
Human-agents Interactions in Multi-Agent Systems: A Case Study of
Human-UAVs Team for Forest Fire Lookouts
Sagir Muhammad Yusuf and Chris Baber
∗
University of Birmingham, B15 2TT, U.K.
Keywords:
Human-agent Team, Mixed-initiative Reasoning, Bayesian Learning, Mixed-initiative Planning.
Abstract:
In this paper, we propose an architecture that uses predictions tools obtained via Bayesian learning algorithms
to monitor the issues of communication, fault tolerance, and adaptation in human-agent mission. The archi-
tecture describes different level of knowledge, planning, and commands differ by their priorities. We tested
the model using forest fire lookouts problem on a simulation platform (AMASE). The process uses the conju-
gate gradient descent algorithm to perform the Bayesian Belief Network training. The output of the training
process is a well-trained BBN for agents’ prediction, estimation, and decision making during communication
failure. The prediction perfection of the human and agents were compared and studied. Although results proof
that human approach is prone to error but is good in terms of emergency commands execution. We suggested
that the use of a well-trained prediction tool (i.e., the output BBN) could be used in monitoring mission during
communication link, hardware, or software breakdown.
1 INTRODUCTION
The human-agents team is applicable in many real-
world applications such as health care system (Kifor
et al., 2006), customer service system (Tecuci et al.,
2007), disaster management (Cacace et al., 2014), etc.
During the interaction, both participants need to be
supportive to each other in order to have a collabora-
tive system. A fully collaborative system tries to bal-
ance the knowledge and reasoning between the agents
and the human experts. Unlike intelligent assistant
where human has knowledge but consult agent for
manipulation purposes or its opposite tutorial assis-
tant (Rich and Sidner, 2007). In order to achieve that,
several issues exist such as effective task distribution,
communication, awareness, control, structuring, eval-
uation, adaptation (Makonin et al., 2016; Tecuci et al.,
2007), and fault tolerance. We here discuss the prob-
lems sequentially.
Task distribution refer to the way of segment-
ing the task and choosing the task performer (Turpin
et al., 2014). That is the issue of who does what
task. The problem becomes complicated in hetero-
geneous agents management because of the presence
of different types of agents. Communications refer to
the mode of receiving commands and knowledge be-
∗
https://www.Birmingham.ac.uk/staff/profiles/computer-
Science/baber-Chris.aspx
tween the collaborative participants (i.e., human-and
the agents) during the mission (Makonin et al., 2016).
It mostly occurs via the use of Graphical User Inter-
face (GUI) structured in what-next approach. Aware-
ness refers to how the human and agents understand
the current situation. That is the level of knowledge
of the participants about the current condition of the
environment (Tecuci et al., 2007). A more advance
approach is reasoning the current situation and pre-
dicting the near future events known as the Situation
Awareness (Endsley, 1995). Control refers to who
will take over initiative at a particular time (Tecuci
et al., 2007). It is the question of who is the cur-
rent boss. Structuring issues refers to the architec-
tural design of the human-agent system. That is how
the component of the system was organised (Makonin
et al., 2016). Evaluation refers to the critical analy-
sis of the participants’ tasks and the expected benefits
in-between the human and the agents (Tecuci et al.,
2007). Adaptation refers to how the agents and the
human learn their environment and mode of opera-
tions (Makonin et al., 2016). The seven aforemen-
tioned aspects refer to the essential aspects of human-
agent interaction, they relied on an effective commu-
nication platform. We suggest the consideration of
hardware or software failure during the interaction
process that could result in communication failure.
These challenges were itemised and solved in
Yusuf, S. and Baber, C.
Human-agents Interactions in Multi-Agent Systems: A Case Study of Human-UAVs Team for Forest Fire Lookouts.
DOI: 10.5220/0009369203470354
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2020) - Volume 1, pages 347-354
ISBN: 978-989-758-395-7; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
347

many kinds of literature works with the assumptions
of reliable hardware, software, and communication
link(Bevacqua et al., 2015; Cacace et al., 2014; Fer-
guson and Allen, 2007). In this paper, we recommend
the consideration of hardware or software breakdown
(i.e., fault tolerance) that could result in communica-
tion and awareness updates failure. Fault tolerance is
the ability of the team to manage any unexpected inci-
dent such as communication link breaking, hardware,
or software error, and all other sort of Byzantine fail-
ures (Araragi, 2005). Therefore, we intend to answer
the following questions in human-agent interaction.
• Is there any approach for tackling communication
failure in human-agent team?
• In the presence of faulty communication link,
hardware, or software, could agents and human
team maintain the same environmental awareness
through appropriate adaptation?
The first question was thrown on the effect of com-
munication failure during the human-agent mission
and how it affects both agent and human knowledge
of the environment. This could be categorised into
two levels. (1) agent-to-agent updates problem, espe-
cially in a multi-agent system, and (2) human-agent
update. For instance, one could wonder the outcome
of human-UAV surveillance mission with communi-
cation failure in the middle of the mission. The mis-
sion could face the following challenges:
• Incomplete data and command management: it
happens when an agent or human proposes a com-
mand, then the command was not successfully re-
ceived or executed due to communication failure
occurrence.
• Agents power management.
• Lack of supportive knowledge: because of com-
munication breakdown, the agents and human will
lack supportive advice. For example, if the agents
are familiar with their environment, they can be
able to suggest some supportive ideas and insights
about any destructive actions of human experts
and vice versa.
To address the aforementioned issues, we propose a
model architecture that utilises collaborative activities
in a human-agent team using Bayesian inference and
learning. Its constraints are the absence of commu-
nication and the prediction accuracy of the predictive
tools for effective system Situation Awareness main-
tenance.
2 RELATED WORK
In human-agent team, agents are capable of making
huge computations, navigation, and large data collec-
tion, etc. within a short period while the human expert
is intelligent enough to extract the information, and
control the mission cognitively (Makonin et al., 2016;
Rich and Sidner, 2007; Tecuci et al., 2007). A chal-
lenge therefore arises in controlling the human-agent
activities such as control, task allocation, communi-
cation, etc within the system.
Different architectures were proposed in manag-
ing aspects of human-agent team management. For
instance, system control can be managed using par-
allel or full execution. In parallel control, the agents
and the human experts learn concurrently and evalu-
ate their outcomes against the objective function satis-
factions on a time-to-time basis (Tecuci et al., 2007).
After the parallel execution, the agents and the hu-
man learn their errors an avoid them in future mis-
sions based on prioritised tasks. Example of sys-
tems that implement such techniques are Diamond-
Help and Collagen (Rich et al., 2001; Rich and Sid-
ner, 2007) .
Overall control involves the precise observation of
the co-participant’s actions and learns from their ac-
tions. The user may guide the agent about the current
situation of the environment, while at the background;
the agent is learning and correcting its errors and mis-
takes. The same thing goes to the human expert in the
absence of enough knowledge; the agent can guide
him/her using a what-next strategy as in RESIN (Yue
et al., 2010), PerCon (Su, ), 2014), ForceSpire (Endert
et al., 2014), and ALIDA (Green et al., 2010). Other
aspects, such as adaptation, awareness, control, evalu-
ation, and system design, were addressed in (Makonin
et al., 2016; Tecuci et al., 2007).
This paper suggests the consideration of system
components failures that could result in communica-
tion, awareness, and adaptation problems. For exam-
ple, imagine a communication failure in human-UAV
team mission at a separation distance of 2 kilometres
with critical battery conditions. How does the agents
that rely on human-expert for control could save the
mission by continuing with the tasks and ensure per-
fect mission delivery? Is there any balanced platform
for monitoring the teams at the absence of the com-
munications links? We pay more emphasis on this
issue and propose a model that will maintain the bal-
ance between the two mission’s participants. This
model uses an accurate predictive tool that handles
uncertainties and runs a parallel system with synchro-
nisation, unlike the traditional approach of recovery.
Regarding awareness handling, DiamondHelp and
HAMT 2020 - Special Session on Human-centric Applications of Multi-agent Technologies
348
Collagen system (Rich et al., 2001; Rich and Sidner,
2007) uses a chat window to maintain the current un-
derstanding of the environment. While the STC sys-
tem learns from the previous users’ experience in line
with commands execution. The propose model varies
by focusing more attention on the accuracy of the pre-
diction tooland current situation awareness analysis
of the system during components failure. The model
tackles the awareness problem using two approaches:
• Analysing current situation.
• Making effective predictions and estimations on
the future situation.
It is similar to the concept of Situation Awareness in
(Endsley, 1995; Stanton et al., 2006) but formalise
with inferential reasoning and fault tolerance. Next
section describes the model in details.
3 THE PROPOSE MODEL
This section introduces the proposed model and ar-
chitecture, which intends to approach the problems of
awareness and fault tolerance in human-agent team.
It uses Bayesian inference and learning in solving the
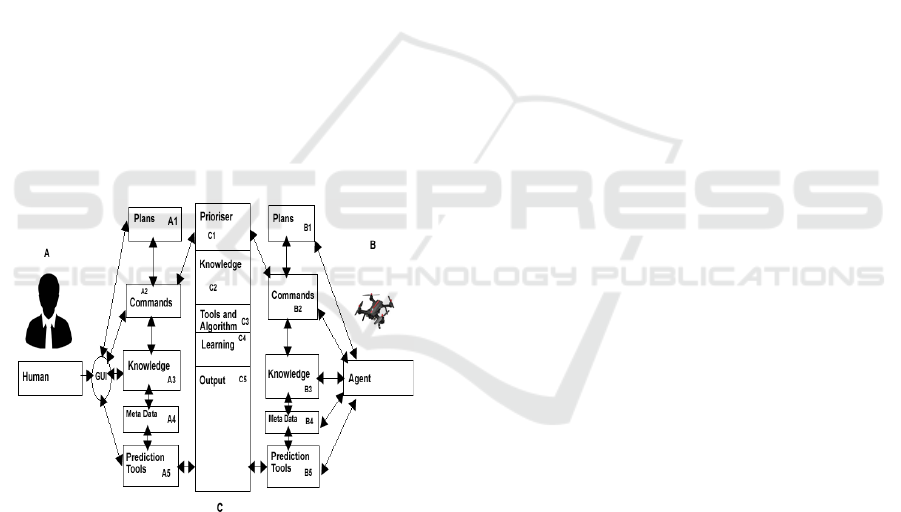
issues. Figure 1 describes the model architecture.
Figure 1: The Propose Model Architecture.
The proposed model has three entities, that is, human,
agent, and the intermediary server labeled A, B, C in
figure 1. We here below explain all these components.
3.1 Human Expert (a)
The human-expert refers to a professional person that
has knowledge of controlling, structuring, and execut-
ing the mission. For example in fire fighting, he/she
could be a well-experienced fire warden officer that
witness many complex and simple cases. In a case
where agents are exposing to a new environment, the
human expert could have more priority in controlling
the mission’s plans, commands, and data flow.
3.1.1 Human Plans (A1)
These are set of to-do actions by the agents propose
by the human expert. It could be a queue or stack
of actions to be performed during the mission by the
agent. For instance, in fire lookouts missions, it could
be a set of places to be visited in sequential order.
3.1.2 Human Commands (A2)
Current executing plan is refer to as a command. This
module is responsible for monitoring the human com-
mands and prioritising them. It monitors the plans
execution states such as completed, interrupted, non-
executable. A command could be mark as complete
when it was opportune to execute all its actions. An
interrupted command is a command that was removed
during execution due to encountering of higher prior-
ity command or lack of available resources (e.g., bat-
tery and computational power) to execute the com-
mand.
3.1.3 Human Knowledge (A3)
Human knowledge refers to the expert’s suggestions
and actions for controlling the system. It could be
inputted via the Graphical User Interface (GUI) and
pass to the hidden server (C) or agent (B) via com-
munication link. Human or agent knowledge could
be updated or prioritise best on the evaluation by the
team in optimising the objective functions.
3.1.4 Human Metadata (A4)
All updates records about the mission are recorded as
the metadata. This could be used to traced the mis-
sion and also be used for training purposes. It could
be exposed to learning algorithms such as gradient de-
scent, expectation maximisation, counting algorithms
etc. (Bottou, 2010; Dempster et al., 1977; Romany-
cia, 2019) to obtain a well-train BBN for making ac-
curate predictions, estimation and decisions.
3.1.5 Human Prediction Tools (A5)
Human predictive tools refers to the well-trained tools
(e.g, trained BBN) for helping the expert in making
predictions estimations, and conclusions. That is, it is
the output of the training process using the available
knowledge. It could be used to estimate or predict
what the agent is doing during the mission or in near
future.
Human-agents Interactions in Multi-Agent Systems: A Case Study of Human-UAVs Team for Forest Fire Lookouts
349

3.2 The Agent (B)
Agent refers to any autonomous hardware entity that
is capable of helping the expert in achieving the mis-
sion. For example, UAV, wheel-robots, legged robots
etc. As an autonomous entity, agent is capable of gen-
erating its plans and executes them. It could also re-
ceive other plans and commands from the human ex-
pert.
3.2.1 Agent’s Plans (B1)
As an autonomous entity, agents could have some
strategies of generating and monitoring their plans by
following certain algorithms. At times agents and hu-
man plans contradict each other when that happens,
the model proposes C1 (figure 1) to prioritise and de-
cide on which plan to be executed.
3.2.2 Agent’s Commands (B2)
Agents execute their plans in a certain structures such
as queue, stack, etc. The conflict between an agent
and human commands could be resolved by the pri-
oritiser C1.
3.2.3 Agent’s Knowledge (B3)
Agents’ knowledge comes from the sensor data,
which could be organised in a situation-based man-
ner. The agent’s knowledge is manage by the human
expert or the prioritser (C1 figure 1) by using different
techniques.
3.2.4 Agent’s Metadata (B4)
During mission execution, agents’ sensors informa-
tion and other valuable data about the environment
(e.g., time, location, etc.) are recorded as metadata to
the agents. These data can be used for learning pur-
poses using any suitable learning algorithms.
3.2.5 Agent’s Prediction Tools (B5)
This is a set of predictions tools such as well-trained
Bayesian Belief Network (BBN) and neuro-fuzzy
system to be used by the agent in making predictions,
estimations, and decisions during the absence of com-
munication link between it and the human expert.
3.3 Connector Server (C)
The connector server comprises the computer that
provides the Graphical User Interface (GUI) for com-
munication and the communication link. For exam-
ple, in human-UAV mission, it could be the linking
the agent, human expert, PC or mobile phone (as de-
scribed by figure 2).
Figure 2: Structure of Human-agent Interaction.
Figure 2 describes the global view of figure 1, It
shows the human labelled as (A), the agent (B), and
the connector PC (C). The communication link (e.g.,
wireless Local Area Network) connects the human
expert, connector server, and the agent.
3.3.1 Prioritiser (C1)
Prioritiser assigns a probability values to plans and
commands for agents’ execution. It a very important
module residing in the connector server. It is capable
of doing that because of the following reasons:
• It receives the knowledge of both human and the
agent. When human sends a command, the server
monitors the agent’s actions on the command and
learns the whole interaction.
• It has high computational capacity.
• It controls the communication link.
Therefore, by considering the aforementioned rea-
sons, the prioritiser have enough resources for priori-
tising tasks. But the human expert also have an ability
to execute an emergency plans.
3.3.2 Knowledge (C2)
The server has the global view of the systems because
it receives data from both human and agents. It moni-
tors and assesses its knowledge based on the satisfac-
tion of the command’s output. The server knowledge
could simply be referred to as the combination of both
the agents and human knowledge contributions.
3.3.3 Tools and Algorithms (C3)
This module comprises of the software to be used in
structuring knowledge for learning process such as
HAMT 2020 - Special Session on Human-centric Applications of Multi-agent Technologies
350

the use of Bayesian Belief Network (BBN) in mod-
elling agents’ knowledge. The selection of the learn-
ing algorithm depends on the nature of the data at
hand. For instance, counting algorithm fits diagnos-
tic problems. But when the data contain latent vari-
ables, conjugate gradient descent or expectation max-
imisation algorithms could be the best options (Bot-
tou, 2010; Dempster et al., 1977; Romanycia, 2019)
.
3.3.4 Learning (C4)
The learning process is responsible for handling the
data, manage its uncertainty, and control the learn-
ing process. The uncertainty could be inputted to the
learning algorithms in one of the following ways (Ro-
manycia, 2019):
• Restricted or unrestricted range: in this approach,
agents can send ranges of knowledge of BBN val-
ues. For example, temperature = [250-300], i.e.,
the value of the temperature is between 250-300
or temperature >30 degrees Celsius.
• Possibility or impossibility list: Setting a list of
the possible values or negating the list to show im-
possibilities in these values. For example temper-
ature ={200, 250, 300}or temperature = ¬ {200,
250, 300}
• Likelihood: the set of likelihood probabilities can
be attached to the possible variables in restricted
or unrestricted form. For instance, temperature =
{200 .8, 250 .1+-1, 300 .1}.
• Complete or incomplete certainty: It happens
when the BBN has a complete doubt about the
variable, or it has no doubt on the variable by pro-
viding its value to the BBN as “?” or actual values.
The output of the learning process is a well-trained
BBN (i.e., if BBN were used in modelling the agent’s
knowledge) serve as the output C5.
3.3.5 Output (C5)
The output of the learning process could be an accu-
rate prediction tool (e.g., well-trained Bayesian Belief
Network, neuro-fuzzy system, etc.). The accuracy of
the prediction tool could be measured by considering
how many times the network predicted a wrong val-
ues known as prediction accuracy rate (Romanycia,
2019). It could be ranged between 0 and 1 with 0 be-
ing the best. The choice of the threshold depends on
the programmer’s choice and learning environment.
In case of highly changing environment, the learning
algorithms could be augmented to prioritised recent
data as in (Bottou, 2010; Romanycia, 2019).
The output network could be replicated to both
agent and human side as their predictive tool in syn-
chronous or asynchronous mode (as discussed in sec-
tion 3.3.1). The higher the mission data, the higher
the perfection of the learned BBN as tested in our ex-
periment. Therefore, this architecture is limited to the
availability of data. In order to solve that issue, we
propose the use of fuzzy logic (set of heuristic to mon-
itor the prediction (Dernoncourt, 2013)) or expert in-
put (to fill in the conditional probability of the BBN)
in the absence of data.
4 IMPLEMENTATION OF THE
MODEL ON REAL-WORD
PROBLEM OF FOREST FIRE
LOOKOUT
We tested the model on the problem of wildfire
searching. Forest fire is one of the world’s major
problems, it kills lots of human and animal lives, de-
stroy millions of acres of land, and affect the cli-
matic conditions (Ingle, 2011). We use a team of
multi-rotors and fixed-wing UAVs mounted with fire
detecting sensors (camera) simulated on Aerospace
Multi-agent Simulation Environment – AMASE (afrl
rq, 2019). The belief of the agent was modelled using
Bayesian Belief Network (BBN) on Netica (Romany-
cia, 2019). Each agent is updating its BBN, and the
data is recorded at the metadata section for training
purposes. We assume the structure in figure 2.
Figure 3 describes two quadrotors and two fixed-
wing UAVs conducting forest fire searching. The in-
set picture shows a human expert from the control
station room with a PC server and could communi-
cate with the agents. The human expert is capable of
seeing all the UAVs data, as described in figure 4 on
AMASE.
From figure 4, the places mark with alphabets de-
notes:
• A represents the UAVs.
• Places marked B and C are the fires.
• D is the UAV’s information (speed, position,
heading, altitude, etc.) visible to the human ex-
pert via the PC connector at the base station..
• E is the sensor data of the UAVs.
• F is the battery level of the UAVs, and
• G is the environmental information sensor data
such as wind speed, wind direction, etc.
The agents could start with an in-built autonomous
searching approach. We use levy flight of (Chawla
Human-agents Interactions in Multi-Agent Systems: A Case Study of Human-UAVs Team for Forest Fire Lookouts
351
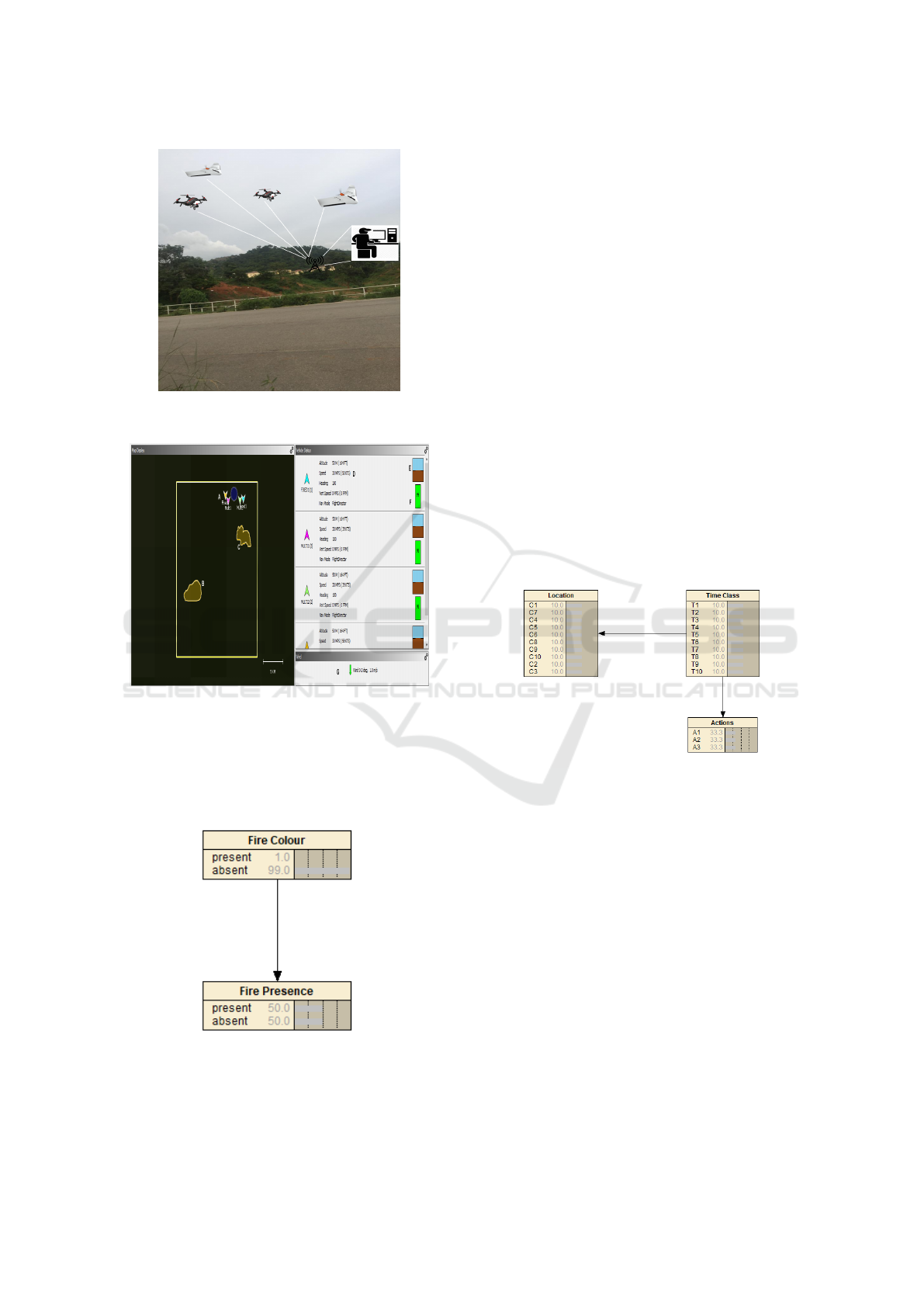
Figure 3: Demonstration of Human-UAVs Team for Forest
Fire Searching.
Figure 4: Implementation of the Propose Architecture on
AMASE.
and Duhan, 2018) to monitor the UAVs waypoints
generations for searching activity. The agents’ belief
was modelled using Bayesian Belief Network on Net-
ica (Romanycia, 2019) as describe by figure 5.
Figure 5: Bayesian Belief Network for Monitoring the
UAVs Belief on Fire Presence.
Figure 5 describes the BBN for monitoring the UAVs
belief on fire presence. Once the UAV’s sensor detects
the fire, it will update the network and its metadata for
training purposes.
5 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
This section describes the methodology and results
of each phase (stage of the model), implemented us-
ing AMASE (afrl rq, 2019) and Netica (Romanycia,
2019) on the forest fire problem discuss in section 4.
All experiments were run on PC with 8GB RAM, in-
tel core i3-6006U @ 2GHZ, and I terabyte external
storage.
The clear idea of the process is the ability to obtain
a nice prediction tool that synchronises both agent and
human expert in the absence of communication. We
use conjugate gradient descent algorithm to train the
Spatio-temporal BBN (figure 6) to produce a possible
location and action of UAV at a given time. Therefore,
during communication, hardware, or software failure
the agents can continue with their mission, and the
human expert could be able to predict the possible lo-
cation and action of the agent at a given time.
Figure 6: Bayesian Belief Network for Monitoring the mis-
sion clock, agent’s location, and actions.
Figure 6 describes a simple BBN for monitoring the
agents’ actions, location, and time. The location
refers to segmented grids of small sizes say (2meters
square). Time class refers to the time range of the mis-
sion clock, e.g., 12:00-12:05. The actions of the agent
(e.g., searching, loitering, projection etc) at a particu-
lar time are recorded for training purposes. The BBN
simply says that, at every time t, the UAV has location
and action doing, this could be predicted by filling of
the BBN conditional probability values using the mis-
sion’s sensor data. If the BBN is well-trained (perhaps
with the prediction error rate of at most 0.1-0.3 out of
the worse 1, depending on the availability of training
data and nature of the environment), it could be used
to trace what action UAV is doing, in which location
at a particular time more especially in a static mission
by given the conditional probabilities obtained from
HAMT 2020 - Special Session on Human-centric Applications of Multi-agent Technologies
352

the learning process. The model could work in dy-
namic missions by prioritising the learning data as in
(Romanycia, 2019). The learning algorithms are also
capable of handling latent variables.
5.1 Testing the Model on Forest Fire
Searching
We tested the model using forest fire searching prob-
lem introduced in section 4 using a team of UAVs
as agents simulated on Aerospace Multi-agent Sim-
ulation Environment -AMASE (afrl rq, 2019). In or-
der to compare the perfection of these techniques, we
tested both the agent’s BBN prediction error rates and
the human prediction perfection. The UAV is con-
tinually generating random waypoint using the bio-
inspired levy flight searching technique of (Chawla
and Duhan, 2018). We evaluate the human expert part
by exposing ten volunteer participants to the system
and then monitor their guess accuracy on waypoint
locations at a particular time. Table 1 describes the
prediction error of the respective BBN.
Table 1: Prediction Error Rate Comparison between UAV
and Human Entry of BBN conditional Probability Table
Values.
BBN
Entry
Source
BBN
Pre-
diction
Error
Number of Training
Data
Human
Expert
0.815 Number of partici-
pants: 10
UAV 0.505 1000
UAV 0.303 2000
UAV 0.216 3000
UAV 0.166 4000
6 DISCUSSION
From the results in table 1 section 5, one can notice
that the UAVs learning prediction error rate is less
than the human error rate. This is unsurprising be-
cause the agents are generating their waypoints base
on a stochastic bio-inspired random approach(levy
flight), and human could not be able to predict what
will happen next. However, the human expert entry
to the system is essential in terms of emergency com-
mands execution for the safety of the UAVs, as dis-
cussed in section 3. Another claim is that the predic-
tion error of the UAVs reduces with an increase in the
number of training data (table 1). The utilisation of
the training data to achieve the maximal outcome was
mark as future work.
6.1 Effect of the Model on Forest Fire
Searching
In terms of communication breakdown or (hardware
breakdown), the learned prediction error could be
used in making accurate predictions estimations, and
decision to control the mission. For example, let us
assume a power breakdown at the base station dur-
ing the human-UAV fire searching describe in sec-
tion 4, the based station could be able to trace their
UAV energy level, failure location (in case it finishes
its battery), location, etc. This removes the neces-
sity of using communication in human-agent inter-
action popularly known as mixed-initiative reason-
ing and planning as in (Bevacqua et al., 2015; Ca-
cace et al., 2014; Ferguson and Allen, 2007; Makonin
et al., 2016; Tecuci et al., 2007). In terms of adapta-
tion, the BBN in figure 6 describes the way of adapt-
ing to the environment by the agent through the pro-
vision of conditional probabilities learning.
Therefore, finally, we here argue that accurate pre-
diction tools obtain via join human-machine learning
can help in monitoring mission during communica-
tion failure and enhance the adaptation in a human-
machine team.
7 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
We proposed an architecture for monitoring the
human-agent team by utilising the best part of the
entities knowledge and producing accurate prediction
tools through the use of machine learning algorithms
(gradient descent or expectation maximisation). We
modelled the agents’ belief using Bayesian Belief
Network (BBN) and expose it to training data. In
order to test the proposed model, we used a forest
fire monitoring by a team of UAVs and human ex-
pert in the base station. The human prediction proofs
to be inaccurate as expected but very useful in terms
of emergency control. We were able to get the pre-
diction accuracy of 0.166 by training the BBN us-
ing 4000 samples of the agent’s data. This is pretty
good for making estimation, predictions, and decision
in the absence of accurate communication. In terms
of the highly changing environment, we propose the
augmentation of the learning algorithms to prioritise
recent cases as in the fading strategy of (Romanycia,
2019).
In the future, we will introduce a clear strategy
Human-agents Interactions in Multi-Agent Systems: A Case Study of Human-UAVs Team for Forest Fire Lookouts
353

for the distributed learning process between the agent
and the human experts. This will propose a complete
concept of parallel learning. We are also planning to
optimise the learning data and dig deeper to explore
the nature of the prediction accuracy, and it is rele-
vant to the available data. Although our model intro-
duces faults tolerance and communication failure or
reduction, a comparative analysis with other systems
in (Makonin et al., 2016; Tecuci et al., 2007) using
real agents marked as future work. We will also look
at how the model and the predictions tools act in a
highly changing environment.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We appreciate the effort of Petroleum Technology
Trust Funds (PTDF) of Nigeria for sponsoring this
project.
REFERENCES
afrl rq (2019). https://github.com/afrl-rq/OpenAMASE.
afrl-rq. original-date: 2017-05-07T13:17:17Z.
Araragi, T. (2005). Fault tolerance for internet agent sys-
tems: In cases of stop failure and byzantine failure.
AAMAS ’05, page 123–124, New York, NY, USA.
ACM. event-place: The Netherlands.
Bevacqua, G., Cacace, J., Finzi, A., and Lippiello, V.
(2015). Mixed-initiative planning and execution
for multiple drones in search and rescue missions.
ICAPS’15, page 315–323. AAAI Press. event-place:
Jerusalem, Israel.
Bottou, L. (2010). Large-scale machine learning with
stochastic gradient descent. page 10.
Cacace, J., Finzi, A., and Lippiello, V. (2014). A mixed-
initiative control system for an aerial service vehi-
cle supported by force feedback. pages 1230–1235.
2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelli-
gent Robots and Systems.
Chawla, M. and Duhan, M. (2018). Levy flights in meta-
heuristics optimization algorithms – a review. Applied
Artificial Intelligence, 32(9-10):802–821.
Dempster, A. P., Laird, N. M., and Rubin, D. B. (1977).
Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the em
algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Se-
ries B (Methodological), 39(1):1–38.
Dernoncourt, F. (2013). Introduction to fuzzy logic.
page 24.
Endert, A., Hossain, M. S., Ramakrishnan, N., North, C.,
Fiaux, P., and Andrews, C. (2014). The human is the
loop: New directions for visual analytics. J. Intell. Inf.
Syst., 43(3):411–435.
Endsley, M. R. (1995). Toward a theory of situation aware-
ness in dynamic systems. [Online; accessed 2019-11-
14].
Ferguson, G. and Allen, J. (2007). Mixed-initiative sys-
tems for collaborative problem solving. AI Magazine,
28(2):23–23.
Green, T. M., Maciejewski, R., and DiPaola, S. (2010). Al-
ida: Using machine learning for intent discernment in
visual analytics interfaces. pages 223–224. 2010 IEEE
Symposium on Visual Analytics Science and Technol-
ogy. ISSN: null.
Ingle, L. B. (2011). Every day is fire day: A study of his-
toric fire towers and lookout life in the great smoky
mountains national park. page 136.
Kifor, T., Varga, L. Z., Vazquez-Salceda, J., Alvarez, S.,
Willmott, S., Miles, S., and Moreau, L. (2006). Prove-
nance in agent-mediated healthcare systems. IEEE In-
telligent Systems, 21(6):38–46.
Makonin, S., McVeigh, D., Stuerzlinger, W., Tran, K., and
Popowich, F. (2016). Mixed-initiative for big data:
The intersection of human + visual analytics + pre-
diction. pages 1427–1436. 2016 49th Hawaii Interna-
tional Conference on System Sciences (HICSS).
Rich, C. and Sidner, C. L. (2007). Diamondhelp: A generic
collaborative task guidance system. AI Magazine,
28(2):33–33.
Rich, C., Sidner, C. L., and Lesh, N. (2001). Collagen:
Applying collaborative discourse theory to human-
computer interaction. AI Magazine, 22(4):15–15.
Romanycia, M. (2019). Netica-j reference manual. page
119.
Stanton, N. A., Stewart, R., Harris, D., Houghton, R. J.,
Baber, C., McMaster, R., Salmon, P., Hoyle, G.,
Walker, G., Young, M. S., Linsell, M., Dymott, R.,
and Green, D. (2006). Distributed situation awareness
in dynamic systems: theoretical development and ap-
plication of an ergonomics methodology. Ergonomics,
49(12-13):1288–1311.
Tecuci, G., Boicu, M., and Cox, M. T. (2007). Seven as-
pects of mixed-initiative reasoning:an introduction to
this special issue on mixed-initiative assistants. AI
Magazine, 28(2):11–11.
Turpin, M., Michael, N., and Kumar, V. (2014). Capt: Con-
current assignment and planning of trajectories for
multiple robots. The International Journal of Robotics
Research, 33(1):98–112.
Yue, J., Raja, A., and Ribarsky, W. (2010). Predictive ana-
lytics using a blackboard-based reasoning agent. vol-
ume 2, pages 97–100. 2010 IEEE/WIC/ACM Interna-
tional Conference on Web Intelligence and Intelligent
Agent Technology. ISSN: null.
HAMT 2020 - Special Session on Human-centric Applications of Multi-agent Technologies
354
