
Reading Students’ Multiple Mental States in Conversation
from Facial and Heart Rate Cues
Shimeng Peng
1a
, Shigeki Ohira
2b
and Katashi Nagao
1c
1
Department of Intelligent Systems, Graduate School of Informatics, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan
2
Information Technology Center, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan
Keywords: Mental States Recognition in Conversation, Multimodal Feature Analysis, Educational Data Analysis,
Facial Data, Heart Rate, Machine Learning, Learning Analytics.
Abstract: Students’ mental states have been widely acknowledged as crucial components for inferring their learning
processes and are closely linked with learning outcomes. Understanding students’ complex mental states
including concentration, confusion, frustration, and boredom in teacher-student conversation could benefit a
human teacher’s perceptual and real-time decision-making capability in providing personalized and adaptive
support in coaching activities. Many lines of research have explored the automatic measurement of students’
mental states in pre-designed human-computer tasks. It still remains a challenge to detect the complex mental
states of students in real teacher-student conversation. In this study, we made such an attempt by describing
a system for predicting the complex mental states of students from multiple perspectives: facial and
physiological (heart rate) cues in real student-teacher conversation scenarios. We developed an advanced
multi-sensor-based system and applied it in small-scale meetings to collect students’ multimodal conversation
data. We demonstrate a multimodal analysis framework. Machine learning models were built by using
extracted interpretable proxy features at a fine-grained level to validate their predictive ability regarding
students’ multiple mental states. Our results provide evidence of the potential value of fusing multimodal data
to understand students’ multiple mental states in real-world student-teacher conversation.
1 INTRODUCTION
There has been increasing attention on students’
complex affective and mental states exposed during
learning interactions from the educational research
community. In the past few years, much research has
validated the correlation of students’ mental states
with measures of their short-term or long-term
learning achievements (Craig et al., 2004; Pardos et
al., 2014; Rodrigo et al., 2012; Calvo & D’Mello,
2010; Feidakis et al., 2013). Holding a small group
meeting composed of teacher-student conversations
is one of the most common ways of coaching
interactions. (Bell & Cowie, 2001; Shepard, 2005)
named this method “assessment conversation,” and it
is an important link in scaffolding learning. In
coaching done in academic small-group meetings, the
teacher tends to strike up task-oriented conversations
to diagnosis students’ learning progress and provide
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9510-2549
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9445-4457
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6973-7340
appropriate intervention by giving comments or
problem solution strategies. It is essential for human
teachers to be sensitive to changes in the mental states
of students order to make real-time decisions on what
kind of support to provide and at what times.
(D’Mello & Graesser, 2012) proposed a typical
resolution cycle that characterizes dynamic changes
in students’ mental states, which has been used as a
classical, theoretically grounded model in
understanding students’ complex mental states
experienced in learning activities. This dynamic
mental-states theory suggests that a student
commonly enters interactive learning activities with a
state of engaged concentration, and this state will
remain until challenges or difficulty emerges, which
may result their state transitioning to one of
confusion. At this point, the student may transition to
one of two paths, go back to being concentrated if
they resolve this confusion. Alternatively, the student
may transition to frustration at which point, the
68
Peng, S., Ohira, S. and Nagao, K.
Reading Students’ Multiple Mental States in Conversation from Facial and Heart Rate Cues.
DOI: 10.5220/0009564000680076
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2020) - Volume 1, pages 68-76
ISBN: 978-989-758-417-6
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

student is unlikely to transition back to confusion or
concentration and may be more likely to transition to
boredom and then quit learning.
Developing an effective monitoring agent that
could sense the occurrence and transition of students’
complex mental states, that is, concentration,
confusion, frustration, boredom, will be beneficial to
helping teachers improve their perceptual and
reasoning capabilities and resolve instances of
“assistance dilemma” in coaching. An intelligent
negative-states-awareness agent could precisely
recognize negative mental states in students,
especially confused and frustrated ones, infer that
students need help catching up with the class, and
alert the teacher to direct their coaching resources and
aim to help students get out of this learning dilemma.
Much research has used univariate modalities
such as video (Grafsgaard et al., 2013), audio
(Forbes-Riley & Litman, 2011) and physiological
measures (Hussain et al., 2011) to detect affective or
mental states in learning activities. Modern sensors
have rendered opportunities to support novel
methodological approaches to measure students’
mental states from multiple perspectives. (Kapoor &
Picard, 2005; Whitehill et al., 2011) adopt
multimodal approaches for mental state detection that
have been explored to improve recognition accuracy.
In this study, a multi-sensor-based data collection
system was developed to record students’ facial
expressions, physiological signals (heart rate), and
audio when holding structured conversations with
teachers in regular small-group meetings at
universities as well as a real-time label annotation
tool for collecting the results of observing meeting
participants for an evaluation regarding speakers’
mental states during conversation. We then propose a
multimodal framework for detecting the complex-
states of speaker-students, that is, concentration,
confusion, frustration, and boredom, by analyzing
multimodal features. Machine learning models were
also generated to validate the predictive performance
of our extracted multimodal features.
2 RELATED WORK
Most research regarding emotion recognition in
conversation (ERC) has been seen as a Natural
Language Process (NLP) task due to the availability
of large-scale conversations datasets related to ERC
on social media platforms like YouTube, Facebook,
Reddit, and Twitter (Poria et al., 2019). Due to the
specific character of social media datasets, ERC has
been developing into a textual emotion recognition
problem. ERC in educational applications mainly
carried out based in human-computer interaction
setups, in which researchers analyzed students’
mental or affective states when they are interacting
with an online tutor system (D’Mello et al., 2006;
D’Mello et al., 2008). The few popular available
multimodal datasets for mental-state recognition in
human-human conversation are based on pre-
designed conversation transcripts, such as IEMOCAP
(Busso et al., 2008), where actors perform scripted
scenarios specifically selected to elicit emotional
expressions, and DailyDialog (Li et al., 2017) in
which chit-chat data generated in daily life is
recorded.
Teacher-student conversation is considered to be
a type of task-oriented human-human conversation
that is generally carried out around a topic and
developed with argumentation logic or through the
guidance of a teacher. It is necessary to use teacher-
student conversations in real coaching scenarios and
explore students’ complex mental states from more
reliable multiple perspectives, which would provide
practical advice for teacher coaching in the real world.
Given the validated and precise prediction
performance regarding students’ mental states done
using facial expression or physiological signals, in
this paper, we attempted to take advantage of sensory
signals including facial and heart rate cues to
challenge the task of predicting students’ mental
states, that is, concentration, confusion, frustration,
and boredom in real teacher-student conversation.
2.1 Physiological-signal-based
Detection
Physiological signals have been commonly used in
analyzing mental states because affective or mental
states are associated with thoughts and feelings,
which are controlled by the autonomic nervous
system, and changes in them can be observed by
physiological signals such as the heart rate (HR) and
brainwaves. (Stevens et al., 2007) used heart rate
signals for detecting engage while students interacted
with a computer. In our previous work (Peng et al.,
2019; Peng et al., 2019), we took advantage of the use
of heart rate signals to predict the appropriateness
students’ answers, and we suggested that students’
mental confidence toward correctly giving answers
could be indicted by their heart rate features. Several
pieces of work (Stevens et al., 2007; Cowley et al.,
2013; Luft et al., 2013; Burt & Obradović, 2013)
analyzed brainwave EEG signals to understand the
cognitive states of students during the learning
process.
Reading Students’ Multiple Mental States in Conversation from Facial and Heart Rate Cues
69

2.2 Facial-signal-based Detection
With the development of computer vision
technologies, human mental states have usually been
detected on the basis of facial signals extracted from
video streams. Among them, eye related features like
eye blinking and eye-gaze analysis have been used to
help understand students’ concentration states
(Koning et al., 2010; Gomes et al., 2013). (L.
Devillers & L. Vidrascu, 2007) characterize human
smiles and laughter by monitoring mouth-noise
related features. (Grafsgaard et al., 2013) used mouth
features to predict overall levels of concentration,
frustration, and learning gain.
2.3 Novelty and Contributions
There are several aspects in which this study is
different from relevant studies. The contributions we
make are (1) instead of students in computer tutor
interaction or pre-designed script-based human-
human conversation activities, we are interested in an
“unplugged” scenario in which a student and his or
her advisor teacher have a conversation in real
coaching activities. We recorded a 3-month long
conversation between students and a teacher held
weekly in a face-to-face small-group meeting. In
these conversations, students started by stating their
research progress, and the teacher initiated the
conversation by asking questions to check students’
learning situations or look for detailed explanations
on uncertain content. Therefore, our research work
was applied and validated on a real-world dataset,
guaranteeing our results’ applicability and
practicality in real-world coaching activities. (2) A
multi-sensor data collection system was developed
and applied in a small group meeting held in a lab, in
which we used the iPhone to track the facial
information of each meeting participant and used the
Apple watch to detect their heart rate signals. Audio
of the entire conversation was recorded and
transcribed into statements by Google Cloud Speech-
to-Text. A real-time mental-state label annotation tool
was built and launched for our system, and meeting
participants were asked to observe and annotate a
speaker’s mental states while the speaker was
speaking. Our multimodal data collection system
could support a 2-3 hours long group meeting
composed of conversation activities held amongst
multiple participants. Participants’ facial data,
physiological data, heart rate, audio, and the context
of the conversation as well as a speaker’s mental
states labels are synchronized, captured, and stored
structurally, and this shows the potential utility of our
system for long-term multimodal dataset collection as
well as for supporting the analysis of real-world
teacher-student conversation; (3) With few
exceptions, most existing work relies on univariate
modality, while our study attempts to propose a
multimodal framework based on multiple data
streams, that is, facial and heart rate signals used for
predicting students’ complex mental states:
concentration, confusion, frustration, and boredom. A
series of aggregated level features were extracted and
discussed as facial and physiological patterns in
characterizing students’ mental sates in conversation.
We generated several machine learning predictive
models to validate the precognitive ability of our
proposed multimodal framework and achieved good
results.
3 MULTIMODAL
CONVERSATION DATA
COLLECTION
3.1 Participants
The participants were 4 undergraduate/graduate
students and their advisor professor, and they ranged
in age from 21 to 24 years. The professor has been
guiding these 4 students for 1 to 2 years by holding
regular small-group progress report meetings every
week. Data for our multimodal dataset was collected
on the basis of these 4 students when they had a
conversation with the professor, in which they
reported their weekly study progress in a small-group
meeting held in a lab.
3.2 Data Collection System and
Procedure
In these conversation-based small group meetings,
students sat in a circle as shown in Fig. 1.
Figure 1: Conversation-based small group meeting.
CSEDU 2020 - 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
70
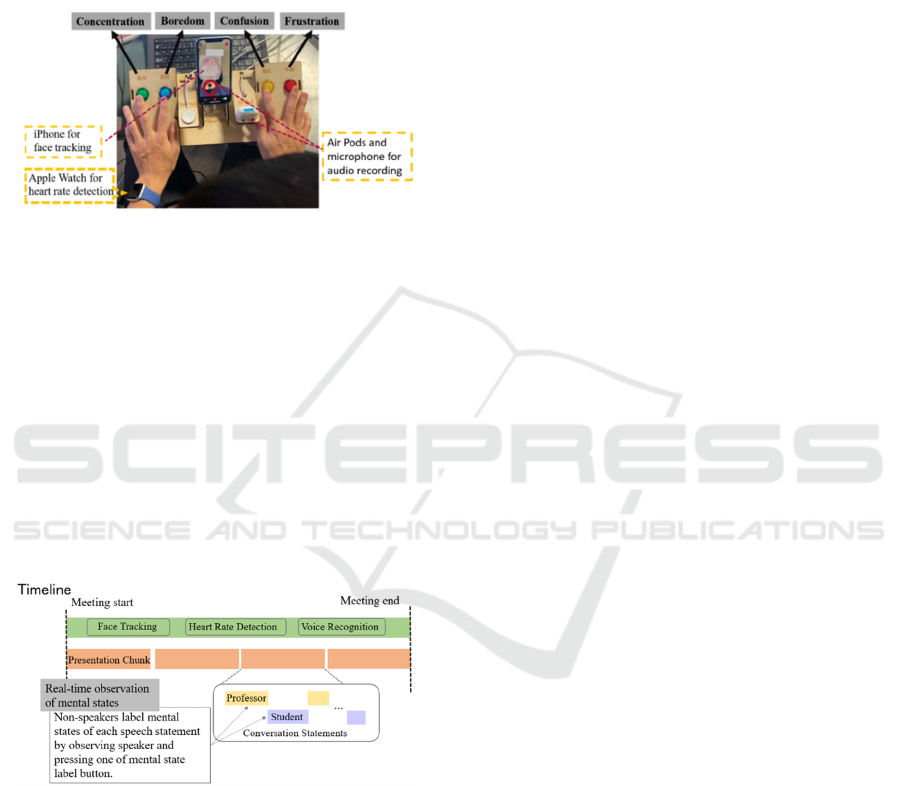
Before the meeting, as shown in Fig. 2, all
participants were asked to start a face tracking
function developed for the iPhone XR, which was
placed on the desk in front of each of them, by
choosing their name and pressing the recording
button. A paired Apple Watch worn on their wrist was
started synchronously to detect their heart rate.
Figure 2: Multi-sensors for multimodal data collection.
An AirPods earphone and a microphone on the chest
were also worn in order to collect the audio data when
they had a conversation with the teacher.
Students reported their research progress while
displaying content related in the form of a
presentation, and the whole meeting was segmented
into four presentation chunks according to the first
and last presentation slides for each student detected
by our system as shown in Fig. 3. For each chunk,
there would be continuous conversation between the
presenting student and teacher in which the teacher
started by asking questions regarding the content
being presented and the student answered them.
Figure 3: Structured meeting content.
A real-time label annotation tool was designed to
collect a speaker’s mental state annotations within the
speech of the conversation. Label annotation could be
generally categorized into self-reporting or
observation by a third party. Self-reporting method
carried out with student answering survey questioners
or watching video after experiments, and recalling
their mental states occurred in experiment (O'Brien &
Toms, 2010, D’Mello & Mills, 2014). Other streams
of work rely on external human observation and
annotation (Parsons & Taylor, 2012), in which
teachers or peers observe students’ mental states on
site or off site and evaluate their mental states.
Since we aimed to collect real-time mental state
labels without interrupting the speaker, we made
mental-state label buttons placed with the other
sensors on the desk. As shown in Fig. 2, there are four
buttons representing four mental states from left to
right: concentration, boredom, confusion, and
frustration. We adopt third party observation method
in which we asked all of the non-speakers (for each
presentation chunk, conversation only occurs
between the presenting student and teacher, so the
other non-presenting students and the listener in
conversation are non-speakers) to observe a speaker’s
mental states during his or her speech and press one
of the buttons to record the start time for observing
the mental states and press the same button again
when they observed the end or transition of the state.
Using our multimodal data collection system, we
recorded and generated structured meeting minutes
including a multimodal dataset of the participants
comprised of facial and heart rate data taken during
the whole meeting. Fig. 3 presents our structured
meeting content as well as rich conversation data
including audio and text information transcribed by
Google Transcribe, speaker information, and mental
state labels within the speech of the conversation.
We collected a total of 11 small-group meetings
for a total of 1320 minutes with a mean length of 330
minutes of multimodal data per student including
video of their face and their heart rate during the
whole meeting. For a single meeting, each student
had a mean of 25-30 minutes per presentation chunk
including research progress statements and
conversations with teacher, with the longest continues
conversation lasting 17 minutes and the shortest only
about 7.2 minutes. Audio and transcript information
for each conversation were also recorded.
Reading Students’ Multiple Mental States in Conversation from Facial and Heart Rate Cues
71
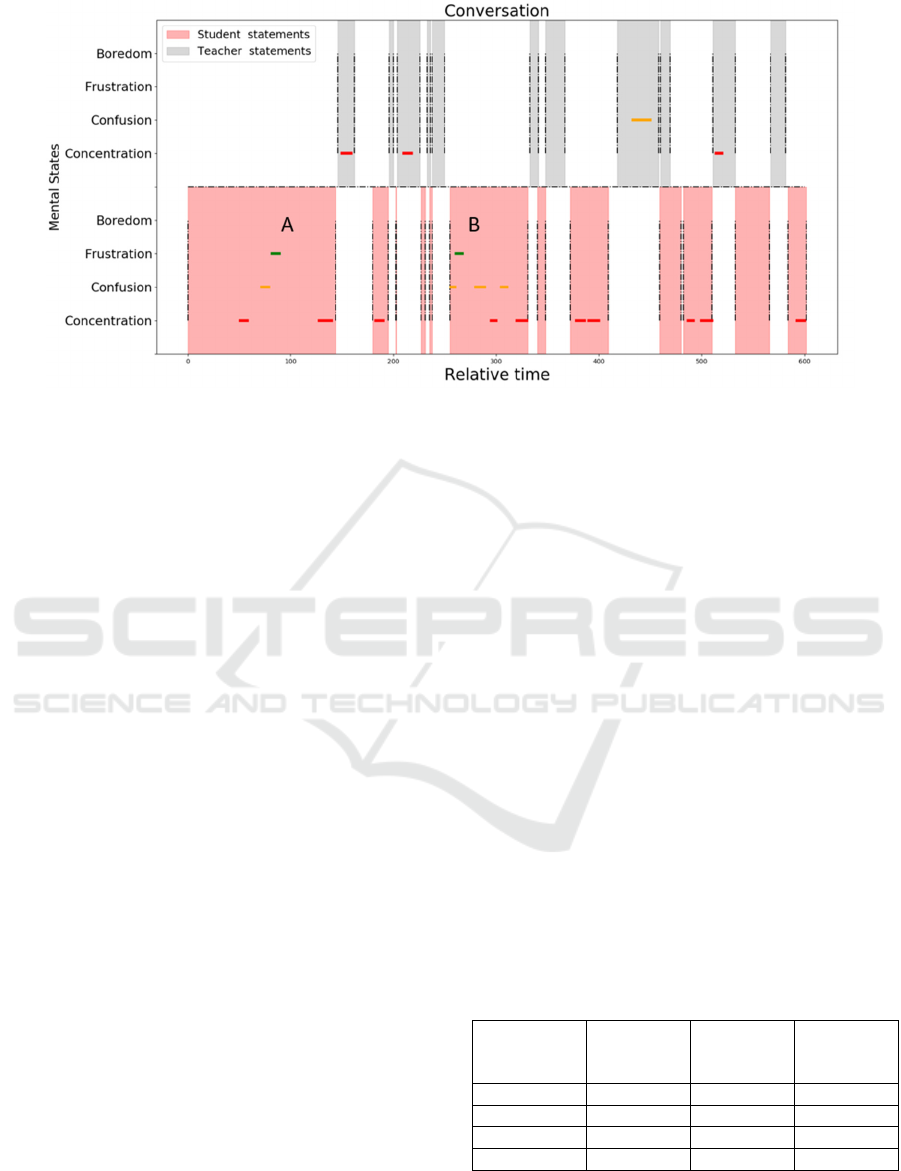
Figure 4: Example of annotated mental states within continues teacher-student conversation. Area with pink is students’
speech, while grey area is teacher’s speech, which is segmented by start and end time along meeting timeline using dotted
line. Horizontal lines inside each speech chunk represent annotated mental states at this speech clip annotated by one non-
speaker. State transition paths: (A) concentrated, confused, frustrated, and back to concentrated; (B) confused, frustrated,
confused, concentrated, confused, and back to concentrated.
4 METHODOLOGY FOR
PREDICTING MULTIPLE
MENTAL STATES
4.1 Qualitative Analysis on Mental
State Annotation
All non-speakers were asked to annotate speaker’s
mental states during speech by pressing one of the
labeled buttons and to press the same button again
when the conclusion or transition of the state was
observed. As shown in Fig. 4, we give an example of
annotated mental states within a continuous teacher-
student conversation. From the information shown in
the figure, (1) annotations mainly occurred for longer
speech. (2) As shown in (A), there is a clear transition
shift from concentration, confusion, frustration, and
back to concentration. (B) The speaker’s mental state
started from confused and transited to frustrated and
then back to confused and then to concentrated. These
two paths support the students’ dynamic mental-state
change theory we introduced at the beginning of this
paper, which guarantees the analyzability of our
experimental dataset. (3) There were fewer
annotations within the teacher’s speech, which may
indicate that the teacher intended to show sparse
mental state changes or their mental states were not
clear enough to be observed.
There were two types of annotators: participant-
student and the teacher, who was also a participant of
the conversation. We adopted Cohen’s Kappa (Landis
& Koch, 1977) to measure the inter-rater agreement
of the two different annotators. If the kappa varies
from 0.41 to 0.6, the agreement level is considered to
be moderate, and if it falls within the range of 0.6–0.8,
the issue is considered to be in substantive agreement
between different subjective opinions. If the kappa is
in the range 0.81–0.99, the two participants can be
considered to have almost reached perfect agreement
We randomly selected 60 speech clips (at least 10 sec
apart) annotated by the teacher and two graduate
school students, and we computed the Kappa value
between teacher and student A, teacher and Student
B, and student A and student B for each mental state
annotation. The results are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Inter-rater agreement (Cohen’s Kappa) of mental
state annotation between teacher and student.
Teacher
vs
Student A
Teacher
vs
Student B
Student A
vs
Student B
Concentration 0.60 0.57 0.59
Confusion 0.58 0.61 0.53
Frustration 0.42 0.42 0.33
Boredom 0.35 0.39 0.37
As seen in Table 1, the inter-rater agreement value for
concentration, confusion, and frustration were
relatively higher than boredom for all annotator
CSEDU 2020 - 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
72

groups. This is perhaps because, in teacher-student
conversations, students do not easily show that they
are bored. Due to the higher inter-rater agreement
level between teacher and student B, we selected the
first frame of the annotation and the next 150 frames
(5 seconds) as one mental state predictive segment.
4.2 Quantitative Analysis
4.2.1 Facial Feature Analysis
We implemented face tracking on the iPhone by
employing ARKit packages (ARKit, 2017), which
utilizes depth sensor data to generate a single facial
mesh over a user’s face and detects various
information of the user’s face, including its position,
orientation, and a series of blend shape coefficients to
represent a corresponding value of specific facial
features recognized by ARKit. The blend shape
coefficient is a floating-point number indicating the
current position of the respective feature relative to its
neutral configuration, ranging from 0.0 (neutral) to
1.0 (maximum movement). Fig. 5 shows an example
using the feature to characterize the eye blinking of
the right eye by measuring the closure of the eyelid.
(a) Natural expression (b) Eye blink right
Figure 5: (a) Natural expression with coefficient = 0.0, (b)
maximum movement of right eye blinking with coefficient
= 1.0 (eyeBlinkRight, 2017).
We extracted a series of facial features describing the
movement patterns of eyes and mouth at an average
frequency of 30 Hz. The first 300 (10 seconds) from
each conversation were used as a baseline for
computing the features.
Eye-related Features: Eye blink action has always
been used in predicting mental states, and we used the
eyeBlinkLeft and eyeBlinkRight coefficients for
describing the closure of the eyelids over the left and
right eyes. The Pearson r score was computed to
measure the correlation coefficients between the two
eyes and was 0.995, which indicates consistency
between the movements of the two eye, and we
calculated the average of eyeBlinkLeft and
eyeBlinkRight coefficient values to characterize eye-
blink patterns. A Savitzky-Colay filter was applied
with a filtering window size of 15 frames to remove
spike artefacts within the eyeBlink time series data.
Eye blink rates were calculated through peak
detection.
We measured several features relative to the eyes
as patterns for describing relative eye movement,
including eyeBlink action frequency, the proportion
of time a student had their eyes closed during blinking
(closure time), the proportion of time the students’
eyes were open, and the amplitude value of eyeBlink.
Mouth-related Features: To characterize the 2D
movement of the mouth, we employed the
mouthOpen/Close coefficients to characterize mouth
movement along the vertical direction with
mouthSmileLeft and mouthSmileRight coefficients
which measure the upward movement of both corner
of the mouth, together with mouthFrownLeft and
mouthFrownRight coefficients which measure
downward movement of both corner of the mouth to
describe the mouth corner movement within four
quadrants. We took the average of mouthSmileRight
and mouthFrownRight to compute the movement of
right corner of the mouth and the average of
mouthSmileLeft and mouthFrownLeft for the left
corner movement. We also took the mean value of
mouthOpen and Close to compute the lip movement.
As shown in Fig. 6, we give an intuitive example
of one student’s mouth actions during conversation
using the features we introduced above: (a) mouth
open, (b) mouth closed, (c) smile (both corners of
mouth shows clear upward movement), and (d)
mouth frown (both corners clear downward
movement).
We then computed the velocity, acceleration of
the lips and both mouth corners, and the proportion of
time students spent smiling and frowning.
4.2.2 Heart Rate Feature Analysis
The heart rate data we collected was at a frequency of
1 Hz. We computed the time domain features
including the mean, standard deviation (std.), root
mean square successive difference (RMSSD), max,
min, variance, and the heart rate trend by calculating
the difference between two adjacent heart rate points.
If the number of positive differences was more than
the negative one, we assumed that this heart rate
period showed an upward trend; if not, it showed a
downward one. We also computed spectral entropy as
frequency domain features. In Table 2, we summarize
the features derived from facial and heart rate signals.
Reading Students’ Multiple Mental States in Conversation from Facial and Heart Rate Cues
73
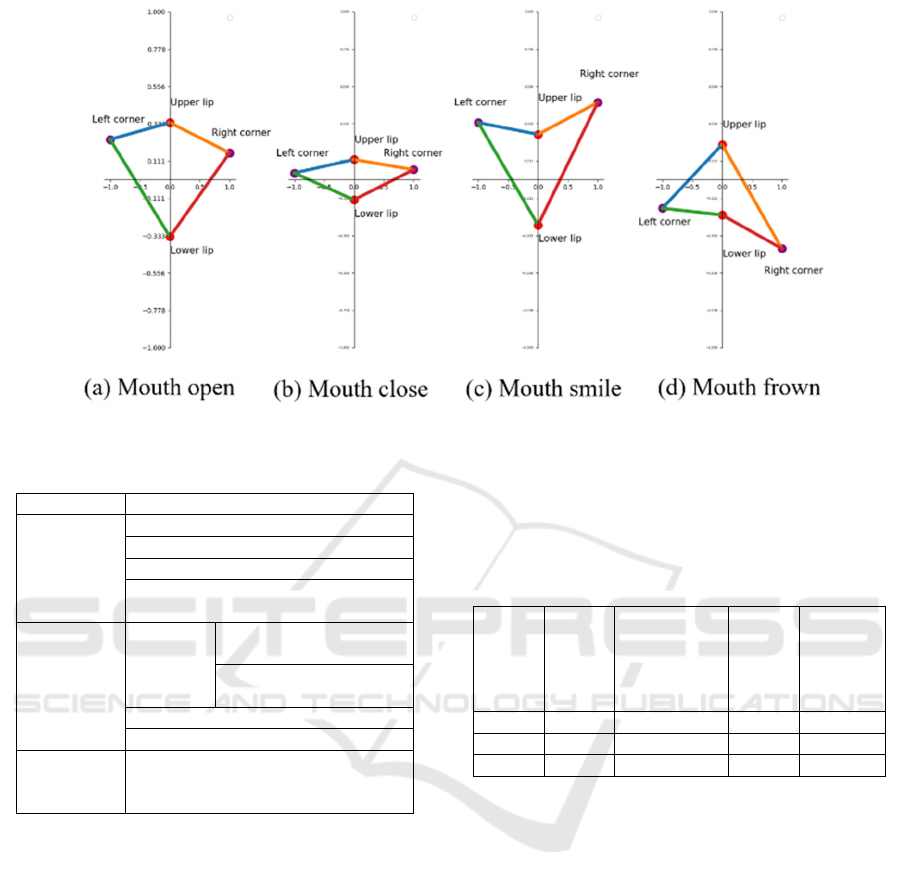
Figure 6: Visualization of mouth actions using mouth related features.
Table 2: Summary of features.
Feature descriptions
Eye-related
features
Eye blink frequency
Proportion of time closed
Proportion of time open
Mean, Std., Max, Min, range
of eye blink amplitude
Mouth-
related
features
Lips
&
mouth
corner
Mean, Std., Max, Min,
range of velocity
Mean, Std., Max, Min,
range of acceleration
Proportion of “smile” time
Proportion of “frown” time
Heart rate-
related
features
Mean, Std. Max, Min, RMSSD,
HR trend
4.3 Predicting Multiple Mental States
In this section, we evaluate the predictive utility of a
combination of feature sets derived from the facial
signals and heart rate signals in predicting the
students’ mental states in conversation. We adopted
Softmax Regression (SR), Multilayer Perceptron
Neural Network (MLP), and Random Forest (RF)
machine learning methods to build multi-class
classifiers for each combination of feature sets and a
leave-conversation block-out method to evaluate the
predictive performance for each multi-class classifier.
We started from the baseline model by using the
raw facial features, mouth and eye related raw signals,
and we then used the aggregated level facial related
features summarized in Table 2. We finally estimated
the performance for a complete set features fusing
multiple modalities by adding raw HR data to raw
facial features and adding aggregated statistic HR
features to aggregated facial features. In Table 3, we
report the macro F1-scores for each classifier.
Table 3: Summary of macro F1-score for each classifier for
different feature sets.
Raw
facial
Aggregated
facial
Raw
facial
and
HR
Aggrega
-ted
facial
and
HR
SR 0.54 0.59 0.51 0.59
MLP 0.64 0.64 0.67 0.63
RF 0.59 0.63 0.62 0.68
From the results shown in Table 3, for raw facial
features, we achieved an F1-score of 0.64 for the
MLP model and 0.59 for the RF model, which
indicates that MLP can better learn interpretable
features from facial raw signals as proxies for the task
of predicting mental states than random forest. Our
proposed aggregated facial features improved the
predictive ability from 0.59 to 0.63 for RF model,
while they did not provide additional information for
the MLP model, which maintained the same F1-score.
Raw HR added additional utility over the raw facial
features, with F1-scores that increased from 0.64 to
0.67 for MLP and from 0.59 to 0.62 for the RF model.
Moreover, the aggregated HR features helped the
aggregated facial features improve the predictive
ability for the RF model but decreased the ability for
the MLP model. These results show that our proposed
feature extraction method could provide a more
interpretable description of students’ different mental
states than as traditional machine learning model, that
CSEDU 2020 - 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
74

is, random forest. Finally, the SR model showed an
overall lower predictive ability than the other two
models. We think that this may indicate the non-linear
relationship between these two modalities, which is
valuable to validate in the future.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper, we aimed to predict students’ complex
mental states, that is, concentration, confusion,
frustration, and boredom in real-world student-
teacher conversation from a multimodal data stream
that included facial and heart rate signals. A multi-
sensor-based multimodal data collection system was
developed and applied in a real group meeting in a lab,
where task-oriented conversation activities occurred
between 4 graduated students and their teacher. We
recorded 11 group meetings to create a dataset for
over 1320 minutes of multimodal data on the basis of
facial and heart rate signals as well as the audio and
textual information of the conversation. A real-time
mental state annotation tool was designed. We asked
all non-speakers in the meeting to annotate mental
state labels for speakers while they made a
presentation. The inter-rater agreement for each
annotated mental state class between the teacher and
student was measured, and we used a teacher and one
student who had a higher consistency level in terms
of annotation for the mental-state annotation results.
We then proposed a multimodal framework for
exploring interpretable multimodal patterns in
predicting students’ mental states in conversation.
Several visual features were extracted for
characterizing eye and mouth movements including
eye blink frequency, the proportion of time for which
eyes are closed or open, the mean, std., max, min, and
range of eye blink amplitude. We measured the
movement of the lip and mouth corners vertically and
in four quadrants, along with the proportion of time
for “mouth smile” and “mouth frown.” We also took
advantage of heart rate data as our physiological
proxy for mental state prediction.
Last, we generated several machine learning
models including Softmax Regression (SR),
Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network (MLP), and
Random Forest (RF) using different multimodal
feature sets. Our proposed multimodal features
(aggregated facial and heart rate features) achieved
the best predictive ability regarding students’ mental
states when using the random forest model. These
results validated our proposed multimodal framework.
The framework could provide fine-grained
interpretable features as a proxy in predicting students’
complex mental states in conversation and also
illustrated the utility of fusing information from
multiple modalities in this prediction task. In addition,
MLP performed well in automatically learning
features from raw facial and heart rate signals, which
may provide evidence for potential possibilities of
predicting students’ real-time mental states.
There are multiple types of future work that could be
considered for our scalable multimodal dataset and
the current prospective experiment’s results. (1) The
teacher (conversation partner)’s multimodal data
were also collected, which we are going to take a deep
dive and analyze the potential utility of interaction
behavior patterns in predicting presenter-students’
mental states. (2) In addition to facial and heart rate
signals, audio and textual information from the
conversation were also collected. We plan to extend
our multimodal framework by adding the
conversation data to improve our prediction ability.
(3) In terms of application, we are going to launch our
mental-state prediction model for use with our data
collection system. We aim to alert teachers when
students are facing an “assistance dilemma” shown
through their confusion and frustration, in order to let
teachers provide a timely and suitable intervention to
improve students’ learning outcomes.
REFERENCES
Apple Inc., Arkit — Apple developer documentation,
https://developer.apple.com/documentation/arkit,
Accessed: 2017-12-04
Busso, C., Bulut, M., Lee, C.-C., Kazemzadeh, A. Mower,
E., Kim, S., Chang, J. N., Lee, S., & Narayanan, S. S.
(2008). IEMOCAP: Interactive emotional dyadic motion
capture database, In: Language Resources and
Evaluation, 42(4), 335.
Bell, B. & Cowie, B. (2001). The characteristics of formative
assessment in science education. In: Science Education,
85(5), 536-553.
Burt, K. B. & Obradović, J. (2013). The construct of
psychophysiological reactivity: Statistical and
psychometric issues. In: Developmental Review, 33(1),
29-57.
Craig, S., Graesser, A., Sullins, J., & Gholson, B. (2004).
Affect and learning: an exploratory look into the role of
affect in learning with AutoTutor. In: Journal of
Educational Media, 29(3), 241-250.
Calvo, R. A. & D'Mello, S. (2010). Affect detection: An
interdisciplinary review of models, methods, and their
applications. In: IEEE Transactions on Affective
Computing, 1(1), 18-37.
Reading Students’ Multiple Mental States in Conversation from Facial and Heart Rate Cues
75

Cowley, B., Ravaja, N. & Heikura, T. (2013). Cardiovascular
physiology predicts learning effects in a serious game
activity. In: Computers & Education, 60(1), 299–309.
D’Mello, S. K., Craig, S. D., Sullins, J., & Graesser, A. C.
(2006). Predicting affective states expressed through an
emote-aloud procedure from AutoTutor’s mixed-
initiative dialogue. In: International Journal of Artificial
Intelligence in Education, 16(1), 3-28.
Devillers, L. & Vidrascu, L. (2007). Real-life emotion
recognition in speech. In: Speaker Classification II. pp.
34–42. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
D’Mello, S. K., Craig, S. D., Witherspoon, A., Mcdaniel, B.,
& Graesser, A. (2008). Automatic detection of learner’s
affect from conversational cues. In: User Modeling and
User-adapted interaction, 18(1-2), 45-80.
D’Mello, S. & Graesser, A. (2012). Dynamics of affective
states during complex learning. In: Learning and
Instruction, 22(2), 145–157.
D’Mello, S. (2013). A selective meta-analysis on the relative
incidence of discrete affective states during learning with
technology. In: Journal of Educational Psychology,
105(4), 1082.
D’Mello, S. & Mills, C. (2014). Emotions while writing
about emotional and non-emotional topics. In:
Motivation and Emotion, 38(1), 140-156.
EyeBlinkRight, Apple developer documentation,
https://developer.apple.com/documentation/arkit/arfacea
nchor/blendshapelocation/2928262-eyeblinkright.
Forbes-Riley, K. & Litman, D. (2011, June). When does
disengagement correlate with learning in spoken dialog
computer tutoring? In: International Conference on
Artificial Intelligence in Education. pp. 81–89. Springer,
Berlin, Heidelberg.
Feidakis, M., Daradoumis, T., & Caballé, S. (2013, January).
Building emotion-aware features in computer supported
collaborative learning (CSCL) systems. In: Alpine
Rendez-Vous (ARV) Workshop on Tools and
Technologies for Emotion Awareness in Computer-
Mediated Collaboration and Learning (ARV 2013).
Gomes, J., Yassine, M., Worsley, M., & Blikstein, P. (2013,
July). Analysing engineering expertise of high school
students using eye tracking and multimodal learning
analytics. In: Educational Data Mining.
Grafsgaard, J. F., Wiggins, J. B., Boyer, K. E., Wiebe, E. N.,
& Lester, J. C. (2013, July). Embodied affect in tutorial
dialogue: student gesture and posture. In: International
Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. pp. 1–
10. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Grafsgaard, J., Wiggins, J. B., Boyer, K. E., Wiebe, E. N., &
Lester, J. (2013, July). Automatically recognizing facial
expression: Predicting engagement and frustration. In:
Educational Data Mining.
Hussain, M. S., AlZoubi, O., Calvo, R. A., & D’Mello, S. K.
(2011, June). Affect detection from multichannel
physiology during learning sessions with AutoTutor. In:
International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in
Education. pp. 131–138. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Kapoor, A. & Picard, R. W. (2005). Multimodal affect
recognition in learning environments, In: Proceedings of
the 13th Annual ACM International Conference on
Multimedia, pp. 677–682.
Koning, B. B. de, Tabbers, H. K., Rikers, R. M., & Paas, F.
(2010). Attention guidance in learning from a complex
animation: Seeing is understanding?, In: Learning and
Instruction
, 20(2), 111–122.
Landis, J. R. & Koch, G. G. (1977). The measurement of
observer agreement for categorical data. In: Biometrics,
159-174.
Li, Y., Su, H., Shen, X., Li, W., Cao, Z., & Niu, S. (2017).
DailyDialog: A manually labelled multi-turn dialogue
dataset. In: arXiv preprint arXiv: pp. 1710-03957.
Luft, C. D., Nolte, G., & Bhattacharya, J. (2013). High-
learners present larger mid-frontal theta power and
connectivity in response to incorrect performance
feedback. In: The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(5), 2029–
2038.
O'Brien, H. L. & Toms, E. G. (2010). The development and
evaluation of a survey to measure user engagement. In:
Journal of the American Society for Information Science
and Technology, 61(1), 50-69.
Pardos, Z. A., Baker, R. S., San Pedro, M. O., Gowda, S. M.,
& Gowda, S. M. (2014). Affective states and state tests:
Investigating how affect and engagement during the
school year predict end-of-year learning outcomes. In:
Journal of Learning Analytics, 1(1), 107-128.
Parsons, J. & Taylor, L. (2012). Student engagement: What
do we know and what should we do? In: University of
Alberta.
Poria, S., Majumder, N., Mihalcea, R., & Hovy, E. (2019).
Emotion recognition in conversation: Research
challenges, datasets, and recent advances. In: IEEE
Access, 7, 100943-100953.
Peng, S., Ohira, S., Nagao, K. (2019). Prediction of Students’
Answer Relevance in Discussion Based on their Heart-
Rate Data, In: International Journal of Innovation and
Research in Educational Sciences (IJIRES), 6(3), 414-
424.
Peng, S., Ohira, S., Nagao, K. (2019). Automatic Evaluation
of Students’ Discussion Skills Based on their Heart Rate.
In: Computer Supported Education, 1022, 572-585,
Springer.
Rodrigo, M. M. T., Baker, R. S., Agapito, J., Nabos, J.,
Repalam, M. C., Reyes, S. S., & San Pedro, M. O. C.
(2012). The effects of an interactive software agent on
student affective dynamics while using; an intelligent
tutoring system. In: IEEE Transactions on Affective
Computing, 3(2), 224-236.
Shepard, L. A. (2005). Linking formative assessment to
scaffolding. In: Educational Leadership, 63(3), 66-70.
Stevens, R. H., Galloway, T., & Berka, C. (2007, July). EEG-
related changes in cognitive workload, engagement and
distraction as students acquire problem solving skills. In:
International Conference on User Modeling. pp. 187–
196. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Whitehill, J., Serpell, Z., Foster, A., Lin, Y. C., Pearson, B.,
Bartlett, M., & Movellan, J. (2011, June). Towards an
optimal affect-sensitive instructional system of cognitive
skills. In: CVPR 2011 Workshops. pp. 20–25. IEEE.
CSEDU 2020 - 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
76
