
Condition Elements Extraction based on PCA Attribute Reduction
and Xgboost
Luzhe Cao
1
, Jinxuan Cao
1
, Haoran Yin
1
, Yongcheng Duan
1
and Xueyan Wu
2
1
College of Information Technology and Network Security, People's Public Security University of China, Beijing, China
2
College of Law and Criminology, People's Public Security University of China, Beijing, China
Keywords: Situation Elements, Situation Elements Extraction, Principal Component Analysis, Xgboost.
Abstract: In order to solve the problems of high data redundancy, unsatisfactory classification effect and low precision
rate of situation elements extraction in large-scale network, a algorithm that extraction of situation elements
based on PCA attribute reduction and Xgboost is proposed. Firstly, PCA is used to reduce the attributes of
the data set, and then Xgboost classifier is constructed to classify and train the data after dimension reduction.
In order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm, NSL-KDD data set was used to test the
proposed algorithm. Through experiments, this algorithm is compared with SVM and other five algorithms.
The experimental results show that the precision rate of the algorithm is greatly improved and the extraction
of situation elements is effectively improved.
1
INTRODUCTION
Network security situation awareness is an insight
into the overall security situation of complex and
heterogeneous networks, aiming at obtaining,
analyzing and predicting the development trend of
elements related to network security. Network
security situation awareness includes three parts:
situation extraction, situation assessment and
situation prediction
(
Qi Ben et al., 2017
)
. Situation
extraction is the premise of situation assessment and
situation prediction. It aims to extract and analyze
factors that influence network security through
screening a large amount of data, and finally form
situation elements.
With a view to the problem of situation elements
extraction, many scholars have made some studies.
American Bass first proposed situation awareness
and obtained situation elements by refining data,
objects and situations (Bass T, 2016).
In order to
solve the problem of situation factor extraction, an
extraction technique based on conception is
proposed. The hierarchical framework is established
through the enhanced probabilistic neural network to
solve the problem that extraction of situation
elements (Li Fangwei et al., 2017).
Li dongyin
improved the precision rate of situation elements
acquisition by establishing improved particle swarm
optimization algorithm and logistic regression
algorithm, neighborhood rough set technology and
situation elements extraction model of MapReduce
distributed framework (Li Dongyin, 2014).
Liu
xiaowu proposed a fusion-based situational
awareness control model for network security and
improved the ability of perceived threat through
hierarchical situational awareness (Liu Xiaowu et al.,
2016).
It can extract situation elements effectively by
constructing the knowledge based on ontology
model (Si cheng et al., 2015).
In view of the need of
prior knowledge in the extraction process of situation
elements, this paper introduced the idea of parallel
reduction on rough set, removes redundant attributes,
and realized the efficient extraction of situation
elements (Zhao Dongmei et al., 2017).A deep self-
coding algorithm is proposed to extract situation
elements to solve the problems of high time
complexity and low classification precision rate (Zhu
Jiang
et al., 2017).
The above research algorithms have achieved
certain results in specific fields. However, data
collected in complex network environments often
has too many dimensions and redundant attributes,
so it is particularly important to reduce dimensions
and redundancy. Therefore, this paper proposes a
algorithm of situation elements extraction based on
PCA (Principal Component Analysis) attribute
reduction and Xgboost (eXtreme Gradient
Boosting).On the one hand, PCA is introduced into
the extraction of network situation elements and
redundant attributes in the data are deleted through
Cao, L., Cao, J., Yin, H., Duan, Y. and Wu, X.
Condition Elements Extraction based on PCA Attribute Reduction and Xgboost.
DOI: 10.5220/0009370002430248
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security (IoTBDS 2020), pages 243-248
ISBN: 978-989-758-426-8
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
243

PCA. On the other hand, the Xgboost classifier is
used for classification training of processed data to
improve the precision rate and effectively improve
the work of situation elements extraction.
2 NETWORK SECURITY
SITUATION ELEMENTS
EXTRACTION
2.1 The Concept of Network Security
Situation Elements
Network security incident refers to a series of
abnormal activities that threaten the operation of
computer network and application system. Network
security situation elements are some internal factors
that cause the occurrence and change of these
security events (Wang sen, 2017).The sources of
security data often have the characteristics of
diversification, they involve a large number of
heterogeneous format information and come from
different devices to network security (Chen y,
2019) .Therefore, in order to have a great effect in
network security protection and the network security
state, it is necessary to focus on the work related to
situation elements. Figure 1 represents the existing
form of situation elements.
Network
environment
safetysecurityincidentsituation elements
Figure 1: Existence form of situation elements.
2.2 The Basic Process of Extracting
Network Security Situation
Elements
The extraction of network security situation elements
refers to collect multi-source heterogeneous data and
analyze these elements in a complex network
environment. In the analysis stage, according to the
established rules, the collected data should be
processed to obtain the basic elements that affect
network security (Guo Jian, 2011).Common
situation elements include data generated by system
operation, data generated by network equipment
(including state information of network equipment
itself and data generated during network equipment
operation) and data generated during network attack.
The key task of situation factor extraction is to find
abnormal behaviors or risk factors in these data
accurately and screen out valuable data (Li Hong,
2017) .In the process of extraction, it is necessary to
conduct attribute reduction for situation factor data,
delete redundant attributes and conduct classification
training. Figure 2 shows the basic flow of situation
elements extraction.
original
data
attribute
reduction
Classification
training
module
situation
elements
Reduction
rules
classification
rules
Figure 2: Basic process of situation elements extraction.
The core of situation elements extraction is to
carry out attribute reduction and data classification.
In the process of attribute reduction, it is necessary
to make comprehensive judgment on multiple
attributes in each piece of information and filter out
the important attributes through dimension reduction
or attribute fusion. In the classification training
module, trainers can be constructed through different
classification rules to train the data after attribute
reduction.
This paper uses PCA on data attribute reduction.
PCA is an algorithm that used in machine learning
dimension reduction commonly. By constructing a
set of orthogonal basis, it will project high dimension
data to a plane, reduce the dimension of data. PCA
minimizes the variance between the principal axis
and the data point by translating the origin of
coordinates and rotating the axes. After the
coordinate transformation, the orthogonal axis with
high variance is removed and the reduced dimension
data set is obtained. This algorithm not only reduces
the dimensions of the data but also preserves most of
the information in the original higher-dimensional
data.
Select Xgboost as the classifier in the
classification training module. Xgboost is an
improvement of the GBDT (Gradient Boosting
Decision Tree) algorithm. GBDT is an iterative
IoTBDS 2020 - 5th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
244
decision tree algorithm in machine learning. It is an
algorithm based on classification and regression tree.
Compared with GBDT, Xgboost takes into account
the complexity of the tree when generating the CART
(Classification And Regression Tree) Tree.
Meanwhile, compared with GBDT, Xgboost uses the
second-derivative expansion and introduces
regularization terms when fitting the loss function to
prevent overfitting. It improves the algorithm
precision rate. Finally, the extraction of situation
elements is completed.
3 CONDITION ELEMENTS
EXTRACTION BASED ON PCA
ATTRIBUTE REDUCTION AND
Xgboost
The multi-source heterogeneous data in the network
has the characteristics of multi dimension and large
scale. Traditional algorithms in the process of
situational elements extraction need a lot of prior
knowledge. When the amount of data is too large, the
influence of subjective will reduce the precision rate
of the situational factors of extraction. Therefore it is
difficult to analyze data effectively and reliably. The
PCA attribute reduction and Xgboost algorithm is
proposed in this paper uses PCA to reduce the
dimension of data and convert multiple indicators
into fewer comprehensive indicators. Then the
Xgboost classifier is used to train and test the data
after sorting data. Finally
,
by completing the
extraction of situation elements, it increases the
precision rate of situation elements extraction.
3.1 PCA Attribute Reduction and
Xgboost Algorithm for Situation
Elements Extraction
PCA algorithm has a good capacity on data
processing, it can reduce the dimensionality of a
large number of complex redundant data and retain
the main information in the data while reducing the
redundancy. However, PCA is generally used for
dimensionality reduction of feature matrix, which is
not suitable for distinguishing different sample
classes. Therefore, its dimensionality reduction
advantage is not suitable for classification. Xgboost
has great advantages in classification, it also can
bring good classification effect and high precision
rate. Therefore, according to the characteristics of
PCA and Xgboost, an algorithm of situation elements
extraction based on PCA attribute reduction and
Xgboost is proposed to improve the classification
effect. The algorithm proposed in this paper is shown
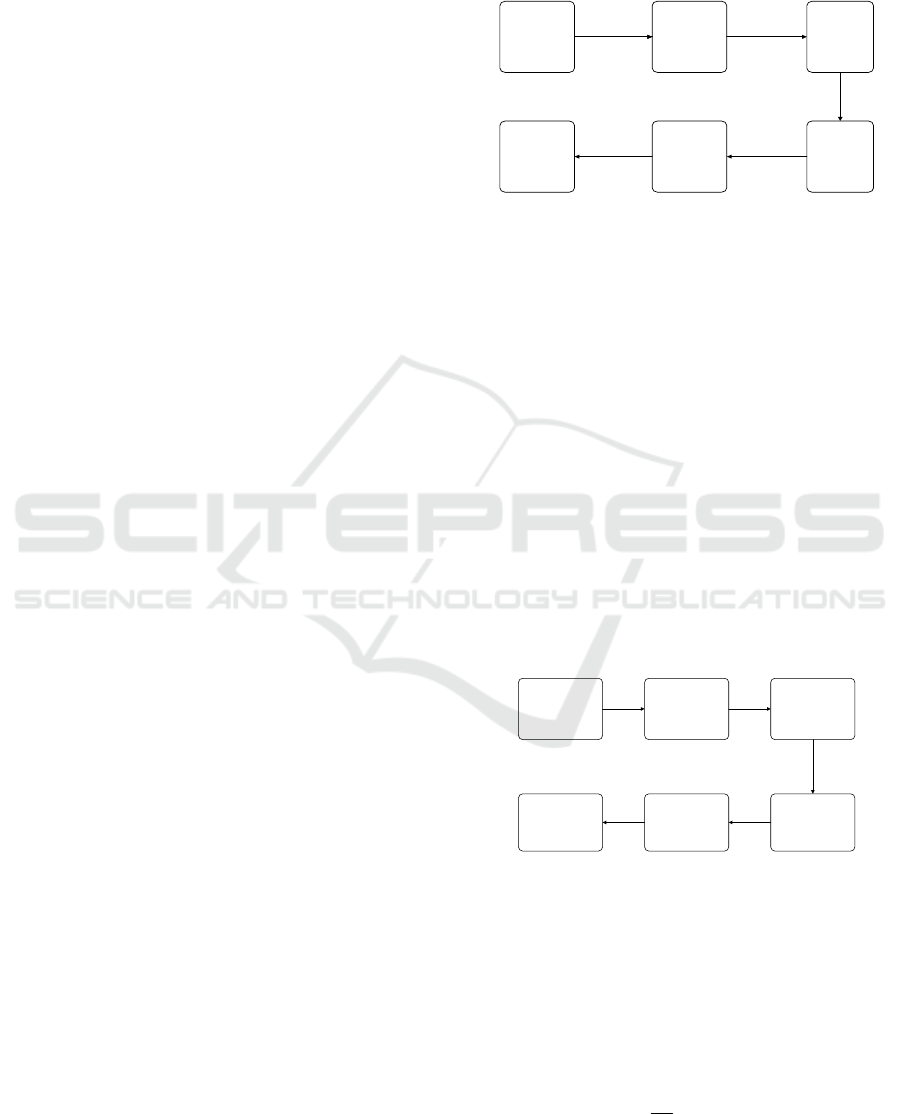
in figure 3.
Rawdata
acquisition
Establish
theoriginal
datamatrix
PCA
attribute
reduction
Buildthe
Xgboost
classifier
model
Testthe
Xgboost
classifier
Thetest
results
Figure 3: Situation elements extraction algorithm based on
PCA attribute reduction and Xgboost.
The steps of the situation elements extraction
algorithm proposed in this paper are as follows:
1) The obtained original m n-dimensional data
are formed into n rows and m columns to establish
the original data matrix X.
2) PCA is used for attribute reduction to obtain
the optimized training samples.
3) According to the data characteristics after
attribute reduction, the Xgboost classifier is selected
to classify and process the data after dimension
reduction. Then it can obtain the Xgboost classifier
model for situation elements extraction.
4) Test the Xgboost classifier and get the
experimental results.
The specific steps for step 2 above are shown in
figure 4.
Removalmean
Calculatethe
covariance
matrix
Calculatethe
eigenvaluesand
eigenvectors
Selectthe
eigenvalue
Retained
eigenvector
Transformthe
data
Figure 4: PCA dimensionality reduction process for data.
3.2
The Specific Steps of PCA
Attribute Reduction
1) Subtract the average value of each row from the
generated data matrix.
2) Calculate the covariance matrix of the sample
matrix.
1
T
C
X
X
m
(1)
Condition Elements Extraction based on PCA Attribute Reduction and Xgboost
245

3) Find the eigenvalues and corresponding
eigenvectors of the covariance matrix C.
4) Rank the eigenvalues from high to small
。
Select
the first k eigenvalues and take the corresponding
eigenvectors of the k eigenvalues as row vectors to
form the eigenvector matrix P.
5) Construct Y=PX, and transform the data into a
new space constructed by k feature vectors, then get
the data reduced to k dimensions.
In the Step 1, the training sample set is processed
to obtain the decentralized sample matrix firstly.
Then, in the Step 2, the algorithm calculates the
covariance matrix C with the new sample matrix.
The covariance matrix C is a square matrix, in order
to calculate the eigenmatrix and eigenvector more
conveniently, the eigenvalue decomposition matrix
algorithm is used to realize the PCA algorithm in the
obtained covariance matrix. Because the noise in the
data often affects the smaller eigenvalues, the
dimension reduction can be achieved by discarding
the smaller eigenvalues.
3.3
Specific Steps for Xgboost
Classifier Training
1) Set the objective function of Xgboost round t as:
1
ˆ
,
1
n
t
lftc
Obj y y f
x
i
tiit
i
(2)
Where,
b
t
Oj
is the objective function of iteration t,
n is the number of samples,
l
is the loss function,
that is the difference between the predicted value and
the real value.
i
y
is the true value of the sample
data,
1
ˆ
t
i
y
is the predicted value of the model in
the t-1 iteration.
()
i
t
f
x
is the newly added function
and can also be understood as a decision tree that can
make the optimization effect better on the basis of
the model in the previous step (t-1). C is the constant
term generated in the calculation process.
2) According to the Taylor expansion of the
second order
1
'''
2
2
fx x fx x x x
ff
x
(3)
Set
1
ˆ
,
1
ˆ
t
l
yy
ii
g
t
t
y
i
(4)
1
2
ˆ
,
1
ˆ
t
yy
ii
h
t
t
y
i
(5)
By substituting
t
g
,
t
h
and
f
t
into
equation (2), the objective function is obtained by
recombining the leaf nodes and removing the
constant term.
1
2
b
2
1
n
T
Oj g
whw
ji
ti
j
ii i
ll
jj
(6)
3) The optimal weight w* and the optimal value
of the corresponding objective function are obtained.
*
g
i
i
l
j
w
j
h
i
i
l
j
(7)
2
1
2
1
g
i
i
T
l
j
Obj T
h
i
j
i
l
j
(8)
According to equation (8), the optimal decision tree
structure is built and the prediction is made.
4 EXPERIMENT AND ANALYSIS
4.1 The Data Set
In this paper, data set is the refined data set NSL-
KDD in the kdd-cup99 data set. Kdd-cup99 data set
is a simulation of the USAF LAN network
connection data for 9 weeks. It is divided into
training data and test data. The experimental data
consists of 41 condition attributes and 1 tag attribute.
The tag attribute types are Normal, DoS, Probe, U2R
and R2L.Table 1 shows the overall distribution of the
NSL-KDD dataset.
Table 1: Data distribution of NSL-KDD.
The data
set
Normal Dos The
Probe
U2R
The
training
set
66532 46335 12443 63
The test
set
9632 7546 2542 208
IoTBDS 2020 - 5th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
246
4.2
Experimental Algorithm and
Result Analysis
In the experiment, Weka3.9.2, an open source
machine learning tool based on JAVA environment
and a data mining tool, was adopted. In the
experiment, we imported the data into Weka3.9.2.
During processing, we processed the data in batches,
processing 100 pieces of data at a time. In the
experiment, Xgboost was selected for classification
in Classifier and PCA was selected for attribute
reduction in evaluatora to construct a Classifier. The
steps are as follows:
1
)
Firstly, a correlation matrix C is generated,
which has 121 rows and 121 columns. Through
observation, it can be seen that this matrix is a real
symmetric matrix. In this matrix the elements on the
main diagonal are all 1, representing the variance of
the dimension. The remaining elements represent the
covariance of the corresponding dimension.
2
)
Calculate the eigenvalues of the covariance
matrix. It can be found from the experimental results
that there are 89 eigenvalues of the calculated
covariance matrix, which have been arranged in a
column from large to small. The range of the
eigenvalues is [0.67, 9.64].
3
)
Generate the eigenvectors corresponding to
the eigenvalues. In the Eigenvector list, there are a
total of 89 eigenvectors from V1 to V89, which
constitute the new eigenmatrix P.
4
)
Calculate the projection of the original matrix
C onto the eigenvector and the matrix Y is the data
after dimension reduction.
5
)
Use the Xgboost construct classifier for
training.
6
)
At the same time, we compare this algorithm
with traditional Xgboost in detail, which can verify
that this algorithm improves precision rate, recall
rate and other aspects. Table 2 compares in detail the
effects of PCA attribute reduction and Xgboost with
those of traditional Xgboost.
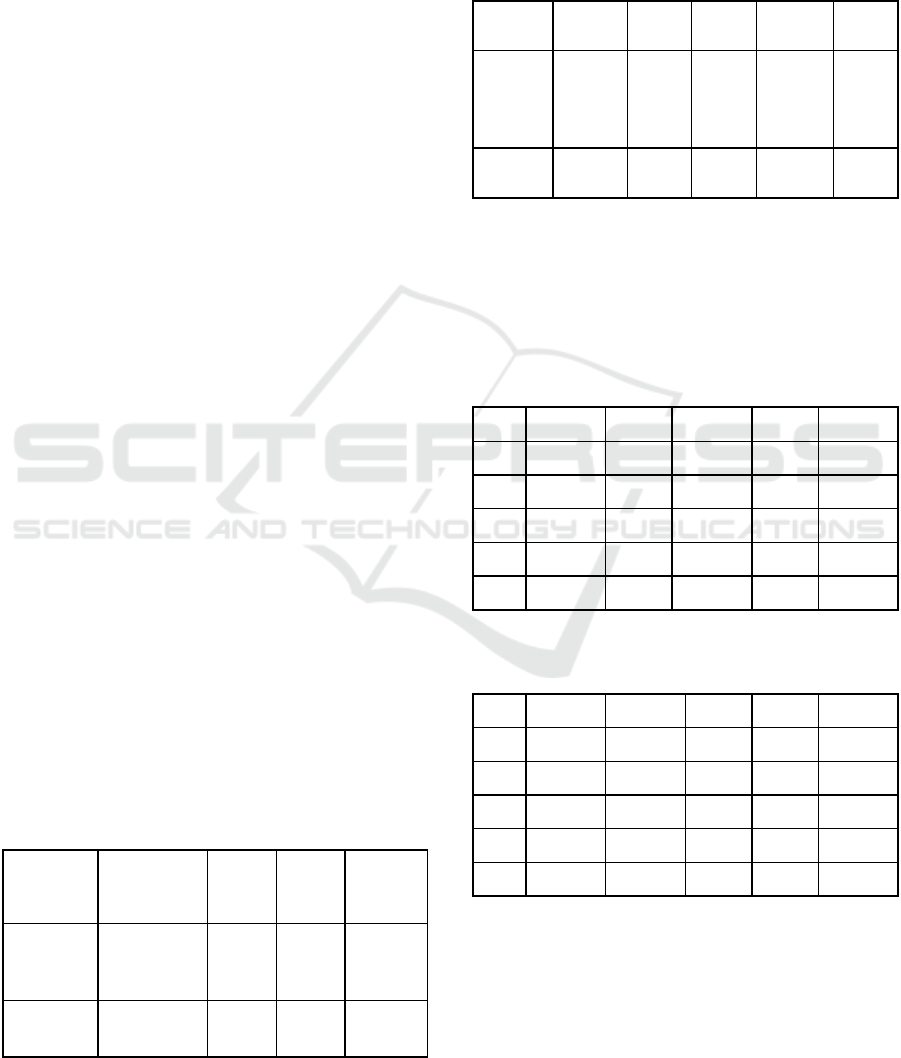
Table 2: Comparison of the effects of the two experimental
algorithms.
precision
rate
The
recall
rate
The F
value
The time
used
PCA -
b
ased
Xgboost
classifier
0.773 0.764 0.769 3.61 s
Xgboost
classifier
0.736 0.745 0.740 6.14 s
As can be seen from table 2, the precision rate of
this algorithm is 0.18% higher than that of traditional
Xgboost. The precision rate is based on the average
precision rate of normal, DOS, r2l, u2r and probe.
Table 3: Shows the precision rate of the two methods in
five categories in the data set.
normal DOS r2l u2r The
probe
PCA -
based
Xgboost
classifier
0.976 0.812 0.030 0.025 0.662
Xgboost
classifier
0.970 0.773 0.052 0.065 0.611
At the same time, the obfuscation matrix is
generated to represent the precision of the two
algorithms. Table 4 and 5 respectively show the
confusion matrix generated by the two algorithms
under the five kinds of data sets.
Table 4: The obfuscation matrix generated by traditional
Xgboost.
a b c d e
a 9420 85 0 0 206
b 1601 5766
0 0 91
c 2577 0 142 0 35
d 182 0 2 13 3
e 776 165 0 0 1480
Table 5: Confusion matrix generated by Xgboost based on
PCA attribute reduction.
a b c d e
a 9474 53 2 2 180
b 1367 6059 0 0 32
c 2667 0 82 2 3
d 128 0 7 5 60
e 566 238 14 0 1603
Table 4 represents the confusion matrix generated
by traditional Xgboost, table 5 is the confusion
matrix generated by Xgboost bsed on PCA attribute
reduction. A stands for normal class data, b for DOS
class data, c for r2l class data, d for u2r class data, e
for probe class data.
ij
x
is the number of data
elements in the row I category that are predicted to
Condition Elements Extraction based on PCA Attribute Reduction and Xgboost
247

be in the column j category. Thus, the main diagonal
elements represent the number of data in a class that
was correctly predicted for right class. If we use the
elements on the main diagonal as the numerator and
the sum of each row as the denominator, we can get
the correct rate of this category of data.
Through the above experiments, we can see that
compared with the Xgboost classifier, the Xgboost
based on PCA attribute reduction has a better effect.
In the experiment, data are imported such as Naive
Bayes ,SVM (Support Vector Machine, the Support
Vector Machine),Random Forests, Xgboost and the
Xgboost model based on PCA attribute reduction for
comparison, comparing their precision rate, recall
rate and
precision rate are observed. Table 6 shows
the comparison of P(
precision rate
),R(
The recall rate
)
and F(
The F value
) with traditional classification
algorithms.
Table 6: Comparison with traditional classification
algorithms.
Category Naive
Bayes
The
SVM
Random
Forests
Xgboost based on
PCA and
Xgboost
P 0.725 0.741 0.737 0.736 0.773
R 0.714 0.735 0.731 0.745 0.764
F 0.719 0.738 0.734 0.740 0.769
It can be seen from the experiments that the effect
of PCA attribute reduction and Xgboost is obviously
better than other classification algorithm. The
precision rate has been improved in several different
categories of data. Thus, compared with the
algorithms such as Naive Bayes, SVM, Random
Forests and Xgboost classification
,
this algorithm
has better classification results and higher precision
rate. Comparing with Naive Bayesian algorithm the
precision rate of this algorithm increased by 5%, the
recall rate increased by 5%. It can be seen that this
algorithm effectively improves the precision rate of
situation elements extraction and the work of
network situation elements extraction.
5
CONCLUSION
Firstly, this paper expounds the research work of
situation elements extraction and summarizes the
current algorithms of situation elements extraction.
According to the characteristics of situation elements
extraction, this paper proposes a situation elements
extraction algorithm based on PCA attribute
reduction and Xgboost. Through experimental
analysis, this algorithm is compared with Naive
Bayes, SVM, Random Forest, Xgboost and other
classification algorithms, which improves the
precision rate and achieves efficient extraction of
network situation elements.
REFERENCES
Qi Ben, Wang Mengdi. Extraction of bayesian situation
elements based on information gain [J]. Information
network security,2017(09):54-57.
BASS, T. Multisensor data fusion for next generation
distributed intrusion detection systems [EB /OL].
[2016-03-10].
Li Fangwei, Wang Sen, Zhu Jiang, Zhang Haibo. Secur ity
situation factor acquisition based on enhance
probabilistic neural network [J]. Telecommunicati ons
technology,2017,57(01):64-71.
Li Dongyin. The research on situation element extraction
of network security based on logistic regression [D].
University, 2014.
Liu Xiaowu, Wang Huiqiang, Lu Hongwu, Yu Jiguo, Shu
wen. Network security situation cognition fusion
sensing control model [J]. Journal of software,
2016,27(08):2099-2114.
Si cheng, Zhang Hongqi, Wang Yongwei, Yang Yingjie.
Ontology-based knowledge base model of network
security situation factors[J]. Computer science,
2015,42(05):173-177.
Zhao Dongmei, Li Hong. Network security situation factor
extraction algorithm based on parallel reduction [J].
Computer application, 2017,37 (04) : 1008-1013.
Zhu Jiang, Mingyue, Wang Sen. Security situation factor
acquisition mechanism based on deep self-coding
network [J]. Computer application, 2017,37 (03) : 771-
776.
Wang sen. Research on acquisition and prediction
technology of network security situation factors [D].
Chongqing: chongqing university of posts and
telecommunications, 2017.
Chen y. research on network security situation awareness
technology [J]. Jiangsu science and technology
information,2019,36(03):38-41.
Guo Jian. Research on situation element acquisition
technology in network security situation awareness
[D]. Liaoning: northeast university,2011.
Li Hong. Research on the extraction of network security
situation factors based on rough set [D]. Hebei: hebei
normal university, 2017.
IoTBDS 2020 - 5th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
248
