
XEL Group Learning – A Socio-technical Framework for
Self-regulated Learning
Shereif Eid and Gábor Kismihók
Learning and Skills Analytic Group, Leibniz Center for Technology and Natural Sciences, Hannover, Germany
Keywords: Socio-technical, e-Learning, Social Learning, Social Media Networks, Recommendation Systems.
Abstract: We describe XEL-Group Learning, a socio-technical framework for socially oriented e-learning. The aim of
the presented framework is to address the lack of holistic pedagogical solutions that take into account
motivational theories, socio–technical factors, and cultural elements in social learning networks. The
presented framework provides initiatives for collaboration by providing a dynamic psycho-pedagogical
recommendation mechanism with validation properties. In this paper, we begin by highlighting the socio-
technical concept associated with socially-oriented e-learning. Next, we describe XEL-GL’s main
mechanisms such as group formation and the semantic matching framework. Moreover, through semantic
similarity measurements, we show how cultural elements, such as the learning subject, can enhance the
quality of recommendations by allowing for more accurate predictions of friends networks.
1 INTRODUCTION
For many decades, standard formal education has
applied strict pedagogical regulations to pressure
students to pursue their studies. Such bureaucracy in
formal settings limits the development of a growth
mindset, i.e. students’ belief that they can develop
their intellectual abilities through performing
challenging tasks (Dobronyi et al., 2019).On the
contrary, recent studies have shown that students
who maintain confidence that they are up to the
challenge of developing their intellectual abilities
are those who adopt more successful learning
strategies (Dobronyi et al., 2019). In other words,
there is a positive correlation between performance
and adopting the growth mindset required to pursue
effective self-regulated learning (SRL) strategies.
Students’ lifestyles outside the classroom are now
characterized by dynamic social interactions,
sharing, creativity, and freedom (McLoughlin and
Lee, 2008; Dabbagh and Kitsantas, 2012). Social
networks and media now offer a more attractive
environment for Collaborative Learning (CL) among
students (McLoughlin and Lee, 2008; Dabbagh and
Kitsantas, 2012). Therefore, the use of social media
among students has significantly increased lately,
particularly for coursework and group-related tasks
(Dabbagh and Kitsantas, 2012).
In general, students are affected by their daily
social habits which include extensive engagement in
social media networks. Therefore, designing new
models for learning which meet the expectations of
digital age student generations, which employ
autonomy and methods to facilitate collective
learning is paramount (McLoughlin and Lee,
2008).At the borderline between directed and self-
directed learning lies the balance between applying
democracy in education and validating the quality of
the learning process. Since the beginning of this
century, there has been a growing consensus that
‘student-led’ CL, supported by teachers, is the
dominant trend (Wheeleret al., 2008).The real
challenge, as suggested by McLoughlin and Lee
(2008), is to trigger self-direction and learner
control, while also offering a valid structure and
appropriate support from a network of students,
teachers, and experts. Addressing the latter
challenge forms the primary motivation of this
study. Nevertheless, our problem of interest is
considering socially oriented e-learning as a socio-
technical system in which the social and technical
components evolve in parallel with emergent
property of interaction between subsystems (Bednar
et al., 2019). This problem has been in rise lately due
to the lack of holistic approaches that address both
social and technological factors, which also take into
344
Eid, S. and Kismihók, G.
XEL Group Learning – A Socio-technical Framework for Self-regulated Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0009418303440351
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2020) - Volume 2, pages 344-351
ISBN: 978-989-758-417-6
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
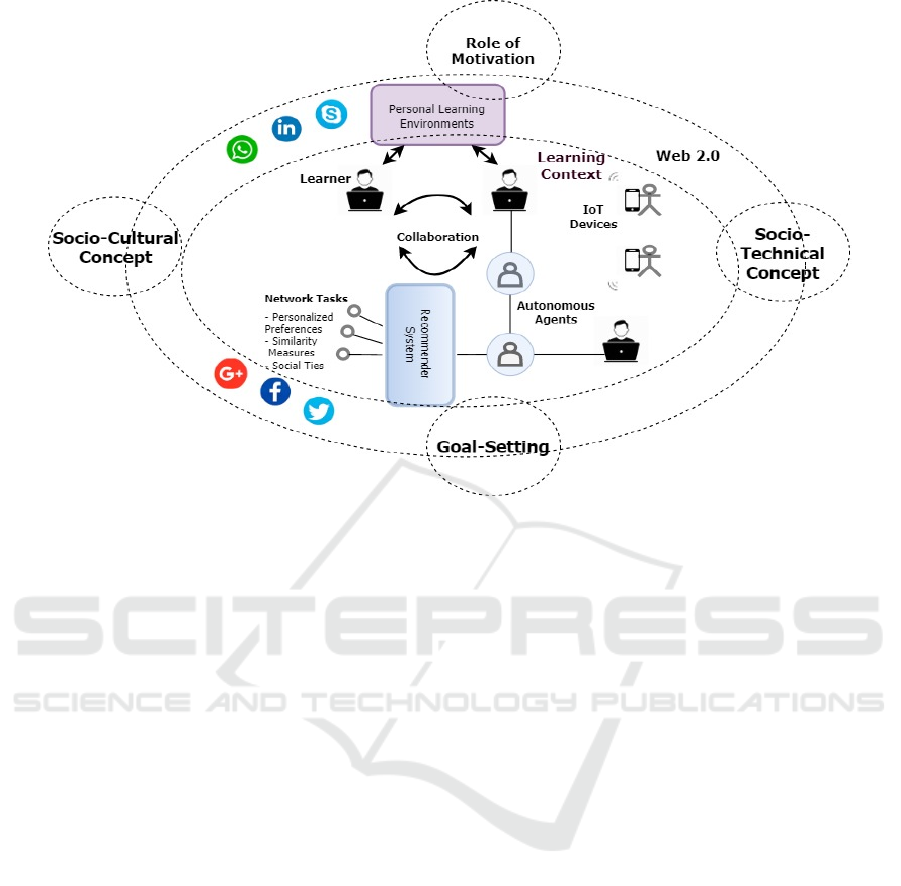
Figure 1: Socio-technical e-learning model based on the industry 5.0 smart working concept.
account motivational theories and cultural elements.
The precise research question we address is:
RQ: How could we validate the quality of e-
learning given a socio-technical perspective that
fosters social, technological, cultural, and
motivational elements?
The contribution we put forward is an exercise-
based socio-technical framework for group learning
called XEL-Group Learning (XEL-GL).We show in
the rest of the paper that XEL-GL exhibits the
following properties:
1. Collaborative goal-setting with validation
and correctness property.
2. A multi-dimensional similarity metrics
based on social ties and semantic
similarity scores between learning
subjects.
3. A dynamic SRL strategy recommender
which uses social ties between network
users, in addition to semantic similarity
between learning topics.
4. An adaptive property by taking into
consideration time-related decay factors.
In the following section, we explain the background
and rationale behind our design and we review
related work. Section 3 describes the main
components of XEL-GL framework. Sections 4 and
5 describe the semantic matching process and
present analysis results of semantic relatedness
between learning topics. Section 5 highlights our
future work. Finally, section 6 concludes the paper.
2 BACKGROUND AND RELATED
WORK
Validating the quality of the learning process in a
socially oriented e-learning environment depends on
many factors that include social, cultural, and
technological elements. The socio-technical and
socio-cultural problems in e-learning have been
addressed in much work recently. For example, the
values of encouragement and providing support to
others are cultural elements which positively
influence social interactions and make group activity
more constructive (Määttä et al.,2012).On the
contrary, online learning in the presence of many
digital cultures ( such as shopping websites and
online games) could have negative effect on student
concentration, therefore, educational interventions
are used to increase student social engagement with
their peers in a CL environment (Tsai,2013).
Therefore, the socio-cultural concept combines both
social and cultural aspects and analyse the effect
cultural elements have on social interactions. On the
other hand, socio-technical studies analyse complex
XEL Group Learning – A Socio-technical Framework for Self-regulated Learning
345

logical processes of interaction between social actors
and technology and how these processes affect
learning activities, such as SRL practices, and
learning outcomes. An example of a socio-technical
problem is how software tools affect handling
cognitive load in CL (Winne et al., 2010).
In general, the approach towards new generation
smart systems, known as industry 5.0, is that social
and technological systems interrelate in an
orchestrated manner to bring about technological
sustainability, i.e. continuous innovation, and human
development (Bednar and Welch, 2019). In other
words, the system of interest, as stated by Bednar
and Welch (2019), is one with an emergent property
of interaction between subsystems. But this also
enforces complexities when designing smart socio-
technical systems that are highly autonomous, which
also comprise a socio-cultural perspective. Drawing
on the ‘smart working’ concept (Bednar and Welch,
2019), figure 1 above illustrates our model of
interest; a socio-technical e-learning model in which
subsystems ideally span technological, cultural,
social, and motivational elements.
2.1 Related Work
Learners join Social Learning Networks (SLN) to
perform a wide variety of collaborative activities,
part of which is query-answering. Query-answering
provides motivation for students to join SLN
wherein students seek informal learning practices,
and they may also follow strategic behaviours to
build social ties in order to solve assignments and
coursework questions. In the socio-technical part of
CL, an emerging field of work is psycho-
pedagogical recommendation mechanisms. Psycho-
Pedagogical Recommenders (PPR) are known to be
based on relevant theoretical models unlike
collaborative filtering recommenders which need
large communities to extract similarity measures
(Lachmann and Kiefel, 2012; Mödritscher et al.,
2011). Moreover, PPR rely on personalized
preferences such as personal profiles, individual
skills, personal study habits, and preferences that
relate to tutoring methods. Thus, PPR approaches
are more flexible to matching a wider variety of
learners’ interests. An example of recent works in
PPR models is the work of Freed et al. (2017) which
presents a recommender system, called PERLS
which provides content recommendation for
SRL.PERLS classifies learning goals based on the
topics of interest. In other words, goals vary from
one topic to another. Recommendations are based on
the personalized preferences that relate to learners’
Figure 2: Main activities in XEL-GL Learning
Framework.
direct and indirect interests. Evidence of direct
interest comes directly form the learner and is
demonstrated by the learner’s self-efficacy to
perform topic-related tasks. Moreover, topics are
hierarchically structured and indirect interest is
evidenced by the relation between current learning
topics and their parent or child topics. Unfortunately,
PERLS is not a CL framework but it only targets
assisting individual learners.
Nussbaumer et al. (2012) present an ontology-
based recommendation system which stores SRL
entities in widgets. SRL entities represent different
SRL activities such as goal-setting, note taking, etc.,
widgets are then used to recommend SRL activities
that best match learners’ preferences. A shortcoming
of their approach is that most of the tasks need to be
executed manually, for example, tutors need to
create specific PLE (Personal Learning
Environment’s) templates and then learners use
these templates to search for the specific widgets
that match their preferences.
3 XEL – GROUP LEARNING
FRAMEWORK
XEL – Group Learning is a query-answering socio-
technical learning framework that offers a holistic
approach to collaborative e-learning. As shown in
figure 2, the XEL-GL system performs three main
tasks, 1.predicting friends networks based on social
ties.2.semantic matching of learning
CSEDU 2020 - 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
346
topics.3.Recommending SRL strategies in the form
of answers to goal-based queries issued by learners.
In our context, goals are conceptually and
syntactically specific, as shown in table 1 below. We
take the SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable,
Relevant, Timely) goal criteria as our reference for
the goal-setting activity in the learning community.
A goal consists of a target tag and a topic. Target
tags are syntactically specific, i.e. limited to a single
word, while the topic represents the concept to
which the target is bound. Contrary to target tags,
learners have the freedom to write their
concept/topic in a free sentence form. Semantic
relatedness between topics contributes to updating
the learner’s friend’s network as we will describe
later. Upon joining the network, learners identify
their topics of interest, and they can issue their goals
in the form of a query that encapsulates a topic and a
target tag. The SRL recommender uses query tuples
to provide the most relevant resource from those in
the friends’ network, particularly it gathers
recommendations from users who have the strongest
ties and with highly similar profiles. Queries/Goals
are identified as in definition 1 below:
Definition 1: A Query is the tuple
,
, where is
the finite set of pre-identified target tags, and is
the finite set of topics. A query
is identified by the
pair
,
, where is the tag associated with topic
.
In our example, the finite set of tags is :{
MEMORIZE, ANALYZE, ANNOTATE, SOLVE,
SUMMARIZE}.
The answer to any query is a SRL
recommendation in the form of a strategic exercise.
Nevertheless, as in learners’ queries, a similar target
tag is assigned to each exercise. Therefore, a tutor
creates an exercise and assigns any tag ∈ but in
this case it refers to the exercise topic, i.e the topic in
this case represents the title of the strategic exercise.
Note that while it is most likely that the target
assigned to any random answer will match a number
of learners’ queries, the semantic relatedness
between a query’s topic and an exercise title is the
key to measuring the semantic similarity between a
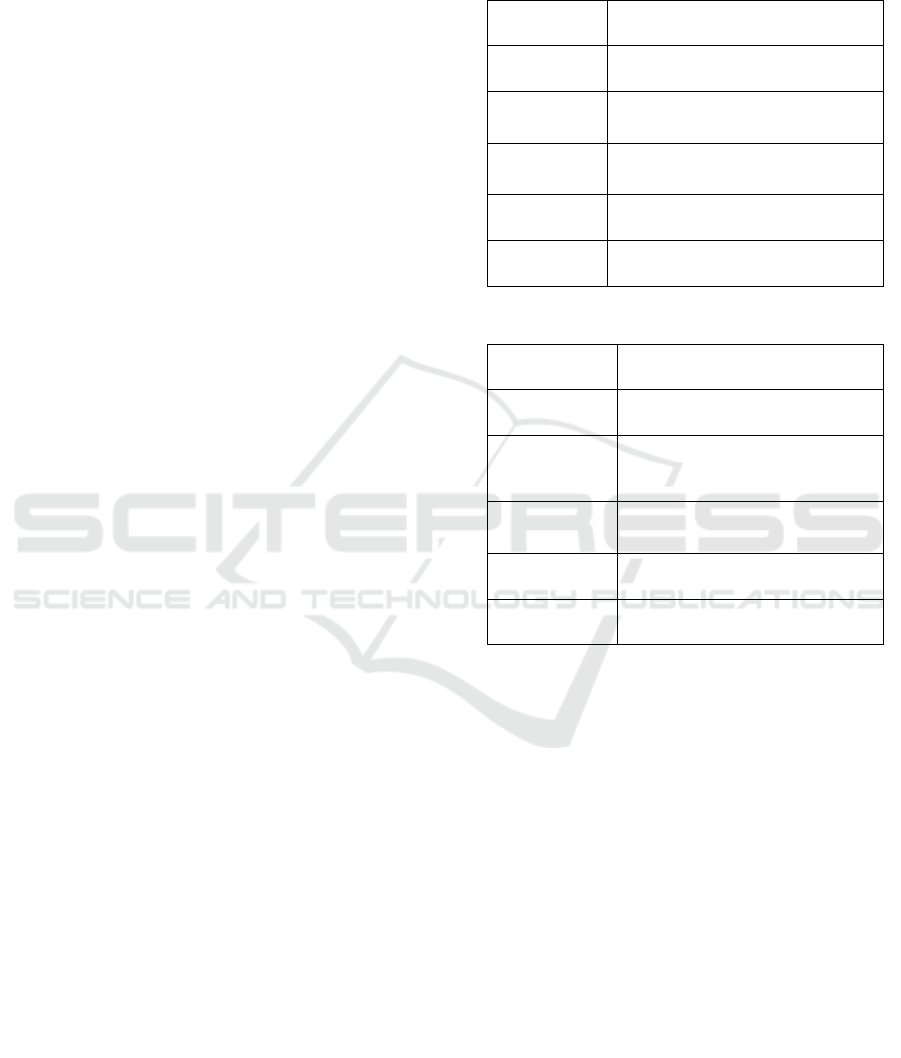
query and its answer. For instance, the first row in
table 1 and the adjacent row in table 2 will score a
high semantic relatedness score as we will show
later, however, the target tags of both rows are
different. In table 1, row 1, the learner’s goal is
‘MEMORIZE’, and for the adjacent exercise in table
2, the target is ‘SUMMARIZE’. Indeed, in our
framework, the tutor’s target is dominant and the
learner’s goal is corrected. In other words, the
system exhibits a correctness property with respect
Table 1: Samples of queries issued by learners.
Goal Learning Topic
MEMORIZE Mexican-American War.
ANALYZE
Origin, composition and internal
structure of the earth.
ANNOTATE
Use of Weapons in Ancient
Civilizations.
SOLVE
Deductive reasoning.
REVISE Psychology of Music
Table 2: Samples of answers issued by tutors.
Goal Exercise Title
SUMMARIZE American Mexican Conflict
ANALYZE Origin, composition and internal
structure of the earth.
ANNOTATE
Use of Weapons in Ancient
Civilizations.
SOLVE
Deductive Reasoning.
MEMORIZE Causes of Thirty Years War
to goals, and in the next iteration the recommender
will automatically update the learner’s target tag
with respect to the associated topic. It should be
noted that the recommendation (answer to learners
query) does not necessarily come directly from
tutors/experts, but rather they may come from other
learners who are closest in the query issuer’s friends
network. This enriches the object relational-model in
our framework and enhances the capability of
providing more accurate predictions.
3.1 Group Formation
YouTube and Flickr provide a successful model of
user-generated content which eliminates the
boundaries between users and creators of contents
(Kazienko et al. 2011; Susarla and Tan, 2012). In
such social network structure, communities of
friends are formed based on shared interests. There
are also ties with channels outside the friendship
network (friends of friends) (Kazienko et al., 2011;
XEL Group Learning – A Socio-technical Framework for Self-regulated Learning
347

Susarla and Tan, 2012).YouTube relies on the social
contagion phenomenon, which means that people’s
tastes about choices and actions are affected by
others (Kazienko et al., 2011). The strength of ties is
identified between different users based on
semantics of multi-dimensional relations. There are
three kinds of connections: 1.Direct Intentional
Relation, 2.Object-based relation with similar roles,
and 3.Object-based relation with different role.
In addition, there are many kinds of ties that can
occur between users, for example, relations that are
based on contact list, shared tags, opinions, etc. Each
type of relation represents a relation level. In XEL-
GL we use the strength of the relation between user
and user to identify the basic logic of group
formation. In this context, we build on the work of
Kazienko et al. (2011). In particular, our interest is
that the overall strength of the relation between user
and user is identified as the quantitative measure
of all activities performed by user towards user as
a fraction of all user ’s activities. Therefore, every
relation level is indexed, assigned a priority factor to
each relation, and an overall strength value of the tie
between and is concluded as follows: (see
Kazienko et al., 2011).
=
∑
∗
∑
(1)
Where is the index of the relation layer,
is
the priority of layer ,
is the strength of the
th
relation from to . Strength of linkage aggregates
all strengths from all relation levels discovered in
the system. Note that values of all strengths for both
relations and ties are ∈ [0,1].
This mechanism represents the socio-technical
component of XEL-GL and it relies on the
fundamental logic of group formation used in social
media networks. In the next section, we describe
how the cultural element, which in our case is the
learning subject, can enhance the accuracy of group
formation in SLN.
4 SEMANTIC MATCHING
FRAMEWORK
Semantic modelling provides the capability of
satisfying information needs of users / social actors
by associating terms to concepts. This can be
manually or autonomously executed by query-
answering techniques. In XEL-GL, semantic
matching is autonomously executed by the
recommender system. The semantic matching
process is the core component of the XEL-GL
framework and its purpose is increasing the accuracy
of group formation; hence, the accuracy of
recommendations is also enhanced. The main task of
the semantic matching component is updating the
friends’ network by adding a topic similarity
dimension to the existing ties. In other words, not
only those who have a higher probability of
interacting are those in the learner’s friends network
but also participants who have highly similar
profiles with respect to topics of interest.
Definition 2: A SLN similarity score is a tuple
{,}where is the set of finite non anonymous
users, and
∈ A is the semantic similarity score
between
,
∈.
Consider the queries
and
issued by
and
,
is the semantic relatedness between
and
, and the similarity between
,
is :
=
∗
(2)
Where
is the
confidence score. Thus,
from equations (1) and (2), the final similarity score
between
and
is concluded as follows:
=
∗
∑
∗
∑
+
∗
∗
(3)
Where
and
are weights assigned to the
final value of the strength of tie and the final value
of the semantic relatedness respectively, and both
weights are ∈
[
0,1
]
.
Assuming the best recommendation for learner
comes from another learner, let’s say
, after
successfully completing a query-answering
transaction between
and
, the system will have
a record of an object-based relation with a similar
role between two learners
and
, and an object-
based relation with different roles between learner
and the tutor who issued the recommended
exercise. In addition, we also have the popularity of
the object, and the semantic relatedness that is based
on the subject of the exercise topic. The semantic
relatedness between two subjects represents the
cultural element which enables measuring an
estimate of the cultural closeness between
and
.
CSEDU 2020 - 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
348
4.1 Distributed Net Similarity Metrics
The net similarity metric is based on the assumption
that dependencies occur between the value of the
strength of tie and the semantic similarity between
and
. In other words, a drop in the semantic
similarity affects the value of the strength of tie
between
and
and the vice versa.In a real-case
scenario, a drop in the strength of tie between
and
could mean that
has not been engaging in
learning activities , thus , recommendations from
user
are less trustworthy than when highly
engaged. Moreover, maintaining a strong tie with
user
while the semantic similarity score is
dropping could be an indication that
is regularly
changing the topics of interest, or may even indicate
a suspicious behaviour in the network. Therefore, we
identify the net value of the semantic similarity
between
and
as follows:
=
+
(4)
Similarly, the net value of the strength of tie
between
and
is:
=
+
(5)
The previous definitions assume strong
dependencies between the value of the strength of tie
and the semantic similarity score. The net value of
the strength of tie is the starting value (strength of
tie) plus/minus the estimate of the total change in the
position of the semantic similarity with respect to
time. From another perspective, the DNSM ties one
variable to the prediction of how the other variable
could behave with respect to a certain time frame.
5 ANALYSIS OF SEMANTIC
MATCHING
For motivation, we analyse the semantic relations
between various topics. Samples of the results are
illustrated in figure 3 and figure 4. In this example,
we compare semantic similarity between topics in
two main subjects; History and Geology. We use the
WS4J (WordNet Similarity for Java) API to measure
semantic similarity/relatedness between topic
sentences. WS4J provides a Java API for several
published semantic similarity algorithms. WS4J has
a number of schemes to calculate semantic
relatedness in WordNet. Fundamentally, however,
WS4J analyses semantic relations between single
words. When comparing sentences, WS4J analyses
the semantic relatedness between all two-word
combinations in sentences
and
, i.e all possible
word pairs
,
where
∈
and
∈
.The scheme we use in our semantic analysis is
called RES scheme with a score range ∈[0,∞], and
0 is the minimum score. The initial results are
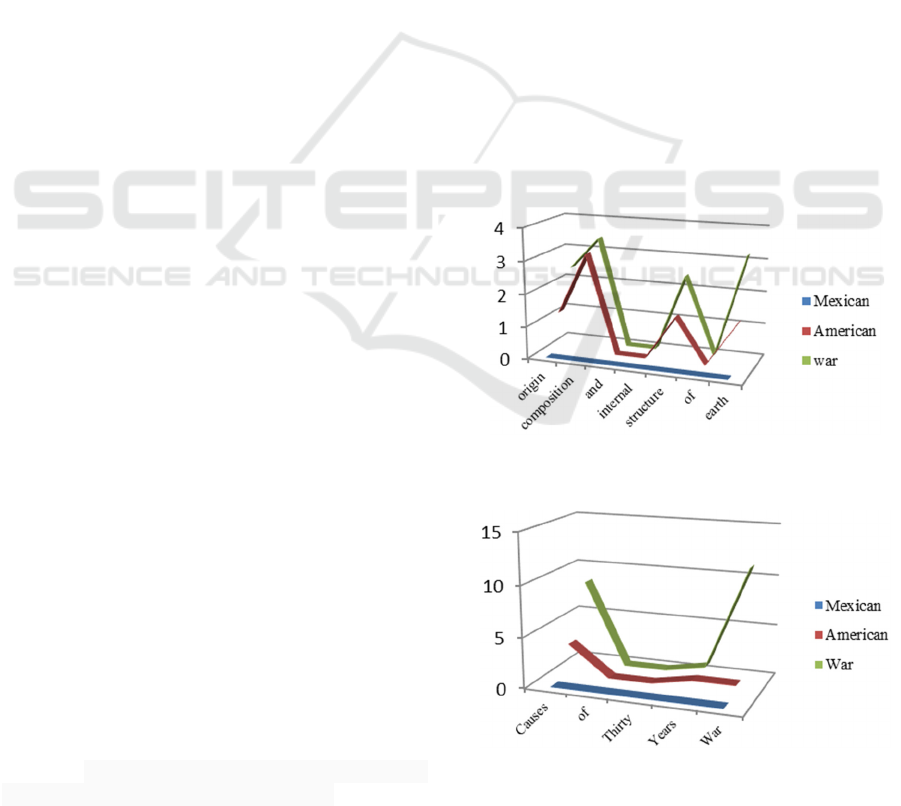
encouraging. Figure 3 shows the semantic similarity
between the History topic ‘Mexican American War’
and the Geology topic ‘Origin Composition and
Internal Structure of Earth’, while figure 4
illustrates the results of the semantic similarity
scores of two history topics ; ‘Mexican American
War’ and ‘Causes of Thirty Years War’. The results
show significant difference between both
comparisons. The maximum semantic relatedness
score achieved for word pairs in comparison 1
, is 3.3826 between the pair
‘’,‘’. Indeed, the maximum
semantic relatedness score for comparison 2
, in figure 4 is for the pair
‘’,‘’ which scored 11.0726,but more
interestingly , the second best result in comparison 2
is for the pair ‘’,‘’ which achieved the
semantic relatedness score: 8.3985.
Figure 3: Semantic relatedness between a History and a
Geology topic.
Figure 4: Semantic relatedness between two History
topics.
XEL Group Learning – A Socio-technical Framework for Self-regulated Learning
349

6 DISCUSSION AND FUTURE
WORK
Our next aim is to relax our assumption that strong
dependencies occur between the strength of social
ties and the semantic similarity of learning topics
through conducting a number of pilot studies. This is
an important socio-cultural perspective of e-learning
to investigate the statistical dependencies between
the learning subject and social ties in SLN. We have
ignored the data distribution scheme and we rather
focused on the socio-technical concept of our
framework. However, some data distribution
schemes can perform decentralized data aggregation
with fast conversion rates. Moreover, they can foster
reputation-based ranking mechanisms in P2P e-
learning such as the one presented by Eid et al.
(2019).Reputation-based ranking/voting can filter
the most trusted learning resource objects (Eid et
al.,2019) which can also enhance the quality of the
recommender component of XEL-GL.
7 CONCLUSION
This paper has presented a socio-technical
framework for group learning in social learning
networks (SLN). The challenge we have addressed
is providing learners with the freedom of identifying
their learning goals and following their preferred
strategies, but at the same time, maintaining the
necessary level of tutoring and developing means of
validation of the quality of SRL (self-regulated
learning) practices. This challenge manifests as a
more complex problem when considering the socio-
technical perspective. Therefore, we have described
XEL-Group Learning (XEL-GL) framework which
provides a holistic approach to e-learning taking into
account motivational, technological, and social
factors. Nevertheless, we have clearly drawn the
distinction between socio-technical and cultural
elements. Our study supports this distinction, for
example, we have shown how the learning subject,
as a cultural element, can enhance the quality of
building social ties in SLN.
REFERENCES
Bembenutty, H. (2011). Self-Regulated Learning: New
Directions for Teaching and Learning, Number 126.
John Wiley & Sons.
Winne, P. H., Nesbit, J. C., Kumar, V., Hadwin, A. F.,
Lajoie, S. P., Azevedo, R., & Perry, N. E. (2006).
Supporting self-regulated learning with gStudy software:
The Learning Kit Project. Technology Instruction
Cognition and Learning, 3(1/2), 105.
Locke, E. A., & Latham, G. P. (2002). Building a
practically useful theory of goal setting and task
motivation: A 35-year odyssey. American
Psychologist, 57(9), 705–717.
Zimmerman, B. J., Bandura, A., & Martinez-Pons, M.
(1992). Self-motivation for academic attainment: The
role of self-efficacy beliefs and personal goal
setting. American educational research journal, 29(3),
663-676.
Dobronyi, C. R., Oreopoulos, P., & Petronijevic, U.
(2019). Goal setting, academic reminders, and college
success: A large-scale field experiment. Journal of
Research on Educational Effectiveness, 12(1), 38-66.
McLoughlin, C., & Lee, M. J. (2008). Future learning
landscapes: Transforming pedagogy through social
software. Innovate: Journal of Online Education, 4(5).
Dabbagh, N., & Kitsantas, A. (2012). Personal Learning
Environments, social media, and self-regulated
learning: A natural formula for connecting formal and
informal learning. The Internet and higher
education, 15(1), 3-8.
Wheeler, S., YEoMAnS, P., & WHEElER, D. (2008). The
good, the bad and the wiki: Evaluating student-
generated content for CL. British journal of
educational technology, 39(6), 987-995.
Kizilcec, R. F., Pérez-Sanagustín, M., & Maldonado, J. J.
(2017). Self-regulated learning strategies predict
learner behavior and goal attainment in Massive Open
Online Courses. Computers & education, 104, 18-33.
Sanchez-Elez, M., Pardines, I., Garcia, P., Miñana, G.,
Roman, S., Sanchez, M., & Risco, J. L. (2014).
Enhancing students’ learning process through self-
generated tests. Journal of Science Education and
Technology, 23(1), 15-25.
Felder, R. M., & Brent, R. (2003). Learning by
doing. Chemical engineering education, 37(4), 282-
309.
Kazienko, P., Musial, K., & Kajdanowicz, T. (2011).
Multidimensional social network in the social
recommender system. IEEE Transactions on Systems,
Man, and Cybernetics-Part A: Systems and
Humans, 41(4), 746-759.
Susarla, A., Oh, J. H., & Tan, Y. (2012). Social networks
and the diffusion of user-generated content: Evidence
from YouTube. Information Systems Research, 23(1),
23-41.
Lachmann, P., & Kiefel, A. (2012, July). Recommending
learning activities as strategy for enabling self-
regulated learning. In 2012 IEEE 12th International
Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (pp.
704-705). IEEE.
Mödritscher, F., Krumay, B., El Helou, S., Gillet, D.,
Nussbaumer, A., Albert, D., ... & Ullrich, C. (2011).
May I suggest? Three PLE recommender strategies in
comparison. Digital Education Review, (20), 1-13.
CSEDU 2020 - 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
350

Kazienko, P., Musial, K., & Kajdanowicz, T. (2011).
Multidimensional social network in the social
recommender system. IEEE Transactions on Systems,
Man, and Cybernetics-Part A: Systems and
Humans, 41(4), 746-759.
Susarla, A., Oh, J. H., & Tan, Y. (2012). Social networks
and the diffusion of user-generated content: Evidence
from YouTube. Information Systems Research, 23(1),
23-41.
Freed, M., Gervasio, M., Spaulding, A., & Yarnall, L.
(2017). Explainable content recommendation for
selfregulated learning. In Proceedings of the
Conference on Advances in Cognitive Systems (Vol.
5).
Nussbaumer, A., Berthold, M., Dahrendorf, D., Schmitz,
H. C., Kravcik, M., & Albert, D. (2012, September). A
mashup recommender for creating personal learning
environments. In International Conference on Web-
Based Learning (pp. 79-88). Springer, Berlin,
Heidelberg.
Shi, Y., Frederiksen, C. H., & Muis, K. R. (2013). A
cross-cultural study of self-regulated learning in a
computer-supported CL environment. Learning and
Instruction, 23, 52-59.
Tsai, C. W. (2013). An effective online teaching method:
The combination of CL with initiation and self-
regulation learning with feedback. Behaviour &
Information Technology, 32(7), 712-723.
Määttä, E., Järvenoja, H., & Järvelä, S. (2012). Triggers of
students’ efficacious interaction in CL
situations. Small Group Research, 43(4), 497-522.
Tsai, C. W. (2013). How to involve students in an online
course: A Redesigned online pedagogy of CL and self-
regulated learning. International Journal of Distance
Education Technologies (IJDET), 11(3), 47-57.
Vuopala, E., Hyvönen, P., & Järvelä, S. (2016).
Interaction forms in successful CL in virtual learning
environments. Active Learning in Higher
Education, 17(1), 25-38.
Winne, P. H., Hadwin, A. F., & Gress, C. (2010). The
learning kit project: Software tools for supporting and
researching regulation of CL. Computers in Human
Behavior, 26(5), 787-793.
Male, G., & Pattinson, C. (2011). Enhancing the quality of
e-learning through mobile technology: A socio-
cultural and technology perspective towards quality e-
learning applications. Campus-Wide Information
Systems, 28(5), 331-344.
Land, S. M., & Zimmerman, H. T. (2015). Socio-technical
dimensions of an outdoor mobile learning
environment: a three-phase design-based research
investigation. Educational Technology Research and
Development, 63(2), 229-255.
Upadhyaya, KT, & Mallik, D. (2013). E-learning as a
socio-technical system: an insight into factors
influencing its effectiveness. Business Perspectives
and Research , 2 (1), 1-12.
Bednar, P. M., & Welch, C. (2019). Socio-technical
perspectives on smart working: Creating meaningful
and sustainable systems. Information Systems
Frontiers, 1-18.
Eid, S., Kismihók, G., & Mol, S. T. (2019, September).
Equilibrium-Based Voting: A Strategy for Electing
Service Providers in P2P E-Learning. In 2019.
XEL Group Learning – A Socio-technical Framework for Self-regulated Learning
351
