 presents the electronic databases from which
we retrieved the papers along with the respective
search strings used to retrieve the papers. The target
databases were ACM Digital Library, IEEE Xplore
and ScienceDirect. All searches were performed on
August 22, 2019.
Table 6 presents the criteria for exclusion and in-
clusion of papers in this review. The OR associated
with the exclusion criteria, means that the exclusion
criteria are independent, i.e., meeting only one cri-
Impact of Developers Sentiments on Practices and Artifacts in Open Source Software Projects: A Systematic Literature Review
33
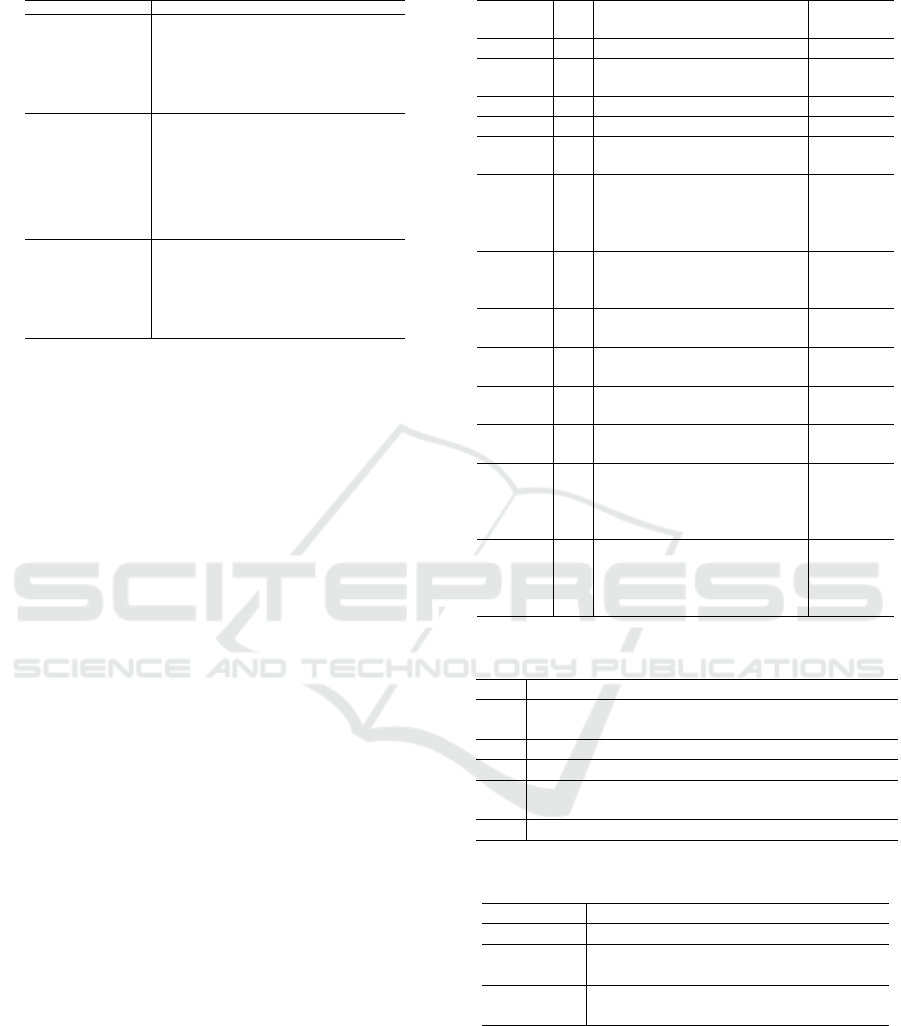
Table 5: Electronic Databases Selected for this SLR.
Database and URL Search Strings
ACM Digital Library
portal.acm.org
(+”software engineering” +(”open source
software” ”OSS” ”open source projects”
”OSP” ”Free and open-source software”
”FOSS” ”free/libre and open-source software”
”F/LOSS” ”FLOSS”) +(”sentiment” ”feeling”
”emotion” ”personality” ”opinion mining”))
IEEE Xplore
ieeexplore.ieee.org
(”software engineering” AND (”open source
software” OR ”OSS” OR ”open source
projects” OR ”OSP” OR ”Free and
open-source software” OR ”FOSS” OR
”free/libre and open-source software” OR
”F/LOSS” OR ”FLOSS”) AND (”sentiment”
OR ”feeling” OR ”emotion” OR ”personality”
OR ”opinion mining”)))
ScienceDirect
sciencedirect.com
(”software engineering” (”open source
software” OR ”OSS” OR ”open source
projects” OR ”OSP” OR ”Free and open-source
software” OR ”FOSS”) (”sentiment” OR
”feeling” OR ”emotion” OR ”personality”
OR ”opinion mining”))
terion is enough to exclude the paper. On the other
hand, the AND connective in the inclusion criteria,
means that all inclusion criteria must met to select the
paper under analysis. Table 6 also presents the qual-
ity criteria used for this review represented as ques-
tions that were adopted and adjusted from Dyba and
Dingsoyr (Dyb
˚
a and Dingsøyr, 2008). A critical ex-
amination following the quality criteria established in
this table was performed in all remaining papers that
passed the exclusion and inclusion criteria. All these
criteria must met (i.e., the answer must be YES for
each one) to permanently select the paper, otherwise
the paper must be excluded. The exclusion, inclusion
and quality criteria were used in the selection process
as presented in Table 7.
According to Table 8, at the end of the selection
process, all the retrieved papers were classified in one
of the three options: Excluded, Not Selected and Se-
lected.
3.2 Execution
The quantitative evolution of papers throughout the
execution of this SLR is summarized in Figure 1. The
figure uses the PRISMA flow diagram (Moher et al.,
2009) and shows the performed steps and the respec-
tive number of documents for each phase of the SLR,
following the outline described in Subsection 3.1.
Table 9 presents the effectiveness of the the search
considering the 229 retrieved papers that after remov-
ing the duplicates provided 220 papers. The elec-
tronic database that more contributed with selected
studies was the ACM Digital Library with five pa-
pers, corresponding to a search effectiveness of 7.8%.
Among the searched electronic repositories, IEEE
Xplore also stands out for presenting 13.6% of ef-
fectiveness of the search string utilized. The twelve
Table 6: Exclusion, Inclusion and Quality Criteria.
Type Id Description Connective
or Answer
Exclusion E1 Published earlier than 2000 OR
Exclusion E2 The paper was not published in a OR
peer-reviewed journal or conference
Exclusion E3 The paper is not written in English OR
Exclusion E4 The paper has less than 4 pages OR
Exclusion E5 The paper does not present a OR
primary study
Inclusion I1 The paper should present a study on AND
the influence of sentiments on
software practices or artifacts
produced by programmers
Inclusion I2 The study should be conducted AND
within the scope of open source
software projects
Inclusion I3 Sentiments should be detected from AND
records made by developers
Quality Q1 Are the aims of the study clearly YES/NO
specified?
Quality Q2 Is the context of the study clearly YES/NO
stated?
Quality Q3 Does the research design support YES/NO
the aims of the study?
Quality Q4 Does the study have an adequate YES/NO
description of the impact of
sentiments on open source software
project practices and artifacts?
Quality Q5 Is the data analysis of the study is YES/NO
rigorous and based on evidence or
theoretical of reasoning instead
non-justified or ad hoc statements?
Table 7: Steps of the Selection Process.
Step Description
1 Apply the search strings to obtain a list of candidate papers in
specific electronic databases.
2 Remove duplicated papers from the list.
3 Apply the exclusion criteria in the listed papers.
4 Apply the inclusion criteria after reading abstracts, introduction
and conclusion in papers not excluded in step 3.
5 Apply quality criteria in selected papers after step 4.
Table 8: Classification Options for Each Retrieved Paper.
Classification Description
Excluded Papers met the exclusion criteria.
Not Selected Papers not excluded due to the exclusion criteria,
but did not meet the inclusion or quality criteria.
Selected Papers did not meet the exclusion criteria and met
both the inclusion and quality criteria.
selected papers represented 4.8% of all 229 retrieved
papers.
ICEIS 2020 - 22nd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
34

Table 9: Effectiveness of the Search.
Database
Papers Retrieved by
the Search String
Selected Papers Search Effectiveness
ACM Digital Library 64 5 7.8%
IEEE Xplore 22 3 13.6%
ScienceDirect 143 3 2.1%
Total 229 11 4.8%
Figure 1: Procedures and its results in the papers selection
process.
Figure 2: Artifacts from which sentiments were identified.
4 RESULTS
The Appendix A shows the list of 11 selected papers
of this systematic review. All studies are labeled as
“SP” followed by the paper reference number through
which the paper can be reached at the end of this doc-
ument. The selected papers were published in confer-
ences and journals.
Figure 2 presents the sources from which senti-
ments were analyzed, according to the 11 selected
studies. Interviews and commits stood out as the main
sources of sentiments analyzed in the selected studies.
Together they represent 54% of the sources of sen-
timents in these studies. Figure 3 presents evidence
collected from the literature to answer the Specific
Research Questions SRQ1 and SRQ2. Each branch
is associated to a Specific Research Question and the
corresponding answers represented in sentences along
with the selected studies from which they were col-
lected. Each branch maps the positive and negative
influence on practices and artifacts.
Table 10 presents in detail the impact of sen-
timent on software practices argued by authors of
the selected papers. The table presents the relation-
ship among the attributes polarity, sentiment, soft-
ware practice and impact for each of the selected
studies. Table 11 has the same purpose focusing on
software artifacts. We can see that most of the arti-
cles (SP01, SP02, SP03, SP04, SP05, SP07, SP08,
SP10 and SP11) discussed how practices have been
affected, and only a few (SP03, SP06, SP09, SP10)
discussed the influence on software artifacts. In this
case, SP03 and SP10 were the only studies to explic-
itly discuss both influence on practices and software
artifacts. We mention the term explicitly because the
authors recognize in the text of the respective papers
the impact of sentiments also on software artifacts.
Despite being indicated only in these two papers, the
artifacts might also suffer the influence of sentiments
as a consequence of performing the practices. For ex-
ample, in Table 10, we can identify that when pro-
ductivity decreases, release expedition is delayed and
process adherence is not enough, there is a tendency
for a source code of low quality. In this case, the sen-
timent of unhappiness was mentioned by the authors
of SP03 and SP10 as the likely root cause.
As can be seen in Tables 10 and 11, there is a
tendency of positive sentiments to positively impact
software practices and/or artifacts. For example, the
Impact of Developers Sentiments on Practices and Artifacts in Open Source Software Projects: A Systematic Literature Review
35

Figure 3: Mental model of identified impacts on software practices and artifacts.
results of SP06 indicated that positive emotions often
lead to few defects. Likewise, sentiments of negative
polarity tend to increase the number of defects. We
have also identified that, according to the authors of
SP04, issue reopening is something to be avoided as
it might indicate that something has gone wrong in
the issue handling. This means that additional effort
must be made to fix it definitely. The results found by
the authors showed that sentiments with negative and
positive polarity can increased rate of issues reopen-
ing. In Tables 10 and 11, we mark sentiments from
studies SP02, SP04, SP06, SP07 and SP09 as Not
specified. The tools used in each study is described
as follows: Senti4SD (Calefato et al., 2018), Sen-
tiStrengthSE (Islam and Zibran, 2017), LIWC (Pen-
nebaker et al., 1999), RNTN (Socher et al., 2013) and
SentiStrength (Thelwall et al., 2012). The tools sup-
ported researchers to automatically identify the polar-
ity (positive or negative) of the sentiments expressed
by the programmers.
We answer the specific research questions (SRQ1
and SRQ2) in the following subsections, respectively.
4.1 Impacts of Positive Sentiments on
Software Practices
The impact of programmers sentiments on open
source software projects in software practices was
registered in the left side of Figure 3. The upper left
side of the same figure portrays the impact of positive
sentiments. According to the same figure and com-
plemented by Table 10, 25% of this impact is asso-
ciated with the Positive Contentment sentiment. The
other registered sentiments Calm, Trust and Happi-
ness account for approximately 12% of the collected
evidence. Roughly 38% of the sentiments associated
with positive polarity was marked as not specified.
Impacts of the Positive Contentment Sentiment.
The paper SP01 conducted interviews with open
source software teams to characterize their perception
regarding the collaborative virtual work in which they
were engaged. The result of the interviews revealed
that the contentment sentiment was associated with
a suitable balance between professional and personal
life. The consequence was productivity improvement
and efficiency of the professionals. One interviewee
reported that ”My impression is that I can be more
productive working from home that working from the
office. I probably also work for more hours than if
I was working in the office. So when I in the office,
I was interrupted very often”. The authors of paper
ICEIS 2020 - 22nd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
36

SP11 pointed out that GitHub provides social coding
features, including the assignment of stars to a given
repository which indeed presumably express interest
or satisfaction with an open source project. Based
on the feedback of 791 programmers, the authors re-
ported that 73% considered the number of stars as a
relevant criterion for using or contributing to a GitHub
project. Of these, 26.5% said that the larger the num-
ber of stars the more influence this fact had on the
decision to use or contribute to a project.
Impacts of the Positive Calm Sentiment. In
SP01 the authors reported that when programmers did
not felt rushed, they can solve problems much more
efficiently. One of the programmers informed that ”I
found that at the end I can really start to answer ques-
tions and solve problems a lot better than when I don’t
feel rushed we have an office and everybody needs to
be here at the same time kind of rules”.
Impacts of the Positive Trust Sentiment. The
paper SP08 investigated the influence of open source
project developers’ trust on global software engineer-
ing processes. The study found evidence of trust as a
possible factor to increase developer confidence. The
consequence is the diffusion of new strategies, includ-
ing social and technical innovations within the dis-
tributed team. In fact, study revealed that the diffusion
trajectory becomes diverse when considering individ-
ual variations on baseline trust.
Impacts of the Positive Happiness Sentiment.
The paper SP10 extracted data from interviews with
software developers and analyzed the possible conse-
quence of happiness and unhappiness in software pro-
cesses and artifacts. The most reported consequence
was the increase of productivity, as shown in these
statements: “When I have this [happy] feeling I can
just code for hours and hours. (...) I felt that my pro-
ductivity grew while I was happy. (...) The better my
mood, the more productive I am”. The authors also
argued that another process influenced by the happi-
ness of developers was software expedition, that be-
came faster. The tasks were sped up without sacrific-
ing quality, and one of the programmers commented
that “it seems more likely to reach my goals faster”.
Programmers from the same study claimed to be full
of energy and with strong focus as a result of happi-
ness. Thus they maintained a sustained flow and were
”unaware of the passing time. (...) I can continue to
code without anymore errors for the rest of the day,
and just knock out lines of code all day”.
Based on the results, the authors stated that happy
developers can also encourage more collaborative
team members, leading to increased collaboration.
The authors realized that happiness leads to more
willingness to share knowledge and to bring col-
leagues together to solve a problem.
Adherence to the process was another conse-
quence of the happiness that was reported by the in-
terviewees in SP10, as explained by a programmer:
“when I am happy to work, I usually try new things
and follow best practices and standards as much as
possible”. Finally, the authors of SP10 stated that the
creative process can also be a positive consequence of
developers being happy, as stated in this response: “if
[...] I have a general good mood, the software process
gets to be creative and very good”.
Impacts of Other Positive Sentiments. In
SP02, the authors studied the sentiments expressed
by contributors during code review activities using
the Senti4SD Sentiment Analysis tool (Calefato et al.,
2018). The authors claimed that reviews with pos-
itive comments have a shorter duration on average.
They argued that the presence of positive sentiments
in comments related to source code reviews seems
to contribute to reducing the review time by an av-
erage of 0.4 day. In the same paper, the authors stated
that the presence of positive sentiments in code re-
view comments seems to have positively affected the
results of these reviews. They found that 91.81% of
successful reviews were identified with positive senti-
ments, and 64.44% of aborted reviews contained neg-
ative sentiments.
The paper SP04 analyzed data available in the
JIRA issue tracking system from eight Apache Soft-
ware Foundation open source projects. Sentiments
were detected in developers comments through the
use of the SentiStrengthSE tool (Islam and Zibran,
2017). The results indicated that sentiments with very
high positive or high negative scores impact in the rate
of issues reopening.
In the paper SP07, the authors analyzed comments
from Github to investigate the correlation between
emotional factors and the speed of bug fixes in open
source software development. The authors realized
that the Bug Fixing Speed (BFS), ie the average num-
ber of problems that have been resolved within a cer-
tain period of time, was lower when the developers’
sentiment proved positive.
4.2 Impacts of Negative Sentiments on
Software Practices
The bottom left side of the Figure 3 shows evidence
of the impact of negative sentiments on software prac-
tices. Among these sentiments, Unhappiness stood
out in the percentage of appearances in the selected
studies (33%). Discontent and Rudeness represented
each 14% of the negative sentiments that influence
software practices. We also identified that 33% of
Impact of Developers Sentiments on Practices and Artifacts in Open Source Software Projects: A Systematic Literature Review
37
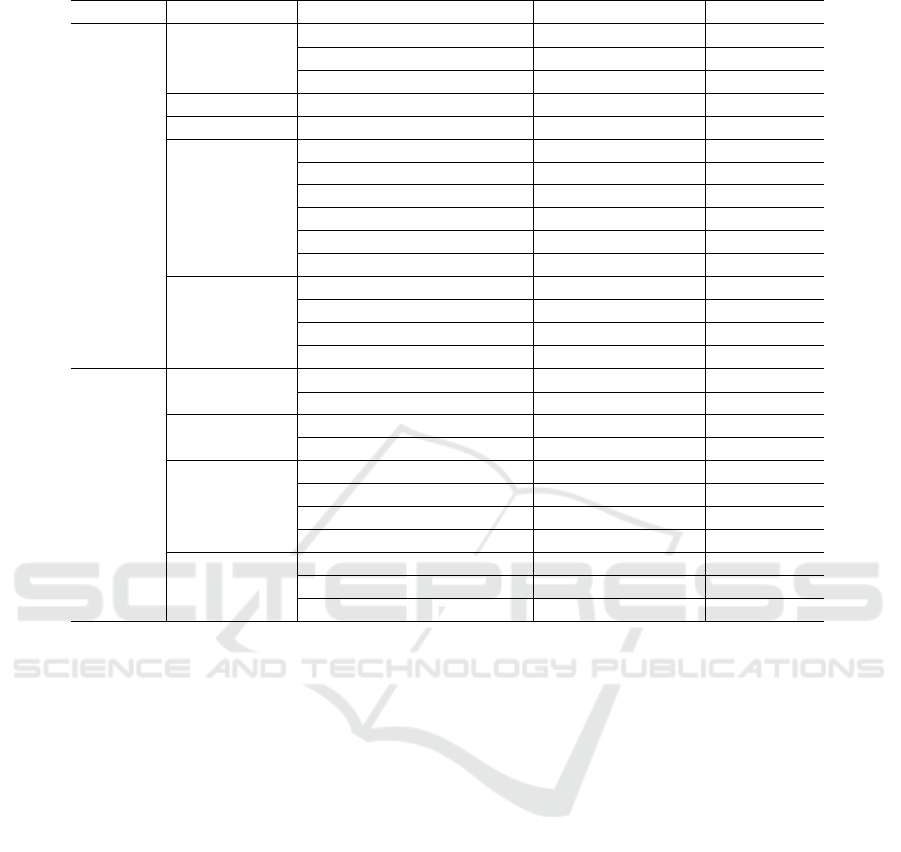
Table 10: Impacts of Sentiments on Software Practices.
Polarity Sentiment Software Practice Impact Studies
Productivity Increase SP01
Contentment Use of project Increased Interest SP11
Contribution to the project Increased Interest SP11
Calm Problem solving Efficiency SP01
Trust Diffusion of technology New strategies SP08
Productivity Higher SP10
Expedition Faster SP10
Positive Happiness Work flow Sustained SP10
Collaboration Increased SP10
Process adherence Increased SP10
Creativity Increase SP10
Code reviews Agility SP02
Not specified Commit acceptance Increase SP02
Reopening of issues Highest incidence SP04
Bug fixing speed Highest SP07
Discontent Use of project Decreased Interest SP11
Contribution to the project Decreased Interest SP11
Rudeness Commit rejection Increase SP05
Commit review Longer SP05
Productivity Lower SP03, SP10
Negative Unhappiness Expedition Delayed SP03, SP10
Process adherence Decrease SP03, SP10
Work flow Broken SP03, SP10
Code reviews Lengthy SP02
Not specified Commit rejection Increase SP02
Reopening of issues Highest incidence SP04
these negative sentiments were not specified.
Impacts of the Negative Discontent Sentiment.
The results of studies by Borges et al. (SP11) show
that three out of four developers consider the number
of stars assigned to GitHub projects before using or
contributing to those projects. The developers com-
mented that the number of stars has a high influence
on their decision of using or contributing to a project.
Impacts of the Negative Rudeness Sentiment.
In the study SP05, the researchers used a tool pro-
posed by Danescu-Niculescu-Mizil et al. (Danescu-
Niculescu-Mizil et al., 2013) to identify a binary out-
put of politeness (polite or uneducated) of particular
text and found that developers who are less active
in open source software projects, when committing
with less polite comments, have a higher likelihood
that your commits will be rejected in the main project
repository. Ortu et al. (SP05) also found that develop-
ers who are less active with lower levels of politeness
were more likely to be unmerged, with a longer re-
viewing process.
Impacts of the Negative Unhappiness Senti-
ment. In the studies SP03 and SP10, Graziotin et al.
extracted sentiments of developers from interviews.
Low productivity was a consequence of the unhappi-
ness most reported by interviews participants.
The result of the research by Graziotion et al.
(SP03 and SP10) show reports that unhappiness is
delaying the execution of process activities: “In both
cases [negative experiences] the emotional toll on me
caused delays to the project”.
In SP03 and SP10, developers declared that un-
happiness caused them to have decreased process ad-
herence, i.e., deviating from the agreed set of prac-
tices. It was reported that unhappiness led developers
to compromise in terms of actions, in order to just get
rid of the job.
Graziotion et al. (SP03 and SP10) stated that un-
happiness causes interruptions in developers’ flow, re-
sulting in adverse effects on the process. As put by a
participant of interview, ”things like that [of unhap-
piness] often cause long delays, or cause one getting
out of the flow, making it difficult to pick up the work
again where one has left off”.
Impacts of Other Negative Sentiments. The re-
searchers of SP02 found that reviews with negative
comments take longer to complete. Negative reviews
required a supplementary time of 1.32 day on aver-
age to be closed than positive ones. In other words,
the average of durations for positive reviews is less
ICEIS 2020 - 22nd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
38
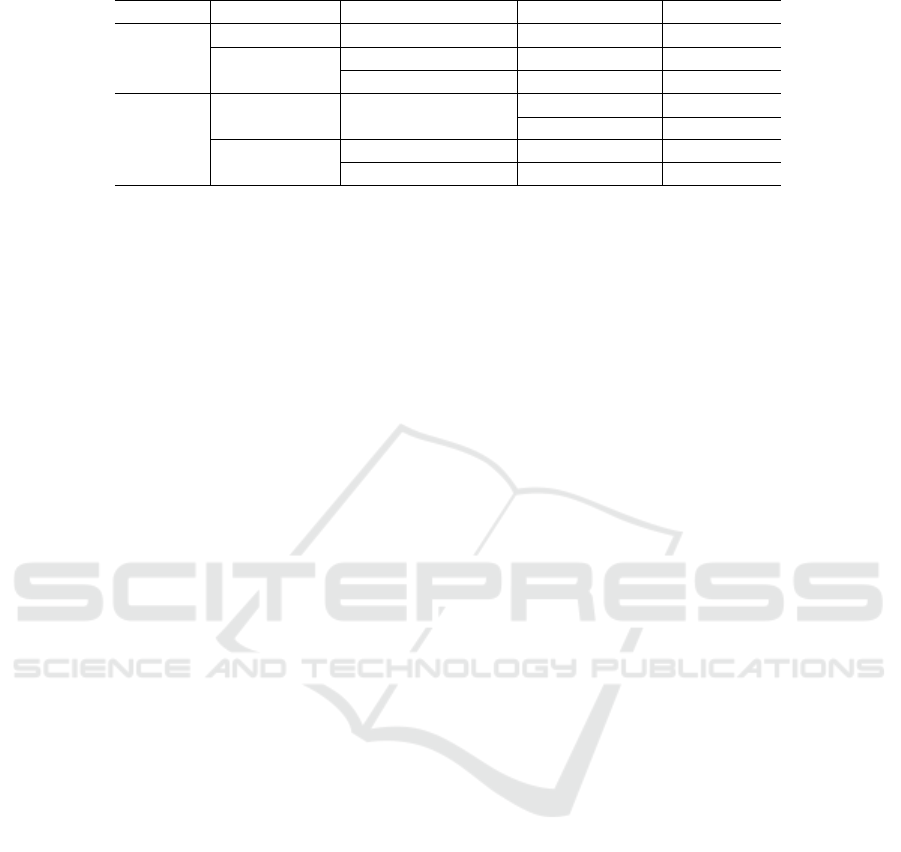
Table 11: Impacts of Sentiments on Software Artifacts.
Polarity Sentiment Software Artifact Impact Studies
Happiness Source code High quality SP10
Positive Not specified Source code Less defective SP06
Commit comments Longer SP09
Unhappiness Source code Low quality SP03, SP10
Deleted SP03, SP10
Negative Not specified Source code More defective SP06
Commit comments Longer SP09
than the average for negative reviews. For instance,
in the Eclipse project, positive reviews last a maxi-
mum of 2.89 days, while reviews containing negative
comments took approximately 5 days of review.
The results from SP02 show that the sentiment ex-
pressed by developers also affects the code review re-
sult. For instance, in Eclipse project, over 93% of
sucessfully merged reviews were tagged as positive,
while 55% out of all abandoned reviews have nega-
tive sentiments into their comments.
Cheruvelil et al. (SP04) found evidence that sug-
gests that negative sentiment correlates with issue re-
opening, although the effect size seems to be rather
small.
4.3 Impacts of Positive Sentiments on
Software Artifacts
The impact of sentiments of programmers in open
source software projects in software artifacts was reg-
istered in the right side of Figure 3. In this case, the
upper right side of the same figure portrays the impact
of positive sentiments.
We observed that 33% of the selected articles indi-
cate that the sentiment of happiness impacts the arti-
facts of open source software projects. Other positive
sentiments affecting artifacts (67%) were not speci-
fied.
Impacts of the Positive Happiness Sentiment.
The high quality of the source code was reported as
a consequence of happiness in the study SP10. The
authors stated that higher quality of code is gener-
ally realized when developers are happy, because they
tend to make less mistakes, see solutions to problems
more easily, and make new connections to improve
the quality of the code. As a result, the code is cleaner,
more readable, better commented and tested, and with
less errors and bugs.
Impacts of Other Positive Sentiments. In the
study SP06, Zhang et al. adopted a Linguistic Inquiry
and Word Count (LIWC) tool (Pennebaker et al.,
1999) to recognize the developers’ sentiment from
email list. It can be observed that the emails whose
emotion value is larger tend to be linked to less defec-
tive source code files.
Islam and Zimbra (SP09) extracted emotions from
the developers’ commit messages using SentiStrength
tool (Thelwall et al., 2012). They found that devel-
opers’ emotions generate statistically significant im-
pacts on the size of commit messages. Developers
post longer comments when they are emotionally ac-
tive.
4.4 Impacts of Negative Sentiments on
Software Artifacts
The bottom right side of the Figure 3 shows evidence
of the impact of negative sentiments on software arti-
facts. Our research has revealed the predominance of
unhappiness (50%) among the sentiments of negative
polarity that impacts the software artifacts produced
by the developers. The other sentiments were not re-
vealed.
Impacts of the Negative Unhappiness Senti-
ment. The result of the interviews conducted by the
authors of SP03 and SP10 revealed that the sentiment
of unhappiness negatively impacts the quality of the
code. The participants reported that “eventually [due
to negative experiences], code quality cannot be as-
sured. So this will make my code messy and more bug
can be found in it”.
In the studies SP03 and SP10, the researchers
stated that programmers discarded the source code
when they were unhappy. Interviewers stated that “I
deleted the code that I was writing because I was a
bit angry”. (...) “I deleted the entire project to start
over with code that didn’t seem to be going in a wrong
direction”.
Impacts of Other Negative Sentiments. In the
study SP09, the authors concluded that when the de-
velopers remain emotionally active, they tend to write
longer commit comments.
Zhang et al., in SP06, realized that the most defec-
tive source code files are related to the email messages
that showed more emotion value from developers.
Impact of Developers Sentiments on Practices and Artifacts in Open Source Software Projects: A Systematic Literature Review
39

5 DISCUSSION
In this section, we answer the research question based
on the results presented during the analysis of the se-
lected studies.
RQ: “What is the impact of sentiments in adopted
software practices and artifacts produced by pro-
grammers in open source software projects?”
The results obtained from the research show the
impacts of developers’ sentiments on software design
practices and artifacts. We realize that positive sen-
timents tend to positively impact software practices
and artifacts. Similarly, negative feelings tend to neg-
atively impact software practices and artifacts. How-
ever, we realize that a positive sentiment can nega-
tively impact, for example, increasing the incidence
of reopening of issues. Or, a negative sentiments can
positively influence, for example, increasing the ac-
ceptance of commits.
Studies show that developers’ sentiments mostly
affect productivity. However, increased productivity
can also be identified by the impact of developers’
sentiments on other practices. For example, reducing
problem correction time increases productivity. Sim-
ilarly, lengthy code reviews decreases productivity.
We realize that the impact of sentiments on soft-
ware practices is often reported when compared to the
impact of sentiments on artifacts. The impacts of de-
veloper sentiments on software artifacts are not ex-
plicitly revealed in most of the articles found. This is
due to the direct relationship of developers with prac-
tices. However the artifacts of software are directly
and indirectly influenced by the sentiments of the de-
velopers through the practices.
Consequences of sentiments in artifacts can affect
software practices. For example, poor quality and
source code disposal can decrease the productivity of
the software development team.
There is then a vicious cycle between software
practices and artifacts that is fed positively or neg-
atively by the sentiments of the developers. These
findings corroborate the understanding of the need for
project managers to engage in promoting a healthy
software development environment.
Studies SP04 and SP09 stand out from the others
because they present a paradox: the impacts caused
by the sentiments revealed by them are the same, re-
gardless of the polarity of sentiment. The results of
SP04 indicated that sentiments with very high posi-
tive or high negative scores have a higher incidence
of reopening of issues. SP09 concluded that develop-
ers tend to write longer comments when they remain
emotionally active (positively or negatively).
The fact that articles SP04 and SP09 have the
same impacts for sentiments of inverse polarity indi-
cates the need for studies on the balance of sentiments
of software developers or on the neutrality of senti-
ments, revealing new possibilities for research in the
area. We found both studies investigating the influ-
ence of sentiments on practices and artifacts as stud-
ies that investigated the influence of practices and ar-
tifacts on sentiments (Zhao et al., 2017) (Singh and
Singh, 2017) (Guzman et al., 2014) (Trainer et al.,
2017).
6 THREATS TO VALIDITY
There are some threats to validity in our study. They
are presented below with the strategies for its mitiga-
tion.
Research Question: Our research questions may
not encompass a full study of the impact of developer
sentiments on open source software project practices
and artifacts. We use the GQM approach to better
define the study objective and research questions.
Search Strings: It is possible that the search
strings we use do not allow the identification of all
studies in the area. We mitigate this threat by expand-
ing the number of electronic repositories searched to
three. All repositories used are specific of the area of
Computing.
Publication Bias: We cannot guarantee that all
relevant primary studies available in electronic repos-
itories have been identified. Some relevant studies
may not have been covered by search strings. We mit-
igate this threat by using alternative search terms and
synonyms of major terms in search strings.
Search Conducted: Each searched electronic
repository has its own search process and we don’t
know how they work or if they work identically. We
mitigate this by adapting the search string for each
electronic repository and assume that equivalent logi-
cal expressions work consistently across all electronic
repositories used.
Data Extraction: The studies were selected ac-
cording to the defined inclusion, exclusion and quality
criteria, but under our judgment. Thus, some studies
may have been selected or not selected incorrectly. To
alleviate this threat, the selection was carried out by
two researchers from different organizations.
7 CONCLUSIONS
This study sought to investigate the impact of devel-
opers’ sentiments on open source software projects.
We conducted a Systematic Literature Review of
ICEIS 2020 - 22nd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
40

peer-reviewed papers available in three electronic
repositories. Analysis of the articles indicated that
sentiments indeed impact on software practices and
artifacts such as productivity, collaboration, and
source code. Evidence indicated to which extent pos-
itive and negative sentiments tend to impact software
practices and artifacts.
Considering that there are sentiments associated
with positive and negative polarity that were marked
as not specified in the selected studies regarding soft-
ware practices, there is still room for further inves-
tigation on the associated sentiments to the specific
impacts. Moreover, there is a tendency of a consider-
able set of open source software projects to have reg-
ular release cycles and to adopted the so called fre-
quent releases. We plan to investigate sentiments in
this context and to which extent they influence soft-
ware productivity. We also want to investigate how
programmers sentiments vary between releases.
REFERENCES
Asri, I. E., Kerzazi, N., Uddin, G., Khomh, F., and Idrissi,
M. J. (2019). An empirical study of sentiments in
code reviews. Information and Software Technology,
114:37 – 54.
Basili, V. R. and Rombach, H. D. (1988). The tame
project: towards improvement-oriented software envi-
ronments. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineer-
ing, 14(6):758–773.
Calefato, F., Lanubile, F., Maiorano, F., and Novielli, N.
(2018). Sentiment polarity detection for software de-
velopment. Empirical Softw. Engg., 23(3):1352–1382.
Cheruvelil, J. and C. da Silva, B. (2019). Developers’ senti-
ment and issue reopening. In 2019 IEEE/ACM 4th In-
ternational Workshop on Emotion Awareness in Soft-
ware Engineering (SEmotion), pages 29–33.
Cruz, S., da Silva, F. Q., and Capretz, L. F. (2015). Forty
years of research on personality in software engineer-
ing: A mapping study. Computers in Human Behav-
ior, 46:94 – 113.
Cruz, S. S. J. O., da Silva, F. Q. B., Monteiro, C. V. F.,
Santos, P., and Rossilei, I. (2011). Personality in soft-
ware engineering: Preliminary findings from a sys-
tematic literature review. In 15th Annual Conference
on Evaluation Assessment in Software Engineering
(EASE 2011), pages 1–10.
Danescu-Niculescu-Mizil, C., Sudhof, M., Jurafsky, D.,
Leskovec, J., and Potts, C. (2013). A computational
approach to politeness with application to social fac-
tors. In Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the
Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1:
Long Papers), pages 250–259, Sofia, Bulgaria. Asso-
ciation for Computational Linguistics.
Dyb
˚
a, T. and Dingsøyr, T. (2008). Empirical studies of agile
software development: A systematic review. Informa-
tion and Software Technology, 50(9):833 – 859.
Graziotin, D., Fagerholm, F., Wang, X., and Abrahamsson,
P. (2017). Consequences of unhappiness while de-
veloping software. In 2nd IEEE/ACM International
Workshop on Emotion Awareness in Software Engi-
neering, SEmotion@ICSE 2017, Buenos Aires, Ar-
gentina, May 21, 2017, pages 42–47.
Guzman, E., Az
´
ocar, D., and Li, Y. (2014). Sentiment
analysis of commit comments in github: An empirical
study. In Proceedings of the 11th Working Conference
on Mining Software Repositories, MSR 2014, pages
352–355, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Islam, M. R. and Zibran, M. F. (2017). Leveraging auto-
mated sentiment analysis in software engineering. In
Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on
Mining Software Repositories, MSR ’17, pages 203–
214, Piscataway, NJ, USA. IEEE Press.
Lenberg, P., Feldt, R., and Wallgren, L. G. (2015). Behav-
ioral software engineering: A definition and system-
atic literature review. Journal of Systems and Soft-
ware, 107:15 – 37.
Michlmayr, M., Fitzgerald, B., and Stol, K.-J. (2015). Why
and how should open source projects adopt time-based
releases? IEEE Software, (2):55–63.
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., Group,
P., et al. (2009). Preferred reporting items for system-
atic reviews and meta-analyses: the prisma statement.
PLoS medicine, 6(7):e1000097.
Pennebaker, J., Francis, M., and Booth, R. (1999). Linguis-
tic inquiry and word count (liwc).
Santos, C., Kuk, G., Kon, F., and Pearson, J. (2013). The
attraction of contributors in free and open source soft-
ware projects. The Journal of Strategic Information
Systems, 22(1):26–45.
Singh, N. and Singh, P. (2017). How do code refactoring
activities impact software developers’ sentiments? -
an empirical investigation into github commits. In
2017 24th Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Confer-
ence (APSEC), pages 648–653.
Singh, V., Sharma, M., and Pham, H. (2017). Entropy
based software reliability analysis of multi-version
open source software. IEEE Transactions on Software
Engineering.
S
´
anchez-Gord
´
on, M. and Colomo-Palacios, R. (2019). Tak-
ing the emotional pulse of software engineering — a
systematic literature review of empirical studies. In-
formation and Software Technology, 115:23 – 43.
Socher, R., Perelygin, A., Wu, J., Chuang, J., Manning,
C. D., Ng, A., and Potts, C. (2013). Recursive deep
models for semantic compositionality over a senti-
ment treebank. In Proceedings of the 2013 Conference
on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Process-
ing, EMNLP 2013, pages 1631–1642, Seattle, Wash-
ington, USA. Association for Computational Linguis-
tics.
Soomro, A. B., Salleh, N., Mendes, E., Grundy, J., Burch,
G., and Nordin, A. (2016). The effect of software en-
gineers’ personality traits on team climate and perfor-
mance: A systematic literature review. Information
and Software Technology, 73:52 – 65.
Stol, K.-J. and Fitzgerald, B. (2015). Inner source–adopting
open source development practices in organizations: a
tutorial. IEEE Software, 32(4):60–67.
Impact of Developers Sentiments on Practices and Artifacts in Open Source Software Projects: A Systematic Literature Review
41

Stone, P. W. (2002). Popping the (pico) question in re-
search and evidence-based practice. Applied Nursing
Research, 15(3):197 – 198.
Thelwall, M., Buckley, K., and Paltoglou, G. (2012). Senti-
ment strength detection for the social web. J. Am. Soc.
Inf. Sci. Technol., 63(1):163–173.
Trainer, E. H., Kalyanasundaram, A., and Herbsleb, J. D.
(2017). e-mentoring for software engineering: A
socio-technical perspective. In Proceedings of the
39th International Conference on Software Engineer-
ing: Software Engineering and Education Track,
ICSE-SEET ’17, pages 107–116, Piscataway, NJ,
USA. IEEE Press.
Wohlin, C. et al. (2012). Experimentation in Software En-
gineering. Springer-Verlag.
Zhao, M., Wang, Y., and Redmiles, D. F. (2017). Using
playful drawing to support affective expressions and
sharing in distributed teams. In 2nd IEEE/ACM Inter-
national Workshop on Emotion Awareness in Software
Engineering, SEmotion@ICSE 2017, Buenos Aires,
Argentina, May 21, 2017, pages 38–41.
APPENDIX A. List of Selected Papers
SP01 & Johri, A. and Teo, H. J. (2018). Achieving
equilibrium through coworking: Work-life balance
in floss through multiple spaces and media use. In
Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium on
Open Collaboration, OpenSym ’18, pages 7:1–7:11,
New York, NY, USA. ACM.
SP02 & Asri, I. E., Kerzazi, N., Uddin, G.,
Khomh, F., and Idrissi, M. J. (2019). An empirical
study of sentiments in code reviews. Information and
Software Technology, 114:37 – 54.
SP03 & Graziotin, D., Fagerholm, F., Wang,
X., and Abrahamsson, P. (2017). Consequences
of unhappiness while developing software. In
2nd IEEE/ACM International Workshop on Emo-
tion Awareness in Software Engineering, SEmo-
tion@ICSE 2017, Buenos Aires, Argentina, May 21,
2017, pages 42–47.
SP04 & Cheruvelil, J. and C. da Silva, B. (2019).
Developers’ sentiment and issue reopening. In 2019
IEEE/ACM 4th International Workshop on Emo-
tion Awareness in Software Engineering (SEmotion),
pages 29–33.
SP05 & Ortu, M., Hall, T., Marchesi, M., Tonelli,
R., Bowes, D., and Destefanis, G. (2018). Mining
communication patterns in software development: A
github analysis. In Proceedings of the 14th Interna-
tional Conference on Predictive Models and Data An-
alytics in Software Engineering, PROMISE’18, pages
70–79, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
SP06 & Zhang, Y., Shen, B., and Chen, Y. (2014).
Mining developer mailing list to predict software de-
fects. In 2014 21st Asia-Pacific Software Engineering
Conference, volume 1, pages 383–390.
SP07 & Yang, B., Wei, X., and Liu, C. (2017).
Sentiments analysis in github repositories: An empir-
ical study. In 2017 24th Asia-Pacific Software En-
gineering Conference Workshops (APSECW), pages
84–89.
SP08 & Wang, Y. and Redmiles, D. (2016). The
diffusion of trust and cooperation in teams with in-
dividuals’ variations on baseline trust. In Proceedings
of the 19th ACM Conference on Computer-Supported
Cooperative Work & Social Computing, CSCW ’16,
pages 303–318, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
SP09 & Islam, M. R. and Zibran, M. F. (2016).
Towards understanding and exploiting developers’
emotional variations in software engineering. In 2016
IEEE 14th International Conference on Software En-
gineering Research, Management and Applications
(SERA), pages 185–192.
SP10 & Graziotin, D., Fagerholm, F., Wang, X.,
and Abrahamsson, P. (2018). What happens when
software developers are (un)happy. Journal of Sys-
tems and Software, 140:32 – 47.
SP11 & Borges, H. and Valente, M. T. (2018).
What’s in a github star? understanding repository
starring practices in a social coding platform. Jour-
nal of Systems and Software, 146:112 – 129.
ICEIS 2020 - 22nd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
42
