
Teaching Business Information Systems in 2020s: Pitfalls, Challenges
and Some Methodological Ideas for Testing
Matthias Hofstetter
a
, Thomas Gees
b
, Reinhard Riedl
c
and Adamantios Koumpis
d
Institut Digital Enabling, Berner Fachhochschule, Department Wirtschaft, Bern, Switzerland
Keywords: Business Information Systems, Management Information Systems, Experiential Teaching Methods, Digital
Skills.
Abstract: In the paper we present experiences from the organisation and running of a Business Information Systems
course for undergraduate students at the Berner Fachhochschule. Aspects related to the teaching style, the
content and the process that have been defined for use are presented and discussed, while the rationale for our
decisions is also outlined. An experiential approach is fostered that allows students to capitalise on their
individual preferences and learning paths, combined with the idea of supporting the acquisition of digital
skills that will allow better use in their current or future working environments.
1 INTRODUCTION
At the Business School of the Berner Fachhochschule
there is a new ambitious programme with the
codename B2020 aiming to introduce a number of
changes in the structure and organisation of the
curricula, not only in terms of how these are
implemented but also during their early-design and
conceptualisation phases. From our side we had the
good luck to afford such an experimentation; as the
planning for the new module coincided with an
internal restructure in our Department, we had the
opportunity to reconsider the teaching of the Business
Information System module on a zero basis. In the
following we present our ideas and motivation and
also some first experiences.
2 THE QUEST FOR
SENSE-MAKING IN TEACHING
2.1 The Textbook
It is not uncommon that people are resistant to
changes, and adopt them only when it is late enough.
a
https://orcid.org/ 0000-0002-9612-1557
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8183-2906
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4483-9997
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2661-7749
This approach has also its positive aspects, as one
may adopt changes that have proven their value,
leaving out the case of wasting efforts in
experimentation. We have been teaching for many
years courses on Business Information Systems – or
as the same course appears in some institutions as
Management Information Systems – and to both
undergraduate and postgraduate and MBA levels.
A core question that has been tantalizing lecturers
was about which textbook to use and, once one made
their mind, how to use it. For sure there are best
sellers and ‘killer’ books in this area – the most
famous should be the Laudon and Laudon book now
in its 16th edition (Laudon, 2019). To not appear
disrespectful or ignoring the contribution that K. C.
Laudon has made to the field, his first book that
appeared in 1974 was rather a breakthrough offering
what was at that time unexpected, namely a study of
the use of computers in government (Laudon, 1974).
However, how seriously can someone consider the
case of using a more than 650 pages textbook to
students of generation Z that – as we are told
‘demonstrate limited attention spans’ exhibit a
‘tremendous reliance upon technology’, ‘blur the
physical and virtual worlds’ – and are often used to
‘communicate in symbols and shortcuts’ (Cook, 2019)?
510
Hofstetter, M., Gees, T., Riedl, R. and Koumpis, A.
Teaching Business Information Systems in 2020s: Pitfalls, Challenges and Some Methodological Ideas for Testing.
DOI: 10.5220/0009790805100517
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2020) - Volume 1, pages 510-517
ISBN: 978-989-758-417-6
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Especially for the book of the Laudons, a mistake
that the authors made was to consider their textbook
as of ephemeral nature, making new editions every
now and then. This helps the business, of course, as
one may see that there is an incredible amount of
‘resources’ apart from the book that includes amongst
others an Instructor's Resource Manual, a Hands-on
MIS Application Data Files, Learning Tracks and
Lecture Notes, PowerPoint Presentations and also the
Annotated PowerPoint Presentations, a Test Bank,
Video Case Instructions and also some ‘Blackboard
course cartridges’. One may wonder what the
lecturer’s job will be – possibly to help students cope
with all the various resources, while seriously running
the risk of replacing the human lecturers with robots
or Alexa boxes in the near future.
As mentioned above, young(er) people have
learned and are now possibly irreversibly used not to
spend much time in reading long texts. They may also
not care much about typologies - why bother
distinguishing between an executive support system
or a decision support system? So all in all we
considered that the best thing we could do was to
abandon the idea of using a textbook.
2.2 Style Matters
2.2.1 Discussion-based
Our idea was to follow a discussion-based style
throughout the entire course. Discussion-based means
that the arrangement of the desks in the class shall not
be the usual one with the desks set up into straight
lines or in a large circle but have no desks at all - the
students will thus have no ‘defense line’ to ‘protect’
them and help them to not be engaged in the
discussions.
We considered that this would also help the
lecturer engage better into the discussions with the
student as being one of them - with the only additional
power to moderate the discussion or choose the
subjects to be discussed in the class. But even to this,
the idea is that during the course the students shall be
able to ‘emancipate’ themselves and co-structure the
course in terms of both content and form. Especially
for the seating arrangements we were prepared for the
need to explain our decision or possibly also account
for our choice. We know that in the academic
environment and especially for matters related to
pedagogic or didactic aspects, the best is to have a list
of academic references to ground one’s arguments.
To this we can recommend amongst others
(Fernandes, 2011), (Gremmen, 2016), (Marx, 1999)
and (Sommer, 1977). As one may see, the idea is not
at all new or ‘revolutionary’ – sometimes less is more.
2.2.2. Empathy
We experience that lots of time is wasted in a course
till the students develop a feeling of trust with the
lecturer. Sometimes, to keep the class order is as
demanding as keeping the world order – or herding
cats (O'Hagan, 2000). We considered that the role of
empathy would be, under certain circumstances, a
catalyst for the success of our experiment.
For the scope of our work, we considered both
kinds of empathy in the human experience (Gerace,
2013):
Emotional empathy, also called affective
empathy or primitive empathy, as the subjective
state resulting from emotional contagion. It is our
automatic drive to respond appropriately to
another’s emotions. This kind of empathy
happens automatically, and often unconsciously.
It has also been referred to as the vicarious
sharing of emotions.
Cognitive empathy as the largely conscious drive
to recognise accurately and understand another’s
emotional state. Sometimes we call this kind of
empathy ‘perspective taking’.
One may now consider what this has to do with
teaching in general and teaching of Business
Information Systems. The WEF listed Emotional
Intelligence as one of the most important skills
employers require from their employees in 2020
(Beckford, 2018).
As people with highly developed Emotional
Intelligence have the qualities needed to succeed in
our modern workplaces, we consider it as essential to
have our students exposed to this experience, offering
them the opportunity to acquire such a skill that might
prove useful throughout their future professional
career. Apart from this, we all recognise that people
with highly developed Emotional Intelligence can
handle pressure healthily, they understand and
cooperate with others, they are good listeners, they
are more open to feedback, they are empathetic, they
set an example for others to follow and they make
more thoughtful and thorough decisions.
2.2.3 Narratives, Storytelling and Social
Media
What does storytelling have to do with teaching of
Business Information System is a good question to
ask. Participation, learning and the construction of
knowledge and understanding evolves on multiple
Teaching Business Information Systems in 2020s: Pitfalls, Challenges and Some Methodological Ideas for Testing
511

time scales (Lemke, 2000) in communities – and a
class is an instance of such a community. Within the
class context, every utterance and episode of
interaction arises from, draws upon, and is responsive
to previous experiences, but also constitutes future
situations, and contexts for learning and knowledge
construction.
When we study participation over longer stretches
of time – as it is the case of an one or two-semester
spanning course, what is significant in relation to
moment-by-moment interaction is not necessarily
relevant in the same way when we examine changing
participation in changing practices over several years
(Lave & Wenger, 1991). An important question
concerns how we take time and temporality into
account when examining students’ participation. One
theoretical solution to this methodological question
can be found in the concept of trajectories of
participation. In the branches of psychology, a
trajectory refers to a path in and across settings which
can be identified and described retrospectively, and
participation is often combined with trajectories to
describe the processes and results of having taken part
in activities over time (Rasmussen, 2012; Ludvigsen,
Rasmussen, Krange, Moen & Middleton, 2011).
For the case of teaching Business Information
System the trajectory is about helping the students
build an understanding of what business information
systems actually are. So it is not only about ERPs or
CRMs or similar – and it is not at all about software.
And such a trajectory can take the form of a narrative.
The preoccupation with “narrative” in social and
human sciences, beginning from the middle of the
twentieth century, can be seen as partaking in a
general philosophical reaction against objectivist or
positivist philosophies, that saw the relation of the
human being to the world in terms of basic
correspondences, with sensory input (empiricism) or
a priori idealistic constructions (rationalism).
Language — and especially extended discourse
— is not just a tool, but also the ‘life-world’ in which
we live and construct our realities (to the role of
language we shall elaborate later in the next
subsection). Thus for Ricœur (1990), personal
identity is essentially the elaboration of a personal
narrative of the self and of the other: narratives draw
together disparate elements of experience and social
positions of the self into a concordant ‘plot’, with a
temporal span. Structuralism, particularly in
linguistics, also had a predilection for narrative; such
a narrative turn also found its correlates in
psychoanalysis (Lacan, 1966; Bettelheim, 1975) —
after all, what does the patient on the divan do other
than produce a self-narrative? — and in social theory
(Foucault, 1971). In the transition from theory to
practice as teaching in itself is about, narrative
approaches have been applied in sociology and
anthropology in order to elicit broad range of ‘voices’
of social categories (e.g. in feminist studies; studies
of ethnic minorities), with a view to combating
inequality (e.g. Hymes, 1996). In organisation
science, group narratives of sectors of an organisation
have been elicited, as a means of understanding
problems with IT integration (Brown, 1998).
Narrative research has also inspired the
development of digital tools for their expression and
sharing. The term ‘Digital Storytelling’ refers to the
practice of using computer-based tools to tell stories,
even by combining several multimedia like photos,
audio, video and graphics.
The interest in users storytelling is witnessed also
by the initiative of Facebook to create personalized
video of each user highlighting the most significant
events in their life since joining the social network in
the form of lookbacks. A similar project has been
developed by Intel (museumofme) that uses
Facebook resources (photos, friends, posts) to create
a video of users’ stories. These initiatives show the
way in the evolution of storytelling, but they build the
video automatically and do not allow users to choose
the events to include in the story.
2.2.4 Role of Language for Student
Engagement
As already mentioned, our plan was to free the course
from the dependence on a textbook. To this, we aimed
to build a repository of ‘stories’ that had relevance to
the area of business information systems. These
didn’t limit to scientific bibliography or academic
literature but, mainly if not primarily, included case
studies and opinion articles. For this we have used the
open access online archive of the business magazine
brand eins (www.brandeins.de), but we encourage the
students to build their own resources repositories.
This is not a trivial task and forms a tangible outcome
for the students as by the end of the course they may
have achieved to have designed and operated their
own ‘business information system’ that may vary
greatly in the degree of technology employment and
in its structure, but may serve the common purpose to
support students throughout the semester for all their
learning needs.
A first aim for exposing students to read stories is
to make them develop an understanding for the field
with questions like:
Why do companies actually need business
information systems?
CSEDU 2020 - 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
512

What should one understand about a business
information system (apart from supporting
accounting and bookkeeping operations)?
How is knowledge transferred amongst
employees by using the business information
system as backbone?
How can a company build value from its business
information system? (Or is it only an ‘empty
phrase’ with no real meaning and if yes, then how
can someone make sense out of it and truly build
value?)
Bureaucracy – how much is it supported by the
introduction of business information systems?
And help get ‘cemented’ into Bureaucracy 2.0?
The idea from the story-telling part is to extract
meaning out of them. Is there something that one
should care about before introducing a new
information system? Is there something that went
wrong in Company X and we should explore more?
One may see here that many textbooks offer
plenty of use cases or case studies. But as we all
know, these are most of the times presented in a
didactic perspective –like: a company in business
sector X and with a corporate profile Y faces
problems with delayed production, loss of customers
base, an unexpected and unexplainable increase of
defect products, etc. and a the introduction of a new
business information system, a new module to the
existing business information system or an App as
extension to a legacy system comes to the rescue. And
though we are all aware that the Harvard Business
School Cases are world renowned for their extensive
and thorough exploration of strategic issues, the
question is how these world-renowned cases will be
useful to our students?
Stories have to be personal and related to the
student’s personal experience sphere. To our luck,
most of our students are also working in parallel to
their studies, so they have a plethora of own
experiences. Or, alternatively, stories have to be
accessible in a form that allows the students to get
close to the surrounding environment and the overall
context that let it happen. The question is how to
organize this unexploited and yet unstructured wealth
of information.
It is to this aim that we consider the role of
language as essential as the students will be able to
reproduce their own experiences and the sense they
make out of them in written or spoken form. Once a
student may decide for a topic they may then start to
specialize on it. To this we may need to elaborate
more in the following section by means of presenting
our didactic concept.
2.3 About the Didactic Concept
Students need to build, as result of the teaching
process, their own individual mental models (Jones,
2011) that reflect the basic notions they were
communicated during the course, and how
relationships between them were suggested by the
tutors. This necessitates from our side the need to
define a basic didactic concept that is based on a
structure like the one presented in Table 1 below.
We are sure that there are many ways to approach
this issue – what was important from our side was to
have the flexibility to stay at a level that is preferred
by each individual tutor. Some of us prefer to teach
higher level content and come up with less abstract or
practical concepts, which are then reflected into
specific competences that need to be developed by the
students, while other tutors prefer to stay at a very
practical level. To this we firmly believe what a
colleague of us once said: “flight altitude depends on
the state of knowledge”. The latter relates to the
knowledge that exists in general for a field but also to
the knowledge ‘possessed’ by the tutor and the
knowledge that is aimed to be communicated and
promoted to the students.
Table 1: Example of didactic concepts related to the
teaching of business information systems.
Content Interconnected
through concepts
Combined with
competences
Below in Tables 2 and 3 we present two content
listings planned for a 6-week course structure (a
normal undergraduate course takes 14 semester
weeks). As it is easy to see, there is a rather wide
degree of differentiation between the two of them.
However, and as long as the content is tightly coupled
with concepts that are reflected into specific
competences, the coherence of the teaching process is
ensured. This means that we have the opportunity to
assess
not only the acceptance of a teaching element
Table 2: Example of content related to the teaching of
business information systems.
Conten
t
About processes and business process essentials.
Corporate and Organisational Information Management
strategies. Typology of BIS systems. Design and
implementation issues.
Knowledge Management aspects of BIS usage. BIS and the
users / user experience aspects.
BIS economies and BIS economics: costing, pricing,
b
udgeting, financing and valuation aspects.
The corporate BIS as corporate asset and collective
intellectual capital.
Culture(s) and future of BIS.
Teaching Business Information Systems in 2020s: Pitfalls, Challenges and Some Methodological Ideas for Testing
513

Table 3: Example of alternate content related to the teaching
of business information systems.
Conten
t
Implementation failures.
Total system vs modular system implementation;
Customization.
Cost budgeting in ERP systems; Intangible and hidden factors.
The value of reengineering;
Vendor best practices vs firm competitive advantage.
ERP risk; Installation options and comparative advantages;
External sources of ERP.
ERP installation project management; ERP Implementation
and maintenance; Training.
by the students, but also to improve it given the state
of the art in the field, good practice from other
colleagues within our institution or also work together
with colleagues in other institutions and countries to
co-create value for the particular teaching subject.
2.3.1 A Word on Assessment
The role of the assessment is, as expected, key.
Adapting and applying learning practices to new
audiences is not as easy or straightforward as it may
seem. Sometimes too much is nothing and too little is
good. The degree of experience of the tutor does not
also guarantee a good learning experience for the
students. In this context, assessing, sharing and
validating good practices and learning experiences is
something that needs to be done in a continuous
fashion and with some type of what we call ‘seamless
collection of data’. This does not need to take the
form of formal evaluations that usually take place
when it is too late but build on informal exchanges
with the students from the start of the course and
during the warm-up phases. It is for this reasons that
we firmly believe that a discussion-based style for the
entire course with a circular arrangement of the desks
is important as it promotes a spirit of welcoming the
exchange of ideas.
Having in mind the trends towards combining
education and entertainment, one may now wonder
how much of each these two ingredients should be
apparent when teaching business information
systems. For example, for the second example in
Table 3, the first content item is about
‘Implementation failures’. There one may build a
rather boring 2-hour course of all possible things that
can go wrong during a business information system
implementation – or try to find relevant scenes from
movies on YouTube and show them during the class.
In this case, the students might discuss them together
and come up to conclusions that will be co-created
during the course. It will be less boring and also more
fun. One may, however, only judge the efficacy of the
approach by the individual learning paths that the
students will build and follow in the weeks after. To
this, short tests that take the form of quizzes can help
the students see if they have achieved the expected
level of competence. Regarding the latter, we are
aware that several institutions use the differentiator,
namely a tool to formulate and organise learning
goals, offered as a moodle plugin and based on the
Differentiator by Ian Byrd, which is based on
Bloom’s Taxonomy (Anderson, 2000).
3 FOCUS AND LEGACY OF THE
COURSE
The focus of such a business information systems
course is usually put on the information system part –
leaving out the term business as trivial or self-
explanatory. For us it is important to let the students
examine in all necessary depth and breadth the notion
of a business. Sometimes a business is related to a
repeated process: Uber drivers run their business in a
similar fashion like conventional taxi drivers do – or
not? But sometimes we have to also arrange a
business only once and we are done with it: leaving
our home to go to a nursing home is also a ‘business’
– it needs some type of an informal information
system to be set up.
With some students we have explored the case of
a diaper information system – so imagine that you are
having your first baby and you have to set up all
necessary processes (which we can comfortably call
business processes) that will let you better plan,
program, budget and execute all relevant actions. So
one may see that there is no need to consider the case
of a multinational company that (apart from torturing
the natives and destroying the environment in some
exotic country) introduces some plan for controlling
their costs – there is the opportunity to study the same
aspects also when considering your own diaper
information system (which no doubt also pollutes the
environment).
Teaching business information system doesn’t
need to be incomprehensibly upscaled to something
bigger for which the students may have no clue. It can
be studied in a smaller scale, letting the students
understand the dynamics of some basic notions like
the concept of information, how we acquire them and
process them and possibly store them in order to be
retrievable in the future. How we organize
information flows amongst the different units of a
company, is the same as how we organize basic
CSEDU 2020 - 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
514

information flows at home with the other family
members.
Do we stick to policies at home, like the
automated order of toilet paper rolls, when the
number of supplies falls below some number?
Probably not, as we are relaxed for some aspects. But
it is good for a business to not run out of essential
supplies (and toilet paper rolls) as they may risk
getting out of business. A complicated automotive
manufacturers supply chain with several supplier tiers
for contractors and subcontractors may seem more
exciting to teach – but we all know that a Späti (late
night grocery shop) or a ‘boring’ corner shop may
have an equally exciting grid of suppliers. And most
probably, as a young professional someone may not
be offered a position to re-design the suppliers
network of Volkswagen. Teaching our students to
find complexity in what appears as simple or trivial
is, we think, the highest service we can offer to them
for their future careers – there are many people out
there in positions that ‘run the show’ without having
any idea about what they are doing. And worst of all:
there is little or no hope that they will ever learn.
Learning is a simple process that may be seriously
hindered or even disabled if people fall victims of the
impostor syndrome and develop a persistent
internalized fear of being exposed as frauds. The only
way they can then manage to not lose their
professional face is to pretend and fake complexity
because they have never learned the simple basic
things that would allow them to develop a clear
understanding.
4 COMPUTER-SUPPORTED
ASPECTS
One may doubt that teaching like the one we have
been describing may not need at all the use of
computer support – this is not true. Quite the
opposite: there is plenty of space for experimentation
and learning assisted with tools that may help the
students acquire essential digital skills. Here we only
mention two of them and elaborate with some
examples:
balsamiq is a graphical user interface website
wireframe builder application. It allows the
designer to arrange pre-built widgets using a
drag-and-drop editor. It allows students to build
relatively easy mockups and prototypes of all
possible types of information systems – so even
the aforementioned diaper information system.
Of course user interface design is not equal to
business information systems, but as we all
know, the latter can only communicate with the
end users through the user interface.
basecamp is a web-based project management
tool with main features such as to-do lists,
milestone management, forum-like messaging,
file sharing, and time tracking. Here the idea is
not to train our students in the use of basecamp –
this is something they may learn in the future
when they actually need it. What is of
importance in the course is to have students
experimenting with the need to make the
transition from other forms of information
organization and flow to some form that brings
together several features as parts of an
application.
One may see that in work environments people
used email in the past to communicate information
and exchange files. Then people started using skype
for both – and many more use WhatsApp for the same
functions. In such a fast-moving field, why not
consider that the engineers involved in the design of
some components of a new car model should not use
Instagram? And follow on Twitter for every
communication that may have appeared in the past on
a notice board?
The technology fads are one thing – they may come
and go – some of them stay with us longer than
expected and some others that we thought would stay
for ever disappear quickly. What is important for the
students to understand is the underlying needs that
can help a company create or build value through the
supported processes and activities. Below we present
the result of a student’s project for a quite interesting
hypothetical though not at all unrealistic scenario:
imagine a company that needs to build their own Data
Science made easy system. The end users themselves
need to define the operations and the user interface.
So, it has to look like something that makes sense for
the users themselves. The students were able to
design the screens on paper – the same as people
would have done some fifty or hundred years before,
and at any point they felt comfortable they were able
to make the transition to use balsamiq. The transition
was not easy: balsamiq is very easy but needs time to
get familiar with. And the first designs were literally
horrible and frustrating.
To achieve a good level of mastering the tool,
students needed to spend sometimes more than 40
hours. Not all students had this time – and we
considered that teaching the students of business
information systems how to use balsamiq would be
wrong.
Teaching Business Information Systems in 2020s: Pitfalls, Challenges and Some Methodological Ideas for Testing
515
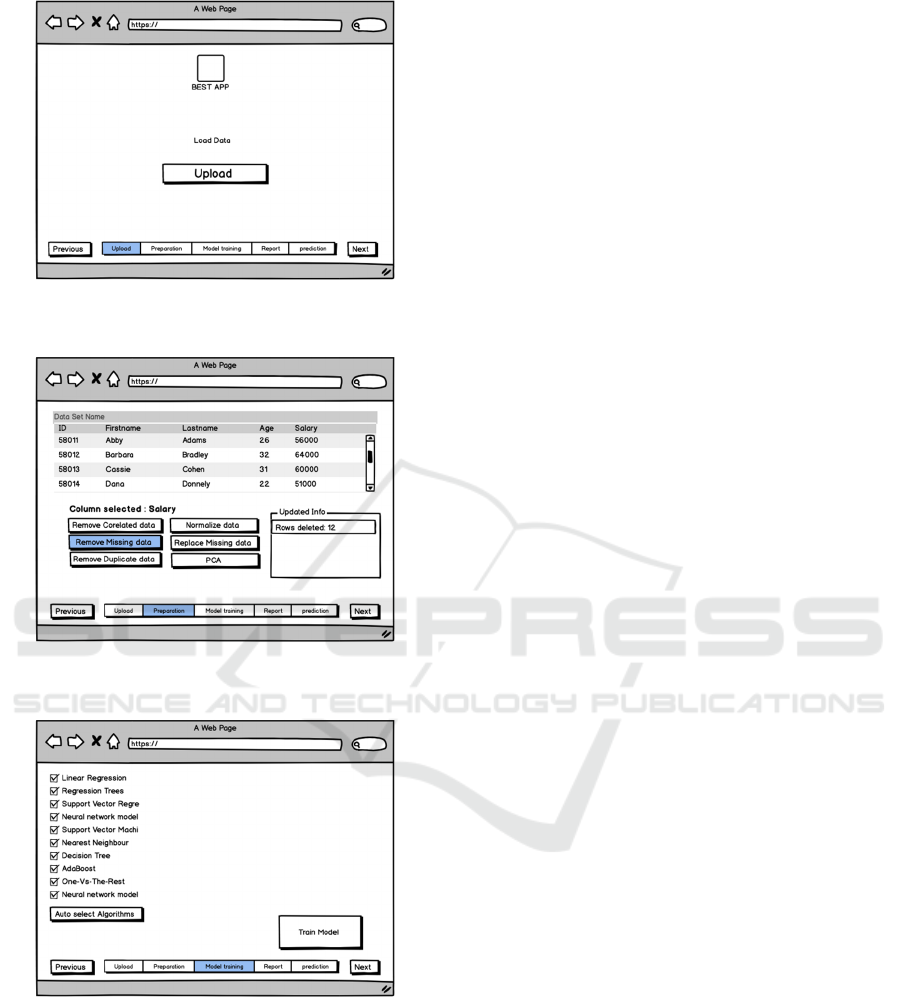
Figure 1: The initial screen of the ‘Data Science Made
Easy’ environment.
Figure 2: What are the meaningful operations to include for
the preparation of the data processing tasks?
Figure 3: And how should the model training step take
place?
5 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSIONS
We all know the proverb that says: give a man a fish
and you feed him for a day - teach him how to fish and
you feed him for his life time. This was good but only
for the past times. Apart from the undeserved gender
bias that only men were worth to be fed or taught how
to fish, nowadays we should rephrase it as follows:
give a person a fish and you feed them for a day -
teach them what fishing is about and you feed them
for their life time.
Teaching business information systems – as other
courses – may become thrillingly exciting if liberated
from the cliché of following what the textbook
industry provides us with. There are of course several
risks and failure possibilities – but this is not an
excuse to use material that has been developed for
some other students. Harvard Business School Cases
may be world renowned for their extensive and
thorough exploration of strategic issues but may be of
little or no value to our students. What is important to
them is to find a narrative that will allow them to
build, during the course lifetime, the necessary levels
of self-confidence so that they will be able to interpret
needs of their business and professional environments
in a sense- and value-making way. Digital skills can
be developed sometimes more successfully by using
analog means.
Many of us use or have to use moodle for teaching
purposes. What we may not know is that Moodle's
founder and main developer Martin Dougiamas grew
up in the Australian ‘outback’, the vast, remote
interior of Australia, in the late 1970s, and had taken
lessons from the School of the Air, giving him from a
young age an insight into distance learning. While he
may be praised for his achievement and his devotion
to the free and open-source software movement, it is
a pity to a priori keep distance with students
especially when the opportunity to offer a superb
teaching and learning experience is so close to us.
As one of our anonymous reviewers mentioned in
their review, it is an open issue ‘if in academic
education we should stop asking students to develop
skills on reading long and scientific texts’, adding that
‘I do not think that students would ever be able to
write or think scientifically, if they are not asked to
practice reading and understanding such texts
(provided a good choice of such texts is made)’, and
concluding with a remark that ‘this might lead to the
banality of the absence of thought, to paraphrase
Hannah Arendt’. We have also from our side made
similar if not the same thoughts and what we see is
that there are no easy answers to give. However, there
is a need to keep alive a continuous dialogue that will
include all sides, so not only the students and the
lecturers but also other stakeholders: education policy
makers as well as companies and organisations of
both the private and the public sector that shall
eventually employ our students. Such a dialogue shall
CSEDU 2020 - 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
516

not give any definitive answers – for the future we
shall all be ready for continuous experimentation. To
this we shall need to develop fast reflexes and change
something that doesn’t work – but also improve
something that already works to work better.
One may possibly wonder how some potentially
superficial information from a (non scientific)
magazine can offer scientific insight to students. Here
we have two things to say: Firstly for those that are
not familiar with the brand eins magazine, it needs to
be noted that the magazine offers insightful and quite
distinctive (to not risk to name them intellectually
elitist) views to problems and phenomena of the
society, the economy and the business which can
initially trigger and continuously enrich the dialogue
on the various course topics. Each of its issues is
focused on some theme that is then elaborated with
essays and analyses. Secondly, the entire idea about
not following a textbook orthodoxy for teaching a
subject like business information systems is that the
subject on its own calls for experimentation and
offers all the opportunities to test unexplored waters.
In the end same like journalism may better get taught
with use of newspapers, business can in a similar
fashion be taught by using as content stories from the
actual frontline.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are thankful to the comments of the two
anonymous reviewers – they have both taken the time
and effort to improve the quality of this paper and
increase its value and impact.
REFERENCES
Anderson L. W., Krathwohl D. R., Airasian P. W.,
Cruikshank K. A., Mayer R. E., Pintrich P. R., Raths J.,
Wittrock M. C. (2000) A Taxonomy for Learning,
Teaching, and Assessing: A Revision of Bloom's
Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, Pearson.
Beckford A. (2018) The Skills You Need To Succeed In 2020.
Forbes, August 2018, access: 10 February 2020,
https://www.forbes.com/sites/ellevate/2018/08/06/the-
skills-you-need-to-succeed-in-2020/
Bettelheim, B. (1975) The Uses of Enchantment: The
Meaning and Importance of Fairy Tales, New York:
Vintage Books.
Brown, A.D. (1998) Narrative, politics and legitimacy in an
IT implementation. Journal of Management Studies,
35(1), 35-58.
Cook V. S. (2019) Generation Z Engaged in the Classroom,
WCET Frontiers, accessed: February 3 2020,
https://wcetfrontiers.org/2019/03/06/generation-z-
engaged-in-the-classroom/
Fernandes, A. C., Huang, J., & Rinaldo, V. (2011). Does
where a student sits really matter? The impact of seating
locations on student classroom learning. International
Journal of Applied Educational Studies, 10(1), 66-77.
Foucault, M. (1974) Die Ordnung des Diskurses:
Inauguralvorlesung am Collège de France, 2. Dezember
1970, Hanser, München 1974.
Gerace A., Day A., Casey S., Mohr P. (2013) An exploratory
investigation of the process of perspective taking in
interpersonal situations. Journal of Relationships
Research. 4: e6, 1–12.
Gremmen, M. C., van den Berg, Y. H., Segers, E., &
Cillessen, A. H. (2016). Considerations for classroom
seating arrangements and the role of teacher
characteristics and beliefs. Social Psychology of
Education, 19(4), 749-774.
Hymes, D. (1996) Ethnography, Linguistics, Narrative
Inequality: Toward an Understanding of Voice, London,
Taylor & Francis.
Jones, N. A. et al. (2011) Mental Models: an interdisciplinary
synthesis of theory and methods, Ecology and Society,16
(1): 46.
Lacan, J. (2006) Écrits: The First Complete Edition in
English, New York, W.W. Norton & Co.
Laudon K. C. (1974) Computers and Bureaucratic Reform:
The Political Functions of Urban Information Systems,
John Wiley and Sons, 1974.
Laudon K. C. and Laudon J. P. (2019) Management
Information Systems: Managing the Digital Firm, 16
th
edition, Pearson
Lave, J. & E. Wenger (1991) Situated learning: Legitimate
peripheral participation. NY: Cambridge University
Press.
Lemke, J. L. (2000) Across the Scales of Time: Artifacts,
Activities, and Meanings in Ecosocial Systems. Mind,
Culture, and Activity, 7 (4), 273-290.
Ludvigsen, S., Rasmussen, I., Ingeborg, K., Moen, A. &
Middleton, D. (2011) Intersecting trajectories of
participation: temporality and learning. In S. Ludvigsen,
A. Lund and R. Säljö (Eds). Learning Across Sites: New
tools, infrastructures and practices, pp. 105-121.
London: Pergamon.
Marx, A., Fuhrer, U., & Hartig, T. (1999). Effects of
classroom seating arrangements on children's question-
asking. Learning Environments Research, 2(3), 249-263.
Mintzberg H. (1994) Rise and Fall of Strategic Planning,
Simon and Schuster.
Moodle (2019) About Moodle - History, accessed: February
11 2020, https://docs.moodle.org/38/en/History
O'Hagan J. (2000) Cat Herders, accessed: February 3 2020,
https://adage.com/videos/eds-cat-herders/897
Rasmussen, Ingvill (2012) Trajectories of participation:
temporality and learning, In Norbert M. Seel (ed.),
Encyclopedia of the Sciences of Learning. Springer.
ISBN 978-1-4419-1428-6. Part 20/T. s 3334 - 3337
Ricœur, P. (1992) Oneself as Another (Soi-même comme un
autre, Chicago, University of Chicago Press.
Sommer, R. (1977). Classroom layout. Theory into Practice,
16(3), 174-175.
Teaching Business Information Systems in 2020s: Pitfalls, Challenges and Some Methodological Ideas for Testing
517
