Accounting and Billing Challenges in Large Scale Emerging Cloud
Technologies
Piyush Harsh
a
and Oleksii Serhiienko
Zurich University of Applied Sciences, Winterthur, Switzerland
Keywords:
Accounting, Billing, IoT, Edge, Fog, Cloud, Architecture.
Abstract:
Billing models which can easily adapt with emerging market opportunities is essential in long term survival
of any business. Accounting and billing is also one of the few processes which has wide impact on legal and
regulatory compliance, revenue lines as well as customer retention models of all businesses. In the era of rapid
technology shifts, with emergence of Fog and Edge deployment models, and marriage of IoT and cloud which
promises smart-everything everywhere, it is paramount to understand what new challenges must be addressed
within any billing framework. In this paper we list several emerging challenges which should be overcome
in architecting any future-ready billing platform. We also present briefly an analysis of few technologies
which could be used in prototyping such a solution. We present our proof of concept experiment along with
initial results highlighting the feasibility of our proposed architecture towards a scalable billing framework for
massively distributed IoT applications at the edge.
1 INTRODUCTION
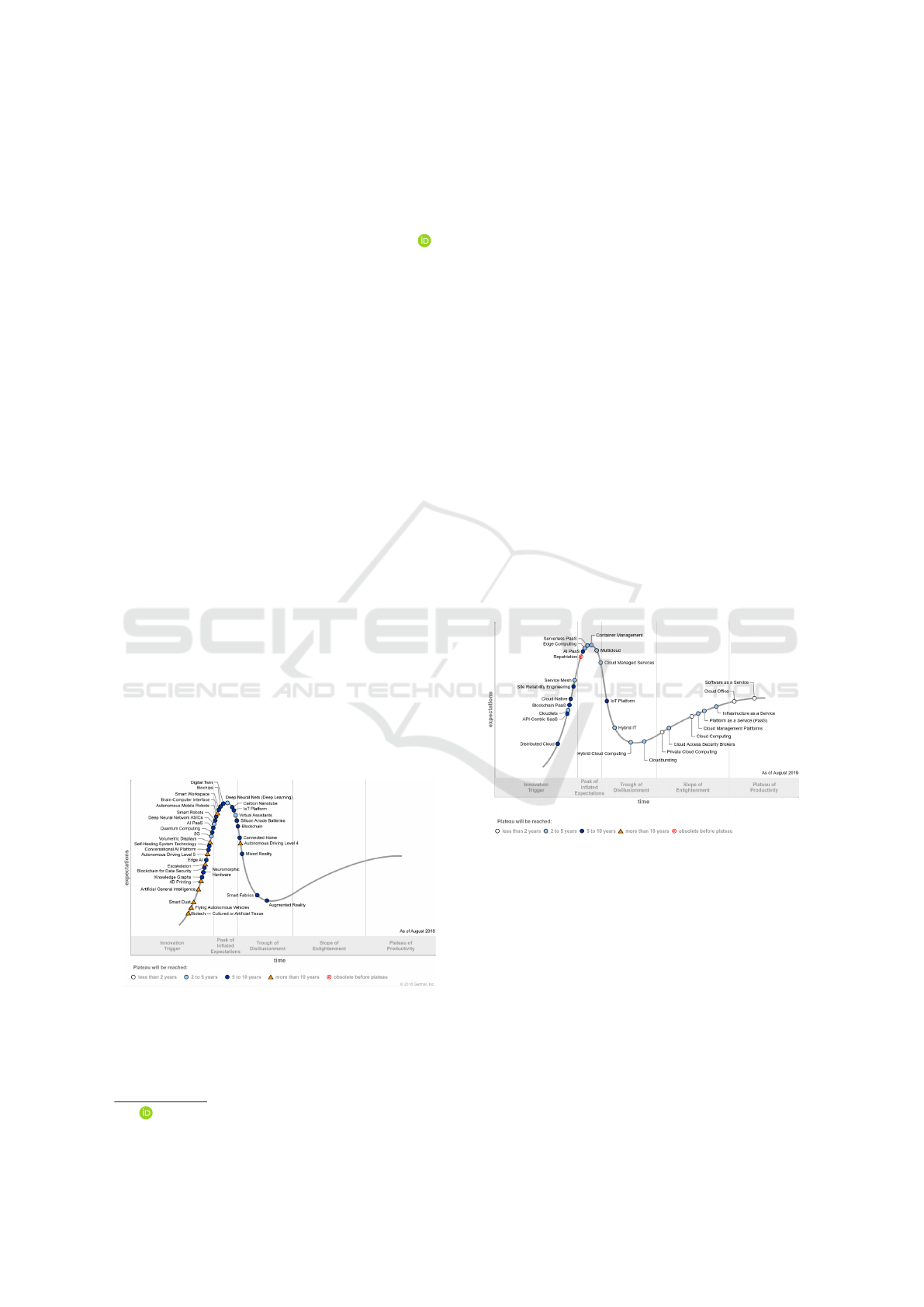
Figures 1 and 2 shows the latest Gartner hype cycle
for emerging technologies and cloud computing. The
report highlights a few technologies such as server-
less PaaS, Edge computing, IoT platforms, connected
homes, among others which should mature within
early-mid part of the coming decade.
Figure 1: Gartner hype cycle: emerging tech (August 2018).
Image source: http://tiny.cc/0uquvy
With the emergence of infrastructure (IaaS) and
platform (PaaS) clouds, the service sectors embraced
and rapidly adopted quick service prototyping, 12-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7787-1176
Figure 2: Gartner hype cycle for cloud computing (August
2019). Image source: http://tiny.cc/zlbwvy
factor application design patterns, dev-ops and agile
best practices. This itself led to rapidly changing ser-
vice ecosystems, highly agile competition landscape,
and increasingly discerning customers who always
wish more for the value of their money.
In (Patanjali et al., 2015), (Skoviera et al., 2017)
authors have discussed architecture and initial proto-
type of a billing framework designed primarily for us-
age based billing, support for converged telco+cloud
billing, among other features. Their work left out
critical discussions such as support for independent
audits, scalability of collectors in light of potentially
millions of data sources, framework scalability, etc.
390
Harsh, P. and Serhiienko, O.
Accounting and Billing Challenges in Large Scale Emerging Cloud Technologies.
DOI: 10.5220/0009415403900399
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science (CLOSER 2020), pages 390-399
ISBN: 978-989-758-424-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
which are crucial elements for success when consid-
ering the deployment scales targeted in some of the
emerging technologies.
The specific aim of our work is to identify key
aspects of some of the emerging technologies, iden-
tify common requirements for a billing framework
in general, and discuss potential challenges in meet-
ing such requirements in the context of these emerg-
ing paradigms. The remainder of this paper is orga-
nized as follows: section 2 discusses key elements of
targeted emerging technologies namely, Fog-, Edge-
computing and discuss specific elements of IoT de-
ployments; section 3 discusses generic requirements
for any accounting and billing solution that deals with
heterogeneous services, data sources, etc. ; section 4
catalogues some of the specific challenges one must
overcome in order to create a solution ready to sup-
port up and coming cloud supported technologies;
and finally section 5 very briefly touches upon some
of the recent technological trends that may help over-
come challenges outlined in this paper. In section 6
we present a very early stage architecture proposal as
a basis of our first prototype solution. Section 8 and 9
presents a proof of concept experiment that validates
use of serverless as one possible building block to-
wards realizing our proposed architecture. This paper
closes with some of the recent work in this field in
section 10 and outlines our upcoming R&D agenda in
section 11.
2 EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES
In this section we describe key technological as well
as deployment characteristics of some of the emerg-
ing cloud assisted technologies. To provide uniform
treatment in a concise manner, each of the targeted
technologies / paradigms are covered along the fol-
lowing dimensions: current definition, business own-
ership model, involvement/interconnection with large
cloud data-centres, users’ involvement in data man-
agement, etc.
2.1 Edge Computing
Edge computing (Shi et al., 2016) (Shi and Dustdar,
2016) (Satyanarayanan, 2017) is defined by the neces-
sity of doing part of data processing at the edge of the
network rather than completely in the cloud in order
to address latency concerns, alleviate limited compute
and battery capacity in users’ end devices, and en-
ables management of security and privacy concerns
of end users by granting more control to them. Table
1 captures key observations and characteristics.
Table 1: Key characteristics of Edge computing.
Dimension Description
business own-
ership
Cloudlets at the edge could re-
side within the user’s adminis-
trative domain under her man-
agement
cloud connec-
tivity
Cloudlets are usually 1 logical
hop away from a cloud ingress,
cloud connectivity could be in-
termittent
data manage-
ment control
user can have finer control
over data anonymization before
sending to cloud
app diversity
at edges
usually similar applications at
edges
unique ac-
counting
observation
large usage streams, uniform
billing and pricing models, au-
dit trails may be challenging to-
wards end devices or nodes de-
ployed in different organization
2.2 Fog Computing
If Edge computing main focus is on responsive, low
latency applications running at scale at the network
edges of Telco networks, the focus of Fog Computing
(Yi et al., 2015) (Vaquero and Rodero-Merino, 2014)
(Dastjerdi and Buyya, 2016) is to extend the cloud
like services at all edges thereby further generalizing
the principles originally proposed by Edge comput-
ing research community. It stitches SDN, software
managed storage, heterogeneous compute elements
together into providing a distributed on-demand pro-
visioning and deployment management of compet-
ing and heterogeneous applications along the entire
data-flow chain from the end devices to edge ele-
ments, intermediate gateways and to large private
and/or public cloud data centers. Both Edge and Fog
computing paradigms support end-devices as active
data generators whereas in many of traditional cloud
use-cases end-users/end-devices are usually data con-
sumers (think Netflix, Dropbox, etc.). But, in Fog-
computing, predominant programming models are
sense-process-actuate and stream processing models
(Dastjerdi and Buyya, 2016). Still it shares the same
concerns outlined in 2.1. Table 2 captures key obser-
vations and characteristics.
2.3 Serverless PaaS
Gartner (Walker, ) defines Serverless PaaS as “A PaaS
offering delivered with serverless characteristics is
serverless PaaS.”. Use of Serverless PaaS frees the de-
veloper from any maintenance as the Serverless PaaS
Accounting and Billing Challenges in Large Scale Emerging Cloud Technologies
391
Table 2: Key characteristics of Fog computing.
Dimension Description
business own-
ership
multi-organization ownership
where business arrangement
exists allowing sharing of com-
pute, network, storage resources
via well defined APIs
cloud connec-
tivity
brings cloud-like services at all
stages, standardized APIs, on-
demand orchestration and au-
tomated life-cycle management
supporting heterogeneous apps
with adequate isolation
data manage-
ment control
user can have finer control
over data anonymization before
sending to cloud
app diversity
at edges
potentially large number of het-
erogeneous apps
unique ac-
counting
observation
heterogeneity of usage data
streams, need for harmoniza-
tion, numerous billing and pric-
ing models, difficulty is main-
taining audit trails to the end de-
vices
Table 3: Key characteristics of Serverless PaaS.
Dimension Description
business own-
ership
Usually owned by a single
provider, although micro-fPaaS
deployments at edge belonging
to different organization is tech-
nically feasible
cloud connec-
tivity
typically tightly integrated with
IaaS cloud infrastructure
data manage-
ment control
state is typically not cached in
Serverless so less chances of
data abuse
app diversity
at edges
potentially large number of het-
erogeneous functions deployed,
capability limited by service re-
strictions normally
unique ac-
counting
observation
micro-billing, tracking execu-
tion lasting milliseconds or even
microseconds
provider shields all internals from the user. Using
Serverless PaaS is more economical as one pays usu-
ally for the actual time taken for a function to exe-
cute. Depending on the access pattern, an application
can see wide variability in latency. Serverless PaaS is
also being offered at the Edges by prominent public
cloud providers
1
. Table 3 captures key observations
and characteristics.
1
Lambda Edge: https://aws.amazon.com/lambda/edge/
2.4 IoT Frameworks
IoT framework refers to a collection of standards,
software and hardware components that enables data
acquisition from sensors, pre-processing and aggre-
gation within local / edge gateways, connectivity with
data-centres for in-depth analytic and long term data
storage, communication channels and signalling to
actuators based on outcome of local or remote anal-
ysis of sensor data (i SCOOP, ). IoT gateways are
becoming more capable and able to perform variety
of tasks depending on use cases. Standards include
M2M communication standards, messaging proto-
cols, etc. to name a few. Sensors and actuators comes
in variety of size and shapes but are usually charac-
terized by low cost and high volume of deployments.
Table 4 captures key observations and characteristics.
Table 4: Key characteristics of IoT frameworks.
Dimension Description
business own-
ership
managed IoT platforms allow
multi-organization owner-
ship model between devices,
platforms and gateways
cloud connec-
tivity
long term storage and deep ana-
lytics is increasingly being con-
ducted in private/public clouds
data manage-
ment control
local IoT gateways may allow
better data control to users, it is
possible to perform aggregation
on anonymous data up the chain
app diversity
at edges
potentially large number of het-
erogeneous IoT sensors and ac-
tuators can be connected via
same messaging infrastructure
unique ac-
counting
observation
potentially large variety of
data-streams, high volume data
spread over large geographical
swaths
Having analyzed these up and coming cloud as-
sisted, potentially large scale technologies, it is clear
that the scale of data volumes, variety of data, low
latency requirements for adequate control, different
scope of data privacy controls, billed amounts deal-
ing from micro-units to large sums, will result in new
challenges which must be addressed right from the
architecture design phase in any sensible accounting,
billing and invoicing system for such technologies.
CLOSER 2020 - 10th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
392

3 ACCOUNTING AND BILLING:
REQUIREMENTS
Let us assume that a reasonable resource monitor-
ing infrastructure is in place for the service under
consideration. We can analyze the requirements on
billing infrastructure depending on whether real time,
pay-as-you-go billing and accounts settlement is de-
sired, or if periodic accounts settlement is sufficient.
Some requirements can also be derived if micro-
billing (Robert et al., 2016) capability is needed in
the solution or not.
3.1 Real Time Billing
Unlike telecommunication services which are nor-
mally linked with one device, in Edge-/Fog- deploy-
ment scenarios, the same billing account may be
linked to numerous agents, services running in dif-
ferent geographical locations. In real time billing,
the service consumption must be tracked in almost
real time and depending on whether enough money
is present in a pre-paid account, services are allowed
or blocked. With this perspective the collection of re-
quirements are presented in table 5 below.
Table 5: Requirements for enabling real time billing.
Name Short description
Fast acquisi-
tion
relevant billable events and us-
age data acquisition by the
billing framework must to rea-
sonably fast
Alerting ability to inform service end-
point of lack of funds in a given
account
Fast process-
ing
fast on-line processing of in-
coming data stream
Sustainable self operating cost should be
low in order to make micro-
billing viable
Awareness System design must support
near real time awareness of dis-
tributed data fragments belong-
ing to same account
3.2 Off-line/Periodic Billing
With periodic billing, the usage data need not be pro-
cessed immediately. The data can be processed in a
batch after the invoicing window has elapsed. The
requirements in this case are not too divergent from
earlier case although the emphasis on timeliness of
processing is not so critical. We can still list a few
requirements (table 6):
Table 6: Requirements for enabling off-line / periodic
billing.
Name Short description
Storage the usage data points needs to
be reliably stored until invoice is
generated
Tamper-proof the storage system should
provide reasonable protection
against data tampering
3.3 Universally Valid
There are a few requirements which are universally
valid irrespective of whether the focus is on real-time
or off-line billing and also irrespective of the vertical
use cases. These are captured in table 7.
Table 7: Universal requirements.
Name Short description
Safety the system must not lose any bil-
lable metrics
De-
duplication
the system must be robust
enough to handle repeated data
without inflating the final in-
voice
Usable the system must have adequate
user interfaces, cli as well as UI
to allow users to interact in a
meaningful way
Harmonization system should be able to sup-
port billable events from variety
of services so as to produce uni-
fied, composite invoices
Flexibility accounting and billing engine
should be flexible enough
to support new tarrif plans,
seasonal promotions, changing
portfolio of products, etc.
Versioning potential to roll back to an ear-
lier known good version of pric-
ing and billing models in case of
errors in updates
4 CHALLENGES TO CONSIDER
Having seen the requirements list as well as general
characteristics of few emerging technologies, let us
analyze some of the challenges which one must ad-
dress properly in order to create a practical solution
with greater probability of user acceptance. Our anal-
ysis will cover the following aspects -
Accounting and Billing Challenges in Large Scale Emerging Cloud Technologies
393

• Computation at edge or in central data-centers
• Centralized wallet management vs distributed ap-
proach for real time cost control
• Feasibility of robust audit trails
4.1 At Edge or in the Core
With large scale IoT deployments, spread geographi-
cally, assimilating large data streams is a known chal-
lenge. The problem becomes acute when large dis-
tance networking pipes are involved. Managing la-
tency in such an uncontrolled environment becomes a
complex challenge. In such situations one must eval-
uate possibility of processing data at the edges versus
centrally somewhere distant. With different organi-
zational units wishing to retain more control over fine
grained data sets, processing increasingly at the edges
is becoming more acceptable, but it brings with it the
challenge of managing heterogeneity in data formats
dynamically (as one can not assume a-priory the full
variety of applications to be handled by the billing ser-
vice at such a wide deployment ranges where multiple
independent organizations may be involved) from the
accounting framework perspective.
Managing data heterogeneity for harmonization
purposes will remain a challenge until all potential
Fog/Edge/IoT applications prepare billable data using
a common global standard. OGF
2
“Usage Record”
format standard - GFD.098 (Mach et al., 2007), and
GFD.204 (Gordon et al., 2013), is a concrete step
along this direction, but it suffers from format limita-
tion as it only supports XML whereas micro-services
increasingly seem to adopt formats such as JSON,
YAML to name some.
4.2 Wallet Management Challenges
One of the challenges gains in prominence for pre-
paid usage of distributed resources. The challenge
increases in difficulty in Edge/Fog deployment sce-
narios where numerous instances of micro-services
belonging to an application may be running in dif-
ferent geographical locations, in data-centers, at the
edge and so on.
Figure 3 shows two extreme approaches where in
centralized mode, all control actions must check with
a centralized wallet to verify whether enough balance
is there to allow an action to proceed. This approach
would lead to increased latency in decision making,
thereby making it inappropriate for several use cases
including IoT deployments. The other approach is de-
centralized whereas the overall prepaid fund is intelli-
2
https://www.ogf.org/
Figure 3: Wallet management strategies.
gently distributed among regions where parts of appli-
cations are running and control decisions can be taken
quickly. Here the fund re-balancing is a challenge
and several predictive approaches exists in the liter-
ature which could be utilized for near-optimal strat-
egy. Several strategies in between these two extremes
must be evaluated to come to a reasonable approach
for prepaid account and service management.
4.3 Reasonable Auditing Capabilities
Audit trails within billing services are required by
several government regulations as a measure for con-
sumer protection. Maintaining a verifiable audit trail
is a complex process involving trust chains, PKI in-
frastructures, etc. In a global scale deployments
which is foreseeable in IoT/Edge/Fog deployment
models, this problem becomes more challenging. Au-
dit trail disruptions at administrative / organizational
boundaries, at various aggregation points, are some
interesting challenges that one should address. Ag-
gregation operation invariably looses individuality of
component samples. Similarly, if there is trust deficit
among independent org units at edge / core of the data
processing trail, it impacts the audit process credibil-
ity.
5 PROMISING TECHNOLOGIES
Based on the described challenges, it’s possible to
provide examples of technologies among existing so-
lutions. In this case serverless area is especially
promising. By its definition, it would cover such
requirements as the low price of computations and
vast scaling possibilities. Many cloud providers al-
ready have IoT platforms based on FaaS technolo-
gies, which allow running functions on the edge de-
vices. There are excellent candidates in the list of
open-source solutions, like OpenWhisk(IBM, ). It is
a serverless platform that can be involved to solve
active devices number grow for a reasonable price.
OpenWhisk has several advantages that lead to reach-
CLOSER 2020 - 10th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
394

ing the discussed target:
• High-level auto-scale possibilities due to good uti-
lization solution
• Flexible pay-as-you-go billing model
• Event-based execution model
Knative(Google, ) is another Kubernetes-based
platform to build, deploy, and manage serverless
workloads. It extends Kubernetes to provide a set
of middleware components that are essential to build
source-centric, and container-based applications that
can run anywhere: on premises, in the cloud, or even
in a third-party data center.
Also in the IoT where data transmits between mul-
tiple networks administrated by different organiza-
tions, the question of security becomes significant.
Blockchain technology would be able to solve this is-
sue and cover a few more e. g., reliability, m2m trans-
actions handling, scalability. IOTA(IOTA, ) presents
their open source solution for IoT platform based on
the blockchain with shared economy. Blockchain
technology promises a compelling vision: decentral-
ized networks allowing open innovation and peer-
to-peer transactions without intermediaries or fees.
However, together with benefits, distributed ledgers
might create the following challenges to overcome:
• Storage - without the central server, all the data
needs to to be stored at the nodes themselves
• Processing power - extra time is required for op-
erated objects encryption
Nevertheless, overcoming these leads to appearing an
optimal platform for IoT with a scalable, decentral-
ized and secure approach.
6 INITIAL ARCHITECTURE
Having seen the potential in some of the upcoming
technologies, in this section we aim to leverage these
for fulfilling some of the goals we are targeting in the
architecture draft specification. The goals of current
architecture specification are listed below -
• Aggregation at the edge as mush as possible
• Dynamic injection of aggregation and harmoniza-
tion functions at the edges
• Decentralized maintenance of audit trails
Wherever possible, candidate technologies are
also shown in the figure 5 below.
We plan to leverage decentralized ledger wherein
all elements in the architecture that handle bill-
able data must participate as (blockchain) nodes.
Figure 4: Architecture proposal v1.0.
The ledgers themselves will provide the verifiable
audit capability allowing traceable analysis of all
data transformation from usage reports till invoicing
stages. We plan to push usage report aggregation, for-
mat harmonization, to the network edges as dynam-
ically deployed functions, capable of being executed
in a FaaS framework. This FaaS layer which will be
setup within IoT gateways or Edge nodes. The data
which will flow into larger data-centers thus will be
highly aggregated samples.
Rest of the processing could then be easily han-
dled by existing billing frameworks including our
own creation “Cyclops”
3
. This architecture being
a work-in-progress will subsequently be modified to
bring in other aspects which have been identified ear-
lier in this paper.
7 DEMONSTRATOR DESIGN
AND ARCHITECTURE
The demonstrator was designed and implemented to
get more insight into IoT/Edge billing use-case. The
architecture of demonstrator is shown in picture 5.
Any IoT devices can be placed to any place with
the access to the internet and connected to the shared
message queue, which represents the role of the typi-
cal endpoint.
Cloud function platform provides the possibility
to manage cloud functions. The functions can be di-
vided for three types:
• Billing functions: generate the bill from the cur-
rent platform, storage and queue usages.
• Admin functions: store and manage all incoming
messages as defined by the platform provider.
3
https://cyclops-billing.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
Accounting and Billing Challenges in Large Scale Emerging Cloud Technologies
395

Figure 5: Demonstrator design.
• Custom functions: perform user and use-case spe-
cific actions required for usage data management
like usage aggregation, an event notification or
more complex logic.
All messages coming from the queue processed by
admin functions and stored locally, storing one IoT-
message would execute at least one function. Further
actions on the dataset stored in the storage entirely
depend on user implementation.
The Billing functions take into account the usage
of executed functions, message queue and storage and
generate the bill on the call. The user has access
to API/GUI to create and manage custom functions,
public message queue where all IoT devices can be
connected, see the generated usage, etc.
8 IMPLEMENTATIONS
For the implementation of the prototype was cho-
sen MQTT Mosquitto broker, 3 RaspbeeryPi devices
located in the same building with sound, tempera-
ture and motion sensors. As the provider of cloud
functions was used OpenSource self-managed Open-
Whisk platform running in OpenStack cloud plat-
form.
Raspberry Pi devices generated records and pub-
lishing them into MQTT broker; motion sensor was
sending the message if the move happened next to it,
temperature sensor average value in some defined pe-
riod, and finally sound sensor regularly sending the
sound metrics. These sensors were chosen to cover
three different use-cases like constant, periodic and
random time metrics sending.
The OpenWhisk platform had one admin function
responsible for storing all incoming messages to in-
fluxdb database and two user-specific ones for alert-
ing if motion is happening and aggregation which
includes aggregation data-points from the database,
send to the next endpoint and delete all aggregated
metrics. Billing functions generate the bills for us-
ages of both - total execution time of all functions and
load of MQTT message queue.
OpenWhisk has no native support for triggering
messages from the queue but it can be solved by cre-
ating a standalone service for keeping the connection
to the event bus and Openwhisk custom feed. The
workflow of the messages is shown in picture 6.
Figure 6: Record flow.
Each message depending on the topic where it
published triggers the corresponding trigger, this trig-
ger is ”clued” to the executable function via the rule.
And in the end, the running function performs the
needed action. Both sound and temperature records
rules trigger the store function for farther aggrega-
tion. The aggregation is done periodically by trigger-
cronjob and activates ibm-composer which is, in this
case, responsible for consequential execution of mul-
tiple functions:
1. Get records and aggregate them
2. Send records to the defined user endpoint
3. Clean the database
All data, code and information about the running
system can be accessed publicly.
CLOSER 2020 - 10th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
396

9 EVALUATION
Openwhisk and evaluation scripts were running on
the same machine on Openstack Platform with the
following characteristics of computational power and
docker:
RAM 4 GB
VCPUs 2 with 2500 Mhz
Disk 40 GB
OS Ubuntu 18.04 bionic
Docker 18.09.0, build 4d60db4
docker-compose 1.21.2, build a133471
The first experiment was done on the evaluation
of the execution time of the billing function com-
pare to the number of messages consumed from the
mosquitto server. The data is collected from system
topic which has a variety of information like size of
all records, speed, number, etc. The graph is shown in
picture 7.
Figure 7: MQTT billing function execution time.
The data into the system topic is coming period-
ically every 5 seconds so the number of messages
doesn’t affect the execution time.
The second experiment was done on the evalu-
ation of billing functions for Openwhisk. Graph 8
shows how the dependency of the execution time of
the billing function to the number of users and number
of function invocations for all of them. In Openwisk,
there is no user concept, for now, so for evaluation
purpose, each workspace was considered as a single
user.
The bill generation is done by querying the Open-
Whik endpoint. By default, only 30 last records can
be displayed but in practice, it is possible to return
the maximum 200. Most of the billing time execu-
tion coming from Openwhisk querying time and more
queries are performed more time for bill generation is
taken. Coming from our use-case(trigger invoke the
action) we have two times more activations(trigger
invokes action) which also increase time for billing
action execution. For the test purpose was used the
Figure 8: Openwhisk billing function execution time.
standard limit for activations query(30 per list) which
lead to increasing the execution time for around 4
times for each dataset and increasing deviation of re-
sults. Increasing the size of the machine to 8 GB of
RAM and 4 CPUs leads to decreasing of execution
time for billing to around 20%. With the initial con-
figuration, we can notice that 1 functions invocation
billed approximately for 1 millisecond. In our use-
case(datapoint store) an average store point execution
took 60 ms. It gives a conclusion that the billing of
one invocation takes 1.5%. If function execution takes
longer the percentage will decrease.
10 RELATED WORK
In this section we wil define some of the concepts
used throught this paper, and also derive inspiration
from related research done in the community. In (Shi
et al., 2016) & (Shi and Dustdar, 2016) the authors de-
fine edge computing together with examples of case
studies, future and present challenges and opportuni-
ties whereas in (Satyanarayanan, 2017) authors an-
swer the question why has edge computing emerged,
what new capabilities does it enable, and where is it
headed.
Together with an edge, fog computing has plenty
of recent publications. The paper(Dastjerdi and
Buyya, 2016) present the hierarchical architecture of
fog computing and its characteristics, compare it with
cloud computing in similarity and differentiation; also
the author covers some challenges and open issues.
The authors have offered a comprehensive definition
of the fog, comprehending technologies as diverse as
cloud, sensor networks, peer-to-peer networks, net-
work virtualisation functions or configuration man-
agement techniques in (Vaquero and Rodero-Merino,
2014). In (Yi et al., 2015) authors offer definition,
Accounting and Billing Challenges in Large Scale Emerging Cloud Technologies
397

characteristics, components and architecture of fog in
the context of IoT.
There is significant amount of research work done
concerning accounting and billing in numerous IT
sectors. The paper (Fleck, 1999) describes an ar-
chitecture for a near real-time billing system for
use in a next-generation communications environ-
ment. The architecture was designed using a Dis-
tributed Processing Environment incorporating light-
weight hierarchical focused trading and a lightweight
transactional engine. The authors in (Jamil et al.,
2004) proposes a model with practical experimen-
tal results utilising serial communication for metering
and billing system for spatially distributed electrical
power clients. Different publication(Loeb, 1995) of-
fer the usage information collection and management
paradigm together with an essential component of
meeting the billing needs for new, distributed broad-
band and multimedia services. The work(Elmroth
et al., 2009) presents a summary of the analysis of
existing Grid accounting systems, including brief de-
scriptions of the different technologies also it offers
accounting and billing for the RESERVOIR project.
The authors in (Lakew et al., 2014) presents a mech-
anism to synchronise accounting records among dis-
tributed accounting system peers. Runtime resource
usage generated from different clusters is synchro-
nised to maintain a single cloud-wide view of the data
so that the system creates a single bill. The paper de-
fines a set of accounting system requirements and an
evaluation which verifies that the solution fulfils these
requirements. The paper(Kloeck et al., 2005) intro-
duce a distributed, dynamical and combined pricing,
allocation and billing system, suitable for wireless in-
frastructure communications systems which are capa-
ble of managing multi-homing.
11 CONCLUSION
In this paper we have analyzed a few emerging cloud-
assisted technologies along common dimensions to
identify accounting and billing challenges inherent
in them. We derived general as well as specific re-
quirements for a billing framework suitable for the
agility and diversity requirements of such technolo-
gies and in the process also identified specific chal-
lenges which must be addressed for meaningful pro-
totypes to be developed. We have briefly proposed
an architecture (which remains a work in progress)
which could be the starting point for prototyping
a viable solution to the challenges outlined above.
Our limited experiments of using popular serverless
framework (Openwhisk) shows the potential of this
technology as a low cost computing platform for
billing related computations, both at the edges and at
the core.
In the near term our goal is to validate some of the
emerging technologies such as distributed ledgers as a
means to support large scale distributed audit require-
ments, and explore possibilities of serverless concepts
embedded in traditional IoT gateways as a means to
push and execute variety of aggregation as well as
usage records collection to the edges, and its further
distribution to remote data processing silos. Detailed
performance and run-time cost analysis must be con-
ducted to verify suitability for special needs of micro-
billing in above identified use case scenarios; and this
we plan to conduct post prototyping of our solution.
The architecture specification will be enhanced to
bring in the elements of distributed wallet manage-
ment to allow low latency control tasks in real-time
prepaid consumption mode.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work is partially funded by the Swiss State
Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation
(SBFI) in association with the European Union Hori-
zon 2020 research and innovation programme via
grant agreement #731535, for the ElasTest project.
The authors would like to express gratitude for addi-
tional funds provided by Innosuisse - the Swiss Inno-
vation Agency via their grant 27189.1 PFES-ES for
project “COMBuST: Container Micro-Billing Simu-
lation Toolkit” for supporting part of the work carried
out.
REFERENCES
Dastjerdi, A. V. and Buyya, R. (2016). Fog computing:
Helping the internet of things realize its potential.
Computer, 49(8):112–116.
Elmroth, E., Marquez, F. G., Henriksson, D., and Fer-
rera, D. P. (2009). Accounting and billing for fed-
erated cloud infrastructures. In 2009 Eighth Interna-
tional Conference on Grid and Cooperative Comput-
ing, pages 268–275.
Fleck, J. (1999). A distributed near real-time billing en-
vironment. In Telecommunications Information Net-
working Architecture Conference Proceedings, 1999.
TINA ’99, pages 142–148.
Google. Knative – kubernetes-based platform to build,
deploy, and manage modern serverless workloads.
https://cloud.google.com/knative/. accessed: 2018-
08-26.
CLOSER 2020 - 10th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
398

Gordon, J., Jones, M., Kennedy, J. A., and M
¨
uller-
Pfefferkorn, R. (2013). Usage Record – Format Rec-
ommendation. GFD 204, Open Grid Forum.
i SCOOP. Iot technology stack – from iot devices,
sensors, actuators and gateways to iot platforms.
https://www.i-scoop.eu/internet-of-things-guide/iot-
technology-stack-devices-gateways-platforms/.
accessed: 2018-07-26.
IBM. Apache openwhisk – open source serverless cloud
platform. https://openwhisk.apache.org/. accessed:
2018-08-26.
IOTA. Iota – a permissionless distributed ledger for a new
economy. https://www.iota.org/. accessed: 2018-08-
26.
Jamil, M., Munir, F., Khan, A. A., and Mirza, A. (2004).
Telemetering billing system for spatially distributed
electrical power clients. In E-Tech 2004, pages 35–
40.
Kloeck, C., Jaekel, H., and Jondral, F. K. (2005). Dynamic
and local combined pricing, allocation and billing sys-
tem with cognitive radios. In First IEEE International
Symposium on New Frontiers in Dynamic Spectrum
Access Networks, 2005. DySPAN 2005., pages 73–81.
Lakew, E. B., Xu, L., Hern
´
andez-Rodr
´
ıguez, F., Elmroth,
E., and Pahl, C. (2014). A synchronization mecha-
nism for cloud accounting systems. In 2014 Interna-
tional Conference on Cloud and Autonomic Comput-
ing, pages 111–120.
Loeb, S. (1995). Interactive billing for broadband and mul-
timedia services. In Community Networking, 1995. In-
tegrated Multimedia Services to the Home., Proceed-
ings of the Second International Workshop on, pages
221–223.
Mach, R., Lepro-Metz, R., and Jackson, S. (2007). Usage
Record – Format Recommendation. GFD 98, Open
Grid Forum.
Patanjali, S., Truninger, B., Harsh, P., and Bohnert, T. M.
(2015). Cyclops: A micro service based approach for
dynamic rating, charging amp; billing for cloud. In
2015 13th International Conference on Telecommuni-
cations (ConTEL), pages 1–8.
Robert, J., Kubler, S., and Traon, Y. L. (2016). Micro-
billing framework for iot: Research amp; technologi-
cal foundations. In 2016 IEEE 4th International Con-
ference on Future Internet of Things and Cloud (Fi-
Cloud), pages 301–308.
Satyanarayanan, M. (2017). The emergence of edge com-
puting. Computer, 50(1):30–39.
Shi, W., Cao, J., Zhang, Q., Li, Y., and Xu, L. (2016). Edge
computing: Vision and challenges. IEEE Internet of
Things Journal, 3(5):637–646.
Shi, W. and Dustdar, S. (2016). The promise of edge com-
puting. Computer, 49(5):78–81.
Skoviera, M., Harsh, P., Serhiienko, O., Belmonte, M. P.,
and Bohnert, T. M. (2017). Monetization of infrastruc-
tures and services. In 2017 European Conference on
Networks and Communications (EuCNC), pages 1–5.
Vaquero, L. M. and Rodero-Merino, L. (2014). Finding
your way in the fog: Towards a comprehensive defini-
tion of fog computing. SIGCOMM Comput. Commun.
Rev., 44(5):27–32.
Walker, M. J. Hype cycle for emerging technologies,
2017. https://www.gartner.com/document/3768572.
accessed: 2018-07-26.
Yi, S., Li, C., and Li, Q. (2015). A survey of fog comput-
ing: Concepts, applications and issues. In Proceed-
ings of the 2015 Workshop on Mobile Big Data, Mo-
bidata ’15, pages 37–42, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Accounting and Billing Challenges in Large Scale Emerging Cloud Technologies
399
