
A Smart Energy Management System for Cross-sectoral Coupling
and Water-energy Nexus
Venkatesh Pampana, Pragya Kirti Gupta and Markus Duchon
fortiss GmbH, Guerickestr. 25, 80805 Munich, Germany
Keywords: Energy Management System, Water-energy Nexus, Cross-sectoral Coupling, Software Architecture, IoT,
Smart City.
Abstract: Cross-sectoral coupling is one of the newly emerging research topics that refers to the idea of interconnecting
and integrating the energy consuming sectors like buildings (heating and cooling), transport, water supply
systems and other energy intensive process with the power-producing sector. The cross-sectoral integration
of the water-energy nexus and the sustainability issues surrounding the availability of clean water and energy
has drawn the attention to the problem from all around the globe. Smart decision-making and control systems
can improve the efficiency of the overall operation of both water and energy systems. At a technological level,
there have been attempts to optimize coupling points between the electricity and water systems to increase
efficiency of both. Most of the optimization and smart decision-making systems focus on energy system and
consider heterogeneous infrastructure in the form of energy consumption devices. In the scope of water-
energy nexus, energy efficient decisions would have implications on water infrastructure. Tools and platforms
for water-energy nexus are required, such that planning and executing the decisions and their implications on
both energy and water infrastructure can be seen. Most of the existing controllers are specifically designed to
efficiently serve either energy or water systems. In this paper, we propose a software architecture for the
platform that is capable of monitoring, controlling, decision making and analysing the effect of decisions for
water and energy nexus.
1 INTRODUCTION
Water-energy nexus is the concept that refers to the
relationship between the water used for energy
production, including both electricity and fuel sources
such as oil and natural gas, and the energy consumed
to extract, purify, deliver, heat/cool, and dispose of
water and wastewater (Spang et al., 2014). It is
inextricably linked to the core of environmentally
sustainable smart cities as shown in Figure 1. Clean
and sustainable water supplies and low carbon energy
access are the essential building blocks for
economies, health and quality of life.
Present day energy and water systems are
interdependent and have to be addressed together
(Olsson, 2012). Extraction, treatment, carriage and
management of drinking water and treatment of
wastewater are both dependent on a substantial
amount of electrical energy. Huge volumes of water
are drawn and consumed from water bodies every day
for electricity generation. Rapid population growth,
increased per capita demand, distortion of availability
of fresh water due to climate change is driving up the
demand for both electricity and water. These trends
raise concerns about the robustness and sustainability
of today's electricity and water systems over the
coming decades.
Scarcity in either water or energy will create
aggravated shortages in both. An appreciation of the
scale of the challenge presented by the energy-water
nexus can be acquired by a consideration of the
degree of coupling between the two systems.
The demand on water resources in the urban
environment requires more efficient water
management to deal with urbanization and population
growth, more complex water facilities in new
buildings, and the deterioration of existing water
infrastructure. There is an urgent need to (a) reduce
the water extracted for use in buildings, (b) promote
water savings, and (c) stop wastage. The ability to
provide appropriate means to intelligently monitor
the water network and analyze real time information
with the help of smart technologies will provide
optimized alternatives to take better actions to
Pampana, V., Gupta, P. and Duchon, M.
A Smart Energy Management System for Cross-sectoral Coupling and Water-energy Nexus.
DOI: 10.5220/0009361901070113
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems (SMARTGREENS 2020), pages 107-113
ISBN: 978-989-758-418-3
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
107

balance the conflict between water demand and
provision.
Figure 1: Water-energy nexus: Building blocks for a
sustainable smart city.
The present day water management and energy
management are primarily centrally controlled
without any interlinking between both of them. The
central control is usually susceptible to downtimes
due to latency, connection loss, damage etc. Current
management systems, often, pose water quality
concerns, complex coordination issues between
energy savings, and operational and maintenance
issues (Cherchi et al., 2015). A loosely coupled,
distributed control and monitoring environment is
needed for betterment in both water and energy
management. A distributed control with central
coordination can produce a localized and robust
control with a platform that collects and analyzes
more data.
It is possible to address the water-energy nexus by
advanced energy efficiency and water management
algorithms, distributed monitoring and control
strategies, state-of-the-art metering infrastructure,
and optimal utilization of distributed energy
resources. Through the pervasive deployment of the
Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced Information
and Communication Technologies (ICT), big energy
data will be generated in terms of volume, speed, and
variety. Smart data analysis of this data can bring
enormous benefits to the energy efficiency and
management (Pindoriya et al., 2018). However, it
must be processed and communicated in an energy
efficient manner.
It is important to note that the challenges
presented by the energy-water nexus and sector
coupling are location specific. The mix of available
water sources, electricity generation options, local
effects of climate change, and societal requirements
together determine the sustainability and robustness
concerns associated with the nexus. This paper
presents an architecture for the platform that is
capable of monitoring, controlling, decision making
and analyzing the effect of decisions for water and
energy nexus through sector coupling. Section II
presents a brief review of issues covered in various
publications on or related to the energy-water nexus
and sector coupling. In Section III, system context,
application area, requirements and proposed system
architecture. Section IV offers some insights of the
proposed platform. Section V concludes the work and
presents potential directions for future work.
2 BACKGROUND
Water management primarily focuses on the
following aspects 1) Improving allocation through
quicker decision-making and control. 2)
Conservation of the resources (energy, water, and
other natural resources) available by improving the
efficiency and recycling the wastewater. Energy
management focuses on 1) Saving energy by
metering the energy consumption and collecting the
data. 2) Reducing dependence on the fossil fuels that
are becoming increasingly limited in supply. 3)
Optimal utilization of Renewable and distributed
energy resources (BizEE Energy Lens, 2019).
Literatures (Public Utilities Board Singapore,
2016; Diniz et al., 2015) discuss the strategies to
improve the energy efficiency of the water supply
systems. Energy management strategies using short-
term water consumption forecasting and computer
modelling to minimize cost of pumping operations
has been explored in (Jentgen et al., 2007; Bagirov et
al., 2015) respectively. Studies have successfully
demonstrated that integrated energy and water
management system provides a number of economic,
environmental and operational benefits, without
compromising on water quality and energy supply
objectives (Cherchi et al., 2015; Jentgen et al., 2007;
Douville & Macknick, 2011).
However, there are limited studies addressing the
water-energy nexus using sector coupling (Green et
al., 2017; Vakilifard et al., 2018). Most of the
approaches highlight the challenges and the need for
integration of renewable energy usage for multiple
sectors like food, water, agriculture etc. None of the
approaches proposed suitable platform architecture
for an integrated energy and water management
system.
SMARTGREENS 2020 - 9th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
108
In this work, we propose an approach where we
address the integrated energy and water management
system by linking various branches of the energy
sector (sector coupling) and utilizing the ICT,
distributed monitoring and optimal utilization and
control of distributed energy resources (renewable
energies and energy storage) for water infrastructure.
Additionally, we propose a software architecture for
the platform that is capable of monitoring,
controlling, decision making and analyzing the effect
of decisions for water and energy nexus.
3 ARCHITECTURE OVERVIEW
A Smart Energy Management System for cross-
sectoral coupling and water-energy nexus should
meet following requirements:
Real-time monitoring support: collecting and
analyzing data from various sensors.
Support multi-communication protocol: In
order to seamlessly integrate with various field
devices and sensors irrespective of their
communication protocol.
Smart decisions based on collected data:
Making smart decisions based on the advanced
optimization techniques and data analysis.
Distributed controlling: To control complex
processes that can be geographically
disseminated using networked control elements
that are distributed throughout the system.
Modular in nature: Easy to maintain, deploy,
update, and develop the software code
components.
Flexible and Scalable: Scalable from building
level to city/municipality level
A service-oriented architecture with open
standard protocols, event-driven programming
model, service bus, and integrative computational and
data infrastructure is well suited for building robust
smart energy management system for water-energy
nexus (Mora et al., 2012; Berres et al., 2017) [11, 12].
We propose a generic architecture for such Energy
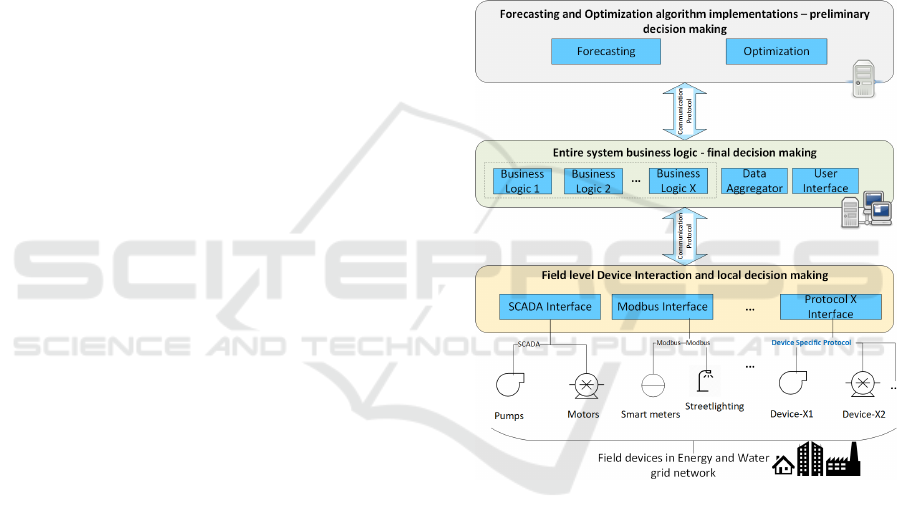
Management System presented in the Figure 2.
The bottom layer has software components
interfacing with the physical hardware devices such
as advanced metering, SCADA devices, IoT sensors
connected at the major process equipment in the
critical infrastructures like Water Treatment Plant
(WTP), Sewage Treatment Plant (STP), street
lighting system etc. that are spread spatially across the
field. This layer is primarily intended for realtime
monitoring and controlling of the field devices.
Custom monitoring and local control logic are
embedded in the interfaces that can exchange data in
device specific protocol (such as MODBUS, REST
API, OPC UA, MBUS, MQTT etc.). It is distributed
in nature with each interfacing component act
standalone. So malfunctioning of any of the
components does not affect the rest of the
components. It is also capable of local decision
making in case of communication
interruption/failures with higher level components or
in emergency situations. These components act as
controllers for respective field devices with which
they communicate. Due to this semi-autonomous
capability of this layer, distributed controlling is
made possible.
Figure 2: Proposed architecture for Energy Management
System for cross-sectoral coupling and water-energy nexus.
Middle layer consists of business logic
components. It receives the inputs from bottom layer
components and forwards it to higher level
components for preliminary decision making.
Though it usually follows the decisions from higher-
level components, during exceptional situations, it
has the final say over how the field devices should
behave. This would help in handling the exceptional
flow of events. One business logic component may
interact with multiple device interfacing components
in the bottom layer.
The improvement of energy efficiency and
effectiveness of water management and optimal
utilization of energy/water can be achieved by
A Smart Energy Management System for Cross-sectoral Coupling and Water-energy Nexus
109

incorporating advanced optimization algorithms and
techniques. Top layer has forecasting and
optimization components based on advanced data
analytics, machine learning techniques, and multi-
dimensional statistical tools. For example,
implementation of optimization components for an
array of energy cost reduction strategies operating
within designated constraints.
4 CASE STUDY
The testbed is located in GIFT City – Gujarat
International Finance Tech City of Gujarat, India. The
GIFT city envisions a smart city infrastructure with
efficient water and energy distribution networks in a
distributed manner. The testbed comprises of a WTP
and street lighting cluster (which is also located close
to WTP) as shown in the Figure 3. Water
infrastructure in GIFT is designed to provide
“potable-water-in-all-taps” with the total water
requirement of over 60 Million Litters per day
(MLD). The present process of WTP consists mainly
of the filtration process, dual media filters (made up
of sand and gravel) and micro cartridge filters. Dosing
is one of the main tasks in chemical and process
engineering in water treatment and as a result, hypo
dosing pumps (HDPs) and air compressors are used
in WTP.
The energy intensive loads like Hypo dosing
pump, Air compressor, etc. are connected to Water
treatment plant (WTP) feeder. Along with the WTP
loads, Solar Photovoltaic (PV) panels with Inverters
and Batteries are also connected to the feeder.
Similarly, Streetlights, Solar PV panels with inverter
and battery are connected to Street lighting feeder.
Additionally, there are interconnecting switches
connected to both feeders that facilitate switching of
batteries from one feeder to the other.
It has been observed that electricity generation
from renewable sources can be used to operate
processes like water supply, sewage plant, street
lighting etc. whereas in case of oversupply of
electricity from renewable sources, water pump or
other city processes can be made operational, thus
making the balance of supply and demand in the
system. This can be achieved by developing an
intelligent optimization framework and integrated
into the system. To check viability and feasibility,
couple of use cases were identified at the Testbed
based on load demand, operating duration, and
switching on-off pattern.
Figure 3: Testbed and use cases at GIFT city.
4.1 Use Cases
4.1.1 Use Case-1
Solar PV and Battery Energy Storage System (BESS)
installations will be utilized effectively to fulfil the
energy demand of the HDP at WTP in GIFT city.
Therefore, it can be anticipated that, by automating
the process control and energy flow to HDP, the
dosing process at WTP is well maintained. At the
same time, by effectively utilizing the solar PV and
BESS systems, the power drawn from the utility grid
can be reduced considerably which will eventually
reduce the operating cost. Similarly, Intelligent street
lighting also has significant potential in energy saving
for smart cities. An additional solar PV and BESS
system installations at GIFT city will be utilized to
supply power to the street light cluster. By automating
the process of energy flow and switching of street
lighting systems, a significant reduction in operating
cost and power drawn from the utility can be
achieved.
The main objective of this use case is to maximize
the use of solar PV system and battery to support the
load of HDP and air compressor in WTP and
minimize the overall cost of energy purchased from
the grid.
4.1.2 Use Case-2
Intelligent sharing of energy between multiple
batteries can further enhance the efficient utilization
of Battery storage systems. This can be achieved by
switching the batteries between the feeder lines (WTP
and Street lighting feeders) based on certain
optimization criteria and reducing the energy utilized
from the power grid. By this way, operation costs and
dependency towards the grid can be further reduced.
SMARTGREENS 2020 - 9th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
110

4.2 System Architecture
A flexible, extensible, lightweight and self-similar
architecture has been deployed at the testbed in order
to implement the identified use cases that were
mentioned above. It follows a layered and
component-based approach to ensure scalability,
flexibility and extensibility with state-of-the-art
communication protocols. An overview of the system
is illustrated in Figure 4.
Figure 4: Software architecture of proposed integrated
water and energy management platform at the Testbed.
The Layer-1 and Layer-2 components are
developed based on an in-house energy management
tool called iEMS. The intelligent Energy
Management System (iEMS) is a decentralized and
distributed energy management system developed in
JAVA programming language. It can be used in micro
grid networks to intelligently manage the energy
resources and connected loads. The iEMS software
application is based on the OSGi framework, which
provides ease of development and deployment of
isolated services. These services or bundles can be
added, removed, or replaced at runtime without
interfering with the overall system at runtime. By
using a modular and component-based approach, we
ensure a highly flexible deployment of the system.
Hence, iEMS can be deployed across several
machines as a distributed system. It supports
numerous hardware. For example, Raspberry Pi,
Beagle Bone, Desktop computers, laptops, embedded
servers etc.
The iEMS core components include library
bundles responsible for information exchange,
database management, message bus interfacing
components, user management, and overall system
health check monitoring components. All the
components exchange information and data through
RabbitMQ message bus.
The bottom layer (Layer-1) has iEMS instances
along with interfacing components (Modbus client
and OPC UA client) that can communicate with field
devices at the water treatment plant and street lighting
cluster. The data is exchanged with aeration blower,
hypo dosing pump, air compressor, and energy meters
over MODBUS protocol, street lighting using REST
protocol and batteries through the OPC UA protocol.
Plant. WTP bundle measures the energy consumption
of hypo dosing pumps, compressor and monitor the
battery parameters (like State-of-Charge, voltage,
temperature, etc) from battery management system
(BMS). The IEC 61499 standard compliant 4DIAC
application is deployed in batteries, which interacts
with battery management system and helps in
monitoring and controlling of batteries over OPC UA
interface. Plant. Streetlight software bundle monitors
the energy consumption of streetlight and battery’s
SOC. Instances of iEMS and other components in this
layer are deployed on Raspberry PIs and are located
close to the field devices.
Layer-2 also consists of instances of iEMS along
with additional components. It receives the measured
data as inputs and forwards it to Optimizer
component for decision-making. The business logic
and flow of events are embedded in this layer. The
business logic components with respect to identified
use cases (BusinessLogic.Usecase1 and
BusinessLogic.Usecase2) are included in this layer.
They act as coordinators. The control signals are sent
to field devices via the components at Layer-1.
Further use cases, which would be identified in the
future, would also be included in this layer.
Decision making involves planning capabilities,
which are provided by the top most layer (Layer-3).
Optimization and forecasting algorithms are
implemented (Generation. Forecast, Demand.
Forecast and Optimizer) using machine learning
algorithms and optimization tools. The energy
optimization algorithms are implemented in GAMS
(General Algebraic Modeling System) and MATLAB
tools. A special interfacing tool has been developed
to integrate and communicate GAMS and MATLAB
tools with the OPC UA server.
The communication channels and protocols at the
testbed are chosen based on various considerations
such as distance between the plants, physical location
of field devices, support to the protocol by different
hardware and data latency requirements. Most of the
A Smart Energy Management System for Cross-sectoral Coupling and Water-energy Nexus
111

installed hardware supports MODBUS or OPC UA
communication protocol. The bottom level software
components (Layer-1) are deployed on Raspberry Pis
and higher level components (Layer-2 and Layer-3)
are deployed in Windows operating system based
workstations. The Raspberry Pis and workstations are
connected through Ethernet/LAN cables. Information
exchange between all the three layers would happen
through the OPC UA protocol.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Coupling of cross-commodity infrastructure and
optimal integration of distributed energy resources is
a challenge for smart cities. In this paper, we
presented an integrated water and energy
management platform architecture to manage the
water and energy infrastructures at GIFT city using
ICT. The testbed identified for this study are STP,
WTP, and street light clusters attached to WTP which
are energized by solar PV, BES, and utility grid. A
detailed description of the testbed is also presented
and then the use cases with their functional
requirements from the test bed have been identified.
A three layered component based architecture has
been proposed to address the energy management and
real time control of the use cases where a multilevel
controlling and monitoring system is proposed. The
proposed platform has the advantage of supporting
heterogeneous device protocols, flexible deployment
of the system, eliminating the latency and interruption
in management of infrastructure. Therefore, an
efficient and uninterrupted water and energy
distribution is possible at the testbed.
As a future step, the implementation will be
carried out in the real environment to test the data
collection and the controlling based on the
optimization values. Furthermore, new use cases will
be identified and proposed platform will be evaluated
through further research work in the future.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is being carried out for on-going research
project called ECO-WET (FKZ 01DQ17020A),
under the flagship of IGSTC (Indo-German Science
and Technology Centre). The Authors would like to
thank Federal Ministry of Education and Research
(BMBF, Germany) and Department of Science and
Technology (DST, India) for funding the research and
development activities of the project.
REFERENCES
Spang, E. S., Moomaw, W. R., Gallagher, K. S., Kirshen,
P. H., and Marks, D. H. (2014). The water consumption
of energy production: an international comparison.
Environmental Research Letters, 9(10), 105002.
G. Olsson 2012. Water and Energy: Threats and
Opportunities. London: IWA Publishing, 2012.
Cherchi, C., Badruzzaman, M., Oppenheimer, J., Bros, C.
M., & Jacangelo, J. G. (2015). Energy and water quality
management systems for water utility’s operations: A
review. Journal of Environmental Management, 153,
108–120.
Pindoriya, N., Duchon, M., Gupta, P. K., Pampana, V.,
Singh, S. N., Giza, J., Hackenberg, B., Rajput, A. K.,
Jethi, J. 2018. Intelligent Hardware-Software Platform
for Efficient Coupling of Water-Energy Nexus in Smart
Cities: A Conceptual Framework. In Proceedings of
Mobility IoT (Guimarães, Portugal, November 21-23,
2018).
BizEE Energy Lens. (2019). The What, Why, and How of
Energy Management. (March 2001). Retrieved October
16, 2019 from https://www.energylens.com/articles/
energy-management.
Public Utilities Board Singapore Pan_Ju_Khuan@ pub.
gov. sg. (2016). Managing the water distribution
network with a Smart Water Grid. Smart Water, 1, 1-
13.
Diniz, A. M. F., de Oliveira Fontes, C. H., Da Costa, C. A.,
& Costa, G. M. N. (2015). Dynamic modeling and
simulation of a water supply system with applications
for improving energy efficiency. Energy Efficiency,
8(2), 417-432.
Jentgen, L., Kidder, H., Hill, R., & Conrad, S. (2007).
Energy management strategies use short‐term water
consumption forecasting to minimize cost of pumping
operations. Journal ‐ American Water Works
Association, 99(6), 86-94.
Bagirov, A. M., Barton, A. F., Mala-Jetmarova, H., Al
Nuaimat, A., Ahmed, S. T., Sultanova, N., &
Yearwood, J. (2013). An algorithm for minimization of
pumping costs in water distribution systems using a
novel approach to pump scheduling. Mathematical and
Computer Modelling, 57(3-4), 873-886.
Douville, C., & Macknick, J. (2011, January). Energy
Usage and Management at a Large Wastewater
Treatment Facility in Boulder, Colorado. In ASME
2011 International Mechanical Engineering Congress
and Exposition (pp. 653-659). American Society of
Mechanical Engineers.
Green, Jennifer, Amit Gandhi, Éadaoin Ilten, Brennan
Lake, Vandana Pandya, Sara Lynn Pesek, Jonars
Spielberg, and Christina Sung (2017). "Reports from
CITE" Solar Powered Water Pumps Evaluation in
India".".
Vakilifard, Negar, Martin Anda, Parisa A. Bahri, and Goen
Ho (2018). "The role of water-energy nexus in
optimising water supply systems–Review of techniques
SMARTGREENS 2020 - 9th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
112

and approaches." Renewable and Sustainable Energy
Reviews 82: 1424-1432.
Mora, D., Taisch, M., Colombo, A. W., & Mendes, J. M.
(2012, July). Service-oriented architecture approach for
industrial “system of systems”: State-of-the-art for
energy management. In IEEE 10th International
Conference on Industrial Informatics (pp. 1246-1251).
IEEE.
Berres, A., Karthik, R., Nugent, P., Sorokine, A., Myers,
A., & Pang, H. (2017, December). System Architecture
Development for Energy and Water Infrastructure Data
Management and Geovisual Analytics. In AGU Fall
Meeting Abstracts.
A Smart Energy Management System for Cross-sectoral Coupling and Water-energy Nexus
113
