
Computational Music Thinking Patterns: Connecting Music
Education with Computer Science Education through the Design of
Interactive Notations
Alexander Repenning, Jürg Zurmühle, Anna Lamprou and Daniel Hug
University of Applied Sciences and Arts Northwestern Switzerland, FHNW School of Education,
Bahnhofstrasse 6, Windisch, Switzerland
Keywords: Computational Thinking, Computational Music Thinking, K-12 Computer Science Education, Music
Education, Elementary School Pre-service Teacher Education.
Abstract: Computational Music Thinking combines computing education and music education with the goal to
overcome common aptitudinal and attitudinal challenges. Many students, and teachers, believe that writing
programs or performing music is beyond their natural abilities. Instead of trying to teach computing and music
separately, Computational Music Thinking employs the design of interactive notations as a synergistic activity
to learn simultaneously about computation and music. On the one hand, music can turn abstract computational
concepts into enjoyable concrete experiences. Computation, on the other hand, can expand students’ notion
of music education well beyond music performance. A course with elementary school pre-service teachers
explored the teaching of Computational Music Thinking through a small set of constructs called
Computational Music Thinking Patterns. These patterns are centered around educational activities to design
interactive notations in accessible as well as engaging ways. Computational Music Thinking Patterns expand
our previous work on Computational Thinking Patterns used in game design and simulation authoring
activities. Data collected from the course suggest highly positive effects on teachers' attitudes towards
believing that Computational Music Thinking is important to their teaching, that Computational Music
Thinking helps the comprehension of computer science and that Computational Music Thinking helps the
comprehension of music.
1 INTRODUCTION
In most elementary schools around the world teachers
are required to teach a wide range of subjects
including language, math, science, and art including
music. Recently, some countries such as Switzerland,
have made computing education, consisting of
programming and Computational Thinking (CT)
(Repenning, Lamprou, Petralito, & Basawapatna,
2019), mandatory. Many schools and teachers
perceive this as a challenge (Gander et al., 2013)
because this requirement adds another subject to the
list of courses to teach. Moreover, unlike the more
traditional subjects’ teachers typically do not have
any programming background and, consequently,
feel ill prepared to teach CT-related courses. Even
pre-service teachers – most of them are recent high
school graduates in their twenties – who are being
trained at a school of education to become teachers,
typically have no experience in computer science. At
the School of Education PH FHNW in Switzerland
pre-service teachers were over 10 times less likely to
have had previous experience in programming
compared to the average Swiss population. A dismal
fraction of 0.2% of these teachers had any
programming experience. Clearly, the majority of
pre-service teachers are not planning to become
teachers because of computation but rather in spite of
it.
Hug has started to explore Computational Music
Thinking (CMT) (Hug et al., 2017) as a notion
combining programming with music through a small
set of manageable constructs called Computational
Music Thinking Patterns that are accessible and
engaging. By pattern we mean design patterns (Lea,
1994) that are reusable forms of a solution common
to design problems. This paper describes five patterns
common to computation and music.
Repenning, A., Zurmühle, J., Lamprou, A. and Hug, D.
Computational Music Thinking Patterns: Connecting Music Education with Computer Science Education through the Design of Interactive Notations.
DOI: 10.5220/0009817506410652
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2020), pages 641-652
ISBN: 978-989-758-417-6
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
641

The idea to teach CT as an interdisciplinary
connection between Computer Science (CS) and
other subjects is not new (Lee, Martin, & Apone,
2014) Examples include the connection of CS with
Math (e.g., (Papert, 1980)), language (e.g. through
storytelling (Werner, Denner, Bliesner, & Rex,
2009)), craft (e.g., (Kafai et al., 2014)), Sports (e.g.,
(Floyd & Sorbara, 2019) and art (e.g., (Knochel &
Patton, 2015). Most of our own experience is rooted
in game design (e.g., (Repenning, 2014)) and
simulation building (e.g., (Basawapatna, Repenning,
Koh, & Savignano, 2014)). Game Design has been
well received by in-service teachers (Repenning et
al., 2015) but Repenning found that while most pre-
service school teachers enjoy game design activities
some are surprisingly skeptical (Repenning et al.,
2019) towards the use of game design activities to
teach CT. One concern is mostly of a pragmatic
nature. In spite of game design being immensely
popular with K-12 students (Alexander, 2014;
Werner et al., 2009; Kafai, 2006), it is not a subject
that elementary school teachers are expected to teach.
However, most elementary school teachers do need to
teach subjects such as Music. Combining CT with
Music into CMT is highly compelling to teachers as
it suggests hitting two birds with one stone. More
importantly, however, computation and music share
important conceptual roots that could significantly
increase students’ fundamental understanding of
systems and notations.
We conceptualize CMT as a highly synergistic
framework supporting students’ interlinked
understanding of CT and music through the
exploration of a collection of CMT constructs that we
call Computational Music Thinking Patterns. These
patterns, in turn, are extensions of the repertoire of
Computational Thinking Patterns (Basawapatna,
2011) originally developed to find universal patterns
describing phenomenalistic object interactions
(Michotte, 1963) common to game design and
simulation building. Some practical definitions of CT
break it down into low level programming concepts
such as sequences, conditionals, and iteration
(Brennan & Resnick, 2012) and even try to assess CT
performance through instruments counting the
presence of these concepts in code (Moreno-León,
Robles, & Román-González, 2015) Frameworks
based on patterns, in contrast, operate at a higher level
by conceptualizing combinations of programming
elements that can add up to a higher goal.
Learning activities are centered around
Computational Music Thinking Patterns make
students design interactive notations. The key idea of
a notation is the affordance to separate representation
and interpretation. Figure 1 shows a music box
containing a cylinder representing a specific song.
This cylinder can be exchanged with a different one
to play a different melody with the same
interpretation mechanism. To use, and more
importantly to design, these kinds of notations
provides a deep understanding of powerful ideas that
are common between music and programming.
Designing interactive notations provides
affordances to make learning activities even more
engaging. Students not only design static
representations of existing songs but can interact with
an ongoing process of music playing through mouse
or keys input changing the notation in real time.
A Computational Music Thinking pilot course
was conducted in the Fall of 2019 with 9 pre-service
elementary teachers. The course covered five
Computational Music Thinking Patterns:
Interpretation, Interaction, Chance, Hierarchy and
Rewrite Rules. In the first part of the 14-week course
the pre-service teachers learned to implement these
patterns. In the second part they started to work in
pairs to develop Zones of Proximal Flow tutorials
(Basawapatna, Repenning, & Savignano, 2019) to
teach K-12 students some of these patterns. This
paper outlines some related work, describes the
patterns and presents course evaluation results.
2 RELATED WORK
There are large bodies of literature in both Music
education with digital technologies (Ruthmann,
Heines, Greher, Laidler, & Saulters, 2010; Cano,
Dittmar, Abeßer, Kehling, & Grollmisch, 2018; King
& Himonides, 2016) and Computational Thinking
(Wing, 2006; Grover & Pea, 2013) education. The
combination of music and computation based on
programming, however, has received much less
attention particularly at the elementary school level.
Discussion of related work here is limited to the
elementary school level.
2.1 Combining CT with Music
The idea of connecting Computational Thinking with
Music has been explored from multiple angles.
Algorithmic composition, for instance, explores the
composition based on formal methods and
computation. Edwards describes computational
notations going back to the “Musikalisches
Würfelspiel” (“musical dice game”, attributed,
among others, to Mozart) based on chance (Edwards,
2011). Aleatoric composition was explored in
CSME 2020 - Special Session on Computer Supported Music Education
642

particular in the 20th century, both driven by the
artistic questioning of musical traditions and the
advent of computers, and the related use of
computation as means of composing and generating
music (Schulze, 2000). The core mechanism is for
computers to play sounds based on rules, which are
based on musical principles. Sequences of sounds, for
instance melodies, are represented as functions
playing a series of (pitched, tonal) sounds. Music can
be composed by composing functions, i.e., functions
calling other functions. This composition process can
be done virtually, that is by writing code representing
functions calling other functions, or tangibly, by
arranging physical objects into compositions. These
objects, in turn, may be passive such as traditional
LEGO bricks representing a music notation (Baratè,
Ludovico, & Malchiodi, 2017) or active such as the
tangible music blocks in the Algo.Rythm system
based on Arduino circuit boards (Peng, 2012).
The use of Computational thinking has also been
proposed specifically in music education (Ruthmann
et al., 2010; Greher & Heines, 2014). The main
motivation and goal also here are to support STEAM
(STEM education with Arts added: Science,
Technology, Engineering, Art, Math) education and
promoting related digital skills in the arts, but with a
stronger focus on musical learning. Greher & Heines
for instance propose Scratch for musical
programming. Their pedagogy makes use of
preparatory exercises, which employ visual symbols
drawn on paper representing musical actions, that
then are executed by children with musical
instruments or objects. When programming musical
code with Scratch, however, they have to rely on
abstract representations of musical processes.
This work also builds on previous work by some
of the authors exploring approaches to CMT with
secondary school children in a workshop setting (Hug
et al., 2017). This work showed that children were
highly motivated to use visual programming
environments to create music and attitudes both
towards music and CS improved.
2.2 Approaches to Programming
With a target audience of elementary school students,
a key challenge in supporting algorithmic
composition is the difficulty of dealing with text-
based programming languages and abstractions of
musical processes. For instance, SonicPI (Sam
Aaron, 2016; Samuel Aaron, Blackwell, & Burnard,
2016) is a powerful life coding environment suitable
even for upper primary school classes but relies on a
specific set of commands aimed exclusively at
providing musical functions. Blocks-based
programming languages such as AgentSheets, Alice,
Scratch and AgentCubes help to overcome syntactic
challenges (Alexander Repenning, 2017). Many
blocks-based programming languages, including
AgentCubes and Scratch, feature music functions
such as MIDI sound tools to trigger sounds. Other
languages such as the Blockly-based tool created by
Baratè et al. (Baratè, Formica, Ludovico, &
Malchiodi, 2017) feature functions to compose
melodies. The goal of this system is to facilitate re-
coding (Nake & Grabowski, 2017) activities where
students are provided a given song which then they
have to re-code by using composing functions
including loops. Another approach is presented by
EarSketch (Freeman & Magerko, 2016; Xambó,
Freeman, Magerko, & Shah, 2016) which presents a
“Computational Music Remixing” environment
which combines the familiar multitrack environment
for playback of audio with coding facilities that can
be used for rule-based playback.
2.3 Interactive Notation Design as
Emergent Principle
Our approach to CMT integrates the creation of
symbols representing musical actions of varying
complexity with the actual coding process. Through
the use of the programming environment
AgentCubes, which employs a blocks-based coding
environment, but also supports the creation of visual
sprites that become rule-based agents, it is possible to
combine the best of two worlds, which turned out to
be a key benefit of the system during the course. We
call the emerging underlying principle “Interactive
Notation Design” (IND) and use it as the main
activity that students engage in to become
Computational Music Thinkers. The focus on
notation is similar to the LEGO Music Notation
project (Baratè, Formica, et al., 2017). Unlike with
the LEGO Music Notional project, however,
notations are not provided for the students. Instead,
students are expected to become Computational
Music Thinkers by experimenting with their own
interactive notations. These notations could be one,
two or even three dimensional. Students design
notations by drawing their own symbols and define
the meaning of their notation through programming.
Moreover, students design interactive notations
including the affordance to interact with the notation
at run time. That is, while the music is playing users
could change the notation by editing, that is moving
and changing symbols, in real time. Students can also
program interactive symbols that are symbols
Computational Music Thinking Patterns: Connecting Music Education with Computer Science Education through the Design of Interactive
Notations
643
reacting to user input such as key events from
keyboards or external input devices such as Makey
Makeys.
3 INTERVENTION: DESIGNING
INTERACTIVE NOTATIONS
Nine pre-service elementary school teachers studying
at the School of Education participated in an elective
course where they were taught five different
Computational Music Thinking Patterns. These pre-
service teachers are, technically speaking, bachelor’s
degree students. Henceforth, and for the sake of
brevity the paper refers to them simply as students.
The course itself consisted of 14 lessons. Each lesson
briefly introduced each Computational Music
Thinking Patterns with the necessary theory and
historical background from music and computation.
The connection between thinking in music and CT
gives students new insights into both topics. They
learn that music is also based on rules that can be
made explicit. Scales and chords are built according
to certain rules, rhythms function according to
hierarchies of emphases, pieces of music are divided
into hierarchical parts. On the other hand,
programmed agents can trigger and influence musical
actions. Melodies or rhythms can be programmed, or
random sound sequences can be invented. The
students learn and experience playfully connections
between music and programming.
The students develop musical games for children
based on the five patterns. This enables the children
to learn about music and about programming by
trying and playing.
In a second step, students explore the pedagogy of
CMT, i.e., the experience of how to teach CMT, by
writing and evaluating ZPF tutorials (Zone of
Proximal Flow Tutorials (Basawapatna et al., 2019).
To build successful ZPF tutorials students must think
about how to provide tiered instructions supporting
differentiation. These ZPF tutorials enable children to
build and program their own worlds in AgentCubes.
The students learn in terms of content about the
relationship between music and computational
thinking. They learn and know rules for programming
music. Methodically, students learn forms of project-
like learning, explorative learning and the concept of
Productive Failure (Kapur, 2008). They mainly work
independently in small project groups and are
supported by the lecturers only as needed.
Participants start with simple programming of
agents in AgentCubes using the first CMT pattern
“interpretation”. They distinguish between a form of
notation (representation) and rules of execution
(interpretation). For many students it was new that
music can be represented not only in classical
notation, but also as pins on a cylinder (music box),
as bars in a sequencer program or as holes in a paper
strip. For programming, a distinction had to be made
between the note and the player. In a sequence of
symbols, the note represents a sequence of sounds.
The player interprets the symbols according to certain
rules and moves through the sequence. First,
individual sounds were assigned to the symbols, then
chords or changing sounds. Even through these
simple programming, very different musical works
became possible.
In the following lessons the students were
introduced to all five CMT patterns and developed
their own projects. The projects were presented in the
group and received feedback for further work. The
sequence and contents of the lessons are shown in
Table 1 below.
Table 1: Computational Music Thinking Course Outline.
Week Theory Practice
1 Introduction:
Music and Computational
Thinking
Recreation of a simple melody
with five notes.
Creation of different kinds of
agents in AgentCubes
2 CMT Pattern 1: Interpretation
Creation of Symbols and Rules of
interpretation
Creation and programming an
own melody
3 CMT Pattern 1:
Interpretation cont.
Playtime
Programming different
Possibilities (Melodies and Chords)
4 CMT Pattern 2: Interaction
Musical elements and parameters
Musical form
Small interaction Projects: Using
keyboard commands and
interfaces (Makey Makey) to
influence the music live.
5 CMT Pattern 3: Chance Programming probabilities
(%change) Music pieces became
unpredictable and therefore more
interesting.
6 CMT Pattern 4: Hierarchy
Pentatonic Sound Systems
The pieces of music followed a
certain form (Rondo) A B A C A
D. The individual parts A B C etc.
then control a certain sequence of
sounds.
7 CMT Pattern 5: Rewriting rules Programming of larger pieces like
a blues or song accompaniment
with chord progressions or more
complex pieces of music
Start with Pitch Project
8 Layers in music: Melody,
Harmony, Rhythm, Bass
Presentation Pitch Project
Peer Review
CSME 2020 - Special Session on Computer Supported Music Education
644
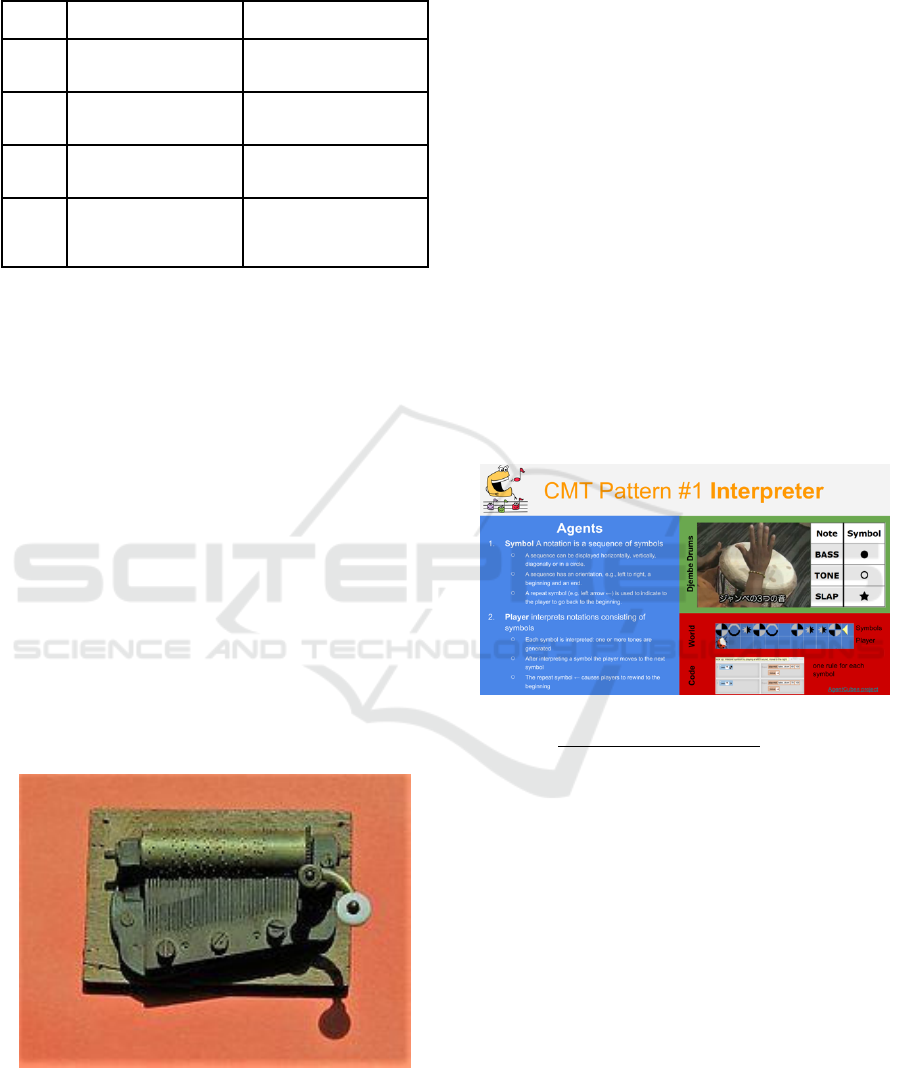
Table 1: Computational Music Thinking Course Outline
(cont.).
Week Theory Practice
9 Hierarchy in rhythm (Measure,
metre, rhythm)
Presentation of Project sketches
Decision for final projects
10-12 Introduction: ZPF Tutorials
Evaluation: Interviews
Work on own Project
Presentation and feedback
13 Presentation Project
Peer Review
14 Evaluation: Questionnaire
Introduction: Other Programs
for Music
All learning activities are based on the design of
interactive notation and evolve from simple rule
replication (procedural programming) to the
development of new rules (declarative
programming).
3.1 Five Computational Music
Thinking Patterns
Below are the detailed descriptions of five
Computational Music Thinking Patterns used in the
course. No claims are made that this list is exhaustive.
3.1.1 Pattern #1: Interpreter
The interpreter pattern is the main Computational
Music Thinking Pattern. It is very powerful in itself
but also serves as the basis for most of the other
Computational Music Thinking Patterns. To that end,
it makes sense in this paper, but also when teaching
students, to spend more time introducing this pattern.
Figure 1: A music box (example from around 1900)
combines notation with interpretation.
The interpreter is used to represent a basic melody,
rhythm or program as a sequence of symbols which
can be executed. In music, the interpreter pattern can
be viewed as an abstraction of a music box (Figure 1).
Music boxes, in turn, are a form of automation. A
music box is a musical instrument producing musical
notes by sensing the presence of pins on a revolving
cylinder or disk. The presence of a pin will trigger a
sound by putting tiny metal rods, which are tuned as
tones of a scale, into vibration. These tuned rods are
arranged in a comb. Abstractly, the pins on a cylinder
serve as notation that gets interpreted by the music
box. Automation and abstraction are key components
of Computational Thinking (Wing, 2006). In
computing, computer programs are sequences of
instructions that are interpreted. Again, there is the
idea of a notation that gets interpreted. Independent
of their manifestations–either as physical
manifestations such as cylinders, disks, and punch
cards found in 19th century music boxes, or as virtual
manifestations such as text based and blocks-based
programming languages found in 21th century
programming languages–the fundamental idea of
interpretation is the same in music and computing.
Figure 2: Computational Music Thinking Pattern #1.
Interpreter: https://go.fhnw.ch/QCQzJK.
To build an interpreter a student first designs a
number of symbols by drawing 2D or 3D shapes (see
World in Figure 2) representing individual sounds.
For instance, students would design three symbols to
represent the three basic sounds of a djembe drum:
bass, tone, and slap. Then, students arrange these
symbols into one, two or even three-dimensional
notations. For instance, they could arrange the
djembe sound symbols into a one-dimensional left to
right sequence representing a rhythm or even a basic
melody. Finally, students program a so-called player
agent (Repenning, Smith, Owen, & Repenning, 2012)
by writing simple rules to interpret the melody like
this:
IF I see the bass symbol THEN I play the
bass sound, and I move to the right.
A rule is needed for each symbol and one more rule
is needed when there is no symbol. When the program
Computational Music Thinking Patterns: Connecting Music Education with Computer Science Education through the Design of Interactive
Notations
645
is run the player agent will play the melody and move
from left to right. Students can change the melody by
rearranging symbols even while the music is playing.
Figures 2-6 illustrate the CMT patterns. They are
meant to work as slides and not as paper Figures.
Each pattern follows a simple color-coding scheme:
blue describes agents with their interactions; green
describes real world analogies; red describes
snapshots of the programming world and code. Some
patterns do not feature all these parts. Some of their
content, particularly the code, requires readers to
zoom. We present the first, and most important
pattern in two column mode for readability but will
have to keep the remaining ones in one column mode
due to paper size limitations. Alternatively, links
below each pattern Figure provide full access to slides
including the project links and the full source code.
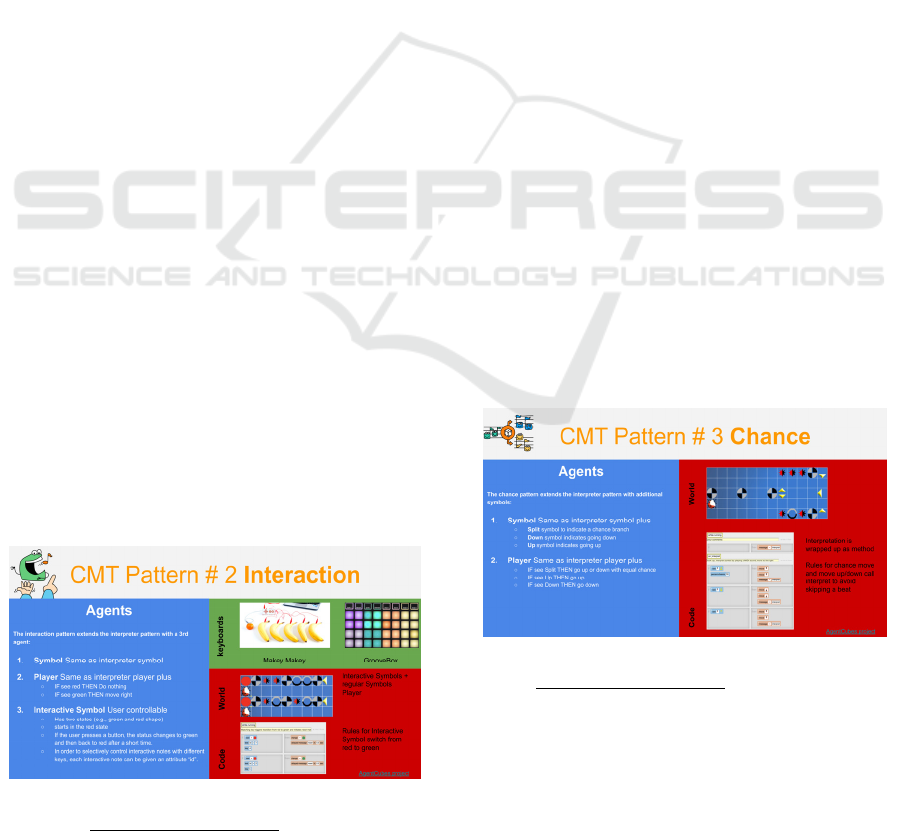
3.1.2 Pattern #2: Interaction
Interaction (Figure 3) enables users to actively
engage with the music making process. That is, the
computer does not just autonomously play previously
composed songs from beginning to end but reacts to
input from the user. This kind of interaction can
unfold at different levels. For instance, at a low level,
a user could press one key causing the computer to
produce one sound. To make this more entertaining
computer keyboards can be replaced with Makey
Makeys (Graves, 2014) which could be connected to
various pieces of fruit in order to create something
called the Banana Piano. Using drum sounds instead
of piano sounds could turn a Banana Piano into a
drum kit where the touch of each fruit plays a
different drum kit sound. However, at a higher level
of abstraction, one would want to establish a more
sophisticated mapping between input and output. One
input should result in many outputs. A groovebox, for
instance, is an electronic or digital musical instrument
featuring pads (large keys optimized for music
applications) that can trigger entire sequences of
sounds.
Figure 3: Computational Music Thinking Pattern #2.
Interaction: https://go.fhnw.ch/2sbSd3.
The interaction pattern, extending the interpreter
pattern, features an interactive symbol reacting to user
input. For instance, this symbol could represent a
traffic light, controlled by the user, toggling between
two states: red and green. The player agent would be
blocked when seeing a red traffic light. It would have
to wait for the user to press a key to make the light
turn green. Traffic light symbols can be put
anywhere, typically at the beginning of a sequence,
but also anywhere in the midst of a sequence to
control music. Notations, extended by interactive
symbols such as the traffic light, turn into powerful
interactive notations enabling users to control music.
3.1.3 Pattern #3: Chance
Chance (Figure 4) in computational music production
often is seen as means to provide elements of surprise
and stimulate creativity and thus plays an important
role in computational music thinking both at
composition time as well as performance time in
particular in post-war “aleatoric” music (Boehmer,
1988; Schulze, 2000). Chance is relatively simple to
compute but harder to employ meaningfully in music.
For instance, a sequence of MIDI instruments playing
at random pitches is not likely to result in great
sounding melodies. Early uses of chance in music
include random dice compositions attributed, for
instance to Mozart (Cope, 1989) mapping the sum of
two dice to a number, between 2 and 12, used as an
index to play one out of 11 different sequences of
sounds. A simple extension to our notation is the
introduction of random split symbol-making the
player moves up or down, with equal chance, to a
different sequence of symbols. Splits could be further
combined into a binary tree of random choices.
Figure 4: Computational Music Thinking Pattern #3.
Chance: https://go.fhnw.ch/eu7o1y.
3.1.4 Pattern #4: Hierarchy
Hierarchies (Figure 5) are fundamental concepts in a
wide variety of fields not only music and CS. A
hierarchy is a representation differentiating at least
CSME 2020 - Special Session on Computer Supported Music Education
646

two different levels. A higher level may contain, or
control, a lower level. In music, a hierarchical
notation would allow a higher level of representation
to control a lower level. An analogy reaching back to
musical boxes (Figure 1) would expand on the notion
of triggering a sound. A master music box would
control a number of subservient music boxes.
Metaphorically speaking, instead of a pin on the
musical cylinder triggering a single sound it would
trigger one of these subservient music boxes. These
subservient music boxes, in turn, would play an entire
melody. Hierarchies can be nested. That is, the lower
level could serve as the higher level to an even lower
level and so on.
Hierarchical control distinguishes two important
cases: synchronous and asynchronous control.
Synchronous control of music boxes suggest that the
master box triggers a subservient music box and then
awaits the completion of the song. Only then does it
continue moving its cylinder. Asynchronous control,
in contrast, does not wait for the completion of the
song of the subservient music box. To reflect this
interaction our notation must provide at least two
levels of interpretation. A higher-level player
interprets high level symbols. Instead of just playing
a sound this interpretation of the higher level activates
a low-level player. In the synchronous case the high-
level player and the low-level player need to
implement some form of handshaking so that the
high-level player can wait for the low-level player to
finish a loop. In the asynchronous case no
handshaking is needed. The high-level player simply
continues. The hierarchy pattern can be used, for
instance, to explore the musical notion called the
rondo. A rondo is a musical form combining
recurring sequences of music serving as main themes,
sometimes called refrains, with contrasting themes,
sometimes called episodes. These various themes are
represented as character symbols, e.g., A and B. A
rondo is then expressed as sequences of these
symbols. Classical rondos include ABA, ABBA,
ABACA, or ABACABA. Figure 5 outlines some
basic rondos. These rondos are played synchronously.
3.1.5 Pattern #5: Rewrite-rules
Graphical rewrite-rules (Figure 6) are declarative
music notations. In blues, chord rewrite-rules, have
been used to create chord progressions producing
boogie woogie. Patterns 1 to 4 define music
procedurally. That is, procedural notations include an
explicit notion of control flow suggesting where the
computation currently is, what to do next and, most
importantly,
how to do it. The player agent can be
Figure 5. Computational Music Thinking Pattern #4.
Hierarchy: https://go.fhnw.ch/6EDCPo.
viewed as the state of the computation indicating how
far along one is to interpret a notation. Through the
process of interpretation, the player explicitly maps
the symbols to instructions such as playing a certain
sound. Declarative programming, captured by pattern
5, in contrast, describes desired outcomes without
specifying how to get there by capturing logic as
IF/THEN rules. In music a graphical rewrite rule
establishes a mapping between sequences of sounds
that have been played with sequences of sounds that
will be played. In other words, a rule describes
IF I heard sound 1, followed by sound
2, followed by sound …
THEN I will play sound a, followed by
sound b, followed by sound c…
Figure 6 shows two rules. The blocks on the left-hand
side of the red arrow denote sounds played in the past.
Blocks on the right-hand side of the arrow denote
sounds that will be played in the future. Rules are
tested from top to bottom. If there is a rule that
matches, that is it’s
IF sequence of sounds matches exactly
the sequence of sounds just played
THEN the then sequence of sounds will
be played.
Figure 6: Computational Music Thinking Pattern #5.
Rewrite-Rules: https://go.fhnw.ch/Evwjtl.
Both, the user, by pressing keys, and the system, by
executing rules, can produce new sounds. User
Computational Music Thinking Patterns: Connecting Music Education with Computer Science Education through the Design of Interactive
Notations
647

suggested sounds have a higher priority than system
suggested sounds. Users and the system react to each
other similar to musicians participating in a jam
session.
3.1.6 Implementing Patterns
Computational Music Thinking Patterns are a
growing collection of combinable constructs that can
be implemented in AgentCubes but also any other
Computational Thinking Tool (Repenning,
Basawapatna, & Escherle, 2016; Repenning,
Basawapatna, & Escherle, 2017) supporting sound
output, mouse and keyboard input. Combinations of
patterns can produce hierarchies that feature chance,
chance controlled by interaction, or rewrite-rules
including chance. Some patterns are simpler to
implement than others. The interpreter, chance and
interaction patterns could be implemented by all
students with very little code. The handshaking of the
hierarchy pattern proved too complex for students
with no programming experience. Finally, the
rewrite-rule pattern requires complex programming
implementing an entire rule-based programming
language. Activities based on rewrite-rules were
limited to students experimenting with their own
rules and not writing their own rule interpreter. This
was because the implementation of a rule interpreter
system requires advanced programming
understanding, e.g., the understanding of recursion,
which our students did not have.
4 METHODS
The paper is based on a variety of data collected
during the 2019 fall semester: Survey data, interviews
and course evaluation data. The following sections
describe in detail the methods used for the study.
Students’ participation in the study was voluntary.
4.1 Procedure
The course comprised 14 sessions. Survey data were
collected from the participants during the first and last
sessions. All surveys were conducted on a computer
in the classroom. For each course the first (pre)
electronic survey was completed by participants in
the beginning of the first introductory lesson, which
represents the baseline pre-data of this study. The
same participants completed a second (post)
electronic survey at the end of the last session (after
14 weeks), representing the post-data. Interviews
were conducted with the students in the same final
session. Finally, a course evaluation (survey data)
was run by the university for all courses including this
one.
4.2 Participants
The sample comprises a total of nine pre-service
primary-level teacher students, six male and three
females. The students were in their fifth semester and
all but two had previously taken the obligatory CS
module consisting of two courses one in the subject
of CS and one in the CS didactics.
4.3 Measures
The pre- and post-surveys consisted of 22 identical
items and contained three groups of questions (see
Table 2): attitude (abb. Att.), skills, and aptitude (abb.
Apt.). A set of twelve 4-point Likert- scale items
(1=strongly disagree, 4=strongly agree) consisted of
questions with regards to the participants’ attitudes
and contained three subgroups: attitude towards
music (five items (Q1, Q2, Q7, Q11, Q17), e.g.
“Learning music is boring for me”), attitude towards
CS (four items (Q3, Q8, Q12, Q21), e.g. “I think that
CS is difficult for me to learn”) and attitude towards
the combination of CS and music (three items (Q4,
Q5, Q6), e.g. “I believe that the combination of CS
and music helps to better understand music”). A
second set of seven 4-point Likert- scale items
(1=strongly disagree, 4=strongly agree) consisted of
questions with regard to the participants’ skills and
consisted also of three subgroups: CS skills (two
items (Q16, Q19), e.g. “I can program”), music skills
(four items (Q14, Q15, Q18, Q20), e.g. “I play an
instrument”) and skills combining music and CS (one
item (Q13): “I make music with the computer”).
Finally, a set of two 4-point Likert- scale items
(1=strongly disagree, 4=strongly agree) consisted of
questions with regards to the participant’s self-
reported aptitude. One with regards to music (Q9): “I
consider myself unmusical” and one with regards to
CS (Q10): “I don't consider myself a computer whiz”.
The survey also contained one open-ended question:
What do you understand by the term "Computational
Music Thinking"?
The interviews consisted of eight open ended
questions that complimented the survey and focused
on motivational aspects.
During the implementation of the course, all
courses at the School of Education were also
evaluated. This evaluation was of a general nature and
mostly targeted the quality of the course and the
teaching. It asked about the design of the course, the
CSME 2020 - Special Session on Computer Supported Music Education
648
pace, difficulty and scope of the material, the quality
of the lecturers and the focus on the students. The
survey consisted of 24 5-point Likert-scale items
grouped in five groups: course (nine items), speed,
difficulty and amount of material (three items),
lectures (six items), students (five items) and overall
evaluation (one item). Because we did not conduct
this evaluation, we do not have access to the data but
only to the results, some of which we present here.
5 RESULTS
At the beginning of our course the participants
indicated on a Likert-Scale from 1 to 4 that music is
very important for them (Q1: M =3.89) and that both
music and CS are quite important for their job as
teachers (Q2, Q3, M= 3.33) while the combination of
the two seems to be less important (Q4, M = 2.78).
The students had a positive attitude towards the
learning benefits of the combination of music and CS.
They seem to believe however, that the combination
helps to understand music more (Q6, M= 3.22) than
it helps to understand CS (Q5, M= 3). They further
believed that CS (Q8, M=2.67) is more difficult to
learn than music is (Q7, M=2). They do not think they
are non-musical (Q9, M=1.56) but they think on
average that they do not have computer affinity (Q10,
M= 2.44). They find learning music (Q11, M=1.89)
less boring than learning CS (Q12, M=2.22). With
regards to music skills, our students indicated good
skills with regards to playing an instrument (Q14,
M=3.22), but they indicate less than average skills
with regards to understanding music (Q18, M=2.33)
and more than average with music theory knowledge
and good singing (Q20, Q15 M=2.78). Furthermore,
even though they indicated an average fascination
with computers and technology (Q21, M=2.56), their
computer gaming skills are average (Q16, M=2.33)
and their programming skills are low (Q19, M =
1.78). Finally, they do not make music with the
computer (Q13, M=1.89).
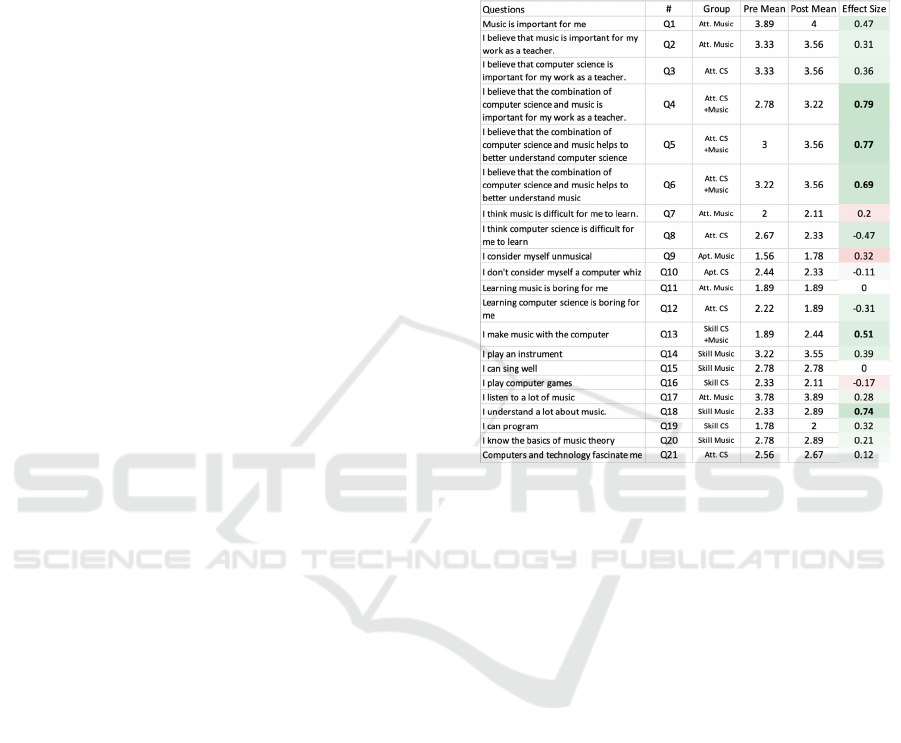
5.1 Pre-post and Effect Sizes
The table below (Table 2) shows the means and the
effect sizes from the pre-post responses. Positive
effects (positive or negative effect sizes suggesting
more desirable, or less undesirable effects) are
marked green. Negative effects (less desirable, or
more undesirable) are marked red. Color saturation is
proportional to effect size (Cohen's d is small: [0.2,
0.5], medium [0.5, 0.8], and large ≥ 0.8). Effects that
are medium and large (|d| ≥ 0.49), are marked bold.
With the exception of Q7, Q9 and Q16 all other post-
means indicate positive shifts after the course.
Table 2: Pre- Post means and effect sizes. Small: [0.2, 0.5),
medium: [0.5, 0.8), large: > 0.8. Desirable effects in Green,
undesirable effects in Red.
5.2 Course Evaluation
As the evaluation was conducted by the school, we
have no access to the raw data but only to the results,
which paint a very positive picture for the course.
Overall our students assessed the course as very good
(M= 4.5, scale 1 to 5). They indicated that the course
provided good practical references for their future
profession (M=3.9) while most importantly they
found the course very important for their professional
practice (M=4.2). The students also felt not only that
they gained a very good insight but that the course
raised their interest in the topic (both M= 4.3).
6 DISCUSSION
Overall, the strongest positive change based on effect
size was in attitudes towards the combination of
music and computer science (Q4, Q5, Q6). The
combination of music and computer science for the
importance for the work as a teacher in general is
rated higher by the students at the end of the course
than at the beginning with an effect size of 0.79. We
assume that the cooperation of two disciplinary
experts had a positive effect on this assessment by the
Computational Music Thinking Patterns: Connecting Music Education with Computer Science Education through the Design of Interactive
Notations
649

students and that the course was successful in
showing how the interdisciplinary combination in the
form of computational music thinking can contribute
to learning in general. This also resonates with the
effect that CS is considered somewhat less difficult to
learn in post. The integration also supported a better
understanding of computer science (effect size 0.77)
and music (effect size 0.69) individually, which
indicates that the interdisciplinary approach also
supports disciplinary development.
The effect size of 0.51 regarding making music
with the computer (Q13), is interesting, as it suggests
that the course supported the notion that
programming can be used to create music, and helped
the participants to discover new ways of making
music with the computer beyond using dedicated
musical software. This is particularly encouraging, as
for most of the participants making music with
programming and without instruments or singing was
something new and unfamiliar before they started the
course.
Looking at the skill related questions, the effect
on programming skills (Q19) was small. In context of
the higher effect on musical competences, this
suggests that the intervention can profit from
previous knowledge of the participants, a finding also
shown in earlier related work (Hug et al., 2017). Out
of the 9 participants 2 had no programming
experience. Initially our programming course
(Repenning et al., 2019) was stated as a requirement.
However, the two participants with no previous
programming experience did not have a problem
picking up programming skills through CMT.
The results of a formal course evaluation showed
high scores in the assessment of the course design (a
good learning atmosphere and active participation)
and in promoting interest in the topic.
At the end of the course an interview was made
with the participants. In this interview the students
indicated high interest in applying the topic in class
and that they could imagine ways to integrate CMT
in their teaching practice, without having to give up
other musical activities they enjoy and feel competent
in executing with the children at school. But also,
some challenges could be identified. Not all schools
have a sufficient number of computers, up-to-date
software or a stable and fast network for several
children to work on projects, and activities can be
relatively time consuming, which requires careful
scaffolding. This concern regarding the application in
the classroom was also reflected in the course
evaluation questionnaire, with a large dispersion of
the rating results in this regard. However, regarding
the specific activities presented in the course, not only
did some students express their confidence in being
able to bring CMT to the classroom, some even
reported positive results from already implementing
CMT pilots in their classrooms.
7 CONCLUSIONS
The combination of music and computational
thinking by two experts in a course for primary
teachers enabled students to learn both subjects
individually and in an interdisciplinary way. Five
Computational Music Thinking Patterns–
interpretation, interactivity, chance, hierarchy and
rewrite-rules–represent high level constructs
integrating fundamental concepts of computation and
music. Students were able to design interactive
notations by using AgentCubes to create their own
worlds, design and animate agents and create and
design sounds as melodies, chords and rhythms. Data
collected from the course suggest significant positive
effects on teachers' attitudes towards believing that
Computational Music Thinking is important to their
teaching, that Computational Music Thinking helps
the comprehension of computer science and that
Computational Music Thinking helps the
comprehension of music.
The mixture of instruction, playtime and project
development with regular peer feedback enabled the
students to develop individual learning paths and
unconventional projects that they could implement
for or with children in school. The participants
developed new perspectives on informatics and
musical thinking and used the computer as a musical
instrument with codes and rules.
Future work will further analyze qualitative data
gathered in the interviews to gain a better
understanding of the attitudes and perspectives in
terms of applying Computational Music Thinking,
designing interactive notations and gaining teaching
practice. In addition, the final projects of the students
are available, which have not yet been systematically
evaluated. All projects were designed and worked in
AgentCubes, different Computational Music
Thinking patterns were applied, and musical topics
were worked on. An important aspect is to better
understand the actual musical concepts embodied in
the participant’s creation in order to integrate it with
specific musical learning goals.
Finally, future work will address the theory-based
further development of the Computational Music
Thinking patterns and the principle and application
Interactive Notation Design as means to integrate
computational thinking and musical thinking. A
CSME 2020 - Special Session on Computer Supported Music Education
650

particular focus lies on enabling the transfer into
teaching practice and applicability in classroom
situations.
Therefore, a second edition of the course is
planned for Fall 2020 and will offer the opportunity
to adapt the course design and fine tune the data
gathering process. Also, collaborations with schools
for pilot courses with children are being prepared in
order to further develop the transfer from teacher
education to classroom application.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This project has been funded by the Hochschullehre
2025 FHNW Lehrfond. The use of AgentCubes was
funded by the Hasler Foundation.
REFERENCES
Aaron, S. (2016). Sonic Pi–performance in education,
technology and art. International Journal of
Performance Arts and Digital Media, 12(2), 171-178.
Aaron, S., Blackwell, A. F., & Burnard, P. (2016). The
development of Sonic Pi and its use in educational
partnerships: Co-creating pedagogies for learning
computer programming. Journal of Music, Technology
and Education, 9(1), 75-94.
Baratè, A., Formica, A., Ludovico, L. A., & Malchiodi, D.
(2017, April). Fostering computational thinking in
secondary school through music-an educational
experience based on google blockly. In International
Conference on Computer Supported Education (Vol. 2,
pp. 117-124). SCITEPRESS.
Baratè, A., Ludovico, L. A., & Malchiodi, D. (2017).
Fostering computational thinking in primary school
through a LEGO®-based music notation. Procedia
computer science, 112, 1334-1344.
Basawapatna, A., Koh, K. H., Repenning, A., Webb, D.C.,
& Marshall, K. S. (2011, March). Recognizing
Computational Thinking Patterns. In Proceedings of
the 42nd ACM technical symposium on Computer
science education (pp. 245-250).
Basawapatna, A., Repenning, A., Koh, K. H., & Savignano,
M. (2014, March). The Consume-Create Spectrum:
Balancing Convenience and Computational Thinking
in STEM Learning. In Proceedings of the 45th acm
technical symposium on computer science education
(pp. 659-664).
Basawapatna, A., Repenning, A., & Savignano, M. (2019,
February). The Zones of Proximal Flow Tutorial:
Designing Computational Thinking Cliffhangers. In
Proceedings of the 50th ACM Technical Symposium on
Computer Science Education (pp. 428-434).
Boehmer, K. (1988). Zur Theorie der offenen Form in der
neuen Musik (2. Auflage ed.). Darmstadt: Tonos.
Brennan, K., & Resnick, M. (2012, April). New
frameworks for studying and assessing the
development of computational thinking. In
Proceedings of the 2012 annual meeting of the
American educational research association,
Vancouver, Canada (Vol. 1, p. 25).
Cano, E., Dittmar, C., Abeßer, J., Kehling, C., &
Grollmisch, S. (2018). Music Technology and
Education. In R. Bader (Ed.), Springer Handbook of
Systematic Musicology (pp. 855-871). Berlin,
Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Cope, D. (1989). Experiments in musical intelligence
(EMI): Non‐linear linguistic‐based composition.
Journal of New Music Research, 18(1-2), 117-139.
Edwards, M. (2011). Algorithmic composition:
computational thinking in music. Communications of
the ACM, 54(7), 58.
Floyd, S. P., & Sorbara, L. (2019, February). Sports
Analytics as a Context for Computational Thinking in
K-12 Education. In Proceedings of the 50th ACM
Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education
(pp. 1282-1282).
Freeman, J., & Magerko, B. (2016). Iterative composition,
coding and pedagogy: A case study in live coding with
EarSketch. Journal of Music, Technology and
Education, 9(1), 57-74.
Gander, W., Petit, A., Berry, G., Demo, B., Vahrenhold, J.,
McGettrick, & Meyer, B. (2013). Informatics
education: Europe cannot afford to miss the boat.
Report of the joint Informatics Europe & ACM Europe
Working Group on Informatics Education.
Graves, C. (2014). Teen experts guide makerspace
makeover.
Knowledge Quest, 42(4), 8.
Greher, G. R., & Heines, J. M. (2014). Computational
thinking in sound: teaching the art and science of music
and technology. New York: Oxford University Press.
Grover, S., & Pea, R. (2013). Computational Thinking in
K–12 A Review of the State of the Field. Educational
Researcher, 42(1), 38-43.
Hug, D., Petralito, S., Hauser, S., Lamprou, A., Repenning,
A., Bertschinger, D., … & Cslovjecsek, M. (2017,
August). Exploring Computational Music Thinking in
a Workshop Setting with Primary and Secondary
School Children. In Proceedings of the 12th
International Audio Mostly Conference on Augmented
and Participatory Sound and Music Experiences (pp. 1-
8).
Kafai, Y. (2006). Playing and Making Games for Learning.
Games and Culture, 1(1), 36-40.
Kafai, Y. B., Lee, E., Searle, K., Fields, D., Kaplan, E., &
Lui, D. (2014). A crafts-oriented approach to
computing in high school: Introducing computational
concepts, practices, and perspectives with electronic
textiles. ACM Transactions on Computing Education
(TOCE), 14(1), 1-20.
Kapur, M. (2008). Productive failure. Cognition and
instruction, 26(3), 379-424.
King, A., & Himonides, E. (2016). Music, technology and
education: critical perspectives (A. King & E.
Computational Music Thinking Patterns: Connecting Music Education with Computer Science Education through the Design of Interactive
Notations
651

Himonides Eds.). Abingdon, Oxon; New York, NY:
Routledge.
Knochel, A. D., & Patton, R. M. (2015). If art education
then critical digital making: Computational thinking
and creative code. Studies in Art Education, 57(1), 21-
38.
Lea, D. (1994). Christopher Alexander: An introduction for
object-oriented designers. ACM SIGSOFT Software
Engineering Notes, 19(1), 39-46.
Lee, I., Martin, F., & Apone, K. (2014). Integrating
computational thinking across the K--8 curriculum.
Acm Inroads, 5(4), 64-71.
Michotte, A. (1963). The Perception of Causality (T. R.
Miles, Trans.). London: Methuen & Co. Ltd.
Moreno-León, J., Robles, G., & Román-González, M.
(2015). Dr. Scratch: Automatic analysis of scratch
projects to assess and foster computational thinking.
RED. Revista de Educación a Distancia, (46), 1-23.
Nake, F., & Grabowski, S. (2017). Think the Image, Don't
Make It! On Algorithmic Thinking, Art Education, and
Re-Coding. Journal of Science and Technology of the
Arts, 9(3), 21-31.
Papert, S. (1980). Mindstorms: Children, computers, and
powerful ideas: New York: Basic Book.
Peng, H. (2012, February). Algo. Rhythm: computational
thinking through tangible music device. In Proceedings
of the Sixth International Conference on Tangible,
Embedded and Embodied Interaction (pp. 401-402).
Repenning, A. (2014, January). Scalable Game Design:
Broadening Participation by Integrating Game Design
and Science Simulation Building into Middle School
Curricula. Paper presented at the Future Directions in
Computing Education, Summit Meeting, Orlado,
Florida.
Repenning, A. (2017). Moving Beyond Syntax: Lessons
from 20 Years of Blocks Programming in AgentSheets.
Journal of Visual Languages and Sentient Systems,
3(July), 68-89.
Repenning, A., Basawapatna, A., & Escherle, N. (2016,
September). Computational Thinking Tools. In 2016
IEEE Symposium on Visual Languages and Human-
Centric Computing (VL/HCC) (pp. 218-222). IEEE.
Repenning, A., Lamprou, A., Petralito, S., & Basawapatna,
A. (2019, July). Making Computer Science Education
Mandatory: Exploring a Demographic Shift in
Switzerland. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM
Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer
Science Education (pp. 422-428).
Repenning, A., Smith, C., Owen, B., & Repenning, N.
(2012, June). AgentCubes: Enabling 3D Creativity by
Addressing Cognitive and Affective Programming
Challenges. In EdMedia+ Innovate Learning (pp. 2762-
2771).
Repenning, A., Webb, D. C., Koh, K. H., Nickerson, H.,
Miller, S. B., Brand, C., . . . & Gutierrez, K. (2015).
Scalable Game Design: A Strategy to Bring Systemic
Computer Science Education to Schools through Game
Design and Simulation Creation. Transactions on
Computing Education (TOCE), 15(2), 1-31.
Repenning A., Basawapatna A. R., & Escherle, N. A.
(2017). Principles of Computational Thinking Tools. In
H. C. Rich P. (Ed.), Emerging Research, Practice, and
Policy on Computational Thinking. Educational
Communications and Technology: Issues and
Innovations (pp. 291-305): Springer, Cham.
Ruthmann, A., Heines, J. M., Greher, G. R., Laidler, P., &
Saulters, C. (2010, March). Teaching computational
thinking through musical live coding in scratch. In
Proceedings of the 41st ACM technical symposium on
Computer science education (pp. 351-355).
Schulze, H. (2000). Das aleatorische Spiel: Erkundung und
Anwendung der nichtintentionalen Werkgenese im 20.
Jahrhundert. München: Fink.
Werner, L., Denner, J., Bliesner, M., & Rex, P. (2009,
April). Can middle-schoolers use Storytelling Alice to
make games?: results of a pilot study. In Proceedings
of the 4th International Conference on Foundations of
Digital Games. (pp. 207 - 214).
Wing, J. M. (2006). Computational Thinking.
Communications of the ACM, 49(3), 33-35.
Xambó, A., Freeman, J., Magerko, B., & Shah, P. (2016).
Challenges and New Directions for Collaborative Live
Coding in the Classroom. In International Conference
of Live Interfaces (ICLI 2016). Brighton, UK.
CSME 2020 - Special Session on Computer Supported Music Education
652
