
Teaching Research Methods for Computer Science Students using
Virtual Learning: A Case Study
Sarah Alhumoud
1
, Areeb Alowisheq
1
and Nora Altwairesh
2
1
Computer Science Department, Al Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University, (IMSIU), Saudi Arabia
2
Information Technology Department, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia
Keywords: Virtual Learning Environment (VLE), Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs).
Abstract: Research skills are crucial for education, and overall scientific prosperity. In Saudi Arabia, a gap exists in the
research skills and knowledge necessary for higher education students. This paper highlights the current state
of university curricula in terms of teaching scientific research skills and methods in Saudi Arabia. Also, it
presents a low-cost learning model, called ASA research camp, that was applied to bridge the knowledge gap.
This exhibits a virtual class that combine qualities of both VLEs and MOOCs. The course spanned three
months in two phases: theoretical for listening and discussion, and practical for guided paper writing. Surveys
show that the 200 participants had maximum learning value with minimal cost. Moreover, on finishing the
course, the members of the practical part, 16 students, were able to publish three papers in Springer Lecture
Notes in its Computer Science book series as a result of the guided paper writing phase.
1 INTRODUCTION
The trend towards online learning starting from
virtual learning environments (VLEs) and advancing
to massive open online courses (MOOCs) has
recently expanded greatly. VLEs are systems such as
Blackboard and Moodle used in the context of
universities and other Higher Education Institutions.
They are usually included with courses whose
instructors are able to give feedback and directly
mark up the papers of a limited number of students.
In contrast, MOOCs are open educational systems
that can be offered from universities but are
independent and vast in terms of the student base.
Examples of MOOCs are edX, Coursera, Udemy, and
Udacity. Worldwide, MOOC courses are offered to
thousands and hundreds of thousands of students.
This raises the possibility of offering higher education
to a wider base of students with minimum to no fees
bridging the gap between privileged and
disadvantaged learners (Kay et al., 2013; Zheng et al.,
2015). MOOCs give students a great chance to learn
from leaders and elite scientists directly. However,
there are some issues related to it, such as a high
dropout rate (Panagiotis Adamopoulos, n.d.; Zheng et
al., 2015), or what Clow calls (Clow, 2013) the
‘funnel of participation’, starting with thousands of
students and ending the course with only a few,
resulting in a 5% passing rate in some cases (Kay et
al., 2013).
Several studies were conducted to measure the
effectiveness of virtual classes as opposed to
traditional face-to-face classes. A marked study was
done in King Abdulaziz University, Saudi Arabia
(Al-Nuaim, 2012). The study shows that courses done
by the Deanship of Distance Learning proved
successful in terms of providing a comparable
educational experience as opposed to traditional
courses. Another study carried out on 122 students in
a Greek university shows that the limited mobile
access could affect using Moodle as an active
learning tool rather than a document repository
(Papadakis et al., 2017). This issue is not widely
problematic in Saudi Arabia as the internet pentation
rate is 93% (Simon Kemp, n.d.) and the mobile
penetration is 126% (CITC, n.d.) as of 2020 and 2019
respectively. This is a success factor to the learning
model we propose. In our learning model, we mix the
VLE and MOOC styles. That is, we open the course
to the public, but at the same time, we provide a
chance for direct contact with instructors. In this case
study, we will review the process and results of our
virtual class (ASA Research Camp). The camp
teaches and gives practice in scientific research
518
Alhumoud, S., Alowisheq, A. and Altwairesh, N.
Teaching Research Methods for Computer Science Students using Virtual Learning: A Case Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0009804205180522
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2020) - Volume 1, pages 518-522
ISBN: 978-989-758-417-6
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
methods and skills for computer science college
students.
This was motivated by the minimal exposure that
students receive to scientific research methods and
techniques in many universities in Saudi Arabia. This
is evident from a review we conducted on the
programs of 10 computing colleges in the largest
Saudi universities in terms of enrolled students. These
10 computing colleges had a total of 35 computer
majors. Each major contained an average of 40
courses in their programs. There were no courses
dedicated to research methods and skills in 30 out of
the 35 majors, and in the 5 remaining ones there was
at most one course as shown in Table 1. The
following universities are under consideration: King
Faisal University (KFU), King Abdulaziz University
(KAU), Al Imam Muhammad Ibn Saud Islamic
University (IMSIU), Umm Al Qura University
(UQU), Qassim Univesity (QU), Taif University
(TU), Taibah University (TaibahU), King Khalid
University (KKU), Jazan University (JazanU), King
Saud University (KSU). In addition to the scarcity of
courses focusing on scientific research, students
rarely have opportunities to be mentored by
experienced researchers, despite the importance of
such opportunities in developing their research skills
(Gonzalez, Cristina, n.d.). On this basis, the goals of
the research camp are as follows:
1) promoting awareness of scientific research
practices between college students; 2) sharing
experiences between attendees and instructors; 3)
providing an easily accessible learning experience
from the premises and comfort of homes in the field
of scientific research; 4) teaching scientific paper
writing through direct mentoring and experiential
learning. 5) providing a complete compressed course
on scientific research concepts starting from idea
selection, to paper writing, and ending with the
paper’s publication and presentation.
This paper sheds light on the research camp
approach, organization and operation. The challenges
experienced by the camp leaders are discussed.
Finally, the reflections and conclusions are
mentioned.
2 RESEARCH CAMP APPROACH
Through the implementation of the ASA research
camp, we sought to answer the following research
questions:
1) Would the camp successfully support learning the
main scientific research concepts in a virtual
learning environment?
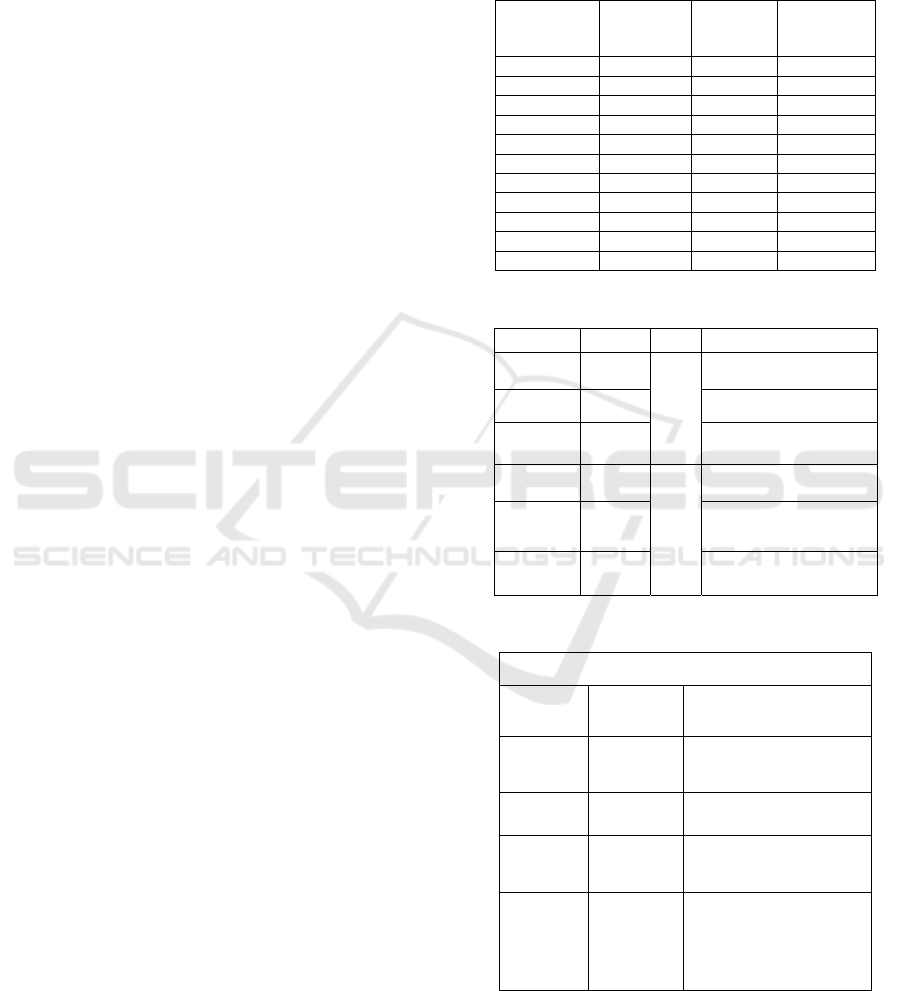
Table 1: Number of Scientific Research Courses in the
largest 10 Universities in Saudi Arabia.
University
#
students
#
Computer
Majors
#Research
courses in all
Majors
KFU 161,204 4 0
KAU 156,505 3 0
IMSIU 107,609 4 1
UQU 102,237 4 1
QU 67,822 3 0
TU 61,138 3 0
TaibahU 57,744 3 0
KKU 56,466 4 2
JazanU 54,306 3 0
KSU 49,501 4 1
TOTAL 35 5
Table 2: Research Camp Timetable.
Time Date Phase Levels
6:00-9:00
PM
1 Oct
Theory
Level 1: Introduction to
scientific paper writing
9:00 PM 7 Oct
Proposal submission
6:00-9:00
PM
8 Oct
Level 2: Presentation
techniques
6:00-9:00
PM
15 Oct
Practice
Level 3: Present accepted
proposals
- 22 Oct -
30 Nov
Level 4: Guided paper
writing
- 30 Nov
Submit paper for review
Table 3: Registration form questions.
Questions
1. Arabic
Full name
6.
University
11. Did you read
scientific papers before?
2. English
Full name
7. Country
12. Did you write a
scientific paper before?
3. Email 8. Level 13. Why join?
4. Mobile 9. Major 14. Your expectation
5. GPA
10. English
Proficiency
15. I’m able to attend
online on the specified
dates and the information
I provided here is correct.
2) Would the students be able to reach the goal of
writing a research paper? In the following section,
the camp organization and operation are
explained.
Teaching Research Methods for Computer Science Students using Virtual Learning: A Case Study
519

2.1 Research Camp Organization
ASA stands for Arabic sentiment analysis and it is the
name of the research group that held the camp, with
the primary investigator being the camp leader and
the first author of this paper. The research camp was
organized into two administrative phases and four
educational levels, Table 2. The administrative
phases include advertisement and registration. The
advertisement was done through a tweet from the
ASA research group’s Twitter account with more
than 1,000 followers and through WhatsApp
messaging. By the fourth day of announcing the
camp, more than 200 applicants had applied. The
registration form questions are listed in Table 3. The
registered applicants were divided into two groups,
campers and listeners. Campers attended and
participated in all levels, whereas listeners attended
the first two levels. Upon analysing the registration
form, campers were selected according to several
criteria related to their answers to questions 10-15.
After finishing the camp levels and upon successful
paper compilation, the campers submitted the paper
for review and publication.
2.2 Research Camp Operation
The camp started with 200 virtual participants
between listeners and campers. The participants were
given a three-hour crash course on scientific research
methods, including idea selection and scrutiny, and
paper structure and writing. The course was
facilitated by WebEx, a web conferencing tool. This
tool offers different functions for students like rise
hand for voice participation and asking questions,
applause, and text chat for communicating issues like
questions or comments. Those functions aid in the
students’ interaction and learning process. A more
complex set of function and tools is offered to the
course instructor those include application sharing,
polls, break-out sessions for breaking students into
smaller groups, and session recording and ending. In
order to move to the next level, campers where asked
to submit a research proposal or select one from the
ideas presented to them and lead by the mentors, and
in both cases, write a brief proposal around it. On
level 2, essential presentation skills are described to
help scientists and researchers who have excellent
work but lack the ability to promote their projects. At
the close of that session, listeners were thanked for
attending, and given a feedback form to fill. Also,
subgroups of participants, campers, were pulled out
into separate virtual classrooms for a tentative
proposal discussion and formation, each group with a
senior researcher mentor. The work on the proposal
continued asynchronously until the time of level 3,
when each group had the chance to present its
proposal. Next, each group had a separate meeting to
setup the communication policy for the next two
months. Meetings to write the paper were continued
until the paper of each group was submitted to the
publication venue.
3 RESEARCH CAMP ANALYSIS
The camp applicants were coming from four different
countries, and from more than 10 universities. The
majority are from Saudi Arabia, as shown in Figure
1. Also, applicants were graduates or studying in one
of the universities shown in Figure 2 with the majority
being from IMSIU. This was expected as the research
group offering the camp is based in IMSIU. The
applicants’ educational backgrounds varied, with the
majority (58%) still studying for their bachelor’s or
having earned it, while 42% were postgraduate
students, Figure 3. The academic majors of applicants
were mainly computer science (CS), at 47%. This was
probable as the reach of advertisement was
propagated dominantly by the research group
members, who are mostly majoring in CS. Coming
next was information systems (IS) at 33%, followed
by 15% of the participants majoring in information
technology (IT).
Ninety nine percent of the participants were
female. This was understandable as the camp was
organised and held by faculty from the female
section, as all universities in Saudi Arabia are split
into two mostly identical sections, males and females.
Also, this could be explained by the ease of
attendance for female participants: at the time the
camp was held, woman were not allowed to drive in
Saudi Arabia, thus the online camp provided a rare
chance to learn from home with no need to arrange
suitable transportation to participate and attend. On
analysing the feedback forms, the feedback we
received was 90% highly positive on the first
two
levels that were presented to both listeners and
campers, Table 4.
The levels were satisfactory to most of the
participants. This could be explained as listeners and
campers were offered rich information in an open
discussion manner.
CSEDU 2020 - 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
520
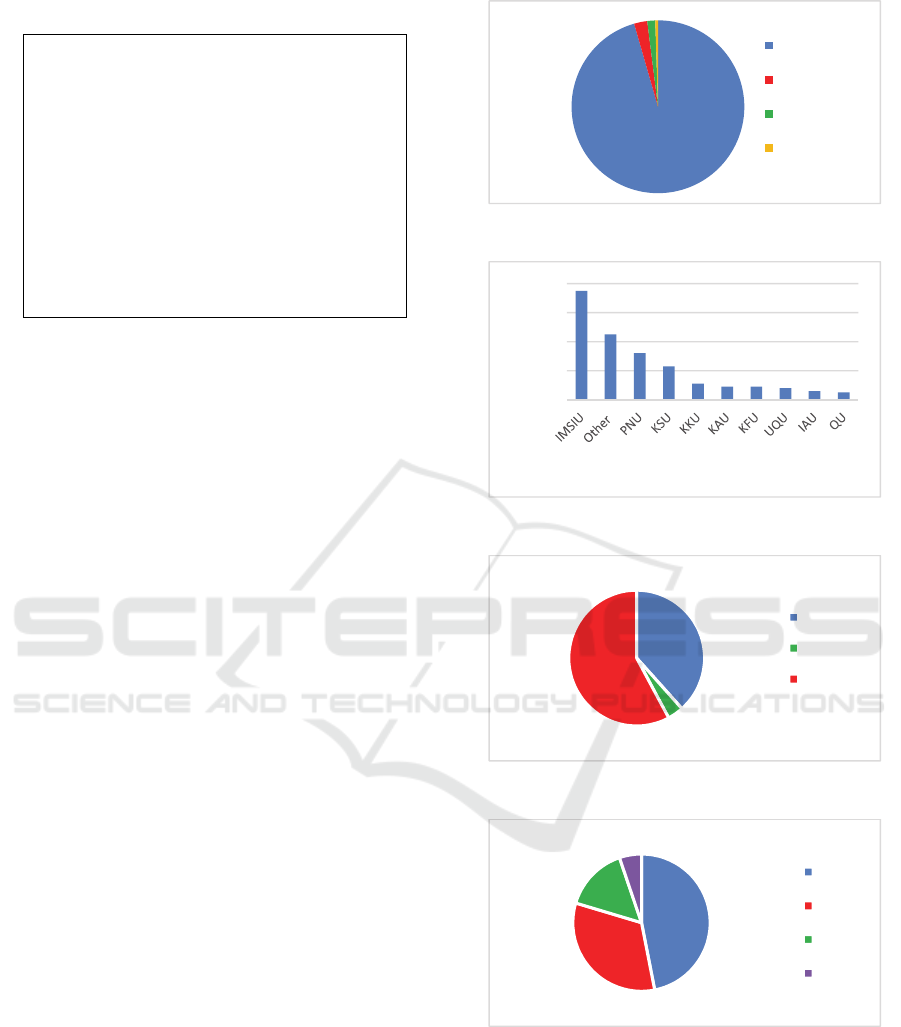
Table 4: Part of the feedback messages.
- thank you, I rarely find someone to guide and
mentor me closely.
- Great start! I've learned more than what I
expected. Thank you so much.
- I learned many things such as how to motivate
myself, steps to write a paper, how to know the
best journals.
- I learned the basics of academic writing,
publishing venues and evaluating them, how to
go about exploring a research problem.
- all the course content is excellent and important.
- this course gave a push to endure research
problems and made me realise that I’m not alone
in that.
Presenting them a rare chance to ask and interact
with experienced researchers with no cost at all. Even
the cost of attending a real class in terms of
transportation and time was deducted. Delivering the
course in a virtual learning environment provides a
chance for both synchronous and asynchronous
communication. This potentially provides deeper and
varied forms of dialogue and interaction between
students and mentors and among peers. This fulfils
socially situated learning, one of the seven eLearning
applied theories described by (Conole et al., 2004).
In the practical part of the course, the campers had
the chance to experience and reflect on scientific
research fundamentals while being mentored to write
a whole paper, fulfilling experiential learning (Conole
et al., 2004). On finishing the camp, the campers had
worked in three groups and written three different
papers with the guidance of a senior researcher in
each group. The papers resulting from those groups
were all published in Springer Lecture Notes in its
Computer Science book series (Almuqren et al.,
2017; AlNegheimish et al., 2017; Alowisheq et al.,
2017)
.
4 RESEARCH CAMP
CHALLENGES
Employing a virtual methodology for teaching the
introduction to scientific research and providing the
means for potential authors to experience writing a
paper with guided mentorship and peer collaboration
had positive outcomes. This however, faced several
challenges, which are as follows: First, given that the
campers group was composed of virtual teams whose
members have not met in person and are from varying
backgrounds having to work on a rigorous scientific
writing project that needed synchronisation and high
coordination, this required a huge leadership effort
Figure 1: Participants' countries.
Figure 2: Participants' affiliations.
Figure 3: Current level of education.
Figure 4: Academic Majors of participants.
for it to succeed. Second, the success of online
meetings depends on the quality of the Internet
connection of the attendees.
Third, although the screening of campers who
joined the paper writing groups went through
different filtering and scrutiny phases, there were still
some essential qualities that could not be discovered
SaudiArabia
Oman
UnitedKingdom
UnitedStates
96%
0
20
40
60
80
Numberofapplicants
Universitiesstudyinginorgraduatedfrom
38%
4%
58%
Master
PhD
Other
47%
33%
15%
5%
CS
IS
IT
Other
Teaching Research Methods for Computer Science Students using Virtual Learning: A Case Study
521

solely by the registration forms. This includes,
English language competency, scientific background,
motivation, and commitment. As a result, some group
members were not active in reaching the goal as other
members. Thus, having some rigorous English
proficiency measures such as IELTS or TOEFL will
aid in setting the expectations early before the writing
levels.
Fourth, keeping the campers learning and
motivated to finish writing the paper with high
commitment in attending the meetings and doing the
writing assignments required a strong effort in
follow-up and coaching, while that happened, we still
lost 3 group members from reaching the final goal.
This is attributed to either inability to continue.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The ASA research camp provided a learning
experience exercising several pedagogical and
educational traits that are required for good learning
such as socially situated learning and experiential
learning. In this course WebEx was used for teaching
scientific research methods to computer science
students. Although the mentors and participants faced
different challenges, they were able to elicit three
academically sound papers in a learning journey that
positively affected campers. The listeners on the first
two levels were also positively affected and learned
with minimal cost. This fulfils the two research
questions we asked on proposing the research camp.
However, to minimise challenges and aid future
success, we suggest having more mentors per
campers’ group with at least two mentors per group.
Also, for guided paper writing starting in level 3, a
group of two mentors and five students at maximum
is suggested. Lastly, as the survey show, only 5
courses among 35 majors in 10 different colleges in
Saudi Arabia are on scientific research. Also, 6 out of
10 colleges do not offer any course on scientific
research. This is a huge gap in teaching scientific
research methods in computer science colleges in
Saudi Arabia that needs to be improved.
REFERENCES
Almuqren, L., Alzammam, A., Alotaibi, S., Cristea, A., &
Alhumoud, S. (2017). A Review on Corpus Annotation
for Arabic Sentiment Analysis. In G. Meiselwitz (Ed.),
Social Computing and Social Media. Applications and
Analytics (pp. 215–225). Springer International
Publishing.
AlNegheimish, H., Alshobaili, J., AlMansour, N., Shiha, R.
B., AlTwairesh, N., & Alhumoud, S. (2017). AraSenTi-
Lexicon: A Different Approach. In G. Meiselwitz (Ed.),
Social Computing and Social Media. Applications and
Analytics (pp. 226–235). Springer International
Publishing.
Al-Nuaim, H. A. (2012). The Use of Virtual Classrooms in
E-learning: A Case Study in King Abdulaziz
University, Saudi Arabia. E-Learning and Digital
Media, 9(2), 211–222. https://doi.org/10.2304/elea.
2012.9.2.211
Alowisheq, A., Alrajebah, N., Alrumikhani, A., Al-
Shamrani, G., Shaabi, M., Al-Nufaisi, M., Alnasser, A.,
& Alhumoud, S. (2017). Investigating the Relationship
Between Trust and Sentiment Agreement in Arab
Twitter Users. In G. Meiselwitz (Ed.), Social
Computing and Social Media. Applications and
Analytics (pp. 236–245). Springer International
Publishing.
CITC. (n.d.). ICT Performance Indicators. Communica-
tions and Information Technology Commissio.
https://www.citc.gov.sa/en/indicators/Indicators%20of
%20Communications%20and%20Information%20Tec
hn/ICT%20Indicators%20in%20the%20Kingdom%20
of%20Saudi%20Arabia%20(Q1%202019).pdf
Clow, D. (2013). MOOCs and the Funnel of Participation.
Proceedings of the Third International Conference on
Learning Analytics and Knowledge, 185–189.
https://doi.org/10.1145/2460296.2460332
Conole, G., Dyke, M., Oliver, M., & Seale, J. (2004).
Mapping pedagogy and tools for effective learning
design. Computer Education, 43, 17–33.
Gonzalez, Cristina. (n.d.). Undergraduate research,
graduate mentoring, and the university’s mission.
Science, 293(5535), 1624–1626.
Kay, J., Reimann, P., Diebold, E., & Kummerfeld, B.
(2013). MOOCs: So Many Learners, So Much
Potential ... IEEE Intelligent Systems, 28(3), 70–77.
https://doi.org/10.1109/MIS.2013.66
Panagiotis Adamopoulos. (n.d.). What Makes a Great
MOOC? An Interdisciplinary Analysis of Student
Retention in Online Courses. Proceedings of the 34th
International Conference on Information Systems, ICIS
’13.
Papadakis, S., Kalogiannakis, M., Sifaki, E., & Vidakis, N.
(2017). Access Moodle Using Smart Mobile Phones. A
case study in a Greek University.
Simon Kemp. (n.d.). DIGITAL 2020: SAUDI ARABIA.
https://datareportal.com/reports/digital-2020-saudi-
arabia
Zheng, S., Rosson, M. B., Shih, P. C., & Carroll, J. M.
(2015). Understanding Student Motivation, Behaviors
and Perceptions in MOOCs. Proceedings of the
18th ACM Conference on Computer Supported
Cooperative Work; Social Computing, 1882–1895.
https://doi.org/10.1145/2675133.2675217
CSEDU 2020 - 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
522
