
An Evaluation of New Global Appearance Descriptor Techniques for
Visual Localization in Mobile Robots under Changing Lighting
Conditions
Vicente Rom
´
an
a
, Luis Pay
´
a
b
, Sergio Cebollada
c
, Adri
´
an Peidr
´
o
d
and
´
Oscar Reinoso
e
Engineering Systems and Automation Department, Miguel Hernandez University, Elche (Alicante), Spain
Keywords:
Localization, Mobile Robots, Global Appearance Descriptors, Omnidirectional Images.
Abstract:
Autonomous robots should be able to carry out localization and map creation in highly heterogeneous zones.
In this work, global appearance descriptors are tested to perform the localization task. It focuses on the use of
an omnidirectional vision sensor as unique source of information and global appearance to describe the visual
information. Global-appearance techniques consist in obtaining a unique vector that describes globally the
image. The main objective of this work is to propose and test new alternatives to build and to handle global
descriptors. In previous experiments the images have been processed without considering the spatial distribu-
tion of the information. In contrast, in this work, the main approach is that relevant information will be in the
central rows. For this reason central rows information is given a higher weight comparing to other zones of the
image. The results show that this consideration can be an interesting presumption to take into account. The
experiments are carried out with real images that have been taken in two different heterogeneous environments
where simultaneously humans and robots work together. For this reason, variations of the lighting conditions,
people who occlude the scene and changes on the furniture may appear.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the last decade, the use of visual information has
extended to improve the autonomy of mobile robots in
many applications. The presence of mobile robots in
different environments has increased, and in order to
cope with more challenging situations their abilities
in perception and interpretation have improved. To
be robustly autonomous in extended, heterogeneous
and changing environments, the mobile robot has a
twofold task. First, a mapping task in which it has to
be able to navigate around the initialy unknown en-
vironment while creating a map. Second, it has to
perform localization task trying to estimate its posi-
tion and orientation in the environment. Among vi-
sion sensors, omnidirectional cameras are an interest-
ing option to carry out these tasks due to their field
of view of 360
o
around the camera axis (Sturm et al.,
2011) and (Pay
´
a et al., 2017).
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3706-8725
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3045-4316
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4047-3841
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4565-496X
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1065-8944
Due to the fact that images contain a big amount
of data, it is required to extract from them relevant
information. Nowadays local appearance descriptors
are well-known and extensively used. These meth-
ods describe specific points or local zones in the im-
age. Among these descriptors SIFT (Lowe, 2004)
and SURF (Bay et al., 2008) are the most known and
used. Murillo et al. (Murillo et al., 2007) solved
a mobile robots navigation problem using local de-
scriptors, Gil et al. (Gil et al., 2011) and Valiente et
al. (Valiente Garc
´
ıa et al., 2012) worked with local
appearance descriptors and omnidirectional cameras.
Relatively good results in navigation have been ob-
tained using local appearance descriptors. Global ap-
pearance descriptors are an alternative method to ex-
tract characteristic information from images and use
this information for mapping and localization.
Global-appearance description methods describe
the image globally obtaining a unique vector per im-
age, which is expected to be more invariant against
global changes in the scene. In addition, as each im-
age is described with a unique vector, the mapping
and localization work is simplified to a pairwise com-
parison between vectors. Over the past few years
some global-appearance descriptors have been stud-
Román, V., Payá, L., Cebollada, S., Peidró, A. and Reinoso, Ó.
An Evaluation of New Global Appearance Descriptor Techniques for Visual Localization in Mobile Robots under Changing Lighting Conditions.
DOI: 10.5220/0009595603770384
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2020), pages 377-384
ISBN: 978-989-758-442-8
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
377

ied. Gist, introduced by Oliva and Torralba (Oliva and
Torralba, 2001), is one of the most extended descrip-
tors, and it has been tested in outdoor environments
for example by Zhou et al. (Zhou et al., 2018) to solve
the localization through matching the robot’s current
view with the best keyframe in the database. Other
option is the Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG),
HOG is used in (Pay
´
a et al., 2018) to solve hierar-
chical mapping and localization tasks. In addition,
there are other important techniques to obtain global
appearance descriptors based on mathematical trans-
formation, such as the Fourier Transform (Menegatti
et al., 2004) or the Radon Transform (Radon, 2005).
These alternatives have been used in works as Paya et
al. (Pay
´
a et al., 2009) to build maps or in Berenguer
et al. (Berenguer et al., 2019) where they used Radon
Transform to estimate the relative height of a mobile
robot. Moreover, during the last recent years, some
authors have used deep learning techniques to cre-
ate new global appearance descriptors. For example,
Xu et al. (Xu et al., 2019) proposed a CNN-based
descriptor to obtain the most probable robot position
and Cebollada et al. (Cebollada et al., 2019) perform
a comparison between analytic global-appearance de-
scriptors and CNN-based descriptors while solving a
mobile robot localization work. Finally, Rom
´
an et al.
(Rom
´
an et al., 2018) studied some of these global ap-
pearance methods in real environments to solve the
localization task under illumination changes.
As shown, global appearance descriptors are de-
fined to be invariant against rotations in the ground
plane when omnidirectional images are used. Global-
appearance methods have summarised the informa-
tion from the panoramic images in horizontal blocks
or cells traditionally. But more recently, other ways
to build the descriptor have appeared, for instance
(Rom
´
an et al., 2019) where vertical cells are evaluated
with interesting results. The current work tries to go
one step beyond in the definition of global-appearance
descriptors, considering that usually, the most impor-
tant is condensed in the horizontal cells situated in the
middle of the panoramic image, because the visual in-
formation in the upper and bottom rows often corre-
sponds to the roof or sky and floor or terrain, which
are visually less significative. For this reason a tech-
nique that increases the weight of the central rows is
studied. This work compares the classic formulation
with a new technique while testing them in a localiza-
tion framework.
2 GLOBAL APPEARANCE
DESCRIPTORS
In this section a review of the global appearance de-
scriptors used in the presented localization task is de-
scribed. The goal of these methods is to extract a
unique vector that globally describes the information
from an image. In this way, relevant information is
keep while reducing amount of memory. Global ap-
pearance descriptors have been used to perform robot
navigation tasks, for example, to solve the kidnapped
robot problem in indoor environments under different
conditions (Su et al., 2017) or to build hierarchical
maps through clustering algorithms (Cebollada et al.,
2019). To perform the localization task, HOG and
Gist descriptors are modified and used in this work.
In both cases the starting point is a panoramic image
i(x,y) ∈ R
N
x
×N
y
and after these methods each image is
reduced to a vector
~
d ∈ R
l×1
.
The first step to build the descriptor is divide the
image in a set of cells. The descriptor size depends
on the number of these cells. The first option stud-
ied in this work is the classic way, used in (Rom
´
an
et al., 2018) where the vector is built with uniformly
distributed and non-overlapped horizontal cells, fig-
ure 1 shows how cells are distributed in this classi-
cal method. Taking into account the idea of giving
more importance to the central rows, a method where
the descriptors are built as traditionally but they are
weighted by a set of factors is evaluated. These fac-
tors are obtained from a Gaussian distribution centred
in the central row of the panoramic image, in such a
way that the information of the central cells is given
more importance than top or bottom cells. This idea
is outlined in figure 2.
Horizontal Cells Descriptor
Vertical Cells Descriptor
a
)
b)
Figure 1: Classical approach to build the HOG global ap-
pearance descriptor of a panoramic image, by defining a set
of horizontal cells.
Figure 2: Method to build the global-appearance descriptor
multiplying descriptor by a gaussian distribution.
ICINCO 2020 - 17th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
378
2.1 Histogram of Oriented Gradients,
HOG
Histogram of Oriented Gradients was described by
Dalal and Triggs (Dalal and Triggs, 2005) and used
by Hofmeister et al. in small and controlled en-
vironments (Hofmeister et al., 2009). It basically
consists in calculating the gradient of the image and
obtaining magnitude and orientation of the gradient
in each pixel. After that, magnitudes and orienta-
tions are evaluated and the descriptor is build by
collecting together the information obtained in each
cell. The methods divide the panoramic images using
uniformly distributed and non-overlapped horizontal
cells. As they collect information from horizontals
rows and panoramic images are used, descriptors are
invariant to rotations of the robot in the ground plane
and they can be use in the localization tasks indepen-
dently on the orientation that the robot has at a spe-
cific time instant.
The descriptor size depends on diverse parame-
ters. This way, the vector length depends on the num-
ber of bins of the orientations histogram b and the
number of cells in which the image is divided k
1
.
HOG descriptor reduces a panoramic image into a
vector whose size is
~
d ∈ R
b·k
1
×1
.
2.2 Gist
This descriptor was initially proposed by Oliva et al.
(Oliva and Torralba, 2006) and it was developed by
Siagian et. al. (Siagian and Itti, 2009) testing its
performance in three different outdoor environments.
This method exposes the image to a specific number
of Gabor filters with different orientations in several
resolution levels. After that, the images are reduced
evaluating their mean intensity in different horizontal
cells.
In this case, the descriptor size will depend on the
number of orientations of Gabor filters m, the number
of cells in which the images are split k
2
and the num-
ber of different resolution models used r. During the
experiments this latter parameter r will be constant,
r=2. For that reasons the descriptor is a vector whose
size is
~
d ∈ R
2·m·k
2
×1
.
2.3 Main Parameters of the Descriptors
The aim of this work is to check the efficiency of the
descriptors in a localization task and to optimize the
main parameters in this new description technique.
Different parameters can be tuned and, as a conse-
quence, the vector that describes the image modifies
its values and size. These parameters can be seen
Table 1: Parameters that impact on the location process.
Descriptor Parameters
HOG b⇒ number of bins per histogram.
k
1
⇒ number of horizontal cells.
Gist m⇒ number of Gabor filters.
k
2
⇒ number of horizontal blocks.
r⇒ different resolution models.
During these experiments r is constant, r = 2, the other parame-
ters take values between [8-32]
Figure 3: Gaussian distributions to obtain the coefficients to
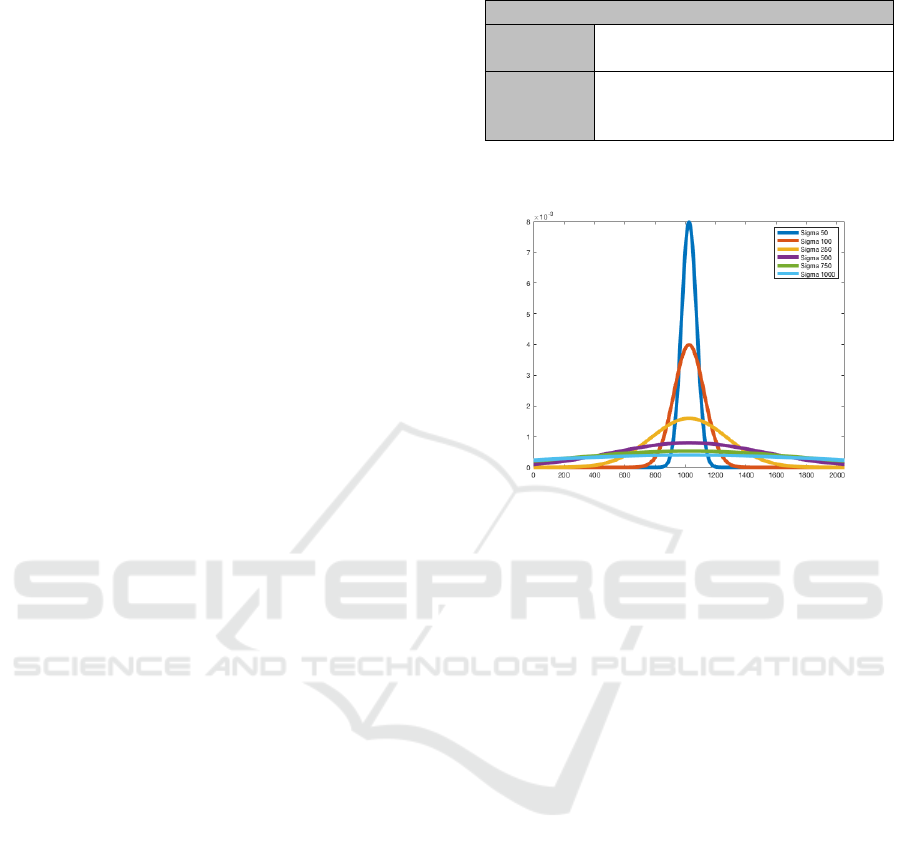
weight each cell, considering different values of sigma.
in table 1. Different values have been tested but, as
shown, these parameters define the descriptor size.
The larger the descriptor is, the more information it
contains but the slower the process will be.
The mainly purpose of this work is to evaluate
the new technique to build descriptors. As pointed
out before, the most important information is situ-
ated on the central rows in a panoramic image and
the top and bottom rows are visually less relevant be-
cause they contain the ceiling and the floor. For this
reason, the descriptors are built using the traditional
decomposition of the image in horizontal cells, but
each cell is weighted with an importance coefficient.
The set of coefficients is obtained from a Gaussian
distribution that gives more importance to the cen-
tral cells. Therefore, the information in these cells
contributes to the final descriptor to a greater extent.
Gaussian distribution can be built with different de-
viation values (σ). Figure 3 shows different Gaus-
sian distributions used during experiments depending
on σ, σ = {50, 100,250,500, 750, 1000}. Values in a
gaussian distributions sum 1 and they are distributed
depending on σ.
An Evaluation of New Global Appearance Descriptor Techniques for Visual Localization in Mobile Robots under Changing Lighting
Conditions
379

Figure 4: Real-life changes in an heterogeneous environ-
ment.
3 DATABASE
The experiments have been carried out through the
use of the COLD dataset (Pronobis and Caputo,
2009) and INNOVA dataset (Amor
´
os et al., 2018).
COLD database offers three different indoor trajec-
tories taken in three buidings (Freiburg, Saarbr
¨
ucken
and Ljubljana ) and INNOVA database offers also an-
other indoor laboratory trajectory the Miguel Hernan-
dez University, Spain. While the COLD database tra-
jectories were taken in different times of the day so
they offer the same environment in three different il-
lumination conditions, INNOVA trajectory was only
captured under cloudy conditions (during the light
hours but the sunlight does not considerably affect
the shots). The selected databases offer the hetero-
geneous and dynamic environment needed to test the
proposed global-appearance methods. The robot trav-
els along some laboratories where people is normally
working, so it has to deal with changes in the environ-
ment such as people walking or position of furniture
and objects and also problems like lighting changes
and occlusions. In the image 4 it is possible to see
some shots taken from the database where it is possi-
ble to observe these real operation conditions.
Among the different trajectories offered by the
datasets, three routes have been chosen as test datasets
to carry out the experiments. Route 1: Freiburg Part
A, Path 2, size 3 (Pronobis and Caputo, 2009), and
Route 2: INNOVA (Amor
´
os et al., 2018). In addition
each dataset has its own training database. Training
database covers the same parts of the environments
with an average distance between images around 0.02
m. Other trajectory specifications can be seen in ta-
ble 2, where it is possible to see the number of im-
ages and average distance between images. Within a
Table 2: Number of images and distance between consecu-
tive images in each route depending on the environment and
lighting conditions.
Trajectory Number Distance
Database of images between Images
Test Route 1 (Cloudy) 2778 0.0370 ± 0.0149 m
Test Route 1 (Night) 2896 0.0357 ± 0.0192 m
Test Route 1 (Sunny) 2231 0.0462 ± 0.0213 m
Training Route 1 (Cloudy) 556 0.1835 ± 0.0594 m
Test Route 2 (Cloudy) 1450 0.1212 ± 0.0410 m
Training Route 2 (Cloudy) 750 0.2397 ± 0.0629 m
selected route all the different specifications (cloudy,
night and sunny) cover approximately the same tra-
jectory, but they where taken in different moments.
Training routes were taken in a cloudy environment.
At the end, the route 1 covers approximately 103 m
and route 2 176 m.
4 EXPERIMENTS
4.1 Model of the Environment
As explained in the previous section, each database
offers a training trajectory which follows approxi-
mately the same route than the test ones. The dis-
tance between images in training dataset is around
0.20m and they were taken during the light hours, but
the sunlight does not considerably affect the images
(cloudy conditions).
Once the model is built with the descriptors of
the training images, the method to solve the local-
ization task consists in comparing the descriptor of
each test image with the descriptors in the model.
The program compares descriptors and calculates the
nearest neighbor by means of the correlation distance
(d(~a,
~
b) = 1 −
~
a
T
d
·
~
b
d
|
a
d
|
·
|
b
d
|
). In this expression:
~a ∈ R
lx1
and
~
b ∈ R
lx1
where: a
i
,b
i
,i = 1, ..., l ;
~a
d
= [a
1
− a,..., a
l
− a];a =
1
l
·
∑
j
·a
j
and
~
b
d
= [b
1
− b,..., b
l
− b];b =
1
l
·
∑
j
·b
j
When the nearest neighbor is calculated the geo-
metric distance between the capture point of the test
image (ground truth) and the capture point of the near-
est neighbor in the model is obtained, and the result
is the error. This geometrical distance can be calcu-
lated because COLD and INNOVA databases offers
the coordinates where each image had been taken but
the coordinates have been only used as ground truth
to check the error. The localization task is carried out
with pure visual information.
ICINCO 2020 - 17th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
380
4.2 Position Estimation
Initially, the training routes are used to create the ref-
erence model. Afterwards, to study the robustness
of the global-appearance descriptors, the test images
are used to solve the localization problem. The local-
ization process evaluates which image in the training
model is the most similar to each test image. This
process has been carried out with the different light-
ing (cloudy, night and sunny). The error is calculated
as the geometric distance between the capture points
of both images. After repeating the process using dif-
ferent descriptors sizes, figures 5, 6 and 7 show the
average error (m) using the classical method, with no
weighting of the rows. Each figure shows the aver-
age localization error obtained after considering all
the test images of a trajectory with specific lighting
conditions.
64 128 256 512 1024 2048
Descriptor size
0.045
0.05
0.055
0.06
0.065
0.07
0.075
0.08
Error [m]
Cloudy
HOG Freiburg
Gist Freiburg
HOG Innova
Gist Innova
Figure 5: Localization error (m) using cloudy dataset versus
descriptor size.
Both, HOG and Gist descriptor provide their best
results when they work with middle size descriptors.
Gist performs better under cloudy and night condi-
tions, with errors between 0.0455 m and 0.2266 m
respectively while HOG outputs an error of 0.0458 m
with cloudy conditions and 0.2337 m with night envi-
ronment. The sunny conditions have the most nega-
tive effect on the localization process, with an error of
1.903 m with Gist and 1.8675 m using HOG. On the
other hand with INNOVA database only cloudy test
images are available. Results are really similar and
the lowest errors are 0.063 m using HOG descriptor
and 0.0618 m using Gist.
The results of the proposed method, which in-
cludes the weighting coefficients, are shown in the
next lines. The localization process is the same as
shown before but now the information in the descrip-
tors is weighted by a set of coefficients obtained from
64 128 256 512 1024 2048
Descriptor size
0.22
0.24
0.26
0.28
0.3
0.32
0.34
0.36
Error [m]
Night
HOG Freiburg
Gist Freiburg
Figure 6: Localization error (m) using night dataset versus
descriptor size.
64 128 256 512 1024 2048
Descriptor size
1.8
1.9
2
2.1
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.5
2.6
Error [m]
Sunny
HOG Freiburg
Gist Freiburg
Figure 7: Localization error (m) using sunny dataset versus
descriptor size.
a Gaussian distribution. Sigma (σ) is varied in order
to evaluate the influence of this parameter. Figures 8,
9 and 10 show the average localization error (m) us-
ing the new proposed method. As before each figure
corresponds with a specific lighting conditions of the
test images condition (cloudy, night and sunny).
Better results are obtained using middle-high σ
values. On Freiburg route and using HOG descriptor
and this technique an error of 0.04598 m is obtained
when σ=500 and cloudy environment, 0.1915 m when
σ=500 and night environment and 0.7505 m when
σ=250 and sunny environment. With Gist descrip-
tor the errors obtained respectively were 0.04538 m
0.2040 m 1.5687 m all of them obtained with σ=250.
On the other hand the lowest error in the INNOVA
route are obtained using σ=750. The minimum error
is 0.0619 m using HOG descriptor and 0.0637 m us-
ing Gist descriptor. These experiments clearly show
An Evaluation of New Global Appearance Descriptor Techniques for Visual Localization in Mobile Robots under Changing Lighting
Conditions
381

50 100 250 500 750 1000
Sigma
0.045
0.05
0.055
0.06
0.065
0.07
0.075
Error [m]
Cloudy
HOG Freiburg
Gist Freiburg
HOG Innova
Gist Innova
Figure 8: Localization error (m) using cloudy dataset versus
sigma in the Gaussian distribution.
50 100 250 500 750 1000
Sigma
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
0.55
Error [m]
Night
HOG Freiburg
Gist Freiburg
Figure 9: Localization error (m) using night dataset versus
sigma in the Gaussian distribution.
50 100 250 500 750 1000
Sigma
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
Error [m]
Sunny
HOG Freiburg
Gist Freiburg
Figure 10: Localization error (m) using sunny dataset ver-
sus sigma in the Gaussian distribution.
that, lower errors are obtained using this new method
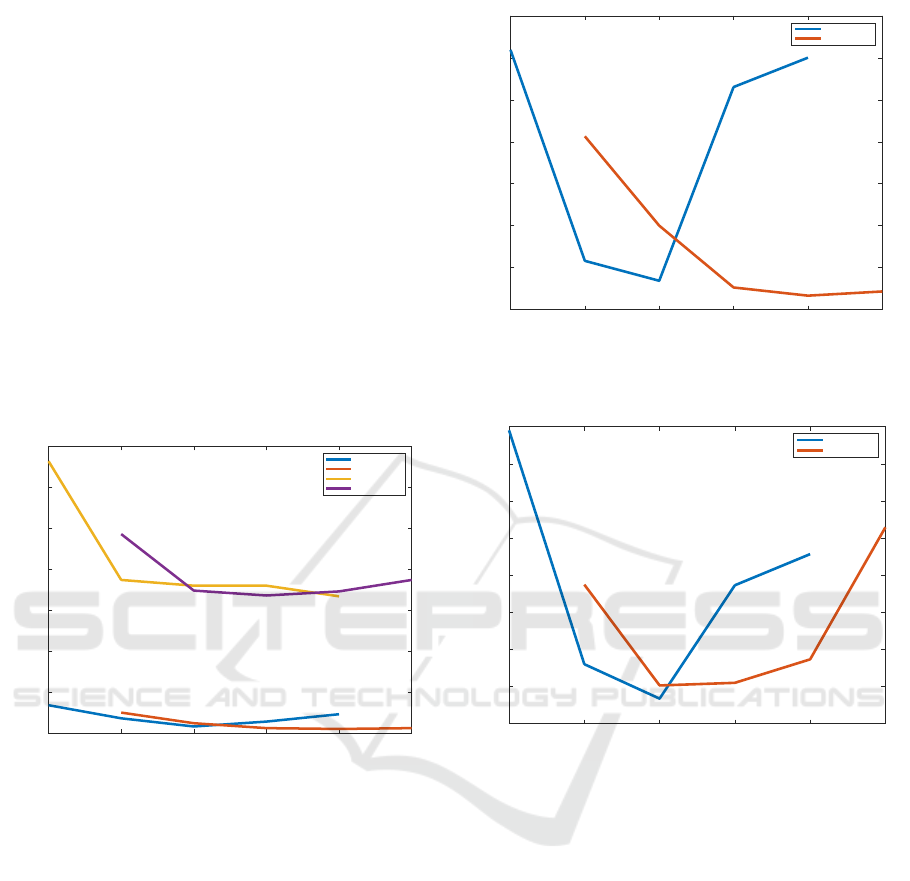
where the descriptors are multiplied by a gaussian dis-
tribution. Best results are obtained with descriptor
size 256 or 512 and taking into account the gaussian
distribution, it is better to multiplied the image with
a distribution σ=250 or σ=500. It can be observed
on figures 11 and 12. They show the best result in
each configuration and it is possible to observe that
using the proposed method the error is lower. The
improvement is specially important when the test im-
ages the images are taken from the sunny environment
database. As seen, localisation error decreases using
the proposed method, especially with HOG descrip-
tor. The methods improve the task but to use it prop-
erly we have to supposed that the image is well dis-
tributed; there is the same quantity of cell and floor,
they are not important on the scene and the camera
is moved parallel to the ground floor. If these condi-
tions are suit the proposed method should improved
the localization task results.
HOG
Cloudy Freiburg Night Freiburg Sunny Freiburg Cloudy Innova
Environment
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2
Error [m]
Classical Method
Proposed Method
Figure 11: Comparison between classical and proposed
methods vs environment while using HOG descriptor.
Gist
Cloudy Freiburg Night Freiburg Sunny Freiburg Cloudy Innova
Environment
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2
Error [m]
Classical Method
Proposed Method
Figure 12: Comparison between classical and proposed
methods vs environment while using Gist descriptor.
ICINCO 2020 - 17th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
382
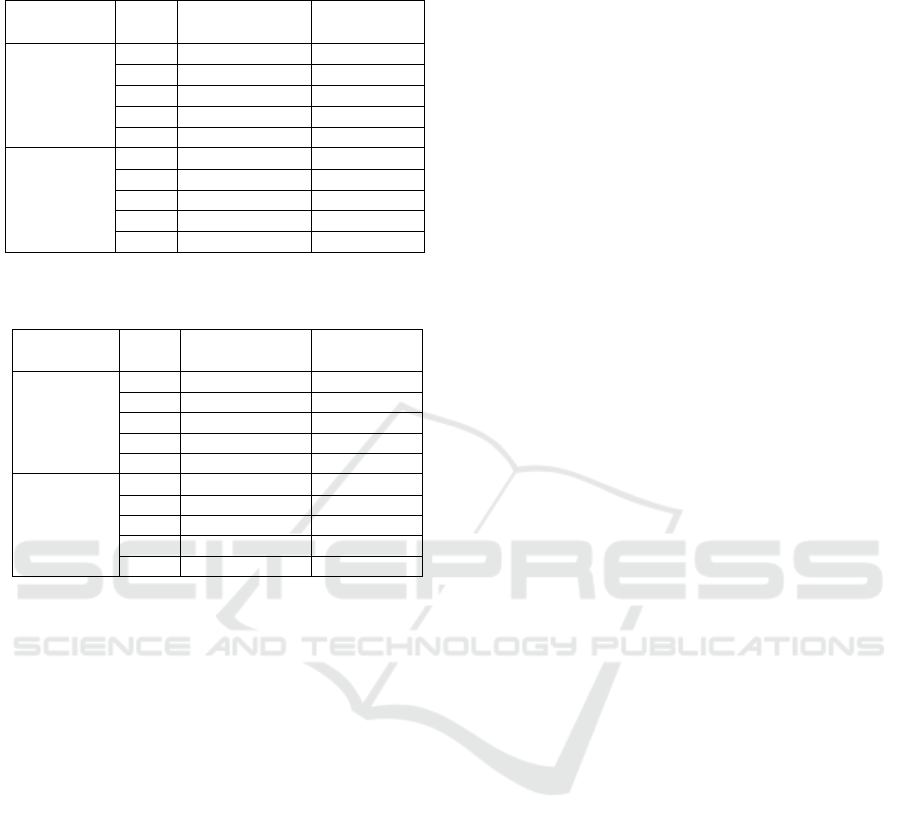
Table 3: Calculation time (s) of the localization process in
the classical method.
Time to build Time
Descriptor Size Descriptor (s) Position (s)
HOG 64 0.0057 0.0836
128 0.0070 0.0844
256 0.0081 0.0858
512 0.0106 0.0895
1024 0.0132 0.1255
Gist 128 0.0295 0.0839
256 0.0458 0.0854
512 0.0643 0.0896
1024 0.1041 0.1252
2048 0.1478 0.1396
Table 4: Calculation time (s) of the localization process in
the new proposed method.
Time to build Time
Descriptor Size Descriptor (s) Position (s)
HOG 64 0.0060 0.0836
128 0.0070 0.0844
256 0.0082 0.0858
512 0.0106 0.0895
1024 0.0134 0.1255
Gist 128 0.0297 0.0839
256 0.0476 0.0854
512 0.0692 0.0896
1024 0.1054 0.1252
2048 0.1478 0.1396
4.3 Computational Cost
A low error is an important characteristic to take into
account when choosing a descriptor. But the com-
putational cost is also an important issue to consider.
For that reason, the necessary time to run the algo-
rithms has also been studied. Table 3 using the classi-
cal method and table 4 using the proposed one show
the time used to build the descriptor and to estimate
the position. The data are given in seconds. As ex-
plained in section 2, the results depend on descriptors’
size and this one depends on the parameters. Taking
that into account, HOG descriptor size is
~
d ∈ R
b·k
1
×1
,
in the same way Gist descriptor size is
~
d ∈ R
r·m·k
2
×1
.
The experiments have been carried out with a CPU
8-Core Intel Xeon E5
R
at 3GHz and using the math-
ematical tool Matlab
R
. These time results are not
absolute, they depend of the computer which runs the
process. But they are comparable because all the cal-
culations have been done with the same machine.
The lower the parameters are, the shorter the de-
scriptor is and for that reason the runtime also is
lower. If table 3 and table 4 are compared, it is possi-
ble to observe that the time used to build the descrip-
tor is almost the same.
Finally, it is possible to observe that the process is
quicker using HOG descriptor that when Gist is used,
especially in the time used to build the descriptor.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The present work studies a new way to use global-
appearance descriptors. The new method is compared
with the traditional one in a localization task. The
study has been made in real scenarios which are spe-
cially challenging due to lighting conditions and hu-
man activity. Using only visual information, global-
appearance descriptors and the new proposed method
described throughout this paper are studied. Once
the images are described the performance of these
descriptors in a localization framework is compared.
Both, geometric localization error and the computa-
tional cost of the process have been studied and the
parameters have been optimised.
First, about the traditional method, while Gist and
HOG offer relatively good results in cloudy and night
environments, the sunny conditions result more chal-
lenging, and HOG presents comparatively better re-
sults than Gist in this case. Second, about the pro-
posed method, the experiments show that it presents
substantial improvements, especially in sunny envi-
ronment. About calculation times, the new method
runs as quick as the traditional one. Observing the re-
sults the proposed method improves the localization
task decreasing the error. Results obtained with HOG
descriptor are better than the results using Gist, even
though both minimise the localization error. As the
run time is practically the same using both methods,
using the proposed method where the image is multi-
plied by a gaussian vector may be a proper way to ob-
tain better results in localization tasks where the base
map has been built in an heterogeneous environment
where changing lighting conditions and human activ-
ity can take part.
This work can be the first step to build more suit-
able description solutions in navigation tasks, spe-
cially when omnidirectional or panoramic images in-
clude a lot of information from the ceiling and/or the
floor. The studied alternative may complement other
classical description methods in order to achieve a ro-
bust localization. Multiply the descriptor by a gaus-
sian distribution should not be considered as a unique
solution but they can contribute towards obtaining re-
sults. Future works can include a study of a more ro-
bust solution, combining for example the new studied
techniques with other measurements or techniques.
An Evaluation of New Global Appearance Descriptor Techniques for Visual Localization in Mobile Robots under Changing Lighting
Conditions
383

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported by the General-
itat Valenciana and the FSE through the grant
ACIF/2018/224, by the Spanish government through
the project DPI 2016-78361-R (AEI/FEDER, UE):
“Creaci
´
on de mapas mediante m
´
etodos de apariencia
visual para la navegaci
´
on de robots.” and by General-
itat Valenciana through the project AICO/2019/031:
“Creaci
´
on de modelos jer
´
arquicos y localizaci
´
on ro-
busta de robots m
´
oviles en entornos sociales”
REFERENCES
Amor
´
os, F., Pay
´
a, L., Mar
´
ın, J. M., and Reinoso, O. (2018).
Trajectory estimation and optimization through loop
closure detection, using omnidirectional imaging and
global-appearance descriptors. Expert Systems with
Applications, 102:273–290.
Bay, H., Ess, A., Tuytelaars, T., and Van Gool, L. (2008).
Speeded-up robust features (surf). Computer vision
and image understanding, 110(3):346–359.
Berenguer, Y., Pay
´
a, L., Valiente, D., Peidr
´
o, A., and
Reinoso, O. (2019). Relative altitude estimation us-
ing omnidirectional imaging and holistic descriptors.
Remote Sensing, 11(3):323.
Cebollada, S., Pay
´
a, L., Valiente, D., Jiang, X., and
Reinoso, O. (2019). An evaluation between global
appearance descriptors based on analytic methods
and deep learning techniques for localization in au-
tonomous mobile robots.
Dalal, N. and Triggs, B. (2005). Histograms of oriented gra-
dients for human detection. In 2005 IEEE Computer
Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition (CVPR’05), volume 1, pages 886–893
vol. 1.
Gil, A., Valiente, D., Reinoso,
´
O., Fern
´
andez, L., and
Mar
´
ın, J. M. (2011). Building visual maps with a
single omnidirectional camera. In ICINCO (2), pages
145–154.
Hofmeister, M., Liebsch, M., and Zell, A. (2009). Vi-
sual self-localization for small mobile robots with
weighted gradient orientation histograms. In 40th In-
ternational Symposium on Robotics (ISR), pages 87–
91. Barcelona.
Lowe, D. G. (2004). Distinctive image features from scale-
invariant keypoints. International journal of computer
vision, 60(2):91–110.
Menegatti, E., Maeda, T., and Ishiguro, H. (2004). Image-
based memory for robot navigation using properties
of omnidirectional images. Robotics and Autonomous
Systems, 47(4):251 – 267.
Murillo, A. C., Guerrero, J. J., and Sagues, C. (2007). Surf
features for efficient robot localization with omnidi-
rectional images. In Robotics and Automation, 2007
IEEE International Conference on, pages 3901–3907.
IEEE.
Oliva, A. and Torralba, A. (2001). Modeling the shape
of the scene: A holistic representation of the spatial
envelope. International journal of computer vision,
42(3):145–175.
Oliva, A. and Torralba, A. (2006). Building the gist of a
scene: The role of global image features in recogni-
tion. Progress in brain research, 155:23–36.
Pay
´
a, L., Fern
´
andez, L., Reinoso,
´
O., Gil, A., and
´
Ubeda, D. (2009). Appearance-based dense maps
creation-comparison of compression techniques with
panoramic images. In ICINCO-RA, pages 250–255.
Pay
´
a, L., Gil, A., and Reinoso, O. (2017). A state-of-the-art
review on mapping and localization of mobile robots
using omnidirectional vision sensors. Journal of Sen-
sors, 2017.
Pay
´
a, L., Peidr
´
o, A., Amor
´
os, F., Valiente, D., and Reinoso,
O. (2018). Modeling environments hierarchically with
omnidirectional imaging and global-appearance de-
scriptors. Remote Sensing, 10(4):522.
Pronobis, A. and Caputo, B. (2009). COLD: COsy Lo-
calization Database. The International Journal of
Robotics Research (IJRR), 28(5):588–594.
Radon, J. (2005). 1.1
¨
uber die bestimmung von funktio-
nen durch ihre integralwerte l
¨
angs gewisser mannig-
faltigkeiten. Classic papers in modern diagnostic ra-
diology, 5:21.
Rom
´
an, V., Pay
´
a, L., Flores, M., Cebollada, S., and
Reinoso,
´
O. (2019). Performance of new global ap-
pearance description methods in localization of mo-
bile robots. In Iberian Robotics conference, pages
351–363. Springer.
Rom
´
an, V., Pay
´
a, L., and Reinoso,
´
O. (2018). Evaluating
the robustness of global appearance descriptors in a
visual localization task, under changing lighting con-
ditions. In ICINCO-RA, pages 258–265.
Siagian, C. and Itti, L. (2009). Biologically inspired mo-
bile robot vision localization. IEEE Transactions on
Robotics, 25(4):861–873.
Sturm, P., Ramalingam, S., Tardif, J.-P., Gasparini, S., Bar-
reto, J., et al. (2011). Camera models and fundamental
concepts used in geometric computer vision. Founda-
tions and Trends
R
in Computer Graphics and Vision,
6(1–2):1–183.
Su, Z., Zhou, X., Cheng, T., Zhang, H., Xu, B., and Chen,
W. (2017). Global localization of a mobile robot us-
ing lidar and visual features. In 2017 IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (RO-
BIO), pages 2377–2383. IEEE.
Valiente Garc
´
ıa, D., Fern
´
andez Rojo, L., Gil Aparicio, A.,
Pay
´
a Castell
´
o, L., and Reinoso Garc
´
ıa, O. (2012). Vi-
sual odometry through appearance-and feature-based
method with omnidirectional images. Journal of
Robotics, 2012.
Xu, S., Chou, W., and Dong, H. (2019). A robust indoor lo-
calization system integrating visual localization aided
by cnn-based image retrieval with monte carlo local-
ization. Sensors, 19(2):249.
Zhou, X., Su, Z., Huang, D., Zhang, H., Cheng, T., and Wu,
J. (2018). Robust global localization by using global
visual features and range finders data. In 2018 IEEE
International Conference on Robotics and Biomimet-
ics (ROBIO), pages 218–223. IEEE.
ICINCO 2020 - 17th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
384
