
Towards the Innovation of High-tech Small-medium Enterprises
(SMEs): The Interview Approach
Wei Xue
1
, Victor Chang
2a
, Yijie Chen
3
and Qianwen Xu
4
1
Zhonghui Accountancy, Suzhou, China
2
School of Computing, Engineering and Digital Technologies, Teesside University, Middlesbrough, U.K.
3
International Business School Suzhou, Xi’an Jiaotong-Liverpool University, Suzhou, China
4
Independent Researcher, Suzhou, China
Keywords: Innovation, Small and Medium-sized Enterprises.
Abstract: With the intensive global market competition, the Chinese central government is paying more attention to the
innovation of SMEs, especially for high-tech SMEs. This paper conducts the interview approach to investigate
the status of innovation and its importance to SMEs in Suzhou. R&D development requires innovation as a
key element. Findings from interviewees are positive towards innovation. Innovation has been used
throughout the SMEs – from strategies, marketing, products to services. This implementation makes SMEs
in Suzhou more competitive than most other cities of China by offering positive thinking and dynamic inputs
to produce more creative products and services. However, problems have been identified. Although SMEs
are the main body of technological innovation, but it is difficult for them to survive. We plan to propose a
framework that contains all factors influencing R&D and carefully set hypotheses. With our mixed-method
approach in our future work, we present more results and analysis based on our findings.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since China opened up its market, Chinese economic
development has been depended on the introduction
of foreign advanced technology and investment. But
the attractiveness of China to foreign investment has
declined with the increase of the labor cost. Now
China's economic development model is facing a real
transformation under a more intense global
competitive situation. China's future economic
development inner driver would come from the
development of domestic enterprises. Of all these
domestic enterprises, small and medium-sized
enterprises (SMEs) are the pillar of the national
economy.
However, in the long run, Chinese SMEs have
been located at the bottom level of the industry chain.
They are characterized by low-quality products, low
price, or technical plagiarism. If Chinese enterprises
cannot move from the current simple processing, low
technology content product manufacturing to the high
value-added product with independent intellectual
property rights, the development will be difficult to
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8012-5852
sustain. Chinese enterprises want to survive and
develop in international competition only through
independent innovation, developing products and
production technology with independent intellectual
property rights and independent brands. Therefore, in
recent years, research on the innovation of enterprises
has been the focus of attention in the field of
economics.
Tan et al. (2015) indicated that China had become the
global largest market and manufacturing factory, and
Chinese innovation capabilities have been largely
advanced as it experienced 30 years' reform and
opened up to the world. China has learned and
enhanced much in the innovation awareness through
the cooperation with foreign companies and partners
(Chung, Leanne, 2014).
2 MANUSCRIPT PREPARATION
Some of the Chinese industries have made significant
progress in the high technology product development
and the business model innovation. McKinsey (2016)
Xue, W., Chang, V., Chen, Y. and Xu, Q.
Towards the Innovation of High-tech Small-medium Enterprises (SMEs): The Interview Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0009489601290135
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business (FEMIB 2020), pages 129-135
ISBN: 978-989-758-422-0
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
129

researched that China performed well in efficiency-
driven and market-focused business innovations, like
new energy, E-commerce, high-speed train and
mobile phones, etc. through this research and survey,
they suggested that the Chinese companies had very
powerful potentially innovation capabilities.
Especially, SMEs are the main body of technological
innovation and the most active group of technological
innovation. SMEs are the main carriers of the
transformation of scientific and technological
achievements, and they are playing an increasingly
important role in promoting the progress of science
and technology, industrial upgrading and economic
growth. According to the disclosure of the central
government (2018), now more than 70% of
technology innovation of China came from SMEs. Xu
(2006) analyzed that SMEs have taken more than
65% patents, 74% technological innovation and 80%
new product development. However, it is difficult for
SMEs to survive for lots of reasons, such as
insufficient financial resources, weak ability to bear
risk, poor attractiveness to talents, etc. According to
the Chinese statistics yearbook (2016), the survival
rate of SMEs only arrives at 10% in the recent ten
years. Therefore, although SMEs account for most of
the technological innovation of China, but their
ability or willingness to innovate constantly is not
high comparatively. From a long-term perspective,
the situation is harmful to the development of China's
economy. Then, it is important to understand the
status of innovation to SMEs and identify the
influencing factors to their ability of continuous
innovation.
Small and medium enterprises would have more
innovation driving motivation because they are
mostly obtaining the profit from the market and the
grants from the government (Cohen and Levinthal,
1990; Romer, 1990; and Van Dijk et al. 1997). But
actually, the innovation willingness from small and
medium enterprises is not very high, because the
long-term technical foundation of small and medium-
sized private enterprises is so weak that there is
insufficient innovation accumulation. Hence, they
generally adopt a low-tech and low-cost development
strategy. Innovation often requires a large amount of
capital, and at the same time, there are larger technical
and market risks. Small and medium-sized
enterprises’ scale is very small, with insufficient
financial resources and weak ability to bear risks.
Moreover, they are always facing a difficult financing
status and a shortage of innovative funds. Some small
and medium-sized enterprises have gradually realized
the importance of technological innovation to the
continuous development of enterprises. Therefore,
they try to implement various innovation activities.
However, patent and other intellectual property rights
are not protected enough, the enforcement of the law
is weak, and the achievements of enterprise
innovation are often harmed by other enterprises in
the same industry without penalizing. So the initiative
of innovation is breaking down.
Radas and Bozic (2009) indicated that SMEs
would confront much more challenges if they want to
initiate innovation and develop innovation
capabilities because SMEs do not have sufficient
capital contribution and technological accumulations.
Then, how to enhance the innovation capabilities has
become the first task for the SME founders or owners
and the government.
But so far, most past literature research mainly
concentrated on public companies and stated-own
companies because it is much easier to obtain
secondary information from the public disclosure.
Some literature has investigated the product
innovation or R&D research (Zhu et al., 2012).
Innovation should be usually considered as the
thought or approach to do something new or different
(Garcia & Calantone, 2002). Baregheh et al. (2009)
indicated that innovation includes multiple stages in
which organizations turn ideas into new or improved
products, services, or processes in order to advance
compete and differentiate themselves in their market
place. The types of innovations Baregheh studied
belongs to product or service and process innovation.
Kahn (2018) defined product or service innovation as
the outcome of the work and process innovation as
the change of the process. However, according to
Azar and Ciabuschi (2017), it is important to consider
not only product or service, and process innovations,
but also organizational and marketing innovation.
Organizational innovation is introducing an up-to-
date method in the enterprise’s business operation,
management, or relations. By conducting
organizational innovation, expenditure on the
administration and transaction may be reduced and
employee satisfaction may be improved
(Rajapathirana and Hui, 2018). Marketing innovation
is the implementation of new methods in product
design, pricing, promotion, or advertising placement
(OECD, 2005). In this paper, the scope of innovation
is not limited to technological and includes
organizational and marketing innovation.
There are some generally accepted main factors
would influence the innovation of enterprises, such as
the industry, the scale, the R&D investment amount,
the government incentives, the history of the
enterprises, the strategy an position of the product, the
leader or founder of the enterprises, the competition,
FEMIB 2020 - 2nd International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business
130

and the economy of the country. But for High-Tech
SMEs in China, Deng (2019) and Shan, Sun (2018)
suggested that the government policies are primary
incentives to push forward the innovation capability
of the enterprises. In Deng’s research (2019), she
found that the main support policies for technology-
based SMEs mainly include tax reductions, financial
subsidies, and talent introduction policies. However,
from her survey, the most obvious benefit for
technology-based SMEs is just tax reduction policies.
In 2017, the Ministry of Finance, the State
Administration of Taxation, and the Ministry of
Science and Technology specifically issued support
policies for the deduction of R & D expenses for
technology-based SMEs, including the evaluation
criteria for technology-based SMEs. Shan and Sun
(2018) studied tax policies much deeper. While they
affirmed this policy, they identified some questions
as well. First of all, since another policy on increasing
the pre-tax deduction ratio of research and
development expenses in 2018, all types of
enterprises that meet the required R & D expenses are
subject to a 75% deduction. Therefore, the tax
deduction policy in 2017 for technology-based SMEs
is not an advantage anymore. Secondly, the restriction
of science and technology has raised the threshold for
SMEs to enjoy the tax policy. Some SMEs engaged
in R & D activities but not meet the evaluation criteria
are prevented from enjoying this special policy
support. Furthermore, the tax deduction policy has
limited support for loss-making technology SMEs.
The loss-making technology SMEs are mostly in the
initial stage. They face greater risks of R & D failure
and investment failure. The demand for various
special policies is particularly strong and the tax
deduction policy cannot solve their problem
promptly.
3 METHOD
The research would select the SMEs around Suzhou
City, and the research would adopt the “Grounded
theory”. The “Grounded theory” was first introduced
by Barney Glaser and Anselm Strauss in 1965, the
principle of the grounded theory is to deduce a
conclusion from the interview or the data, so it is also
called that how to discover the nature and conclusion
from the data. This research method is more useful to
appraise the comparative importance of different
factors influencing the innovation.
The research would be performed in the case
study focusing on the discussion with the talent from
the SMEs located in Suzhou cities, which has a
national high-tech industrial base as well as one of the
important central cities in the Yangtze River Delta.
Among all the cities in the Jiang Su province,
Suzhou's comprehensive strength of scientific and
technological innovation has ranked among the top
for ten consecutive years. According to the Suzhou
government, its total social R & D investment
accounts for 2.78% of GDP, the contribution rate of
scientific and technological progress reaches 64.5%
and the output value of high-tech industries accounted
for 47.7% of the total output value of industries
(Suzhou Statistics Bureau, 2019). At present, society
and economy are constantly changing, and the
emergence of high-tech industries has become an
important technology to promote economic growth in
the century. He (2016) explained three main ways on
how high-tech industries promote the development of
the economy. First of all, high-tech industries have
higher added value, faster update speeds, higher
investment returns, and lower investment risks
compared with other economic sectors, leading to a
large advantage. Secondly, high-tech industries
improve the labor productivity of employees
effectively as well. Finally, the emergence of high-
tech industries changed the traditional technology and
promoted the development of enterprises. Therefore,
increasing efforts to develop high-tech industries in
Suzhou has played an important role in economic
growth.
The research would adopt a one to one interview
approach. The research is based on collecting
evidence and keywords around the core question
concerning innovation. This research employs the
interview approach for two reasons. On the one hand,
the government statistics might mislead the research
result because many innovation activities in SMEs are
ignored by their survey. The majority of the SMEs do
not have a formal or fixed R&D or innovation
department internally (Kleinknecht, 1987).
Therefore, the data the government collected may not
be complete. However, in this research, which
focuses on the city level instead of a province or a
country level, conducting the interview approach is
easier for us to identify the relative importance of
different factors to the innovation of SMEs. On the
other hand, the interview approach allows the
interviewee to express themselves in a more freedom
way. Compared with questionnaires or statistics, the
information collected from the interviews provides
the primary information for research, which is more
direct and convincing. The research sample includes
50 employees from 10 SMEs and ten government
officers. The names of the sample enterprises are
anonymized and their basic information is presented
Towards the Innovation of High-tech Small-medium Enterprises (SMEs): The Interview Approach
131
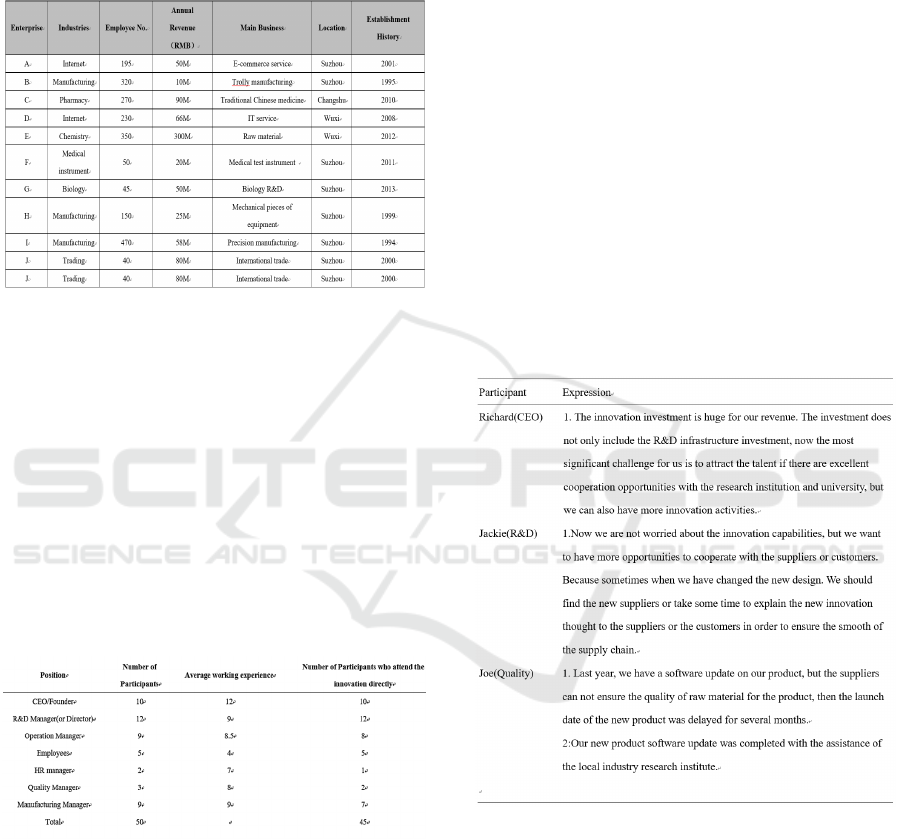
in Table 1. They have covered several industries,
including the Internet, manufacturing, pharmacy,
trading, etc. and the years of establishment range
from 6 to 25 years.
Table 1: The basic information of sample enterprises.
These 50 employees from the enterprises would
include the owner or the founder, the CEO, or the
general manager, the technology or operation middle
level management, as well as high-level employees.
The SMEs participants’ demographics are shown in
Table 2. Among these participants, expect the five
employees whose average working experience is four
years, other roles' average working experience are all
greater than seven years. Besides, most of the
participants take part in the innovation activities
directly, which makes them suitable to be the
interviewees when studying innovations of high-tech
SMEs.
Table 2: The participants’ demographics from enterprises.
The interviewees would reply to the questions
under the guidance of each theme questions, which
allow them to express themselves and show the key
points in their thoughts. The interviews were recorded
during the process. Two processes were used for
coding. First, there was an intensive listening and re-
listening to the interviews to take notes of the
keywords. Then there was much more careful coding
for themes and sub-themes. Some of these themes
came from the past literature and some were
developed out of the case.
4 RESEARCH FINDINGS
When the interview was completed and the interview
contents are recorded, the research adopted the
approaches suggested by Hou et al. (2014). This
research concluded two constructs from the interview
participants’ disclosure that are “Innovation
cooperation” and “innovation orientation”. Also, a
new concept, “IP transaction platform," was found
during the interview.
Summary of selected interviews is presented in
Table 3. In the past literature, very little attention has
been paid to the Innovation cooperation, except the
research performed by De Marchi (2012) is the first
one that indicated the influence of cooperation on the
R&D. Giovannetti and Piga (2017) performed
empirical research and indicated that active
cooperation played an active impact on the innovation
of enterprises. We did obtain the same response from
the interview and discussion with the participants.
Table 3: Summary of selected interviews.
The summary from the interview outcome is as
follows. First, innovation is critical to some sectors
such as the pharmaceutical and high-tech industry,
since they need to implement new concepts and ideas
into product development. They also spend a
significant amount of funds for research and
development. Second, innovation can drive the way
that Suzhou Industry Parks can function. Aiming to
be competitive in mainland China, innovation has
been used throughout the SMEs – from strategies to
concepts, from implementations to marketing and
from products to services. Third, innovation means it
FEMIB 2020 - 2nd International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business
132
has influenced the way each business entity works,
such as allowing the remote working, portfolio-based
outputs and team dynamics. It has changed the
businesses to think and act positively, and respond to
the markets and customers as soon as possible, and
embrace challenges. As a result, innovation has
offered positive thinking and dynamic inputs for each
individual and organization to produce more creative
products and services, and to think ahead of the
market response and customer demands (Zhou et al.,
2005). For example, private car sharing, smart
manufacturing, smart toys and smart caring can be
successful and sustainable business models in Suzhou,
while other parts of China are still in exploring stages.
These interview outcomes can offer valuable
knowledge which are not yet in the current literature.
5 DISCUSSION
For a significant period of time, studies on innovation
activities have been focused on technology and R&D
innovation, which was considered as the main factor
in improving the performance and growth of the
enterprises (Fagerberg, 1994). Some scholars and
researches have indicated that innovation in modern
industries and businesses should be much broader
than the traditional high technology and R&D
activities (Marsili & Salter, 2006; Schmidt and
Rammer, 2007). The research findings agree with
them and found that in high-tech SMEs in Suzhou,
innovation is not limited to product or service
innovation and process innovation anymore. The
concept of innovation can also be implemented in the
organization or marketing.
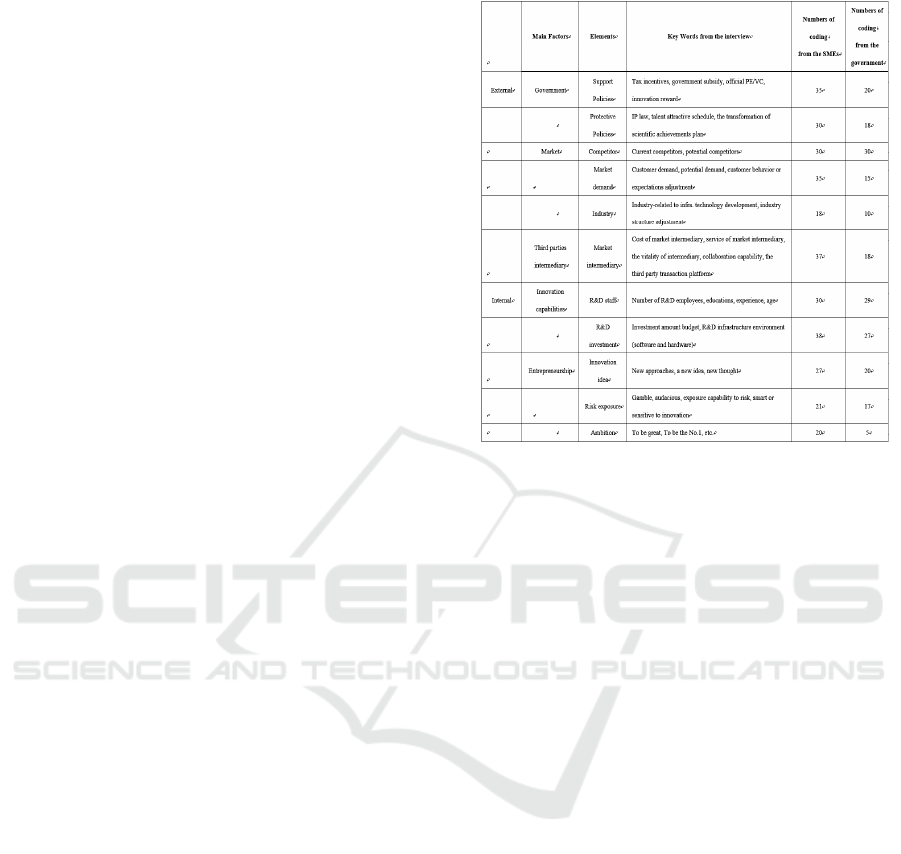
The framework that contains the factors influencing
the innovation of high-tech SMEs can be constructed
from the interviews and it is shown in Table 4.
The influencing factors can be categorized into
external factors and internal factors. External factors
include the government, market and third parties.
Internal factors consist of innovation capabilities and
entrepreneurship.
Firstly, the relevant government policies, such as
government subsidy, tax incentives, have positive
impacts on the innovation of high-tech SMEs.
However, the results of interviews indicate that
financial support form the government cannot
fundamentally solve the financing problem for SMEs
without a good financial environment. In addition,
high-tech SMEs require highly relevant laws and
protections from the government to protect their
innovation achievements.
Table 4: The framework of influencing factors.
The influencing factors can be categorized into
external factors and internal factors. External factors
include the government, market and third parties.
Internal factors consist of innovation capabilities and
entrepreneurship.
Firstly, the relevant government policies, such as
government subsidy, tax incentives, have positive
impacts on the innovation of high-tech SMEs.
However, the results of interviews indicate that
financial support form the government cannot
fundamentally solve the financing problem for SMEs
without a good financial environment. In addition,
high-tech SMEs require highly relevant laws and
protections from the government to protect their
innovation achievements.
Secondly, SMEs with good marketing capability can
grasp technical market requirements or expectations
faster; then, they can update their product or service
quickly and lead to a positive impact on market
performance. In addition, market competition and
industry development cause high-tech SMEs to
produce a sense of crisis and urgency, thus make
pressure into motive force.
Thirdly, innovation cooperation with the third party
has a positive influence on the innovation of high-
tech SMEs. The results indicate that innovation
searches may be difficult for SMEs as most of them
do not have much external contact and the cost and
time spent on the search may be too high for them.
Service intermediaries can help SMEs to achieve a
balance between cost and benefit of innovation search
as they interact with numerous enterprises and they
have become a warehouse with knowledge and
Towards the Innovation of High-tech Small-medium Enterprises (SMEs): The Interview Approach
133

opportunity. With help from these third parties, the
innovation of high-tech SMEs will be promoted.
Fourthly, innovation capability is the guarantee of the
technological innovation drive of SMEs and the
innovation capability comes from the talents.
However, according to the interviews, it is difficult
for high-tech SMEs to attract high-level talents
because most of them cannot afford the increasing
employment cost.
Finally, entrepreneurship impacts the innovation of
high-tech SMEs positively. With proactiveness,
innovation-oriented leadership and strong risk-
bearing ability, a high-tech SME is more willing to
innovate continuously.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The paper presents the status of innovation and its
importance to SMEs in Suzhou while adopting a
qualitative approach. R&D development requires
innovation as a key element. Factors that can
influence the success and delivery of R&D can
largely impact the effectiveness of products and
services in Suzhou. This can also affect its GDP
contributions in Suzhou, since it is heavily dependent
on revenue from high-tech and R&D firms in Suzhou
Industrial Park, Suzhou, China. Findings from
interviewees are positive towards innovation.
However, problems have been identified. This paper
provides guidance for the high-tech SMEs on how to
develop and maintain their innovation willingness
and capability. In addition, this paper provides
references for the local government on how to adopt
appropriate approaches to encourage SMEs forward
to innovation. We plan to propose a framework that
contains all factors influencing R&D and carefully set
hypotheses. With our mixed-method approach in our
future work, we present more results and analysis
based on our findings.
REFERENCES
Azar, G., & Ciabuschi, F. (2017). Organizational
innovation, technological innovation, and export
performance: The effects of innovation radicalness
and extensiveness. International Business Review,
26(2), 324-336.
Baregheh, A., Rowley, J., Sambrook, S. (2009). Towards a
multidisciplinary definition of innovation.
Management Decision, 47, 1323-1339
B. Van Dijk, R. Den Hertog, B. Menkveld, D. Thurik
(1997). Some new evidence on the determinants large
and small firm determinants. Small Business
Economics, 9 (4), 335-343
Chinese statistics year book (2016). National Bureau of
Statistics of China.
In:http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2011/indexeh.htm
accessed on 1 February 2020.
Chung, L. (2014). Headquarters' managerial intentionality
and reverse transfer of practices, Manag. Int. Rev., 54
(2), 225-252
Deng, Y.G. (2019). Research on the Improvement of
Independent Innovation Ability of Technology based
SMEs—Taking the power industry of Zhuzhou as an
example. Science Technology and Industry, 19(6), 84-
88
Fagerberg, J. (1994). Technology and international
differences in growth rates. Journal of Economic
Literature, 32(3), 1147-1175.
Garcia, R., & Calantone, R. (2002). A critical look at
technological innovation typology and innovativeness
terminology: a literature review. Journal of Product
Innovation Management: An international publication
of the product development & management
association, 19(2), 110-132.
Giovannetti, E., & Piga, C. A. (2017). The contrasting
effects of active and passive cooperation on innovation
and productivity: Evidence from British local
innovation networks. International Journal of
Production Economics, 187, 102-112.
He JM (2016). The contribution and role of China's high-
tech industry to economic growth. China Economy
and Trade, (13), 45-45.
Kahn, K. B. (2018). Understanding innovation. Business
Horizons, 61(3), 453-460.
Kleinknecht, A. (1987). Measuring R&D in small firms:
How much are we missing? The Journal of Industrial
Economics, 36(2):253-256.
Kuo, Y.K., Kuo, T.H., Ho, LA (2014). Enabling innovative
ability: Knowledge sharing as a mediator. Industrial
Management & Data Systems, 114 (5), 696-710.
Marsili, O., & Salter, A. (2006). The dark matter of
innovation: design and innovative performance in
Dutch manufacturing. Technology analysis &
strategic management, 18(5), 515-534.
Mckinsey Global Institute (2016). The China Effect on
Global Innovation, October. McKinsey &
Company.In http://www.mckinseychina.com/wp-
content/uploads/2015/07/mckinsey-china-effect-on-
global-innovation-2015.pdf?bd0bde〉on 15 Jan 2016.
OECD. (2005). The Measurement of Scientific and
Technological Activities Oslo Manual. Guidelines for
Collecting and Interpreting Innovation Data. In (3rd
ed.). Paris: OECD EUROTAT.
Romer, P.M. (1990). Endogenous technological change.
Journal of Political Economy
, 78, 71-102
Radas, L. Bozic (2009). The antecedents of SME
innovativeness in an emerging transition economy,
Technovation, 29, 438-450
Rajapathirana, R. J., & Hui, Y. (2018). Relationship
between innovation capability, innovation type, and
FEMIB 2020 - 2nd International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business
134

firm performance. Journal of Innovation &
Knowledge, 3(1), 44-55.
Schmidt, T., & Rammer, C. (2007). Non-technological and
technological innovation: strange bedfellows?. ZEW-
Centre for European Economic Research Discussion
Paper, (07-052).
Shan, W.L., Sun, HZ (2018). Problems and
countermeasures of R&D expenses additional
deduction policy for small and medium sized scientific
and technological enterprises. Journal of Hebei
University of Engineering (Social Science Edition),
35(4), 12-14
Suzhou Statistics Bureau (2019). Statistical Communiqué
on Suzhou National Economic and Social
Development 2018, Available at
http://www.zfxxgk.suzhou.gov.cn/sjjg/szstjj/201905/t
20190515_1165289.html (Accessed: 27 Jan 2020)
Tan, K. H., Zhan, Y., Ji, G., Ye, F., & Chang, C. (2015).
Harvesting big data to enhance supply chain
innovation capabilities: An analytic infrastructure
based on deduction graph. International Journal of
Production Economics, 165, 223-233.
De Marchi, V. (2012). Environmental innovation and R &
D cooperation: empirical evidence from Spanish
manufacturing firms. Research Policies, 41 (3), 614-
623
Cohen, W.M., Levinthal, DA (1990). Absorptive capacity:
A new perspective on learning and innovation.
Administrative Science Quarterly, 35, 126-138
Xu, G.H. (2006). Several significant issues related to
independent innovation. Journal of Chinese Soft
Science, Vol (10), 1-10
Zhu, Y., Wittmann, X., Peng, M.W. (2012). Institution-
based barriers to innovation in SMEs in China. Asia
Pac. J. Manag., 29 (4), 1131-1142
Zhou, K. Z., Yim, C. K., & Tse, D. K. (2005). The effects
of strategic orientations on technology-and market-
based breakthrough innovations. Journal of Marketing,
69(2), 42-60.
Towards the Innovation of High-tech Small-medium Enterprises (SMEs): The Interview Approach
135
